Abstract
A significant increase in the demand for quality healthcare has resulted from people becoming more aware of health issues. With blockchain, healthcare providers may safely share patient information electronically, which is especially important given the sensitive nature of the data contained inside them. However, flaws in the current blockchain design have surfaced since the dawn of quantum computing systems. The study proposes a novel quantum-inspired blockchain system (Qchain) and constructs a unique entangled quantum medical record (EQMR) system with an emphasis on privacy and security. This Qchain relies on entangled states to connect its blocks. The automated production of the chronology indicator reduces storage capacity requirements by connecting entangled BloQ (blocks with quantum properties) to controlled activities. We use one qubit to store the hash value of each block. A lot of information regarding the quantum internet is included in the protocol for the entangled quantum medical record (EQMR). The EQMR can be accessed in Medical Internet of Things (M-IoT) systems that are kept private and secure, and their whereabouts can be monitored in the event of an emergency. The protocol also uses quantum authentication in place of more conventional methods like encryption and digital signatures. Mathematical research shows that the quantum converged blockchain (QCB) is highly safe against attacks such as external attacks, intercept measure -repeat attacks, and entanglement measure attacks. We present the reliability and auditability evaluations of the entangled BloQ, along with the quantum circuit design for computing the hash value. There is also a comparison between the suggested approach and several other quantum blockchain designs.
1. Introduction
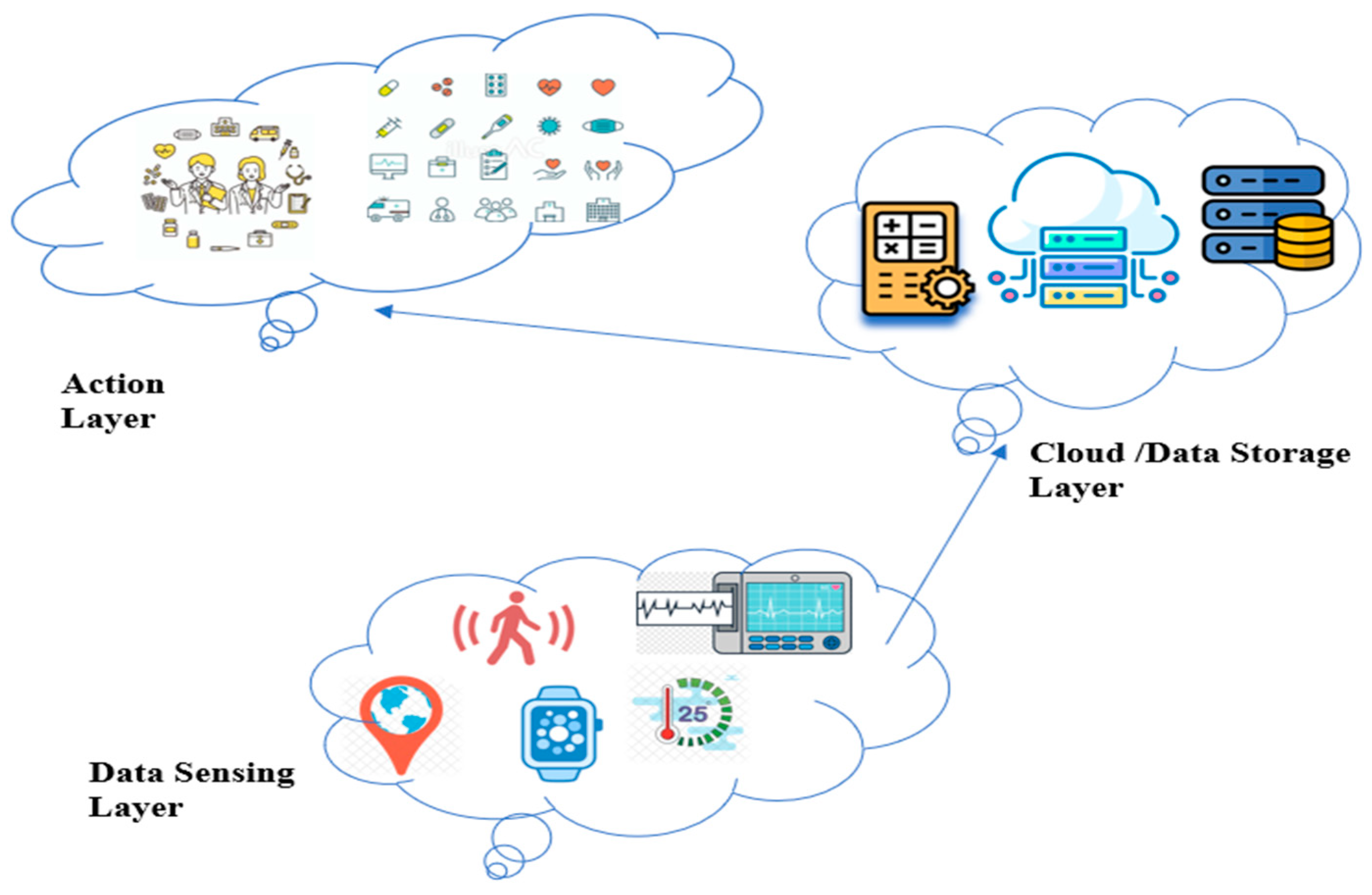
Thanks to Satoshi Nakamoto, who introduced the world to the concept of Bitcoin in 2008 [1], a novel method of conducting financial transactions emerged. Bitcoin was the first fully decentralized electronic cash method that could be relied upon. Because of the brilliant blockchain system that underlies it, Bitcoin is secure even without any kind of centralized administration because of its brilliant blockchain system. Blockchain, or distributed ledger technology, records transactions in an immutable ledger of ever-expanding blocks. In multi-party environments, it may provide a novel cooperative trust paradigm [2]. The number of blockchain use cases in the IoT related to public health has increased [3]. In order to intelligently identify, track the location of, monitor, and operate a wide range of things, including humans, the Internet of Things [4] enables their connection and collaboration over the internet. The Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) [5] connects sensor devices such as health gadgets, integrated healthcare equipment, fixed medical apparatus, and networks that track patients’ vitals and access varied patient medical records to provide valuable data for later treatment. Sensing, networking, and actions all make up the M-IoT’s three-tiered architecture. Figure 1 depicts a light-weight version of the M-IoT network model.
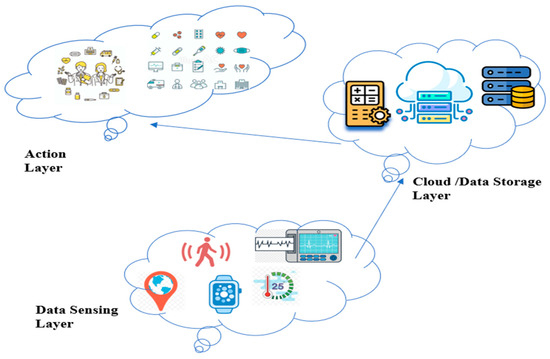
Figure 1.
Conceptualization of M-IoT systems as a layer.
Multiple sorts of decentralized healthcare facilities generate massive amounts of health records every day. When patients need to relocate to medical institutions, they sometimes have to undergo additional testing, making the exchange of electronic medical information between such hospitals essential. Electronic medical records (EMRs) are incredibly confidential due to their diagnostic and therapeutic implications [6]. Since information leakage happens throughout the flow of information among EMRs [7], keeping EMRs private and secure is a major concern. These difficulties with huge data can be overcome, according to a literature review [8], thanks to their special characteristics, such as distributed storage and immutability. Combining blockchain technology with big data offers the following advantages: Blockchain’s decentralized storage is well suited for data exchange between different medical organizations, and its one-of-a-kind data-encoding techniques make it difficult for unauthorized users to access it. EMRs saved on the blockchain network are protected and trustworthy because of the blockchain’s immutable data format, which prevents unauthorized changes to the records. Third, fraud can be avoided: Current big data cannot help with detecting phony communications. Hospitals and clinics can instantly verify the authenticity of potentially tampered electronic medical records thanks to blockchain technology. Healthcare organizations can now use data from multiple sources to provide comprehensive and methodical diagnoses using analytics that monitor data in real time. Integrating blockchain technology with IoMT systems (BIoMT) can guarantee the anonymity, security, and authenticity of every electronic medical record. Hospitals and clinics can transfer electronic medical records (EMRs) and retrieve their history at any time to check for tampering [9]. Digital signatures and elliptic curve cryptography [10] are two examples of the traditional cryptographic techniques on which blockchain technology depends; both have their own security flaws [11]. Quantum machines [12], developed alongside quantum information processing [13] and quantum computing devices [14], pose a threat to current blockchain systems. The Shor and Grover algorithms [15] have such high computational requirements that malevolent medical organizations will monopolize block generation. By all the above means, it is obvious that blockchain is in quantum danger [16], and it is therefore necessary to migrate to quantum mechanics properties exploiting blockchain and entangled quantum health records (EQHRs) by using the new security features of quantum cryptography [17]. Quantum blockchain and electronic medical records have made great strides in theory, but they still face several obstacles in practice. It is difficult to guarantee the security of EMRs that rely on conventional blockchain because they are vulnerable to quantum computer attacks. Researchers have only scratched the surface of what quantum blockchain can do in terms of data processing and exact data structure. In order to protect blockchain networks against quantum computer attacks, this research proposes a new physics-inspired blockchain network.
1.1. Key Findings and Observations
Emerging Applications: Prevailing research emphasizes quantum computing’s capacity to transform several facets of healthcare, such as genetic analysis, medical data management, and medication discovery. When it comes to medical infrastructure, blockchain technology is known for its ability to provide transparent and safe data sharing.
Integration Challenges: Healthcare stands to gain a great deal from both blockchain and quantum computing, but combining the two will be no easy feat. Adoption is hindered by issues with scalability, seamless integration, and fulfilling regulatory requirements.
Security and Privacy: When designing a healthcare system, privacy and security must be top priorities. To fix security flaws and prevent manipulation and unauthorized access to patient data, researchers have concentrated on creating cryptographic methods and consensus processes.
Quantum-Resistant Solutions: In order to protect blockchain technology against potential future cryptographic assaults, there is an increasing demand for solutions that are resistant to quantum computing. In light of this difficulty, quantum blockchain technology is being considered as a potential solution to guarantee the permanent safety of patient records.
1.2. Gaps in the Literature
Quantum-Assisted Healthcare Applications: Quantum computing has been the subject of much theoretical investigation, but few large-scale investigations have shown concrete implementations or use cases in healthcare.
Interoperability and Standards: Although there is some discussion of the difficulties associated with medical architectural data standards and interoperability in the existing literature, there is little insight into how blockchain and quantum computing could solve these problems.
Regulatory Considerations: There is a lack of literature on the regulatory consequences of medical architectures that use quantum-assisted blockchain technology, despite the fact that regulatory compliance is an essential part of healthcare data management.
Quantum-Blockchain Performance: Quantum blockchain has been suggested as a way to share healthcare data in a safe and scalable way, but there have not been any studies that actually test it out in real-life healthcare environments to see how it works.
In order to fill these gaps, researchers in quantum computing, blockchain, and healthcare must work together. To achieve the maximum potential of blockchain technology with quantum assistance in healthcare architectures, future research should concentrate on regulatory compliance, performance assessments, and practical implementations.
2. Contribution and Motivation
From the above, it is clear that research on the quantum blockchain is clearly in its early stages, as this demonstrates. So, this study proposes QUMA, a quantum blockchain-based system for processing medical data. It is a full-fledged concept with excellent security, secrecy, and practicality. The following are the notable innovations and contributions:
- A whole new network of Quantum Mechanics-based chains for Highly Advanced Medical Information Networking (QMEDCHAIN) is being developed. We use entangled states to connect the quantum blockchain nodes. A single qubit stores the hash values for individual blocks, and the regulated actions required to combine quantum blocks automatically create time stamps.
- An innovative protocol for entangled quantum medical records (EQMRs) is proposed, and the data flow and processing in the network are explained in detail. This protocol implements a quantum authentication technique. The feasibility of the new EQMR protocol is explained by linked simulations, and its security aspects are fully realizable. Additionally, the mechanism of information processing in the network is elucidated via an example.
- This study provides an in-depth evaluation of security measures. The theory-derived security research demonstrates the EQMR protocol’s security against three common types of attacks: external attacks, measurement replay attacks, and entanglement attacks. The correctness and traceability analyses of the BloQ are well presented. This study also compares the proposed QMEDCHAIN with numerous current blockchain models, particularly quantum blockchain systems.
The following is the outline for this paper. Section 2 describes the theoretical underpinnings of quantum mechanics postulates, quantum hash generation (QHF), and quantum embeddings (QE). Section 3 describes the concerns about blockchain’s security in light of forthcoming quantum computing, as well as the notations used in the research. Section 4 describes the existing work. Section 5 discusses the proposed system’s QUMEDCHAIN data format, QHF, QE, and BloQ representation. Section 6 describes the EQMR protocol procedure and validation process for health records. Section 7 discusses the proposed system’s collision rate and multi-collision analysis. Section 8 focuses on EQMR protocol attacks and analyses and information traceability, and it concludes with qualitative and quantitative comparisons with existing systems. In Section 9, the paper comes to a close.
3. Concerns about Blockchain’s Security in Light of Forthcoming Quantum Computing
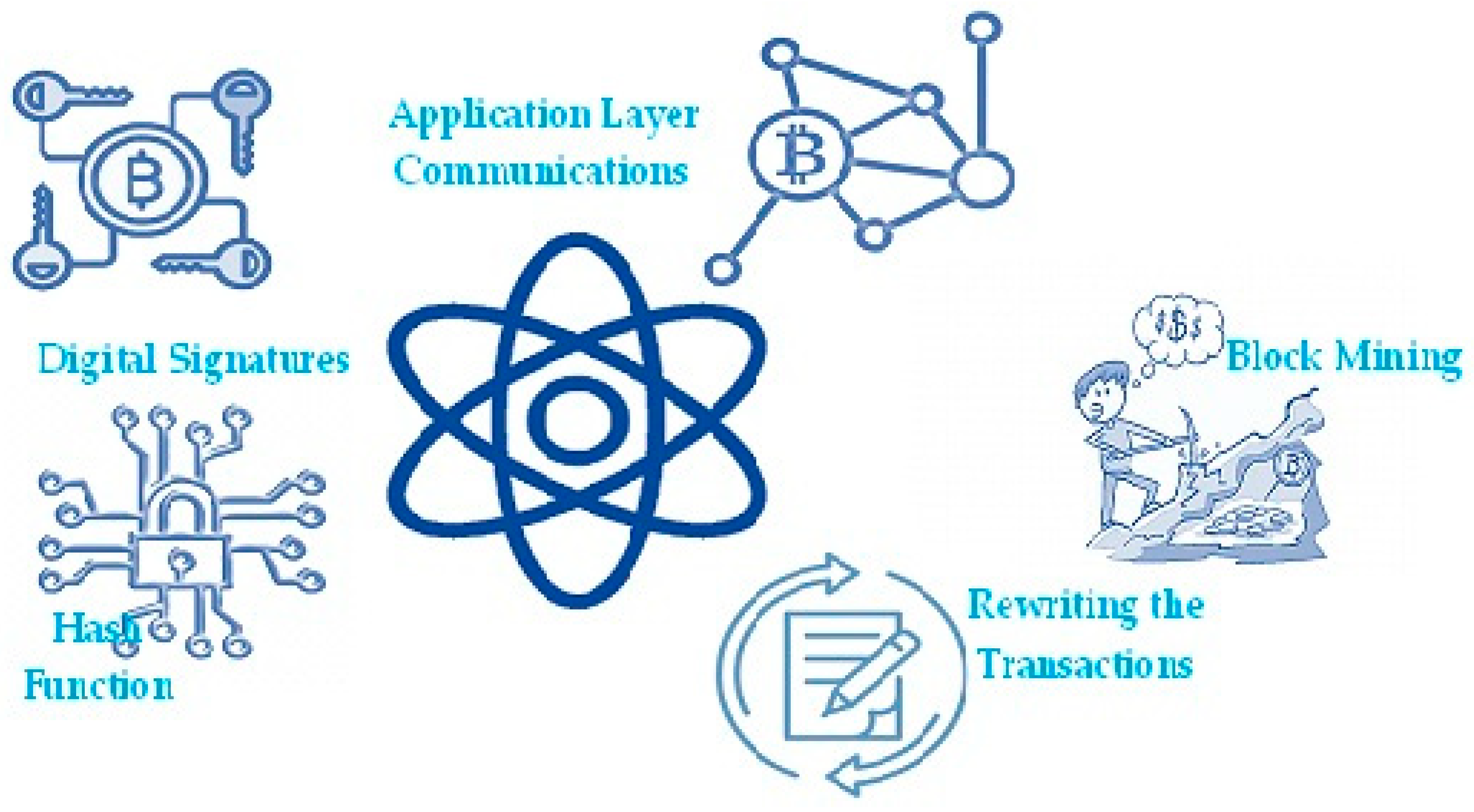
There will be possibilities and threats to digital technology in the new paradigm that quantum computing ushers in. When powerful quantum computers crack a number of crucial encryption techniques in use today, there will be a plethora of new threats. Since blockchain is primarily a cryptographic system, it is vulnerable to these kinds of attacks. The above five threats have been identified as when blockchain technology and quantum computing meet, according to research [18,19,20]. As the number theory is the basis for cryptography and hash functions, the quantum algorithm known as Grover’s algorithm may search an unsorted database with N items in O(√N) time, as opposed to the conventional techniques which take O(N) time. Since quantum computers are so effective at reversing hash functions, the security and immutability of blockchain data are jeopardized. Figure 2 exhibits the areas of blockchain that are vulnerable to quantum threats.
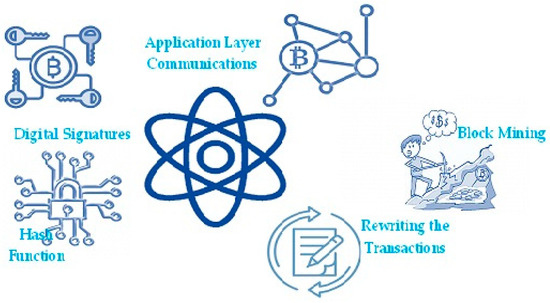
Figure 2.
Quantum threats to blockchain.
4. Associated Works
Ever since the Internal Report 8105 [21] from NIST in 2016, the fact that contemporary encryption is vulnerable to quantum attacks has been widely recognized. As the blockchain system is based on classical cryptographic algorithms, quantum computations have become the scourge of the blockchain system. Considering the famous blockchain system Ethereum, account abstraction (ERC-4337) [22] has been introduced for users’ accounts to be quantum resistant. Having the advantage of plug-and-play or modular architecture concepts in the Hyperledger fabric, we will be able to replace the quantum-resistant system in place according to the situation. Among blockchain experts, this is the consensus view. Many are aware of the impending arrival of quantum computers, but there is no pressing need to act on this information just yet. Furthermore, we still lack a complete understanding of the consequences of quantum computers’ attacking capabilities on blockchain platforms. Few of the world’s most prominent blockchain technology summits even touch on the subject. Although the study is more fascinating from an academic point of view than an empirical perspective, it is nevertheless worth discussing.
Consistent with our presentation in “Concerns about blockchain’s security in light of forthcoming quantum computing,” the literature [23,24,25] has appropriately addressed the big picture of the threat that quantum computers pose to blockchain technology. In order to decipher blockchain network encryption, several researchers have been building models to estimate how many qubits would be required. Based on the literature [26], if the surface code, code cycle time, response time, and physical gate error were to be used to crack the encryption in one hour, it would need 317 × 106 physical qubits. Conversely, a single day would require thirteen million physical qubits to decrypt the encryption. Though many researchers claim different qubits to decrypt, the exact number of physical qubits required for this function remains unknown. In August 2023, Ed Gerck, a researcher, claimed that the RSA-2048 key had been broken, which stirred the entire research community. There is some prior research that suggests ways to protect blockchain networks and protocols against quantum computer assaults. There are two main schools of thought when it comes to blockchain technology proposals: quantum blockchain (QUAB) and post-quantum (PQB). Using quantum phenomena such as quantum key distribution (QKD) to secure interaction among nodes and entangled properties to enable no tampering of transactions and avoid double spending, quantum blockchain (QUAB) networks are able to withstand quantum attacks [27,28,29,30]. Scientists created a blockchain system that is both permissive and secure against quantum attacks [31] to combat the threat that quantum computing brings to blockchain technology. To obtain blockchain consensus, the developed one uses a voting-based consensus algorithm and a digital signature mechanism based on QKD. Because digital signatures are vulnerable to quantum computer assaults, [32] used quantum key distribution (QKD) networks the same year to enable safe authentication on blockchain networks. Also, the authors employed an information-theoretic broadcast system in which everyone on the network agreed on fresh blocks on equal terms, as opposed to leaving the creation of new blocks up to a single miner. In 2019, they developed the Logicontract unconditionally safe signing technique based on quantum key distribution [32]. In 2021, [33] suggested a protocol for building a blockchain infrastructure that would allow for safe data transfer between Internet of Things devices and would use quantum walk technology for identification and encoding. By combining quantum infant technology with a conventional blockchain capable of processing stateful smart contracts, [34] successfully built a basic hybrid classical–quantum payment system. In order to circumvent the issue of quantum banknotes’ lack of trustworthiness, they utilized blockchain technology to create a public-key quantum money system that utilized quantum states as currency. Actually, the paper does not give an explanation of the structure of quantum blockchain; it just builds a quantum money system using conventional blockchain. Based on their theoretical framework, [35] conducted a qualitative study of American EHR users in 2020 and investigated the potential commercial and academic applications of blockchain technology for EHR, security, and storage. Several characteristics features of blockchain [36] has been discussed for the secured transmission of HER. An innovative blockchain-based credibility score-based approach (CSA) was proposed in [37] to guarantee the integrity and confidentiality of electronic health records. There are still major practical concerns with quantum blockchain and electronic health records, despite numerous academic achievements in both areas. Traditional blockchain-based EHRs are susceptible to quantum computing assaults, which makes security maintenance a challenge. While studies on quantum blockchain’s exact data structure and information processing are still in their infancy, what little there is shows promise. Another group offers a fascinating method for hash chain-based digital signatures. While these post-quantum blockchain projects show great promise, they do not yet offer comprehensive solutions for blockchain networks that are resilient to quantum technologies; at present, these outlines are limited to safeguarding digital signatures and assets. Furthermore, every single proposal does not aim to improve upon any pre-existing blockchain network; the only exception to this is the Matri CT protocol, which is relevant to the Monero coin. Hence, safeguarding the present assets held in existing blockchain networks, totaling thousands of millions of dollars, does not directly follow from this.
Despite numerous scientific advances in QUAB and EMRs, several practical problems persist. Traditional blockchain-based EMRs are difficult to secure because they are vulnerable to quantum computer attacks. Research on the exact structure of data and how QUAB processes information remains in its infancy.
5. QUMEDCHAIN—Quantum Mechanics-Based Chain for Highly Advanced Medical Information Networking
This section provides an overview of the suggested quantum mechanics-based blockchain (QMEDCHAIN), explains how the entangled quantum health record (EQHR) protocol works, and provides an illustrative case supported by relevant simulations.
5.1. The Data Structure of Classical Blockchain vs. Quantum Blockchain
Table 1 lists the notations used and their explanations in the research work. Table 2 demonstrates that the data structures of quantum blocks include both a header and a body in comparison with classical blockchains. The header of a block contains the data necessary for mining. The current block’s body contains a directory of hospital records. As we are engaging with medical records, information is very sensitive, and if the qubits get into the superposition, we may tend to lose information. We connect the Qblocks (quantum register) together using the Z gate, a unitary gate that operates on a single qubit.

Table 1.
Explanations of commonly used basic notation.

Table 2.
QMEDCHAIN vs. classical blockchain data structures.
More specifically, it changes the value from 1 to −1 while leaving 0 unmodified. A 180-degree (radians) rotation about the qubit’s Z axis accomplishes this. This rotation changes the qubit’s phase. The preceding array describes the function of Z gates: In the case of qubits, two bracket vectors stand in for the computational bases of 0 and 1.
In the above matrix, the computational base of 1 has been flipped to −1, which shows that when the qubit is |0⟩, no action will be performed. Once the qubit is measured, it will not change the state and avoids the superposition state.
Measurement
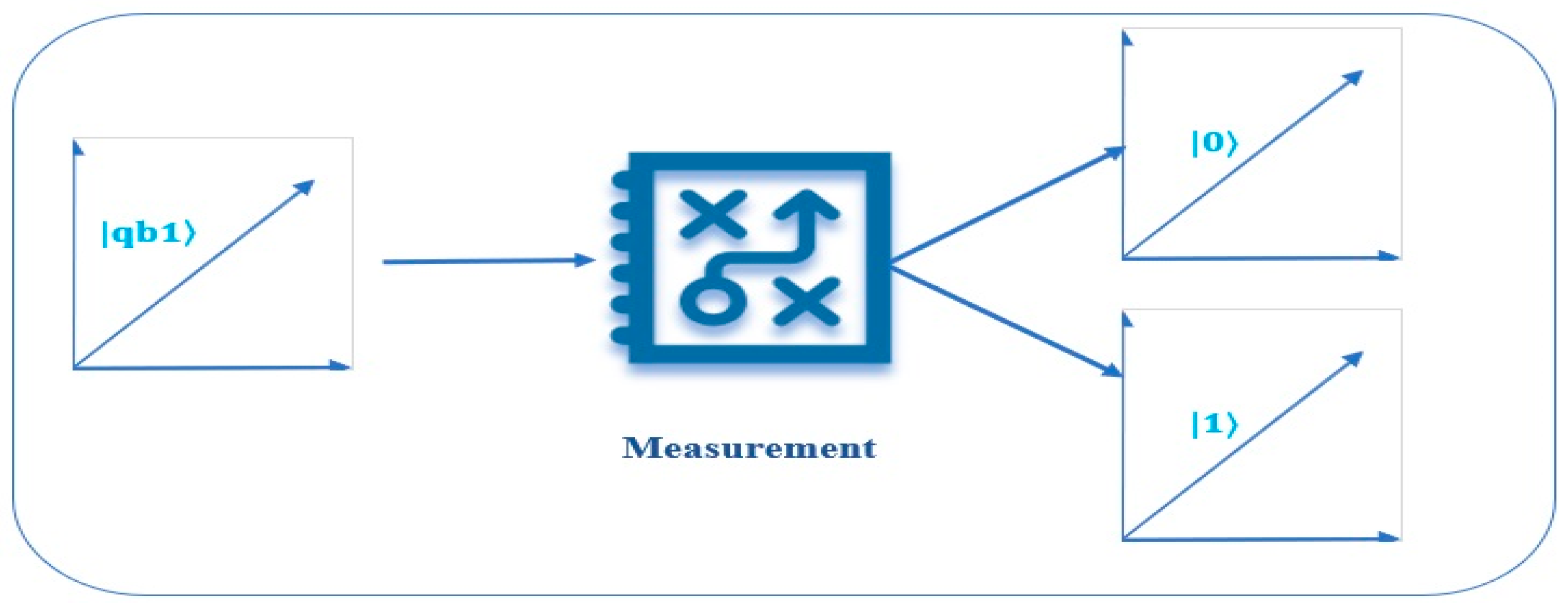
Here, we use a Hermitian operator H on the measurement quantum block. The eigenvector’s amplitude, represented by ‘a’, determines the likelihood of the register collapsing into one of its eigenvectors in the operator that is proportional to |a|2. If that were the case, the probability of |y|2 and |x|2 would cause our qubit |qb1⟩ = y|0⟩ + x|1⟩ to collapse to |0⟩ and |1⟩, respectively, as illustrated in Figure 3. It is standard practice in quantum computing to use the aforementioned matrix while measuring. In the computational basis, this reduces our qubits to a binary value of |0⟩ or |1⟩. What this clearly shows us is that our qubit’s behavior is further complicated:
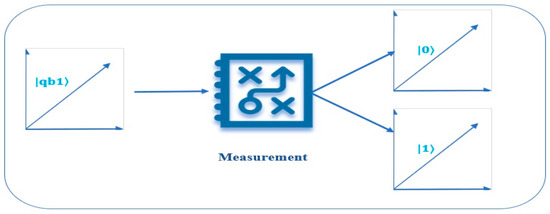
Figure 3.
Collapse of |qb1⟩ into |0⟩ and |1⟩.
To begin, our qubit vector’s magnitude must always be calibrated to 1, as the likelihood of getting a measurement is 1. Moreover, the act of measuring disrupts the superposition of our qubit, resulting in the loss of the data contained within its amplitude. The fact that we can only receive a yes-or-no response in spite of all the details stored in these qubit states is a disappointing limitation of quantum computer science.
5.2. Quantum Hash Generation
Here, we describe the development of a QHF via refinements to the 1-D discrete-time quantum walk on a sphere for two particles. The quantum walks of two walkers whose paths are constrained to the circle is described by a 1-D, two-particle discrete-time quantum walk on a circle. Then, the operators and becomes the following:
In this case, is analogous to . For the full conditional shift operator , we have ⊗ . For each step of the walk, if the last 4-bits of the message that is sent is 10(11), then the interaction will be W0W1(W2W3).
For instance, if the input is ‘011111011’, then the last state of the walk is represented as follows:
where 0 = ( ⊗ 0), 1 = ( ⊗ 1), and so on. Then, the initial condition of the entire quantum system |ψ⟩ is described by the following:
|ψ⟩0 = |a, b⟩⊗|c1, c2⟩
|c1, c2⟩ = (α|000⟩ + β|001⟩ + ϒ|010⟩ + δ|011⟩ + ε|100⟩ + ζ|101⟩ + η|110⟩ + θ|111⟩
The controlled alternative quantum walk method finally yields an N × N matrix of probability distributions. This matrix may be used to generate the hash of message m.
5.3. Quantum Embedding
Quantum embedding (QE) utilizes a quantum feature map to visualize bits as states of quantum matter (Qubits) in a Hilbert space. Using conventional datapoint ‘i’, it generates a quantum state |⟩ by adjusting the settings of a quantum circuit’s gates. The abstract representation of the conversion of classical blockchain to quantumized blockchain is shown in Figure 4.

Figure 4.
An abstract representation of the conversion of classical blockchains to quantumized blockchains.
Consider traditional input data (bits), which consists of K instances, each of which has L attributes.
where is the L-dimensional vector for k = 1, 2, 3…… K. We can employ several embedding approaches to incorporate these data into quantum subsystems, such as qubits or Qblocks. A quick explanation of the technique called basis embedding is provided below.
The process of basis embedding (BE) entails associating every data point with a computing ground state within a quantum-bit system. Therefore, we must represent traditional information as a sequence of 0 s and 1 s. The embedded quantum state pertains to the transformation of a string of bits into the corresponding states of the quantum layer, where a specific quantum state represents each bit.
As an illustration, the value of i, which is equal to 110111, is denoted by the quantum state of a six-qubit system, specifically denoted as |110111⟩. Therefore, each quantum layer corresponds to a single unit of traditional bits.
Let us examine the traditional dataset of health records denoted as H, which has been discussed before. In the context of basis embedding (BE), it is required that each instance be represented as a binary string composed of N bits.
Specifically, an example is denoted as (, …, ), where each is either 0 or 1 for i = 1, …, N. Given that every attribute is encoded using unitary bits (a single bit), it is possible to unambiguously associate each input example with the corresponding quantum state |⟩.
This implies that the minimum requirement for the number of quantum components, denoted as n, must be equal to or greater than N. The superpositions of every base state are a useful way to represent the full dataset as follows:
As an illustration, consider a classical dataset consisting of four examples, denoted as = 0000 and = 0111. The basic encoding method in (7) utilizes a pair of qubits to represent the states |⟩ = |0000⟩ and |⟩ = |0111⟩, leading to the following:
Now that the above dataset has been embedded as qubits (6), the state of the four Qblocks can be represented as follows:
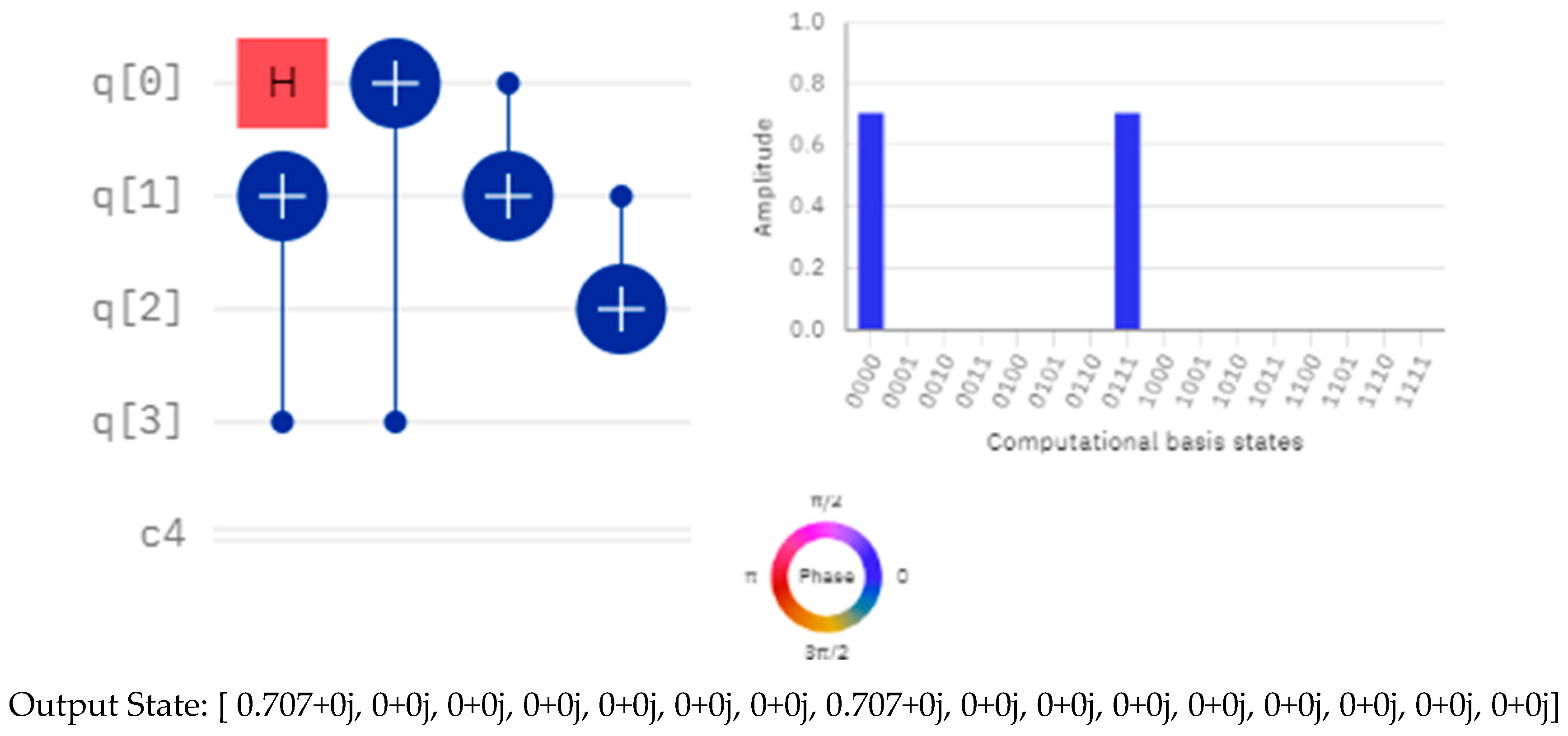
One quantum bit can store a sequence of n bits, resulting in a significant reduction in resource usage. The subsequent passage serves as a tangible illustration of Figure 5.
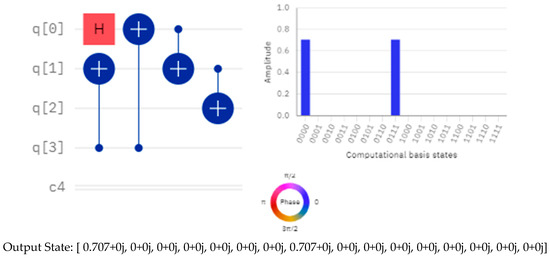
Figure 5.
A tangible illustration of quantum embedding with 4 qubits and its computational basis states.
5.4. Representations of Qblocks
Equation (9) clearly shows that storing a sequence of ‘n’ bits requires only one quantum bit, significantly reducing resource usage. The fine-grained form of Equation (9) will represent the Qblocks as follows in Table 3.

Table 3.
Representation of Qblocks.
6. Quantum Entangled Medical Record (EQMR) Protocol
With the help of information-sensing technologies, the Internet of Health Things (IoHT) aims to intelligently identify an area or location and track, manage, and monitor healthcare amenities. The proposed blockchain-based quantum health record system maintains public health record management (HRM) across numerous healthcare providers to provide better healthcare management for patients. By allowing doctors to access each other’s notes, patients will be able to monitor and ensure that all treatment procedures are being carried out correctly. The use of shared health records facilitates transparency throughout the treatment process, enabling the effective supervision and monitoring of each step of treatment. We created a quantum-based hospital network to maintain a quantum blockchain system.
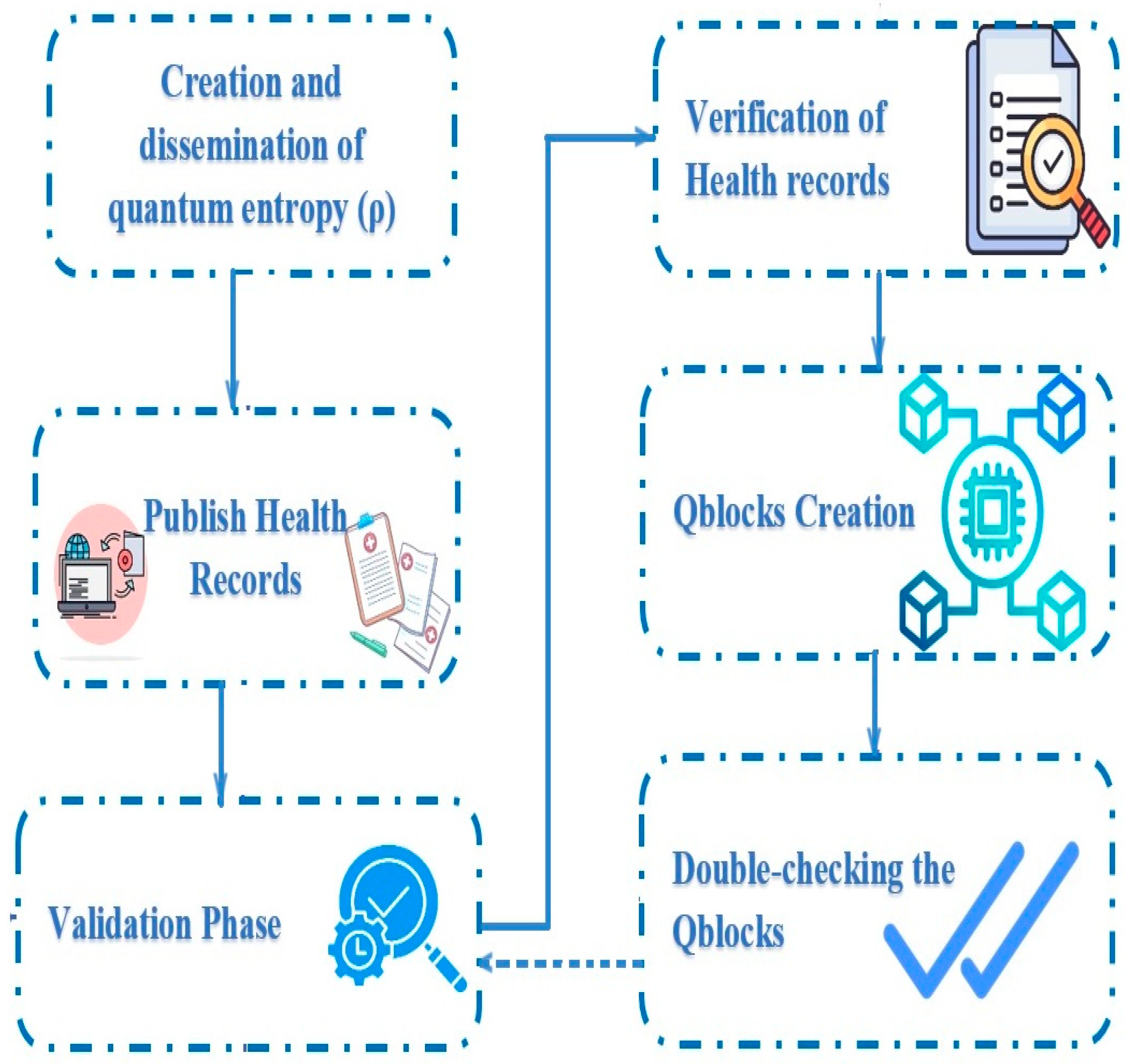
As soon as the arrangement is live, instruments begin producing raw health data for patients, and doctors begin entering the data as a health record. A group of hospitals and other medical facilities have banded together to create a quantum network and keep a quantum blockchain up and running. When the system is live, sensors collect raw patient health data, which doctors and nurses then add to treatment records. These records will include the patient’s identification. A patient’s health record comprises these data, their generation time, and their origins. The procedure’s schematic and the QHR protocol’s flowchart are depicted in Figure 6. The procedure’s detailed steps are as follows:
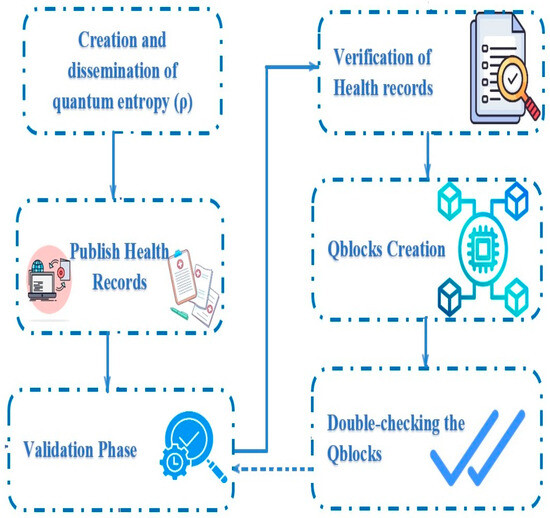
Figure 6.
A flowchart of the EQHR protocol’s procedure.
6.1. Creation and Dissemination of Quantum Entropy
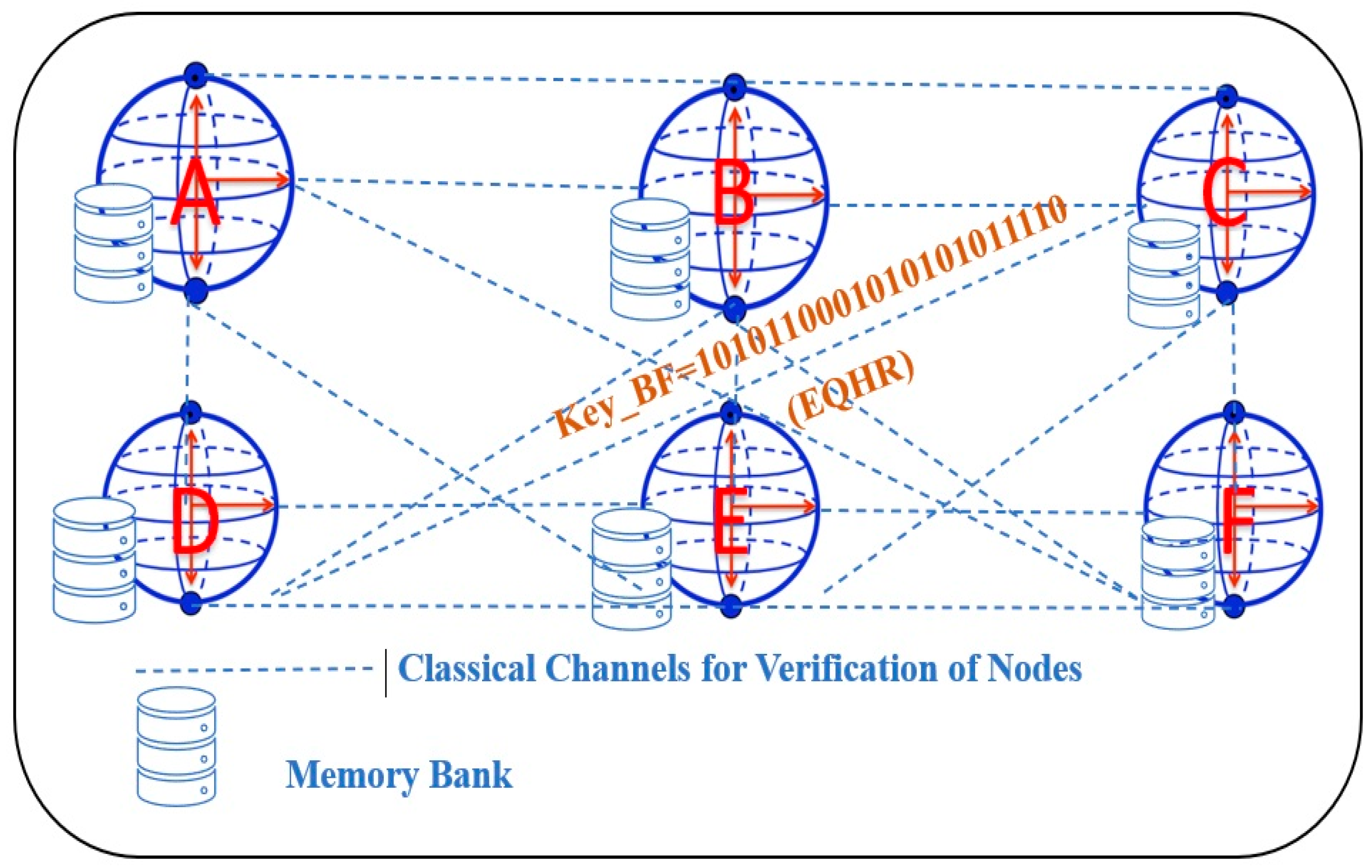
Multiple branches of the hospital collaborate to establish a secure quantum information network. All of the nodes are trustworthy and can reliably exchange quantum and classical data, as well as prepare, store, and measure quantum states. Let each node have access to quantum entropy so that post-quantum keys may be created using pure quantum randomness. If individual nodes fail to generate sufficient quantum entropy of the lowest value (0.02), they can access a central source through a quantum-resistant link. A quantum network distributes the same N-key string in an unconditionally secure manner to each pair of quantum nodes. Take, for instance, the six-node quantum network seen in Figure 7. A–F are the six nodes, and any two of them can have a conversation with the others. Each node has the ability to store, prepare, and send quantum states.
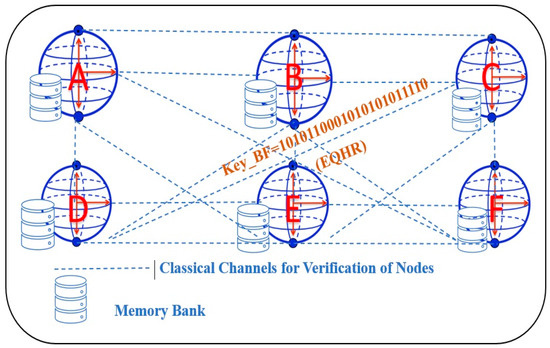
Figure 7.
A six-node quantum network for verification process.
Each pair of nodes communicates with each other using a mix of quantum and classical channels, and they use the same set of keys, each with a length of 20, for example: 1010110001010101011110. The EQHR protocol is responsible for key distribution.
Following the dissemination of the health record data, nodes D, E, and F will send requests for verification to node A, while nodes A, B, and C will send verification calls to node D. Here, we will pretend that node D has decided to send node A a validation request. Assuming that all 20 Bell states prepared by node D’ are “,” the network will use these states to authenticate users. Node D delivers the sequence S2 to node A, who picks particles at locations 2, 4, 6, 10, 13, 15, 17, and 19 for measurement. Table 4 displays the underlying measurements and the resulting values.

Table 4.
Measurement of base input and its corresponding output of particles at positions 2, 4, 6, 10, 13, 15, 17, and 19.
6.2. Publish Health Records
Now, let us say that node “A” in the quantum network is interested in making its health records public. The hash of the health record is programmed on the “A” network to other nodes in the qnet. Assuming that two health records are produced during the period, nodes B and F would each make available a health record (health record B, HB) and node F’s health record (health record F, HF). All of the other nodes obtain information about the health record, including the patient’s identifier, the data’s origins, a timestamp, and the data hash (Table 5).

Table 5.
Equivalent bits in the hash value and the ratio to and .
6.3. Validation Phase
To counteract attacks from near-term computing, the QUAB network employs quantum authentication in the place of a conventional digital signature and cryptography algorithms. After obtaining A’s health data, each node will issue a validation request to her. To better illustrate the steps involved in the validation process, we use the subsequent scenario, in which D sends a validation request to A. The following flowchart provides a representation of the identity-validation process.
6.4. Verification of Health Records
After establishing A’s identity, the remaining nodes in the network check the hash to ensure the health record is accurate. If there are no issues, we add the health record to the bank of health records for compilation.
6.5. Qblocks’ Creation
The intervals of block production are managed for approximately ten minutes, utilizing the uncertainty of obtaining arbitrary numbers, and every healthcare organization spends their savings fighting for recordkeeping privileges. In view of that, node “B” has been given access to the books. He will now package the health records in the health records bank that are due to be packed into blocks during the time period and send them out to the other nodes.
6.6. Double-Checking the Qblocks
Once “B” broadcasts the Qblock information, the remaining nodes verify the Qblock hash value, the adherence to the hardness objective and mining nonce, and the accuracy of the health record list in the block. Each of the nodes in the Qnet adds the Qblock to its private replica of the QUAB if all the data contained in the Qblock are accurate; otherwise, the block is deleted. Each Qblock’s hash values establish entangled states with the others.
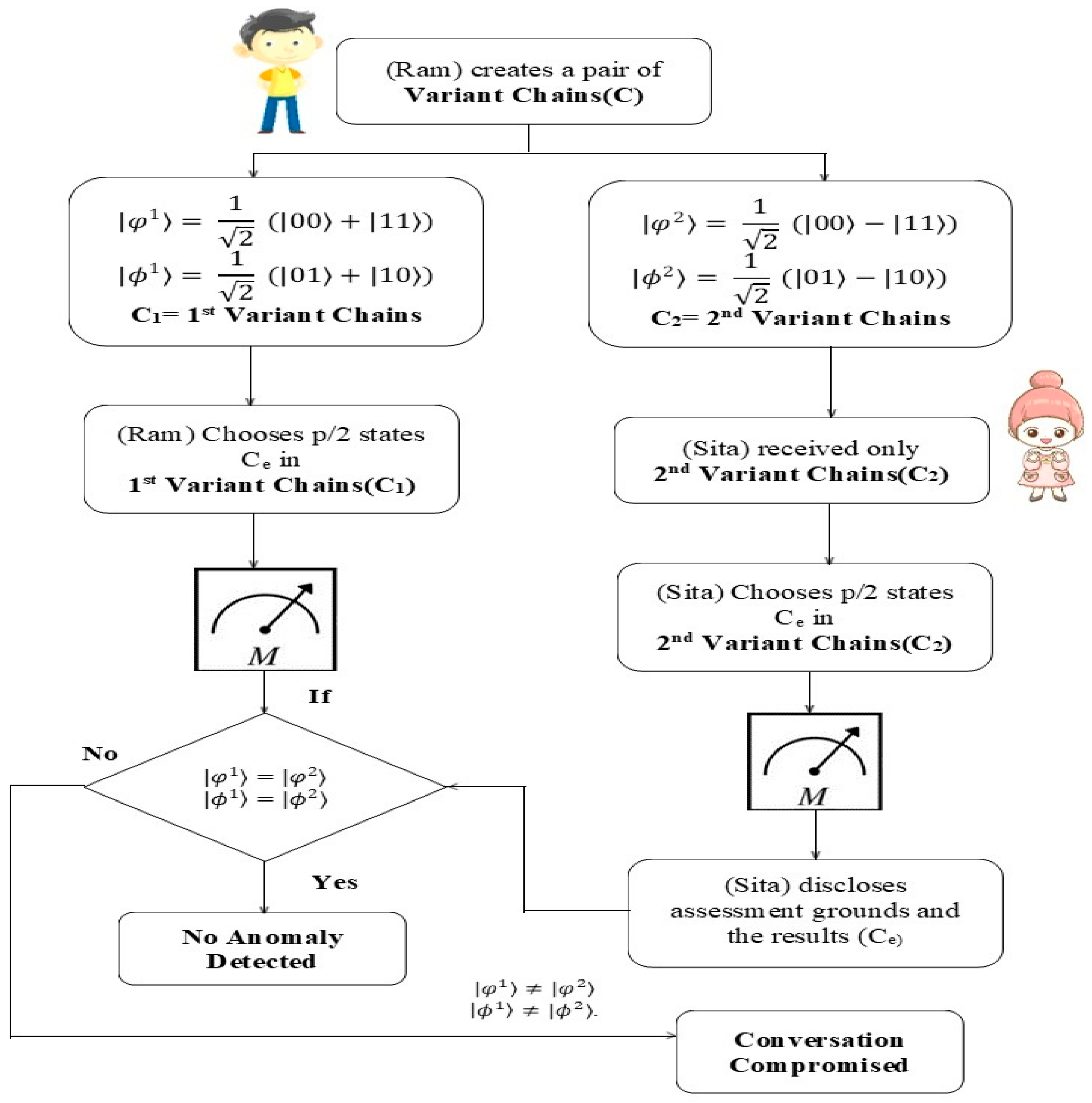
6.7. Validation Process and Its Descriptions
S1: (Ram) selects and prepares himself a chain from the following Equations (10)–(13), C = {|ψ1⟩, |ψ2⟩.... |ψ (n/2) ⟩}, while also recording his various states. Here, Equations (10) and (11) are C1, which is the first variant chain, and Equations (12) and (13) are the second variant chain.
S2: With each phase or position in C, (Ram) retains the first variant to create chain C1, and (Sita) receives the second variant to form chain C2. To identify anomalies, (Sita) chooses p/2 and states Ce in C2. After recording the states of Ce and arbitrarily selecting assessment grounds to detect variants in Ce, she discloses both the assessment grounds and the results. When measuring the Ce variations, Ram uses the same evaluation criteria and then correlates the findings. Both variables’ performances on the state’s evaluation are related; the following Table 6 exhibits the same.

Table 6.
Selected variant chain assessment values.
When the error probability is below the specified limit, (Ram) and (Sita) proceed to (S3). If not, they discard the selected variants when and . If not, it is considered an attempt at eavesdropping, leading to the termination of the conversation.
S3: Both (Ram) and (Sita) prefer unitary transformations, which preserve the inner product of the selected chain variants, which is more powerful than the operation used in (S1). Based upon the type of information that Ram wants to send to Sita, he will apply the quantum gates to his qubit. For instance, (Ram) just transmits (Sita) the value ‘00’ without touching his qubit if he wishes to do so. To convey the number ‘01’, Ram modifies his qubit by applying the phase flip Z, which changes its quantum state to Equation (12). (Ram) uses the NOT gate to communicate the integer ‘10’, providing the result equation. Equation (13) is the result of applying NOT and Z to send’11’. Then, based on the assessment of the different selected chain variants, validation can be conducted.
Figure 8 demonstrates the above entire scenario of Ram seeking validation from Sita.
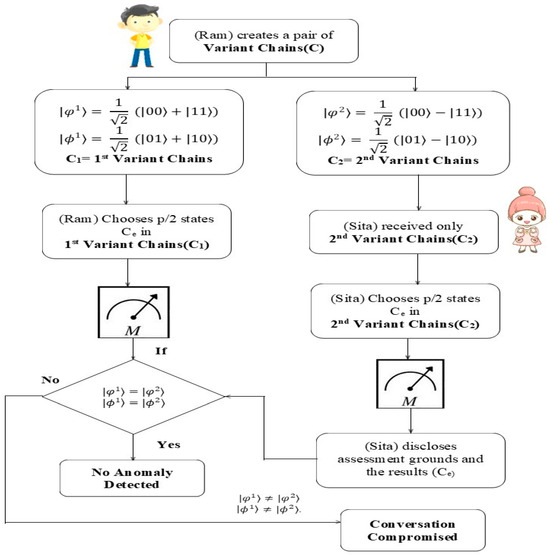
Figure 8.
A flowchart for Ram seeking validation from Sita.
7. Results and Analysis
This section discusses the experimental set up along with system results for collision rate and multi hash collision analysis.
7.1. Experimental Setup
The experimental setting will be our starting point. For our simulations, we use a Python framework for IBM’s open-source quantum software development kit, Qiskit 1.0, and for EQHR simulations, we use DESERT. We employ several PQCs as benchmarks [12]. We use Qiskit’s fake provider module, which includes noisy simulators that simulate actual IBM Quantum systems using system snapshots, for benchmark execution. This module is called fake kolkatav2 [27 qubit]. The correlation map, underlying gates, and qubit parameters are fundamental pieces of data about the developed QMEDCHAIN that are contained in these snapshots. When evaluating performance, we use the following:
7.2. Collision Rate
When a specific input dataset is sent into a QHF, the collision rate (CLR) may be used as a measure to quantify the number of collisions. It can be represented as (14).
Here, freqavg–normal and SD denote the average frequency of hash values and the standard deviation generated by a specific function for a given input dataset, and is the sum of all the potential hash values that an n-qubit quantum hash circuit is capable of achieving.
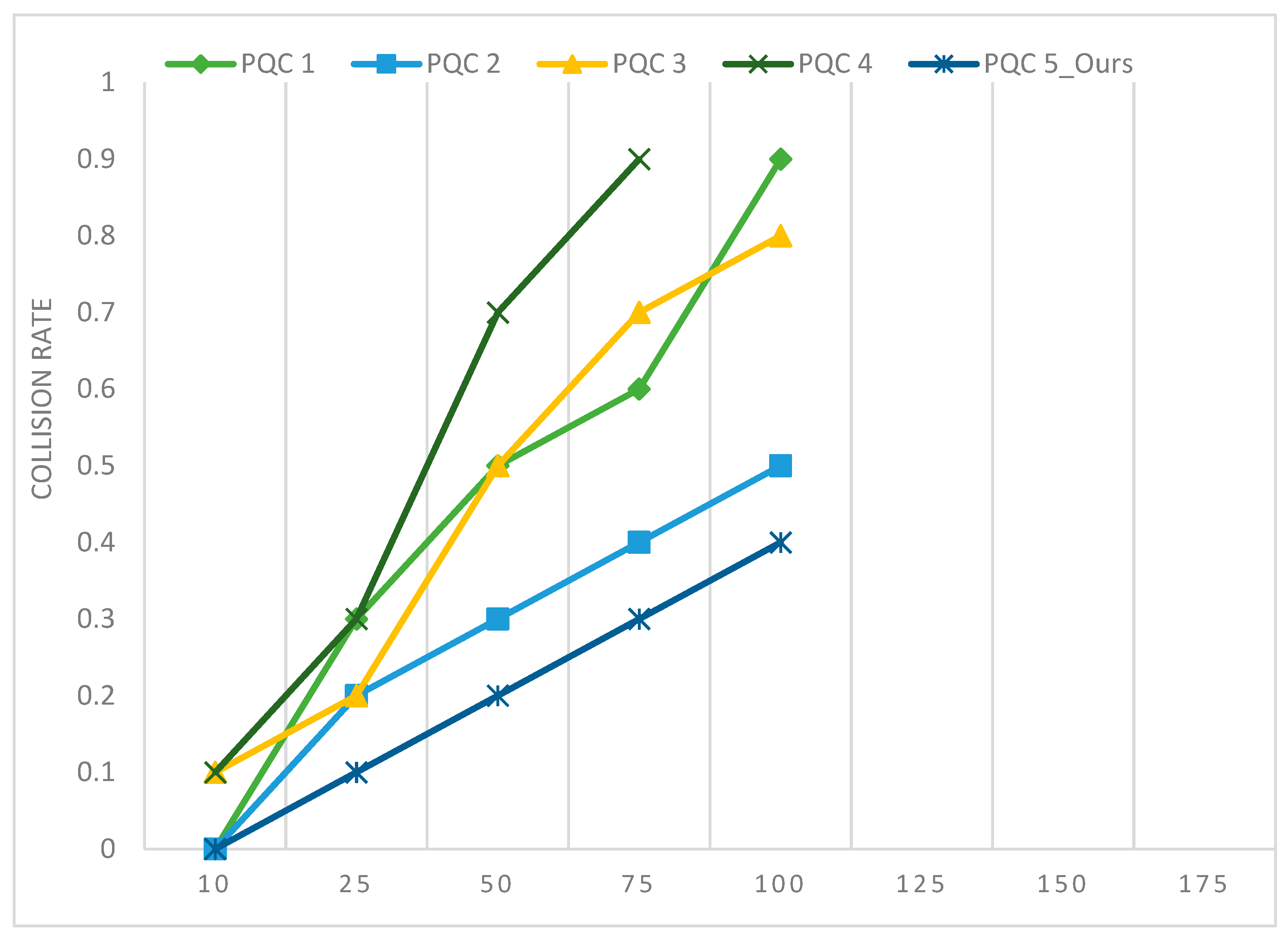
When applied to the provided input data, a lower collision rate implies that the QHF performs better. Figure 9 exhibits the lower collision rate in the PQC5 benchmark used in the generation of QHF.
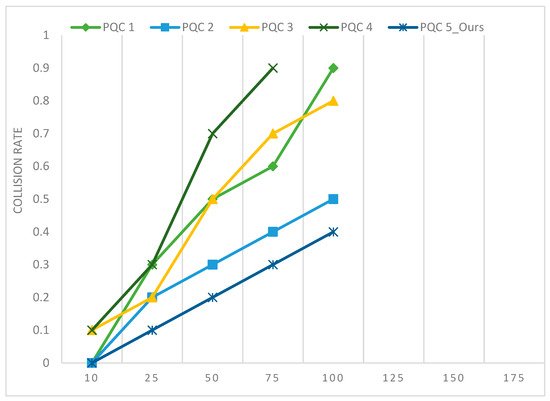
Figure 9.
PQC benchmarks and their collision response to different batch sizes. Run on fake kolkatav2 [27 qubit].
7.3. Multi Hash Collision Resistance Analysis
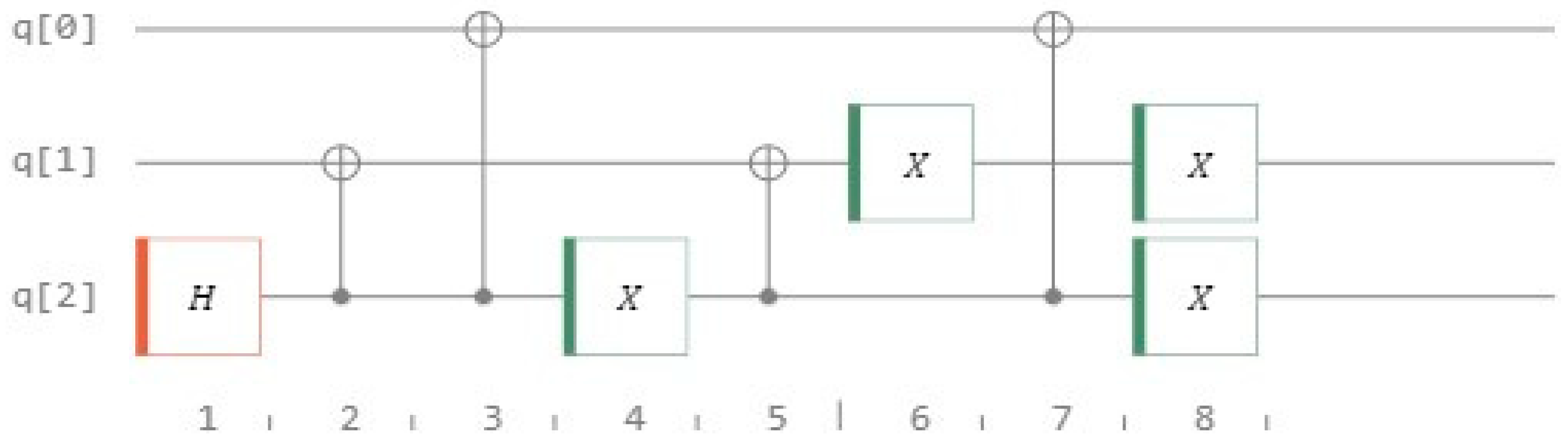
For a blockchain to remain unalterable and traceable back to its source, collision resistance in the hash function is crucial. Core to the operation of the proposed system is the Markov chain with a memory-based hash function. The quantum hash function’s security is ensured not by solving difficult mathematical problems but by the limitless possibilities of the beginning state and its immutable nature of assessment. The acquired normal distribution, or Bell curve, provides no beneficial data without knowledge of the beginning states. Modulo operators are then used to convert the hash value to the normal distribution. This relationship is one-to-many, making it irreversible. It is quite difficult to reverse-engineer a hash value into its original normal distribution. We evaluate the hash algorithm’s robustness against collisions here. All it takes to run the test is changing a single bit in a sequence of messages and seeing what happens to the hash created. Here, the generated 256-bit hashes are based on a total of 1000 quantum walks. The following Figure 10 exhibits the quantum walk with one step forward (four-cycle node) with 8 classical bits to store previous walk. The circuit design performs a quantum walk with the aid of two gates: Hadamard (H) and classical Not (X). Pick an arbitrary value M at random, and then swap the message’s 1st, final, 100th, and 1000th bits to arrive at Mfirst, Mlast, M100, and M1000.
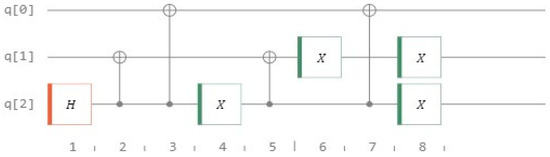
Figure 10.
Quantum walk one step forward, on a 4-noded cycle.
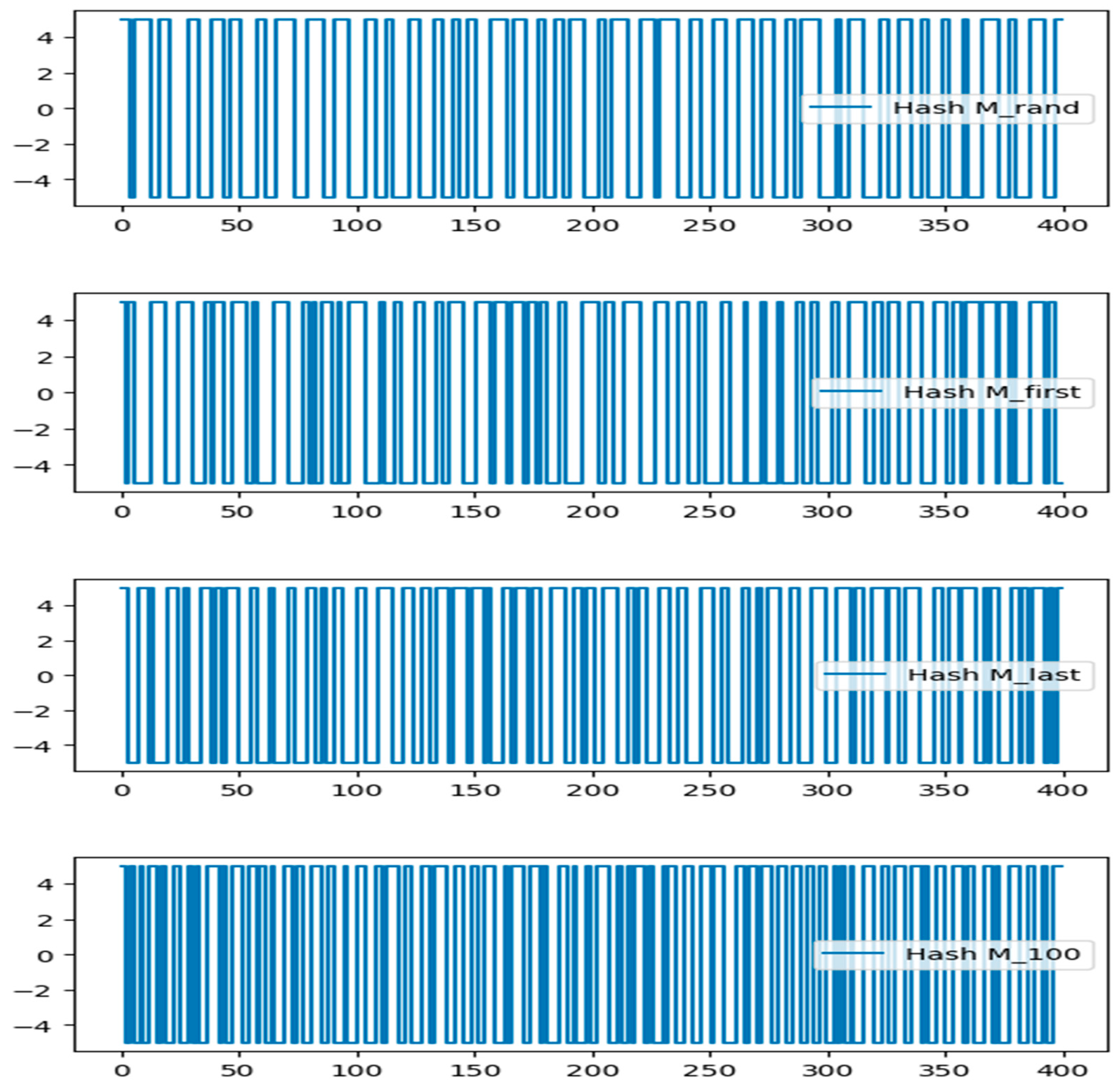
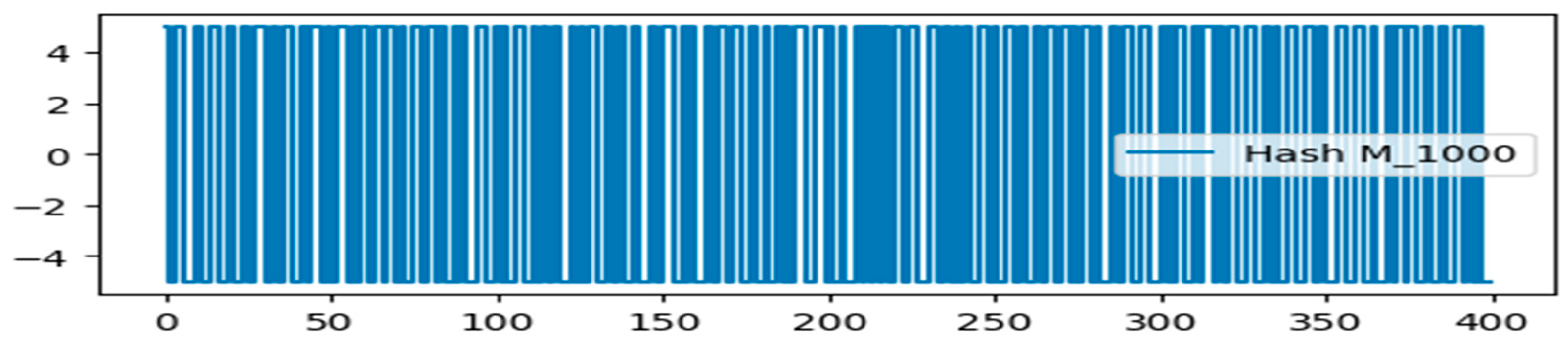
In Figure 11, we can see how five slightly altered hash values compare to the original message. A hash variance of at least 35% is possible with a modification of just 0.25 percent in the randomly chosen message string. The little-modified message produces a hash value that significantly differs from the original message. Because of its strong statistical features and ability to prevent data corruption or manipulation, the so-called hash value constructed using the Markov chain with memory makes the blockchain network extremely valuable.
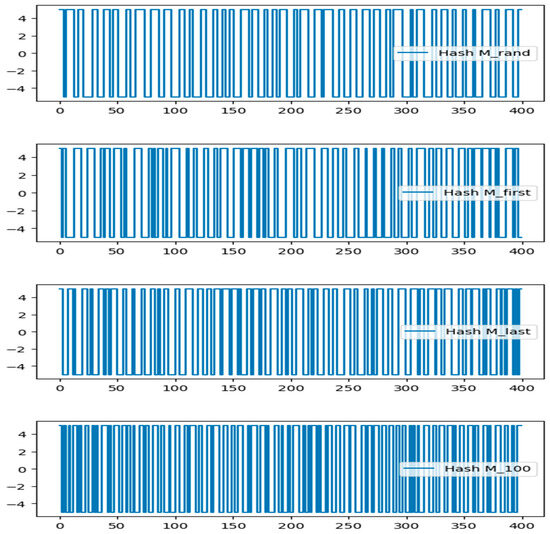
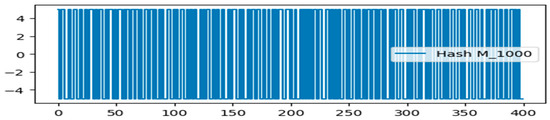
Figure 11.
Plots of various quantum hash values (Mrand, Mfirst, Mlast, M100, M1000).
8. EQHR Attacks and Analysis
We conduct a thorough analysis of our protocol’s safety here. For the EQHR protocol, it is important to think about both external assaults from snoopers and inside attacks from deceitful players. As a result, EQHR protocols require a more involved security evaluation than QKD methods.
8.1. Outside Attack
Consider adding an adversary node to the network. Ravana plans to distribute a bogus health record outside of the restricted quantum network in order to disrupt the patient’s regular care. After receiving this health data, the other nodes will need to send an identification request to Ravana. The proposed system’s bloQs use quantum key distribution (QKD), which means that the key’s information is needed. This means that Ravana cannot finish the validation stage and illegally leak the fake health file. Therefore, this QUAB network can ensure the safe and effective functioning of the EQHR protocol by discouraging malevolent players from disseminating false health information.
Measurement-Resending Attack (Worst-Case Scenario)
First, we will look at the assault that uses measurement resending. Ravana returns the measured photons to Ram or Sita once he has intercepted them at the end of Step 3 or Step 1 (Figure 8). But before the eavesdropping check, Ravana cannot tell the difference between real and fake photons. Therefore, he selects the measurement bases at random. This leads Ravana to reveal himself during the eavesdropping stage, where he makes several mistakes. If kn is big enough, the likelihood that he reveals herself will approach 100%, which is (1 − (3/4) 2kn).
8.2. A Simple Intercept–Resend Attack
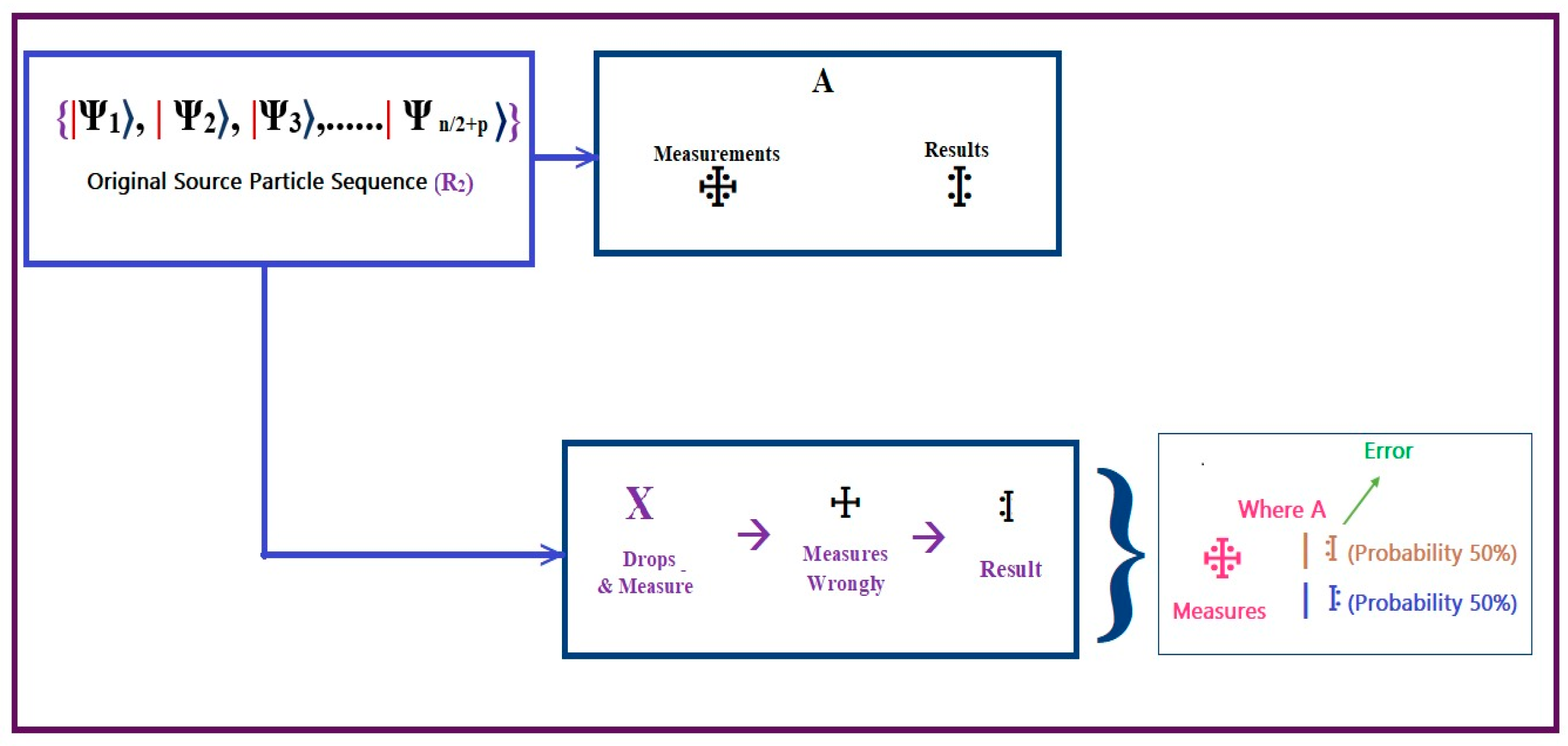
For the sake of argument, let us say Ravana desires to seize the key among Sita and the remaining ones, so he may publish a bogus health file and disrupt the patient’s regular treatment by means of an intercept–resend attack. Consider the scenario where Rama sends a request for identification to Sita. In such a scenario, if some ‘X’ intercepts the transmitted particle sequence R2 (second step of algorithm 1) and ‘X’ starts measuring the original transmitted particle based on {|+, then the Bell state of the particle sequence R2 produces a new vector space, in which all the states related to it will be in different spaces and in entangled positions. Following the measurement, ‘Ravana’ will prepare the element sequencing RX and transmit it to ‘Rama’, along with the intercepted sequence. If only Ram(A)’ suspects the particle sequence received, then there is a 50% probability that RX may hold the same value of R1, i.e., in another sense, . The following figure exhibits the entire scenario of the intercept–resend attack on the system.
Since ‘X’ will be immediately exposed if he or she attempts an IR attack on the process of verification between two quantum blocks, he or she will be unable to steal any confidential information. On this medical quantum blockchain (MQB) network, IR attacks are impossible to pull off. The entire scenario is illustrated in Figure 12.
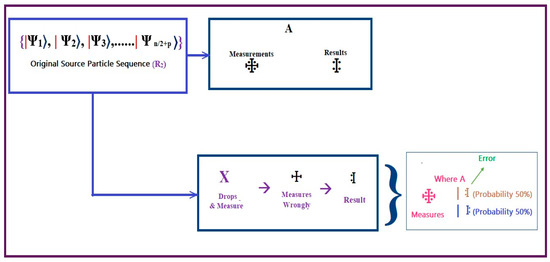
Figure 12.
Intercept–resend attack of the system.
The eavesdropper, Ravan, lurks in the quantum channel, hoping to seize a valuable electronic health record. Because of this, he is able to circumvent the EQHR protocol by transmitting fake EHR data to another block.
As shown in Figure 12, Ravan’s 50% mistake rate per estimate during the security check phase is due to his inability to discriminate between a particle’s linear and diagonal bases.
In other words, the likelihood of detecting Ravan’s assault for a single-particle decoy qubit is 0.75 (0.5 + 0.5 × 0.5). Now let us assume that there are SEE quantum-state transitions and SHE times of security checks in the blockchain system over a period of time; then, SEE + SHE = E.
Let t = SHE/E. For E = 1,2,3………, the probability that Ravan will be identified is 0.75t, 0.75t + 0.75t(1 − 0.75t), 0.75t + 0.75t(1 − 0.75t) + 0.75t + 0.75t(1 − 0.75t)2, …….
After E rounds of quantum messaging, the probability of Ravan being detected or identified is as follows:
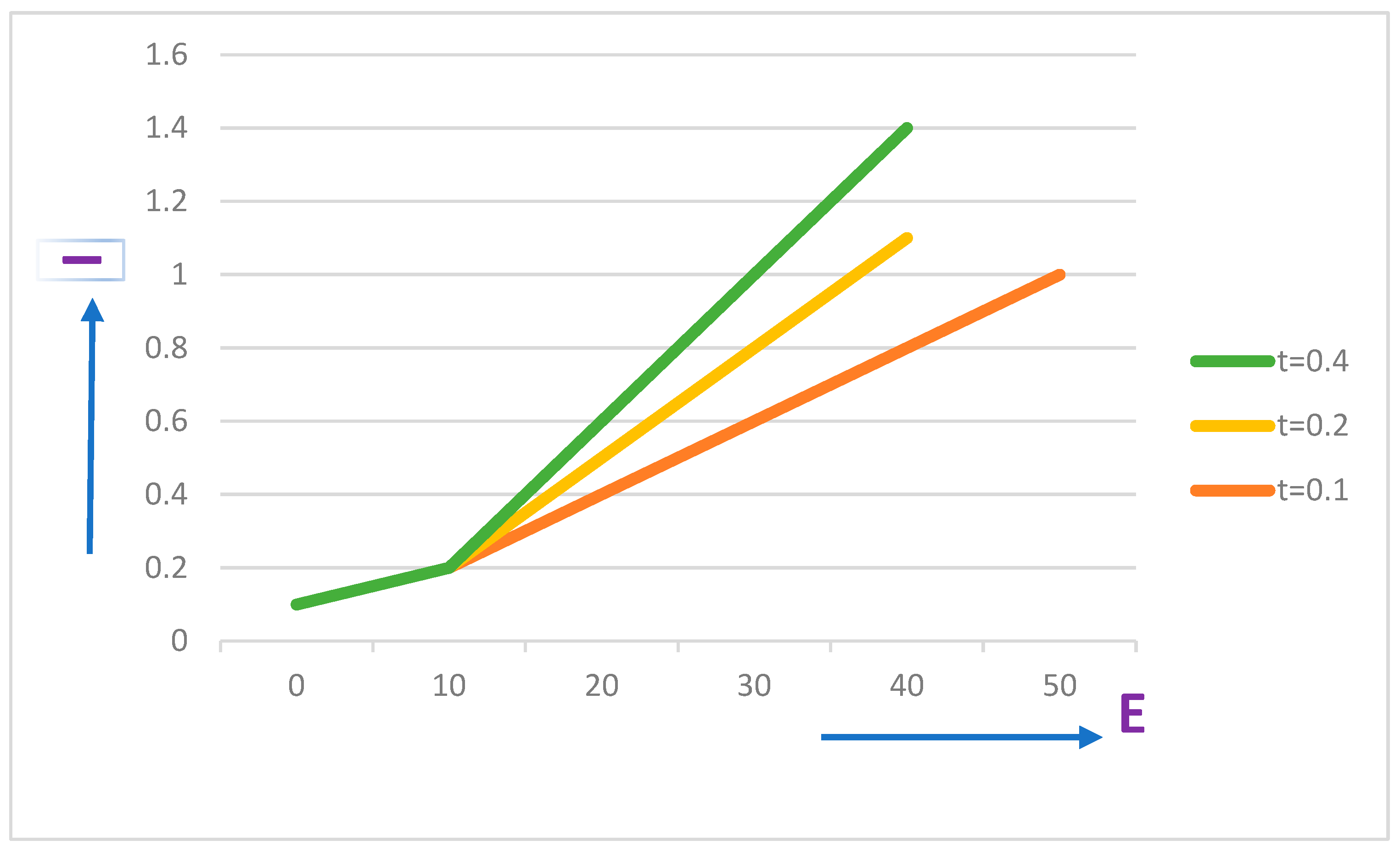
Assuming that t = 0.1, 0.2, and 0.4, then the relationship between I and E is shown in Figure 13, when E⇾ ∞ and I ⇾1.
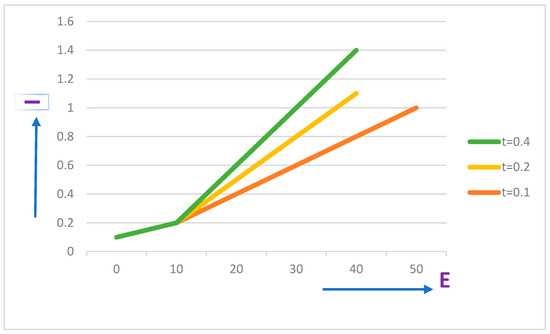
Figure 13.
Probability of Ravan being identified or detected under intercept–resend attacks. Orange line: t = 0.1, yellow line: t = 0.2, green line: t = 0.4.
8.3. Entanglement Measure Attack (ENMA)
Let us say Ravana (X) is attempting to publish a bogus health report by stealing the key that links node Rama to the other nodes in the network via an entanglement measure attack. Consider the scenario when Rama seeks Sita’s approval for authentication. Ravana must use isomorphism to entangle the electron in transport with the supplementary atom in her hands, with the goal of obtaining knowledge of the particle that is being targeted. The definition of isomorphism is expressed as Equations (16) and (17), which are the following:
Here, = 1 and = 1. , which is obviously the supplementary particle of the ‘X’—the intruder.
Therefore, the algorithm must take into account isomorphism to avoid exposing the espionage process. We refrain from performing standard logical or arithmetic operations on qubits as we would on traditional computers. In quantum computing, the concepts of “while statement” and “branching statement” do not exist. To handle qubits using the interference principle of quantum physics, we substitute unitary operators. These look sophisticated, yet are, in fact, simple to use.
Here, and = 0 and |+| − |-|. When all of these things line up, it is clear that the surjective bounded operation will be of the following form:
The surjective bounded operator places the apprehended and additional particles in separate quantum spaces, so the extra photons cannot provide Ravana with reliable information. So, there is no way for Ravana to exploit the algorithm using an ENMA and learn anything. We have a working version of the algorithm if Ravana successfully intercepts the transmitted R2 sequence in an algorithmic fashion and then performs the surjective bounded operation with the particles under his control. The above equation displays the states of the Qblocks following a surjective bounded operation.
Consider the Bell state ; following the surjective bounded operation, the additional particle acquires a state of entanglement with the Bell state.
Rama now has a 0.25 percent chance of determining the proper Bell state, so it is likely that the eavesdropping procedure will pick up on Ravan’s presence. If Ravan attempts an ENMA attack on the verification process between two quantum spaces, Ravan will undoubtedly be exposed and rendered unable to obtain any sensitive data.
8.4. Validity and Auditability of Quantum Blocks
Even if Ravana wanted to alter the contents of a Qblock, she would be unlikely to do so because she could not alter the hash value of both current and subsequent blocks at the same time. By storing the verified information in the Qblock, the DQHR protocol can guarantee the secrecy and correctness of the data in the Qblock.
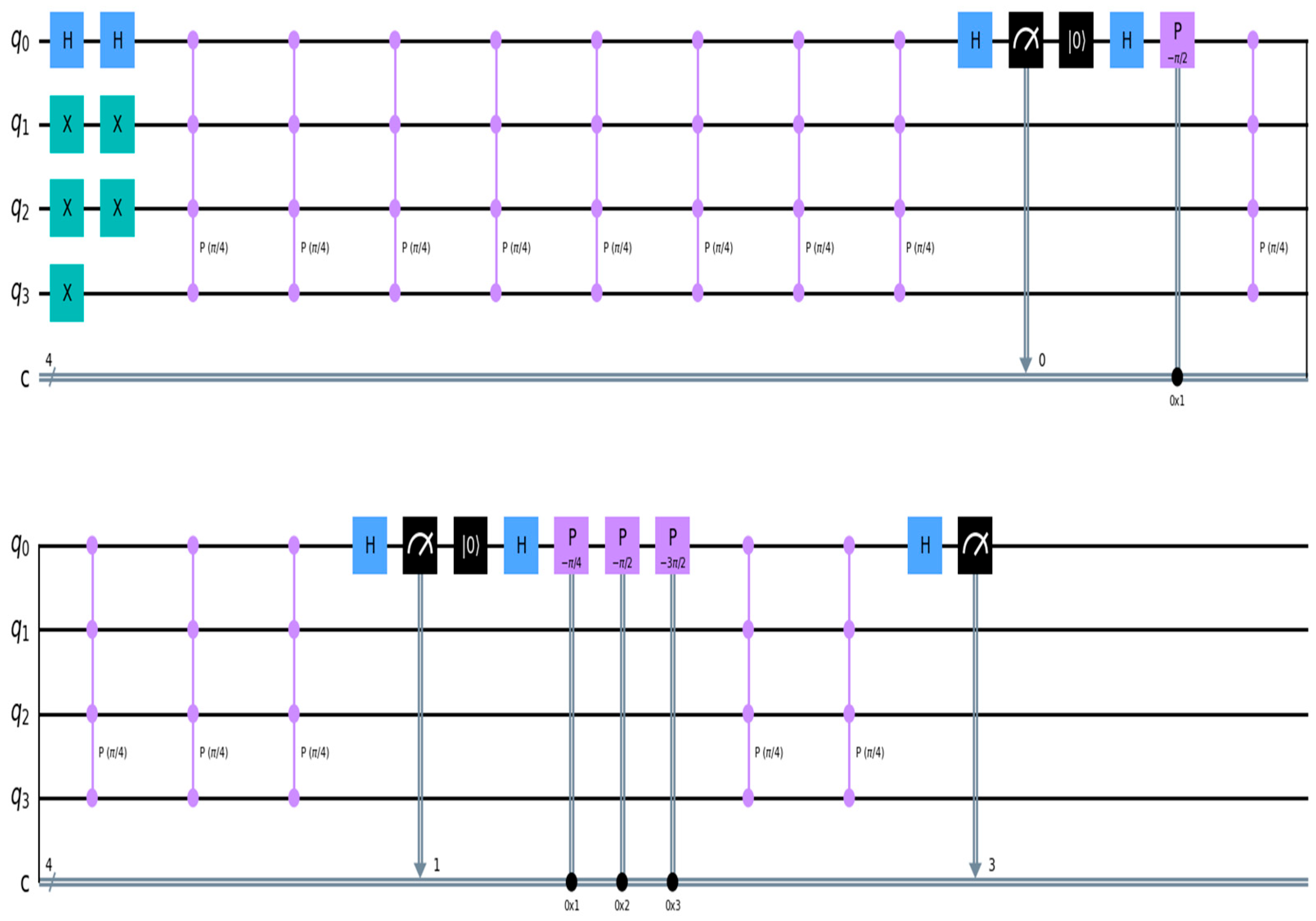
The quantum phase estimation (QPE) procedure can determine the relative phase of the timestamp associated with a specific block in a chain of blocks linked by entangled states for data location and auditing. Employing an adequate number of additional particles can precisely retrieve the phase value. We need to find the phase factors in the quantum state that correspond to the time |t⟩, taking into account the fact that ‘a’ is the quantity of additional particles. We can set the quantum state time ‘t’ using the chronology indicator of the mined data. If k = 1, 2, 3, …, a − 1, then it is possible to perform an oracle operation with controlled ||⟩. The above finding suggests that the quantum blockchain suggested in this article can guarantee the precision of the data included inside the Qblock and accomplish data tracking by retrieving the hash of every piece of data at the proper moment. The relative phase at time |t⟩ may be extracted using the quantum circuit diagram shown in Figure 14.
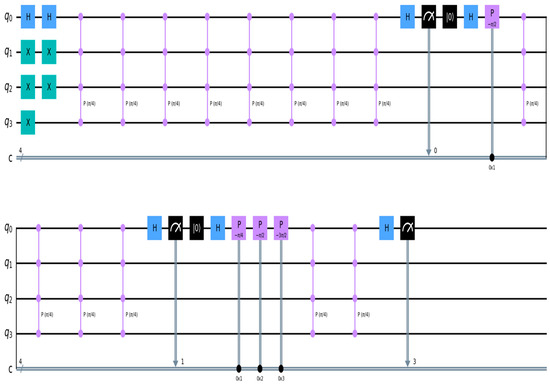
Figure 14.
The schematic representation of the quantum circuit to determine the phase distribution of a quantum state.
8.5. Information Traceability Analysis
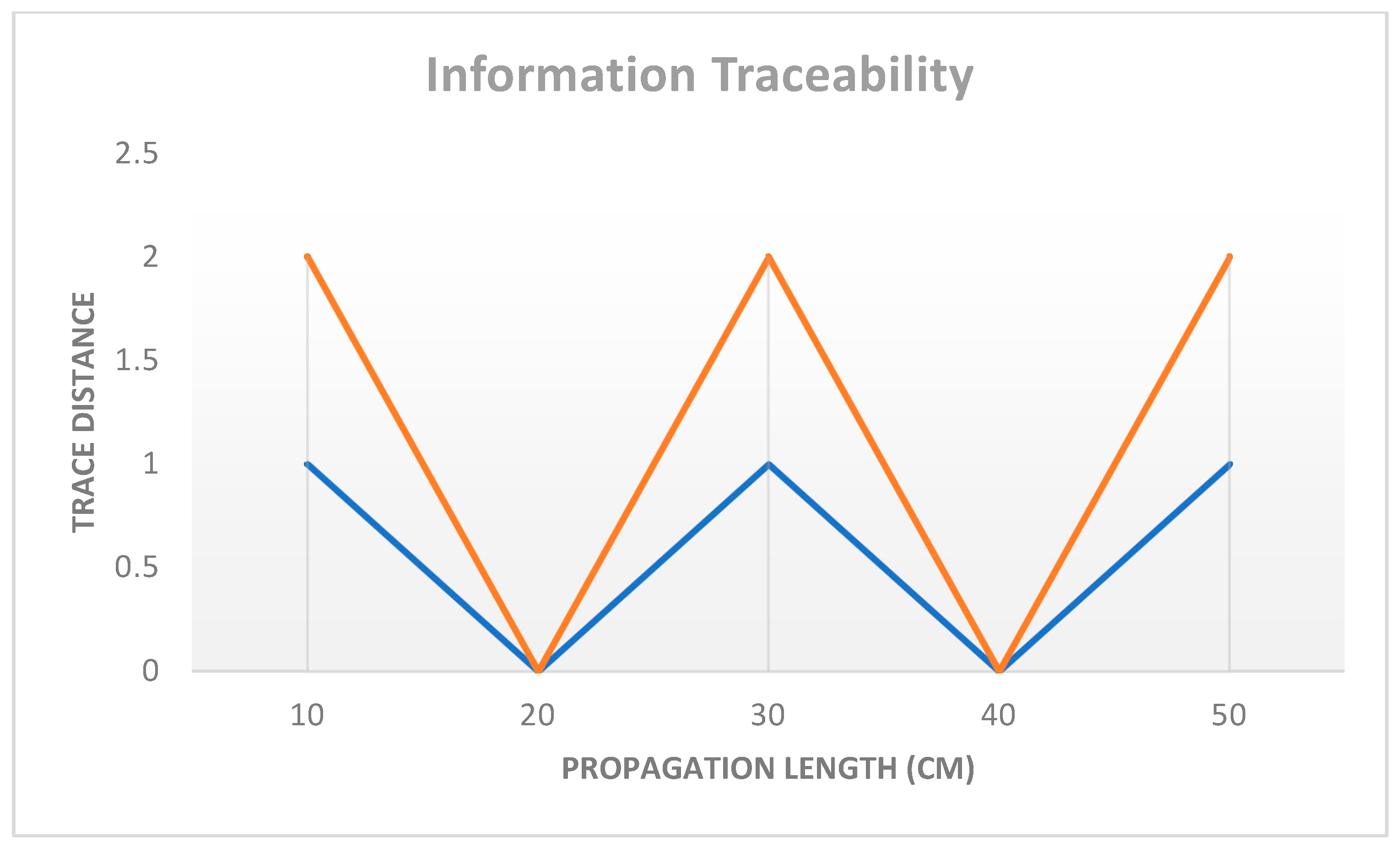
Given the unusual nature of the data flow in our experimental setting, it is reasonable to question whether simpler time-independent Hamiltonians like H can model more general types of evolutions. More precisely, the introduction of data pertaining to several variables of a magnitude beyond the control of a traditional channel into the environment triggers a truly quantum information flow. Figure 15 shows the data flow in the system environment, with a maximum data trace of 2.0 and a propagation length of over 10 cm. The orange curve represents the best-case trace distance, whereas the blue curve represents the worst-case.
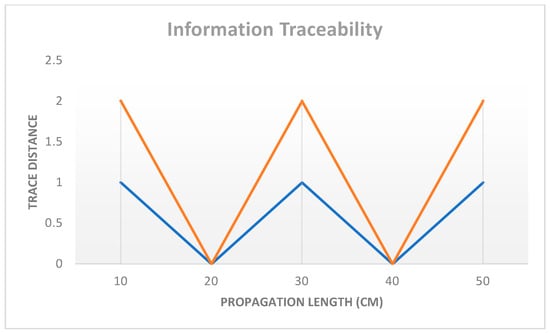
Figure 15.
Transformation of data existing inside the system’s context. The unitary is almost the same as a generalized swap at a propagation length of 10.01 cm, with a maximum trace distance of 2.0 in an ideal setting. Orange line: Best case, blue line: worst case.
8.6. A Review of Accomplishment
Here, we take a look at various current blockchain models and compare them to the proposed quantum blockchain. Table 7 and Table 8 display the qualitative and quantitative comparisons among the references [38,39,40].

Table 7.
Qualitative comparisons with existing systems.

Table 8.
Quantitative comparisons with existing systems.
Improving upon previous designs, [38] suggests an NTRU lattice-based postquantum blockchain architecture for the Internet of Things. Thanks to its efficient underlying lattice structure, the technique narrows down transaction sizes from hundreds of gigabytes to a few kilobytes. To provide a broad foundation for future performance enhancement, the authors also proposed an aggregate signature across the NTRU lattice and segregated witnesses.
An overview of recent advances in the construction of quantum-safe systems, an examination of the vulnerabilities of existing cryptographic methods to computational and technological innovations, and possible remedies to these vulnerabilities are the primary takeaways from [39].
The study in [40] discusses the well-known field of quantum computing, how it threatens current encryption, and how researchers are developing algorithms to estimate how many qubits would be required to breach the blockchain security system.
We have designed QUMA with all quantum features and properties in comparison to existing systems [38,39,40]. The use of quantum walks in QUMA outperforms traditional algorithms by an exponential factor. In many real-world applications, quantum walks outperform conventional algorithms by a factor of multiple. This is true for tasks like assessing NAND trees, locating triangles, and the element distinctness problem. Also, the quantum entropy measures how unpredictable or random a system’s state is.
9. Conclusions
Healthcare professionals must share electronic medical records, but they must treat this information as extremely private. Blockchain technology can facilitate a multi-party trust model by providing accessible, immutable, and transparent electronic health records. Nevertheless, with the progress of near-term quantum computing techniques, vulnerabilities in the current blockchain architecture have emerged. This study offers a physics-inspired blockchain network that is actually quantum computing and creates a new entangled quantum health record (EQHR) protocol with privacy and security at the forefront of their respective architectures. The data blocks that make up this physics-inspired blockchain are linked via states (bloQ) of entanglements. The protocol for the Quantumized Health Record (QHR) goes into great detail about quantum information processing. IoMT systems ensure the security and privacy of health information, enabling constant tracking of its whereabouts. According to the computational study’s findings, the QUAB network is impenetrable to quantum computer attacks. We evaluate the precision of the quantum block and its audit trail. This article also contrasts several competing QUAB models with its own.
In order to improve safety and effectiveness, QUAB makes use of quantum entanglement, a feature that is absent from standard blockchain. This paper’s suggested framework for quantum blockchains provides more detail about the information-processing mechanism of the health record protocol and the data structure of quantum blockchains than previous research has found. However, there are still restrictions to this work. This study does not specify the extent to which we should implement the EMR procedure in practice. We have not yet tested it in a genuine experimental context due to logistical limitations. As technology develops further, quantum information processing and its networking will be fully integrated into the World Wide Web (WWW). Eventually, the quantum internet will incorporate not only QKD but also other information security technologies. On the other hand, the current system for quantum information transfer is still in its infancy and undergoing expansion. Regrettably, the implementation of a quantum blockchain necessitates a unique type of quantum network. Before testing in a real quantum system, the QUAB architecture and EQHR protocol proposed in this paper must overcome the first obstacle—noise interference. It is also important to solve the problem of sustaining Qstates over a prolonged period of time. The real-world difficulty lies in solving the problem of maintaining the stability of quantum states carried by block carriers. Table 7 shows that the proposed QUMEDCHAIN will have greater impact in health information-processing systems. Future studies should focus on improving quantum blockchain methodology and practical applications, which stores health data for precise prediction analysis. Additional work is required to create a working quantum blockchain with a transport layer that can run on a real quantum computer, is easy to implement, and offers great security and scalability.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.B.; methodology, A.B.; software, B.S.; validation, B.S.; formal analysis, A.B.; investigation, A.B.; resources, A.B.; data curation, A.B.; writing—A.B.; writing—review and editing, B.S.; visualization, A.B.; supervision, BS; project administration, BS.; funding acquisition, B.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
The work was supported by Visvesvaraya Scheme-Phase-II, Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology, India.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Nakamoto, S. Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System. 2008. Available online: https://bitcoin.org/bitcoin.pdf (accessed on 20 February 2023).
- Miao, J.; Wang, Z.; Wu, Z.; Ning, X.; Tiwari, P. A blockchain-enabled privacy-preserving authentication management protocol for Internet of Medical Things. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 237, 121329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Sharma, H.K.; Kapoor, M. Integration of IoMT and Blockchain in Smart Healthcare System. In Blockchain for Secure Healthcare Using Internet of Medical Things (IoMT); Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Tiwari, P.; Zymbler, M. Internet of Things is a revolutionary approach for future technology enhancement: A review. J. Big Data 2019, 6, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamalov, F.; Pourghebleh, B.; Gheisari, M.; Liu, Y.; Moussa, S. Internet of Medical Things Privacy and Security: Challenges, Solutions, and Future Trends from a New Perspective. Sustainability 2023, 15, 3317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beasley, J.W.; Holden, R.J.; Sullivan, F. Electronic health records: Research into design and implementation. Br. J. Gen. Pract. 2011, 61, 604–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yeo, L.H.; Banfield, J. Human Factors in Electronic Health Records Cybersecurity Breach: An Exploratory Analysis. Perspect. Health Inf. Manag. 2022, 19, 1i. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Habib, G.; Sharma, S.; Ibrahim, S.; Ahmad, I.; Qureshi, S.; Ishfaq, M. Blockchain Technology: Benefits, Challenges, Applications, and Integration of Blockchain Technology with Cloud Computing. Future Internet 2022, 14, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harman, L.B.; Flite, C.A.; Bond, K. Electronic health records: Privacy, confidentiality, and security. AMA J. Ethics 2012, 14, 712–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamba, S.; Sharma, M. An Efficient Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm (ECDSA). In Proceedings of the 2013 International Conference on Machine Intelligence and Research Advancement, Katra, India, 21–23 December 2013; pp. 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalra, S.; Sood, S.K. Elliptic Curve Cryptography: Current Status and Research Challenges. In High Performance Architecture and Grid Computing. HPAGC 2011. Communications in Computer and Information Science; Mantri, A., Nandi, S., Kumar, G., Kumar, S., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; Volume 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raussendorf, R.; Briegel, H. A one-way quantum computer. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 86, 5188–5191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spiller, T.P. Quantum information processing: Cryptography, computation, and teleportation. Proc. IEEE 1996, 84, 1719–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuarqoub, A. Security Challenges Posed by Quantum Computing on Emerging Technologies. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Future Networks and Distributed Systems (ICFNDS ‘20). Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, 26–27 November 2020; p. 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.K.; Krishna, E.H.V.; Ushasri, R.; Jahnavi, V.; Prakash, K.B.; Imambi, S. Implementation of Grover’s and Shor’s Algorithms In Quantum Machine Learning. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Intelligent and Innovative Technologies in Computing, Electrical and Electronics (IITCEE), Bengaluru, India, 27–28 January 2023; pp. 967–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedorov, A.K.; Kiktenko, E.O.; Lvovsky, A.I. Quantum computers put blockchain security at risk. Nature 2018, 563, 465–467. Available online: https://link.gale.com/apps/doc/A573163765/AONE? (accessed on 20 February 2023).
- Sehgal, S.K.; Gupta, R. Quantum Cryptography and Quantum Key. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Industrial Electronics Research and Applications (ICIERA), New Delhi, India, 22–24 December 2021; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavroeidis, V.; Vishi, K.; Zych, M.D.; Jøsang, A. The impact of quantum computing on present cryptography. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2018, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allende-Lopez, M.; Da Silva, M.M. Quantum Technologies: Digital Transformation, Social Impact, and Cross-sector Disruption. Inter-American Bank 2019, 1–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuaib, M.; Hassan, N.H.; Usman, S.; Alam, S.; Sam, S.M.; Samy, G.A.-L.N. Effect of Quantum computing on Blockchain-based Electronic Health Record Systems. In Proceedings of the 2022 4th International Conference on Smart Sensors and Application (ICSSA), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 26–28 July; 2022; pp. 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Jordan, S.; Liu, Y.-K.; Moody, D.; Peralta, R.; Perlner, R.; Smith-Tone, D. NIST Report on Post-Quantum Cryptography (2026). Available online: https://nvlpubs.nist.gov/nistpubs/ir/2016/nist.ir.8105.pdf (accessed on 20 February 2023).
- Ethereum’s Pathway of Handling Quantum. Available online: https://www.erc4337.io/ (accessed on 20 February 2023).
- Aumasson, J.P. The impact of quantum computing on cryptography. Comput. Fraud. Secur. 2017, 6, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, Z.M.; Askar, S. Resistant blockchain cryptography to quantum computing attacks. Int. J. Sci. Bus. 2021, 5, 116–125. [Google Scholar]
- Punathumkandi, S.; Boscovic, D. A survey on quantum-safe blockchain system. In Proceedings of the Annual Computer Security Applications, Conference, Austin, TX, USA, 5–9 December 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Webber, M.; Elfving, V.; Weidt, S.; Hensinger, W.K. The impact of hardware specifications on reaching quantum advantage in the fault tolerant regime. AVS Quantum Sci. 2022, 4, 013801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiktenko, E.O.; Pozhar, N.O.; Anufriev, M.N.; Trushechkin, A.S.; Yunusov, R.R.; Kurochkin, Y.V.; Lvovsky, A.I.; Fedorov, A.K. Quantum-secured blockchain. Quantum Sci. Technol. 2018, 3, 035004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Qu, J.; Liu, P.; Yu, J. A blockchain smart contract based on light- weighted quantum blind signature. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 138657–138668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajan, D.; Visser, M. Quantum blockchain using entanglement in time. Quantum Rep. 2019, 1, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H. Quantum relay blockchain and its applications in key service. In Proceedings of the 2020 4th International Conference on Cryptography, Security and Privacy, Nanjing, China, 10–12 January 2020; pp. 95–99. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.-L.; Chen, X.B.; Xu, G.; Yuan, K.G.; Liu, W.; Yang, Y.X. A novel quantum blockchain scheme base on quantum entanglement and DPoS. Quantum Inf. Process 2020, 19, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Sopek, M.; Wang, Q.; Kulicki, P. Towards Quantum-Secured Permissioned Blockchain: Signature, Consensus, and Logic. Entropy 2019, 21, 887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ablayev, F.; Bulychkov, D.; Sapaev, D.; Vasiliev, A.; Ziatdinov, M. Quantum-assisted blockchain. Lobachevskii J. Math. 2018, 39, 957–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Latif, A.; Abd-El-Atty, B.; Mehmood, I.; Muhammad, K.; Peng, J. Quantum-inspired blockchain-based cybersecurity: Securing smart edge utilities in iotbased smart cities. Inf. Process. Manag. 2021, 58, 102549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coladangelo, A.; Sattath, O. A quantum money solution to the blockchain scalability problem. Quantum 2020, 4, 297–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stafford, T.; Treiblmaier, H. Characteristics of a blockchain ecosystem for secure and sharable electronic medical records. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2020, 67, 1340–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, S.; Manoj, M.; Gadekallu, T.; Kumar, N.; Maddikunta, P.; Bhattacharya, S.; Suh, D.; Piran, M. A blockchain-based credibility scoring framework for electronic medical records. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Globecom Workshops (GC Wkshps), Taipei, Taiwan, 7–11 December 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Wu, F.; Zheng, Z. Post quantum blockchain architecture for internet of things over NTRU lattice. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0279429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Fedorov, A.K. Deploying hybrid quantum-secured infrastructure for applications: When quantum and post-quantum can work together. Front. Quantum Sci. Technol. 2023, 2, 1164428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allende, M.; León, D.L.; Cerón, S.; Pareja, A.; Pacheco, E.; Leal, A.; Da Silva, M.; Pardo, A.; Jones, D.; Worrall, D.J.; et al. Quantum-resistance in blockchain networks. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 5664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).