Perinatal and Childhood Risk Factors of Adverse Early Childhood Developmental Outcomes: A Systematic Review Using a Socioecological Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.2. Search Strategy and Data Extraction
2.3. Quality or Risk of Bias Assessment
2.4. Data Synthesis
3. Results
3.1. Study Selection and Characteristics
3.2. Adverse Early Childhood Developmental Outcomes
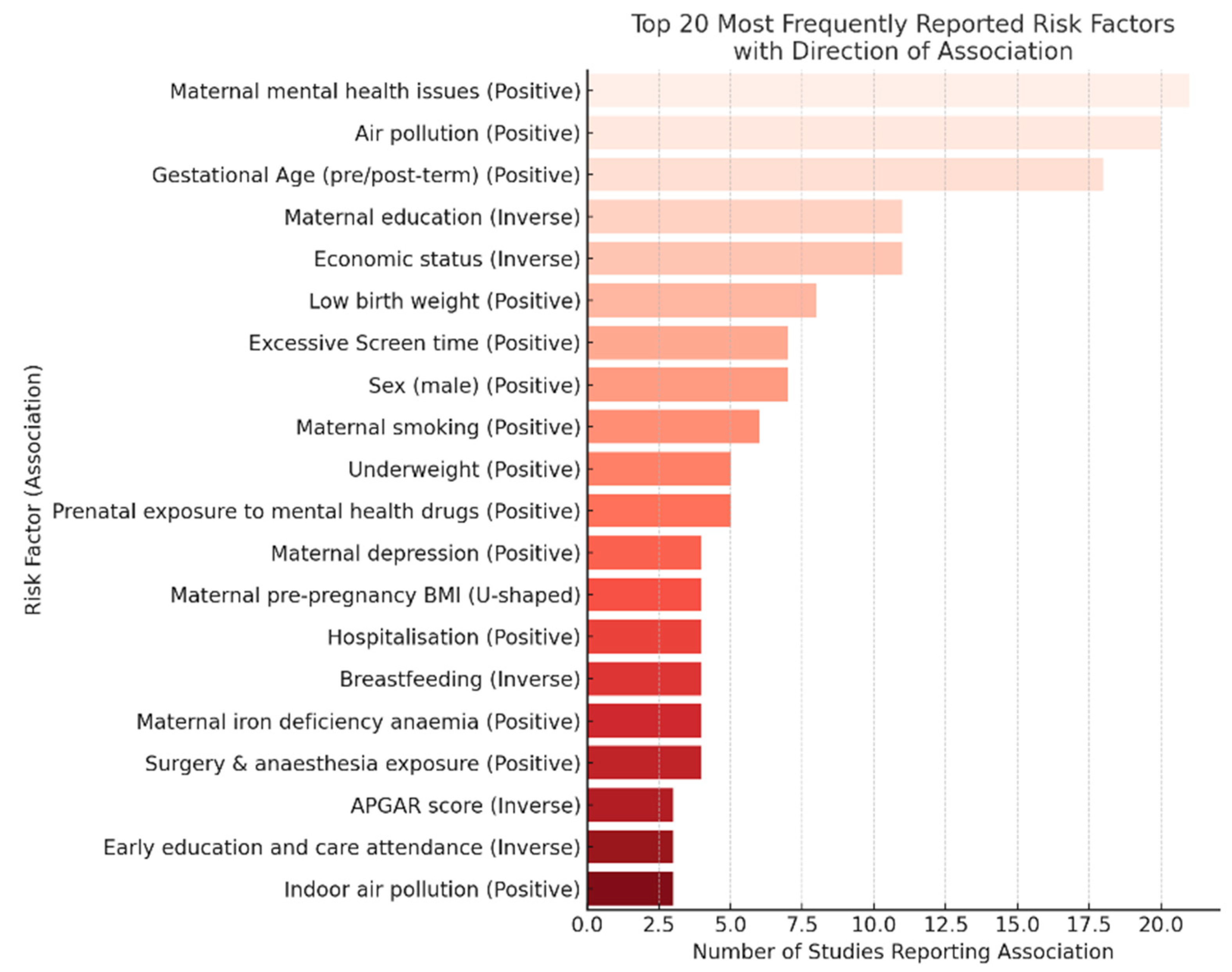
3.3. Risk Factors of Adverse Early Childhood Developmental Outcomes
3.3.1. Individual-Level Risk Factors
3.3.2. Interpersonal and Household-Level Risk Factors
3.3.3. Community/Organisational-Level Factors
3.3.4. Societal, Policy/Program-Level Factors
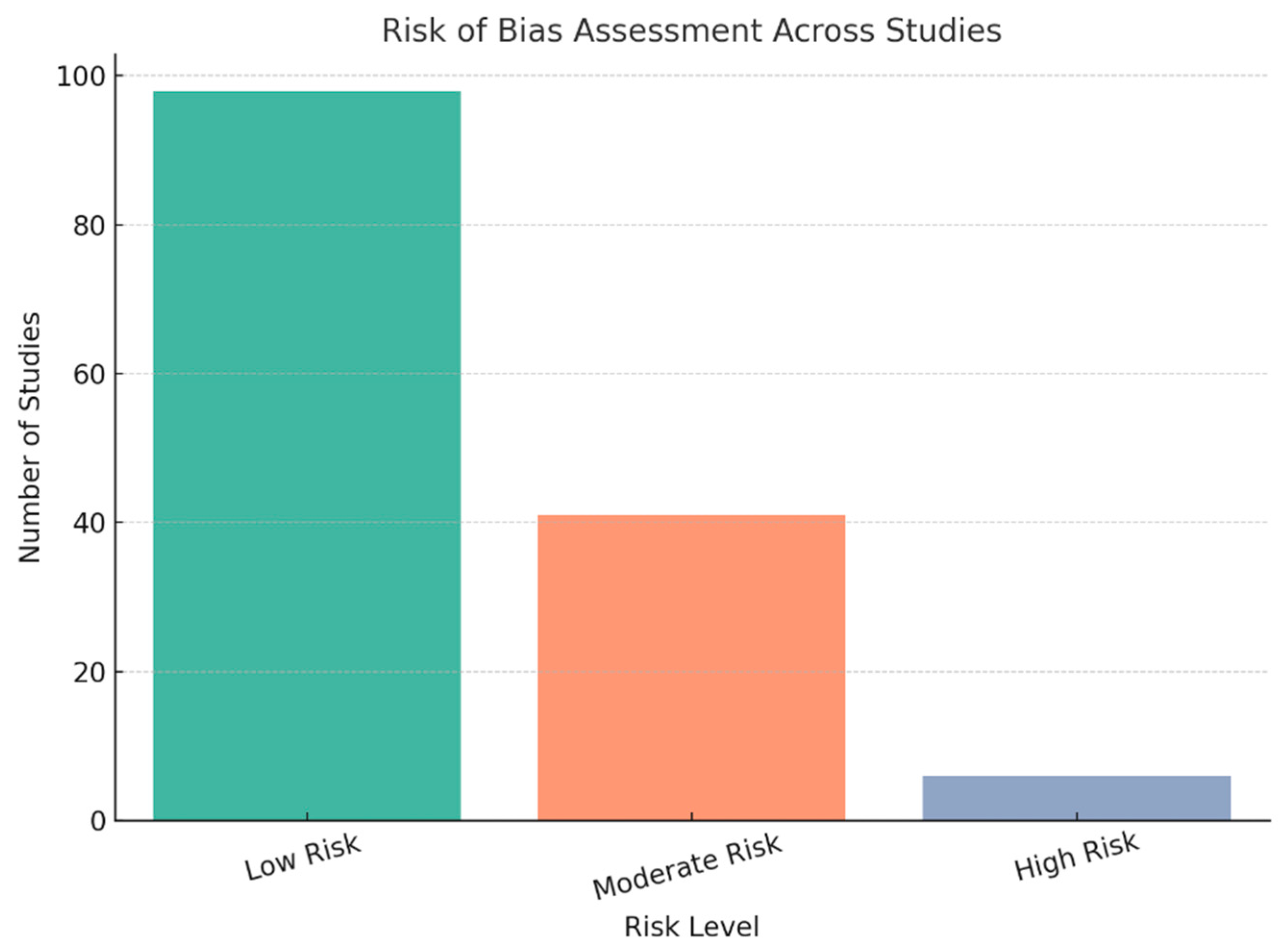
3.4. Quality or Risk of Bias Assessment
4. Discussion
4.1. Research and Policy Implications
4.2. Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Black, M.M.; Walker, S.P.; Fernald, L.C.H.; Andersen, C.T.; DiGirolamo, A.M.; Lu, C.; McCoy, D.C.; Fink, G.; Shawar, Y.R.; Shiffman, J.; et al. Early childhood development coming of age: Science through the life course. Lancet 2017, 389, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Early Child Development: A Powerful Equalizer; Final Report for the World Health Organization’s Commission on the Social Determinants of Health; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Early Childhood Development and Disability; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Sartika, R.; Ismail, D.; Rosida, L. Factors that affect cognitive and mental emotional development of children: A scoping review. J. Health Technol. Assess. Midwifery 2021, 2620, 5653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panjeti-Madan, V.N.; Ranganathan, P. Impact of screen time on children’s development: Cognitive, language, physical, and social and emotional domains. Multimodal Technol. Interact. 2023, 7, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-H.; Lin, K.-L.; Chen, C.-L.; Chiou, H.; Chang, C.-J.; Chen, P.-H.; Wu, C.-Y.; Lin, K.-C. Sleep problems during early and late infancy: Diverse impacts on child development trajectories across multiple domains. Sleep Med. 2024, 115, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, A.J.; Temple, J.A.; Robertson, D.L.; Mann, E.A. Long-term effects of an early childhood intervention on educational achievement and juvenile arrest: A 15-year follow-up of low-income children in public schools. JAMA 2001, 285, 2339–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coates, S.; Gaensbauer, T.J. Event trauma in early childhood: Symptoms, assessment, intervention. Child Adolesc. Psychiatr. Clin. N. Am. 2009, 18, 611–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crockett, L.K.; Ruth, C.A.; Heaman, M.I.; Brownell, M.D. Education Outcomes of Children Born Late Preterm: A Retrospective Whole-Population Cohort Study. Matern Child Health J. 2022, 26, 1126–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Angiulli, A.; Warburton, W.; Dahinten, S.; Hertzman, C. Population-level associations between preschool vulnerability and grade-four basic skills. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinkman, S.A.; Gialamas, A.; Rahman, A.; Mittinty, M.N.; Gregory, T.A.; Silburn, S.; Goldfeld, S.; Zubrick, S.R.; Carr, V.; Janus, M.; et al. Jurisdictional, socioeconomic and gender inequalities in child health and development: Analysis of a national census of 5-year-olds in Australia. BMJ Open 2012, 2, e001075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, S.; Yeung, E.; Bell, E.; Insaf, T.; Ghassabian, A.; Bell, G.; Muscatiello, N.; Mendola, P. Prenatal and early life exposures to ambient air pollution and development. Environ. Res. 2019, 174, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ialongo, N.S.; Domitrovich, C.; Embry, D.; Greenberg, M.; Lawson, A.; Becker, K.D.; Bradshaw, C. A randomized controlled trial of the combination of two school-based universal preventive interventions. Dev. Psychol. 2019, 55, 1313–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duko, B.; Gebremedhin, A.T.; Tessema, G.A.; Dunne, J.; Alati, R.; Pereira, G. The effects of pre-eclampsia on social and emotional developmental vulnerability in children at age five in Western Australia: A population data linkage study. J. Affect. Disorders 2024, 352, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duko, B.; Gebremedhin, A.T.; Tessema, G.A.; Pereira, G. Influence of preterm birth on the association between gestational diabetes mellitus and childhood developmental vulnerability: A causal mediation analysis. World J. Pediatr. 2023, 20, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abubakar, A.; Holding, P.; Van de Vijver, F.J.R.; Newton, C.; Van Baar, A. Children at risk for developmental delay can be recognised by stunting, being underweight, ill health, little maternal schooling or high gravidity. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2010, 51, 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collier, L.R.; Gregory, T.; Harman-Smith, Y.; Gialamas, A.; Brinkman, S.A. Inequalities in child development at school entry: A repeated cross-sectional analysis of the Australian Early Development Census 2009–2018. Lancet Reg. Health–West. Pac. 2020, 4, 100057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batchelor, J.M.; Thomas, K.S.; Akram, P.; Azad, J.; Bewley, A.; Chalmers, J.R.; Cheung, S.T.; Duley, L.; Eleftheriadou, V.; Ellis, R.; et al. Home-based narrowband UVB, topical corticosteroid or combination for children and adults with vitiligo: HI-Light Vitiligo three-arm RCT. Health Technol. Assess 2020, 24, 1–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atalell, K.A.; Pereira, G.; Duko, B.; Nyadanu, S.D.; O’donnell, M.; Tessema, G.A. Prenatal and early childhood exposure to biothermal stress and developmental vulnerability at school entry in Western Australia: A population-based cohort study. Environ. Int. 2025, 202, 109642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atalell, K.A.; Pereira, G.; Duko, B.; Nyadanu, S.D.; Skirbekk, V.; Tessema, G.A. Developmental vulnerability in children from culturally and linguistically diverse backgrounds in Western Australia: A population-based study. World J. Pediatr. 2025, 21, 744–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almasri, N.A.; Saleh, M.; Abu-Dahab, S.; Malkawi, S.H.; Nordmark, E. Development of a Cerebral Palsy Follow-up Registry in Jordan (CPUP-Jordan). Child Care Health Dev. 2018, 44, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Taking Action with Social Determinants of Health Frameworks and Tools; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Boonzaaijer, M.; Suir, I.; Mollema, J.; Nuysink, J.; Volman, M.; Jongmans, M. Factors associated with gross motor development from birth to independent walking: A systematic review of longitudinal research. Child Care Health Dev. 2021, 47, 525–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cage, J.; Kobulsky, J.M.; McKinney, S.J.; Holmes, M.R.; Berg, K.A.; Bender, A.E.; Kemmerer, A. The Effect of Exposure to Intimate Partner Violence on Children’s Academic Functioning: A Systematic Review of the Literature. J. Fam. Violence 2022, 37, 1337–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho Ferreira, R.D.; Alves, C.R.L.; Guimaraes, M.A.P.; Menezes, K.K.P.D.; Castro Magalhaes, L.D. Effects of early interventions focused on the family in the development of children born preterm and/or at social risk: A meta-analysis. J. Pediatr. 2020, 96, 20–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, E.; Leong, P.; Malouf, R.; Quigley, M.A. Long-term cognitive and school outcomes of late-preterm and early-term births: A systematic review. Child Care Health Dev. 2016, 42, 297–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brain Development Cooperative Group. Total and regional brain volumes in a population-based normative sample from 4 to 18 Years: The NIH MRI Study of Normal Brain Development. Cereb. Cortex 2012, 22, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moola, S.; Munn, Z.; Tufanaru, C.; Aromataris, E.; Sears, K.; Sfetcu, R.; Currie, M.; Lisy, K.; Qureshi, R.; Mattis, P.; et al. Chapter 7: Systematic Reviews of Etiology and Risk; JBI Manual for Evidence Synthesis; Joanna Briggs Institute: Adelaide, Australia, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Munn, Z.; Moola, S.; Lisy, K.; Riitano, D.; Tufanaru, C. Methodological guidance for systematic reviews of observational epidemiological studies reporting prevalence and cumulative incidence data. Int. J. Evid.-Based Healthc. 2015, 13, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aboud, F.E.; Bougma, K.; Lemma, T.; Marquis, G.S. Evaluation of the effects of iodized salt on the mental development of preschool-aged children: A cluster randomized trial in northern Ethiopia. Matern Child Nutr. 2017, 13, e12322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhamrait, G.K.; Christian, H.; O’Donnell, M.; Pereira, G. Gestational age and child development at school entry. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atalell, K.A.; Pereira, G.; Duko, B.; Nyadanu, S.D.; Tessema, G.A. Perinatal and early life risk factors of adverse early childhood developmental outcomes: Protocol for systematic review using socioecological model. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0311500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotschall, T. EndNote 20 desktop version. J. Med. Libr. Assoc. JMLA 2021, 109, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouzzani, M.; Hammady, H.; Fedorowicz, Z.; Elmagarmid, A. Rayyan—A web and mobile app for systematic reviews. Syst. Rev. 2016, 5, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buccheri, R.K.; Sharifi, C.O. Critical Appraisal Tools and Reporting Guidelines for Evidence-Based Practice. Worldviews Evid.-Based Nurs. 2017, 14, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porritt, K.P.; Gomersall, J.J.; Lockwood, C.P. JBI’s Systematic Reviews: Study Selection and Critical Appraisal. Am. J. Nurs. 2014, 114, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyadanu, S.D.; Dunne, J.; Tessema, G.A.; Mullins, B.; Kumi-Boateng, B.; Lee Bell, M.; Duko, B.; Pereira, G. Prenatal exposure to ambient air pollution and adverse birth outcomes: An umbrella review of 36 systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 306, 119465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schölmerich, V.L.; Kawachi, I. Translating the socio-ecological perspective into multilevel interventions: Gaps between theory and practice. Health Educ. Behav. 2016, 43, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lane, H.; Porter, K.; Estabrooks, P.; Zoellner, J. A systematic review to assess sugar-sweetened beverage interventions for children and adolescents across the socioecological model. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2016, 116, 1295–1307.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonard, D.; Buettner, P.; Thompson, F.; Makrides, M.; McDermott, R. Early childhood anaemia more than doubles the risk of developmental vulnerability at school-age among Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander children of remote Far North Queensland: Findings of a retrospective cohort study. Nutr. Diet. 2020, 77, 298–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.N.; Babu, M.R.; Chowdhury, M.A.B.; Rahman, M.M.; Hasan, N.; Kabir, R.; Uddin, J. Early childhood developmental status and its associated factors in Bangladesh: A comparison of two consecutive nationally representative surveys. BMC Public Health 2023, 23, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozkan, M.; Senel, S.; Arslan, E.A.; Karacan, C.D. The socioeconomic and biological risk factors for developmental delay in early childhood. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2012, 171, 1815–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rana, J.; Luna-Gutiérrez, P.; Haque, S.E.; Nazif-Muñoz, J.I.; Mitra, D.K.; Oulhote, Y. Associations between household air pollution and early child development among children aged 36–59 months in Bangladesh. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 2022, 76, 667–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razaz, N.; Cnattingius, S.; Persson, M.; Tedroff, K.; Lisonkova, S.; Joseph, K. One-minute and five-minute Apgar scores and child developmental health at 5 years of age: A population-based cohort study in British Columbia, Canada. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e027655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, M.L.; Perry, K.E.; Thapa, B.; Adhikari, R.P.; Weissman, A. Malnutrition matters: Association of stunting and underweight with early childhood development indicators in Nepal. Matern. Child Nutr. 2022, 18, e13321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strobel, N.A.; Richardson, A.; Shepherd, C.C.J.; McAuley, K.E.; Marriott, R.; Edmond, K.M.; McAullay, D.R. Modelling factors for aboriginal and Torres strait islander child neurodevelopment outcomes: A latent class analysis. Paediatr. Perinat. Epidemiol. 2020, 34, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wall-Wieler, E.; Roos, L.L.; Gotlib, I.H. Maternal depression in early childhood and developmental vulnerability at school entry. Pediatrics 2020, 146, e20200794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, S.; Duku, E.; Brownell, M.; Enns, J.; Forer, B.; Guhn, M.; Minh, A.; Muhajarine, N.; Janus, M. Sex differences in the socioeconomic gradient of children’s early development. SSM-Popul. Health 2020, 10, 100512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukanya, G.; Prabha, S.; Samsuzzaman, M.; Niladri, B.; Das, D.K. Developmental delay among children under two years of age in slums of Burdwan municipality: A cross.sectional study. J. Fam. Med. Prim. Care 2021, 10, 1945–1949. [Google Scholar]
- Kerai, S.; Almas, A.; Guhn, M.; Forer, B.; Oberle, E. Screen time and developmental health: Results from an early childhood study in Canada. BMC Public Health 2022, 22, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curtin, M.; Madden, J.; Staines, A.; Perry, I.J. Determinants of vulnerability in early childhood development in Ireland: A cross-sectional study. BMJ Open 2013, 3, e002387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, C.; Iwai-Shimada, M.; Nakayama, S.F.; Isobe, T.; Kobayashi, Y.; Tatsuta, N.; Taniguchi, Y.; Sekiyama, M.; Michikawa, T.; Yamazaki, S.; et al. Association of prenatal exposure to cadmium with neurodevelopment in children at 2 years of age: The Japan Environment and Children’s Study. Environ. Int. 2021, 156, 106762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Moura, D.R.; Costa, J.C.; Santos, I.S.; Barros, A.J.D.; Matijasevich, A.; Halpern, R.; Dumith, S.; Karam, S.; Barros, F.C. Risk factors for suspected developmental delay at age 2 years in a Brazilian birth cohort. Paediatr. Perinat. Epidemiol. 2010, 24, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razaz, N.; Boyce, W.T.; Brownell, M.; Jutte, D.; Tremlett, H.; Marrie, R.A.; Joseph, K.S. Five-minute Apgar score as a marker for developmental vulnerability at 5 years of age. Arch. Dis. Child.-Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2016, 101, F114–F120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halpern, R.; Barros, A.J.; Matijasevich, A.; Santos, I.S.; Victora, C.G.; Barros, F.C. Developmental status at age 12 months according to birth weight and family income: A comparison of two Brazilian birth cohorts. Cad Saude Publica 2008, 24, S444–S450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, H.A.L.; Sudfeld, C.R.; Leite, A.J.M.; Machado, M.M.T.; Rocha, S.G.M.O.; Campos, J.S.; Silva, A.C.E.; Correia, L.L. Maternal and neonatal factors associated with child development in Ceara, Brazil: A population-based study. BMC Pediatr. 2021, 21, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Hao, M.; Han, W.; Yamauchi, T. Factors associated with nutritional status and motor development among young children. Nurs. Health Sci. 2019, 21, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smithers, L.G.; Searle, A.K.; Chittleborough, C.R.; Scheil, W.; Brinkman, S.A.; Lynch, J.W. A whole-of-population study of term and post-term gestational age at birth and children’s development. BJOG-Int. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2015, 122, 1303–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballantyne, M.; Benzies, K.M.; McDonald, S.; Magill-Evans, J.; Tough, S. Risk of developmental delay: Comparison of late preterm and full term Canadian infants at age 12 months. Early Hum. Dev. 2016, 101, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gleason, J.L.; Gilman, S.E.; Sundaram, R.; Yeung, E.; Putnick, D.L.; Vafai, Y.; Saha, A.; Grantz, K.L. Gestational age at term delivery and children’s neurocognitive development. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2021, 50, 1814–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanly, M.; Falster, K.; Chambers, G.; Lynch, J.; Banks, E.; Homaira, N.; Brownell, M.; Eades, S.; Jorm, L. Gestational Age and Child Development at Age Five in a Population-Based Cohort of Australian Aboriginal and Non-Aboriginal Children. Paediatr. Perinat. Epidemiol. 2018, 32, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, J.; Barnett, A.L.; Lin, Y.; Guan, H.Y.; Sun, Y.J.; Williams, G.J.; Fu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Du, W. Association of Gestational Age at Birth With Subsequent Neurodevelopment in Early Childhood: A National Retrospective Cohort Study in China. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 10, 860192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junge, C.; Garthus-Niegel, S.; Slinning, K.; Polte, C.; Simonsen, T.B.; Eberhard-Gran, M. The Impact of Perinatal Depression on Children’s Social-Emotional Development: A Longitudinal Study. Matern. Child Health J. 2017, 21, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerstjens, J.M.; de Winter, A.F.; Bocca-Tjeertes, I.F.; Ten Vergert, E.M.; Reijneveld, S.A.; Bos, A.F. Developmental delay in moderately preterm-born children at school entry. J. Pediatr. 2011, 159, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, J.L.; Drews-Botsch, C.; Sales, J.M.; Flers, W.D.; Kramer, M.R. Describing the Shape of the Relationship Between Gestational Age at Birth and Cognitive Development in a Nationally Representative U.S. Birth Cohort. Paediatr. Perinat. Epidemiol. 2016, 30, 571–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sansavini, A.; Savini, S.; Guarini, A.; Broccoli, S.; Alessroni, R.; Faldella, G. The effect of gestational age on developmental outcomes: A longitudinal study in the first 2 years of life. Child Care Health Dev. 2011, 37, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, A.L.; Vollenhoven, B.J.; Hiscock, R.J.; Stern, C.J.; Walker, S.P.; Cheong, J.L.Y.; Quach, J.L.; Hastie, R.; Wilkinson, D.; McBain, J.; et al. School-age outcomes among IVF-conceived children: A population-wide cohort study. PLoS Med. 2023, 20, e1004148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindquist, A.; Hastie, R.; Kennedy, A.; Gurrin, L.; Middleton, A.; Quach, J.; Cheong, J.; Walker, S.P.; Hiscock, R.; Tong, S. Developmental outcomes for children after elective birth at 39 weeks’ gestation. JAMA Pediatr. 2022, 176, 654–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, M.J.; Kariuki, M.; Dean, K.; Laurens, K.R.; Tzoumakis, S.; Harris, F.; Carr, V.J. Childhood developmental vulnerabilities associated with early life exposure to infectious and noninfectious diseases and maternal mental illness. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry Allied Discip. 2018, 59, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kariuki, M.; Raudino, A.; Green, M.J.; Laurens, K.R.; Dean, K.; Brinkman, S.A.; Lenroot, R.K.; Liu, E.; Harris, F.; Luo, L.; et al. Hospital admission for infection during early childhood influences developmental vulnerabilities at age 5 years. J. Paediatr. Child Health 2016, 52, 882–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fardell, J.E.; Hu, N.; Wakefield, C.E.; Marshall, G.; Bell, J.; Lingam, R.; Nassar, N. Impact of Hospitalizations due to Chronic Health Conditions on Early Child Development. J. Pediatr. Psychol. 2023, 48, 799–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, M.F.; Bayliss, D.M.; Glauert, R.; Harrison, A.; Ohan, J.L. Chronic illness and developmental vulnerability at school entry. Pediatrics 2016, 137, e20152475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janus, M.; Reid-Westoby, C.; Lee, C.; Brownell, M.; Maguire, J.L. Association between severe unaddressed dental needs and developmental health at school entry in Canada: A cross-sectional study. BMC Pediatr. 2019, 19, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, A.; Šarkić, B.; Enticott, J.C.; Richardson, Z.; Buck, K. Developmental vulnerability of Australian school-entry children with hearing loss. Aust. J. Prim. Health 2020, 26, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, J.N.; Roder, D.; Turnbull, D.; Hunkin, H. The impact of cancer on early childhood development: A linked data study. J. Pediatr. Psychol. 2021, 46, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohde, J.F.; Goyal, N.K.; Slovin, S.R.; Hossain, J.; Pachter, L.M.; Di Guglielmo, M.D. Association of positional plagiocephaly and developmental delay within a primary care network. J. Dev. Behav. Pediatr. 2021, 42, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, M.R.; Brownell, M.; Chateau, D.G.; Dragan, R.D.; Burchill, C.; Fransoo, R.R. Neurodevelopmental Assessment in Kindergarten in Children Exposed to General Anesthesia before the Age of 4 Years. Anesthesiology 2016, 125, 667–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Leary, J.D.; Janus, M.; Duku, E.; Wijeysundera, D.N.; To, T.; Li, P.; Maynes, J.T.; Faraoni, D.; Crawford, M.W. Influence of Surgical Procedures and General Anesthesia on Child Development Before Primary School Entry Among Matched Sibling Pairs. JAMA Pediatr 2019, 173, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Leary, J.D.; Janus, M.; Duku, E.; Wijeysundera, D.N.; To, T.; Li, P.; Maynes, J.T.; Crawford, M.M.W. A population-based study evaluating the association between surgery in early life and child development at primary school entry. Anesthesiology 2016, 125, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flick, R.P.; Katusic, S.K.; Colligan, R.C.; Wilder, R.T.; Voigt, R.G.; Olson, M.D.; Sprung, J.; Weaver, A.L.; Schroeder, D.R.; Warner, D.O. Cognitive and behavioral outcomes after early exposure to anesthesia and surgery. Pediatrics 2011, 128, e1053–e1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roux, S.M.L.; Donald, K.A.; Brittain, K.; Phillips, T.K.; Zerbe, A.; Nguyen, K.K.; Andrea, S.; Max, K.; Elaine, J.A.; Landon, M. Neurodevelopment of breastfed HIV-exposed uninfected and HIV-unexposed children in South Africa. AIDS 2018, 32, 1781–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Loo, K.; Yang, H.; Wang, Q.; Duan, R.; Xiao, X.; Song, X.; Yang, S.; et al. Neurodevelopmental outcomes in young children born to HIV-positive mothers in rural Yunnan, China. Pediatr. Int. 2018, 60, 618–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhury, S.; Mayondi, G.K.; Williams, P.L.; Leidner, J.; Shapiro, R.; Diseko, M.; Ajibola, G.; Holding, P.; Tepper, V.; Makhema, J.; et al. In-utero exposure to antiretrovirals and neurodevelopment among HIV-exposed-uninfected children in Botswana. AIDS 2018, 32, 1173–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, R.; Shi, Y.; Zhou, H.; Yue, A.; Zhang, L.; Sylvia, S.; Medina, A.; Rozelle, S. Micronutrient deficiencies and developmental delays among infants: Evidence from a cross-sectional survey in rural China. BMJ Open 2015, 5, e008400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, S.M.; Hannon, G.; Khashan, A.S.; Hourihane, J.O.; Kenny, L.C.; Kiely, M.; Murray, D.M. Thin-for-gestational age infants are at increased risk of neurodevelopmental delay at 2 years. Arch. Dis. Child Fetal. Neonatal. Ed. 2017, 102, F197–F202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, A.; Scalzi, D.; Lynch, J.; Smithers, L.G. Do thin, overweight and obese children have poorer development than their healthy-weight peers at the start of school? Findings from a South Australian data linkage study. Early Child. Res. Q. 2016, 35, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Hu, J.; Yang, L.; Gao, M.; Li, L.; Ding, N.; Ma, Y.; Wen, D. Bidirectional association of neurodevelopment with growth: A prospective cohort study. BMC Pediatr. 2021, 21, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allel, K.; Abou Jaoude, G.; Poupakis, S.; Batura, N.; Skordis, J.; Haghparast-Bidgoli, H. Exploring the Associations between Early Childhood Development Outcomes and Ecological Country-Level Factors across Low- and Middle-Income Countries. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pokharel, A.; Webb, P.; Miller, L.C.; Zaharia, S.; Shrestha, R.; Davis, D.; Trevino, J.A.; Baral, K.P.; Paudel, K.; Ghosh, S. Relationship between Animal Sourced Food Consumption and Early Childhood Development Outcomes. Nutrients 2023, 15, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utami, N.H.; ayani Sekartini, R.; Kolopaking, R.; Besral Khusun, H. Cognitive performance of 4 to 6-year-old children: A longitudinal study. Paediatr. Indones. 2023, 63, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eickmann, S.H.; de Lira, P.I.; Lima Mde, C.; Coutinho, S.B.; Teixeira Mde, L.; Ashworth, A. Breast feeding and mental and motor development at 12 months in a low-income population in northeast Brazil. Paediatr. Perinat. Epidemiol. 2007, 21, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jedrychowski, W.; Perera, F.; Jankowski, J.; Butscher, M.; Mroz, E.; Flak, E.; Kaim, I.; Lisowska-Miszczyk, I.; Skarupa, A.; Sowa, A. Effect of exclusive breastfeeding on the development of children’s cognitive function in the Krakow prospective birth cohort study. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2012, 171, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallenborn, J.T.; Levine, G.A.; Carreira dos Santos, A.; Grisi, S.; Ra Brentani, A.; Fink, G. Breastfeeding, Physical Growth, and Cognitive Development. Pediatrics 2021, 147, e2020008029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.Q.; Wang, Y.P.; Zou, S.Y.; Mi, X.Y.; Kc, A.; Zhou, H. Association of iron supplementation and deworming with early childhood development: Analysis of Demographic and Health Surveys in ten low- and middle-income countries. Eur. J. Nutr. 2021, 60, 3119–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leao, O.A.D.; Bertoldi, A.D.; Domingues, M.R.; Murray, J.; Santos, I.S.; Barros, A.J.D.; Matijasevich, A.; Mielke, G.I. Cross-sectional and prospective associations between screen time and childhood neurodevelopment in two Brazilian cohorts born 11 years apart. Child Care Health Dev. 2023, 5, e13165. [Google Scholar]
- Rithipukdee, N.; Kusol, K. Factors Associated with the Suspected Delay in the Language Development of Early Childhood in Southern Thailand. Children 2022, 9, 662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha, H.A.L.; Correia, L.L.; Leite, A.M.; Machado, M.M.T.; Lindsay, A.C.; Rocha, S.G.M.O.; Campos, J.S.; Silva, A.C.E.; Sudfeld, C.R. Screen time and early childhood development in Ceara, Brazil: A population-based study. BMC Public Health 2021, 21, 2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varadarajan, S.; Venguidesvarane, A.G.; Ramaswamy, K.N.; Rajamohan, M.; Krupa, M.; Christadoss, S.B.W. Prevalence of excessive screen time and its association with developmental delay in children aged <5 years: A population-based cross-sectional study in India. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0254102. [Google Scholar]
- Demirci, A.; Kartal, M. The prevalence of developmental delay among children aged 3-60 months in Izmir, Turkey. Child Care Health Dev. 2016, 42, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falster, K.; Hanly, M.; Banks, E.; Lynch, J.; Chambers, G.; Brownell, M.; Eades, S.; Jorm, L.; Myers, J.E. Maternal age and offspring developmental vulnerability at age five: A population-based cohort study of Australian children. PLoS Med. 2018, 15, e1002558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, X.N.; Sun, X.R.; Liu, Q.L.; Zha, S.W.; Chen, Y.H.; Mao, C.; Xu, X. Prenatal and neonatal risk factors associated with children’s developmental status at ages 4–7: Lessons from the Jiangsu China birth defects prevention cohort. Child Care Health Dev. 2015, 41, 712–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno-Giménez, A.; Campos-Berga, L.; Nowak, A.; Sahuquillo-Leal, R.; D’Ocon, A.; Hervás, D.; Navalón, P.; Vento, M.; García-Blanco, A. Impact of maternal age on infants’ emotional regulation and psychomotor development. Psychol. Med. 2022, 52, 3708–3719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syrengelas, D.; Kalampoki, V.; Kleisiouni, P.; Konstantinou, D.; Siahanidou, T. Gross motor development in full-term Greek infants assessed by the Alberta Infant Motor Scale: Reference values and socioeconomic impact. Early Hum. Dev. 2014, 90, 353–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, C.L.; Christensen, D.; Stafford, J.; Venn, A.; Preen, D.; Zubrick, S.R. Associations between clusters of early life risk factors and developmental vulnerability at age 5: A retrospective cohort study using population-wide linkage of administrative data in Tasmania, Australia. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e033795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, C.C.; Riggs, J.; Guyon-Harris, K.; Harrison, L.; Huth-Bocks, A. Effects of Intimate Partner Violence and Home Environment on Child Language Development in the First 3 Years of Life. J. Dev. Behav. Pediatr. JDBP 2019, 40, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trumpff, C.; De Schepper, J.; Erfaeillie, J.; Vercruysse, N.; Van Oyen, H.; Moreno-Reyes, R.; Tafforeau, J.; Vanderpas, J.; Vandevijvere, S. Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH) Concentration at Birth in Belgian Neonates and Cognitive Development at Preschool Age. Nutrients 2015, 7, 9018–9032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, T.A.; Kievit, R.A.; Astle, D.E. Maternal mental health mediates links between socioeconomic status and child development. Curr. Psychol. 2023, 42, 21967–21978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, M.F.; Glauert, R.; Roos, L.L.; Wall-Wieler, E. Examining the relationship between maternal mental health-related hospital admissions and childhood developmental vulnerability at school entry in Canada and Australia. Bjpsych Open 2023, 9, e29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burger, M.; Einspieler, C.; Niehaus, D.J.; Unger, M.; Jordaan, E.R. Maternal mental health and infant neurodevelopment at 6 months in a low-income South African cohort. Infant Ment. Health J. 2022, 43, 849–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornish, A.M.; McMahon, C.A.; Ungerer, J.A.; Barnett, B.; Kowalenko, N.; Tennant, C. Postnatal depression and infant cognitive and motor development in the second postnatal year: The impact of depression chronicity and infant gender. Infant Behav. Dev. 2005, 28, 407–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deave, T.; Heron, J.; Evans, J.; Emond, A. The impact of maternal depression in pregnancy on early child development. BJOG-Int. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2008, 115, 1043–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González, G.; Moraes, M.; Sosa, C.; Umpierrez, E.; Duarte, M.; Cal, J.; Ghione, A. Maternal postnatal depression and its impact on child neurodevelopment: A cohort study. Rev. Chil. Pediatr.-Chile 2017, 88, 360–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gül, H.; Gül, A.; Kara, K. Maternal depression, anxiety, psychoticism and paranoid ideation have effects on developmental delay types of infants: A study with clinical infant-mother dyads. Arch. Psychiatr. Nurs. 2020, 34, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibanez, G.; Bernard, J.Y.; Rondet, C.; Peyre, H.; Forhan, A.; Kaminski, M.; Saurel-Cubizolles, M.-J.; EDEN mother-child cohort study group. Effects of Antenatal Maternal Depression and Anxiety on Children’s Early Cognitive Development: A Prospective Cohort Study. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keim, S.A.; Daniels, J.L.; Dole, N.; Herring, A.H.; Siega-Riz, A.M.; Scheidt, P.C. A prospective study of maternal anxiety, perceived stress, and depressive symptoms in relation to infant cognitive development. Early Hum. Dev. 2011, 87, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mensah, F.K.; Kiernan, K.E. Parents’ mental health and children’s cognitive and social development: Families in England in the Millennium Cohort Study. Soc. Psychiatry Psychiatr. Epidemiol. 2010, 45, 1023–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neamah, H.H.; Sudfeld, C.; McCoy, D.C.; Fink, G.; Fawzi, W.W.; Masanja, H.; Danaei, G.; Muhihi, A.; Kaaya, S.; Fawzi, M.C.S. Intimate partner violence, depression, and child growth and development. Pediatrics 2018, 142, e20173457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polte, C.; Junge, C.; von Soest, T.; Seidler, A.; Eberhard-Gran, M.; Garthus-Niegel, S. Impact of Maternal Perinatal Anxiety on Social-Emotional Development of 2-Year-Olds, A Prospective Study of Norwegian Mothers and Their Offspring: The Impact of Perinatal Anxiety on Child Development. Matern. Child Health J. 2019, 23, 386–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quevedo, L.; Silva, R.; Godoy, R.; Jansen, K.; Matos, M.; Tavares Pinheiro, K.; Pinheiro, R.T. The impact of maternal post-partum depression on the language development of children at 12 months. Child Care Health Dev. 2012, 38, 420–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramchani, P.; Stein, A.; Evans, J.; O’Connor, T.G.; Team, A.S. Paternal depression in the postnatal period and child development: A prospective population study. Lancet 2005, 365, 2201–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, A.M.; Youssef, G.J.; Teague, S.; Sunderl, M.; Le Bas, G.; Macdonald, J.A.; Mattick, R.P.; Allsop, S.; Elliott, E.J.; Olsson, C.A.; et al. Association of maternal and paternal perinatal depression and anxiety with infant development: A longitudinal study. J. Affect. Disord. 2023, 338, 278–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, R.; Chakraborty, M.; Bhattacharya, K.; Roychoudhury, T.; Mukherjee, S. Impact of perinatal maternal depression on child development. Indian J. Psychiatry 2022, 64, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shuffrey, L.C.; Sania, A.; Brito, N.H.; Potter, M.; Springer, P.; Lucchini, M.; Rayport, Y.K.; Du Plessis, C.; Odendaal, H.J.; Fifer, W.P. Association of maternal depression and anxiety with toddler social-emotional and cognitive development in South Africa: A prospective cohort study. BMJ Open 2022, 12, e058135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith-Nielsen, J.; Lange, T.; Wendelboe, K.I.; von Wowern, R.K.; Væver, M.S. Associations Between Maternal Postpartum Depression, Infant Social Behavior With a Stranger, and Infant Cognitive Development. Infancy 2019, 24, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.D.; Biggs, B.-A.; Tran, T.; Simpson, J.A.; Hanieh, S.; Dwyer, T.; Fisher, J.; Nizami, Q. Impact on infants’ cognitive development of antenatal exposure to iron deficiency disorder and common mental disorders. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urizar, G.G.; Muñoz, R.F., Jr. Role of Maternal Depression on Child Development: A Prospective Analysis from Pregnancy to Early Childhood. Child Psychiatry Hum. Dev. 2022, 53, 502–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, S.; Bishop, S.L.; Ceja, T.; Hanna-Attisha, M.; LeWinn, K. Neurodevelopmental profiles of preschool-age children in Flint, Michigan: A latent profile analysis. J. Neurodev. Disord. 2021, 13, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dean, J.C.S.; Hailey, H.; Moore, S.J.; Lloyd, D.J.; Turnpenny, P.D.; Little, J. Long term health and neurodevelopment in children exposed to antiepileptic drugs before birth. J. Med. Genet. 2002, 39, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handal, M.; Skurtveit, S.; Furu, K.; Hernandez-Diaz, S.; Skovlund, E.; Nystad, W.; Selmer, R. Motor development in children prenatally exposed to selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors: A large population-based pregnancy cohort study. BJOG Int. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2016, 123, 1908–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Veere, C.N.; de Vries, N.K.S.; van Braeckel, K.; Bos, A.F. Intra-uterine exposure to selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), maternal psychopathology, and neurodevelopment at age 2.5 years-Results from the prospective cohort SMOK study. Early Hum. Dev. 2020, 147, 105075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singal, D.; Chateau, D.; Struck, S.; Lee, J.B.; Dahl, M.; Derksen, S.; Katz, L.Y.; Ruth, C.; Hanlon-Dearman, A.; Brownell, M. In utero antidepressants and neurodevelopmental outcomes in kindergarteners. Pediatrics 2020, 145, e20191157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Lu, D.; Xue, L.; Ren, P.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, J. Association between Placental Inflammatory Pathology and Offspring Neurodevelopment at 8 Months and 4 and 7 Years of Age. J. Pediatr. 2020, 225, 132–137.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berglund, S.K.; Torres-Espínola, F.J.; García-Valdés, L.; Segura, M.T.; Martínez-Zaldívar, C.; Padilla, C.; Rueda, R.; García, M.P.; McArdle, H.J.; Campoy, C. The impacts of maternal iron deficiency and being overweight during pregnancy on neurodevelopment of the offspring. Br. J. Nutr. 2017, 118, 533–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smithers, L.G.; Gialamas, A.; Scheil, W.; Brinkman, S.; Lynch, J.W. Anaemia of Pregnancy, Perinatal Outcomes and Children’s Developmental Vulnerability: A Whole-of-Population Study. Paediatr. Perinat. Epidemiol. 2014, 28, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, S.; Lerner, E.; Needlman, R.; Salvator, A.; Singer, L.T. Cocaine, anemia, and neurodevelopmental outcomes in children: A longitudinal study. J. Dev. Behav. Pediatr. 2004, 25, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghassabian, A.; Sundaram, R.; Wylie, A.; Bell, E.; Bello, S.C.; Yeung, E. Maternal medical conditions during pregnancy and gross motor development up to age 24 months in the Upstate KIDS study. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2016, 58, 728–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warshafsky, C.; Pudwell, J.; Walker, M.; Wen, S.W.; Smith, G.N.; Preeclampsia New Emerging, T. Prospective assessment of neurodevelopment in children following a pregnancy complicated by severe pre-eclampsia. BMJ Open 2016, 6, e010884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holst, C.; Jorgensen, S.E.; Wohlfahrt, J.; Nybo Andersen, A.-M.; Melbye, M. Fever during pregnancy and motor development in children: A study within the Danish National Birth Cohort. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2015, 57, 725–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bin, Y.S.; Cistulli, P.A.; Roberts, C.L.; Ford, J.B. Childhood health and educational outcomes associated with maternal sleep apnea: A population record-linkage study. Sleep 2017, 40, zsx158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razaz, N.; Joseph, K.; Boyce, W.T.; Guhn, M.; Forer, B.; Carruthers, R.; Marrie, R.A.; Tremlett, H. Children of chronically ill parents: Relationship between parental multiple sclerosis and childhood developmental health. Mult. Scler. J. 2016, 22, 1452–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motoki, N.; Inaba, Y.; Shibazaki, T.; Misawa, Y.; Ohira, S.; Kanai, M.; Kurita, H.; Tsukahara, T.; Nomiyama, T.; Kamijima, M.; et al. Insufficient maternal gestational weight gain and infant neurodevelopment at 12 months of age: The Japan Environment and Children’s Study. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2022, 181, 921–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.M.; Lu, J.R.; Yan, S.Q.; Tao, F.B.; Huang, K. Maternal Pre-Pregnancy Body Mass Index, Gestational Weight Gain and Children’s Cognitive Development: A Birth Cohort Study. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinkle, S.N.; Schieve, L.A.; Stein, A.D.; Swan, D.W.; Ramakrishnan, U.; Sharma, A.J. Associations between maternal prepregnancy body mass index and child neurodevelopment at 2 years of age. Int. J. Obes. 2012, 36, 1312–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Yu, X.; Keim, S.; Li, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J. Maternal prepregnancy obesity and child neurodevelopment in the Collaborative Perinatal Project. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2014, 43, 783–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widen, E.M.; Nichols, A.R.; Kahn, L.G.; Factor-Litvak, P.; Insel, B.J.; Hoepner, L.; Dube, S.M.; Rauh, V.; Perera, F.; Rundle, A. Prepregnancy obesity is associated with cognitive outcomes in boys in a low-income, multiethnic birth cohort. BMC Pediatr. 2019, 19, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, M.; Molino, A.R.; Ribeiro, M.V.; Mariano, M.; Martins, S.S.; Caetano, S.C.; Surkan, P.J. Maternal Pregnancy Intention and Developmental Outcomes in Brazilian Preschool-Aged Children. J. Dev. Behav. Pediatr. JDBP 2021, 42, e15–e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleem, H.T.; Surkan, P.J. Parental pregnancy wantedness and child social-emotional development. Matern Child Health J. 2014, 18, 930–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.M.; Khan, M.N. Early childhood development and its association with maternal parity. Child Care Health Dev. 2023, 49, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhamrait, G.K.; Taylor, C.L.; Pereira, G. Interpregnancy intervals and child development at age 5: A population data linkage study. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e045319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhamrait, G.; O’Donnell, M.; Christian, H.; Pereira, G. Is early childhood development impeded by the birth timing of the younger sibling? PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0268325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duko, B.; Gebremedhin, A.T.; Tessema, G.A.; Alati, R.; Pereira, G. Average treatment effect of maternal prenatal tobacco smoking on offspring developmental vulnerability in early childhood. Ann. Epidemiol. 2023, 78, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Julvez, J.; Ribas-Fito, N.; Torrent, M.; Forns, M.; Garcia-Esteban, R.; Sunyer, J. Maternal smoking habits and cognitive development of children at age 4 years in a population-based birth cohort. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2007, 36, 825–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slykerman, R.F.; Thompson, J.M.D.; Clark, P.M.; Becroft, D.M.O.; Robinson, E.; Pryor, J.E.; Wild, C.J.; Mitchell, E.A. Determinants of developmental delay in infants aged 12 months. Paediatr. Perinat. Epidemiol. 2007, 21, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehby, G.L.; Prater, K.; McCarthy, A.M.; Castilla, E.E.; Murray, J.C. The Impact of Maternal Smoking during Pregnancy on Early Child Neurodevelopment. J. Hum. Cap. 2011, 5, 207–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormack, C.; Hutchinson, D.; Burns, L.; Youssef, G.; Wilson, J.; Elliott, E.; Allsop, S.; Najman, J.; Jacobs, S.; Rossen, L.; et al. Maternal and partner prenatal alcohol use and infant cognitive development. Drug Alcohol. Depend 2018, 185, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, M.F.; Bayliss, D.M.; Glauert, R.; Ohan, J.L. Using linked data to investigate developmental vulnerabilities in children of convicted parents. Dev. Psychol. 2018, 54, 1219–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, A.L.; Hentschel, E.; Fulcher, I.; Rava, M.S.; Abdulkarim, G.; Abdalla, O.; Said, S.; Khamis, H.; Hedt-Gauthier, B.; Wilson, K. Caregiver parenting practices, dietary diversity knowledge, and association with early childhood development outcomes among children aged 18–29 months in Zanzibar, Tanzania: A cross-sectional survey. BMC Public Health 2022, 22, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, K.; Tofail, F.; Frongillo, E.; Rasmussen, K.; Arifeen, S.; Persson, L.; Huda, S.N.; Hamadani, J.D. Household food security is associated with early childhood language development: Results from a longitudinal study in rural Bangladesh. Child Care Health Dev. 2010, 36, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basnet, S.; Frongillo, E.A.; Nguyen, P.H.; Moore, S.; Arabi, M. Maternal resources for care are associated with child growth and early childhood development in Bangladesh and Vietnam. Child Care Health Dev. 2022, 48, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Rodríguez, J.; Díaz-López, A.; Canals-Sans, J.; Arija, V. Maternal Vitamin B12 Status during Pregnancy and Early Infant Neurodevelopment: The ECLIPSES Study. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingues, M.R.; Matijasevich, A.; Barros, A.J.; Santos, I.S.; Horta, B.L.; Hallal, P.C. Physical activity during pregnancy and offspring neurodevelopment and IQ in the first 4 years of life. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e110050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turunç, G.; Kisbu-Sakarya, Y. Parents’ Attitudes Toward Domestic Violence as a Risk Factor for Early Childhood Development: Testing an Actor-Partner Interdependence Model Using UNICEF MICS. J. Interpers. Violence 2022, 37, NP21476–NP21501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitten, T.; Green, M.J.; Tzoumakis, S.; Laurens, K.R.; Harris, F.; Carr, V.J.; Dean, K. Early developmental vulnerabilities following exposure to domestic violence and abuse: Findings from an Australian population cohort record linkage study. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2022, 153, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, J.; Adhia, A.; Bhatia, A.; Charles, D.; Yousafzai, A.K. Intimate partner violence, maternal and paternal parenting, and early child development. Pediatrics 2020, 145, e20192955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horton, M.K.; Rundle, A.; Camann, D.E.; Boyd Barr, D.; Rauh, V.A.; Whyatt, R.M. Impact of prenatal exposure to piperonyl butoxide and permethrin on 36-month neurodevelopment. Pediatrics 2011, 127, e699–e706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tofail, F.; Vahter, M.; Hamadani, J.D.; Nermell, B.; Huda, S.N.; Mohammad, Y.; Rahman, M.; Grantham-McGregor, S.M. Effect of arsenic exposure during pregnancy on infant development at 7 months in rural Matlab, Bangladesh. Environ. Health Perspect. 2009, 117, 288–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, F.P.; Rauh, V.; Whyatt, R.M.; Tsai, W.; Tang, D.; Diaz, D.; Hoepner, L.; Barr, D.; Tu, Y.-H.; Camann, D.; et al. Effect of prenatal exposure to airborne polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons on neurodevelopment in the first 3 years of life among inner-city children. Environ. Health Perspect. 2006, 114, 1287–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, S.Y.; Du, J.B.; Chi, X.; Zhu, Y.Y.; Wang, X.Y.; Meng, Q.X.; Ling, X.; Diao, F.; Song, C.; Jiang, Y.; et al. Associations between antenatal corticosteroid exposure and neurodevelopment in infants. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2022, 227, 759.e1–759.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrow, C.E.; Stra, E.S.; Anthony, J.C.; Ofir, A.Y.; Xue, L.; Reyes, M.B. Influence of prenatal cocaine exposure on early language development: Longitudinal findings from four months to three years of age. J. Dev. Behav. Pediatr. 2003, 24, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, A.; Wan, Y.; Mahai, G.; Qian, X.; Li, Y.; Xu, S.; Xia, W. Association of Prenatal Exposure to Organophosphate, Pyrethroid, and Neonicotinoid Insecticides with Child Neurodevelopment at 2 Years of Age: A Prospective Cohort Study. Environ. Health Perspect. 2023, 131, 107011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reardon, A.J.F.; Hajihosseini, M.; Dinu, I.; Field, C.J.; Kinniburgh, D.W.; MacDonald, A.M.; Dewey, D.; England-Mason, G.; Martin, J.W. Maternal co-exposure to mercury and perfluoroalkyl acid isomers and their associations with child neurodevelopment in a Canadian birth cohort. Environ. Int. 2023, 178, 108087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.H.; Ha, E.H.; Liao, H.F.; Jeng, S.F.; Su, Y.N.; Wen, T.W.; Lien, G.W.; Chen, C.Y.; Hsieh, W.S.; Chen, P.C. Perfluorinated compound levels in cord blood and neurodevelopment at 2 years of age. Epidemiology 2013, 24, 800–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Moon, N.; Ji, E.; Moon, H.B. Effects of postnatal exposure to phthalate, bisphenol a, triclosan, parabens, and per- and poly-fluoroalkyl substances on maternal postpartum depression and infant neurodevelopment: A korean mother-infant pair cohort study. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 96384–96399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, A.M.; Cordoba, L.; Cano, J.C.; Hern ez-Bonilla, D.; Pardo, L.; Schnaas, L.; Smith, D.R.; Menezes-Filho, J.A.; Mergler, D.; Lindh, C.H.; et al. Prenatal mancozeb exposure, excess manganese, and neurodevelopment at 1 year of age in the Infants’ Environmental Health (ISA) study. Environ. Health Perspect. 2018, 126, EHP1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Zhang, J.; Wu, C.; Lv, S.; Lu, D.; Qi, X.; Jiang, S.; Feng, C.; Yu, H.; Liang, W.; et al. Associations of prenatal and childhood chlorpyrifos exposure with Neurodevelopment of 3-year-old children. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 251, 538–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Luo, R.F.; Wang, T.Y.; Gao, J.J.; Liu, C.F. Prenatal Exposure to Environmental Tobacco Smoke and Early Development of Children in Rural Guizhou Province, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polanska, K.; Krol, A.; Merecz-Kot, D.; Ligocka, D.; Mikolajewska, K.; Mirabella, F.; Chiarotti, F.; Calamandrei, G.; Hanke, W. Environmental Tobacco Smoke Exposure during Pregnancy and Child Neurodevelopment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivero, M.; Vilaseca, R.; Cantero, M.-J.; Valls-Vidal, C.; Leiva, D. Relations between Positive Parenting Behavior during Play and Child Language Development at Early Ages. Children 2023, 10, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha, H.A.L.; Correia, L.L.; Leite, Á.J.M.; Rocha, S.G.M.O.; Albuquerque, L.d.S.; Machado, M.M.T.; Campos, J.S.; e Silva, A.C.; Sudfeld, C.R. Positive Parenting Behaviors and Child Development in Ceará, Brazil: A Population-Based Study. Children 2022, 9, 1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Z.; Su, X.; Ni, Y.; Luo, T.; Hua, J. Association between the home environment and development among 3- to 11-month infants in Shanghai, China. Child Care Health Dev. 2022, 48, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drago, F.; Scharf, R.J.; Maphula, A.; Nyathi, E.; Mahopo, T.C.; Svensen, E.; Mduma, E.; Bessong, P.; McQuade, E.T.R. Psychosocial and environmental determinants of child cognitive development in rural South Africa and Tanzania: Findings from the mal-ed cohort. BMC Public Health 2020, 20, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grippo, A.; Zhu, K.X.; Yeung, E.H.; Bell, E.M.; Bonner, M.R.; Tian, L.L.; Mendola, P.; Mu, L. Indoor air pollution exposure and early childhood development in the Upstate KIDS Study. Environ. Res. 2023, 234, 116528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrijheid, M.; Martinez, D.; Aguilera, I.; Bustamante, M.; Ballester, F.; Estarlich, M.; ernandez-Somoano, A.; Guxens, M.; Lertxundi, N.; Martinez, M.D.; et al. Indoor air pollution from gas cooking and infant neurodevelopment. Epidemiology 2012, 23, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirci, A.; Kartal, M. Sociocultural risk factors for developmental delay in children aged 3-60 months: A nested case-control study. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2018, 177, 691–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girchenko, P.; Tuovinen, S.; Lahti-Pulkkinen, M.; Lahti, J.; Savolainen, K.; Heinonen, K.; Pyhälä, R.; Reynolds, R.M.; Hämäläinen, E.; Villa, P.M.; et al. Maternal early pregnancy obesity and related pregnancy and pre-pregnancy disorders: Associations with child developmental milestones in the prospective PREDO Study. Int. J. Obes. 2018, 42, 995–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christian, H.; Ball, S.J.; Zubrick, S.R.; Brinkman, S.; Turrell, G.; Boruff, B.; Foster, S. Relationship between the neighbourhood built environment and early child development. Health Place 2017, 48, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, A.; Gibberd, A.; Hanly, M.J.; Banks, E.; Eades, S.; Clapham, K.; Falster, K. Social and emotional developmental vulnerability at age five in Aboriginal and non-Aboriginal children in New South Wales: A population data linkage study. Int. J. Equity Health 2019, 18, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falster, K.; Hanly, M.; Edwards, B.; Banks, E.; Lynch, J.W.; Eades, S.; Nickel, N.; Goldfeld, S.; Biddle, N. Preschool attendance and developmental outcomes at age five in Indigenous and non-Indigenous children: A population-based cohort study of 100,357 Australian children. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 2021, 75, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, N.; Richards, B.; Sun, J.; Webers, A.; Sincovich, A. Early childhood education and child development in four countries in East Asia and the Pacific. Early Child. Res. Q. 2019, 47, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.M.; Mishra, G.D.; Moss, K.M.; Yang, I.A.; Lycett, K.; Knibbs, L.D. Maternal and Childhood Ambient Air Pollution Exposure and Mental Health Symptoms and Psychomotor Development in Children: An Australian Population-Based Longitudinal Study. Environ. Int. 2022, 158, 107003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, P.; Chiang, T.L.; Wu, C.D.; Shu, B.C.; Lung, F.W.; Guo, Y.L. Air pollution during the perinatal period and neurodevelopment in children: A national population study in Taiwan. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2023, 65, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, Y.H.M.; Hsu, H.H.L.; Coull, B.A.; Bellinger, D.C.; Kloog, I.; Schwartz, J.; Wright, R.O.; Wright, R.J. Prenatal particulate air pollution and neurodevelopment in urban children: Examining sensitive windows and sex-specific associations. Environ. Int. 2016, 87, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvis, I.; Davis, Z.; Sbihi, H.; Brauer, M.; Czekajlo, A.; Davies, H.W.; Gergel, S.E.; Guhn, M.; Jerrett, M.; Koehoorn, M.; et al. Assessing the association between lifetime exposure to greenspace and early childhood development and the mediation effects of air pollution and noise in Canada: A population-based birth cohort study. Lancet Planet. Health 2021, 5, e709–e717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lertxundi, A.; Baccini, M.; Lertxundi, N.; Fano, E.; Aranbarri, A.; Martínez, M.D.; Ayerdi, M.; Álvarez, J.; Santa-Marina, L.; Dorronsoro, M.; et al. Exposure to fine particle matter, nitrogen dioxide and benzene during pregnancy and cognitive and psychomotor development in children at 15 months of age. Environ. Int. 2015, 80, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odo, D.B.; Yang, I.A.; Dey, S.; Hammer, M.S.; van Donkelaar, A.; Martin, R.V.; Dong, G.-H.; Yang, B.-Y.; Hystad, P.; Knibbs, L.D. A cross-sectional analysis of long-term exposure to ambient air pollution and cognitive development in children aged 3–4 years living in 12 low- and middle-income countries. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 318, 120916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porta, D.; Narduzzi, S.; Badaloni, C.; Bucci, S.; Cesaroni, G.; Colelli, V.; Davoli, M.; Sunyer, J.; Zirro, E.; Schwartz, J.; et al. Air pollution and cognitive development at age 7 in a prospective Italian birth cohort. Epidemiology 2016, 27, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.P.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Li, J.L.; Zhou, Y.H.; Luo, R.R.; Meng, X.; Zhang, Y. Prenatal exposure to ambient fine particulate matter and early childhood neurodevelopment: A population-based birth cohort study. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 785, 147334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.J.; Zhang, H.L.; Li, J.X.; Liao, J.Q.; Liu, J.T.; Hu, C.; Sun, X.; Zheng, T.; Xia, W.; Xu, S.; et al. Prenatal and early postnatal exposure to ambient particulate matter and early childhood neurodevelopment: A birth cohort study. Environ. Res. 2022, 210, 112946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.; Park, H.; Hong, Y.C.; Ha, M.; Kim, Y.; Kim, B.N.; Kim, Y.; Roh, Y.M.; Lee, B.E.; Ryu, J.M.; et al. Prenatal exposure to PM10 and NO2 and children’s neurodevelopment from birth to 24 months of age: Mothers and Children’s Environmental Health (MOCEH) study. Sci. Total. Environ. 2014, 481, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freire, C.; Ramos, R.; Puertas, R.; Lopez-Espinosa, M.J.; Julvez, J.; Aguilera, I.; Cruz, F.; Fernandez, M.-F.; Sunyer, J.; Olea, N. Association of traffic-related air pollution with cognitive development in children. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 2010, 64, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Zhou, L.L.; Xu, J.; Kan, H.D.; Chen, R.J.; Chen, S.W.; Hua, H.; Liu, Z.; Yan, C. Effects of prenatal exposures to air sulfur dioxide/nitrogen dioxide on toddler neurodevelopment and effect modification by ambient temperature. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 230, 113118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Shang, G.; Wang, L.; Sun, Y.; Osborn, A.; Rozelle, S. The relationship between birth season and early childhood development: Evidence from northwest rural China. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0205281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goto, R.; Frodl, T.; Skokauskas, N. Armed Conflict and Early Childhood Development in 12 Low- and Middle-Income Countries. Pediatrics 2021, 148, e2021050332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bornstein, M.H.; Rothenberg, W.A.; Lansford, J.E.; Bradley, R.H.; Deater-Deckard, K.; Bizzego, A.; Esposito, G. Child Development in Low- and Middle-Income Countries. Pediatrics 2021, 148, e2021053180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, C.L.; Christensen, D.; Venn, A.J.; Preen, D.B.; Stafford, J.; Hansen, E.; Jose, K.; Zubrick, S. Use of administrative record linkage to examine patterns of universal early childhood health and education service use from birth to Kindergarten (age four years) and developmental vulnerability in the Preparatory Year (age five years) in Tasmania, Australia. Int. J. Popul. Data Sci. 2021, 6, 1681. [Google Scholar]
- Chartier, M.J.; Brownell, M.D.; Isaac, M.R.; Chateau, D.; Nickel, N.C.; Katz, A.; Sarkar, J.; Hu, M.; Taylor, C. Is the Families First Home Visiting Program Effective in Reducing Child Maltreatment and Improving Child Development? Child Maltreatment 2017, 22, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enns, J.E.; Nickel, N.C.; Chartier, M.; Chateau, D.; Campbell, R.; Phillips-Beck, W.; Sarkar, J.; Burland, E.; Katz, A.; Santos, R.; et al. An unconditional prenatal income supplement is associated with improved birth and early childhood outcomes among First Nations children in Manitoba, Canada: A population-based cohort study. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2021, 21, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christians, J.K.; Ahmadzadeh-Seddeighi, S.; Bilal, A.; Bogdanovic, A.; Ho, R.; Leung, E.V.; MacGregor, M.A.; Nadasdy, N.M.; Principe, G.M. Sex differences in the effects of prematurity and/or low birthweight on neurodevelopmental outcomes: Systematic review and meta-analyses. Biol. Sex Differ. 2023, 14, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, B.E.; Leppert, M.O.C.; German, K.; Lehmann, C.U.; Adams-Chapman, I.; Council on Children with Disabilities; Committee on Fetus and Newborn. Primary Care Framework to Monitor Preterm Infants for Neurodevelopmental Outcomes in Early Childhood. Pediatrics 2023, 152, e2023062511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Y.M.; Cho, D.H.; Kim, J.K. Developmental outcomes of very low birth weight infants with catch-up head growth: A nationwide cohort study. BMC Pediatr. 2023, 23, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jańczewska, I.; Wierzba, J.; Jańczewska, A.; Szczurek-Gierczak, M.; Domżalska-Popadiuk, I. Prematurity and Low Birth Weight and Their Impact on Childhood Growth Patterns and the Risk of Long-Term Cardiovascular Sequelae. Children 2023, 10, 1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glover Williams, A.; Odd, D. Investigating the association between post-term birth and long term cognitive, developmental and educational impacts: A systematic review and Meta-analysis. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal. Med. 2020, 33, 1253–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenabi, E.; Farashi, S.; Salehi, A.M.; Parsapoor, H. The association between post-term births and autism spectrum disorders: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2023, 28, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Oliveira, K.H.D.; de Almeida, G.M.; Gubert, M.B.; Moura, A.S.; Spaniol, A.M.; Hernandez, D.C.; Pérez-Escamilla, R.; Buccini, G. Household food insecurity and early childhood development: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Matern. Child Nutr. 2020, 16, e12967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tandon, P.S.; Tovar, A.; Jayasuriya, A.T.; Welker, E.; Schober, D.J.; Copeland, K.; Dev, D.A.; Murriel, A.L.; Amso, D.; Ward, D.S. The relationship between physical activity and diet and young children’s cognitive development: A systematic review. Prev. Med. Rep. 2016, 3, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irigaray, T.Q.; Pacheco, J.B.; Grassi-Oliveira, R.; Fonseca, R.P.; Leite, J.C.d.C.; Kristensen, C.H. Child maltreatment and later cognitive functioning: A systematic review. Psicol. Reflexão E Crítica 2013, 26, 376–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madigan, S.; McArthur, B.A.; Anhorn, C.; Eirich, R.; Christakis, D.A. Associations between screen use and child language skills: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Pediatr. 2020, 174, 665–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, W. The Influence of Screen Media Usage on Child Social Development: A Systematic Review. J. Educ. Humanit. Soc. Sci. 2023, 8, 2110–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carson, V.; Hunter, S.; Kuzik, N.; Wiebe, S.A.; Spence, J.C.; Friedman, A.; Tremblay, M.S.; Slater, L.; Hinkley, T. Systematic review of physical activity and cognitive development in early childhood. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2016, 19, 573–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, N.; Ayyub, M.; Sun, H.; Wen, X.; Xiang, P.; Gao, Z. Effects of physical activity on motor skills and cognitive development in early childhood: A systematic review. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 2760716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonough, D.J.; Liu, W.; Gao, Z. Effects of physical activity on children’s motor skill development: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 8160756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCann, S.; Perapoch Amadó, M.; Moore, S.E. The Role of Iron in Brain Development: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutema, B.T.; Sorrie, M.B.; Megersa, N.D.; Yesera, G.E.; Yeshitila, Y.G.; Pauwels, N.S.; De Henauw, S.; Abbeddou, S.; Metwally, A.M. Effects of iron supplementation on cognitive development in school-age children: Systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0287703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giugliani, E.; Horta, B.; Loret de Mola, C.; Lisboa, B.; Victora, C. Effect of breastfeeding promotion interventions on child growth: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Paediatr. 2015, 104, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, M.M.; Herrin, W.E.; Gulere, G.B. Using the Uganda National Panel Survey to analyze the effect of staple food consumption on undernourishment in Ugandan children. BMC Public Health 2017, 18, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carson, V.; Stearns, J.; Janssen, I. The Relationship Between Parental Physical Activity and Screen Time Behaviors and the Behaviors of their Young Children. Pediatr. Exerc. Sci. 2015, 27, 390–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astiz, M.; Heyde, I.; Fortmann, M.I.; Bossung, V.; Roll, C.; Stein, A.; Grüttner, B.; Göpel, W.; Härtel, C.; Obleser, J.; et al. The circadian phase of antenatal glucocorticoid treatment affects the risk of behavioral disorders. Nat Commun. 2020, 11, 3593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerz, A.; Bell, K.; White, M.; Thompson, A.; Suter, M.; McKechnie, R.; Gallegos, D. Development and preliminary validation of a brief household food insecurity screening tool for paediatric health services in Australia. Health Soc. Care Community 2021, 29, 1538–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iglesias, L.; Canals, J.; Arija, V. Effects of prenatal iron status on child neurodevelopment and behavior: A systematic review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 58, 1604–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camprubi Robles, M.; Campoy, C.; Garcia Fernandez, L.; Lopez-Pedrosa, J.M.; Rueda, R.; Martin, M.J. Maternal Diabetes and Cognitive Performance in the Offspring: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrobas Velilla, T.; Varo Sánchez, G.; Romero García, I.; Melguizo Madrid, E.; Rodríguez Sánchez, F.I.; León Justel, A. Prevalence of severe hypercholesterolemia observed in different hospitals in Andalusia and Ceuta. Clin. Investig. Arter. 2021, 33, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaeizadeh, G.; Mansournia, M.A.; Keshtkar, A.; Farahani, Z.; Zarepour, F.; Sharafkhah, M.; Kelishadi, R.; Poustchi, H. Maternal education and its influence on child growth and nutritional status during the first two years of life: A systematic review and meta-analysis. eClinicalMedicine 2024, 71, 102574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks-Gunn, J.; Klebanov, P.; Smith, J.R.; Lee, K. Effects of combining public assistance and employment on mothers and their young children. Women Health 2001, 32, 179–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkadi, A.; Kristiansson, R.; Oberklaid, F.; Bremberg, S. Fathers’ involvement and children’s developmental outcomes: A systematic review of longitudinal studies. Acta Paediatr. 2008, 97, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emmers, D.; Jiang, Q.; Xue, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, B.; Dill, S.-E.; Qian, Y.; Warrinnier, N.; et al. Early childhood development and parental training interventions in rural China: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Glob Health 2021, 6, e005578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Ssewanyana, D.; Martin, M.C.; Lye, S.; Moran, G.; Abubakar, A.; Marfo, K.; Marangu, J.; Proulx, K.; Malti, T. Supporting Child Development Through Parenting Interventions in Low- to Middle-Income Countries: An Updated Systematic Review. Front Public Health 2021, 9, 671988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clifford, H.; Telethon Kids, I. Environmental Health Challenges in Remote Aboriginal Australian Communities: Clean Air, Clean Water, and Safe Housing; Telethon Kids Institute: Subiaco, Western Australia, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ninti One, L. Culture, Housing, Remoteness and Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Child Development: Evidence from the Longitudinal Study of Indigenous Children; Ninti One Limited: Alice Springs, Australia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kadir, A.; Shenoda, S.; Goldhagen, J.; Pitterman, S. The Effects of Armed Conflict on Children. Pediatrics 2018, 142, e20182586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nores, M.; Barnett, W.S. Benefits of early childhood interventions across the world: (Under) Investing in the very young. Econ. Educ. Rev. 2010, 29, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sameroff, A.J. Environmental context of child development. J. Pediatr. 1986, 109, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagenlocher, M.; Renaud, F.G.; Haas, S.; Sebesvari, Z. Vulnerability and risk of deltaic social-ecological systems exposed to multiple hazards. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 631, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Study Characteristics | Number of Studies | Percent |
|---|---|---|
| Year of publication | ||
| 2021–2024 | 72 | 41.14 |
| 2011–2020 | 87 | 49.7 |
| 2002–2010 | 16 | 9.2 |
| Study country | ||
| Australia | 33 | 18.9 |
| Canada | 19 | 10.9 |
| US | 20 | 11.4 |
| China | 17 | 9.7 |
| Multi-country *** | 12 | 6.9 |
| Brazil | 11 | 6.3 |
| Spain | 8 | 4.6 |
| UK | 7 | 4 |
| Bangladesh | 5 | 2.9 |
| Norway | 4 | 2.3 |
| Others * | 39 | 22.3 |
| Study design | ||
| Cohort | 144 | 82.3 |
| Cross-sectional | 18 | 10.3 |
| Survey | 12 | 6.9 |
| Case–control | 1 | 0.57 |
| Measurement tools | ||
| Early developmental vulnerability instrument | 47 | 26.9 |
| Early development index | 11 | 6.3 |
| Bayley Scales of Infant Development | 38 | 21.7 |
| Age and stage questionnaire | 20 | 11.4 |
| Wechsler intelligence, preschool and primary scale | 7 | 4 |
| Others ** | 52 | 29.7 |
| Developmental Domains and Specific Outcomes Reported in Each Study | Number of Studies |
|---|---|
| Physical development (n = 115 studies) | |
| Physical health and well-being | 28 |
| Physical development | 3 |
| Motor development | 22 |
| Gross motor development | 29 |
| Fine motor development | 24 |
| Psychomotor developmental index | 9 |
| Cognitive development (n = 120 studies) | |
| Language and cognitive | 28 |
| Cognitive development | 34 |
| Mental developmental index | 13 |
| Learning and learning disability, literacy, and numeracy | 9 |
| Problem-solving | 13 |
| Full-scale IQ | 10 |
| Verbal IQ | 7 |
| Performance IQ | 6 |
| Language and communication development (n = 90 studies) | |
| Communication and general knowledge | 28 |
| Language | 27 |
| Expressive language | 10 |
| Receptive language | 9 |
| Communication | 16 |
| Social–emotional development (n = 96 studies) | |
| Social competence | 30 |
| Emotional maturity | 30 |
| Social–emotional development | 22 |
| Personal social development | 16 |
| Unspecified subdomains (n = 37 studies) | |
| Developmental vulnerability | 17 |
| Developmental delay | 20 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Atalell, K.A.; Pereira, G.; Duko, B.; Nyadanu, S.D.; Tessema, G.A. Perinatal and Childhood Risk Factors of Adverse Early Childhood Developmental Outcomes: A Systematic Review Using a Socioecological Model. Children 2025, 12, 1096. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12081096
Atalell KA, Pereira G, Duko B, Nyadanu SD, Tessema GA. Perinatal and Childhood Risk Factors of Adverse Early Childhood Developmental Outcomes: A Systematic Review Using a Socioecological Model. Children. 2025; 12(8):1096. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12081096
Chicago/Turabian StyleAtalell, Kendalem Asmare, Gavin Pereira, Bereket Duko, Sylvester Dodzi Nyadanu, and Gizachew A. Tessema. 2025. "Perinatal and Childhood Risk Factors of Adverse Early Childhood Developmental Outcomes: A Systematic Review Using a Socioecological Model" Children 12, no. 8: 1096. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12081096
APA StyleAtalell, K. A., Pereira, G., Duko, B., Nyadanu, S. D., & Tessema, G. A. (2025). Perinatal and Childhood Risk Factors of Adverse Early Childhood Developmental Outcomes: A Systematic Review Using a Socioecological Model. Children, 12(8), 1096. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12081096









