Effect of Midazolam Premedication on Salivary Cortisol Levels in Pediatric Patients with Negative Frankl Behavior: A Pilot Study
Abstract
Highlights
- Midazolam premedication in pediatric patients with “definitely negative” Frankl behavior was associated with significantly lower post-treatment salivary cortisol levels compared to non-sedated patients.
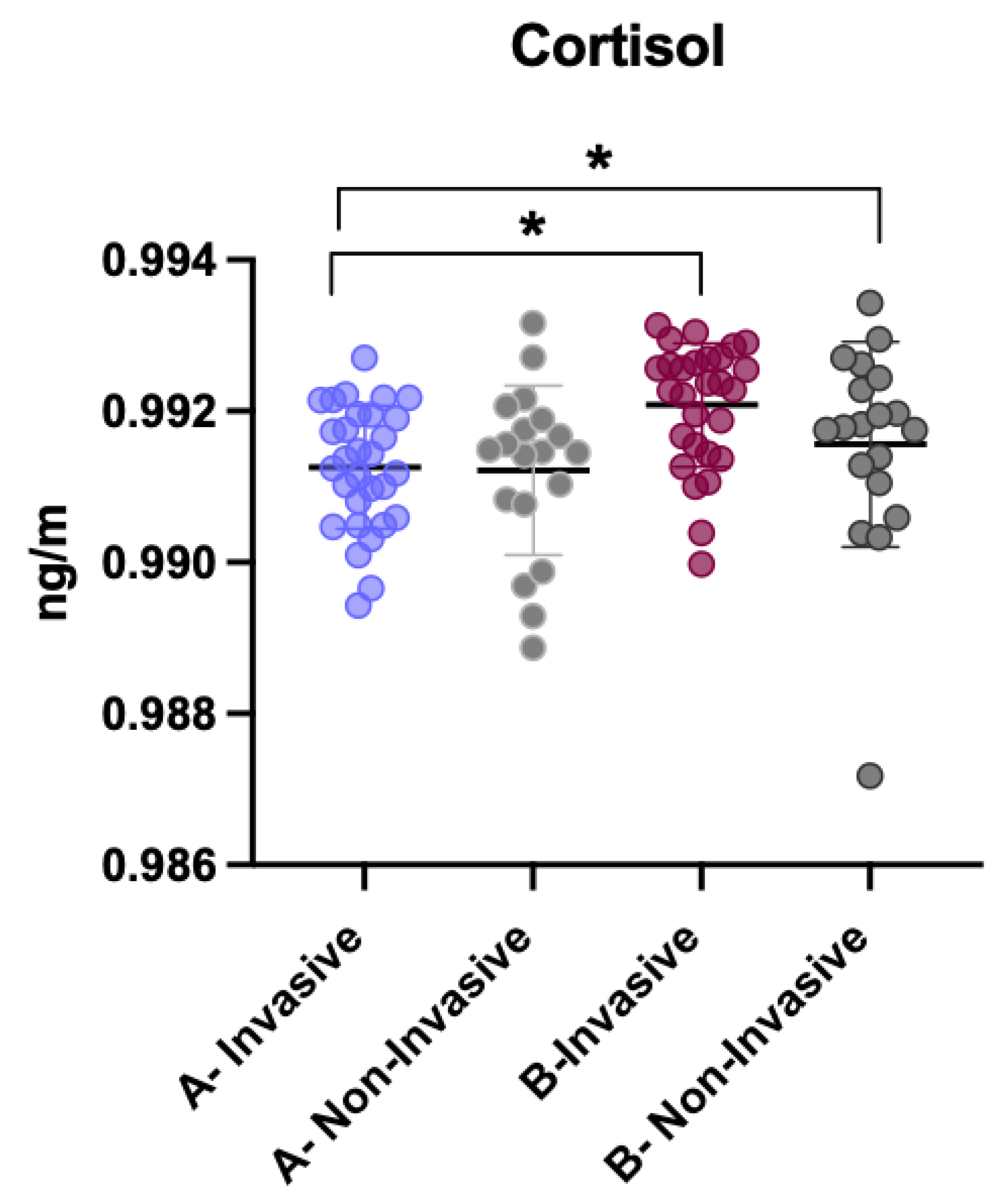
- Invasive dental procedures produced a marked increase in cortisol levels, while non-invasive treatments did not significantly alter cortisol concentrations.
- Midazolam may help reduce physiological stress in uncooperative pediatric dental patients, particularly during invasive procedures.
- Salivary cortisol measurement is a feasible and non-invasive biomarker for as-sessing stress and evaluating the impact of behavioral and pharmacological inter-ventions in pediatric dentistry.
Abstract
1. Introduction
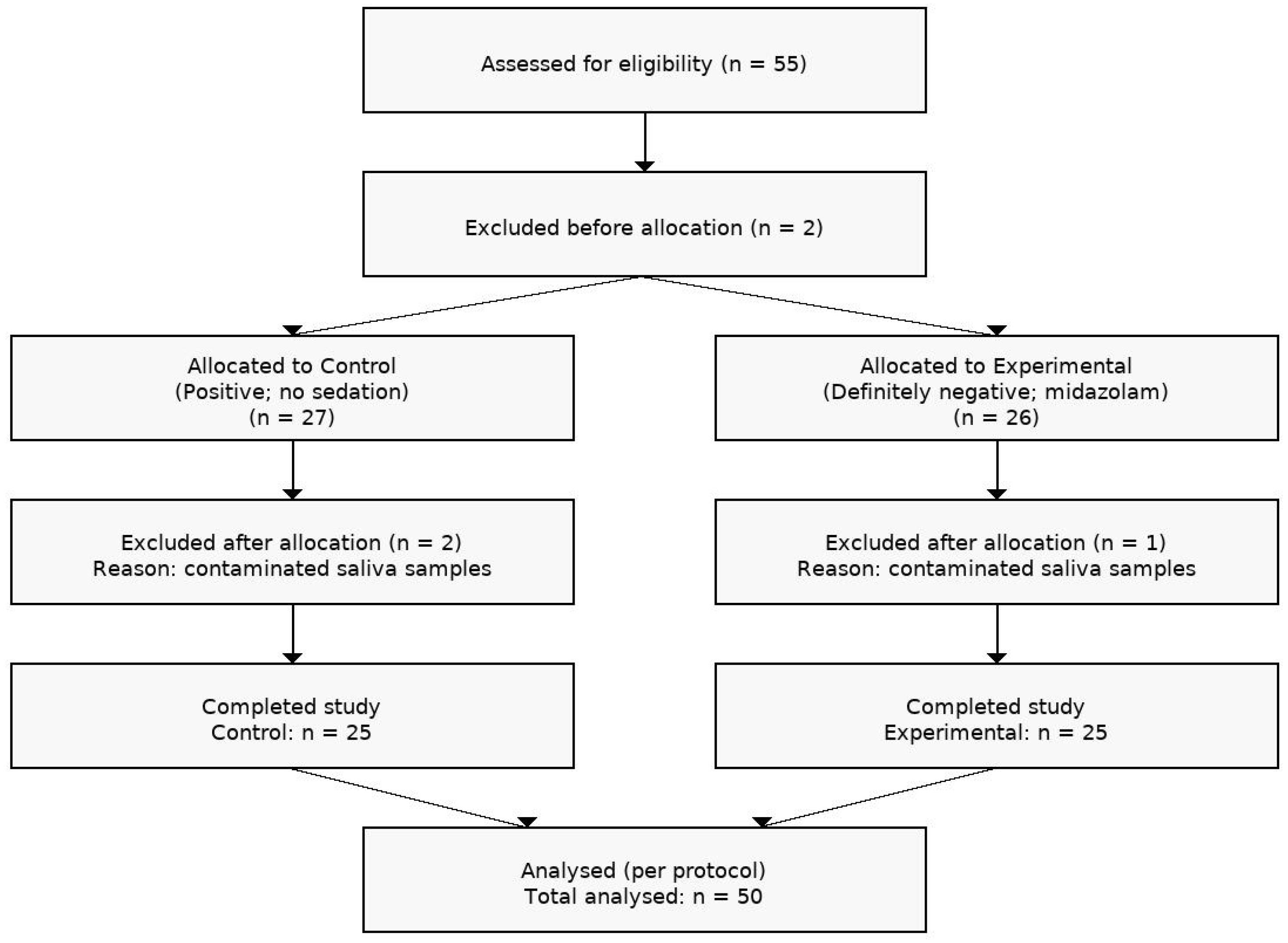
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Inclusion Criteria
2.3. Exclusion Criteria
2.4. Variable Definitions
2.5. Ethical Considerations
2.6. Research Procedure
2.7. Saliva Sample Collection
2.8. Laboratory Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
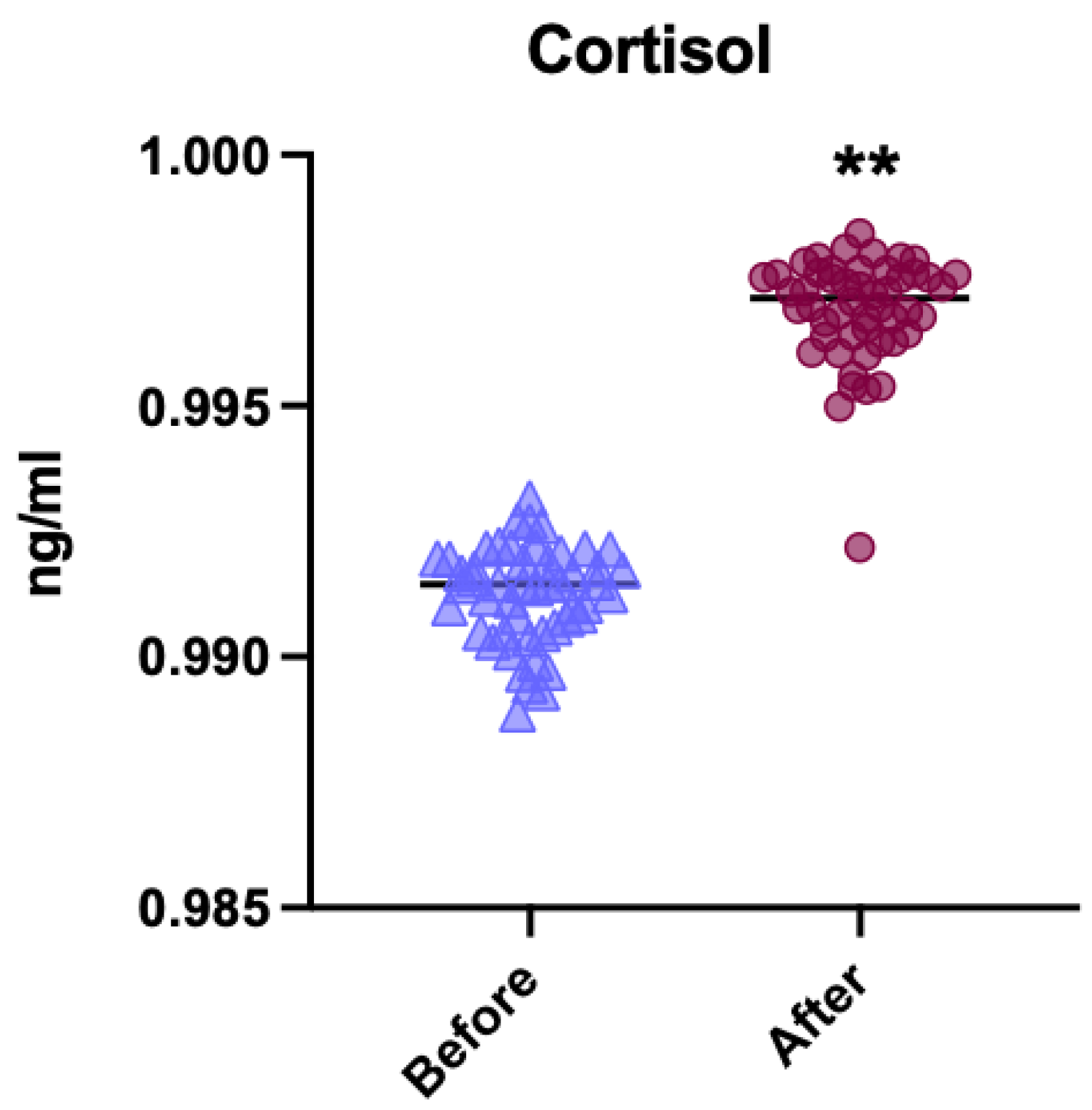
3.1. General Comparison of Cortisol Levels
3.2. Analysis of Cortisol Levels in Premedicated vs. Non-Premedicated Patients Before the Intervention
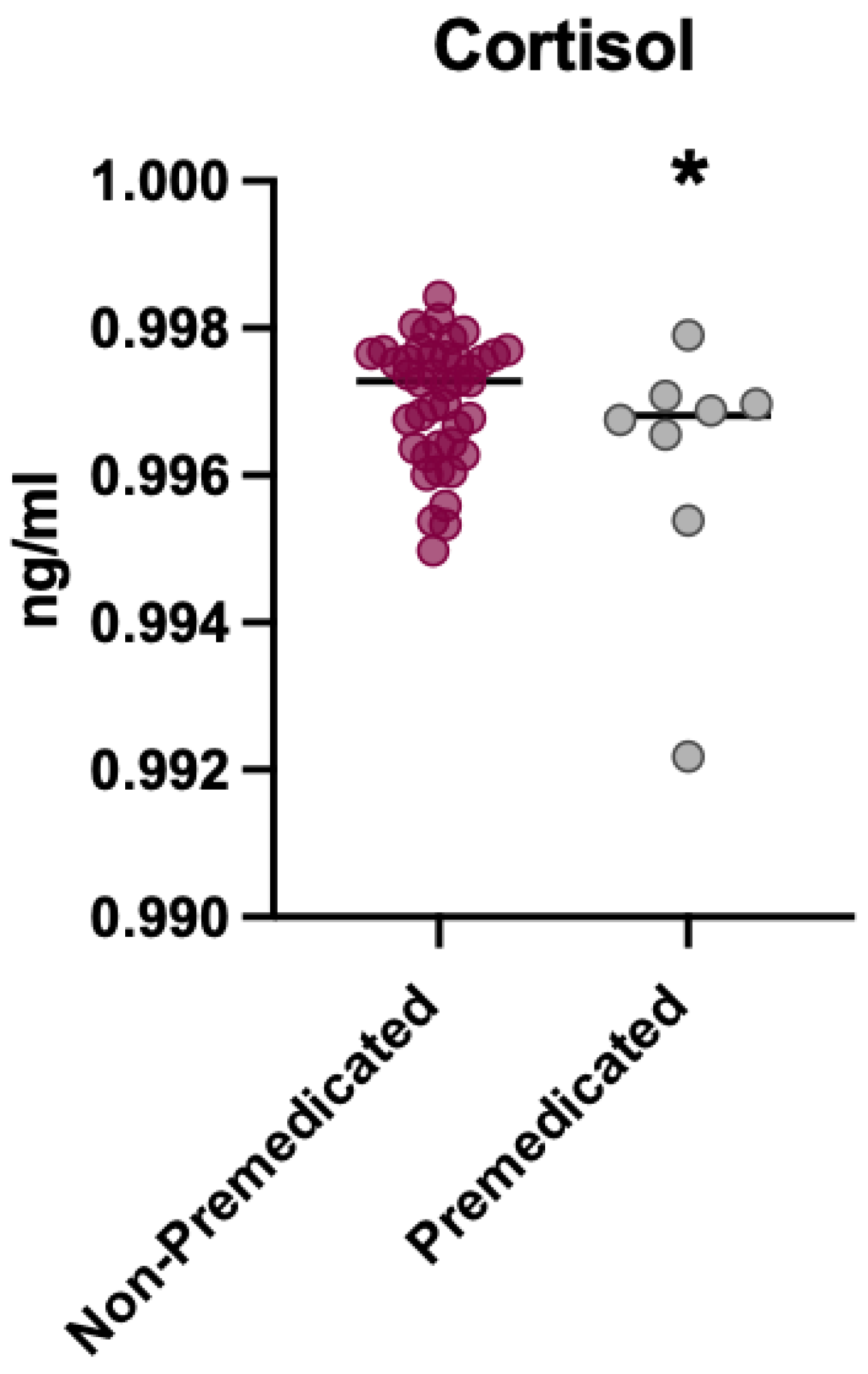
3.3. Analysis of Cortisol Levels in Premedicated vs. Non-Premedicated Patients After the Intervention
3.4. Comparison of Cortisol Levels Between Invasive and Non-Invasive Treatments
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hussein, T.O.; Akşit-Bıçak, D. Management of Post-Traumatic Dental Care Anxiety in Pediatric Dental Practice-A Clinical Study. Children 2022, 9, 1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almaummar, M.; Althabit, H.O.; Pani, S. The impact of dental treatment and age on salivary cortisol and alpha-amylase levels of patients with varying degrees of dental anxiety. BMC Oral Health 2019, 19, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdy, S.F.; Farag, M.S.M.S.; Helmy, Y.S.; Abo-Elsoud, A.A. Enhancing Pediatric Dental Care: The Influence of Virtual Reality. Eur. J. Dent. 2024, 18, 1030–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hugar, S.; Kohli, N.; Soneta, S.; Saxena, N.; Kadam, K.; Gokhale, N. Psychological behavior management techniques to alleviate dental fear and anxiety in 4–14-year-old children in pediatric dentistry: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Dent. Res. J. 2022, 19, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, G.S.; Anabuki, A.A.; Viana, K.A.; Corrêa-Faria, P.; Moterane, M.M.; Tedesco, T.K.; Costa, P.S.; Hosey, M.T.; Raggio, D.P.; Costa, L.R.; et al. Sedation versus protective stabilization for dental treatment of children with caries and challenging behavior at the dentist (CHOOSE): A study protocol for a non-randomized clinical trial. BMC Oral Health 2021, 21, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugaavel, A.K.; Asokan, S.; John, B.J.; Priya, G.; Devi, G.J.; Practitioner, G. Comparison of Behavior and Dental Anxiety During Intranasal and Sublingual Midazolam Sedation-A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Clin. Pediatr. Dent. 2016, 40, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goettems, M.L.; Zborowski, E.J.; Costa, F.d.S.; Costa, V.P.P.; Torriani, D.D. Nonpharmacologic Intervention on the Prevention of Pain and Anxiety During Pediatric Dental Care: A Systematic Review. Acad. Pediatr. 2017, 17, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cianetti, S.; Lombardo, G.; Lupatelli, E.; Pagano, S.; Abraha, I.; Montedori, A.; Caruso, S.; Gatto, R.; de Giorgio, S.; Salvato, R. Dental fear/anxiety among children and adolescents. A systematic review. Eur. J. Paediatr. Dent. 2017, 18, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Quesada, J.R.B.; Gaig, C.L.; Jimenéz, A.; de Deza, J.E.E.S. Evaluación de la colaboración en el paciente odontopediatrico. Arch. Odontoestomatol. 1994, 10, 86–92. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, F.; Wu, Y. Procedural sedation in pediatric dentistry: A narrative review. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1186823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, T.; Nelson, G. The Role of Sedation in Contemporary Pediatric Dentistry. Dent. Clin. N. Am. 2013, 57, 145–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashley, P.; Anand, P.; Andersson, K. Best clinical practice guidance for conscious sedation of children undergoing dental treatment: An EAPD policy document. Eur. Arch. Paediatr. Dent. 2021, 22, 989–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, H.S.; Corrêa-Faria, P.; Silva, T.A.; Paiva, S.M.; Costa, P.S.S.; Batista, A.C.; Costa, L.R. Oral midazolam reduces cortisol levels during local anaesthesia in children: A randomised controlled trial. Braz. Oral Res. 2015, 29, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, T.M.; Xu, Z. Pediatric dental sedation: Challenges and opportunities. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dent. 2015, 7, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moterane, M.M.; Anabuki, A.A.; Costa, L.R. Child Stress and Behaviour During Restorative Treatment under Non-Pharmacological Techniques and Sedation: A Case Series. Pesqui. Bras. Odontopediatria Clin. Integr. 2023, 23, e220041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furlan, N.F.; Gavião, M.B.D.; Barbosa, T.S.; Nicolau, J.; Castelo, P.M. Salivary Cortisol, Alpha-Amylase and Heart Rate Variation in Response to Dental Treatment in Children. J. Clin. Pediatr. Dent. 2012, 37, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordero, M.J.A.; López, A.M.S.; Villar, N.M.; García, G.I.; López, M.A.R.; Piñero, A.O.; Castell, E.C. Cortisol salival como indicador de estrés fisiológico en niños y adultos; revisión sistemática. Nutr. Hosp. 2014, 29, 960–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, Y.; Chaturvedy, S.; Marwah, N.; Chaturvedi, S.; Agarwal, S.; Agarwal, N. Salivary cortisol and Alpha-amylase-biomarkers of estress in chiuldren undeergoing extraction: An in vivo Study. Int. J. Clin. Pediatr. Dent. 2018, 11, 214–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaki, S.M.; Bakry, N.S.; Baghlaf, K.K. The effect of audiovisual distraction on children’s behavior during dental treatment: A randomized controlled clinical trial. J. Contemp. Dent. Pract. 2020, 21, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Tyagi, R. Behavioral and physiological effects of audio distraction on anxious pediatric dental patients. J. Indian. Soc. Pedod. Prev. Dent. 2011, 29, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Main, S.; Carrilho, M.; Alessandri-Bonetti, A.; Sawicki, C.; Rao, J.; Hall, S.; Sangalli, L. Salivary Markers as potential stress descriptors for pediatric dental patients: A literature review. Child 2025, 14, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheta, S.A.; AlSarheed, M. Oral midazolam sedation for children undergoing dental treatment. Saudi Med. J. 2009, 30, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Gheware, A.; Jagtap, S.; Mangalgi, A.; Killedar, M. Comparison of two different dosages of oral midazolam for conscious sedation in pediatric dental patients. J. Indian Soc. Pedod. Prev. Dent. 2016, 34, 213–218. [Google Scholar]
- Alzahrani, S.H.; Othman, M.E.; Alqahtani, A.S. A systematic review of oral midazolam sedation in pediatric patients: Efficacy and safety considerations. Paediatr. Anaesth. 2021, 31, 431–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP). Pediatric Medication Dosing Guidelines. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Department of Pediatrics. 2021. Available online: https://www.med.unc.edu/pediatrics/cccp/wp-content/uploads/sites/1156/gravity_forms/1-188e5632d99d8f770a150fd48b72fb22/2021/02/Pediatric-Medication-Dosing-Guildelines.pdf (accessed on 19 March 2025).
- Shindova, M.P.; Belcheva, A.B. Behaviour evaluation scales for pediatric dental patients—Review and clinical experience. Folia Medica 2014, 56, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fux-Noy, A.; Zeineh, R.; Shmueli, A.; Halperson, E.; Ram, D.; Moskovitz, M. Anxiety during the dental care of children aged 4 to 6 years over three consecutive visits. J. Clin. Pediatr. Dent. 2023, 47, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attri, J.P.; Sharan, R.; Makkar, V.; Gupta, K.K.; Khetarpal, R.; Kataria, A.P. Conscious sedation: Emerging trends in pediatric dentistry. Anesth. Essays Res. 2017, 11, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, H.S.; Miranda, A.R.; Viana, K.A.; Batista, A.C.; Costa, P.S.; Daher, A.; Machado, G.d.C.M.; Sado-Filho, J.; Vieira, L.A.C.; Corrêa-Faria, P.; et al. Intranasal sedation using ketamine and midazolam for pediatric dental treatment (NASO): Study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials 2017, 18, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baakdah, R.A.; Turkistani, J.M.; Al-Qarni, A.M.; Al-Abdali, A.N.; Alharbi, H.A.; Bafaqih, J.A.; Alshehri, Z.S. Pediatric dental treatments with pharmacological and non-pharmacological interventions: A cross-sectional study. BMC Oral Health 2021, 21, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Characteristic | Midazolam Group (n = 25) | Control Group (n = 25) | Total (n = 50) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, mean ± SD (years) | 8.1 ± 2.3 | 8.3 ± 2.1 | 8.2 ± 2.2 |
| Sex, n (%) | |||
| - Male | 14 (56%) | 14 (56%) | 28 (56%) |
| - Female | 11 (44%) | 11 (44%) | 22 (44%) |
| Type of procedure, n (%) | |||
| - Invasive | 15 (60%) | 12 (48%) | 27 (54%) |
| - Non-invasive | 10 (40%) | 13 (52%) | 23 (46%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aura-Tormos, J.I.; Marqués-Martínez, L.; Garcia-Miralles, E.; Torres-Cuevas, I.; Quartararo, B.; Guinot-Barona, C. Effect of Midazolam Premedication on Salivary Cortisol Levels in Pediatric Patients with Negative Frankl Behavior: A Pilot Study. Children 2025, 12, 1097. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12081097
Aura-Tormos JI, Marqués-Martínez L, Garcia-Miralles E, Torres-Cuevas I, Quartararo B, Guinot-Barona C. Effect of Midazolam Premedication on Salivary Cortisol Levels in Pediatric Patients with Negative Frankl Behavior: A Pilot Study. Children. 2025; 12(8):1097. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12081097
Chicago/Turabian StyleAura-Tormos, Juan Ignacio, Laura Marqués-Martínez, Esther Garcia-Miralles, Isabel Torres-Cuevas, Bianca Quartararo, and Clara Guinot-Barona. 2025. "Effect of Midazolam Premedication on Salivary Cortisol Levels in Pediatric Patients with Negative Frankl Behavior: A Pilot Study" Children 12, no. 8: 1097. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12081097
APA StyleAura-Tormos, J. I., Marqués-Martínez, L., Garcia-Miralles, E., Torres-Cuevas, I., Quartararo, B., & Guinot-Barona, C. (2025). Effect of Midazolam Premedication on Salivary Cortisol Levels in Pediatric Patients with Negative Frankl Behavior: A Pilot Study. Children, 12(8), 1097. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12081097







