Adapted Basketball Training Improves Fitness and Motivation in Adolescents with Moderate Obesity: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
- •
- H1: Greater reduction in BMI
- •
- H2: Greater improvements in physical fitness
- •
- H3: Higher levels of motivation
- •
- H4: Enhanced technical execution of basketball skills
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Procedure
2.3. Adapted Basketball Program
2.4. Anthropometric Measurement
2.5. Intermittent Fitness Test 15-15 (Spartacus Test)
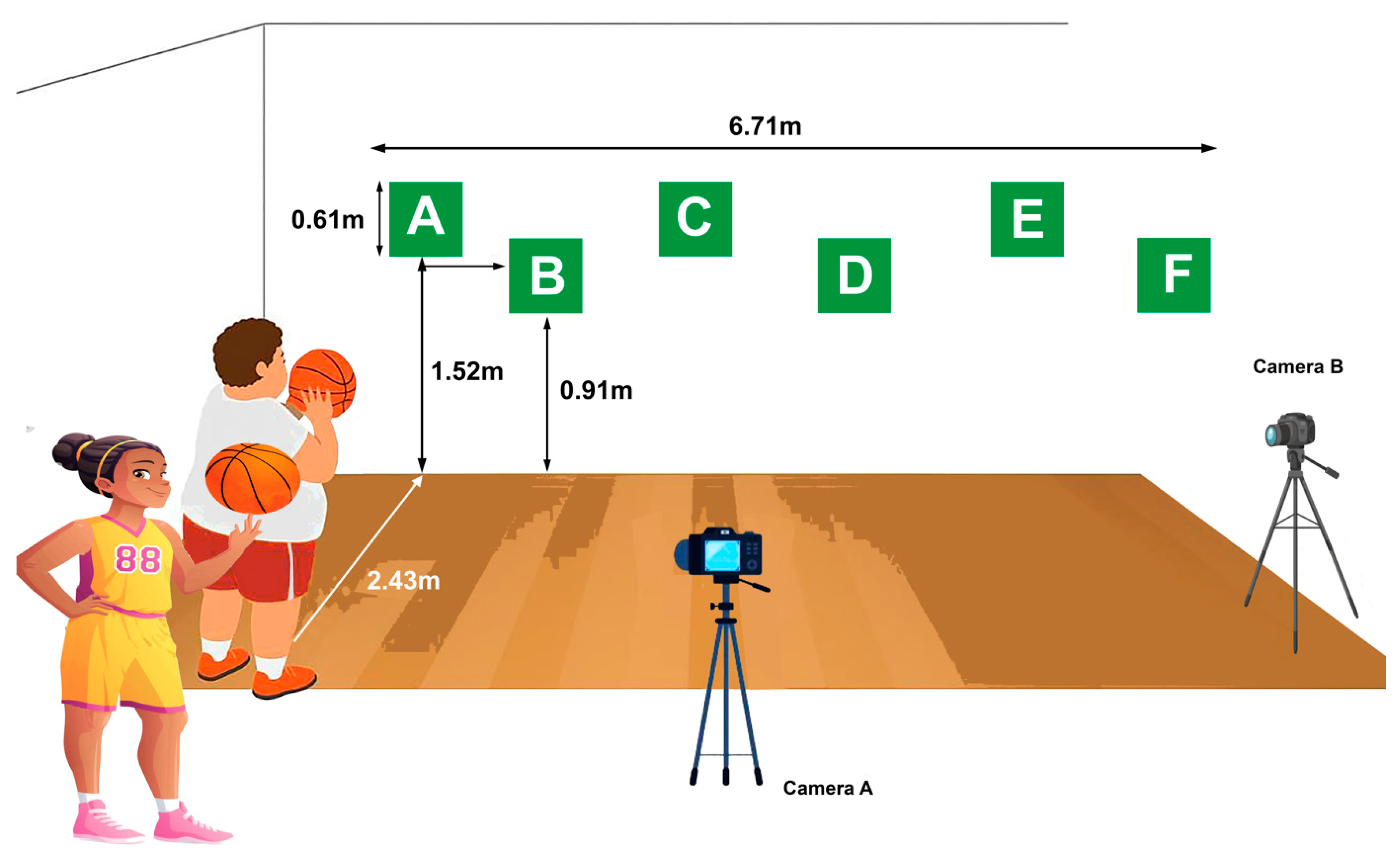
2.6. Technical Accuracy Assessment
2.6.1. Passing Accuracy
2.6.2. Shooting Accuracy
2.6.3. Dribbling Mastery
2.7. Motivation Assessment
2.8. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
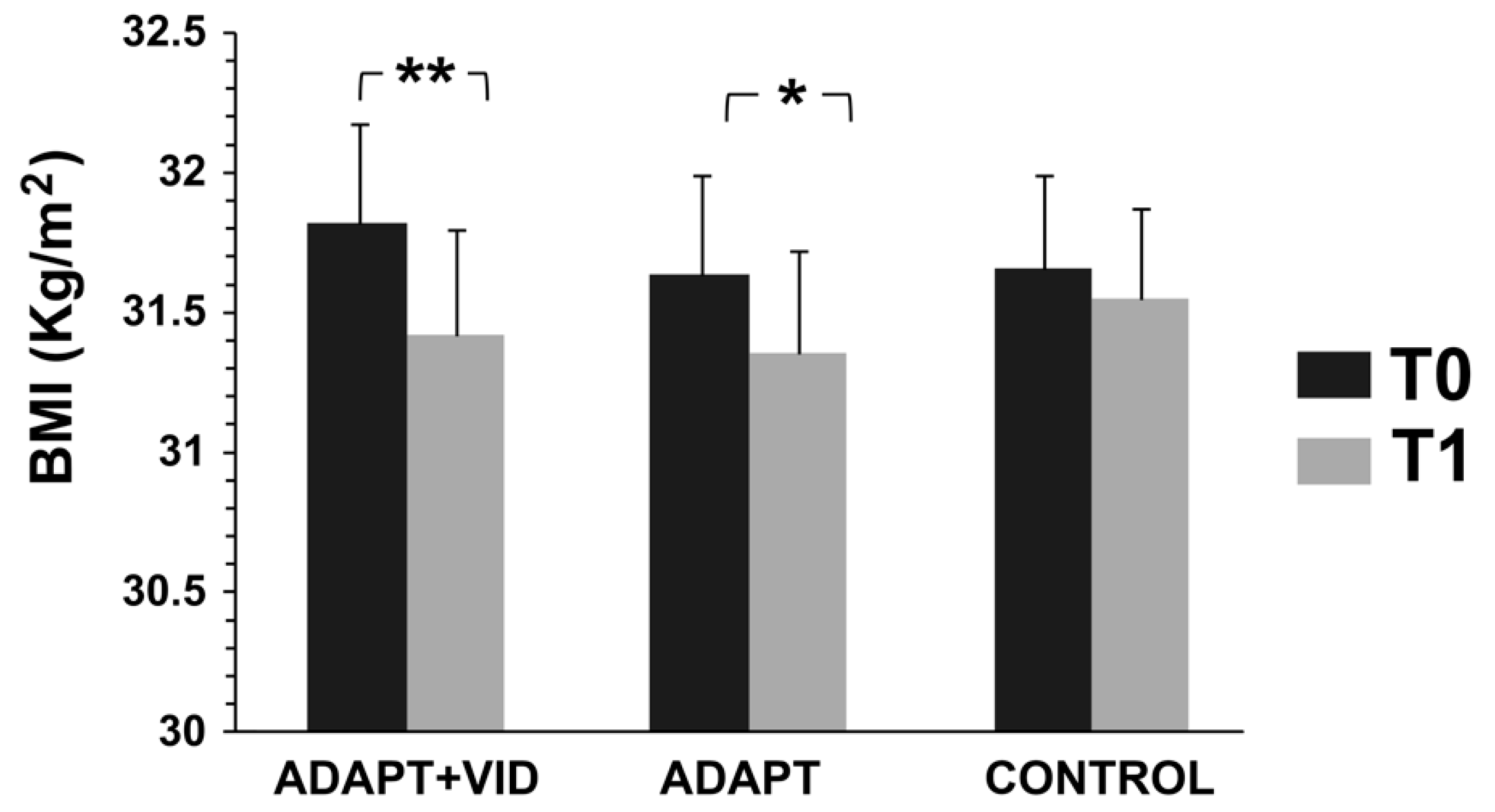
3.1. Body Mass Index
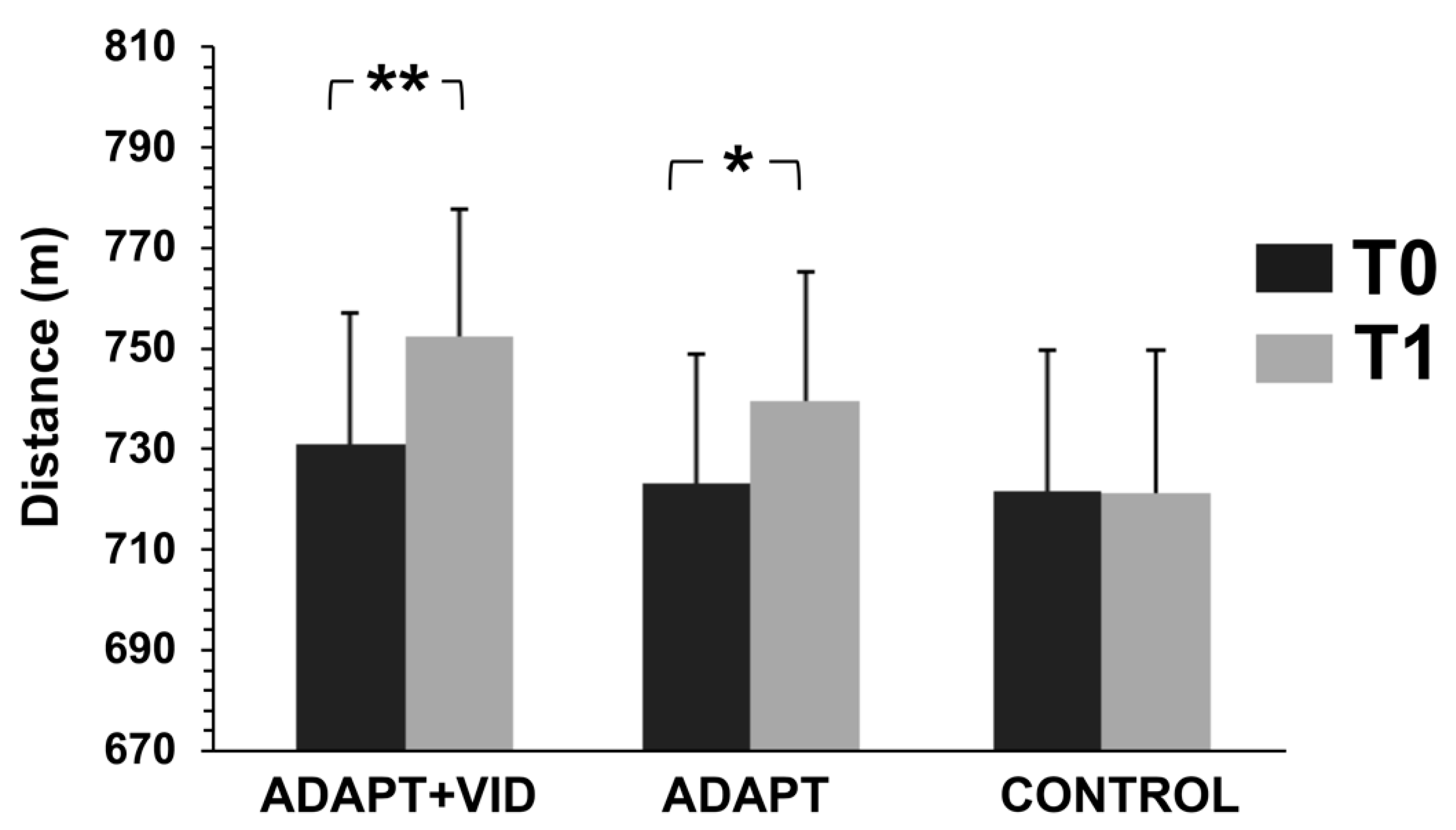
3.2. Physical Fitness
3.3. Technical Accuracy
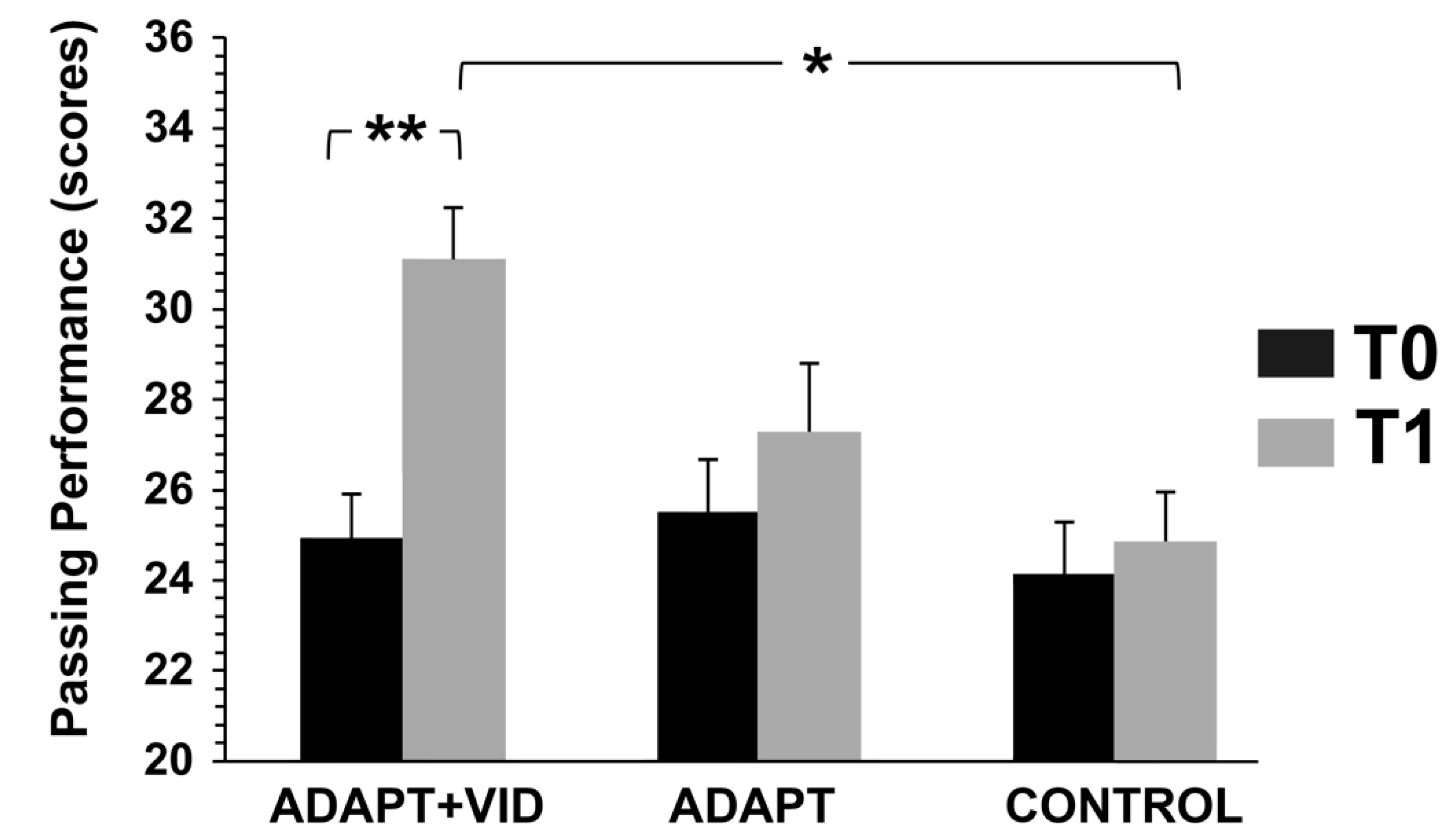
3.3.1. Passing Performance
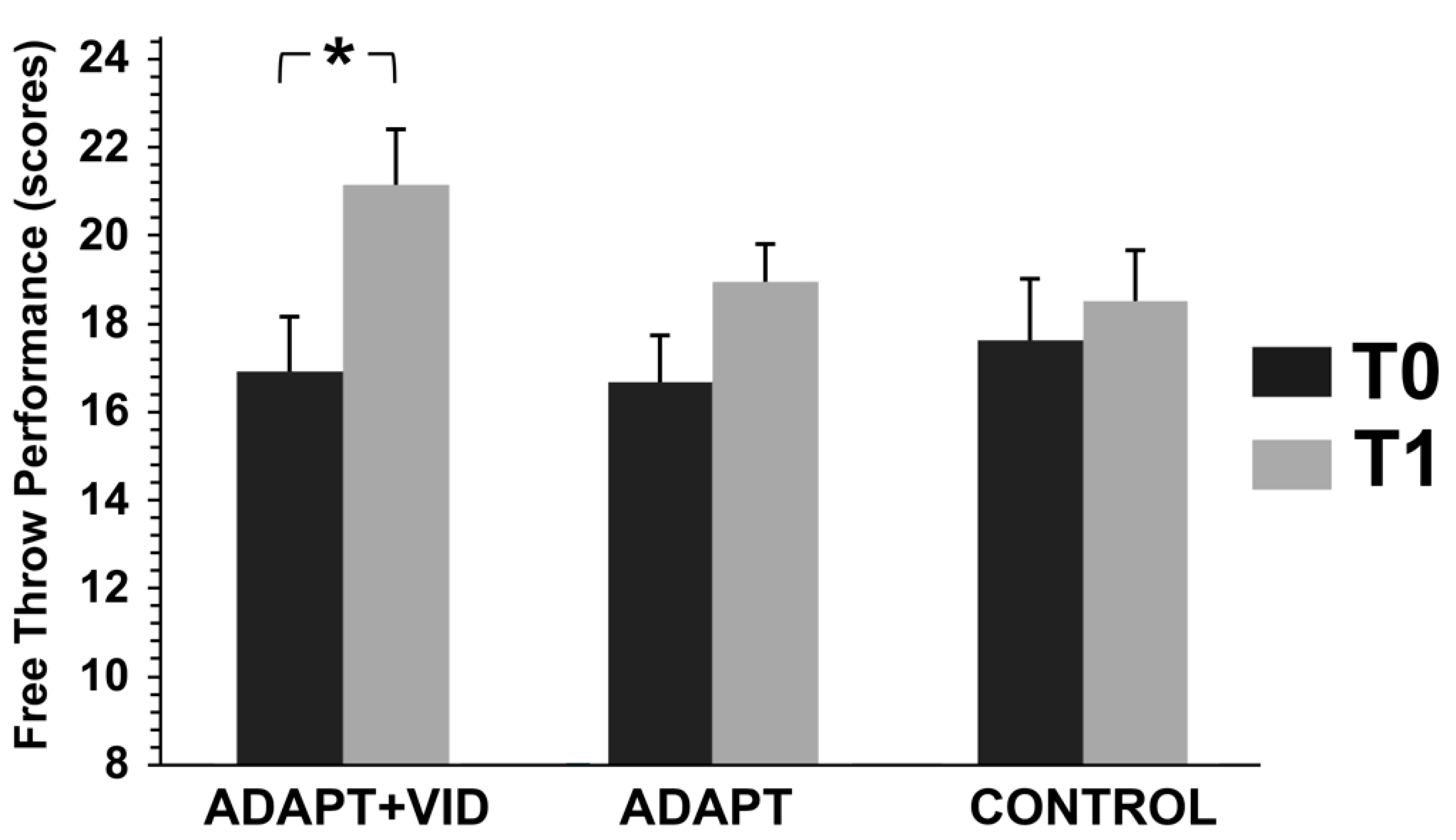
3.3.2. Free Throw Performance
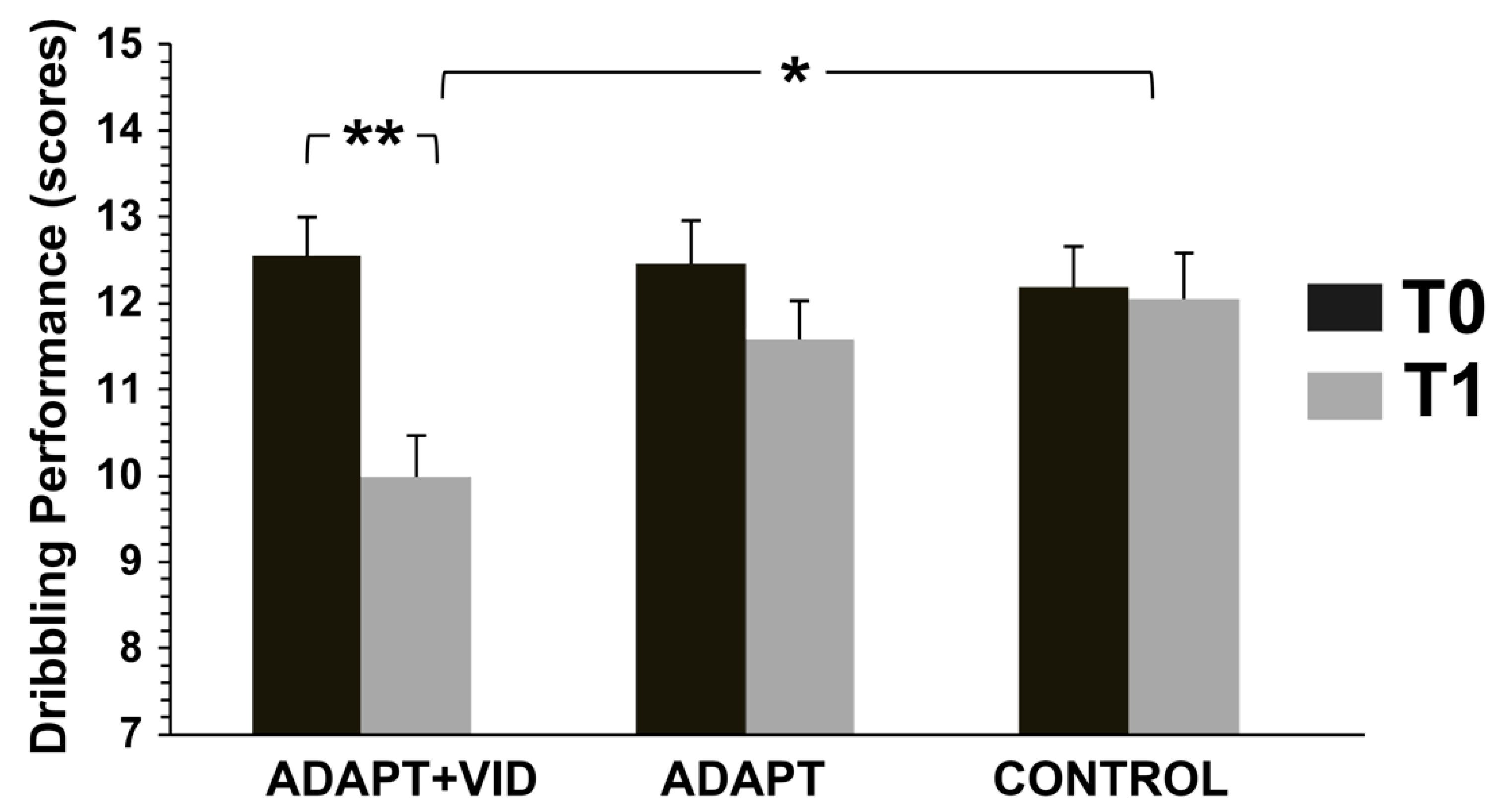
3.3.3. Dribbling Performance
3.4. Motivation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; Ni, Y.; Yi, C.; Fang, Y.; Ning, Q.; Shen, B.; Zhang, K.; Liu, Y.; Yang, L.; et al. Global Prevalence of Overweight and Obesity in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JAMA Pediatr. 2024, 178, 800–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chusan, Y.A.C.; Eneli, I.; Hennessy, E.; Pronk, N.P.; Economos, C.D. Next Steps in Efforts to Address the Obesity Epidemic. Annu. Rev. Public Health 2025, 46, 171–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, S.R.; Arnett, D.K.; Eckel, R.H.; Gidding, S.S.; Hayman, L.L.; Kumanyika, S.; Robinson, T.N.; Scott, B.J.; St. Jeor, S.; Williams, C.L. Overweight in children and adolescents: Pathophysiology, consequences, prevention, and treatment. Circulation 2005, 111, 1999–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- So, H.K.; Nelson, E.A.; Li, A.M.; Wong, E.M.; Lau, J.T.; Guldan, G.S.; Mak, K.H.; Wang, Y.; Fok, T.F.; Sung, R.Y. Secular changes in height, weight and body mass index in Hong Kong Children. BMC Public Health 2008, 8, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timkova, V.; Mikula, P.; Nagyova, I. Psychosocial distress in people with overweight and obesity: The role of weight stigma and social support. Front Psychol. 2025, 15, 1474844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slimi, O.; Muscella, A.; Marsigliante, S.; Bahloul, M. The impact of adapted exercises in basketball on the perception of the difficulty and physical enjoyment of students with overweight. Heliyon 2024, 10, e29190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, K.M.; Shin, S.; Tarnopolsky, M.; Taylor, V.H. Association of depression & health related quality of life with body composition in children and youth with obesity. J. Affect. Disord. 2015, 172, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, S.H.; Kahathuduwa, C.N.; Binks, M. Physical activity and obesity: What we know and what we need to know. Obes. Rev. 2016, 17, 1226–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Cheikh, I.; Marzouki, H.; Selmi, O.; Cherni, B.; Bouray, S.; Bouhlel, E.; Bouassida, A.; Knechtle, B.; Chen, Y.S. Effect of water-based aerobic training on anthropometric, biochemical, cardiovascular, and explosive strength parameters in young overweight and obese women: A randomized controlled trial. PeerJ 2025, 13, e19020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhelst, J.; Béghin, L.; Fardy, P.S.; Bui-Xuan, G.; Mikulovic, J. A conative educational model for an intervention program in obese youth. BMC Public Health 2012, 12, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasiri, S.; Dehghanizade, J. Comparison of the Effect of Teaching Games for Understanding and Traditional Pedagogy on Futsal Game Performance, Some Factors of Physical Fitness and Physical Activity Level in Obese Students. J. Sports Mot. Dev. Learn. 2025, 17, 103–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojanović, D.; Momčilović, V.; Zadražnik, M.; Ilić, I.; Koničanin, A.; Padulo, J.; Russo, L.; Stojanović, T. School-Based TGfU Volleyball Intervention Improves Physical Fitness and Body Composition in Primary School Students: A Cluster-Randomized Trial. Healthc. 2023, 11, 1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khayati, A.; Sahli, F.; Ghouili, H.; Labbadi, R.; Selmi, O.; Sahli, H.; Jebabli, N.; Romdhani, A.; Zghibi, M.; Haddad, M. Effects of coach-delivered verbal encouragement on the physiological and psychological responses of adolescent players in small-sided basketball games. Front Psychol. 2024, 15, 1392668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspar, V.; Gil-Arias, A.; Del Villar, F.; Práxedes, A.; Moreno, A. How TGfU Influence on Students’ Motivational Outcomes in Physical Education? A Study in Elementary School Context. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.H.; Huang, C.H.; Hsu, W.T. A comparison of the learning effects between TGfU-SE and TGfU on learning motivation, sport enjoyment, responsibility, and game performance in physical education. Front Psychol. 2023, 14, 1165064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Xue, H.; Wang, W.; Wang, Y. Parental Expectations and Child Screen and Academic Sedentary Behaviors in China. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2017, 52, 680–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinho, C.; Farinha, J.; Lisboa, S.; Bagatini, N.; Leites, G.; Voser, R.; Gaya, A.R.; Reischak-Oliveira, A.; Cunha, G.d.S. Effects of a small-sided soccerprogram on health parameters in obese children. Rev. Bras. Med. Esporte 2022, 29, e2021_0398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soylu, Y.; Arslan, E.; Killit, B.; Lane, A.M. Effects of coach encouragement on psychophysiological responses and technical actions in different small-sided soccer games. Int. J. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 2023, 22, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammami, M.A.; Guerchi, M.; Selmi, O.; Sehli, F.; Ghouili, H.; Stângaciu, O.A.; Marinău, M.A.; Galeru, O.; Alexe, D.I. Effect of Verbal Encouragement on Physical Fitness, Technical Skill and Physiological Response during Small-Sided Soccer Games. Sustainability 2023, 15, 3624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chatzisarantis, N.; Spray, C.M.; Biddle, S.J.H. Achievement goal profiles in school physical education: Differences in self-determination, sport ability beliefs, and physical activity. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, D.G.; Pelletier, L.; Moutão, J.; Cid, L. Examining the motivational determinants of enjoyment and the intention to continue of persistent competitive swimmers. Int. J. Sport Psychol. 2018, 49, 484–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilit, B.; Arslan, E.; Akca, F.; Aras, D.; Soylu, Y.; Clemente, F.M.; Nikolaidis, P.T.; Rosemann, T.; Knechtle, B. Effect of Coach Encouragement on the Psychophysiological and Performance Responses of Young Tennis Players. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crane, J.; Temple, V. A systematic review of dropout from organized sport among children and youth. Eur. Phys. Educ. Rev. 2014, 21, 114–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souissi, M.A.; Souissi, H.; Elghoul, Y.; Masmoudi, L.; Trabelsi, O.; Ammar, A.; Chtourou, H.; Souissi, N. Information Processing and Technical Knowledge Contribute to Self-Controlled Video Feedback for Children Learning the Snatch Movement in Weightlifting. Percept. Mot. Ski. 2021, 128, 1785–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trabelsi, O.; Gharbi, A.; Souissi, M.A.; Mezghanni, N.; Bouchiba, M.; Mrayeh, M. Video modeling examples are effective tools for self-regulated learning in physical education: Students learn through repeated viewing, self-talk, and mental rehearsal. EurPhy. Educ. Rev. 2022, 28, 341–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Zhou, L.; Briggs, R.O.; Nunamaker, J.F., Jr. Instructional video in e-learning: Assessing the impact of interactive video on learning effectiveness. Inf. Manag. 2006, 43, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- H’mida, C.; Degrenne, O.; Souissi, N.; Rekik, G.; Trabelsi, K.; Jarraya, M.; Bragazzi, N.L.; Khacharem, A. Learning a Motor Skill from Video and Static Pictures in Physical Education Students-Effects on Technical Performances, Motivation and Cognitive Load. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 9067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souissi, M.A.; Trabelsi, O.; Souissi, H.; Elghoul, Y.; Ammar, A.; Chamari, K.; Souissi, N. The video feedback viewing in novice weightlifters: Total control strategy improves snatch technique during learning. Int. J. Sports Sci. Coach 2022, 17, 1408–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiken, C.A.; Fairbrother, J.T.; Post, P.G. The effects of self-controlled video feedback on the learning of the basketball set shot. Front Psychol. 2012, 11, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palao, J.M.; Hastie, P.; Cruz, P.G.; Ortega, E. The impact of video technology on student performance in physical education. Technol. Pedagogy Educ. 2015, 24, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Bu, D.; Yu, S.; Sun, Y.; Wang, J.; Lee, T.C.T.; Baker, J.S.; Gao, Y. Effects of a School-Based Physical Activity Intervention for Obesity, Health-Related Physical Fitness, and Blood Pressure in Children with Intellectual Disability: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 12015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branco, B.H.M.; Mariano, I.R.; de Oliveira, L.P.; Bertolini, S.M.M.G.; de Oliveira, F.M.; Araújo, C.G.A.; Adamo, K. Sports and Functional Training Improve a Subset of Obesity-Related Health Parameters in Adolescents: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Front Psychol. 2021, 11, 589554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bredt, S.; Camargo, D.S.; Torres, J.; Praça, G.M.; de Andrade, A.G.P.; Paolucci, L.A.; da Costa, I.T.; Chagas, M.H. Multidimensional analysis of players’ responses in basketball small-sided games: The impact of changing game rules. Int. J. Sports Sci. Coach. 2023, 18, 1501–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Ronda, L.; Ric, A.; Llabres-Torres, I.; de las Heras, B.; Schelling, X. Position-dependent cardiovascular response and time-motion analysis during training drills and friendly matches in elite male basketball players. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2016, 30, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey, O.; Maïano, C.; Nicol, C.; Mercier, C.S.; Vallier, J.M. Psycho-Physiological Responses of Obese Adolescents to an Intermittent Run Test Compared with a 20-M Shuttle Run. J. Sports Sci. Med. 2016, 15, 451–459. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, T. The Effect of Upper Extremity Fatigue on Grip Strength and Passing Accuracy in Junior Basketball Players. J. Hum. Kinet. 2013, 37, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Quílez-Maimón, A.; Rojas-Ruiz, F.J.; Delgado-García, G.; Courel-Ibáñez, J. The Q-Pass Index: A Multifactorial IMUs-Based Tool to Assess Passing Skills in Basketball. Sensors 2021, 21, 4601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleary, T.J.; Zimmerman, B.J.; Keating, T. Training physical education students to self-regulate during basketball free throw practice. Res. Q. Exerc. Sport 2006, 77, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tapsell, L.C.; Binnie, M.J.; Lay, B.S.; Dawson, B.T.; Goods, P.S.R. Validity and Reliability of a Field Hockey-Specific Dribbling Speed Test. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2022, 36, 1720–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavlović, L.; Lazić, A.; Čović, N.; Pišot, R.; Petronijević, M.; Milanović, Z. Dribble deficit as an effective measure of dribbling ability independent of sprinting performance in professional female handball players. Front Physiol. 2025, 15, 1506893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guay, F.; Vallerand, R.J.; Blanchard, C. On the Assessment of Situational Intrinsic and Extrinsic Motivation: The Situational Motivation Scale (SIMS). Motiv. Emot. 2000, 24, 175–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tannoubi, A.; Ouergui, I.; Srem-Sai, M.; Hagan, J.E.; Quansah, F.; Azaiez, F. Effectiveness of Video Modeling in Improving Technical Skills in Young Novice Basketball Players: A Quasi-Experimental Study. Children 2023, 10, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Abdullah, B.B.; Abu Saad, H.B.; Wang, Q. The effect of using video in teaching to acquire content knowledge in physical education—A systematic review. Int. J. Acad. Res. Bus. Soc. Sci. 2024, 14, 1332–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schack, T.; Essig, K.; Frank, C.; Koester, D. Mental representation and motor imagery training. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, C.; Kim, T.; Schack, T. Observational practice promotes action-related order formation in long-term memory: Investigating action observation and the development of cognitive representation in complex motor action. J. Mot. Learn. Dev. 2017, 6, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saiki-Ishikawa, A.; Agrios, M.; Savya, S.; Forrest, A.; Sroussi, H.; Hsu, S.; Basrai, D.; Xu, F.; Miri, A. Hierarchy between Forelimb Premotor and Primary Motor Cortices and Its Manifestation in Their Firing Patterns. eLife 2024, 13, RP103069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandura, A. Social Foundations of Thought and Action; SAGE: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1986; Volume 2, pp. 23–28. [Google Scholar]
- Celnik, P.; Stefan, K.; Hummel, F.; Duque, J.; Classen, J.; Cohen, L.G. Encoding a motor memory in the older adult by action observation. Neuroimage 2006, 29, 677–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paas, F.; Van Merrienboer, J.J.G. Cognitive-Load Theory: Methods to Manage Working Memory Load in the Learning of Complex Tasks. Curr. Dir. Psychol. Sci. 2020, 29, 394–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buszard, T.; Farrow, D.; Verswijveren, S.J.J.M.; Reid, M.; Williams, J.; Polman, R.; Ling, F.C.M.; Masters, R.S.W. Working Memory Capacity Limits Motor Learning When Implementing Multiple Instructions. Front Psychol. 2017, 8, 1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, P.; Vansteenkiste, M.; Parker, P.; Kingsford-Smith, A.; Zhou, S. Cognitive Load Theory and Its Relationships with Motivation: A Self-Determination Theory Perspective. Educ. Psychol. Rev. 2024, 36, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandura, A. Freeman, W.H., Ed.; Self-Efficacy: The Exercise of Control; Worth Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Law, B.; Hall, C. Observational Learning Use and Self-Efficacy Beliefs in Adult Sport Novices. Psychol. Sport Exerc. 2009, 10, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, R.R.; Williams, A.M.; Scott, M.A. Learning from demonstrations: The role of visual search during observational learning from video and point-light models. J. Sports Sci. 2002, 20, 253–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Rodríguez, A.; Gostian-Ropotin, L.A.; Beltrán-Velasco, A.I.; Belando-Pedreño, N.; Simón, J.A.; López-Mora, C.; Navarro-Jiménez, E.; Tornero-Aguilera, J.F.; Clemente-Suárez, V.J. Sporting Mind: The Interplay of Physical Activity and Psychological Health. Sports 2024, 12, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faílde-Garrido, J.M.; Ruiz Soriano, L.; Simón, M.A. Levels of physical activity and their relationship with motivational determinants, self-regulation, and other health-related parameters in university students. Psychol. Rep. 2021, 125, 1952–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verloigne, M.; De Bourdeaudhuij, I.; Tanghe, A.; D’Hondt, E.; Theuwis, L.; Vansteenkiste, M.; Deforche, B. Self-determined motivation towards physical activity in adolescents treated for obesity: An observational study. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2011, 8, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Power, T.; Desha, L.; Matthews, J.; O’Brien, K. Motivation types and physical activity levels in adolescents: The role of autonomous motivation in promoting healthy behaviors. J. Adolesc. Health 2011, 49, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deci, E.L.; Ryan, R.M. The “what” and “why” of goal pursuits: Human needs and the self-determination of behavior. Psychol. Inq. 2000, 11, 227–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilić, T.; Stojanović, S.; Rančić, D.; Jorgić, B.M.; Cristian, R.S.; Iordan, D.A.; Mircea, C.C.; Leonard, S.; Onu, I. Relationship between Physical Activity Levels and Academic Performance in Adolescents from Serbia. Children 2024, 11, 1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hills, A.P.; King, N.A.; Armstrong, T.P. The contribution of physical activity and sedentary behaviours to the growth and development of children and adolescents: Implications for overweight and obesity. Sports Med. 2007, 37, 533–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, I.; Leblanc, A.G. Systematic review of the health benefits of physical activity and fitness in school-aged children and youth. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2010, 7, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Li, Y.; Cai, L.; Wang, Y. Effects of physical activity interventions on cognitive performance of overweight or obese children and adolescents: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Pediatr. Res. 2021, 89, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moeini, B.; Rezapur-Shahkolai, F.; Bashirian, S.; Doosti-Irani, A.; Afshari, M.; Geravandi, A. Effect of interventions based on regular physical activity on weight management in adolescents: A systematic review and a meta-analysis. Syst. Rev. 2021, 10, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slimi, O.; Marsigliante, S.; Ciardo, V.; Bahloul, M.; Selmi, O.; Jebabli, N.; Muscella, A. The effects of adapted physical education sessions on the empathy of female students with overweight. Front. Psychol. 2023, 14, 1170446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazurek, K.; Zmijewski, P.; Krawczyk, K.; Czajkowska, A.; Kęska, A.; Kapuscinski, P.; Mazurek, T. High Intensity Interval and Moderate Continuous Cycle Training in a Physical Education Programme Improves Health-Related Fitness in Young Females. Biol. Sport 2016, 33, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drigny, J.; Gremeaux, V.; Dupuy, O.; Gayda, M.; Bherer, L.; Juneau, M.; Nigam, A. Effect of Interval Training on Cognitive Functioning and Cerebral Oxygenation in Obese Patients: A Pilot Study. J. Rehabil. 2014, 46, 1050–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fillon, A.; Miguet, M.; O’Malley, G.; Mathieu, M.E.; Masurier, J.; Julian, V.; Cardenoux, C.; Pereira, B.; Rey, O.; Duclos, M.; et al. Is the SPARTACUS 15-15 test an accurate proxy for the assessment and tracking of maximal aerobic capacities in adolescents with obesity? J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2020, 32, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ho, S.S.; Dhaliwal, S.S.; Hills, A.P.; Pal, S. The effect of 12 weeks of aerobic, resistance or combination exercise training on cardiovascular risk factors in the overweight and obese in a randomized trial. BMC Public Health. 2012, 12, 704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racil, G.; Ben Ounis, O.; Hammouda, O.; Kallel, A.; Zouhal, H.; Chamari, K.; Amri, M. Effects of high vs. moderate exercise intensity during interval training on lipids and adiponectin levels in obese young females. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2013, 113, 2531–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouerghi, N.; Khammassi, M.; Boukorraa, S.; Feki, M.; Kaabachi, N.; Bouassida, A. Effects of a high-intensity intermittent training program on aerobic capacity and lipid profile in trained subjects. Open Access J. Sports Med. 2014, 5, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigal, R.J.; Alberga, A.S.; Goldfield, G.S.; Prud’homme, D.; Hadjiyannakis, S.; Gougeon, R.; Phillips, P.; Tulloch, H.; Malcolm, J.; Doucette, S.; et al. Effects of aerobic training, resistance training, or both on percentage body fat and cardiometabolic risk markers in obese adolescents: The healthy eating aerobic and resistance training in youth randomized clinical trial. JAMA Pediatr. 2014, 168, 1006–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, P.W.; Wong, D.P.; Ngo, J.K.; Liang, Y.; Kim, C.G.; Kim, H.S. Effects of high-intensity intermittent running exercise in overweight children. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2015, 15, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouerghi, N.; Fradj, M.K.B.; Bezrati, I.; Khammassi, M.; Feki, M.; Kaabachi, N.; Bouassida, A. Effects of high-intensity interval training on body composition, aerobic and anaerobic performance and plasma lipids in overweight/obese and normal-weight young men. Biol. Sport. 2017, 34, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robineau, J.; Lacome, M.; Piscione, J.; Bigard, X.; Babault, N. Concurrent training in rugby sevens: Effects of high-intensity interval exercises. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2017, 12, 336–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Week | Main Session Objective | CONT Group (Traditional Program) | ADAPT Group (Adapted Program) | ADAPT + VID Group (Adapted Program with Educational Videos) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Week 1 | Discovery and familiarization | Introduction to basketball rules and basic techniques. | Same content, but alternating between low-intensity drills and fun, playful activities. | Same as ADAPT group, with prior viewing of a video summarizing rules and fundamental techniques. |
| Weeks 2–3 | Development of individual skills | Standard 1-on-1 offensive and defensive drills. | Defender limited to one hand; may only engage after the attacker initiates movement. | Same as ADAPT group, preceded by an instructional video on passing, dribbling, and shooting. |
| Weeks 4–5 | Reinforcement of team play | 3-on-3 drills with standard offensive and defensive roles. | Drills modified to 3 attackers vs. 2 defenders (offensive advantage). | Same as ADAPT group, with a demonstrative video showing principles of attacking play in a 3v2 setup. |
| Weeks 6–8 | Application in real game situations | 5-on-5 matches with free substitutions based on students’ preferences. | 5-on-5 matches with mandatory substitutions at each offensive transition. | Same as ADAPT group, with a summary video highlighting collective game principles in match situations. |
| Motivational Dimensions | ADAPT + VID | ADAPT | CONTROL | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T0 | T1 | T0 | T1 | T0 | T1 | |
| Intrinsic Motivation | 3.58 ± 1.43 | 5.26 ± 1.41 **# | 3.56 ± 1.29 | 4.61 ± 1.33 * | 3.44 ± 0.98 | 3.33 ± 1.46 |
| Identified Regulation | 3.84 ± 1.17 | 4.00 ± 1.45 | 3.50 ± 1.29 | 3.94 ± 1.16 | 3.78 ± 1 | 3.83 ± 1.20 |
| External Regulation | 3.79 ± 1.32 | 3.89 ± 1.20 | 3.83 ± 0.99 | 3.56 ± 1.15 | 3.67 ± 1.28 | 3.72 ± 1.07 |
| Amotivation | 4.11 ± 1.20 | 2.84 ± 1.07 **# | 4.17 ± 0.99 | 3.56 ± 1.29 | 3.89 ± 1.02 | 4.39 ± 1.29 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Slimi, O.; Souissi, M.A.; Marsigliante, S.; Badicu, G.; Vveinhardt, J.; Muscella, A. Adapted Basketball Training Improves Fitness and Motivation in Adolescents with Moderate Obesity: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Children 2025, 12, 1262. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12091262
Slimi O, Souissi MA, Marsigliante S, Badicu G, Vveinhardt J, Muscella A. Adapted Basketball Training Improves Fitness and Motivation in Adolescents with Moderate Obesity: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Children. 2025; 12(9):1262. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12091262
Chicago/Turabian StyleSlimi, Oumayma, Mohamed Abdelkader Souissi, Santo Marsigliante, Georgian Badicu, Jolita Vveinhardt, and Antonella Muscella. 2025. "Adapted Basketball Training Improves Fitness and Motivation in Adolescents with Moderate Obesity: A Randomized Controlled Trial" Children 12, no. 9: 1262. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12091262
APA StyleSlimi, O., Souissi, M. A., Marsigliante, S., Badicu, G., Vveinhardt, J., & Muscella, A. (2025). Adapted Basketball Training Improves Fitness and Motivation in Adolescents with Moderate Obesity: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Children, 12(9), 1262. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12091262









