Effect of Abdominal Adiposity on the Impact of Plantar Force in the Foot Support of Obese and Overweight Schoolchildren
Highlights
- •
- Abdominal adiposity, measured via ultrasound, was a strong predictor of increased foot pronation (on both right and left sides);
- •
- A high-to-moderate association was observed between abdominal fat thickness and pronated foot support.
- •
- Abdominal adiposity contributes directly to postural and orthopedic changes in children, specifically pronated foot support.
- •
- Changes in foot posture observed in overweight and obese children may predispose them to pain and orthopedic complications during growth, highlighting the critical need for early assessment and intervention.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Sample and Study Design
2.2. Clinical Evaluation Protocol
2.2.1. Foot Posture Index-FPI Evaluation Protocol
- (A)
- Palpation of the Talus Head
- (B)
- Supra and Inframalleolar Lateral Curvature
- (C)
- Position of the Heel in the Frontal Plane
- (D)
- Prominence of the talonavicular joint
- (E)
- Height and congruence of the medial longitudinal arch
- (F)
- Abduction and adduction of the forefoot in relation to the hindfoot
2.2.2. Ultrasound of Subcutaneous and Intra-Abdominal Fat
3. Statistical Analysis
4. Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brzęk, A.; Sołtys, J.; Gallert-Kopyto, W.; Gwizdek, K.; Plinta, R. Body Posture in Children with Obesity—The Relationship to Physical Activity (PA). Pediatr. Endocrinol. Diabetes Metab. 2016, 22, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; Ni, Y.; Yi, C.; Fang, Y.; Ning, Q.; Shen, B.; Zhang, K.; Liu, Y.; Yang, L.; et al. Global Prevalence of Overweight and Obesity in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JAMA Pediatr. 2024, 178, 800–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jelalian, E.; Evans, E.W. Behavioral Intervention in the Treatment of Obesity in Children and Adolescents: Implications for Mexico. Nutr. Rev. 2017, 75 (Suppl. S1), 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC). Worldwide Trends in Body-Mass Index, Underweight, Overweight, and Obesity from 1975 to 2016: A Pooled Analysis of 2416 Population-Based Measurement Studies in 128.9 Million Children, Adolescents, and Adults. Lancet 2017, 390, 2627–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiess, W.; Kirstein, A.S.; Stein, R.; Vogel, M. Obesity after the COVID-19 Pandemic and Beyond. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 35, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira-de-Almeida, C.A.; Del Ciampo, L.A.; Ferraz, I.S.; Del Ciampo, I.R.L.; Contini, A.A.; Ued, F.D.V. COVID-19 and Obesity in Childhood and Adolescence: A Clinical Review. J. Pediatr. 2020, 96, 546–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jebeile, H.; Kelly, A.S.; O’Malley, G.; Baur, L.A. Obesity in Children and Adolescents: Epidemiology, Causes, Assessment, and Management. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2022, 10, 351–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, A.A.; Kundt, G.; Lenschow, U.; Schuff-Werner, P.; Kienast, W. Improvement of Early Vascular Changes and Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Obese Children after a Six-Month Exercise Program. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2006, 48, 1865–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.D.; Fu, E.; Kobayashi, M.A. Prevention and Management of Childhood Obesity and Its Psychological and Health Comorbidities. Annu. Rev. Clin. Psychol. 2020, 16, 351–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.; Al-Ani, O.; Al-Ani, F. Children’s Behaviour and Childhood Obesity. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Diabetes Metab. 2024, 30, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flynn, A.C.; Suleiman, F.; Windsor-Aubrey, H.; Wolfe, I.; O’Keeffe, M.; Poston, L.; Dalrymple, K.V. Preventing and Treating Childhood Overweight and Obesity in Children up to 5 Years Old: A Systematic Review by Intervention Setting. Matern. Child Nutr. 2022, 18, e13354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, L.M.; Lai, S.K.; Veldman, S.L.C.; Hardy, L.L.; Cliff, D.P.; Morgan, P.J.; Zask, A.; Lubans, D.R.; Shultz, S.P.; Ridgers, N.D.; et al. Correlates of Gross Motor Competence in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sports Med. 2016, 46, 1663–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, C.M.; Reis, N.D.D.; Castro, A.O.; Höfelmann, D.A.; Kodaira, K.; Silva, M.T.; Galvão, T.F. Prevalence of Childhood Obesity in Brazil: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Pediatr. 2021, 97, 490–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boucher, F.; Handrigan, G.A.; Mackrous, I.; Hue, O. Childhood Obesity Affects Postural Control and Aiming Performance during an Upper Limb Movement. Gait Posture 2015, 42, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calcaterra, V.; Marin, L.; Vandoni, M.; Rossi, V.; Pirazzi, A.; Grazi, R.; Patané, P.; Silvestro, G.S.; Carnevale Pellino, V.; Albanese, I.; et al. Childhood Obesity and Incorrect Body Posture: Impact on Physical Activity and the Therapeutic Role of Exercise. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 16728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Rocha, E.S.; Bratz, D.T.; Gubert, L.C.; de David, A.; Carpes, F.P. Obese children experience higher plantar pressure and lower foot sensitivity than non-obese. Clin. Biomech. 2014, 29, 822–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, S.M.; Sumar, B.; Dixon, K.A. Musculoskeletal Pain in Overweight and Obese Children. Int. J. Obes. 2014, 38, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gettys, F.K.; Jackson, J.B.; Frick, S.L. Obesity in Pediatric Orthopaedics. Orthop. Clin. N. Am. 2011, 42, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Runhaar, J.; Koes, B.W.; Clockaerts, S.; Bierma-Zeinstra, S.M. A Systematic Review on Changed Biomechanics of Lower Extremities in Obese Individuals: A Possible Role in Development of Osteoarthritis. Obes. Rev. 2011, 12, 1071–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulgarón, E.R. Childhood Obesity: A Review of Increased Risk for Physical and Psychological Comorbidities. Clin. Ther. 2013, 35, A18–A32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, S.R. Complications of Obesity in Children and Adolescents. Int. J. Obes. 2009, 33 (Suppl. S1), S60–S65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilleard, W.; Smith, T. Effect of Obesity on Posture and Hip Joint Moments during a Standing Task, and Trunk Forward Flexion Motion. Int. J. Obes. 2007, 31, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayartai, M.E.; Schaer, C.E.; Luomajoki, H.; Tringali, G.; De Micheli, R.; Sartorio, A. Differences in spinal posture and mobility between children/adolescents with obesity and age-matched normal-weight individuals. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 15570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aleixo, A.A.; Guimarães, E.L.; Walsh, I.A.P.; Pereira, K. Influence of Overweight and Obesity on Posture, Overall Praxis and Balance in Schoolchildren. J. Hum. Growth Dev. 2012, 22, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowling, A.M.; Steele, J.R.; Baur, L.A. What Are the Effects of Obesity in Children on Plantar Pressure Distributions? Int. J. Obes. 2004, 28, 1514–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.H.; Zhang, K.; Tan, G.Q.; Yang, J.; Liu, Z.C. Effects of Obesity on Dynamic Plantar Pressure Distribution in Chinese Prepubescent Children during Walking. Gait Posture 2013, 37, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mickle, K.J.; Steele, J.R.; Munro, B.J. Is the Foot Structure of Preschool Children Moderated by Gender? J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2008, 28, 593–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez-Ormeño, E.; Aguado, X.; Delgado-Abellán, L.; Mecerreyes, L.; Alegre, L.M. Foot Morphology in Normal-Weight, Overweight, and Obese Schoolchildren. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2013, 172, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redmond, A.C.; Crosbie, J.; Ouvrier, R.A. Development and Validation of a Novel Rating System for Scoring Standing Foot Posture: The Foot Posture Index. Clin. Biomech. 2006, 21, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, B.K.G.; Penha, P.J.; Penha, N.L.J.; Andrade, R.M.; Ribeiro, A.P.; João, S.M.A. The Influence of Gender and Body Mass Index on the FPI-6 Evaluated Foot Posture of 10- to 14-Year-Old School Children in São Paulo, Brazil: A Cross-Sectional Study. J. Foot Ankle Res. 2017, 10, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, A.M.; Karimi, L. The Relationship between Paediatric Foot Posture and Body Mass Index: Do Heavier Children Really Have Flatter Feet? J. Foot Ankle Res. 2015, 8, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakuno, T.; Tomita, L.M.; Tomita, C.M.; Giuliano, I.C.; Ibagy, A.; Perin, N.M.; Poeta, L.S. Sonographic Evaluation of Visceral and Subcutaneous Fat in Obese Children. Radiol. Bras. 2014, 47, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina-García, C.; Álvarez-Salvago, F.; Pujol-Fuentes, C.; López-del-Amo-Lorente, A.; Ramos-Petersen, L.; Martínez-Sebastián, C.; Martínez-Amat, A.; Jiménez-García, J.D.; De Diego-Moreno, M. Descriptive Study of the Influence of Foot Type on Physical Characteristics, Laxity, Strength and Baropodometry in Children Aged 5 to 10 Years. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 8578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Mei, Q.; Wang, Y.; He, J.; Shao, E.; Fernandez, J.; Gu, Y. Understanding foot conditions, morphologies and functions in children: A current review. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1192524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, S.; Stücker, R.; Rupprecht, M. Orthopädische Probleme bei Adipositas im Kindes- und Jugendalter [Orthopedic Problems in Overweight and Obese Children]. Klin. Padiatr. 2016, 228, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczepanowska-Wolowiec, B.; Sztandera, P.; Kotela, I.; Zak, M. Body weight-dependent foot loads, assessed in terms of BMI and adiposity, in school-aged children: A cross sectional study. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Şahan, T.Y.; Türker, D.; Söyler, O. Comparison of plantar pressure distribution in underweight, normal, overweight, and obese adolescents: A cross-sectional study evaluation of plantar pressure in adolescents. Prosthet. Orthot. Int. 2023, 47, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hills, A.P.; Hennig, E.M.; McDonald, M.; Bar-Or, O. Plantar Pressure Differences between Obese and Non-Obese Adults: A Biomechanical Analysis. Int. J. Obes. 2001, 25, 1674–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browning, R.C.; Kram, R. Effects of Obesity on the Biomechanics of Walking at Different Speeds. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2007, 39, 1632–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, C.; Zamora, J. The Effects of Obesity on Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Pathology. Foot Ankle Int. 2007, 28, 996–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, S.; Carlsohn, A.; Mueller, J.; Baur, H.; Mayer, F. Influence of Obesity on Foot Loading Characteristics in Gait for Children Aged 1 to 12 Years. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0149924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riddiford-Harland, D.L.; Steele, J.R.; Storlien, L.H. Does Obesity Influence Foot Structure in Prepubescent Children? Int. J. Obes. 2000, 24, 541–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taisa, F.N.; de Almeida, B.T.; Lobo, C.P.H. Comparison of Static Footprints and Pedobarography in Obese and Non-Obese Children. Foot Ankle Int. 2008, 29, 1141–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mickle, K.J.; Steele, J.R. Obese Older Adults Suffer Foot Pain and Foot-Related Functional Limitation. Gait Posture 2015, 42, 442–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Moreno, J.M.; Calvo-Muñoz, I.; Gómez-Conesa, A.; López-López, J.A. Obesity and Overweight as Risk Factors for Low Back Pain in Children and Adolescents: A Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Obes. 2024, 48, 612–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butterworth, P.A.; Landorf, K.B.; Gilleard, W.; Urquhart, D.M.; Menz, H.B. The Association between Body Composition and Foot Structure and Function: A Systematic Review. Obes. Rev. 2014, 15, 348–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catan, L.; Amaricai, E.; Onofrei, R.R.; Popoiu, C.M.; Iacob, E.R.; Stanciulescu, C.M.; Cerbu, S.; Horhat, D.I.; Suciu, O. The Impact of Overweight and Obesity on Plantar Pressure in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Garcia, P.; Molina-Molina, A.; Smeets, A.; Migueles, J.H.; Ortega, F.B.; Vanrenterghem, J. Effects of Integrative Neuromuscular Training on the Gait Biomechanics of Children with Overweight and Obesity. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2022, 32, 1119–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


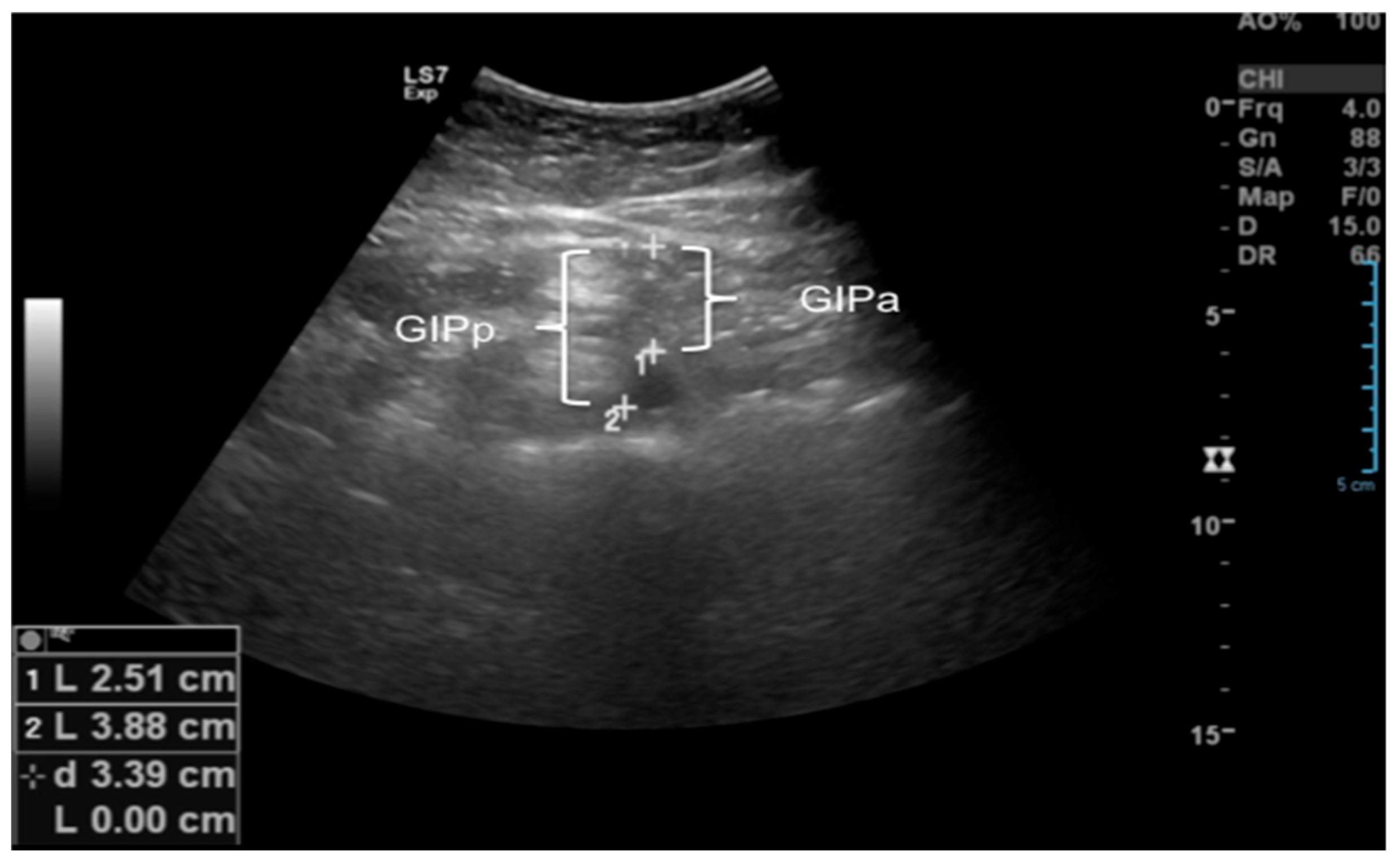

| Variables | GE (n = 20) | GOW (n = 20) | GO (n = 25) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 13.4 ± 1.3 | 14.2 ± 1.3 | 14.2 ± 1.3 | 0.448 |
| Weight (kg/cm2) | 46.0 ± 8.6 | 50.1 ± 7.4 | 50.1 ± 7.4 | 0.019 * |
| Height (cm) | 1.5 ± 0.7 | 1.6 ± 0.7 | 1.6 ± 0.7 | 0.123 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 18.2 ± 3.6 | 19.6 ± 2.3 | 19.6 ± 2.3 | 0.001 * |
| Foot | GE (n = 20) | GOW (n = 20) | GO (n = 25) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FPI right | 0.4 ± 0.2 | 1.8 ± 0.6 | 1.9 ± 0.3 | 0.001 * |
| FPI left | 0.5 ± 0.2 | 1.7 ± 0.8 | 2.0 ± 0.8 | 0.024 * |
| Abdominal Ultrasound | GE (n = 20) | GOW (n = 20) | GO (n = 25) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subcutaneous cellular tissue (SCCT, cm) | 0.43 ± 0.28 | 1.03 ± 0.71 | 1.66 ± 0.75 | 0.001 * |
| Minimum subcutaneous cellular tissue (minimum SCCT, cm) SCCT | 0.34 ± 0.16 | 0.65 ± 0.48 | 1.08 ± 0.51 | <0.001 *& |
| Maximum subcutaneous cellular tissue (maximum SCCT, cm) | 0.56 ± 0.34 | 1.19 ± 0.77 | 1.83 ± 0.78 | 0.010 * |
| Preperitoneal fat (PPF, cm) | 0.12 ± 0.04 | 0.14 ± 0.09 | 0.15 ± 0.09 | 0.583 |
| Minimum preperitoneal fat (minimum PPF, cm) | 0.12 ± 0.03 | 0.12 ± 0.07 | 0.12 ± 0.05 | 0.101 |
| Maximum preperitoneal fat (maximum PPF, cm) | 0.58 ± 0.27 | 0.76 ± 0.25 | 0.91 ± 0.26 | <0.001 * |
| Intra-peritoneal fat (IPFa—anterior wall of the aorta, cm) | 3.41 ± 0.66 | 3.66 ± 0.96 | 4.41 ± 1.17 | 0.003 *& |
| Intraperitoneal fat (IPFp—posterior wall of aorta, cm) | 4.21 ± 0.73 | 4.50 ± 1.17 | 5.33 ± 1.22 | 0.028 * |
| Intraperitoneal fat (IPF—lesser omentum, cm) | 0.81 ± 0.15 | 0.94 ± 0.24 | 1.15 ± 0.33 | 0.001 *& |
| Total abdominal fat (cm) | 4.76 ± 0.80 | 5.65 ± 1.55 | 7.13 ± 1.64 | <0.001 *& |
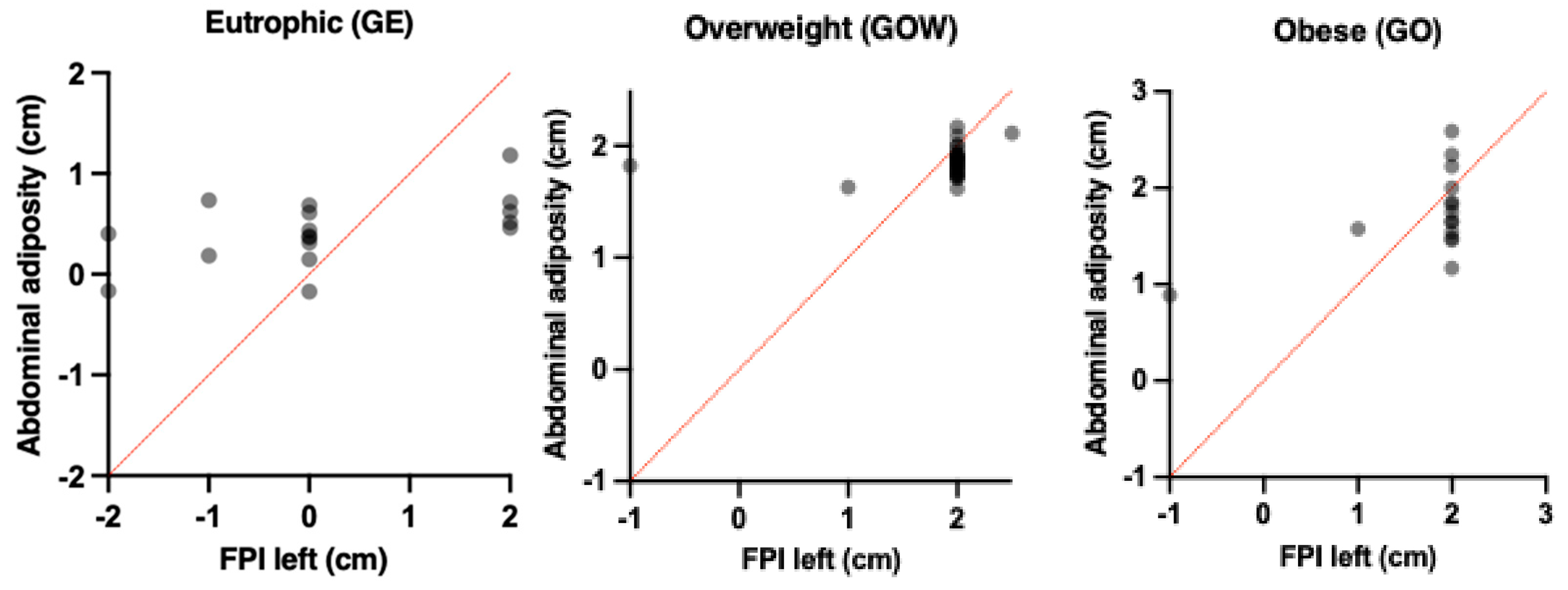
| Groups | Abdominal Adiposity (cm) | FPI Right (cm) | β | t | r | r2 | IC | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eutrophic (GE) | 4.76 ± 0.80 | 0.4 ± 0.2 | 2.5 | 1.0 | 0.04 | 0.00 | 0.2;1.0 | 0.563 |
| Overweight (GOW) | 5.65 ± 1.55 | 1.8 ± 0.6 | 0.15 | 0.3 | 0.12 | 0.01 | 1.8;2.0 | 0.018 * |
| Obese (GO) | 7.13 ± 1.64 | 1.9 ± 0.3 | 0.11 | 2.0 | 0.41 | 0.16 | 1.4;2.1 | 0.005 * |
| Groups | Abdominal Adiposity (cm) | FPI Left (cm) | β | t | r | r2 | IC | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eutrophic (GE) | 4.76 ± 0.80 | 0.5 ± 0.2 | 1.8 | 0.49 | 0.06 | 0.00 | 0.2;1.1 | 0.630 |
| Overweight (GOW) | 5.65 ± 1.55 | 1.7 ± 0.8 | 0.15 | 1.6 | 0.21 | 0.04 | 1.6;2.2 | 0.029 * |
| Obese (GO) | 7.13 ± 1.64 | 2.0 ± 0.8 | 0.35 | 1.9 | 0.54 | 0.29 | 1.2;2.1 | 0.034 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ribeiro, A.P.; Pereira, D.B.; Berger, G.F.; Ismail, K.M.; Morais, M.D.; Martins, M.S.F. Effect of Abdominal Adiposity on the Impact of Plantar Force in the Foot Support of Obese and Overweight Schoolchildren. Children 2025, 12, 1553. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12111553
Ribeiro AP, Pereira DB, Berger GF, Ismail KM, Morais MD, Martins MSF. Effect of Abdominal Adiposity on the Impact of Plantar Force in the Foot Support of Obese and Overweight Schoolchildren. Children. 2025; 12(11):1553. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12111553
Chicago/Turabian StyleRibeiro, Ana Paula, Daniel Borges Pereira, Gabrielle Fontura Berger, Kemely Muraiber Ismail, Maitê Duarte Morais, and Mayara Slaiman Fares Martins. 2025. "Effect of Abdominal Adiposity on the Impact of Plantar Force in the Foot Support of Obese and Overweight Schoolchildren" Children 12, no. 11: 1553. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12111553
APA StyleRibeiro, A. P., Pereira, D. B., Berger, G. F., Ismail, K. M., Morais, M. D., & Martins, M. S. F. (2025). Effect of Abdominal Adiposity on the Impact of Plantar Force in the Foot Support of Obese and Overweight Schoolchildren. Children, 12(11), 1553. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12111553






