Lower-Limb Amputation in Children and Adolescents—A Rare Encounter with Unique and Special Challenges
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population and Design
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria for Amputations
2.3. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria for Complications
2.4. Study Variables
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic and Clinical Characteristics
3.2. Complications following Amputations
3.3. Revisions Secondary to Complications
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Griffet, J. Amputation and prosthesis fitting in paediatric patients. Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. 2016, 102 (Suppl. 1), S161–S175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masood Jawaid, I.A.; Kaimkhani, G.M. Current indications for major lower limb amputations at Civil Hospital, Karachi. Pak. J. Surg. 2008, 24, 228–231. [Google Scholar]
- Abou-Zamzam, A.M., Jr.; Teruya, T.H.; Killeen, J.D.; Ballard, J.L. Major lower extremity amputation in an academic vascular center. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2003, 17, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olasinde, A.A.; Oginni, L.M.; Bankole, J.O.; Oluwadiya, K.S. Indications for amputations in Ile-Ife, Nigeria. Niger. J. Med. J. Natl. Assoc. Resid. Dr. Niger. 2002, 11, 118–121. [Google Scholar]
- Jahmani, R.; Paley, D. Stump Overgrowth after Limb Amputation in Children, In Limb Amputation; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Chalya, P.L.; Mabula, J.B.; Dass, R.M.; Ngayomela, I.H.; Chandika, A.B.; Mbelenge, N.; Gilyoma, J.M. Major limb amputations: A tertiary hospital experience in northwestern Tanzania. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2012, 7, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paudel, B.; Shrestha, B.K.; Banskota, A.K. Two faces of major lower limb amputations. Kathmandu Univ. Med. J. 2005, 3, 212–216. [Google Scholar]
- Van Der Meij, W.K.N. No Leg to Stand On: Historical Relation between Amputation Surgery and Prostheseology; University of Groningen: Groningen, The Netherlands, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Jenyo, M.; Diya, K.; Olakulehin, O. Limb amputations in Osogbo, Nigeria. Afr. J. Trauma 2004, 2, 80–82. [Google Scholar]
- Kidmas, A.; Nwadiaro, C.; Igun, G. Lower limb amputation in Jos, Nigeria. East Afr. Med. J. 2004, 81, 427–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwankwo, O.; Katchy, A. Surgical limb amputation: A five-year experience at Hilltop Orthopedic Hospital Enugu, Nigeria. Niger. J. Orthop. Trauma 2004, 3, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sié Essoh, J.B.; Kodo, M.; Djè Bi Djè, V.; Lambin, Y. Limb amputations in adults in an Ivorian teaching hospital. Niger. J. Clin. Pract. 2009, 12, 245–247. [Google Scholar]
- Solagberu, B. The scope of amputations in a Nigerian teaching hospital. Afr. J. Med. Med. Sci. 2001, 30, 225–227. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Greive, A.C.; Lankhorst, G.J. Functional outcome of lower-limb amputees: A prospective descriptive study in a general hospital. Prosthet. Orthot. Int. 1996, 20, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pernot, H.F.; Winnubst, G.M.; Cluitmans, J.J.; De Witte, L.P. Amputees in Limburg: Incidence, morbidity and mortality, prosthetic supply, care utilisation and functional level after one year. Prosthet. Orthot. Int. 2000, 24, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rommers, G.M.; Vos, L.D.; Groothoff, J.W.; Schuiling, C.H.; Eisma, W.H. Epidemiology of lower limb amputees in the north of The Netherlands: Aetiology, discharge destination and prosthetic use. Prosthet. Orthot. Int. 1997, 21, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umaru, R.; Gali, B.; Ali, N. Role of inappropriate traditional splintage in limb amputation in Maiduguri, Nigeria. Ann. Afr. Med. 2004, 3. Available online: https://tspace.library.utoronto.ca/handle/1807/4100 (accessed on 17 May 2022).
- Yusof, M.I.; Sulaiman, A.R.; Muslim, D.A. Diabetic foot complications: A two-year review of limb amputation in a Kelantanese population. Singap. Med. J. 2007, 48, 729–732. [Google Scholar]
- Abraham, E.; Pellicore, R.J.; Hamilton, R.C.; Hallman, B.W.; Ghosh, L. Stump overgrowth in juvenile amputees. J. Pediatric Orthop. 1986, 6, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aitken, G. Overgrowth of the amputation stump. Interclin Inf. Bull 1962, 1, 66–71. [Google Scholar]
- Aitken, G.T. Surgical Amputation in Children. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 1963, 45, 1735–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedorak, G.T.; Watts, H.G.; Cuomo, A.V.; Ballesteros, J.P.; Grant, H.J.; Bowen, R.E.; Scaduto, A.A. Osteocartilaginous transfer of the proximal part of the fibula for osseous overgrowth in children with congenital or acquired tibial amputation: Surgical technique and results. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2015, 97, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neal, M.L.; Bahner, R.; Ganey, T.M.; Ogden, J.A. Osseous overgrowth after amputation in adolescents and children. J. Pediatric Orthop. 1996, 16, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenholder, M.; Davids, J.R.; Gruber, H.E.; Blackhurst, D.W. Surgical management of juvenile amputation overgrowth with a synthetic cap. J. Pediatric Orthop. 2004, 24, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, E. Operative treatment of bone overgrowth in children who have an aquired or congenital amputation. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 1996, 78, 1287–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourke, H.E.; Yelden, K.C.; Robinson, K.P.; Sooriakumaran, S.; Ward, D.A. Is revision surgery following lower-limb amputation a worthwhile procedure? A retrospective review of 71 cases. Injury 2011, 42, 660–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
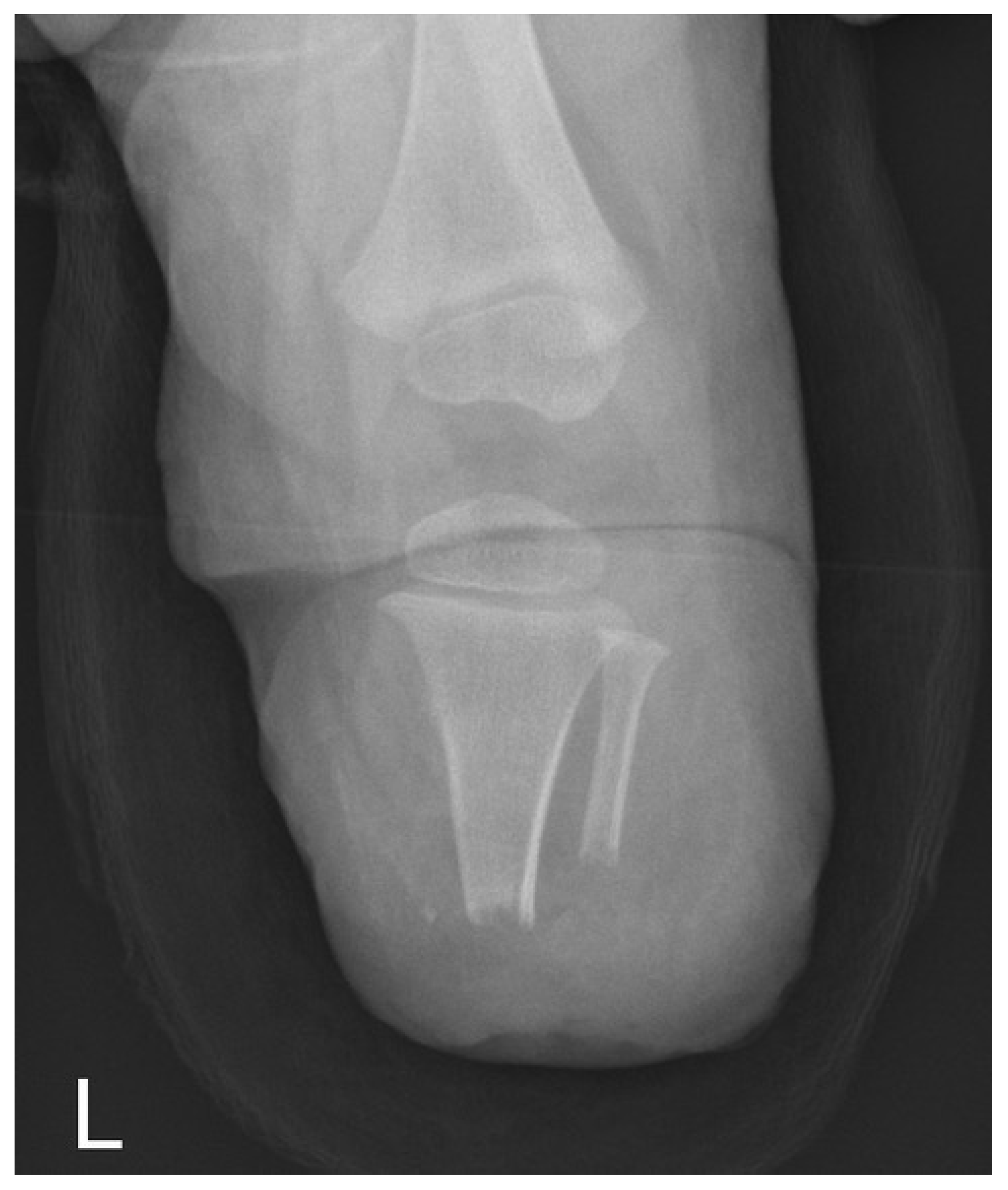
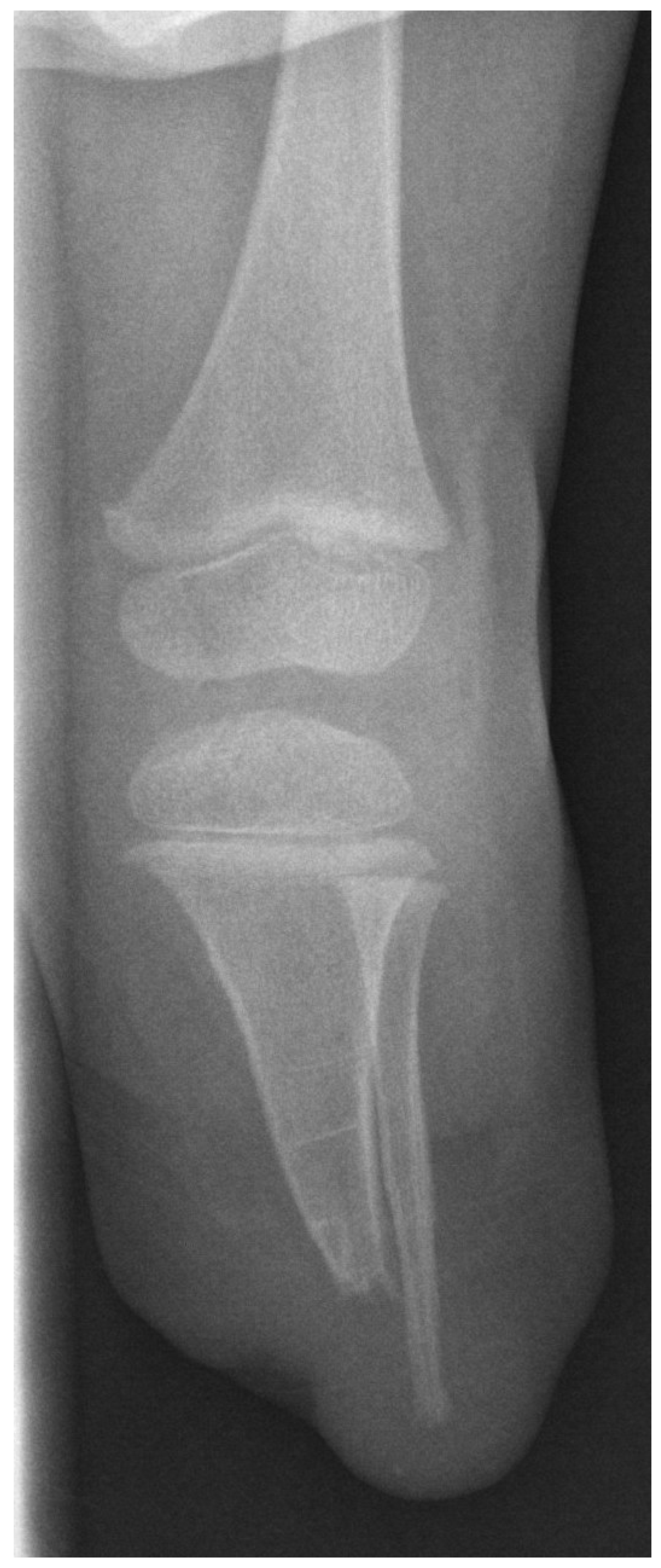
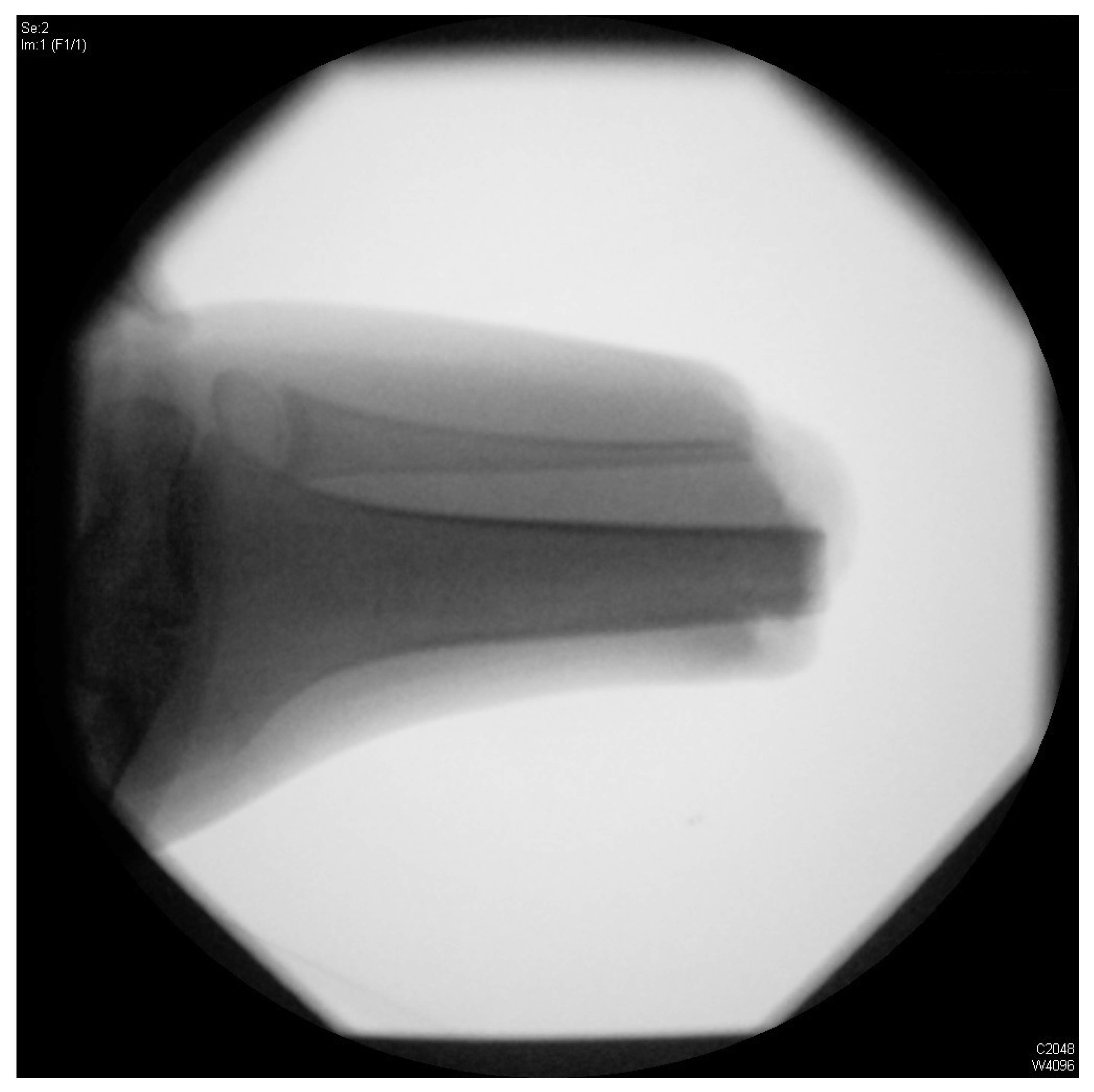
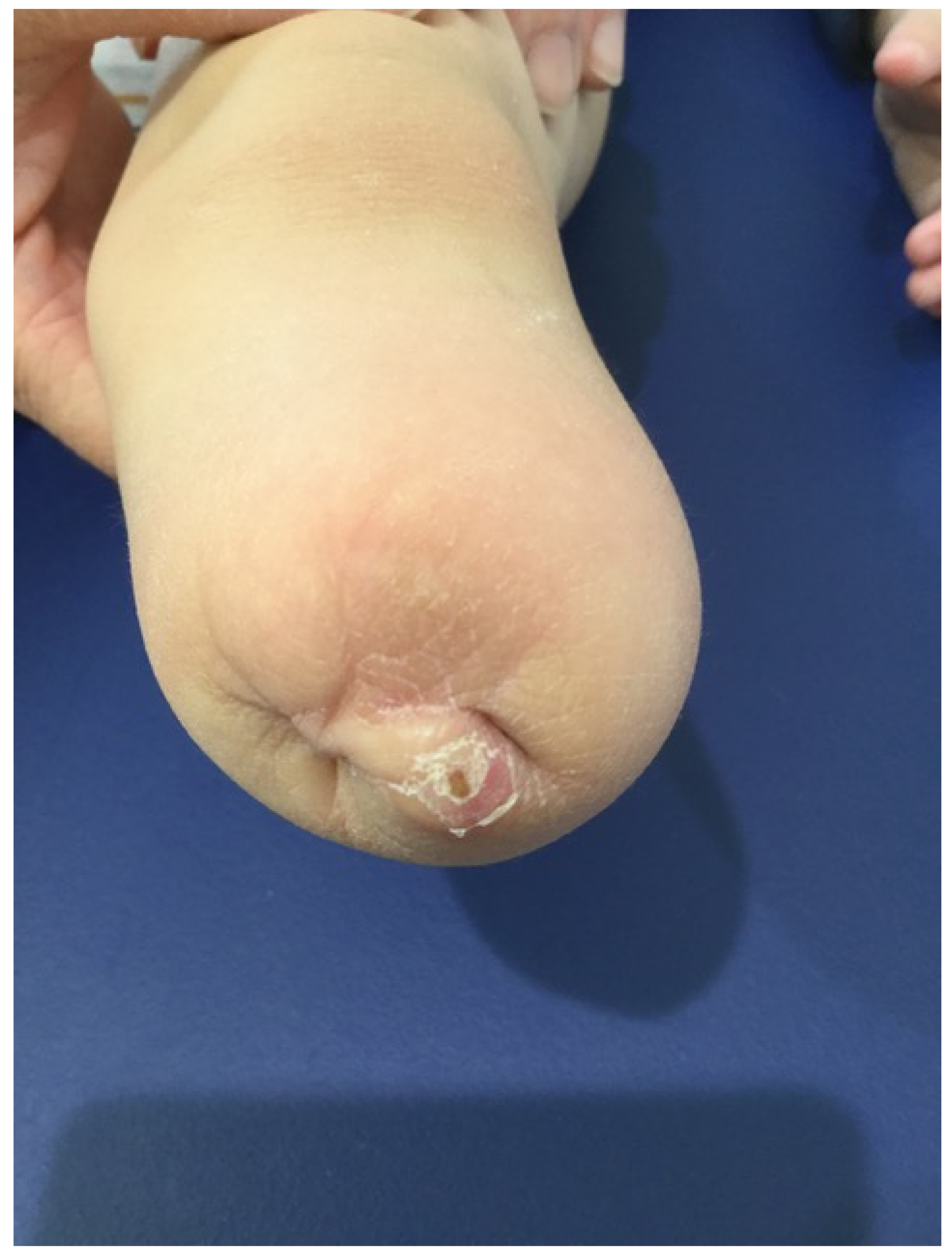
| Variable | Subcategory | Total Population (n = 22) |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years); mean (SD) | ||
| 12 (5.1) | ||
| Gender; n (%) | ||
| Male | 14 (63.6%) | |
| Female | 8 (36.4%) | |
| Causes of Amputation; n (%) | ||
| Tumor | 16 (72.7%) | |
| Infection | 1 (4.5%) | |
| Dysmelia | 3 (13.6%) | |
| Circulation | 2 (9.1%) | |
| Total | 22 (100%) | |
| Level of Amputation; n (%) | ||
| Transtibial | 2 (9.1%) | |
| Transfemoral | 15 (68.2%) | |
| Hemipelvectomy | 2 (9.1%) | |
| Hip-disarticulation | 3 (13.6%) | |
| Total | 22 (100%) | |
| Complications; n (%) | ||
| 10 (45.45%) | ||
| Revision Surgery due to complications; n (%) | ||
| 10 (45.45%) | ||
| Variables | Number (%) |
|---|---|
| Revision with stump shortening + reconstruction with bone cartilage cap plasty | 1 (11.1%) |
| Stump revision with ablation of bone tips | 1 (11.1%) |
| Stump shortening and stump revision | 3 (33.3%) |
| Stump shortening with periosteoplasty | 2 (22.2%) |
| Stump cap plasty with bone wedge from iliac crest | 1 (11.1%) |
| Resection of exostosis and bony aspects | 1 (11.1%) |
| Total | 9 (100%) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Horsch, A.; Gleichauf, S.; Lehner, B.; Ghandour, M.; Koch, J.; Alimusaj, M.; Renkawitz, T.; Putz, C. Lower-Limb Amputation in Children and Adolescents—A Rare Encounter with Unique and Special Challenges. Children 2022, 9, 1004. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9071004
Horsch A, Gleichauf S, Lehner B, Ghandour M, Koch J, Alimusaj M, Renkawitz T, Putz C. Lower-Limb Amputation in Children and Adolescents—A Rare Encounter with Unique and Special Challenges. Children. 2022; 9(7):1004. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9071004
Chicago/Turabian StyleHorsch, Axel, Svenja Gleichauf, Burkhard Lehner, Maher Ghandour, Julian Koch, Merkur Alimusaj, Tobias Renkawitz, and Cornelia Putz. 2022. "Lower-Limb Amputation in Children and Adolescents—A Rare Encounter with Unique and Special Challenges" Children 9, no. 7: 1004. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9071004
APA StyleHorsch, A., Gleichauf, S., Lehner, B., Ghandour, M., Koch, J., Alimusaj, M., Renkawitz, T., & Putz, C. (2022). Lower-Limb Amputation in Children and Adolescents—A Rare Encounter with Unique and Special Challenges. Children, 9(7), 1004. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9071004






