Abstract
The surging prevalence of diabetes globally necessitates advancements in non-invasive diagnostics, particularly for the early detection of cardiovascular anomalies associated with the condition. This study explores the efficacy of Pulse Wave Analysis (PWA) for distinguishing diabetic from non-diabetic individuals through morphological examination of pressure pulse waveforms. The research unfolds in four phases: data accrual, preprocessing, Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) model construction, and performance evaluation. Data were procured using a multipara patient monitor, resulting in 2000 pulse waves equally divided between healthy individuals and those with diabetes. These were used to train, validate, and test three distinct CNN architectures: the conventional CNN, Visual Geometry Group (VGG16), and Residual Networks (ResNet18). The accuracy, precision, recall, and F1 score gauged each model’s proficiency. The CNN demonstrated a training accuracy of 82.09% and a testing accuracy of 80.6%. The VGG16, with its deeper structure, surpassed the baseline with training and testing accuracies of 90.2% and 86.57%, respectively. ResNet18 excelled, achieving a training accuracy of 92.50% and a testing accuracy of 92.00%, indicating its robustness in pattern recognition within pulse wave data. Deploying deep learning for diabetes screening marks progress, suggesting clinical use and future studies on bigger datasets for refinement.
1. Introduction
Pulse Wave Analysis (PWA) is a technique that involves the morphological analysis of the pressure pulse waveform [1]. It is a method that has been widely used in both clinical and research settings for the diagnosis and monitoring of various diseases [2,3]. In PWA, time-domain metrics calculate time-based parameters, offering insights into aspects like cardiac contraction timing, blood flow dynamics, arterial stiffness, and vascular health [4]. Frequency-domain components, through Fourier transformation, examine different frequency components in the waveform, providing insights into autonomic nervous system activity, arterial stiffness, and vascular tone [2,5]. Waveform analysis assesses the shape of the arterial pressure waveform, calculating parameters such as the augmentation index, reflection coefficient, and pulse wave velocity, which offer insights into arterial stiffness, wave reflection patterns, and overall vascular health [3].
The statistical analysis applies regression and multivariate analysis to explore relationships between pulse wave parameters and clinical or demographic variables [6]. However, it is important to highlight that machine learning and deep learning, subsets of artificial intelligence (AI), stand out due to their ability to learn from data and make predictions, thereby enhancing the precision and effectiveness of PWA. Machine learning algorithms are not explicitly programmed but learn from data, making them particularly useful when conclusive evidence is lacking and aiding in decision-making [7]. With the availability of large datasets and the increasing capabilities of machine learning approaches, the clinical benefits of AI are poised to increase while minimizing patient risk [8]. This underscores the superiority and importance of machine learning over traditional statistical analysis in the context of PWA [9]. The introduction of Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), a cornerstone of deep learning, into our study, represents a leap forward in handling and analyzing large datasets of pulse wave images. By automatically learning feature hierarchies from data, CNNs offer unprecedented precision in classifying and interpreting pulse waveforms, marking a pivotal shift towards more accurate, non-invasive diabetes diagnosis [10].
Diabetes, a persistent metabolic condition that impacts millions globally, heightens the likelihood of cardiovascular complications [11,12]. This disease can cause alterations in the pulse wave patterns due to its detrimental effects on arterial function and structure. [13]. The global prevalence of diabetes has nearly doubled over the past few decades, inflicting a heavy burden on healthcare systems worldwide. Early and accurate diagnosis is critical for effective management, yet current diagnostic methods can be invasive, time-consuming, or unreliable [14,15]. Hence, PWA could serve as a valuable instrument for evaluating the vascular well-being of individuals with diabetes and for detecting preliminary indicators of cardiovascular harm [16].
Despite the potential of PWA, there are certain limitations, such as the need for expert knowledge to interpret pulse wave data, time-consuming analysis processes, and a lack of precision in manual analysis [17]. However, advances in artificial intelligence offer hope of overcoming these limitations through computational analysis of pulse wave signals [4,18]. Pulse waveforms contain a wealth of physiological information that can indicate prediabetic conditions if interpreted correctly [2]. CNNs, an AI technique modeled on mammalian visual cortex structure, are uniquely suited for automatically extracting subtle waveform features relevant to diabetes risk [19,20].
The photoplethysmography (PPG) method, a non-invasive optical measurement technique, necessitates only basic equipment such as smartphone cameras or specialized wearable sensors [21,22,23,24,25]. Researchers have recently demonstrated that CNN-based analysis of PPG pulse wave signals achieves diabetic screening accuracy on par with fasting plasma glucose and oral glucose tolerance tests. PWA with CNNs promises earlier, pain-free diabetes detection by harnessing the pattern recognition capabilities of deep learning [26,27,28,29]. As research continues to refine predictive algorithms on large PPG datasets, this AI-driven methodology could become a widely accessible and life-saving diagnostic tool. The integration of smart pulse waveform analytics into routine primary care could identify at-risk patients much sooner, enabling timely interventions that prevent full-blown diabetes and associated complications [30].
Studies have demonstrated that combining PPG with machine learning algorithms can classify blood glucose levels with high accuracy. For example, an ensemble bagged trees algorithm achieved an accuracy of 98% in classifying blood glucose levels based on PPG signals, making it a promising tool for early diabetes detection. Furthermore, the integration of near-infrared (NIR) technology with PPG has been explored for non-invasive glucose monitoring, showing potential for accurate glucose prediction and monitoring. These advancements suggest that while PWA may not directly diagnose early diabetes, its applications, in combination with advanced algorithms and technologies, can contribute significantly to non-invasive monitoring and early detection strategies [29].
This study delved into the application of CNNs in classifying finger pulse wave images, aiming to distinguish between diabetic and non-diabetic individuals. It leveraged advanced image-based analysis via deep learning models, marking a shift from traditional (PPG) waveform feature extraction. The research also involved the development and evaluation of CNN models for analyzing pulse wave images obtained from a multiparameter patient monitor. These images underwent preprocessing for size normalization and contrast enhancement. Three primary CNN architectures—a custom CNN, Visual Geometry Group (VGG), and Residual Network (ResNet) were trained on this dataset. The models directly classified the images, bypassing conventional feature extraction. Their performance was assessed using metrics such as accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score.
The study underscored the significance of PWA in assessing diabetes. Despite the potential of PWA, challenges, such as the need for expert interpretation and precision issues, persisted. The study illuminated the transformative potential of artificial intelligence, particularly CNNs, in surmounting these challenges. It is important to emphasize that the primary aim of this study was not to innovate new machine learning architectures but to apply proven models, such as VGG and ResNet, as effective tools for distinguishing between PPG images of healthy individuals and diabetes patients. These established models were chosen for their well-documented success and reliability in medical imaging tasks, allowing the research to leverage mature technologies to enhance diagnostic methods for diabetes and highlight the practical application of AI in clinical settings. The incorporation of CNN-based analysis of PPG signals suggested the possibility of earlier and non-invasive diabetes detection. This AI-based method could improve diabetes care by enabling early interventions and preventative measures.
2. Materials and Methods
The study was approved by the Ethics Review Committee of the University of Kelaniya (ERC/UOK/FS/2022/019). The research was conducted in the medical clinics of the District Base Hospital, Kiribathgoda, Family Medicine Clinic, Faculty of Medicine, University of Kelaniya, and Gampaha Wickramarachchi Ayurveda Teaching Hospital. Healthy individuals were selected from among those who accompanied patients to these clinics.
2.1. Inclusion Criteria
The inclusion criteria for the study were carefully defined to ensure the validity of the results. For the group of individuals with diabetes, the criteria included a confirmed diagnosis of type 2 diabetes, an age of 18 years or older, and no history of cardiovascular diseases. The control group was selected based on criteria ensuring participants were in good health and free from significant medical conditions or major surgical history. Eligibility required a Body Mass Index (BMI) within the healthy range of 18.5–24.9 kg/m2, oxygen saturation levels above 95% indicating efficient lung function, a stable pulse rate between 60 to 100 beats per minute signifying normal heart rhythm, and blood pressure within the normal range, specifically below 120/80 mmHg but not less than 90/60 mmHg.
2.2. Exclusion Criteria
The study excluded individuals who fell into the following categories: those under the age of 18, individuals with severe psychiatric illnesses or cognitive impairments that could interfere with the interview process, individuals suffering from acute or chronic infections, pregnant women, lactating mothers, cancer patients, individuals with undiagnosed medical conditions.
2.3. Sample Size
For the study, 115 individuals were selected to form the diabetic cohort, while 61 individuals were enlisted as part of the healthy control group. The method of screening the study participants is depicted in Figure 1.
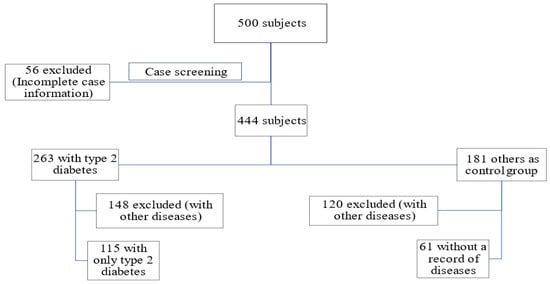
Figure 1.
The process of screening the study participants.
2.4. Data Collection
Information of the participants, collected through an interviewer-administered questionnaire, considered various variables, including age, gender, past medical history, presence of other illnesses, drug history, surgical history, Body Mass Index (BMI), recorded investigation findings, and diagnosis. This comprehensive approach ensured a thorough understanding of each participant’s health status and background.
The study collected finger pulse waves from participants using a photoplethysmography (PPG) device integrated into the multiparameter patient monitor (Model: Datalys 760, Manufacturer: Lutech Medical, New York, NY, USA), as illustrated in Figure 2. The participants were instructed to sit comfortably and breathe normally during the measurement. The sensor was securely attached to the left index finger of each participant. Systolic blood pressure (SBP), diastolic blood pressure (DBP), mean arterial pressure (MAP), oxygen saturation (SpO2), and pulse rate were also obtained from the patient monitor. Standardized protocols were followed during data collection, including consistent use of PPG devices and controlled environments to minimize measurement variability.
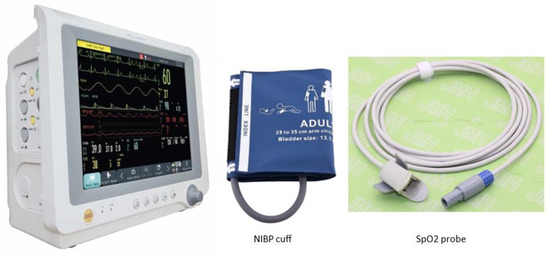
Figure 2.
Lutech Datalys 760 Multipara Patient Monitor with non-invasive blood pressure (NIBP) cuff and SPO2 probe.
2.5. Data Preprocessing
Pulse images obtained from the patient monitor underwent processing to extract over eight single pulse wave cycles from each participant, from which 2000 pulse wave cycles were subsequently selected. These cropped pulse wave images then underwent further preprocessing, which involved resizing the images to a standard size and rescaling the pixel values within a specific range (80 × 105). This step was crucial to ensure consistency in the data used for subsequent analysis. Each group, diabetic and healthy, had a total of 1000 cycles, split into training (60%), validation (20%), and testing (20%) sets, as detailed in Table 1.

Table 1.
Distribution of pulse wave data for model training, validation, and testing in healthy and type 2 diabetic groups.
2.6. Model Development and Evaluation
Preprocessed images served as the input for three distinct types of neural networks: Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN), Visual Geometry Group networks (VGG), and Residual Networks (ResNet). Each of these networks was trained and tested using the preprocessed pulse wave images. The performance of each network was then evaluated based on four key metrics: accuracy, precision, recall, and F1 score.
Accuracy is a measure of the overall correctness of the model, representing the proportion of total predictions that are correct. Precision, on the other hand, measures the proportion of positive identifications that were actually correct. Recall, also known as sensitivity, measures the proportion of actual positives that were identified correctly. The F1 score provides a single metric that combines both precision and recall, offering a balanced measure of the model’s performance [31]. Through this rigorous evaluation process, the study aimed to assess the effectiveness of CNN, VGG, and ResNet networks in classifying preprocessed pulse wave images.
2.7. Refining CNN Model Architecture
In this study, the layers of the CNN model were manually adjusted to achieve optimal performance. This approach was taken to balance model complexity and computational efficiency, ensuring the model is both effective and practical. Manually adjusting the layers allowed us to fine-tune the model, thereby avoiding overfitting or underfitting and achieving better generalization to new data. Additionally, by optimizing the number of layers, we ensured that the model remained computationally efficient, making it feasible to train and deploy without excessive resource consumption. This careful balance of complexity and efficiency was crucial in developing a robust and practical model tailored to the specific requirements of our study.
The adjustment process began with a basic CNN structure, gradually adding layers while monitoring performance. At each stage, key metrics such as accuracy, loss, and validation performance were evaluated to determine the impact of each layer change. Layers were iteratively refined, with convolutional layers adjusted for feature extraction and pooling layers optimized for dimensionality reduction. Hyperparameters, including learning rate, batch size, and activation functions, were fine-tuned to align with network structure changes. The final model configuration underwent validation on a separate dataset to ensure robust performance beyond the training data, confirming the effectiveness of these manual adjustments.
Initially, Conv2D, max-pooling, and dense layers were modified to assess their impact on results. Subsequently, batch normalization layers were introduced, followed by the addition of dropout layers, to further optimize the model. However, the model did not perform well with batch normalization layers; hence, the final model omits these layers. Figure 3 illustrates the architecture of the CNN model.
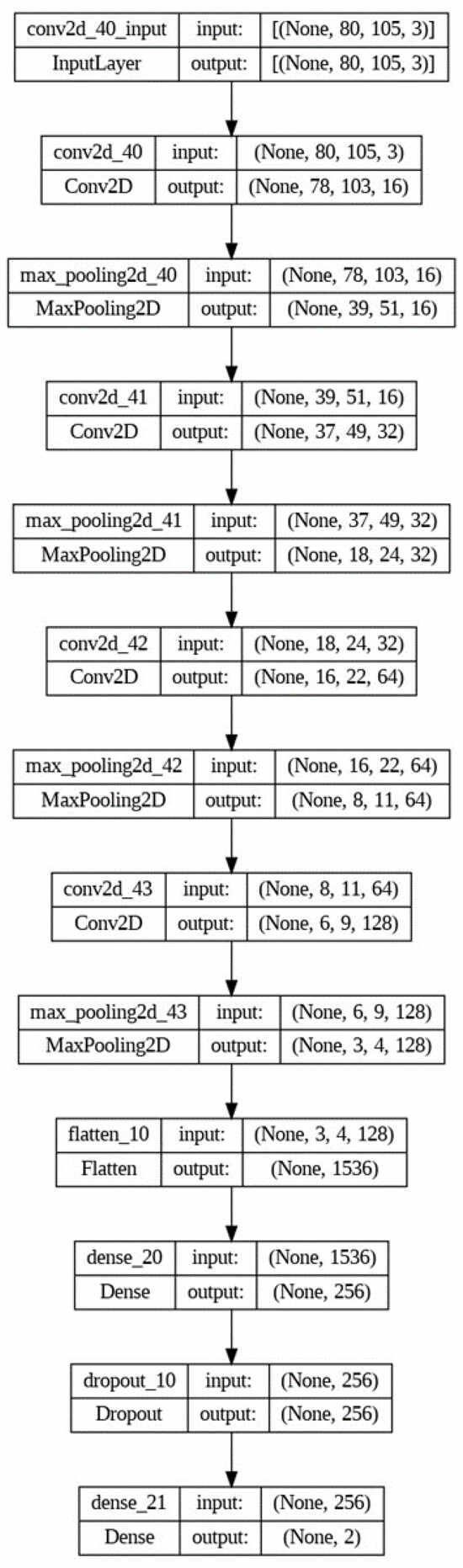
Figure 3.
Architecture of the CNN model.
2.8. Pre-Trained Models
The next experiments were conducted with pre-trained models to further enhance performance. VGG16 and ResNet18 were selected for their complementary strengths to enhance model performance, ensuring robustness, efficiency, and effective feature extraction tailored to our specific dataset and research objectives. VGG16 is a well-established, robust model with a strong track record in various image recognition tasks, making it a reliable choice for initial experimentation. Its 16-layer architecture is suitable for our dataset, allowing for efficient feature extraction without excessive computational resources. Furthermore, VGG16’s simplicity reduces training complexity, and its widespread use in transfer learning scenarios means it can leverage pre-trained weights from large datasets like ImageNet to improve performance on smaller datasets. On the other hand, the pre-trained ResNet18 model offers further improvements in accuracy and robustness due to its residual learning framework. Designed to optimize the efficiency of convolutional layers through residual connections, ResNet18 helps mitigate the vanishing gradient problem and improve training efficiency. Its architecture balances depth and computational efficiency, making it well-suited for our dataset size compared to larger models like ResNet50. Additionally, ResNet18’s residual connections prevent output degradation that can occur with deeper networks, ensuring stable performance. Its design also allows for greater adaptability in various tasks, making it a versatile choice for improving model performance [32]. Therefore, it is essential to carefully select different models and optimize their parameters and hyperparameters within our experiments.
3. Results
3.1. Presentation of Pulse Waveform Data
Figure 4 displays a pulse waveform captured from a 44-year-old healthy male using the multipara patient monitor. The waveform is characterized by a series of rhythmic peaks and troughs, which represent the systolic and diastolic phases of the cardiac cycle. Each peak likely corresponds to the heart’s contraction, propelling blood through the arteries, while the troughs likely represent the heart at rest. This regular pattern suggests normal cardiovascular function and serves as a baseline for comparison with waveforms from patients with medical conditions.

Figure 4.
Pulse waveform of a 44-year-old healthy male.
Figure 5 presents a detailed pulse waveform acquired from a 62-year-old female patient diagnosed with type 2 diabetes mellitus, managed with oral hypoglycemic agents. This waveform may show variations in amplitude and frequency compared to the healthy control in Figure 3, reflecting potential cardiovascular changes due to diabetes. Such changes might include increased arterial stiffness or variations in pulse pressure, which are crucial indicators of diabetes-related complications. Analyzing this waveform can provide insights into the cardiovascular health of diabetic patients and help in the early detection of diabetes-related issues.
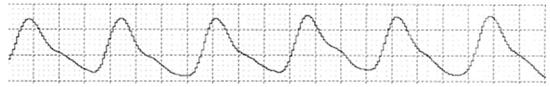
Figure 5.
Pulse waveform of a 62-year-old female with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Figure 6 demonstrates the initial stages of data preprocessing, specifically applied to pulse waveform images extracted from a patient monitor. This figure shows a series of cropped and resized single pulse wave images from both healthy individuals and patients with diabetes. These steps are crucial for enhancing the quality and consistency of the data, facilitating accurate feature extraction, and model training. The images in Figure 5 illustrate the variability in pulse waveforms, providing a visual representation of the data used in the study. This figure underscores the importance of preprocessing in preparing diverse pulse wave data for reliable analysis and comparison.
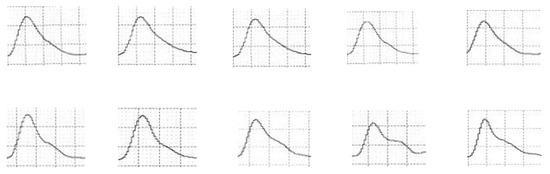
Figure 6.
A selection of cropped and resized single pulse wave images.
3.2. Comparative Performance of Neural Network Models
Table 2 presents a comparative analysis of the performance metrics for three different neural network models, CNN, VGG16, and ResNet18, in the context of classifying pulse wave images for diabetes diagnosis. For each model, the table lists the training accuracy, overall testing accuracy, overall precision, overall recall, and overall F1 score, all expressed as percentages. The CNN model shows a balanced performance with around 80% across all metrics, indicating its capability but also suggesting room for improvement. The VGG16 model improves upon this, particularly in precision, reaching over 90% in training accuracy and demonstrating substantial effectiveness in testing scenarios. The ResNet18 model outperforms the others across all metrics, with notably high precision and recall rates, leading to the highest F1 score of 92.31%. This table underscores the varying capabilities of each model in handling the task of diabetes diagnosis through pulse wave image analysis, with ResNet18 showing superior performance in accurately identifying diabetic conditions.

Table 2.
Accuracy, precision, recall, and f1 score of different models.
Figure 7, Figure 8 and Figure 9 provide a visual representation of the learning curves associated with the CNN, VGG16, and ResNet18 models, respectively. These curves are instrumental in understanding how each model’s performance evolved over the course of training.
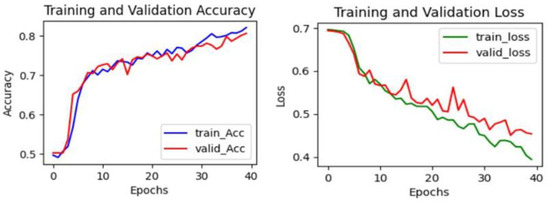
Figure 7.
The learning curve in CNN.
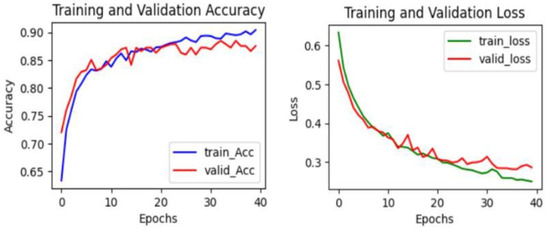
Figure 8.
The learning curve in VGG16.
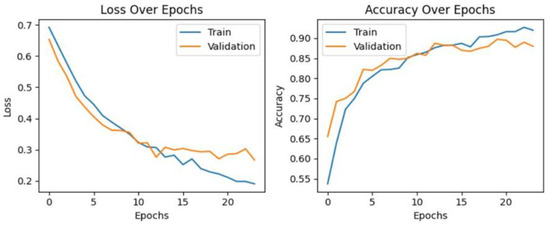
Figure 9.
The learning curve in ResNet18.
3.3. Statistical Analysis
Descriptive statistics were utilized to provide a detailed summary of the demographic and clinical information of the participants. This method offered an extensive understanding of the characteristics of the participants, confirming that the control group was matched in terms of age and gender.
For this study, it was essential to select healthy individuals free from any other diseases to accurately compare their pulse waves with those of diabetes patients. Including individuals with other diseases could have introduced confounding variables, potentially skewing the results. These stringent selection criteria helped control for such factors, thereby enhancing the reliability of our comparisons and the validity of our study’s findings. Table 3 presents the descriptive statistics of the demographic and clinical data of the participants, comparing the Diabetic group (n = 115) and the Control group (n = 61). The study groups were well-matched in terms of age and gender. However, significant differences were observed in several cardiovascular parameters, such as SBP (p < 0.001), DBP (p < 0.001), PP (p < 0.001), MAP (p < 0.001), and oxygen saturation (p < 0.001), confirming the successful identification of distinct physiological profiles between diabetic and non-diabetic individuals.

Table 3.
Descriptive statistics of the demographic and clinical data of the subjects.
4. Discussion
4.1. Analysis of Model Efficacy
Diabetes significantly impacts pulse wave morphology by increasing arterial stiffness, altering blood viscosity, and affecting vascular resistance. These physiological changes are reflected in the PPG signal, which measures blood volume changes in the microvascular bed of tissue. As arterial stiffness increases, the velocity of the pulse wave rises, resulting in changes to the timing and amplitude of the systolic peak in the PPG waveform. Additionally, elevated blood glucose levels lead to increased blood viscosity, which affects the shape and duration of the diastolic component of the PPG signal. Vascular resistance, influenced by microvascular complications from diabetes, further alters the overall shape and frequency components of the PPG waveform [2].
Machine learning models, particularly CNNs, are highly effective in detecting these variations. These models extract hierarchical features from the PPG signal, identifying intricate patterns associated with diabetic conditions that may not be visible to the human eye. The convolutional layers of CNNs capture local and global patterns within the PPG data, allowing the model to learn the distinguishing characteristics of diabetes-induced changes. However, due to the complex nature of model training and testing, it is challenging to pinpoint specific changes in pulse wave morphology. The models are trained on large datasets to recognize subtle variations, some of which are too minute for human detection but can be effectively identified by machine learning algorithms. In this study, CNNs analyzed the preprocessed images, examining 8400 pixels to capture subtle differences in pulse wave morphology. The CNN models effectively identified the changes, enhancing early and non-invasive diabetes detection.
The presented results, as shown in Table 2, are the performance metrics of different neural network models, including CNN, VGG16, and ResNet18, in classifying preprocessed pulse wave images for diabetes diagnosis. The CNN model exhibited a training accuracy of 82.09%, and its overall testing accuracy of 80.6% indicates a commendable ability to generalize to new, unseen data. Precision, recall, and F1 scores hovering around 80% highlight a well-balanced performance in correctly classifying both positive and negative instances. While CNNs are known for their capability in image classification, these results suggest a robust application in the context of diabetes diagnosis through pulse wave analysis.
The VGG16 model, characterized by a deeper architecture with 90.2% training accuracy, demonstrated a strong overall testing accuracy of 86.57%. The precision, recall, and F1 score values consistently exceeding 80% signify the model’s effectiveness in identifying diabetic and non-diabetic cases. The VGG16 architecture’s ability to capture intricate features in pulse wave images contributes to its success in achieving higher accuracy compared to the CNN model.
The ResNet18 model emerged as the top performer with a remarkable training accuracy of 92.50% and an impressive overall testing accuracy of 92.00%. The model exhibited high precision (93.20%), indicating a low rate of false positives, and an exceptional recall (91.43%), signifying a minimal rate of false negatives. The overall F1 score of 92.31% reflects a well-balanced trade-off between precision and recall. The ResNet’s ability to handle the vanishing gradient problem and capture relevant features in pulse wave images contributes to its superior performance.
When considering the overall results, all models exhibit satisfactory performance, with all performance metrics surpassing 80%. However, the CNN model demonstrates comparatively lower performance than the other two models. Notably, precision is a crucial metric in this study, particularly for predicting diabetic patients. The VGG16 model displays a notably higher precision value, exceeding 90%, but the resNet18 model shows the highest precision. Additionally, the F1 score, being the harmonic mean of both precision and recall, serves as another robust performance metric. The highest F1 score is achieved by the ResNet18 model. Moreover, the ResNet18 model also achieves the highest test accuracy.
The evaluation revealed that while all models achieved satisfactory performance levels with metrics surpassing 80%, the CNN model lagged behind its counterparts, VGG16 and ResNet18. The comparative analysis highlighted precision as a pivotal metric for this study, emphasizing the need for models to not only identify diabetic conditions accurately but also to minimize false positives, which is crucial in medical diagnostics.
When evaluating the learning curves, all three models display favorable trends. The accuracy graphs for each model exhibit consistent improvement. In these graphs, both validation and training curves gradually ascend. Additionally, no significant gap was observed between the validation and training curves. Furthermore, the absence of fluctuations in either the validation or training curves provides compelling evidence that all models are undergoing effective learning. These observations suggest that there may be no issues with overfitting or underfitting, indicating robust and well-generalized performance across all models. The loss curves consistently decrease with epochs, exhibiting minimal fluctuations in both validation and training curves. Additionally, there is no significant gap between the training and validation loss curves, indicating effective model learning. These observations suggest that all models are learning well and are thus more generalizable. Furthermore, both VGG16 and ResNet18 models demonstrate considerably lower loss values compared to the CNN model. This indicates that both the VGG16 and ResNet18 models have lower errors compared to the CNN model.
The findings of this study have significant implications for the field of non-invasive diabetes diagnosis. The success of these deep learning models, especially the VGG16 and ResNet18 architectures, suggests their potential integration into clinical practice. These models could serve as efficient tools for automated diabetes screening, offering a timely and accurate assessment of individuals based on pulse wave characteristics.
Despite these promising results, it is important to acknowledge the limitations of the study. The dataset size and composition may influence the models’ generalizability, and further validation on diverse and larger datasets is warranted. Additionally, real-world clinical deployment would require rigorous testing and validation across different populations and healthcare settings.
4.2. Superiority of ResNet18
Despite the commendable performance exhibited by all the models evaluated in this study, the ResNet18 model distinctly excelled, demonstrating outstanding accuracy, precision, and F1 score metrics. This marked superiority not only highlights ResNet18’s adeptness in navigating the intricacies associated with pulse wave image classification but also emphasizes its enhanced proficiency in accurately identifying and differentiating between diabetic and non-diabetic pulse wave patterns.
The remarkable performance of ResNet18 can be largely attributed to its cutting-edge architectural design, which innovatively circumvents the vanishing gradient issue—a common challenge in training deep neural networks. This problem often leads to a significant deterioration in the network’s ability to learn from data as the gradient signals used in training decrease exponentially with each layer, making deeper network training ineffective. However, ResNet18 incorporates residual learning blocks that introduce shortcut connections, effectively allowing the gradient to bypass certain layers. This mechanism ensures that the network maintains a robust learning capability throughout its depth, thereby preventing the degradation of performance as the network architecture becomes more complex.
This architectural innovation is particularly beneficial for tasks that require the analysis of complex and nuanced data, such as the classification of pulse wave images for diabetes diagnosis. The ability to train deeper networks without a drop in performance means that ResNet18 can learn more detailed and subtle features from pulse wave images, which are crucial for accurately distinguishing between the subtle variances characteristic of diabetic versus non-diabetic pulse patterns.
4.3. Implications for Diabetes Diagnosis
The achievement of deep learning models in the accurate classification of pulse wave images for the purpose of diabetes diagnosis represents a transformative advance in medical diagnostics. This progress is particularly pivotal in the realm of non-invasive diabetes screening methods. Such techniques stand to revolutionize the way diabetes is identified and managed by offering a means to detect the condition early on without the need for intrusive medical procedures. This early detection is crucial, as it opens the door to timely interventions that can halt or slow the progression of diabetes, thereby reducing the risk of developing severe complications associated with the disease.
Moreover, the precision of these models in distinguishing between diabetic and non-diabetic individuals through pulse wave analysis represents a significant advancement in personalized medicine. By leveraging the nuanced data extracted from pulse wave images, healthcare providers can tailor treatment and management plans to the individual, taking into account the specific characteristics and risk factors of each patient. This approach not only enhances the effectiveness of diabetes management strategies but also significantly improves the patient experience by minimizing unnecessary treatments and focusing on what is most effective for each person.
Additionally, the adoption of non-invasive screening methods for diabetes diagnosis has the potential to greatly improve patient compliance and comfort. The non-invasive nature of pulse wave analysis makes it a more appealing option for patients, encouraging more people to undergo screening. This increased participation in screening programs can lead to the identification and management of diabetes in a larger portion of the population, ultimately leading to better public health outcomes.
4.4. Future Directions
The performance disparities observed among the models, with ResNet18 emerging as the most effective, highlight the importance of continued research in this area. Precision in diagnosing conditions such as diabetes is critical, underscoring the need for models that can deliver highly accurate results. Future studies should focus on validating these findings across larger and more diverse datasets to enhance the models’ robustness and applicability in clinical settings. Expanding the dataset size and diversity will help ensure that the models are capable of performing well across different populations and conditions, facilitating their integration into clinical practice and paving the way for broader application of AI in healthcare.
5. Conclusions
This research successfully explored the application of convolutional neural networks in the classification of pulse wave images for diabetes diagnosis. The study demonstrated that deep learning models, particularly ResNet18, exhibit promising accuracy and reliability in distinguishing between diabetic and non-diabetic individuals based on pulse wave characteristics. Additionally, the VGG16 model demonstrates significant precision value, but resnet18 has the highest precision value, which is crucial for this research. Overall, all models have been learned effectively and are more generalizable. Therefore, the findings of this study suggest that these models can effectively classify diabetic patients from healthy persons, but the best model is resnet18, with the highest accuracy, around 92%. These results underscore the potential for incorporating deep learning techniques into non-invasive diabetes screening, representing a significant advancement towards more personalized and efficient healthcare solutions. The study suggests further investigation and validation with larger, more diverse datasets to reinforce these outcomes and facilitate their application in clinical settings.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.G. and C.J.; conducted the literature review, H.G.; writing—original draft preparation, H.G. and R.R.; data analysis, R.R., H.G. and T.K.; review, editing and supervision, S.K., J.L., C.J., U.H., D.P. and T.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Research and Publication Division at the University of Kelaniya, grant number RP/03/02/08/03/2022.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was approved by the Ethics Review Committee of the University of Kelaniya (ERC/UOK/FS/2022/019, approval date 14 January 2023) for studies involving humans.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available at the request of the corresponding author for ethical reasons.
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our gratitude to the Research and Publication Division at the University of Kelaniya, which supported our work through grant RP/03/02/08/03/2022. Special acknowledgment is extended to the staff at Base Hospital Kiribathgoda, the Family Medicine Clinic at the University of Kelaniya, and Gampaha Wickramarachchi Ayurveda Teaching Hospital, and all study participants.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Poleszczuk, J.; Debowska, M.; Dabrowski, W.; Wojcik-Zaluska, A.; Zaluska, W.; Waniewski, J. Subject-specific pulse wave propagation modeling: Towards enhancement of cardiovascular assessment methods. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0190972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proença, M.; Renevey, P.; Braun, F.; Bonnier, G.; Delgado-Gonzalo, R.; Lemkaddem, A.; Verjus, C.; Ferrario, D.; Lemay, M. Pulse Wave Analysis Techniques. In The Handbook of Cuffless Blood Pressure Monitoring; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 107–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouz, K.; Scheeren, T.W.L.; De Backer, D.; Saugel, B. Pulse Wave Analysis to Estimate Cardiac Output. Anesthesiology 2021, 134, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.T.; Wu, H.K.; Wang, C.L.; Yang, Y.-L.; Wu, W.-H.; Tsai, T.-H.; Chang, H.-H. Modeling the Pulse Signal by Wave-Shape Function and Analyzing by Synchrosqueezing Transform. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, H.; Chen, J.; Liu, Y. Micro-piezoelectric pulse diagnoser and frequency domain analysis of human pulse signals. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. Sci. 2018, 5, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, L.J.; Qi, Z.; Tu, L.P.; Zhang, Y.-H.; Zhu, L.-P.; Xu, J.-T.; Zhang, Z.-F. The Association of Radial Artery Pulse Wave Variables with the Pulse Wave Velocity and Echocardiographic Parameters in Hypertension. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 2018, 5291759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekov, E.; Miravitlles, M.; Petkov, R. Artificial intelligence and machine learning in respiratory medicine. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2020, 14, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratwani, R.M.; Bates, D.W.; Classen, D.C. Patient Safety and Artificial Intelligence in Clinical Care. JAMA Health Forum. 2024, 5, e235514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Geng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Ye, T. Pulse Wave Analysis Method of Cardiovascular Parameters Extraction for Health Monitoring. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gajdova, J.; Karasek, D.; Goldmannova, D.; Krystynik, O.; Schovanek, J.; Vaverkova, H.; Zadrazil, J. Pulse wave analysis and diabetes mellitus. A systematic review. Biomed. Pap. 2017, 161, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Díez, R.; Egaña-Gorroño, L.; Senatus, L.; Shekhtman, A.; Ramasamy, R.; Schmidt, A.M. Diabetes and Cardiovascular Complications: The Epidemics Continue. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2021, 23, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee; ElSayed, N.A.; Aleppo, G.; Bannuru, R.R.; Beverly, E.A.; Bruemmer, D.; Collins, B.S.; Cusi, K.; Darville, A.; Das, S.R.; et al. Summary of Revisions: Standards of Care in Diabetes—2024. Diabetes Care 2024, 47 (Suppl. S1), S5–S10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Zhang, G.; Liao, S. Pulse Wave Analysis. In Advanced Biomedical Engineering; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinetti, G.; Mutoli, M.; Greco, S.; Riccio, F.; Ben-Aicha, S.; Kenneweg, F.; Jusic, A.; de Gonzalo-Calvo, D.; Nossent, A.Y.; Novella, S.; et al. Cardiovascular complications of diabetes: Role of non-coding RNAs in the crosstalk between immune and cardiovascular systems. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2023, 22, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, M. Global Report on Diabetes. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241565257 (accessed on 1 February 2024).
- Song, D.K.; Hong, Y.S.; Sung, Y.A.; Lee, H. Risk factor control and cardiovascular events in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0299035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saugel, B.; Kouz, K.; Scheeren, T.W.; Greiwe, G.; Hoppe, P.; Romagnoli, S.; de Backer, D. Cardiac output estimation using pulse wave analysis—Physiology, algorithms, and technologies: A narrative review. Br. J. Anaesth. 2021, 126, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quanyu, E. Pulse Signal Analysis Based on Deep Learning Network. BioMed Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 6256126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavkar, V.C.; Shinde, A.A. Machine learning algorithms for Diabetes prediction and neural network method for blood glucose measurement. Indian J. Sci. Technol. 2021, 14, 869–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyoung, T.; Weng, W.L.; Hu, T.Y.; Lee, C.C.; Wu, L.W.; Hsiu, H. Machine-Learning Classification of Pulse Waveform Quality. Sensors 2022, 22, 8607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Thakor, N. Photoplethysmography Revisited: From Contact to Noncontact, From Point to Imaging. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2016, 63, 463–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Seok, H.S.; Kim, S.S.; Shin, H. Photoplethysmogram Analysis and Applications: An Integrative Review. Front. Physiol. 2022, 12, 808451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferizoli, R.; Karimpour, P.; May, J.M.; Kyriacou, P.A. Arterial stiffness assessment using PPG feature extraction and significance testing in an in vitro cardiovascular system. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Wowern, E.; Östling, G.; Nilsson, P.M.; Olofsson, P. Digital Photoplethysmography for Assessment of Arterial Stiffness: Repeatability and Comparison with Applanation Tonometry. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovisotto, G.; Turner, H.; Eberz, S.; Martinovic, I. Seeing Red: PPG biometrics using smartphone cameras. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 3565–3574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hettiarachchi, C.; Chitraranjan, C. A Machine Learning Approach to Predict Diabetes Using Short Recorded Photoplethysmography and Physiological Characteristics. In Artificial Intelligence in Medicine; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 322–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.R. Pulse Photoplethysmogram System for Diabetes Assessment. U.S. Patent 14/470,927, 3 March 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zanelli, S.; Yacoubi, M.A.; Hallab, M.; Ammi, M. Type 2 Diabetes Detection with Light CNN from Single Raw PPG Wave. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 57652–57665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susana, E.; Ramli, K.; Murfi, H.; Apriantoro, N.H. Non-Invasive Classification of Blood Glucose Level for Early Detection Diabetes Based on Photoplethysmography Signal. Information 2022, 13, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikonomou, E.K.; Khera, R. Machine learning in precision diabetes care and cardiovascular risk prediction. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2023, 22, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goutte, C.; Gaussier, E. A Probabilistic Interpretation of Precision, Recall and F-Score, with Implication for Evaluation. In Proceedings of the 27th European conference on Advances in Information Retrieval Research, Santiago de Compostela, Spain, 21–23 March 2005; pp. 345–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borawar, L.; Kaur, R. ResNet: Solving Vanishing Gradient in Deep Networks. In Proceedings of International Conference on Recent Trends in Computing; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2023; pp. 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).