Outcome Prognostic Factors in MRI during Spica Cast Therapy Treating Developmental Hip Dysplasia with Midterm Follow-Up
Abstract
:1. Introduction
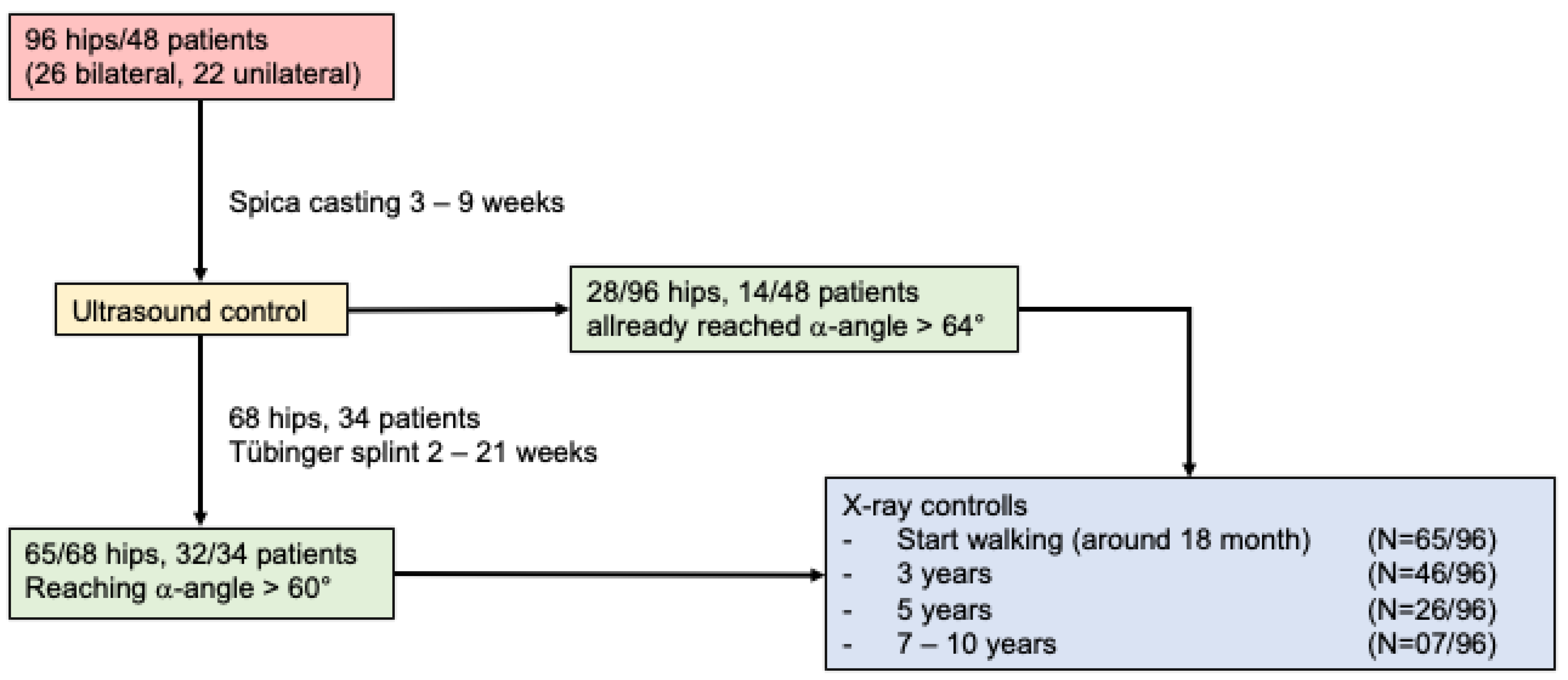
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Patients Population
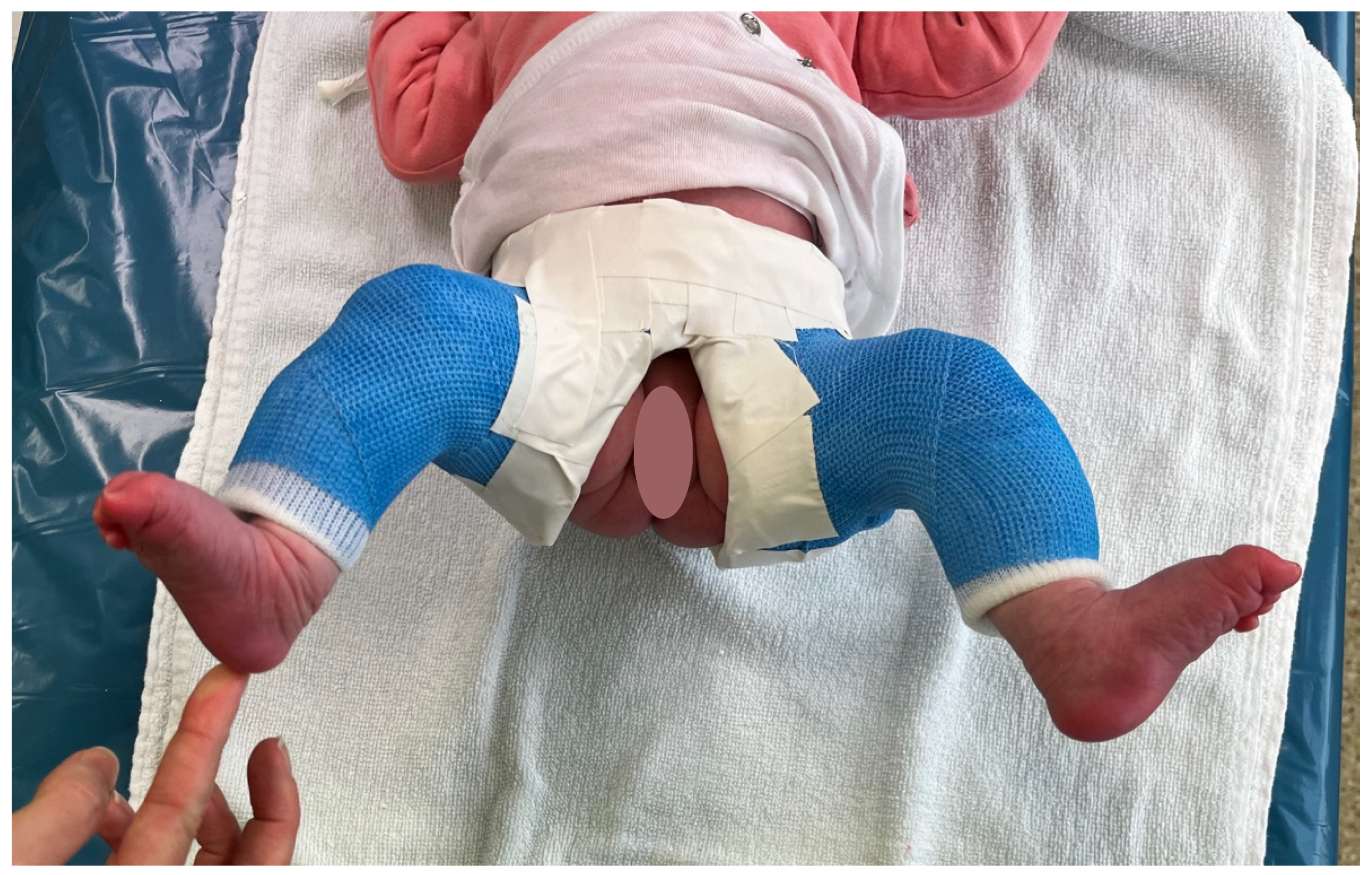
2.2. Treatment Technique
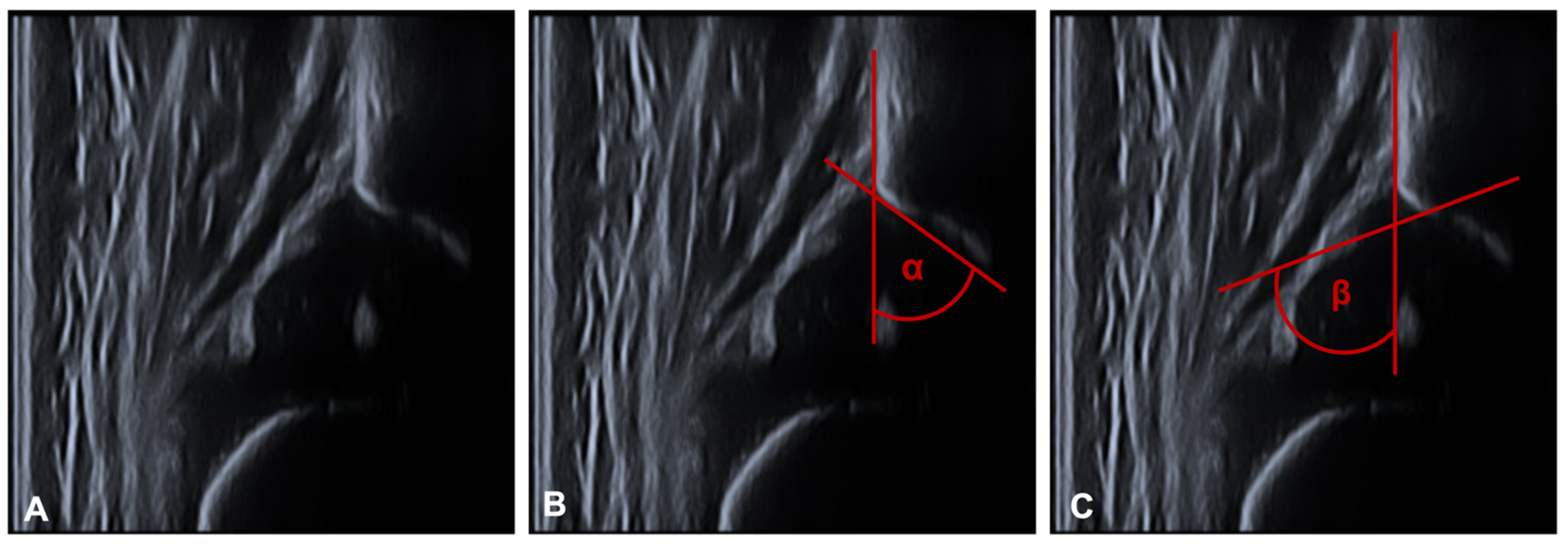
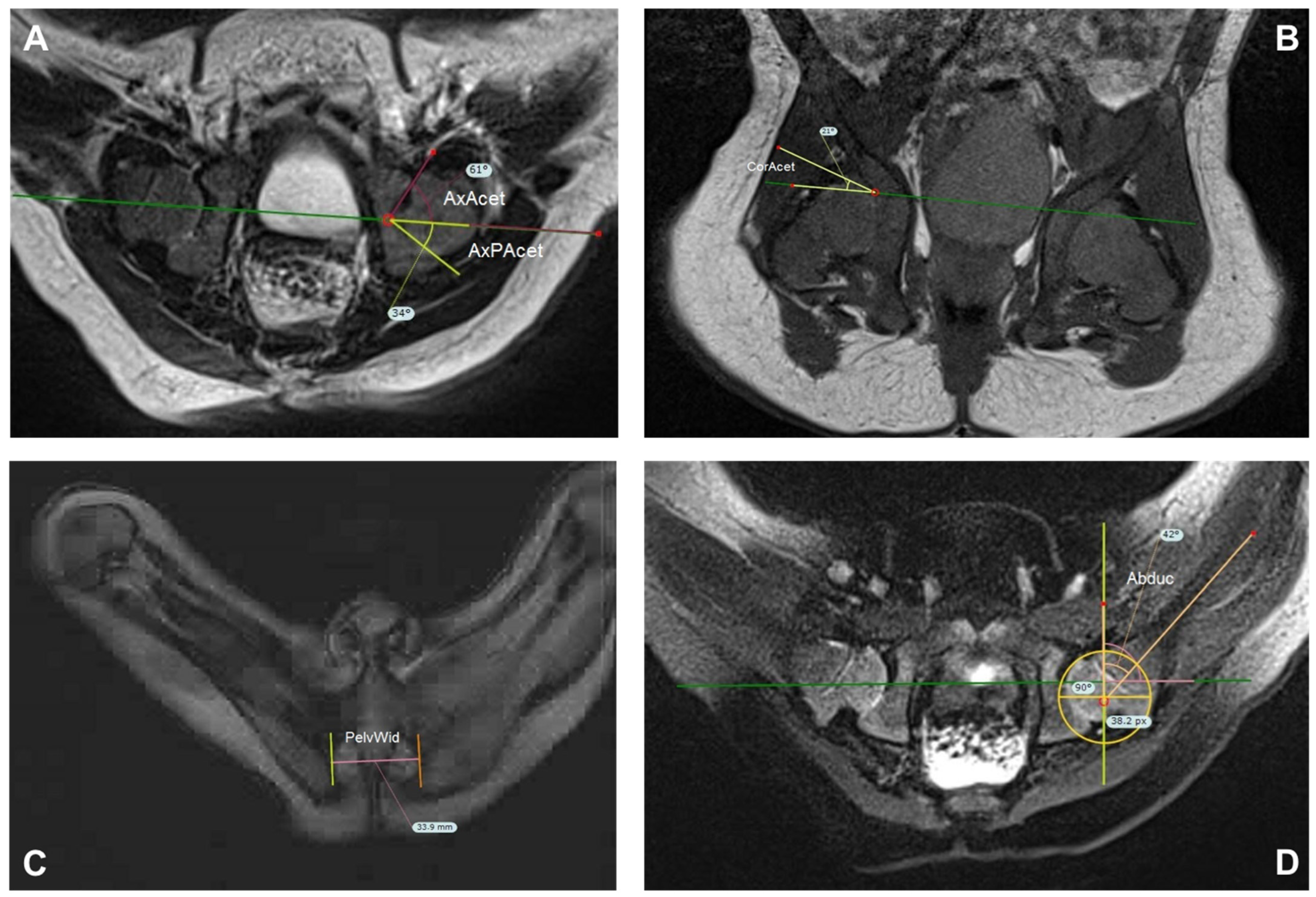
2.3. Measurements
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Sonographic Evaluation
3.2. Magnetic Resonance Imaging Measurements
3.3. Radiographic Evaluation
3.4. Complications
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vaquero-Picado, A.; González-Morán, G.; Gil Garay, E.; Moraleda, L. Developmental dysplasia of the hip: Update of management. EFORT Open Rev. 2019, 4, 548–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harsanyi, S.; Zamborsky, R.; Krajciova, L.; Kokavec, M.; Danisovic, L. Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip: A Review of Etiopathogenesis, Risk Factors, and Genetic Aspects. Medicina 2020, 56, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.; Doudoulakis, K.J.; Khurwal, A.; Sarraf, K.M. Developmental dysplasia of the hip. Br. J. Hosp. Med. 2020, 81, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.C.; Eberson, C.P. Growth and development of the child’s hip. Orthop. Clin. 2006, 37, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zusman, N.; Lieberman, E.; Goldstein, R.Y. Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip. Pediatrics 2019, 143, e20181147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ziegler, J.; Thielemann, F.; Mayer-Athenstaedt, C.; Günther, K.P. The natural history of developmental dysplasia of the hip. A meta-analysis of the published literature. Orthopade 2008, 37, 515–516, 518–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstein, S.L. Natural history and treatment outcomes of childhood hip disorders. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1997, 344, 227–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedge, J.H.; Wasylenko, M.J. The natural history of congenital disease of the hip. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. Vol. 1979, 61, 334–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pavone, V.; Testa, G.; Riccioli, M.; Evola, F.R.; Avondo, S.; Sessa, G. Treatment of Developmental Dysplasia of Hip with Tubingen Hip Flexion Splint. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2015, 35, 485–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tschauner, C.; Klapsch, W.; Baumgartner, A.; Graf, R. Maturation curve of the ultrasonographic alpha angle according to Graf’s untreated hip joint in the first year of life. Z. Orthop. Ihre Grenzgeb. 1994, 132, 502–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadhav, S.P.; More, S.R.; Shenava, V.; Zhang, W.; Kan, J.H. Utility of immediate postoperative hip MRI in developmental hip dysplasia: Closed vs. open reduction. Pediatr. Radiol. 2018, 48, 1096–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrera, C.A.; Cohen, S.A.; Sankar, W.N.; Ho-Fung, V.M.; Sze, R.W.; Nguyen, J.C. Imaging of developmental dysplasia of the hip: Ultrasound, radiography and magnetic resonance imaging. Pediatr. Radiol. 2019, 49, 1652–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelitz, M.; Guenther, K.P.; Gunkel, S.; Puhl, W. Reliability of radiological measurements in the assessment of hip dysplasia in adults. Br. J. Radiol. 1999, 72, 331–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eberhardt, O.; Zieger, M.; Wirth, T.; Fernandez, F.F. Determination of femoral head position with transinguinal ultrasound in DDH treatment. Z. Orthop. Unf. 2009, 147, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberhardt, O.; Zieger, M.; Langendoerfer, M.; Wirth, T.; Fernandez, F.F. Determination of hip reduction in spica cast treatment for DDH: A comparison of radiography and ultrasound. J. Child. Orthop. 2009, 3, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mehdizadeh, M.; Dehnavi, M.; Tahmasebi, A.; Shishvan, S.A.M.K.; Kondori, N.B.; Shahnazari, R. Transgluteal ultrasonography in spica cast in postreduction assessment of developmental dysplasia of the hip. J. Ultrasound 2019, 23, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bos, C.F.; Bloem, J.L.; Obermann, W.R.; Rozing, P.M. Magnetic resonance imaging in congenital dislocation of the hip. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. Vol. 1988, 70, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Westhoff, B.; Wild, A.; Seller, K.; Krauspe, R. Magnetic resonance imaging after reduction for congenital dislocation of the hip. Arch. Orthop. Trauma. Surg. 2003, 123, 289–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wirth, T.; Haake, M.; Hahn-Rinn, R.; Walthers, E. Magnetic resonance tomography in diagnosis and therapy follow-up of patients with congenital hip dysplasia and hip dislocation. Z. Orthop. Ihre Grenzgeb. 1998, 136, 210–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Duan, F.; Guo, W.; Wang, D.; Qin, X.; Fu, G.; Chen, T. Consistency of Indices Obtained via Hip Medial Ultrasound and Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Reduction and Spica Cast Treatment for Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2021, 47, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dibello, D.; Odoni, L.; Pederiva, F.; Di Carlo, V. MRI in Postreduction Evaluation of Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip: Our Experience. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2019, 39, 449–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandel, D.M.; Loder, R.T.; Hensinger, R.N. The predictive value of computed tomography in the treatment of developmental dysplasia of the hip. J. Pediatric Orthop. 1998, 18, 794–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanton, R.P.; Capecci, R. Computed tomography for early evaluation of developmental dysplasia of the hip. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 1992, 12, 727–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Liu, Y.; Chen, W.; Li, J.; Canavese, F.; Xu, H. Closed reduction and dynamic cast immobilization in patients with developmental dysplasia of the hip between 6 and 24 months of age. Eur. J. Orthop. Surg. Traumatol. 2019, 29, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, M.S.; Betz, B.W.; Halanski, M.A. Comparison of hip reduction using magnetic resonance imaging or computed tomography in hip dysplasia. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2011, 31, 525–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaremko, J.L.; Wang, C.C.; Dulai, S. Reliability of indices measured on infant hip MRI at time of spica cast application for dysplasia. HIP Int. 2014, 24, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf, R. Classification of hip joint dysplasia by means of sonography. Arch. Orthop. Trauma. Surg. 1984, 102, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf, R. Fundamentals of sonographic diagnosis of infant hip dysplasia. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 1984, 4, 735–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf, R. Hip sonography: 20 years experience and results. Hip Int. 2007, 17 (Suppl. S5), S8–S14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, A.P.; Doddabasappa, S.N.; Mulpuri, K. Evidence-based management of developmental dysplasia of the hip. Orthop. Clin. N. Am. 2014, 45, 341–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidl, T.; Lohmaier, J.; Hölker, T.; Funk, J.; Placzek, R.; Trouillier, H.H. Reduction of unstable and dislocated hips applying the Tubingen hip flexion splint? Orthopade 2012, 41, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernau, A. The Tubingen hip flexion splint in the treatment of hip dysplasia. Z. Orthop. Ihre Grenzgeb. 1990, 128, 432–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tönnis, D. Congenital Dysplasia and Dislocation of the Hip in Children and Adults; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Graf, R. Hip sonography in infancy. Procedure and clinical significance. Fortschr. Med. 1985, 103, 62–66. [Google Scholar]
- Hefti, F. Kinderorthopädie in der Praxis; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; Volume 3, p. 929. [Google Scholar]
- Sankar, W.N.; Gornitzky, A.L.; Clarke, N.M.; Herrera-Soto, J.A.; Kelley, S.P.; Matheney, T.; Mulpuri, K.; Schaeffer, E.K.; Upasani, V.V.; Williams, N.; et al. Closed Reduction for Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip: Early-term Results From a Prospective, Multicenter Cohort. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2019, 39, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Guo, Y.; Shen, X.; Liu, H.; Mei, H.; Xu, H.; Canavese, F.; Chinese Multi-Center Pediatric Orthopedic Study Group (CMPOS). Radiographic outcome of children older than twenty-four months with developmental dysplasia of the hip treated by closed reduction and spica cast immobilization in human position: A review of fifty-one hips. Int. Orthop. 2019, 43, 1405–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, B.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Andreacchio, A.; Pavone, V.; Pereria, B.; Xu, H.; Canavese, F. Post-operative radiograph assessment of children undergoing closed reduction and spica cast immobilization for developmental dysplasia of the hip: Does experience matter? Int. Orthop. 2018, 42, 2725–2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haruno, L.S.; Kan, J.H.; Rivlin, M.J.; Rosenfeld, S.B.; Schallert, E.K.; Zhu, H.; Shenava, V.R. Spica MRI predictors for epiphyseal osteonecrosis after closed reduction treatment of dysplasia of the hip. J. Pediatr. Orthop. B 2019, 28, 424–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Li, M.; Qu, X.; Cao, Y.; Liu, X.; Luo, C.; Zhang, Y. Efficacy of closed reduction for developmental dysplasia of the hip: Midterm outcomes and risk factors associated with treatment failure and avascular necrosis. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2020, 15, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Gao, S.; Sun, J.; Yang, Y.; Song, Y.; Han, R.; Lei, G. Predictive values for the severity of avascular necrosis from the initial evaluation in closed reduction of developmental dysplasia of the hip. J. Pediatr. Orthop. B 2013, 22, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandergugten, S.; Traore, S.Y.; Docquier, P.-L. Risk factors for additional surgery after closed reduction of hip developmental dislocation. Acta Orthop. Belg. 2016, 82, 787–796. [Google Scholar]
- Terjesen, T.; Horn, J.; Gunderson, R.B. Fifty-year follow-up of late-detected hip dislocation: Clinical and radiographic outcomes for seventy-one patients treated with traction to obtain gradual closed reduction. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2014, 96, e28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, Y.; Cai, H.; Wang, Z. Quality of reduction and prognosis of developmental dysplasia of the hip: A retrospective study. HIP Int. 2016, 26, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotlarsky, P.; Haber, R.; Bialik, V.; Eidelman, M. Developmental dysplasia of the hip: What has changed in the last 20 years? World J. Orthop. 2015, 6, 886–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, T.; Cooperman, D.R.; Thompson, G.H.; Ballock, R.T. Closed reduction for treatment of development dysplasia of the hip in children. Am. J. Orthop. 2007, 36, 82–84. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
| Sequence | FOV (mm) | Voxel Size (mm) | Slice Thickness (mm) | Gap (%) | Foldover Direction | TR (ms) | TE (ms) | Acquisition Matrix |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cor PD tse 320 | 160 | 0.5 × 0.5 × 2.0 | 2.0 | 10 | RL | 1500 | 24 | 160 |
| Cor T2 tseRB 320 | 200 | 0.6 × 0.6 × 2.0 | 2.0 | 10 | FH | 3180 | 97 | 200 |
| Axial T2 tseRB fs 320 | 200 | 0.6 × 0.6 × 2.0 | 2.0 | 20 | RL | 2900 | 73 | 200 |
| Axial T2 tseRB 320 | 200 | 0.6 × 0.6 × 2.0 | 2.0 | 20 | RL | 3400 | 97 | 200 |
| Axial PD tseR 320 | 200 | 0.6 × 0.6 × 2.0 | 2.0 | 20 | RL | 1800 | 22 | 200 |
| Sag PD tse 384 re/li | 160 | 0.5 × 0.4 × 2.0 | 2.0 | 10 | AP | 1500 | 35 | 160 |
| Initial Graf Type | 28 Hips Reached Alpha Angle of 64° or More after Spica Casting |
|---|---|
| 1 | 10/28 |
| 2a | 3/28 |
| 2c | 4/28 |
| 3a | 5/28 |
| D | 4/28 |
| Unknown (no initial ultrasound) | 2/28 |
| Mean Start Cast | Standard Deviation | Mean End Therapy | Standard Deviation | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| alpha | In total | 52.2 | 9.8 | 65.6 | 3.3 |
| female | 52.2 | 9.6 | 65.7 | 3.4 | |
| male | 51.8 | 11.4 | 64.5 | 1.8 | |
| beta | In total | 74.2 | 9.3 | 63.9 | 6.8 |
| female | 74.0 | 9.9 | 64.0 | 7.0 | |
| male | 75.1 | 7.9 | 63.7 | 5.8 |
| Mean First MRI | Standard Deviation | Mean Second MRI | Standard Deviation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abd | 53.5 (39.3–66.2) | 5.2 | 53.4 (29.0–62.1) | 6.7 |
| AxAcet | 49.6 (32.8–68.2) | 7.1 | 50.0 (32.8–62.4) | 6.6 |
| AxPAcet | 46.8 (36.1–63.5) | 6.0 | 46.8 (4.6–69.1) | 9.3 |
| CorAcet | 25.6 (11.8–44.9) | 6.6 | 24.2 (11.7–47.6) | 7.8 |
| PelvWid | 35.8 (28.7–51.0) | 5.0 | 38.2 (32.0–52.0) | 5.1 |
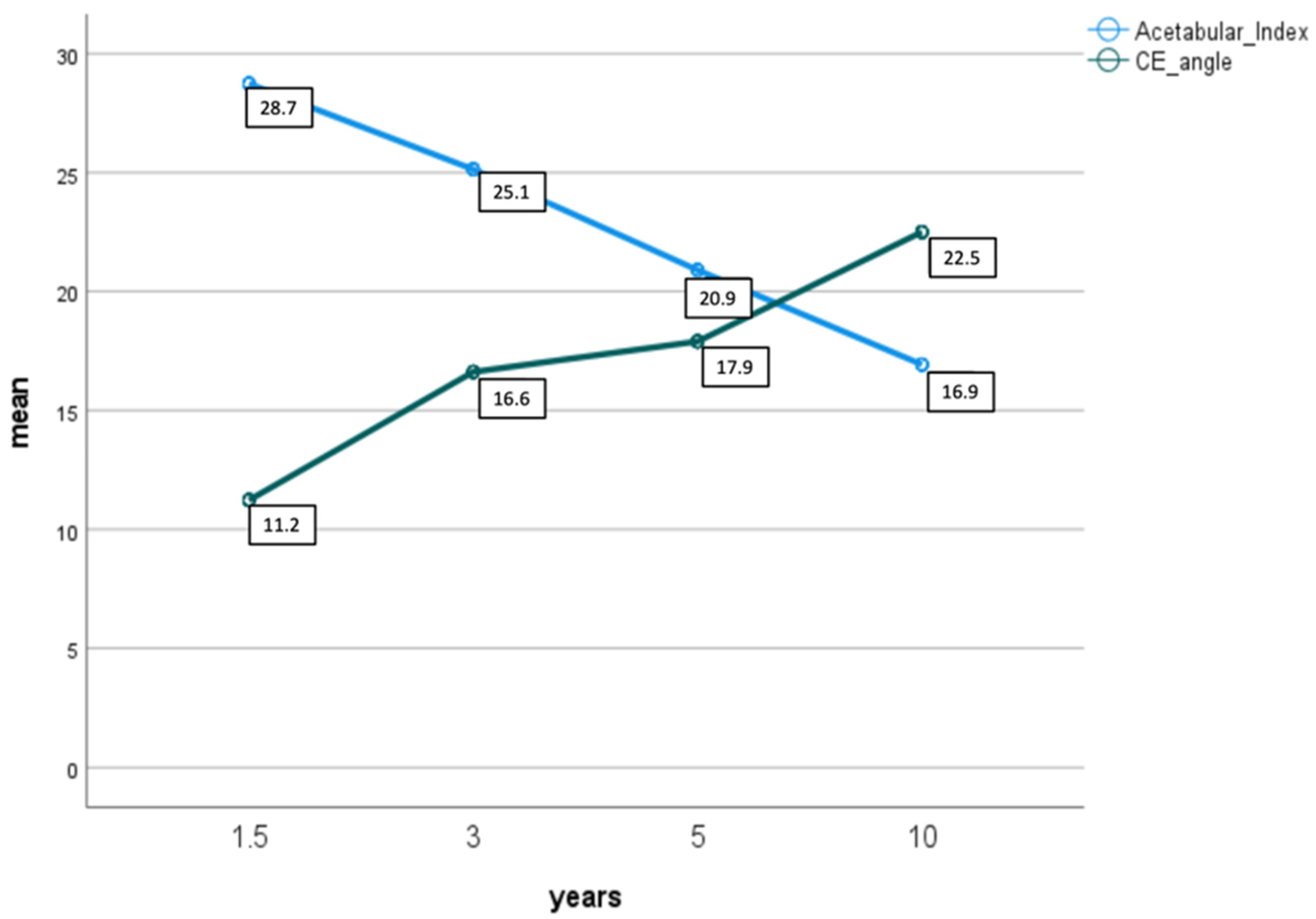
| Years | Excellent (α ≥ 64°) | Good (α < 64°) | Poor (α < 60°) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | n | n | |||||
| 1.5–2 | AI | 65 | 28.6 (s = 4.0) | 10 | 29.5 (s = 4.2) | 1 | 26.0 |
| CE | 11.3 (s = 8.3) | 8.8 (s = 8.8) | 18.0 | ||||
| 3 | AI | 46 | 25.1 (s = 4.8) | 9 | 24.11 (s = 5.6) | 1 | 22.0 |
| CE | 16.4 (s = 5.6) | 17.8 (s = 5.6) | 21.0 | ||||
| 5 | AI | 26 | 19.2 (s = 4.3) | 8 | 21.5 (s = 5.2) | 1 | 17.0 |
| CE | 18.4 (s = 4.0) | 18.38 (s = 3.8) | 20.0 | ||||
| 10 | AI | 7 | 16.3 (s = 3.9) | 3 | 15.33 (s = 5.9) | 0 | |
| CE | 22.6 (s = 5.4) | 24.33 (s = 4.7) | |||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gather, K.S.; Mavrev, I.; Gantz, S.; Dreher, T.; Hagmann, S.; Beckmann, N.A. Outcome Prognostic Factors in MRI during Spica Cast Therapy Treating Developmental Hip Dysplasia with Midterm Follow-Up. Children 2022, 9, 1010. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9071010
Gather KS, Mavrev I, Gantz S, Dreher T, Hagmann S, Beckmann NA. Outcome Prognostic Factors in MRI during Spica Cast Therapy Treating Developmental Hip Dysplasia with Midterm Follow-Up. Children. 2022; 9(7):1010. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9071010
Chicago/Turabian StyleGather, Katharina Susanne, Ivan Mavrev, Simone Gantz, Thomas Dreher, Sébastien Hagmann, and Nicholas Andreas Beckmann. 2022. "Outcome Prognostic Factors in MRI during Spica Cast Therapy Treating Developmental Hip Dysplasia with Midterm Follow-Up" Children 9, no. 7: 1010. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9071010
APA StyleGather, K. S., Mavrev, I., Gantz, S., Dreher, T., Hagmann, S., & Beckmann, N. A. (2022). Outcome Prognostic Factors in MRI during Spica Cast Therapy Treating Developmental Hip Dysplasia with Midterm Follow-Up. Children, 9(7), 1010. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9071010






