The Significance of Elevated sST2 in Children with Kawasaki Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. sST2 Measurement
2.3. Clinical and Laboratory Data Collection
2.4. Imaging Data
3. Definitions and Diagnostic Criteria
3.1. Inclusion Criteria
3.2. Exclusion Criteria
- Duration of fever exceeded 10 days at the time of hospital admission;
- sST2 testing was not performed, as measurements were only available on working days;
- Administration of IVIG or corticosteroids within one month prior to sST2 testing.
3.3. Diagnostic Criteria for Myocardial Damage (MD)
3.4. Patient Groups
- Myocardial Damage (MD)
- 2.
- Coronary Artery Lesions (CAL)
- 3.
- Multi-Organ Damage (MOD)
- 4.
- IVIG-Resistant KD (IVIG-R KD)
4. Statistical Analysis
Ethical Approval
5. Results
5.1. The Age and Gender Distribution of Children with KD
5.2. Comparison of sST2 Levels Among Different Groups
5.3. Comparison of Other Indicators Among Different Groups
5.4. Correlation Analysis Between sST2 and Other Indicators
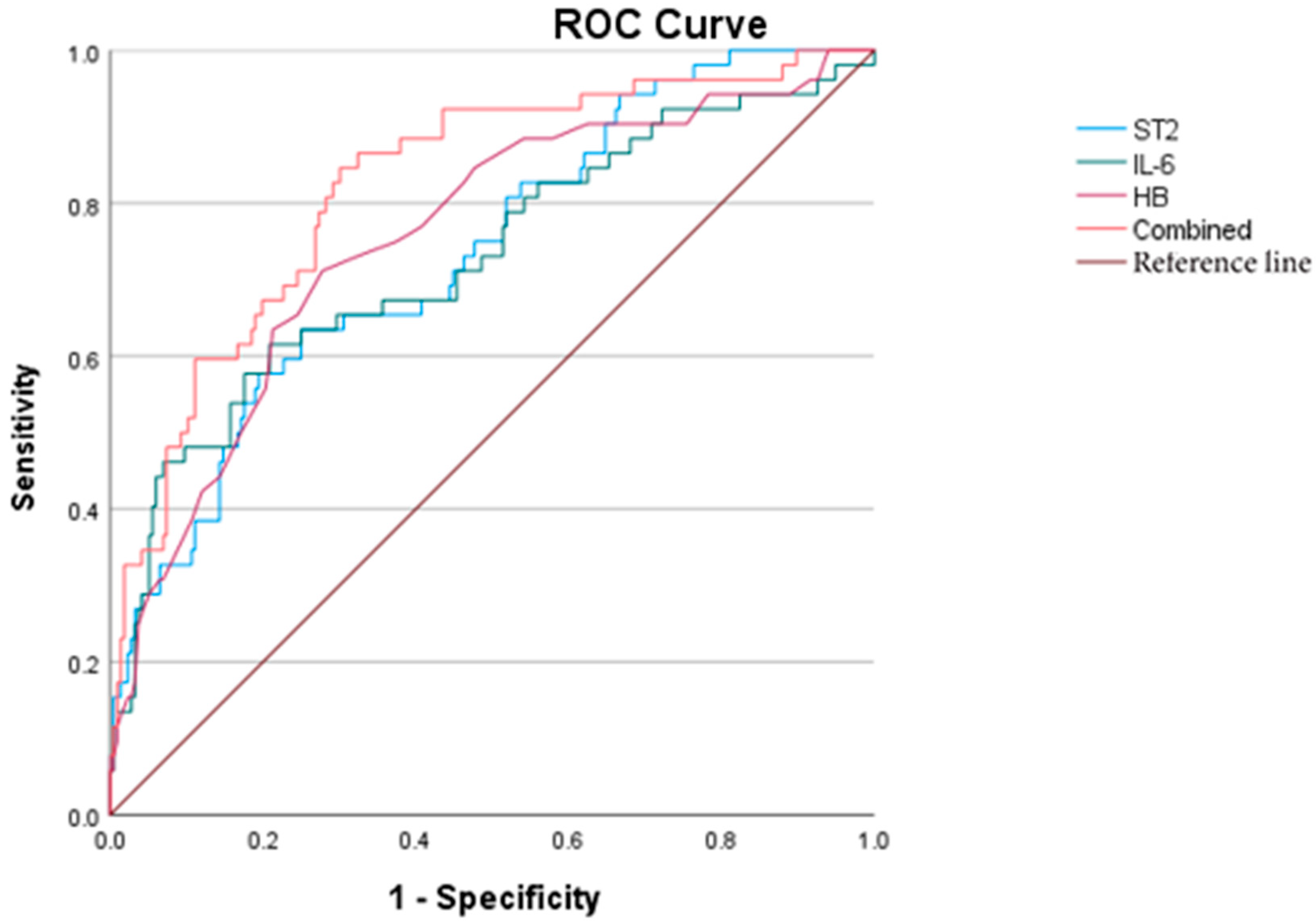
5.5. KD Combined with MD
5.6. KD Combined with CAL
5.7. KD Combined with MOD
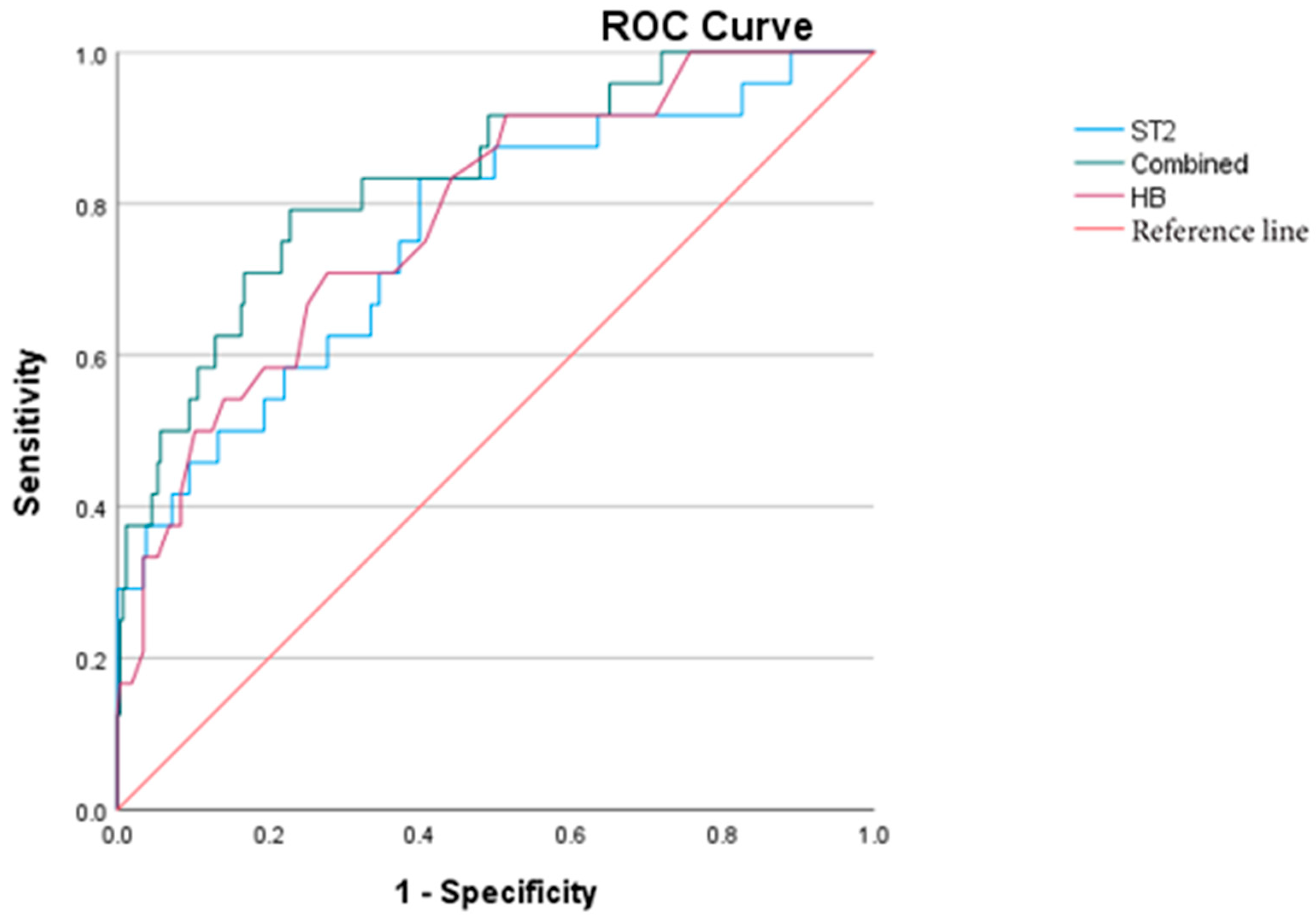
5.8. IVIG-R KD
5.9. Clinical Data of Four Cases with ST2 > 200 ng/mL
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jone, P.-N.; Tremoulet, A.; Choueiter, N.; Dominguez, S.R.; Harahsheh, A.S.; Mitani, Y.; Zimmerman, M.; Lin, M.-T.; Friedman, K.G. Update on diagnosis and management of Kawasaki disease: A scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2024, 150, e481–e500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabi, M.; Andreozzi, L.; Frabboni, I.; Dormi, A.; Corinaldesi, E.; Lami, F.; Cicero, C.; Tchana, B.; Francavilla, R.; Sprocati, M.; et al. Non-coronary cardiac events, younger age, and IVIG unresponsiveness increase the risk for coronary aneurysms in Italian children with Kawasaki disease. Clin. Rheumatol. 2021, 40, 1507–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homsak, E.; Gruson, D. Soluble ST2: A complex and diverse role in several diseases. Clin. Chim. Acta 2020, 507, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okada, S.; Yasudo, H.; Ohnishi, Y.; Matsuguma, C.; Fukano, R.; Motonaga, T.; Waniishi, T.; Hasegawa, S. Interleukin-33/ST2 Axis as Potential Biomarker and Therapeutic Target in Kawasaki Disease. Inflammation 2023, 46, 480–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotsiou, O.S.; Gourgoulianis, K.I.; Zarogiannis, S.G. IL-33/ST2 Axis in Organ Fibrosis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Pascual-Figal, D.A.; Januzzi, J.L. The biology of ST2: The International ST2 Consensus Panel. Am. J. Cardiol. 2015, 115 (Suppl. S7), 3B–7B. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Turnquist, H.R.; Hoffman, R.; Billiar, T.R. Role of the IL-33-ST2 axis in sepsis. Mil. Med. Res. 2017, 4, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCrindle, B.W.; Rowley, A.H.; Newburger, J.W.; Burns, J.C.; Bolger, A.F.; Gewitz, M.; Baker, A.L.; Jackson, M.A.; Takahashi, M.; Shah, P.B.; et al. American Heart Association Rheumatic Fever, Endocarditis, and Kawasaki Disease Committee of the Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young; Council on Cardiovascular and Stroke Nursing; Council on Cardiovascular Surgery and Anesthesia; and Council on Epidemiology and Prevention. Diagnosis, Treatment, and Long-Term Management of Kawasaki Disease: A Scientific Statement for Health Professionals from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2017, 135, e927–e999, Erratum in Circulation 2019, 140, e181–e184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, T.; Ayusawa, M.; Suzuki, H.; Abe, J.; Ito, S.; Kato, T.; Kamada, M.; Shiono, J.; Suda, K.; Tsuchiya, K.; et al. Revision of diagnostic guidelines for Kawasaki disease (6th revised edition). Pediatr. Int. 2020, 62, 1135–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitz, J.; Owyang, A.; Oldham, E.; Song, Y.; Murphy, E.; McClanahan, T.K.; Zurawski, G.; Moshrefi, M.; Qin, J.; Li, X.; et al. IL-33, an interleukin-1-like cytokine that signals via the IL-1 receptor-related protein sST2 and induces T helper type 2-associated cytokines. Immunity 2005, 23, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savarimuthu, S.; Goel, P.; Harky, A. Soluble ST2: A valuable prognostic marker in heart failure. Heart Fail. Rev. 2022, 27, 2155–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, M. Chinese expert consensus on biomarkers for heart failure. Chin. J. Lab. Med. 2020, 43, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, S.; Sakai, A.; Ohnishi, Y.; Yasudo, H.; Motonaga, T.; Fukano, R.; Waniishi, T.; Sugiyama, M.; Hasegawa, S. Necrotic Change of Tunica Media Plays a Key Role in the Development of Coronary Artery Lesions in Kawasaki Disease. Circ. J. 2024, 88, 1709–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Algarni, A.S.; Alamri, N.M.; Khayat, N.Z.; Alabdali, R.A.; Alsubhi, R.S.; Alghamdi, S.H. Clinical practice guidelines in multisystem inflammatory syndrome (MIS-C) related to COVID-19: A critical review and recommendations. World J. Pediatr. 2022, 18, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kabeerdoss, J.; Pilania, R.K.; Karkhele, R.; Kumar, T.S.; Danda, D.; Singh, S. Severe COVID-19, multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children, and Kawasaki disease: Immunological mechanisms, clinical manifestations and management. Rheumatol. Int. 2021, 41, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kakkar, R.; Lee, R.T. The IL-33/ST2 pathway: Therapeutic target and novel biomarker. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 827–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hoshino, S.; Jain, S.; Shimizu, C.; Roberts, S.; He, F.; Daniels, L.B.; Kahn, A.M.; Tremoulet, A.H.; Gordon, J.B.; Burns, J.C. Biomarkers of inflammation and fibrosis in young adults with history of Kawasaki disease. Int. J. Cardiol. Heart Vasc. 2021, 36, 100863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
| Groups | Age (year) | Male (%) | Pyear | Pgender | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MD | A (17) | 2.0 (0.6~3.0) | 9 (52.94) | 0.061 | 0.464 |
| B (270) | 2.5 (1.5~4.0) | 167 (61.85) | |||
| CAL | C (48) | 1.9 (0.8~2.7) | 40 (83.33) | 0.003 | <0.001 |
| D (239) | 2.5 (1.5~4.0) | 136 (56.90) | |||
| MOD | E (58) | 2.7 (1.0~4.0) | 36 (62.07) | 0.849 | 0.896 |
| F (229) | 2.4 (1.4~4.0) | 140 (61.14) | |||
| IVIG-R KD | G (24) | 2.8 (1.8~5.0) | 17 (70.83) | 0.109 | 0.318 |
| H (263) | 2.4 (1.4~4.0) | 159 (60.46) |
| Groups | sST2 (ng/mL) | Z | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MD | A (17) | 55.53 (41.97~120.58) | −3.150 | 0.002 |
| B (270) | 38.28 (27.25~57.60) | |||
| CAL | C (48) | 42.82 (32.24~71.78) | −2.086 | 0.037 |
| D (239) | 38.35 (27.14~57.46) | |||
| MOD | E (58) | 59.58 (37.47~96.14) | −5.380 | <0.001 |
| F (229) | 37.49 (26.33~51.83) | |||
| IVIG-R KD | G (24) | 65.67 (43.96~183.66) | −4.214 | <0.001 |
| H (263) | 37.73 (27.29~55.62) |
| PWBC | PHB | PPLT | PCRP | PIL-6 | PESR | Ppro-BNP | PD-dimer | PALB | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A vs. B | 0.001 | 0.134 | 0.046 | 0.018 | 0.002 | 0.348 | <0.001 | 0.003 | 0.072 |
| C vs. D | 0.37 | 0.001 | 0.011 | 0.039 | 0.076 | 0.933 | 0.037 | 0.005 | 0.032 |
| E vs. F | 0.002 | <0.001 | 0.002 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.772 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| G vs. H | 0.032 | <0.001 | 0.05 | <0.001 | 0.001 | 0.288 | 0.009 | 0.002 | <0.001 |
| Indexes | r | Sig. | 95% Confidence Interval (CI) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower Limit | Upper Limit | ||||
| sST2 | WBC | 0.301 | <0.001 | 0.188 | 0.405 |
| HB | −0.333 | <0.001 | −0.434 | −0.222 | |
| PLT | 0.196 | <0.001 | 0.079 | 0.308 | |
| CRP | 0.412 | <0.001 | 0.308 | 0.506 | |
| IL-6 | 0.456 | <0.001 | 0.352 | 0.548 | |
| ESR | 0.105 | 0.08 | −0.016 | 0.223 | |
| NT-pro BNP | 0.419 | <0.001 | 0.315 | 0.514 | |
| D-dimer | 0.367 | <0.001 | 0.258 | 0.467 | |
| ALB | −0.403 | <0.001 | −0.499 | −0.299 | |
| Factor | Influence Factor | B | SE | Wald | p | OR | 95%CI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower Limit | Upper Limit | |||||||
| single | sST2 | 0.011 | 0.004 | 7.043 | 0.008 | 1.011 | 1.003 | 1.020 |
| WBC | 0.099 | 0.035 | 7.788 | 0.005 | 1.104 | 1.030 | 1.183 | |
| CRP | 0.012 | 0.004 | 10.034 | 0.002 | 1.012 | 1.004 | 1.019 | |
| multi | sST2 | 0.004 | 0.006 | 0.544 | 0.461 | 1.004 | 0.993 | 1.015 |
| WBC | 0.051 | 0.044 | 1.324 | 0.250 | 1.052 | 0.965 | 1.147 | |
| CRP | 0.007 | 0.005 | 1.909 | 0.167 | 1.007 | 0.997 | 1.017 | |
| Factor | Influence Factor | B | SE | Wald | p | OR | 95%CI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower Limit | Upper Limit | |||||||
| single | sST2 | 0.010 | 0.004 | 7.680 | 0.006 | 1.010 | 1.003 | 1.017 |
| HB | −0.049 | 0.015 | 11.031 | <0.001 | 0.952 | 0.924 | 0.980 | |
| PLT | 0.003 | 0.001 | 10.512 | 0.001 | 1.003 | 1.001 | 1.005 | |
| CRP | 0.009 | 0.003 | 11.073 | <0.001 | 1.009 | 1.004 | 1.014 | |
| ALB | −0.120 | 0.046 | 6.804 | 0.009 | 0.887 | 0.811 | 0.971 | |
| age | −0.253 | 0.103 | 6.024 | 0.014 | 0.776 | 0.634 | 0.950 | |
| gender | 1.332 | 0.409 | 10.612 | 0.001 | 3.787 | 1.700 | 8.437 | |
| multi | sST2 | 0.003 | 0.005 | 0.284 | 0.594 | 1.003 | 0.993 | 1.012 |
| HB | −0.013 | 0.019 | 0.505 | 0.477 | 0.987 | 0.951 | 1.024 | |
| PLT | 0.002 | 0.001 | 2.889 | 0.089 | 1.002 | 1.000 | 1.004 | |
| CRP | 0.005 | 0.004 | 1.411 | 0.235 | 1.005 | 0.997 | 1.012 | |
| ALB | −0.065 | 0.059 | 1.204 | 0.272 | 0.937 | 0.834 | 1.053 | |
| age | −0.174 | 0.110 | 2.503 | 0.114 | 0.840 | 0.677 | 1.043 | |
| gender | 1.430 | 0.435 | 10.804 | 0.001 | 4.179 | 1.781 | 9.803 | |
| Factor | Influence Factor | B | SE | Wald | p | OR | 95%CI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower Limit | Upper Limit | |||||||
| single | sST2 | 0.025 | 0.005 | 24.92 | <0.001 | 1.025 | 1.015 | 1.035 |
| WBC | 0.078 | 0.026 | 8.91 | 0.003 | 1.081 | 1.027 | 1.137 | |
| HB | −0.085 | 0.016 | 28.99 | <0.001 | 0.918 | 0.890 | 0.947 | |
| PLT | 0.002 | 0.001 | 7.97 | 0.005 | 1.002 | 1.001 | 1.004 | |
| IL-6 | 0.005 | 0.001 | 22.39 | <0.001 | 1.005 | 1.003 | 1.008 | |
| D-dimer | 0.001 | 0.000 | 16.44 | <0.001 | 1.001 | 1.001 | 1.002 | |
| multi | sST2 | 0.013 | 0.005 | 6.01 | 0.014 | 1.013 | 1.003 | 1.024 |
| HB | −0.067 | 0.021 | 10.65 | 0.001 | 0.935 | 0.898 | 0.974 | |
| IL-6 | 0.003 | 0.001 | 5.79 | 0.016 | 1.003 | 1.001 | 1.006 | |
| WBC | −0.021 | 0.040 | 0.28 | 0.600 | 0.979 | 0.905 | 1.059 | |
| PLT | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.51 | 0.477 | 1.001 | 0.998 | 1.003 | |
| Factor | Influence Factor | B | SE | Wald | p | OR | 95%CI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower Limit | Upper Limit | |||||||
| single | sST2 | 0.026 | 0.005 | 24.142 | <0.001 | 1.025 | 1.016 | 1.037 |
| HB | −0.107 | 0.022 | 23.786 | <0.001 | 0.899 | 0.861 | 0.938 | |
| CRP | 0.017 | 0.003 | 24.584 | <0.001 | 1.017 | 1.010 | 1.024 | |
| IL-6 | 0.003 | 0.001 | 6.239 | 0.013 | 1.003 | 1.001 | 1.005 | |
| ALB | −0.243 | 0.069 | 12.369 | <0.001 | 0.785 | 0.685 | 0.898 | |
| multi | sST2 | 0.017 | 0.006 | 7.987 | 0.005 | 1.017 | 1.005 | 1.029 |
| HB | −0.062 | 0.027 | 5.354 | 0.021 | 0.940 | 0.892 | 0.991 | |
| CRP | 0.006 | 0.005 | 1.143 | 0.285 | 1.006 | 0.995 | 1.016 | |
| IL-6 | 0.000 | 0.001 | 0.416 | 0.519 | 1.000 | 0.999 | 1.002 | |
| ALB | 0.059 | 0.086 | 0.477 | 0.490 | 1.061 | 0.897 | 1.256 | |
| Case | Gender | Age | sST2 (ng/mL) | Fever | Treatment | MOD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1# 19 kg 107 cm | F | 3.5 y | >200 | Admission 7 d Regressive10 d | IVIG 4 g/kg Dex5 mg*2 d Methylmethicone: 2 mg/kg*7 d 1.5 mg/kg*7 d 1 mg/kg*1 d Prednisone Po 14 d ALB IV 40 g | Cardiogenic shock Acute heart failure Hypoproteinemia (27.1 g/L) Hypokalemia, hyponatremia, Pneumonia Aseptic encephalitis (EEG 2–3 Hz) Localized peritonitis Thrombocytopenia |
| 2# 13.5 kg 102 cm | M | 3 y | >200 | Admission 9 d Regressive20 d | IVIG 2 g/kg Methylmethicone: 20 mg/kg*3 d 2 mg/kg*3 d 1 mg/kg*1 d Prednisone Po 7 d ALB IV 10 g | CAA: LM4.7 mm, Z = 6.07, 3 m recovered Liver damage (ALT 95 U/L) Hypoproteinemia (24 g/L) Leukemoid reaction Aseptic encephalitis (EEG 5–7 Hz) Pneumonia, |
| 3# 9.3 kg 82 cm | M | 23 m | 285.4 | Admission 5 d Regressive27 d | IVIG 4 g/kg Methylmethicone 20 mg/kg*3 d 10 mg/kg*3 d 2 mg/kg*4 d 1 mg/kg*10 d Prednisone Po 10 d TNF inhibitor 5 mg/kg ALBI V 70 g | CAA: LM5.6 mm (Z = 11.1) RCA6.5 mm (Z = 12) Liver damage (ALT 434 U/L) Hypoproteinemia (24.2 g/L) Aseptic encephalitis (CSF:WBC66, Pro 0.56) Pleural effusion Moderate anemia (HGB = 76 g/L) |
| 4# 29 kg 130 cm | F | 9 y | 287.2 | Admission 6 d Regressive 22 d | IVIG 3 g/kg Methylmethicone: 2 mg/kg*6 d 1 mg/kg*7 d 0.7 md/kg*3 d Prednison Po 10 d ALBIV 60 g CTX 2 mg/kg IV | CAA: LAD 6.9 mm (Z = 7.63) persist RCA7.7 mm (Z = 10.63) persist Hypoproteinemia (20.6 g/L) Aseptic encephalitis (EEG 4–7 Hz) Knee joint effusion Granulocytopenia Hyponatremia, Moderate anemia (HGB = 86 g/L) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Chu, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, H. The Significance of Elevated sST2 in Children with Kawasaki Disease. Children 2025, 12, 868. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12070868
Yang Z, Xu Y, Chu Y, Li J, Wang H. The Significance of Elevated sST2 in Children with Kawasaki Disease. Children. 2025; 12(7):868. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12070868
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Zhaohua, Yunming Xu, Yanqiu Chu, Jinghao Li, and Hong Wang. 2025. "The Significance of Elevated sST2 in Children with Kawasaki Disease" Children 12, no. 7: 868. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12070868
APA StyleYang, Z., Xu, Y., Chu, Y., Li, J., & Wang, H. (2025). The Significance of Elevated sST2 in Children with Kawasaki Disease. Children, 12(7), 868. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12070868






