Macrophage Activation Syndrome in Kawasaki Disease: Insights from a Systematic Literature Review on Diagnosis, Clinical Features, and Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
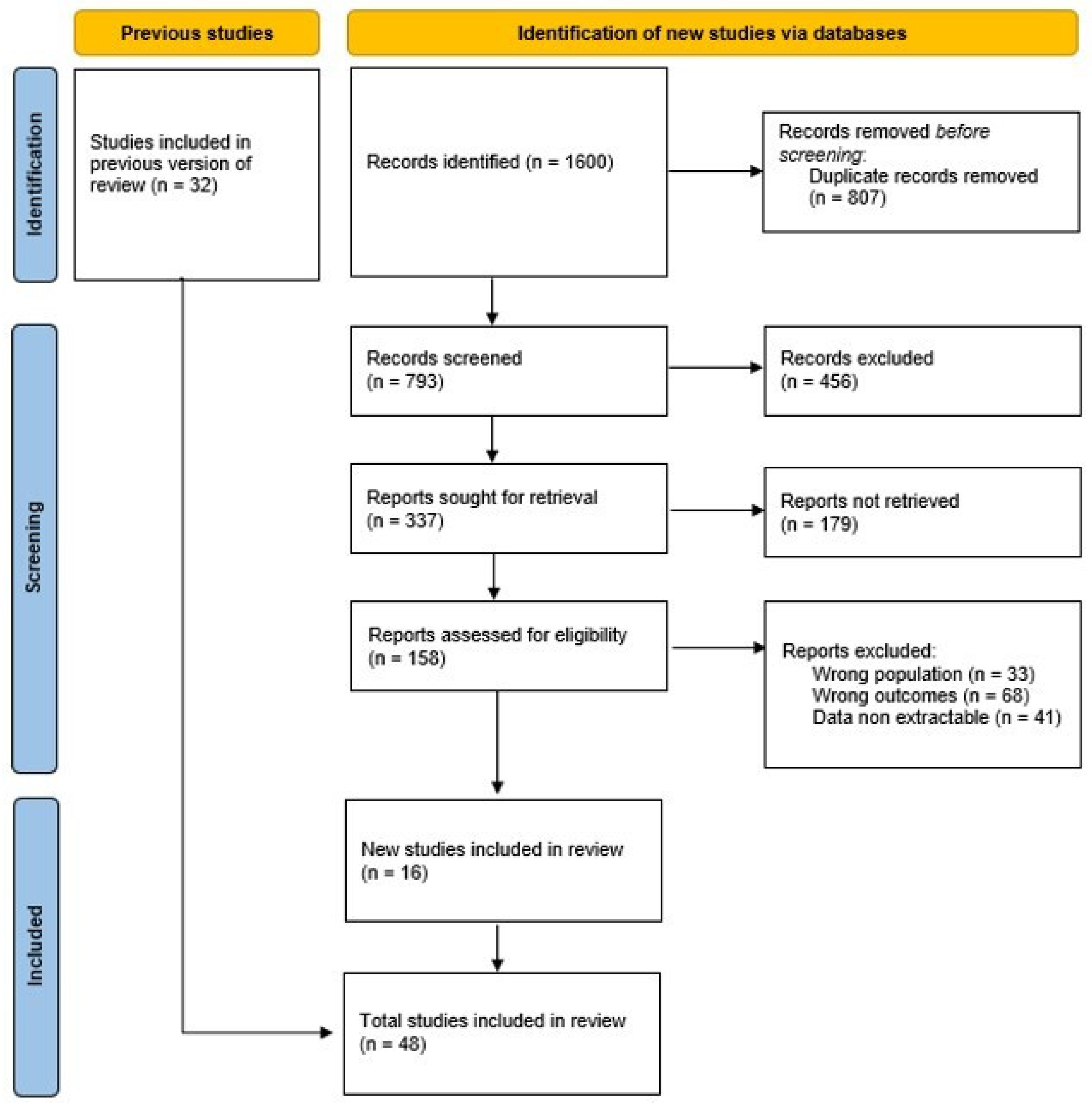
2. Material and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jone, P.-N.; Tremoulet, A.; Choueiter, N.; Dominguez, S.R.; Harahsheh, A.S.; Mitani, Y.; Zimmerman, M.; Lin, M.T.; Friedman, K.G.; American Heart Association Rheumatic Fever, Endocarditis, and Kawasaki Disease Committee of the Council on Lifelong Congenital Heart Disease and Heart Health in the Young; et al. Update on Diagnosis and Management of Kawasaki Disease: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2024, 150, e481–e500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.S. Predictors and management of intravenous immunoglobulin-resistant Kawasaki disease. Korean J. Pediatr. 2019, 62, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.B.; Lee, S.Y. Macrophage activation syndrome in children with Kawasaki disease: Diagnostic and therapeutic approaches. World J. Pediatr. 2020, 16, 566–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizuta, M.; Shimizu, M.; Irabu, H.; Usami, M.; Inoue, N.; Nakagishi, Y.; Wada, T.; Yachie, A. Comparison of serum cytokine profiles in macrophage activation syndrome complicating different background rheumatic diseases in children. Rheumatology 2021, 60, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strippoli, R.; Caiello, I.; De Benedetti, F. Reaching the threshold: A multilayer pathogenesis of macrophage activation syndrome. J. Rheumatol. 2013, 40, 761–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, K.M.; Linghu, B.; Szustakowski, J.D.; Husami, A.; Yang, F.; Zhang, K.; Filipovich, A.H.; Fall, N.; Harley, J.B.; Nirmala, N.R.; et al. Whole-Exome Sequencing Reveals Overlap Between Macrophage Activation Syndrome in Systemic Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis and Familial Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014, 66, 3486–3495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigrovic, P.A. Macrophage Activation Syndrome. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravelli, A.; Grom, A.A.; Behrens, E.M.; Cron, R.Q. Macrophage activation syndrome as part of systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis: Diagnosis, genetics, pathophysiology and treatment. Genes. Immun. 2012, 13, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Pavón, S.; Yamazaki-Nakashimada, M.A.; Báez, M.; Borjas-Aguilar, K.L.; Murata, C. Kawasaki Disease Complicated with Macrophage Activation Syndrome: A Systematic Review. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2017, 39, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Gong, F.; Zhu, W.; Fu, S.; Zhang, Q. Macrophage activation syndrome in Kawasaki Disease: More common than we thought? Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2015, 44, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, U.Y.; Han, S.B.; Lee, S.Y.; Jeong, D.C. Should refractory Kawasaki disease be considered occult macrophage activation syndrome? Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2017, 46, e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Shang, S.; Zhang, C.; Liu, T.; Yang, Z.; Tang, Y. Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis at Initiation of Kawasaki Disease and Their Differential Diagnosis. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2010, 27, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henter, J.I.; Horne, A.C.; Aricó, M.; Egeler, R.M.; Filipovich, A.H.; Imashuku, S.; Ladisch, S.; McClain, K.; Webb, D.; Winiarski, J.; et al. HLH-2004: Diagnostic and therapeutic guidelines for hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2007, 48, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cron, R.Q.; Davi, S.; Minoia, F.; Ravelli, A. Clinical features and correct diagnosis of macrophage activation syndrome. Expert. Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2015, 11, 1043–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravelli, A.; Minoia, F.; Davì, S.; Horne, A.; Bovis, F.; Pistorio, A.; Aricò, M.; Avcin, T.; Behrens, E.M.; De Benedetti, F.; et al. 2016 Classification Criteria for Macrophage Activation Syndrome Complicating Systemic Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis: A European League Against Rheumatism/American College of Rheumatology/Paediatric Rheumatology International Trials Organisation Collaborative Initiative. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016, 68, 566–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.B.; Lee, S.Y.; Jeong, D.C.; Kang, J.H. Should 2016 Criteria for Macrophage Activation Syndrome be applied in children with Kawasaki disease, as well as with systemic-onset juvenile idiopathic arthritis? Ann Rheum Dis. 2016, 75, e44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, C.; She, X.; Chen, J. Kawasaki disease complicated with shock syndrome, macrophage activation syndrome, and acute abdomen in children: Two case reports. Front. Pediatr. 2023, 11, 1152242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattalini, M.; Della Paolera, S.; Zunica, F.; Bracaglia, C.; Giangreco, M.; Verdoni, L.; Meini, A.; Sottile, R.; Caorsi, R.; Zuccotti, G.; et al. Defining Kawasaki disease and pediatric inflammatory multisystem syndrome-temporally associated to SARS-CoV-2 infection during SARS-CoV-2 epidemic in Italy: Results from a national, multicenter survey. Pediatr. Rheumatol. 2021, 19, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latino, G.A.; Manlhiot, C.; Yeung, R.S.; Chahal, N.; McCrindle, B.W. Macrophage Activation Syndrome in the Acute Phase of Kawasaki Disease. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2010, 32, 527–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhee, S.; Kim, D.; Cho, K.; Rhim, J.W.; Lee, S.Y.; Jeong, D.C. Under-Recognized Macrophage Activation Syndrome in Refractory Kawasaki Disease: A Wolf in Sheep’s Clothing. Children 2022, 9, 1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafferman, A.; Birmingham, J.D.; Cron, R.Q. High dose anakinra for treatment of severe neonatal Kawasaki disease: A case report. Pediatr. Rheumatol. 2014, 12, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lind-Holst, M.; Hartling, U.B.; Christensen, A.E. High-dose anakinra as treatment for macrophage activation syndrome caused by refractory Kawasaki disease in an infant. BMJ Case Rep. 2019, 12, e229708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilania, R.K.; Jindal, A.K.; Johnson, N.; Prithvi, A.; Vignesh, P.; Suri, D.; Rawat, A.; Gupta, A.; Singh, S. Macrophage activation syndrome in children with Kawasaki disease: An experience from a tertiary care hospital in northwest India. Rheumatology 2021, 60, 3413–3419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Liu, Y.; Yan, W.; Zhang, T.; Wang, P.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, P.; Fan, Z.; Yu, H. Single center clinical analysis of macrophage activation syndrome complicating juvenile rheumatic diseases. Pediatr. Rheumatol. 2024, 22, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.Y.; Xiao, M.; Zhou, D.; Yan, F.; Zhang, Y. Platelet and ferritin as early predictive factors for the development of macrophage activation syndrome in children with Kawasaki disease: A retrospective case-control study. Front. Pediatr. 2023, 11, 1088525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maheshwari, A.; Gulati, S.; Kakkar, V.; Kavya, D.R.; Aggarwal, M.; Basu, S.; Mahto, D. Clinical and Laboratory Profile of Macrophage Activation Syndrome in Kawasaki Disease: A Single Centre Cross-Sectional Study. Indian Pediatr. 2024, 61, 723–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, S.; Liu, M.; Wang, D.; Xu, C.; Zhang, L. A Case of Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis following Refractory Kawasaki Disease. Klin. Padiatr. 2020; Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.R.; Kwon, Y.H.; Yoo, E.S.; Ryu, K.H.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, H.M.; Lee, Y.H. Clinical characteristics of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis following kawasaki disease: Differentiation from recurrent kawasaki disease. Blood Res. 2013, 48, 254–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, P.; Luo, Y.; Liu, X.; Xu, J.; Liu, C. Kawasaki Disease Complicated with Macrophage Activation Syndrome: Case Reports and Literature Review. Front. Pediatr. 2019, 7, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roh, D.E.; Kwon, J.E.; Choi, H.J.; Kim, Y.H. Importance of serum ferritin level for early diagnosis and differentiation in patients with Kawasaki disease with macrophage activation syndrome. Children 2021, 8, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguz, M.M.; Sahin, G.; Altinel Acoglu, E.; Polat, E.; Yucel, H.; Oztek Celebi, F.Z.; Unsal, H.; Akcaboy, M.; Sari, E.; Senel, S. Secondary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in pediatric patients: A single center experience and factors that influenced patient prognosis. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 36, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.K.; Kim, H.G.; Cho, S.J.; Hong, Y.M.; Sohn, S.; Yoo, E.S.; Chung, W.S.; Ryu, K.H. Clinical characteristics of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis related to Kawasaki disease. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2011, 28, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechtel, A.S.; Joyce, M. A Case of Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis and Kawasaki Disease: Concurrent or Overlapping Diagnoses? J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2017, 40, e32–e33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, D.; Niyogi, P. Macrophage Activation Syndrome in Kawasaki Disease. Indian Pediatr. 2014, 51, 148–149. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, L.X.; Zhu, Y.; Sun, L.; Ma, H.H.; Yang, S.R.; Zeng, H.S.; Xiao, J.H.; Yu, H.G.; Guo, L.; Xu, Y.P.; et al. Clinical and laboratory features, treatment, and outcomes of macrophage activation syndrome in 80 children: A multi-center study in China. World J. Pediatr. 2020, 16, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera-Rodriguez, L.; Pardo-Díaz, E.; Moreno-Espinosa, S.; Scheffler-Mendoza, S.; Ruiz-Ontiveros, M.A.; Garrido-García, L.M.; Iglesias-Amaya, A.; Yamazaki-Nakashimada, M.A. Use of Infliximab in the Treatment of Macrophage Activation Syndrome Complicating Kawasaki Disease. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 43, e448–e451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilania, R.K.; Arora, K.; Gupta, A.; Vignesh, P.; Suri, D.; Singh, S. A 5-year-old boy with Kawasaki disease shock syndrome, myocarditis and macrophage activation syndrome. J. Paediatr. Child. Health 2021, 57, 1312–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Shi, L.; Deng, Y.J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.W. Kawasaki disease shock syndrome complicated with macrophage activation syndrome in a 5-month old boy. Medicine 2019, 98, e14203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bossi, G.; Codazzi, A.C.; Vinci, F.; Clerici, E.; Regalbuto, C.; Crapanzano, C.; Veraldi, D.; Moiraghi, A.; Marseglia, G.L. Efficacy of Anakinra on Multiple Coronary Arteries Aneurysms in an Infant with Recurrent Kawasaki Disease, Complicated by Macrophage Activation Syndrome. Children 2022, 9, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendricks, M.; Pillay, S.; Davidson, A.; De Decker, R.; Lawrenson, J. Kawasaki disease preceding haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: Challenges for developing world practitioners. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2010, 54, 1023–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, C.; McCarthy, P.; van Hoff, J.; Porter, G., Jr. Kawasaki disease associated with reactive hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2008, 27, 1116–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doğan, V.; Karaaslan, E.; Özer, S.; Gümüşer, R.; Yılmaz, R. Hemophagocytosis in the acute phase of fatal Kawasaki disease in a 4 month-old girl. Balk. Med. J. 2016, 33, 470–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, N.; Sankar, J. Macrophage activation syndrome: A rare complication of incomplete Kawasaki disease. Ann. Trop. Paediatr. 2010, 30, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.F.; Wang, J.J.; Wu, Y.; Liu, H.H.; Hu, P. Complete atrioventricular block and macrophage activation syndrome simultaneously occurred in a 6-year-old chinese girl with kawasaki disease. J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2020, 26, e324–e325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avčin, T.; Tse, S.M.L.; Schneider, R.; Ngan, B.; Silverman, E.D. Macrophage activation syndrome as the presenting manifestation of rheumatic diseases in childhood. J. Pediatr. 2006, 148, 683–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- al-Eid, W.; al-Jefri, A.; Bahabri, S.; al-Mayouf, S. Hemophagocytosis complicating Kawasaki disease. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2000, 17, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mousavi, M.S.; Assari, R.; Tahghighi, F.; Eshaghi, H.; Ziaee, V. Prolonged fever and intravenous immunoglobulin resistance in kawasaki disease: Should macrophage activation syndrome be considered? Iran. J. Pediatr. 2019, 29, e69170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alalawi, O.E.; Al-Khalifa, S.M. Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) with History of Kawasaki Disease (KD). Bahrain Med. Bull. 2020, 42, 76–78. [Google Scholar]
- Rajagopala, L.; Jagoda, J.; Gunatilaka, M.L. P163 The cytokine horror: Kawasaki disease shock syndrome complicated with macrophage activation syndrome. Rheumatology 2022, 61 (Suppl. S1), keac133.162. [Google Scholar]
- Corinaldesi, E.; Fabi, M.; Scalabrini, I.; Praticò, E.R.; Andreozzi, L.; Torcetta, F.; Lanari, M. Kawasaki Disease Complicated with Macrophage Activation Syndrome: The Importance of Prompt Diagnosis and Treatment–Three Case Reports. Rheumato 2023, 3, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jinkawa, A.; Shimizu, M.; Nishida, K.; Kaneko, S.; Usami, M.; Sakumura, N.; Irabu, H.; Takakuwa, M.; Inoue, N.; Mizuta, M.; et al. Cytokine profile of macrophage activation syndrome associated with Kawasaki disease. Cytokine 2019, 119, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, A.A.; Sadeghi, P.; Torshizi, M.M. Macrophage Activation Syndrome as the First Impression of Kawasaki Disease; A Case Report. Int. J. Pediatr. 2019, 7, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Yang, Z. Severe Recurrent Fever Episodes with Clinical Diagnosis of Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis, Incomplete Kawasaki Disease and Systemic-Onset Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis: A Case Report and Literature Review. Front. Pediatr. 2020, 8, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, K.; Takahashi, K.; Fujiwara, S.; Maruyama, T.; Obinata, K. Kawasaki Disease Followed by Haemophagocytic Syndrome. Eur. J. Pediatr. 1998, 157, 610–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohga, S.; Ooshima, A.; Fukushige, J.; Ueda, K. Histiocytic Haemophagocytosis in a Patient with Kawasaki Disease: Changes in the Hypercytokinaemic State. Eur. J. Pediatr. 1995, 154, 539–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palazzi, D.L.; McClain, K.L.; Kaplan, S.L. Hemophagocytic syndrome after Kawasaki disease. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2003, 22, 663–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonini, G.; Pagnini, I.; Innocenti, L.; Calabri, G.B.; De Martino, M.; Cimaz, R. Macrophage activation syndrome/Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis and Kawasaki disease. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2010, 55, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Titze, U.; Janka, G.; Schneider, E.M.; Prall, F.; Haffner, D.; Classen, C.F. Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis and Kawasaki disease: Combined manifestation and differential diagnosis. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2009, 53, 493–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, M.; Hoshina, T. Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis prior to the diagnosis of Kawasaki disease. Indian Pediatr. 2015, 52, 78. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bose, K.; Saha, S.; Saha, P.; Mondal, P. Macrophage activation syndrome: A potentially fatal complication of kawasaki disease. Arch. Rheumatol. 2015, 30, 178–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, S.; Yoshimura, K.; Tanabe, Y.; Kimata, T.; Noda, Y.; Kawasaki, H.; Kaneko, K. A Child with Epstein-Barr Virus-Associated Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis Complicated by Coronary Artery Lesion Mimicking Kawasaki Disease Clinical and Laboratory Observations. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2013, 35, e317–e319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sztajnbok, F.; Fonseca, A.R.; Campos, L.R.; Lino, K.; Rodrigues, M.C.F.; Silva, R.M.; de Almeida, R.G.; Perazzio, S.F.; Carvalho, M.F.F. Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis and macrophage activation syndrome: Two rare sides of the same devastating coin. Adv. Rheumatol. 2024, 64, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makino, N.; Nakamura, Y.; Yashiro, M.; Kosami, K.; Matsubara, Y.; Ae, R.; Aoyama, Y.; Yanagawa, H. Nationwide epidemiologic survey of Kawasaki disease in Japan, 2015–2016. Pediatr. Int. 2019, 61, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulloh, R.M.R.; Mayon-White, R.; Harnden, A.; Ramanan, A.V.; Tizard, E.J.; Shingadia, D.; Michie, C.A.; Lynn, R.M.; Levin, M.; Franklin, O.D.; et al. Kawasaki disease: A prospective population survey in the UK and Ireland from 2013 to 2015. Arch. Dis. Child. 2019, 104, 640–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tacke, C.E.; Breunis, W.B.; Pereira, R.R.; Breur, J.M.; Kuipers, I.M.; Kuijpers, T.W. Five years of Kawasaki disease in the Netherlands: A national surveillance study. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2014, 33, 793–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakob, A.; Whelan, J.; Kordecki, M.; Berner, R.; Stiller, B.; Arnold, R.; von Kries, R.; Neumann, E.; Roubinis, N.; Robert, M.; et al. Kawasaki Disease in Germany: A Prospective, Population-based Study Adjusted for Underreporting. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2016, 35, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corinaldesi, E.; Pavan, V.; Andreozzi, L.; Fabi, M.; Selvini, A.; Frabboni, I.; Lanzoni, P.; Paccagnella, T.; Lanari, M. Environmental Factors and Kawasaki Disease Onset in Emilia-Romagna, Italy. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, F.F.; Laranjo, S.; Mota Carmo, M.; Brito, M.J.; Cruz Ferreira, R. Twelve Years of Kawasaki Disease in Portugal: Epidemiology in Hospitalized Children. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2017, 36, 364–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matteritano, A.; David, G.; Bagnato, C.; Beninati, A.; Frisina, C.; Iaria, G.; Bagnato, A. Cascio Haemophagocytic syndrome in rheumatic patients. A systematic review. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2012, 16, 1414–1424. [Google Scholar]
- Porritt, R.A.; Markman, J.L.; Maruyama, D.; Kocaturk, B.; Chen, S.; Lehman, T.J.A.; Lee, Y.; Fishbein, M.C.; Noval Rivas, M.; Arditi, M. Interleukin-1 Beta-Mediated Sex Differences in Kawasaki Disease Vasculitis Development and Response to Treatment. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2020, 40, 802–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, H.; Sugimura, T.; Akagi, T.; Sato, N.; Hashino, K.; Maeno, Y.; Kazue, T.; Eto, G.; Yamakawa, R. Long-term consequences of Kawasaki disease. A 10- to 21-year follow-up study of 594 patients. Circulation 1996, 94, 1379–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogata, S.; Tremoulet, A.H.; Sato, Y.; Ueda, K.; Shimizu, C.; Sun, X.; Jain, S.; Silverstein, L.; Baker, A.L.; Tanaka, N.; et al. Coronary artery outcomes among children with Kawasaki disease in the United States and Japan. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 168, 3825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miselli, F.; Mastrolia, M.V.; Simonini, G.; Trapani, S.; Calabri, G.B. Splenomegaly in Kawasaki Disease: A Pitfall in Diagnosis. J. Pediatr. 2023, 257, 113359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.W.; Kim, S.H. Clinical aspects of splenomegaly as a possible predictive factor of coronary artery changes in Kawasaki disease. Cardiol. Young 2019, 29, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tizard, E.J. Complications of Kawasaki disease. Curr. Paediatr. 2005, 15, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, H.; Waddington, C.; Geddes, J.; Newburger, J.W.; Burgner, D. Facial nerve palsy complicating Kawasaki disease. Pediatrics 2008, 122, e783–e785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zhou, K.; Hua, Y.; Wu, M.; Liu, L.; Shao, S.; Wang, C. Neurological involvement in Kawasaki disease: A retrospective study. Pediatr. Rheumatol. Online J. 2020, 18, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minoia, F.; Davì, S.; Horne, A.; Demirkaya, E.; Bovis, F.; Li, C.; Lehmberg, K.; Weitzman, S.; Insalaco, A.; Wouters, C.; et al. Clinical features, treatment, and outcome of macrophage activation syndrome complicating systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis: A multinational, multicenter study of 362 patients. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014, 66, 3160–3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakoory, B.; Geerlinks, A.; Wilejto, M.; Kernan, K.; Hines, M.; Romano, M.; Piskin, D.; Ravelli, A.; Sinha, R.; Aletaha, D.; et al. The 2022 EULAR/ACR Points to Consider at the Early Stages of Diagnosis and Management of Suspected Haemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis/Macrophage Activation Syndrome (HLH/MAS). Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023, 75, 1714–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldo, F.; Erkens, R.G.A.; Mizuta, M.; Rogani, G.; Lucioni, F.; Bracaglia, C.; Foell, D.; Gattorno, M.; Jelusic, M.; Anton, J.; et al. Current treatment in macrophage activation syndrome worldwide: A systematic literature review to inform the Metaphor project. Rheumatology 2025, 64, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gietka, P.; Książyk, J.B.; Machaczka, M.; Buda, P. The influence of various therapeutic regimens on early clinical and laboratory response and outcome of children with secondary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Arch. Med. Sci. 2016, 14, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamada, H.; Suzuki, H.; Onouchi, Y.; Ebata, R.; Terai, M.; Fuse, S.; Okajima, Y.; Kurotobi, S.; Hirai, K.; Soga, T.; et al. Efficacy of primary treatment with immunoglobulin plus ciclosporin for prevention of coronary artery abnormalities in patients with Kawasaki disease predicted to be at increased risk of non-response to intravenous immunoglobulin (KAICA): A randomised controlled, open-label, blinded-endpoints, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2019, 393, 1128–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, P.; Cron, R.Q.; Hartwell, J.; Manson, J.J.; Tattersall, R.S. Silencing the cytokine storm: The use of intravenous anakinra in haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis or macrophage activation syndrome. Lancet Rheumatol. 2020, 2, e358–e367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koizumi, K.; Hoshiai, M.; Katsumata, N.; Toda, T.; Kise, H.; Hasebe, Y.; Kono, Y.; Sunaga, Y.; Yoshizawa, M.; Watanabe, A.; et al. Infliximab regulates monocytes and regulatory T cells in Kawasaki disease. Pediatr. Int. 2018, 60, 796–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, Y.; Liu, R.; Zhou, Z.X.; Shi, X.D.; Ding, Y.C.; Li, J.G. Ruxolitinib treatment permits lower cumulative glucocorticoid dosing in children with secondary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Pediatr. Rheumatol. 2021, 19, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanagawa, H.; Nakamura, Y.; Yashiro, M.; Ojima, T.; Tanihara, S.; Oki, I.; Zhang, T. Results of the Nationwide Epidemiologic Survey of Kawasaki Disease in 1995 and 1996 in Japan. 1998. Available online: http://www.pediatrics.org/cgi/content/full/ (accessed on 10 December 2024).
- Nakamura, Y.; Aso, E.; Yashiro, M.; Uehara, R.; Watanabe, M.; Oki, I.; Yanagawa, H. Mortality Among Persons with a History of Kawasaki Disease in Japan. Circ. J. 2008, 72, 134–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.E.; Kwak, Y.; Huh, J.W.; Yoo, E.S.; Ryu, K.H.; Sohn, S.; Hong, Y.M. Differentiation between incomplete Kawasaki disease and secondary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis following Kawasaki disease using N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide. Korean J. Pediatr. 2018, 61, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Age | 5.2 y (Mean) 4 y (Median) 0.13–17 y (Range) |
| Sex | Males 116 (65.9%) Females 60 (34.1%) |
| Type of KD | Complete 87/139 (62.6%) Incomplete 50/139 (36%) Atypical 2/139 (1.4%) |
| Fever | 176/176 (100%) |
| Splenomegaly | 87/176 (49.4%) |
| Hepatomegaly | 51/115 (44.3%) |
| Cardiac involvement | 59/159 (37.1%) |
| CNS involvement | 27/115 (23.5%) |
| Respiratory distress | 22/115 (19.1%) |
| Bleeding | 15/115 (13%) |
| Renal involvement | 11/115 (9.6%) |
| BCG scar redness | 3/115 (2.6%) |
| Laboratory Data | N. Patients | Mean | Median | Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 136 | 9.16 | 9.4 | 4.5–9.9 |
| Leucocyte (×109/L) | 120 | 11.598 | 8640 | 100–38,300 |
| Neutrophil count (×109/L) | 63 | 6318 | 2236 | 96–33,900 |
| Platelet count (×106/L) | 149 | 272,542 | 88,000 | 2800–1,213,000 |
| ESR (mm/h) | 94 | 41.2 | 42 | 2–110 |
| CRP (mg/dL) | 111 | 10.78 | 10.6 | 0.4–32.48 |
| AST (U/L) | 115 | 329.2 | 186 | 17–1468 |
| ALT (U/L) | 110 | 249.8 | 143 | 10–1099 |
| LDH (U/L) | 82 | 1562.7 | 1190 | 205–4487 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 75 | 2.87 | 2.8 | 2.13–3.7 |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 160 | 259.7 | 247.5 | 39–956 |
| Fibrinogen (mg/dL) | 148 | 194.4 | 175 | 28–678 |
| Ferritin (ng/mL) | 170 | 9468.3 | 2376 | 283–121,527 |
| Therapy | N. Patients |
|---|---|
| IVIG | 174/176 (98.8%) |
| Additional doses of IVIG | 63/174 (36.2%) |
| Corticosteroids | 144/174 (82.8%) |
| Cyclosporine A | 50/174 (28.7%) |
| Etoposide | 35/174 (20.1%) |
| Cyclophosphamide | 1/174 (0.6%) |
| Methotrexate | 1/174 (0.6%) |
| Anakinra | 6/174 (3.4%) |
| Infliximab | 18/174 (10.3%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Inguscio, G.; Romano, S.; Mastrolia, M.V.; Simonini, G.; Giani, T. Macrophage Activation Syndrome in Kawasaki Disease: Insights from a Systematic Literature Review on Diagnosis, Clinical Features, and Treatment. Children 2025, 12, 349. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12030349
Inguscio G, Romano S, Mastrolia MV, Simonini G, Giani T. Macrophage Activation Syndrome in Kawasaki Disease: Insights from a Systematic Literature Review on Diagnosis, Clinical Features, and Treatment. Children. 2025; 12(3):349. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12030349
Chicago/Turabian StyleInguscio, Giulia, Stefano Romano, Maria Vincenza Mastrolia, Gabriele Simonini, and Teresa Giani. 2025. "Macrophage Activation Syndrome in Kawasaki Disease: Insights from a Systematic Literature Review on Diagnosis, Clinical Features, and Treatment" Children 12, no. 3: 349. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12030349
APA StyleInguscio, G., Romano, S., Mastrolia, M. V., Simonini, G., & Giani, T. (2025). Macrophage Activation Syndrome in Kawasaki Disease: Insights from a Systematic Literature Review on Diagnosis, Clinical Features, and Treatment. Children, 12(3), 349. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12030349






