Leveraging Transformer with Self-Attention for Multi-Label Emotion Classification in Crisis Tweets
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Single-Label Emotion Classification
2.2. Multi-Label Emotion Classification
2.3. Transformer-Based Approach to Multi-Label Classification
2.4. Applications of Emotion Classification
3. Methods
3.1. Dataset and Preprocessing
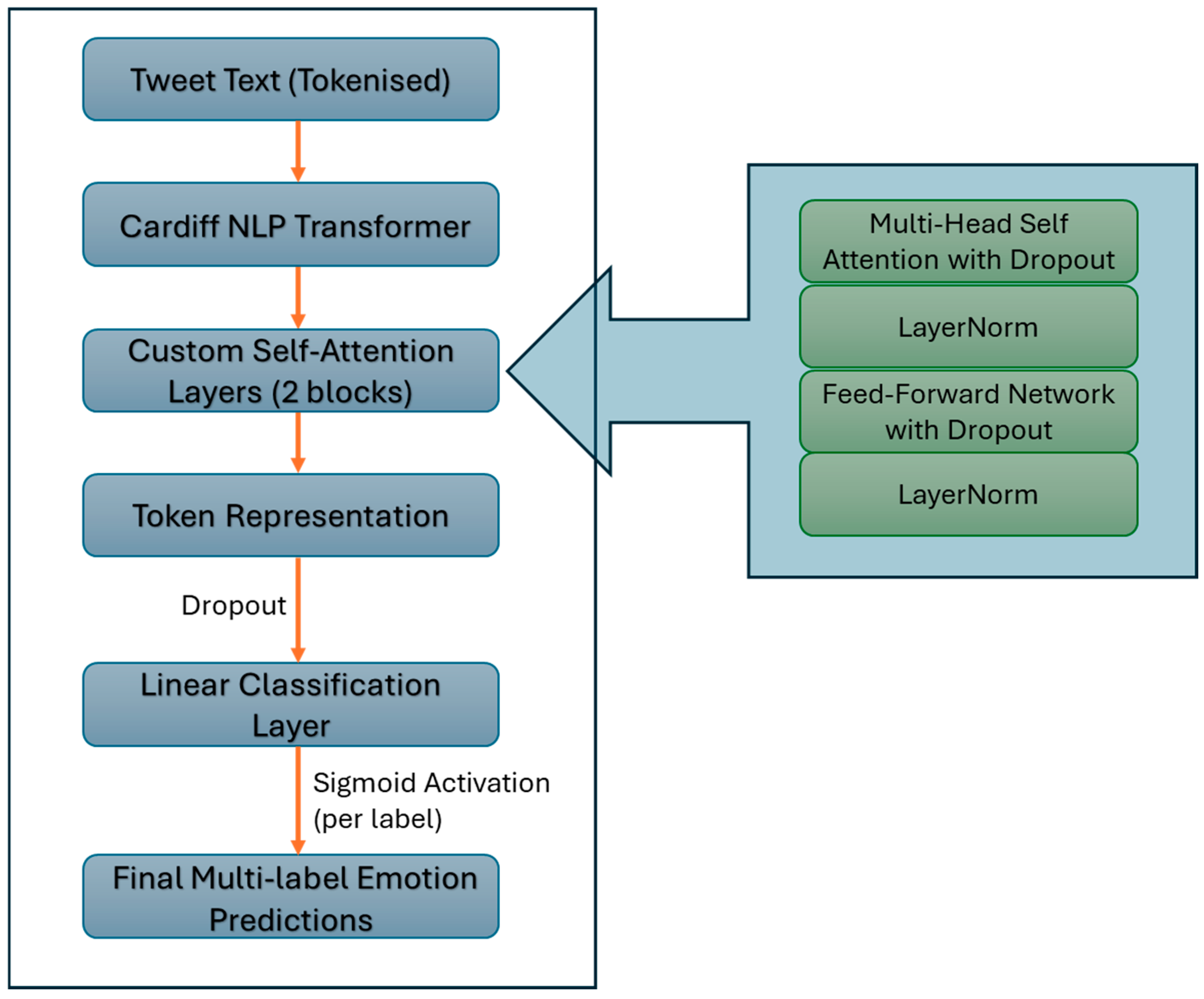
3.2. Model Architecture
- Multi-Head Self-Attention: This mechanism allows the model to attend to different positions within the token sequence simultaneously, capturing diverse aspects of the tweet’s context. Eight attention heads are used, providing sufficient capacity to model multiple contextual relationships without introducing excessive computational complexity. Each head projects the input into a subspace to learn specialized attention patterns, enabling the model to focus on words or phrases that are most indicative of specific emotions.
- Layer Normalization: Applied both after the attention output and the subsequent feed-forward layers, layer normalization standardizes activations to stabilize training and improve convergence.
- Feed-Forward Network (FFN): The FFN transforms the token embeddings through a two-layer fully connected network with a Gaussian Error Linear Unit (GELU) activation function between layers. The first linear layer expands the dimensionality of embeddings to four times their original size (hidden size × 4), enabling the network to learn more complex, nonlinear feature transformations. GELU activation is chosen for its smooth, non-monotonic curve that combines properties of Rectified Linear Unit (ReLU) and sigmoid functions, enhancing gradient flow and performance.
- Dropout Layers: Dropout with a rate of 0.2 is applied after both the attention and FFN components to reduce overfitting by randomly disabling neurons during training. This value was determined empirically, balancing regularization with the model’s ability to learn meaningful token-level patterns relevant to emotion classification.
3.3. Loss Function and Class Imbalance Handling
3.4. Training Procedure and Optimization
3.5. Evaluation and Threshold Optimization
- Micro-F1 Score: Aggregates contributions of all labels to compute a global F1 score, sensitive to overall performance.
- Macro-F1 Score: Calculates F1 per label and averages, treating all labels equally.
- Hamming Loss: Fraction of incorrect labels to the total number of labels.
- Jaccard Similarity Index: Measures overlap between predicted and true label sets on a per-sample basis.
3.6. Implementation Details
4. Results
Ablation Study
5. Case Study: Christchurch Earthquake
5.1. Dataset Description
5.2. Emotion Distribution
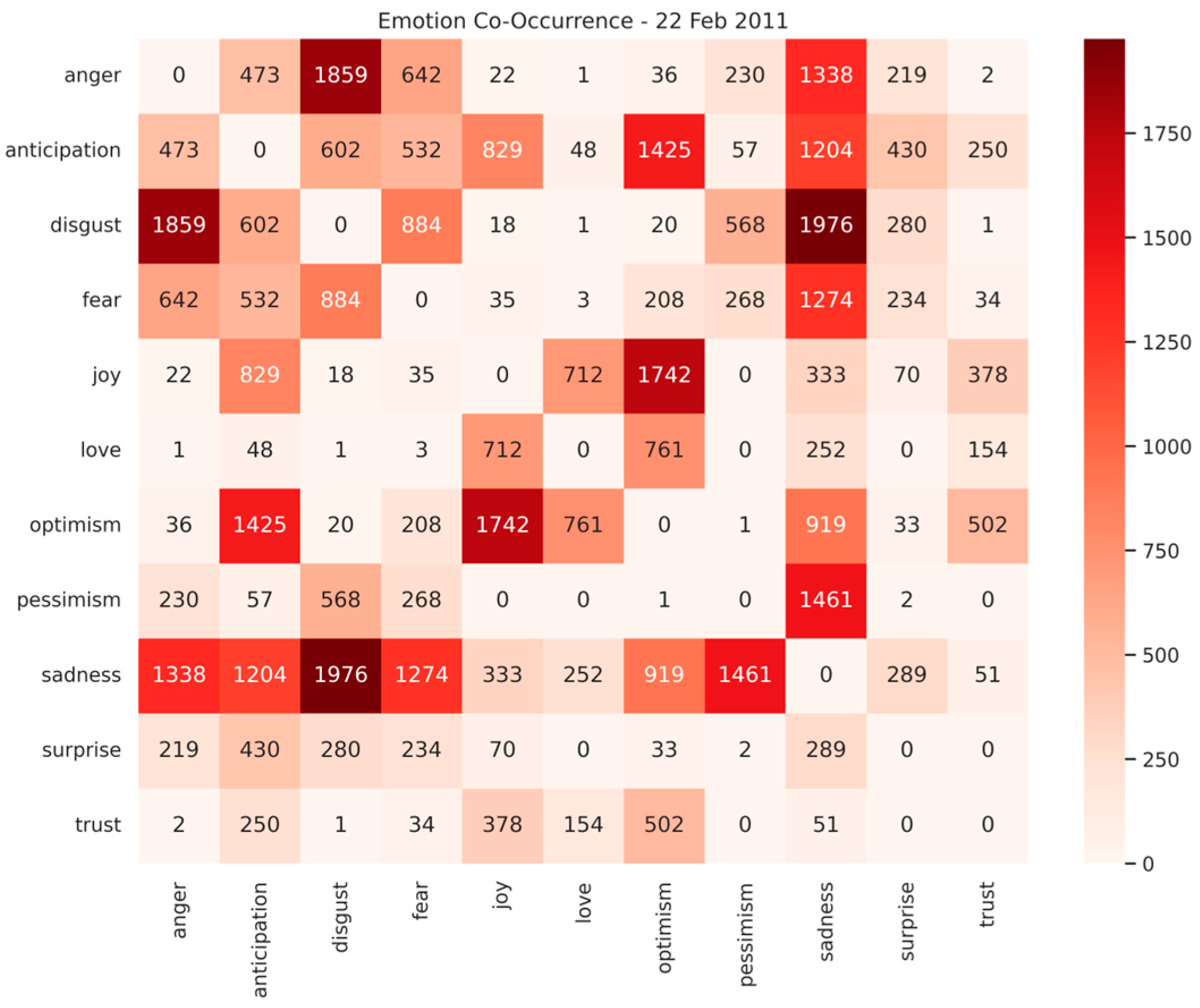
5.3. Emotion Co-Occurrence
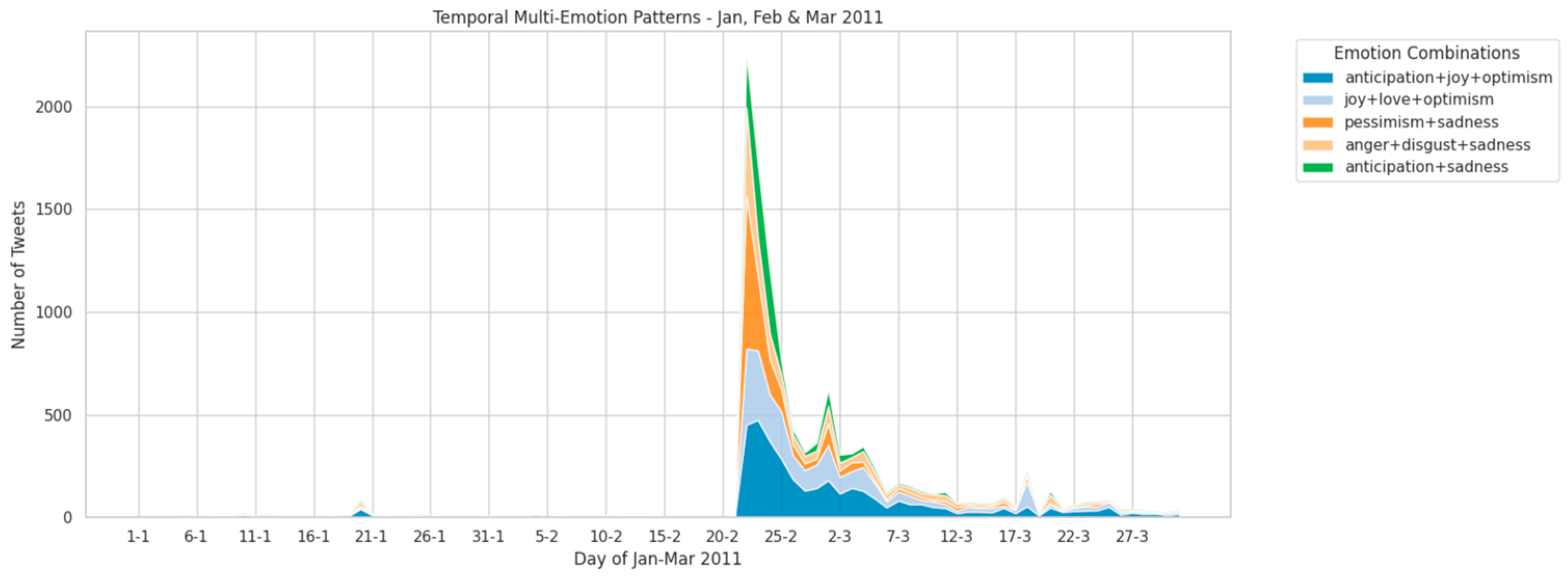
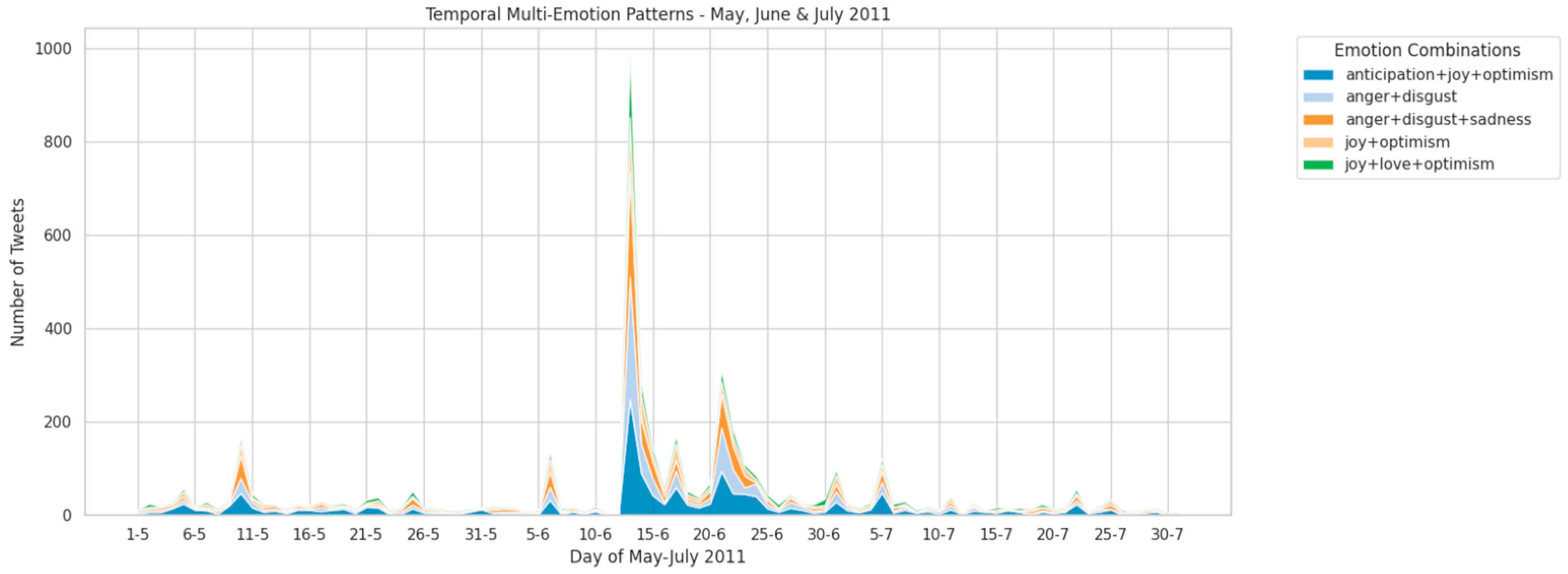
5.4. Temporal Multi-Emotions Dynamics
6. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RNN | Recurrent Neural Networks |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Networks |
| BERT | Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers |
| RoBERTA | A Robustly Optimized BERT Pretraining Approach |
| GPT | Generative Pre-Trained Transformer |
| SVM | Support Vector Machine |
| LSTM | Long Short-Term Memory |
| GRU | Gated Recurrent Unit |
| BiLSTM | Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory |
| MME | Multi-label Maximum Entropy |
| JBNN | Joint Binary Neural Network |
| JBCE | Joint Binary Cross-Entropy |
| LVC | Latent Variable Chain |
| ELMo | Embeddings from Language Models |
| MLkNN | Multi-label K-Nearest Neighbors |
| LDA | Latent Dirichlet Allocation |
| LEM | Latent Emotion Memory |
| ALBERT | A Lite BERT |
| TLMAN | Text-Label Mutual Attention Network |
| GCN | Graph Convolutional Networks |
| NLP | Natural Language Processing |
| ERC | Emotion Recognition in Conversation |
| FFN | Feed-Forward Network |
| GELU | Gaussian Error Linear Unit |
| ReLU | Rectified Linear Unit |
| CLS | Classification |
| BCE | Binary Cross-Entropy |
| AMP | Automatic Mixed Precision |
| DeBERTa | Decoding-enhanced BERT with Disentangled Attention |
| SA | Self-Attention |
| SC | Simple Classifier |
| DC | Deeper Classifier |
References
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, L.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is All you Need. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.-W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. BERT: Pre-training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1810.04805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ott, M.; Goyal, N.; Du, J.; Joshi, M.; Chen, D.; Levy, O.; Lewis, M.; Zettlemoyer, L.; Stoyanov, V. RoBERTa: A Robustly Optimized BERT Pretraining Approach. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1907.11692. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, T.B.; Mann, B.; Ryder, N.; Subbiah, M.; Kaplan, J.; Dhariwal, P.; Neelakantan, A.; Shyam, P.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; et al. Language models are few-shot learners. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 1877–1901. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, D.Q.; Vu, T.; Tuan Nguyen, A. BERTweet: A pre-trained language model for English Tweets. In Proceedings of the 2020 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing: System Demonstrations, Online, 16–20 November 2020; pp. 9–14. [Google Scholar]
- Camacho-collados, J.; Rezaee, K.; Riahi, T.; Ushio, A.; Loureiro, D.; Antypas, D.; Boisson, J.; Espinosa Anke, L.; Liu, F.; Martínez Cámara, E. TweetNLP: Cutting-Edge Natural Language Processing for Social Media. In Proceedings of the 2022 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing: System Demonstrations, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 7–11 December 2022; pp. 38–49. [Google Scholar]
- Bandhakavi, A.; Wiratunga, N.; Padmanabhan, D.; Massie, S. Lexicon based feature extraction for emotion text classification. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2017, 93, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimenez, R.; Gaviola, M.; Sabellano, M.J.; Gorro, K. Emotion Classification of Duterte Administration Tweets Using Hybrid Approach. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Software and e-Business, Hong Kong, 28–30 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Aslam, N.; Rustam, F.; Lee, E.; Washington, P.B.; Ashraf, I. Sentiment Analysis and Emotion Detection on Cryptocurrency Related Tweets Using Ensemble LSTM-GRU Model. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 39313–39324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharti, S.K.; Varadhaganapathy, S.; Gupta, R.K.; Shukla, P.K.; Bouye, M.; Hingaa, S.K.; Mahmoud, A. Text-Based Emotion Recognition Using Deep Learning Approach. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 2022, 2645381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glenn, A.; LaCasse, P.M.; Cox, B.A. Emotion classification of Indonesian Tweets using Bidirectional LSTM. Neural Comput. Appl. 2023, 35, 9567–9578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anbazhagan, K.; Kurlekar, S.; Brindha, T.V.; Sudhish Reddy, D. Twitter Based Emotion Recognition Using Bi-LSTM. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on Trends in Quantum Computing and Emerging Business Technologies, Pune, India, 22–23 March 2024; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Shaw, C.; LaCasse, P.; Champagne, L. Exploring emotion classification of indonesian tweets using large scale transfer learning via IndoBERT. Soc. Netw. Anal. Min. 2025, 15, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.Y.; Rao, Y.; Jin, F.; Chen, H.; Xiang, X. Multi-label maximum entropy model for social emotion classification over short text. Neurocomputing 2016, 210, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, A.M.G.; Cerri, R.; Paraiso, E.C.; Mantovani, R.G.; Junior, S.B. Applying multi-label techniques in emotion identification of short texts. Neurocomputing 2018, 320, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Xia, R. Joint Binary Neural Network for Multi-label Learning with Applications to Emotion Classification. In Proceedings of the Natural Language Processing and Chinese Computing, Hohhot, China, 26–30 August 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.; Trabelsi, A.; Qin, X.; Farruque, N.; Zaiane, O.R. Seq2Emo for Multi-label Emotion Classification Based on Latent Variable Chains Transformation. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1911.02147. [Google Scholar]
- Jabreel, M.; Moreno, A. A Deep Learning-Based Approach for Multi-Label Emotion Classification in Tweets. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameer, I.; Ashraf, N.; Sidorov, G.; Gómez-Adorno, H. Multi-label Emotion Classification using Content-Based Features in Twitter. Comput. Y Sist. 2020, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarbazi-Azad, S.; Akbari, A.; Khazeni, M. ExaAEC: A New Multi-label Emotion Classification Corpus in Arabic Tweets. In Proceedings of the 2021 11th International Conference on Computer Engineering and Knowledge (ICCKE), Mashhad, Iran, 28–29 October 2021; pp. 465–470. [Google Scholar]
- Ashraf, M.; Saeed, M.; Ali, F.; Ahmad, W. Multi-label emotion classification of Urdu tweets using machine learning and deep learning techniques. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2022, 8, e896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Shi, T.; Zhou, G.; Liu, M.; Yin, Z.; Yin, L.; Zheng, W. Emotion classification for short texts: An improved multi-label method. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2023, 10, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maragheh, H.K.; Gharehchopogh, F.S.; Majidzadeh, K.; Sangar, A.B. A Hybrid Model Based on Convolutional Neural Network and Long Short-Term Memory for Multi-label Text Classification. Neural Process. Lett. 2024, 56, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, F.; Kang, X.; Nishide, S.; Guan, Z.; Ren, F. A fusion model for multi-label emotion classification based on BERT and topic clustering. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Artificial Intelligence and Robotics, Kitakyushu, Japan, 1–10 August 2020; SPIE: Bellingham, DC, USA, 2020; Volume 11574. [Google Scholar]
- Fei, H.; Ji, D.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, Y. Topic-Enhanced Capsule Network for Multi-Label Emotion Classification. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2020, 28, 1839–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, H.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, Y.; Ji, D. Latent Emotion Memory for Multi-Label Emotion Classification. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 2020, 34, 7692–7699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acheampong, F.A.; Nunoo-Mensah, H.; Chen, W. Transformer models for text-based emotion detection: A review of BERT-based approaches. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2021, 54, 5789–5829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahanin, Z.; Ismail, M.A.; Singh, N.S.S.; AL-Ashmori, A. Hybrid Feature Extraction for Multi-Label Emotion Classification in English Text Messages. Sustainability 2023, 15, 12539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameer, I.; Bölücü, N.; Siddiqui, M.H.F.; Can, B.; Sidorov, G.; Gelbukh, A. Multi-label emotion classification in texts using transfer learning. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 213, 118534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Chen, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Du, Y.; Li, X. Mutual Attention Network for Multi-label Emotion Recognition with Graph-Structured Label Representations. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on Ubiquitous Computing and Communications (IUCC), Chengdu, China, 20–22 December 2024; pp. 168–175. [Google Scholar]
- Malik, U.; Bernard, S.; Pauchet, A.; Chatelain, C.; Picot-Clemente, R.; Cortinovis, J. Pseudo-Labeling with Large Language Models for Multi-Label Emotion Classification of French Tweets. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 15902–15916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, M.H.F.; Inkpen, D.; Gelbukh, A.F. Instruction Tuning of LLMs for Multi-label Emotion Classification in Social Media Content. In Proceedings of the Canadian AI, Guelph, ON, Canada, 27–31 May 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Brynielsson, J.; Johansson, F.; Jonsson, C.; Westling, A. Emotion classification of social media posts for estimating people’s reactions to communicated alert messages during crises. Secur. Inform. 2014, 3, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthony, P.; Hoi Ki Wong, J.; Joyce, Z. Identifying emotions in earthquake tweets. AI Soc. 2025, 40, 2909–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Hu, D. Social Media Analytics for Disaster Response: Classification and Geospatial Visualization Framework. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 4330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.; He, Z.; Zhou, C.; Zhu, W. Multi-class multi-label classification of social media texts for typhoon damage assessment: A two-stage model fully integrating the outputs of the hidden layers of BERT. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2024, 17, 2348668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojanovski, D.; Strezoski, G.; Madjarov, G.; Dimitrovski, I. Emotion identification in FIFA world cup tweets using convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the 2015 11th International Conference on Innovations in Information Technology (IIT), Dubai, United Arab Emirates, 1–3 November 2015; pp. 52–57. [Google Scholar]
- Fagbola, T.M.; Abayomi, A.; Mutanga, M.B.; Jugoo, V.R. Lexicon-Based Sentiment Analysis and Emotion Classification of Climate Change Related Tweets. In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Soft Computing and Pattern Recognition (SoCPaR 2021), Online, 15–17 December 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Deniz, E.; Erbay, H.; Cosar, M. Multi-Label Classification of E-Commerce Customer Reviews via Machine Learning. Axioms 2022, 11, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adesokan, A.; Madria, S.K.; Nguyen, L. HatEmoTweet: Low-level emotion classifications and spatiotemporal trends of hate and offensive COVID-19 tweets. Soc. Netw. Anal. Min. 2023, 13, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral, R.C.; Han, S.C.; Poon, J.; Nenadic, G. MM-EMOG: Multi-Label Emotion Graph Representation for Mental Health Classification on Social Media. Robotics 2024, 13, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farasalsabila, F.; Utami, E.; Raharjo, S. Multi-Label Classification using BERT for Cyberbullying Detection. In Proceedings of the 2024 4th International Conference of Science and Information Technology in Smart Administration (ICSINTESA), Balikpapan, Indonesia, 12–13 July 2024; pp. 195–200. [Google Scholar]
- Meder, T.; Meertens Instituut, A.N. Online Coping with the First Wave: Covid Humor and Rumor on Dutch Social Media (March–July 2020). Folk.-Electron. J. Folk. 2021, 82, 135–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, F.B.; Haque, A.; Mougouei, D.; Sichman, J.S.; Singh, M.P.; Evans, S. Investigating the Emotional Response to COVID-19 News on Twitter: A Topic Modelling and Emotion Classification Approach. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 16883–16897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olusegun, R.; Oladunni, T.; Audu, H.; Houkpati, Y.; Bengesi, S. Text Mining and Emotion Classification on Monkeypox Twitter Dataset: A Deep Learning-Natural Language Processing (NLP) Approach. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 49882–49894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.; Gao, J.; Chen, W. DeBERTaV3: Improving DeBERTa using ELECTRA-Style Pre-Training with Gradient-Disentangled Embedding Sharing. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2111.09543. [Google Scholar]
- Plutchik, R. A psychoevolutionary theory of emotions. Soc. Sci. Inf. 1982, 21, 529–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klucken, T.; Schweckendiek, J.; Koppe, G.; Merz, C.J.; Kagerer, S.; Walter, B.; Sammer, G.; Vaitl, D.; Stark, R. Neural correlates of disgust- and fear-conditioned responses. Neuroscience 2012, 201, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Models | Micro-F1 | Macro-F1 | Hamming Loss | Average Jaccard Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DeBERTa-v3-base | 0.6258 | 0.5250 | 0.1762 | 0.5039 |
| BERTweet-base | 0.7014 | 0.6049 | 0.1436 | 0.5767 |
| Cardiff NLP | 0.7030 | 0.6059 | 0.1371 | 0.5818 |
| Cardiff NLP + SA + deep classifier | 0.7123 | 0.6165 | 0.1375 | 0.6047 |
| Cardiff NLP + SA + simple classifier | 0.7208 | 0.6192 | 0.1330 | 0.6066 |
| Labels | Precision | Recall | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|
| anger | 0.7452 | 0.8540 | 0.7959 |
| anticipation | 0.3476 | 0.5242 | 0.4180 |
| disgust | 0.7256 | 0.8621 | 0.7880 |
| fear | 0.7603 | 0.7603 | 0.7603 |
| joy | 0.9088 | 0.7985 | 0.8495 |
| love | 0.5928 | 0.7500 | 0.6622 |
| optimism | 0.7127 | 0.8241 | 0.7644 |
| pessimism | 0.3962 | 0.4200 | 0.4078 |
| sadness | 0.7287 | 0.7094 | 0.7189 |
| surprise | 0.5000 | 0.3143 | 0.3860 |
| trust | 0.1842 | 0.1628 | 0.1728 |
| Model Variant | Micro-F1 | Macro-F1 | Hamming Loss | Average Jaccard Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cardiff NLP (baseline) | 0.7030 | 0.6059 | 0.1371 | 0.5818 |
| Cardiff NLP + 1 SA + SC | 0.7062 | 0.6123 | 0.1394 | 0.5856 |
| Cardiff NLP + 2 SA + SC | 0.7208 | 0.6192 | 0.1330 | 0.6066 |
| Cardiff NLP + 1 SA + DC | 0.6922 | 0.6031 | 0.1511 | 0.5659 |
| Cardiff NLP + 2 SA + DC | 0.7123 | 0.6165 | 0.1375 | 0.6047 |
| Tweets | Emotions |
|---|---|
| Almost exactly where last night’s #EQNZ was, poor buggers! Near QEII stadium” | anger, disgust, sadness |
| “#2011Awards—Grumpiest Bitch of the Year Award goes to ....... Mother Nature! #Eqnz #Chch” | anger, disgust, joy |
| “Just sending a huge happy Xmas eve out to those in Christchurch. Stay warm and safe! #EQNZ” | joy, love, optimism |
| “Bad earthquake scaring me and then rocking long enough to make me motion sick. Bad. #eqnz” | anger, disgust, fear |
| “Kids didn’t wake up so I’m happy :-) #eqnz” | joy, optimism |
| “That gave me a fright. #eqnz” | fear |
| “The bloody angel has bungied off the tree again #eqnz” | anger, disgust |
| “Feel like I want to do something to help #eqnz Arohanui We do hope it settles down soon and you can get some peace.” | anticipation, joy, optimism |
| “Not impressed by the 4.45 am 4.4 #eqnz Haven’t been able to get back to sleep :(“ | disgust, pessimism, sadness |
| “Thinking of all our friends and their nearest n dearest in ChCh—stay strong Tweeps #eqnz” | joy, love, optimism, trust |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Anthony, P.; Zhou, J. Leveraging Transformer with Self-Attention for Multi-Label Emotion Classification in Crisis Tweets. Informatics 2025, 12, 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics12040114
Anthony P, Zhou J. Leveraging Transformer with Self-Attention for Multi-Label Emotion Classification in Crisis Tweets. Informatics. 2025; 12(4):114. https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics12040114
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnthony, Patricia, and Jing Zhou. 2025. "Leveraging Transformer with Self-Attention for Multi-Label Emotion Classification in Crisis Tweets" Informatics 12, no. 4: 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics12040114
APA StyleAnthony, P., & Zhou, J. (2025). Leveraging Transformer with Self-Attention for Multi-Label Emotion Classification in Crisis Tweets. Informatics, 12(4), 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics12040114






