The Role of Stress in Venipuncture Pain in Adolescents: Secondary Analysis of a Prospective Observational Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Study Design
2.2.1. Perceived Stress Scale (PSS)
2.2.2. Pubertal Development Scale (PDS)
2.2.3. Venipuncture
2.2.4. Pain Rating Scales
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Relationships Between Stress and Pain at Baseline
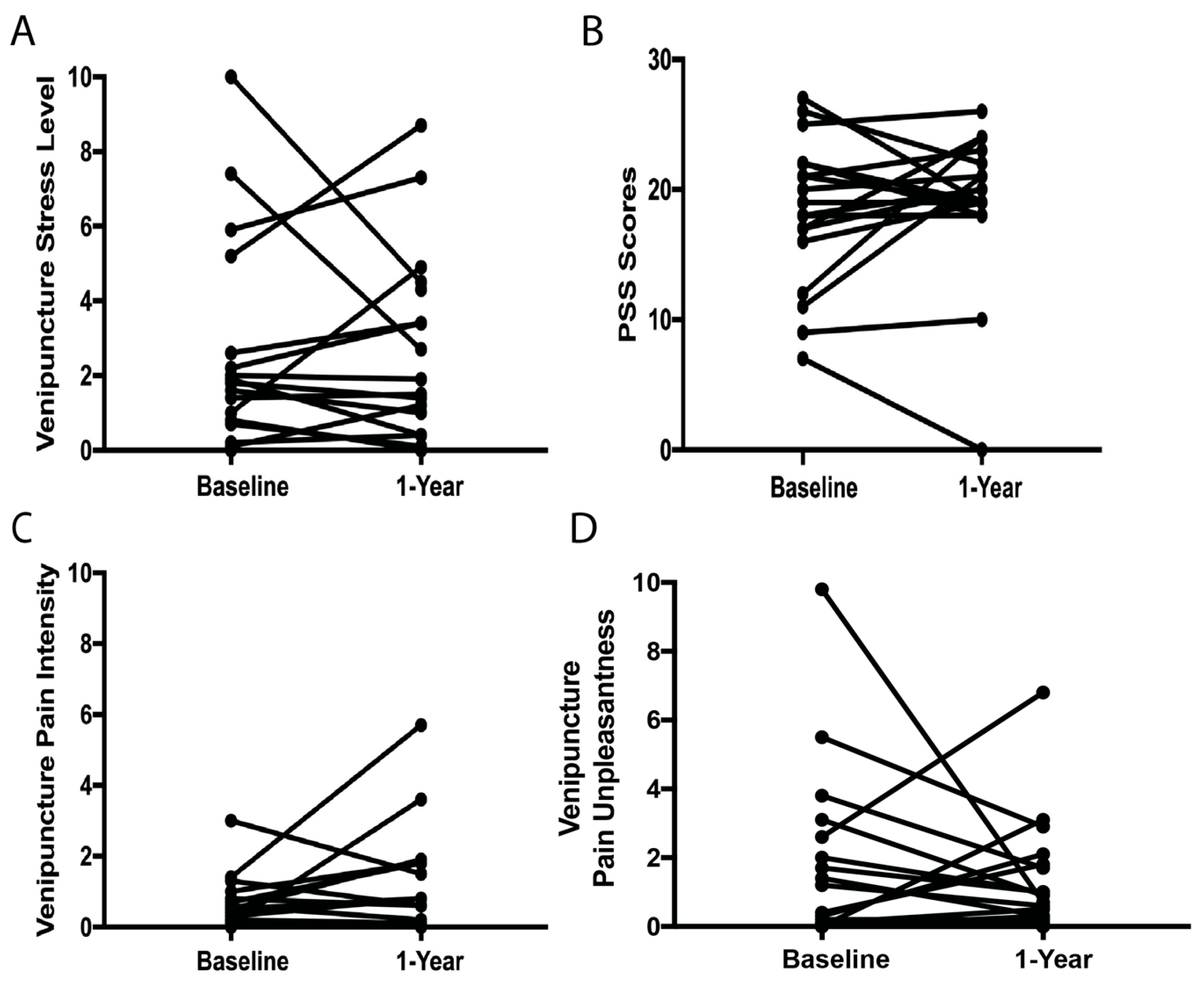
3.2. Relationships Between Stress and Pain at Baseline and 1-Year Follow-Up
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| VAS | Visual Analog Scale |
| PSS | Perceived Stress Scale |
| PDS | Pubertal Development Scale |
References
- Taddio, A.; McMurtry, C.M.; Logeman, C.; Gudzak, V.; de Boer, A.; Constantin, K.; Lee, S.; Moline, R.; Uleryk, E.; Chera, T.; et al. Prevalence of pain and fear as barriers to vaccination in children—Systematic review and meta-analysis. Vaccine 2022, 40, 7526–7537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLenon, J.; Rogers, M.A.M. The fear of needles: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Adv. Nurs. 2019, 75, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taddio, A.; Ipp, M.; Thivakaran, S.; Jamal, A.; Parikh, C.; Smart, S.; Sovran, J.; Stephens, D.; Katz, J. Survey of the prevalence of immunization non-compliance due to needle fears in children and adults. Vaccine 2012, 30, 4807–4812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, R.M.; Luhmann, J.; Zempsky, W.T. Clinical implications of unmanaged needle-insertion pain and distress in children. Pediatrics 2008, 122 (Suppl. S3), S130–S133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, G.B.; Boon, C.M.; van Linden van den Heuvell, G.F.; van de Wiel, H.B. The occurrence of high levels of acute behavioral distress in children and adolescents undergoing routine venipunctures. Pediatrics 1992, 90 Pt 1, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fradet, C.; McGrath, P.J.; Kay, J.; Adams, S.; Luke, B. A prospective survey of reactions to blood tests by children and adolescents. Pain 1990, 40, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loeffen, E.A.H.; Mulder, R.L.; Font-Gonzalez, A.; Leroy, P.; Dick, B.D.; Taddio, A.; Ljungman, G.; Jibb, L.A.; Tutelman, P.R.; Liossi, C.; et al. Reducing pain and distress related to needle procedures in children with cancer: A clinical practice guideline. Eur. J. Cancer 2020, 131, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, S.; Gianaros, P.J.; Manuck, S.B. A Stage Model of Stress and Disease. Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 2016, 11, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birnie, K.A.; Noel, M.; Chambers, C.T.; Uman, L.S.; Parker, J.A. Psychological interventions for needle-related procedural pain and distress in children and adolescents. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 10, Cd005179. [Google Scholar]
- Lunoe, M.M.; Bolin, A.E.; Drendel, A.L. An Evaluation of High Preprocedural Anxiety and Venipuncture Pain Experienced by Young Children. Pediatr. Emerg. Care 2021, 37, e621–e624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisogni, S.; Dini, C.; Olivini, N.; Ciofi, D.; Giusti, F.; Caprilli, S.; Gonzalez Lopez, J.R.; Festini, F. Perception of venipuncture pain in children suffering from chronic diseases. BMC Res. Notes 2014, 7, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMurtry, C.M.; Pillai Riddell, R.; Taddio, A.; Racine, N.; Asmundson, G.J.; Noel, M.; Chambers, C.T.; Shah, V. Far From “Just a Poke”: Common Painful Needle Procedures and the Development of Needle Fear. Clin. J. Pain 2015, 31 (Suppl. S10), S3–S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodenough, B.; Thomas, W.; Champion, G.D.; Perrott, D.; Taplin, J.E.; von Baeyer, C.L.; Ziegler, J.B. Unravelling age effects and sex differences in needle pain: Ratings of sensory intensity and unpleasantness of venipuncture pain by children and their parents. Pain 1999, 80, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodenough, B.; Kampel, L.; Champion, G.D.; Laubreaux, L.; Nicholas, M.K.; Ziegler, J.B.; McInerney, M. An investigation of the placebo effect and age-related factors in the report of needle pain from venipuncture in children. Pain 1997, 72, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de França Moreira, M.; Gamboa, O.L.; Pinho Oliveira, M.A. Association between severity of pain, perceived stress and vagally-mediated heart rate variability in women with endometriosis. Women Health 2021, 61, 937–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Booker, S.; Cardoso, J.; Cruz-Almeida, Y.; Sibille, K.T.; Terry, E.L.; Powell-Roach, K.L.; Riley, J.L., 3rd; Goodin, B.R.; Bartley, E.J.; Addison, A.S.; et al. Movement-evoked pain, physical function, and perceived stress: An observational study of ethnic/racial differences in aging non-Hispanic Blacks and non-Hispanic Whites with knee osteoarthritis. Exp. Gerontol. 2019, 124, 110622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edman, J.S.; Greeson, J.M.; Roberts, R.S.; Kaufman, A.B.; Abrams, D.I.; Dolor, R.J.; Wolever, R.Q. Perceived Stress in Patients with Common Gastrointestinal Disorders: Associations with Quality of Life, Symptoms and Disease Management. Explore 2017, 13, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takegami, N.; Akeda, K.; Yamada, J.; Nishimura, A.; Sudo, A. Association between low back pain and psychological stress response in a Japanese population-based study. J. Orthop. Sci. 2024, 29, 749–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, A.G.; Fischer-White, T.G.; Anderson, J.G.; Adelstein, K.E.; Murugesan, M.; Lewis, J.E.; Scott, M.M.; Gaykema, R.P.; Goehler, L.E. Stress, Inflammation and Pain: A Potential Role for Monocytes in Fibromyalgia-related Symptom Severity. Stress Health 2016, 32, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilder-Smith, C.H.; Song, G.; Yeoh, K.G.; Ho, K.Y. Activating endogenous visceral pain modulation: A comparison of heterotopic stimulation methods in healthy controls. Eur. J. Pain 2009, 13, 836–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Greenspan, J.D.; Ohrbach, R.; Fillingim, R.B.; Maixner, W.; Renn, C.L.; Johantgen, M.; Zhu, S.; Dorsey, S.G. Racial/ethnic differences in experimental pain sensitivity and associated factors—Cardiovascular responsiveness and psychological status. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0215534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, S.; Kamarck, T.; Mermelstein, R. A global measure of perceived stress. J. Health Soc. Behav. 1983, 24, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, C.M.; Kronfli, T.; Buenaver, L.F.; Smith, M.T.; Berna, C.; Haythornthwaite, J.A.; Edwards, R.R. Situational versus dispositional measurement of catastrophizing: Associations with pain responses in multiple samples. J. Pain 2010, 11, 443–453.e442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, R.R.; Campbell, C.M.; Fillingim, R.B. Catastrophizing and experimental pain sensitivity: Only in vivo reports of catastrophic cognitions correlate with pain responses. J. Pain 2005, 6, 338–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, K.E.; Thorn, B.E.; Ward, L.C. An evaluation of sex differences in psychological and physiological responses to experimentally-induced pain: A path analytic description. Pain 2004, 112, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granot, M.; Weissman-Fogel, I.; Crispel, Y.; Pud, D.; Granovsky, Y.; Sprecher, E.; Yarnitsky, D. Determinants of endogenous analgesia magnitude in a diffuse noxious inhibitory control (DNIC) paradigm: Do conditioning stimulus painfulness, gender and personality variables matter? Pain 2008, 136, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nahman-Averbuch, H.; Banerjee, G.; Brown, J.; McMichael, A.; Ben Abdallah, A.; Buday, S.; Baranski, T.; Haroutounian, S.; Barch, D.; Garwood, S.; et al. The role of puberty in experimental pain sensitivity in healthy adolescent girls. Pain Rep. 2025, 10, e1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, G.B.J.; McMichael, A.; Ben Abdallah, A.; Buday, S.; Baranski, T.; Haroutounian, S.; Barch, D.; AuBuchon, J.; Nahman-Averbuch, H. Androgens and experimental pain sensitivity in healthy adolescent girls. Pain 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Yosipovitch, G.; Tang, M.; Dawn, A.G.; Chen, M.; Goh, C.L.; Huak, Y.; Seng, L.F. Study of psychological stress, sebum production and acne vulgaris in adolescents. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2007, 87, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siqueira, L.; Diab, M.; Bodian, C.; Rolnitzky, L. Adolescents becoming smokers: The roles of stress and coping methods. J. Adolesc. Health 2000, 27, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Li, J.; Dai, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, S. Factor Structure of the 10-Item Perceived Stress Scale and Measurement Invariance Across Genders Among Chinese Adolescents. Front. Psychol. 2020, 11, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carskadon, M.A.; Acebo, C. A self-administered rating scale for pubertal development. J. Adolesc. Health 1993, 14, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koopman-Verhoeff, M.E.; Gredvig-Ardito, C.; Barker, D.H.; Saletin, J.M.; Carskadon, M.A. Classifying Pubertal Development Using Child and Parent Report: Comparing the Pubertal Development Scales to Tanner Staging. J. Adolesc. Health 2020, 66, 597–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LiaBraaten, B.M.; Linneman, N.; Czarnecki, M.L.; Davies, W.H.; Zhang, L.; Simpson, P.M.; Jastrowski Mano, K.E.; Weisman, S.J.; Hainsworth, K.R. Stress Numerical Rating Scale-11: Validation in Pediatric Inpatient and Outpatient Pain Settings. Pain Manag. Nurs. 2023, 24, e7–e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawker, G.A.; Mian, S.; Kendzerska, T.; French, M. Measures of adult pain: Visual Analog Scale for Pain (VAS Pain), Numeric Rating Scale for Pain (NRS Pain), McGill Pain Questionnaire (MPQ), Short-Form McGill Pain Questionnaire (SF-MPQ), Chronic Pain Grade Scale (CPGS), Short Form-36 Bodily Pain Scale (SF-36 BPS), and Measure of Intermittent and Constant Osteoarthritis Pain (ICOAP). Arthritis Care Res. 2011, 63 (Suppl. S11), S240–S252. [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher, E.J.; Bijur, P.E.; Latimer, C.; Silver, W. Reliability and validity of a visual analog scale for acute abdominal pain in the ED. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2002, 20, 287–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijur, P.E.; Silver, W.; Gallagher, E.J. Reliability of the visual analog scale for measurement of acute pain. Acad. Emerg. Med. 2001, 8, 1153–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghadir, A.H.; Anwer, S.; Iqbal, A.; Iqbal, Z.A. Test-retest reliability, validity, and minimum detectable change of visual analog, numerical rating, and verbal rating scales for measurement of osteoarthritic knee pain. J. Pain Res. 2018, 11, 851–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, D.D.; Bush, F.M.; Long, S.; Harkins, S.W. A comparison of pain measurement characteristics of mechanical visual analogue and simple numerical rating scales. Pain 1994, 56, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, D.D.; McGrath, P.A.; Rafii, A.; Buckingham, B. The validation of visual analogue scales as ratio scale measures for chronic and experimental pain. Pain 1983, 17, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myles, P.S.; Urquhart, N. The linearity of the visual analogue scale in patients with severe acute pain. Anaesth. Intensive Care 2005, 33, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, A.O.; Peri-Okonny, P.; Gosch, K.; Thomas, M.; Mena, C.; Hiatt, W.R.; Jones, P.G.; Provance, J.B.; Labrosciano, C.; Jelani, Q.U.; et al. Association of Perceived Stress Levels With Long-term Mortality in Patients With Peripheral Artery Disease. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e208741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, S.V.; Smolderen, K.G.; Buchanan, D.M.; Li, Y.; Spertus, J.A. Perceived stress in myocardial infarction: Long-term mortality and health status outcomes. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2012, 60, 1756–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sexton, K.A.; Walker, J.R.; Graff, L.A.; Bernstein, M.T.; Beatie, B.; Miller, N.; Sargent, M.; Targownik, L.E. Evidence of Bidirectional Associations Between Perceived Stress and Symptom Activity: A Prospective Longitudinal Investigation in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2017, 23, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endrighi, R.; Waters, A.J.; Gottlieb, S.S.; Harris, K.M.; Wawrzyniak, A.J.; Bekkouche, N.S.; Li, Y.; Kop, W.J.; Krantz, D.S. Psychological stress and short-term hospitalisations or death in patients with heart failure. Heart 2016, 102, 1820–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vierck, C.J.; Green, M.; Yezierski, R.P. Pain as a stressor: Effects of prior nociceptive stimulation on escape responding of rats to thermal stimulation. Eur. J. Pain 2010, 14, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannibal, K.E.; Bishop, M.D. Chronic stress, cortisol dysfunction, and pain: A psychoneuroendocrine rationale for stress management in pain rehabilitation. Phys. Ther. 2014, 94, 1816–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiton, R.L.; Greenspan, J.D. Sex differences in endogenous pain modulation by distracting and painful conditioning stimulation. Pain 2007, 132 (Suppl. S1), S134–S149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedén, L.; von Essen, L.; Ljungman, G. Children’s self-reports of fear and pain levels during needle procedures. Nurs. Open 2020, 7, 376–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, C.T.; Taddio, A.; Uman, L.S.; McMurtry, C.M. Psychological interventions for reducing pain and distress during routine childhood immunizations: A systematic review. Clin. Ther. 2009, 31 (Suppl. S2), S77–S103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, M.K.; Choi, M.Y. Effect of Distraction Intervention for Needle-Related Pain and Distress in Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 9159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lluesma-Vidal, M.; Carcelén González, R.; García-Garcés, L.; Sánchez-López, M.I.; Peyro, L.; Ruiz-Zaldibar, C. Effect of Virtual Reality on Pediatric Pain and Fear During Procedures Involving Needles: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JMIR Serious Games 2022, 10, e35008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suleman, S.K.; Yahya, N.; Nilsson, S.; Enskär, K. Comparative efficacy of pharmacological and non-pharmacological interventions for mitigating pain and anxiety associated with venipuncture: A randomised controlled trial. BMJ Paediatr. Open 2024, 8, e002881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, K.M.; Gaffey, A.E.; Schwartz, J.E.; Krantz, D.S.; Burg, M.M. The Perceived Stress Scale as a Measure of Stress: Decomposing Score Variance in Longitudinal Behavioral Medicine Studies. Ann. Behav. Med. 2023, 57, 846–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahman-Averbuch, H.; Li, R.; Boerner, K.E.; Lewis, C.; Garwood, S.; Palermo, T.M.; Jordan, A. Alterations in pain during adolescence and puberty. Trends Neurosci. 2023, 46, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blankenburg, M.; Boekens, H.; Hechler, T.; Maier, C.; Krumova, E.; Scherens, A.; Magerl, W.; Aksu, F.; Zernikow, B. Reference values for quantitative sensory testing in children and adolescents: Developmental and gender differences of somatosensory perception. Pain 2010, 149, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blankenburg, M.; Meyer, D.; Hirschfeld, G.; Kraemer, N.; Hechler, T.; Aksu, F.; Krumova, E.K.; Magerl, W.; Maier, C.; Zernikow, B. Developmental and sex differences in somatosensory perception--a systematic comparison of 7- versus 14-year-olds using quantitative sensory testing. Pain 2011, 152, 2625–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badali, M.; Pillai, R.; Craig, K.; Giesbrecht, K.; Chambers, C. Accuracy of children’s and parents’ memory for a novel painful experience. Pain Res. Manag. 2000, 5, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlova, M.; Pirwani, A.F.; Thomas, J.; Birnie, K.A.; Wan, M.; Chambers, C.T.; Noel, M. A Randomized Controlled Trial of a Parent-Led Memory-Reframing Intervention to Reduce Distress and Pain Associated with Vaccine Injections in Young Children. Children 2023, 10, 1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisman, S.J.; Bernstein, B.; Schechter, N.L. Consequences of inadequate analgesia during painful procedures in children. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 1998, 152, 147–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.; Tran, N.K.; Momper, J.D.; Green, D.J.; Burckart, G.J. Pediatric and Adult Placebo Response Rates in Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trials Submitted to the US Food and Drug Administration 2012–2020. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2022, 62, 970–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auerbach, M.; Tunik, M.; Mojica, M. A randomized, double-blind controlled study of jet lidocaine compared to jet placebo for pain relief in children undergoing needle insertion in the emergency department. Acad. Emerg. Med. 2009, 16, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Estimate | SE | T Ratio | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline Venipuncture Pain Intensity (n = 40) | ||||
| Specific stress | 0.185 | 0.046 | 4.00 | <0.001 |
| General stress | 0.005 | 0.029 | 0.17 | 0.864 |
| Agent [both] | −0.234 | 0.238 | −0.98 | 0.332 |
| Agent [cream] | 0.598 | 0.394 | 1.52 | 0.138 |
| Baseline Venipuncture Pain Unpleasantness (n = 40) | ||||
| Specific stress | 0.378 | 0.116 | 3.27 | 0.002 |
| General stress | −0.016 | 0.074 | −0.21 | 0.831 |
| Year 1 General Stress | Year 1 Specific Stress | Year 1 Venipuncture Pain Intensity | Year 1 Venipuncture Pain Unpleasantness | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline general stress (n = 19) | R2 = 0.322, p = 0.011 | R2 = 0.026, p = 0.508 | R2 = 0.082, p = 0.234 | R2 = 0.142, p = 0.112 |
| Baseline specific stress (n = 17) | R2 = 0.076, p = 0.284 | R2 = 0.389, p = 0.007 | R2 = 0.002, p = 0.853 | R2 = 0.007, p = 0.747 |
| Baseline venipuncture pain intensity (n = 19) | R2 = 0.025, p = 0.517 | R2 = 0.005, p = 0.763 | R2 = 0.133, p = 0.124 | R2 = 0.133, p = 0.125 |
| Baseline venipuncture pain unpleasantness (n = 19) | R2 = 0.043, p = 0.397 | R2 = 0.095, p = 0.200 | R2 = 0.092, p = 0.206 | R2 = 0.043, p = 0.395 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brown, J.; Ademuyiwa, Z.; Wu-Chen, E.; Nahman-Averbuch, H. The Role of Stress in Venipuncture Pain in Adolescents: Secondary Analysis of a Prospective Observational Study. Children 2025, 12, 776. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12060776
Brown J, Ademuyiwa Z, Wu-Chen E, Nahman-Averbuch H. The Role of Stress in Venipuncture Pain in Adolescents: Secondary Analysis of a Prospective Observational Study. Children. 2025; 12(6):776. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12060776
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrown, Joel, Zoe Ademuyiwa, Elizabeth Wu-Chen, and Hadas Nahman-Averbuch. 2025. "The Role of Stress in Venipuncture Pain in Adolescents: Secondary Analysis of a Prospective Observational Study" Children 12, no. 6: 776. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12060776
APA StyleBrown, J., Ademuyiwa, Z., Wu-Chen, E., & Nahman-Averbuch, H. (2025). The Role of Stress in Venipuncture Pain in Adolescents: Secondary Analysis of a Prospective Observational Study. Children, 12(6), 776. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12060776





