Neuroinflammation as a Novel Therapeutic Frontier for Sanfilippo Syndrome
Abstract
1. Introductory Cues About the Mucopolysaccharidoses
2. The Puzzle of Sanfilippo Syndrome
3. The Development of Neurodysfunction in Mucopolysaccharidoses
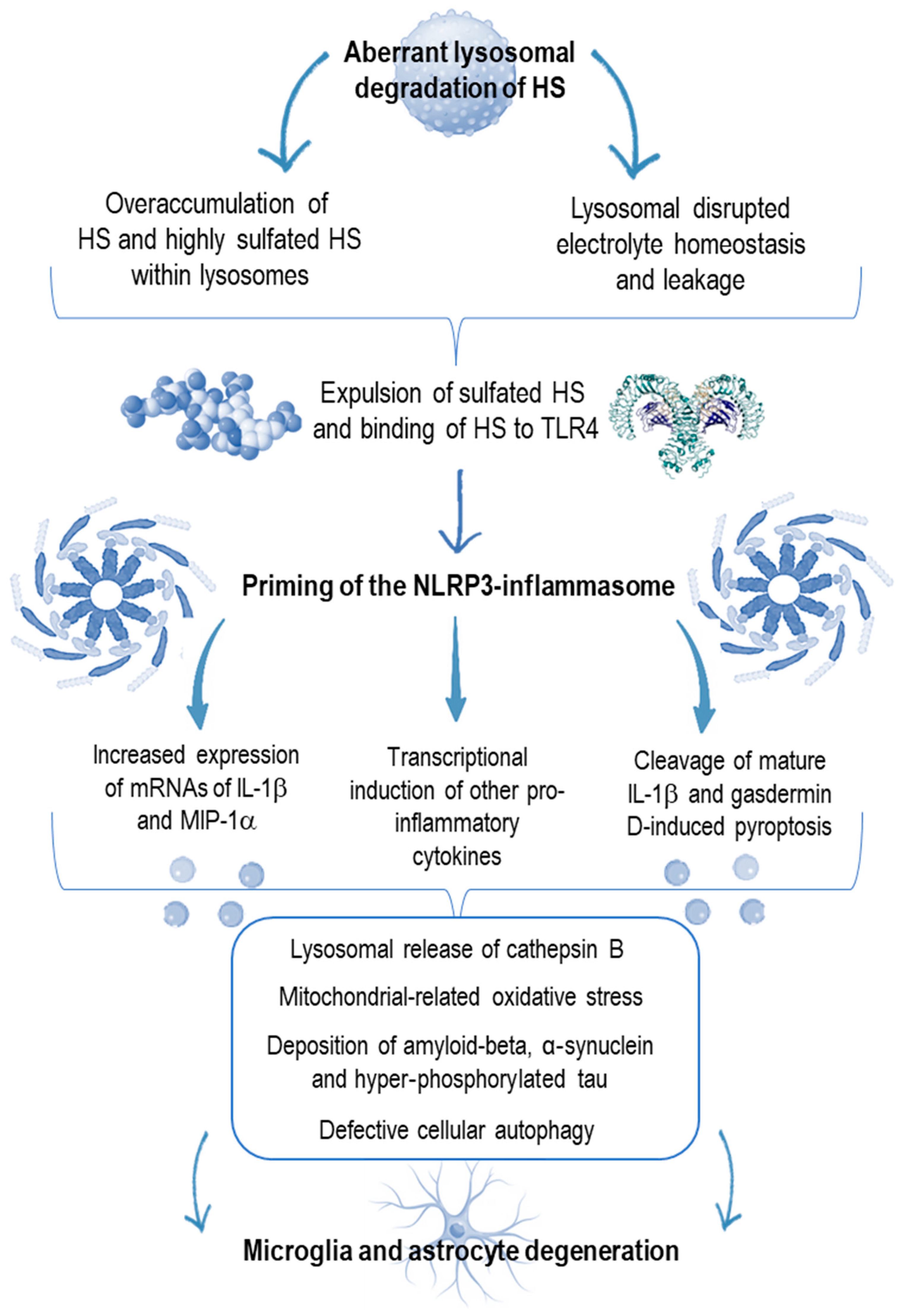
4. Innate Immunity Derangement in Neurologic Disorders
5. A Pro-Inflammatory Milieu in Sanfilippo Syndrome Mimicking the Kaleidoscopic Features of Autoinflammation
6. Targeting Neuroinflammation as a New Goal in the Sanfilippo Syndrome
7. Conclusive Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khan, S.A.; Peracha, H.; Ballhausen, D.; Wiesbauer, A.; Rohrbach, M.; Gautschi, M.; Mason, R.W.; Giugliani, R.; Suzuki, Y.; Orii, K.E.; et al. Epidemiology of mucopolysaccharidoses. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2017, 121, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachman, R.; Martin, K.W.; Castro, S.; Basto, M.A.; Adams, A.; Teles, E.L. Radiologic and neuroradiologic findings in the mucopolysaccharidoses. J. Pediatr. Rehabil. Med. 2010, 3, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigante, D.; Segni, G. Cardiac structural involvement in mucopolysaccharidoses. Cardiology 2002, 98, 18–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, B.; Galvin, N.; Vogler, C.; Birkenmeier, E.H.; Sly, W.S. Neuropathology of murine mucopolysaccharidosis type VII. Acta Neuropathol. 1996, 92, 562–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipiński, P.; Różdżyńska-Świątkowska, A.; Wiśniewska, K.; Rusecka, J.; Ługowska, A.; Żuber, Z.; Jezela-Stanek, A.; Cyske, Z.; Gaffke, L.; Pierzynowska, K.; et al. Mucopolysaccharidoses-what clinicians need to know: A clinical, biochemical, and molecular overview. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muenzer, J. Early initiation of enzyme replacement therapy for the mucopolysaccharidoses. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2014, 111, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahanpanah, M.; Jafari, L.; Behfar, M.; Alipour, N.; Ahad, F.; Mohseni, R.; Mohsenipour, R.; Setoodeh, A.; Heidari, M.; Ashrafi, M.R.; et al. Long-term outcomes of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in mucopolysaccharidoses patients without radiation. Clin. Transpl. 2025, 39, e70188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alyazidi, A.S.; Muthaffar, O.Y.; Baaishrah, L.S.; Shawli, M.K.; Jambi, A.T.; Aljezani, M.A.; Almaghrabi, M.A. Current concepts in the management of Sanfilippo syndrome (MPS III): A narrative review. Cureus 2024, 16, e58023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escolar, M.L.; Jones, S.A.; Shapiro, E.G.; Horovitz, D.D.G.; Lampe, C.; Amartino, H. Practical management of behavioral problems in mucopolysaccharidoses disorders. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2017, 122, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winner, L.K.; Rogers, M.L.; Snel, M.F.; Hemsley, K.M. Biomarkers for predicting disease course in Sanfilippo syndrome: An urgent unmet need in childhood-onset dementia. J. Neurochem. 2023, 166, 481–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinowska, M.; Wilkinson, F.L.; Langford-Smith, K.J.; Langford-Smith, A.; Brown, J.R.; Crawford, B.E.; Vanier, M.T.; Grynkiewicz, G.; Wynn, R.F.; Ed Wraith, J.; et al. Genistein improves neuropathology and corrects behaviour in a mouse model of neurodegenerative metabolic disease. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e14192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piotrowska, E.; Jakóbkiewicz-Banecka, J.; Tylki-Szymanska, A.; Liberek, A.; Maryniak, A.; Malinowska, M.; Czartoryska, B.; Puk, E.; Kloska, A.; Liberek, T.; et al. Genistin-rich soy isoflavone extract in substrate reduction therapy for Sanfilippo syndrome: An open-label, pilot study in 10 pediatric patients. Curr. Ther. Res. 2008, 69, 166–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.; Rust, S.; Langford-Smith, K.; Weisberg, D.; Canal, M.; Breen, C.; Hepburn, M.; Tylee, K.; Vaz, F.M.; Vail, A.; et al. High dose genistein in Sanfilippo syndrome: A randomised controlled trial. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2021, 44, 1248–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, S.H.; Elsharkawi, I.; Le, S.Q.; Prill, H.; Mangini, L.; Cooper, J.D.; Lawrence, R.; Sands, M.S.; Crawford, B.E.; Dickson, P.I. Biochemical evaluation of intracerebroventricular rhNAGLU-IGF2 enzyme replacement therapy in neonatal mice with Sanfilippo B syndrome. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2021, 133, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muschol, N.; Koehn, A.; von Cossel, K.; Okur, I.; Ezgu, F.; Harmatz, P.; de Castro Lopez, M.J.; Couce, M.L.; Lin, S.P.; Batzios, S.; et al. A phase I/II study on intracerebroventricular tralesinidase alfa in patients with Sanfilippo syndrome type B. J. Clin. Investig. 2023, 133, e165076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandolfo, O.; Parker, H.; Bigger, B. Innate immunity in mucopolysaccharide diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swaroop, M.; Brooks, M.J.; Gieser, L.; Swaroop, A.; Zheng, W. Patient iPSC-derived neural stem cells exhibit phenotypes in concordance with the clinical severity of mucopolysaccharidosis I. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2018, 27, 3612–3626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodbury, M.E.; Ikezu, T. Fibroblast growth factor-2 signaling in neurogenesis and neurodegeneration. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2014, 9, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, R.; Brown, J.R.; Al-Mafraji, K.; Lamanna, W.C.; Beitel, J.R.; Boons, G.J.; Esko, J.D.; Crawford, B.E. Disease-specific non-reducing end carbohydrate biomarkers for mucopolysaccharidoses. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2012, 8, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, C.; Hendson, G.; Jevon, G.; Matlock, T.; Yu, J.; Aklujkar, M.; Ng, K.Y.; Clarke, L.A. Murine MPS I: Insights into the pathogenesis of Hurler syndrome. Clin. Genet. 1998, 53, 349–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bigger, B.W.; Begley, D.J.; Virgintino, D.; Pshezhetsky, A.V. Anatomical changes and pathophysiology of the brain in mucopolysaccharidosis disorders. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2018, 125, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maccari, F.; Sorrentino, N.C.; Mantovani, V.; Galeotti, F.; Fraldi, A.; Volpi, N. Glycosaminoglycan levels and structure in a mucopolysaccharidosis IIIA mice and the effect of a highly secreted sulfamidase engineered to cross the blood-brain barrier. Metab. Brain Dis. 2017, 32, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, F.L.; Holley, R.J.; Langford-Smith, K.J.; Badrinath, S.; Liao, A.; Langford-Smith, A.; Cooper, J.D.; Jones, S.A.; Wraith, J.E.; Wynn, R.F.; et al. Neuropathology in mouse models of mucopolysaccharidosis type I, IIIA and IIIB. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, H.K.; Moreno, R.J.; Ashwood, P. Innate immune dysfunction and neuroinflammation in autism spectrum disorder (ASD). Brain Behav. Immun. 2024, 22, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashwood, P.; Krakowiak, P.; Hertz-Picciotto, I.; Hansen, R.; Pessah, I.N.; Van de Water, J. Associations of impaired behaviors with elevated plasma chemokines in autism spectrum disorders. J. Neuroimmunol. 2011, 232, 196–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Barres, B.A. Microglia and macrophages in brain homeostasis and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 18, 225–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henske, E.P.; Jóźwiak, S.; Kingswood, J.C.; Sampson, J.R.; Thiele, E.A. Tuberous sclerosis complex. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primer 2016, 2, 16035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, R.; Zhang, S.; Meng, L.; Wang, L.; Han, Z.; Gui, J.; Yang, J.; Cheng, L.; Xie, L.; Jiang, L. The activation of the microglial NLRP3 inflammasome is involved in tuberous sclerosis complex-related neuroinflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zou, J.; Han, L.; Rensing, N.; Wong, M. Microglial activation during epileptogenesis in a mouse model of tuberous sclerosis complex. Epilepsia 2016, 57, 1317–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Meng, J.; Xu, Q.; Long, T.; Bi, F.; Chang, C.; Liu, W. Rapamycin improves the neuroprotection effect of inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome activation after TBI. Brain Res. 2019, 1710, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.S.; Kim, M.J.; Chaugule, S.; Mayer, E.; DeSouza, N.; Ma, H.; Xie, J.; Lee, K.Y.; Li, S.; Gravallese, E.; et al. Nature-inspired IL-1 targeted therapy to treat chronic inflammatory diseases. Mol. Ther. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonaro, C.M.; D’Angelo, M.; He, X.; Eliyahu, E.; Shtraizent, N.; Haskins, M.E.; Schuchman, E.H. Mechanism of glycosaminoglycan-mediated bone and joint disease: Implications for the mucopolysaccharidoses and other connective tissue diseases. Am. J. Pathol. 2008, 172, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Termeer, C.; Benedix, F.; Sleeman, J.; Fieber, C.; Voith, U.; Ahrens, T.; Miyake, K.; Freudenberg, M.; Galanos, C.; Simon, J.C. Oligosaccharides of hyaluronan activate dendritic cells via toll-like receptor 4. J. Exp. Med. 2002, 195, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, M.-Y.; Kwak, J.E.; Seol, B.; Lee, D.Y.; Jeon, H.; Cho, Y.S. A novel human model of the neurodegenerative disease GM1 gangliosidosis using induced pluripotent stem cells demonstrates inflammasome activation. J. Pathol. 2015, 237, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ausseil, J.; Desmaris, N.; Bigou, S.; Attali, R.; Corbineau, S.; Vitry, S.; Parent, M.; Cheillan, D.; Fuller, M.; Maire, I.; et al. Early neurodegeneration progresses independently of microglial activation by heparan sulfate in the brain of mucopolysaccharidosis IIIB mice. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, C.; Hůlková, H.; Dridi, L.; Dormoy-Raclet, V.; Grigoryeva, L.; Choi, Y.; Langford-Smith, A.; Wilkinson, F.L.; Ohmi, K.; DiCristo, G.; et al. Neuroinflammation, mitochondrial defects and neurodegeneration in mucopolysaccharidosis III type C mouse model. Brain 2015, 138 Pt 2, 336–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohmi, K.; Kudo, L.C.; Ryazantsev, S.; Zhao, H.Z.; Karsten, S.L.; Neufeld, E.F. Sanfilippo syndrome type B, a lysosomal storage disease, is also a tauopathy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 8332–8337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winder-Rhodes, S.E.; Garcia-Reitböck, P.; Ban, M.; Evans, J.R.; Jacques, T.S.; Kemppinen, A.; Foltynie, T.; Williams-Gray, C.H.; Chinnery, P.F.; Hudson, G.; et al. Genetic and pathological links between Parkinson’s disease and the lysosomal disorder Sanfilippo syndrome. Mov. Disord. 2012, 27, 312–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujitsuka, H.; Sawamoto, K.; Peracha, H.; Mason, R.W.; Mackenzie, W.; Kobayashi, H.; Yamaguchi, S.; Suzuki, Y.; Orii, K.; Orii, T.; et al. Biomarkers in patients with mucopolysaccharidosis type II and IV. Mol. Genet. Metab. Rep. 2019, 19, 100455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramaniam, S.; Stansberg, C.; Cunningham, C. The interleukin 1 receptor family. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2004, 28, 415–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holley, R.J.; Ellison, S.M.; Fil, D.; O’Leary, C.; McDermott, J.; Senthivel, N.; Langford-Smith, A.W.W.; Wilkinson, F.L.; D’Souza, Z.; Parker, H.; et al. Macrophage enzyme and reduced inflammation drive brain correction of mucopolysaccharidosis IIIB by stem cell gene therapy. Brain 2018, 141, 99–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigante, D. Autoinflammatory syndromes behind the scenes of recurrent fevers in children. Med. Sci. Monit. 2009, 15, RA179-87. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rigante, D. A systematic approach to autoinflammatory syndromes: A spelling booklet for the beginner. Expert. Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2017, 13, 571–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigante, D.; Cantarini, L.; Imazio, M.; Lucherini, O.M.; Sacco, E.; Galeazzi, M.; Brizi, M.G.; Brucato, M. Autoinflammatory diseases and cardiovascular manifestations. Ann. Med. 2011, 4, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantarini, L.; Iacoponi, F.; Lucherini, O.M.; Obici, L.; Brizi, M.G.; Cimaz, R.; Rigante, D.; Benucci, M.; Sebastiani, G.D.; Brucato, A.; et al. Validation of a diagnostic score for the diagnosis of autoinflammatory diseases in adults. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2011, 24, 695–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathy, S.K.; Kumar, A.; Das, S.; Wander, A.; Kundu, S. Updates in the management of hereditary periodic fever syndromes in children. Cureus 2025, 17, e82284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, N.; Jeltema, D.; Duan, Y.; He, Y. The NLRP3 inflammasome: An overview of mechanisms of activation and regulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguree, S. Iron-inflammasome crosstalk in adipose tissue: Unresolved roles of NLRP3 and IL-1beta in metabolic inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arfi, A.; Richard, M.; Gandolphe, C.; Bonnefont-Rousselot, D.; Thérond, P.; Scherman, D. Neuroinflammatory and oxidative stress phenomena in MPS IIIA mouse model: The positive effect of long-term aspirin treatment. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2011, 103, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingham, P.J.; Pocock, J.M. Microglial secreted cathepsin B induces neuronal apoptosis. J. Neurochem. 2001, 76, 1475–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiRosario, J.; Divers, E.; Wang, C.; Etter, J.; Charrier, A.; Jukkola, P.; Auer, H.; Best, V.; Newsom, D.L.; McCarty, D.M.; et al. Innate and adaptive immune activation in the brain of MPS IIIB mouse model. J. Neurosci. Res. 2009, 87, 978–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özdemir, Ö. Cold-induced urticaria and development of anaphylaxis. Allergol. Immunopathol. 2024, 52, 103–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigante, D.; Frediani, B.; Galeazzi, M.; Cantarini, L. From the Mediterranean to the sea of Japan: The transcontinental odyssey of autoinflammatory diseases. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 485103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayraktaroglu, I.; Ortí-Casañ, N.; Van Dam, D.; De Deyn, P.P.; Eisel, U.L.M. Systemic inflammation as a central player in the initiation and development of Alzheimer’s disease. Immun. Ageing 2025, 22, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.H. Immuno-metabolic diseases and therapeutics: Molecular mechanisms via inflammasome signaling. Cell Commun. Signal. 2025, 23, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, R.; Saavedra, D.; Mittal, M.; Lemos, J.R.N.; Hirani, K. Inflammasome activation and accelerated immune aging in autoimmune disorders. Front. Aging 2025, 6, 1688060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, J.R. TNF-mediated inflammatory disease. J. Pathol. 2008, 214, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arkachaisri, T.; Lehman, T.J. Use of biologics in the treatment of childhood rheumatic diseases. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2000, 2, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantarini, L.; Rigante, D.; Lucherini, O.M.; Cimaz, R.; Laghi Pasini, F.; Baldari, C.T.; Benucci, M.; Simonini, G.; Di Sabatino, V.; Brizi, M.G.; et al. Role of etanercept in the treatment of tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated periodic syndrome: Personal experience and review of the literature. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2010, 23, 701–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federico, G.; Rigante, D.; Pugliese, A.L.; Ranno, O.; Catania, S.; Stabile, A. Etanercept induces improvement of arthropathy in chronic infantile neurological cutaneous articular (CINCA) syndrome. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2003, 32, 312–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fecarotta, S.; Gasperini, S.; Parenti, G. New treatments for the mucopolysaccharidoses: From pathophysiology to therapy. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2018, 44 (Suppl. 2), 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonaro, C.M.; Ge, Y.; Eliyahu, E.; He, X.; Jepsen, K.J.; Schuchman, E.H. Involvement of the Toll-like receptor 4 pathway and use of TNF-alpha antagonists for treatment of the mucopolysaccharidoses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sc. USA 2010, 107, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliyahu, E.; Wolfson, T.; Ge, Y.; Jepsen, K.J.; Schuchman, E.H.; Simonaro, C.M. Anti-TNF-alpha therapy enhances the effects of enzyme replacement therapy in rats with mucopolysaccharidosis type VI. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Panda, S.P.; Abomughaid, M.M.; Lakhanpal, S.; Avinash, D.; Jha, N.K.; Gupta, R. Microglial pyroptosis in neurological disorders: Mechanistic crosstalk, metabolic triggers, and therapeutic frontiers. Metab. Brain Dis. 2025, 40, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muschol, N.; Giugliani, R.; Jones, S.A.; Muenzer, J.; Smith, N.J.C.; Whitley, C.B.; Donnell, M.; Drake, E.; Elvidge, K.; Melton, L.; et al. Sanfilippo syndrome: Consensus guidelines for clinical care. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2022, 17, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigante, D. The fresco of autoinflammatory diseases from the pediatric perspective. Autoimmun. Rev. 2012, 11, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigante, D. The protean visage of systemic autoinflammatory syndromes: A challenge for inter-professional collaboration. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2010, 14, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rigante, D.; Ansuini, V.; Caldarelli, M.; Bertoni, B.; La Torraca, I.; Stabile, A. Hydrocephalus in CINCA syndrome treated with anakinra. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2006, 22, 334–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, H.; Ellison, S.M.; Holley, R.J.; O’Leary, C.; Liao, A.; Asadi, J.; Glover, E.; Ghosh, A.; Jones, S.; Wilkinson, F.L.; et al. Haematopoietic stem cell gene therapy with IL-1Ra rescues cognitive loss in mucopolysaccharidosis IIIA. EMBO Mol. Med. 2020, 12, e11185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polgreen, L.E.; Chen, A.H.; Pak, Y.; Luzzi, A.; Morales Garval, A.; Acevedo, J.; Bitan, G.; Iacovino, M.; O’Neill, C.; Eisengart, J.B. Anakinra in Sanfilippo syndrome: A phase 1/2 trial. Nat. Med. 2024, 30, 2473–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coll, R.C.; Robertson, A.A.B.; Chae, J.J.; Higgins, S.C.; Muñoz-Planillo, R.; Inserra, M.C.; Vetter, I.; Dungan, L.S.; Monks, B.G.; Stutz, A.; et al. A small-molecule inhibitor of the NLRP3 inflammasome for the treatment of inflammatory diseases. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Jiang, H.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Yang, Y.; Tao, J.; Deng, X.; Liang, G.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, W.; et al. Tranilast directly targets NLRP3 to treat inflammasome-driven diseases. EMBO Mol. Med. 2018, 10, e8689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiesinger, A.M.; Bigger, B.; Giugliani, R.; Scarpa, M.; Moser, T.; Lampe, C.; Kampmann, C.; Lagler, F.B. The inflammation in the cytopathology of patients with mucopolysaccharidoses—Immunomodulatory drugs as an approach to therapy. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 863667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiesinger, A.M.; Bigger, B.; Giugliani, R.; Lampe, C.; Scarpa, M.; Moser, T.; Kampmann, C.; Zimmermann, G.; Lagler, F.B. Development of a novel tool for individual treatment trials in mucopolysaccharidosis. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2025, 48, e12816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parente, A.; Borzacchiello, L.; Giaccio, M.; Bamundo, M.; Rubino, R.; D’Auria, L.; Monaco, A.; Fraldi, A. Progressive activation of the astrocyte A1 phenotype underlies microglia-astroglia crosstalk and contributes to neuroinflammation in neuronopathic MPS. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2025, 146, 109224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| MPS Subtype | Eponym | Causative Gene | Deficient Enzyme | Accumulated Glycosaminoglycans | General Clinical Manifestations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I-H | Hurler | IDUA | alpha-L-iduronidase | DS, HS | Coarse face, severe intellectual disability, short stature, dysostosis multiplex, organomegaly, corneal clouding, heart valvular abnormalities |
| I-S | Scheie | IDUA | alpha-L-iduronidase | DS, HS | Joint stiffness, moderate skeletal anomalies, corneal clouding, normal neurologic development |
| I-HS | Hurler-Scheie | IDUA | alpha-L-iduronidase | DS, HS | Less severe clinical manifestations in comparison with Hurler disease |
| II | Hunter | IDS | iduronate 2-sulfatase | DS, HS | Coarse face, short stature, skeletal deformities, organomegaly, heart valvular abnormalities, hearing loss |
| III-A | Sanfilippo | SGSH | N-sulfoglucosamine sulfohydrolase | HS | Coarse face, severe regression of neurodevelopment, autism-like behaviors |
| III-B | Sanfilippo | NAGLU | alpha-N-acetylglucosaminidase | HS | Coarse face, severe regression of neurodevelopment, autism-like behaviors |
| III-C | Sanfilippo | HGSNAT | alpha-glucosaminide N-acetyltransferase | HS | Coarse face, severe regression of neurodevelopment, autism-like behaviors |
| III-D | Sanfilippo | GNS | N-acetylglucosamine-6-sulfate sulfatase | HS | Coarse face, severe regression of neurodevelopment, autism-like behaviors |
| IV-A | Morquio A | GALNS | N-acetylgalactosamine 6-sulfatase | KS, CS | Coarse face, severely short stature, skeletal abnormalities, pectus carinatum, joint hypermobility, corneal clouding, hearing loss, normal neurologic development |
| IV-B | Morquio B | GLB1 | beta-galactosidase 1 | KS | Coarse face, short stature, skeletal abnormalities, joint hypermobility, corneal clouding, hearing loss, normal neurologic development |
| VI | Maroteaux-Lamy | ARSB | N-acetylgalactosamine-4-sulfatase | DS | Coarse face, dysostosis multiplex, organomegaly, corneal clouding, hearing loss, normal neurologic development |
| VII | Sly | GUSB | beta-glucuronidase | DS, HS, CS | Coarse face, short stature, severe intellectual disability |
| IX | Natowicz | HYAL1 | hyaluronidase | HA | Soft tissue masses, mildly short stature, joint mobility restriction, susceptibility to develop ear infections |
| Study Number | Target | Type of MPS | Sponsor | Site | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT06567769 | Safety, tolerability, efficacy, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of recombinant human heparan N-sulfatase administered via intra-cerebroventricular access device (phase 1 study) | III-A | GC Biopharma Corp | Multi-center | Recruiting |
| NCT02053064 | Long-term follow-up of patients treated by intracerebral SAF-301 gene therapy | III-A | Lysogene | Amsterdam, The Netherlands; Manchester, United Kingdom | Completed (for 4 patients) |
| NCT02060526 | Safety and efficacy of recombinant human heparan-N-sulfatase via intrathecal drug delivery in a randomized controlled open-label study (phase 2 study) | III-A | Shire | Multi-center | Completed (for 21 patients) |
| NCT04360265 | Safety, tolerability and efficacy of UX111 (previously known as ABO-102) | III-A | Ultragenyx Pharmaceutical Inc | Multi-center | Enrolling by invitation |
| NCT01299727 | Long-term safety and clinical outcome of recombinant human heparan N-sulfatase via intrathecal administration in an open-label extension of the study HGT-SAN-055 | III-A | Takeda (Shire) | Amsterdam, The Netherlands; Manchester, United Kingdom | Completed (for 12 patients) |
| NCT01509768 | Disease natural course | III-B | Shire | Multi-center | Completed (for 19 patients) |
| NCT03300453 | Intracerebral administration of adenovirus-associated viral vector containing the human N-acetylglucosaminidase cDNA in an open-label study (phase 1–2 study) | III-B | UniQure Biopharma B.V. | Single-center (Paris, Le Kremlin-Bicetre Cedex, France) | Completed (for 4 patients) |
| NCT05825131 | Retrospective and prospective natural history | III-C | Phoenix Nest | Bron, France; Dallas, TX (USA) | Recruiting |
| NCT05648851 | Retrospective and prospective natural history | III-D | Phoenix Nest | Single-center (New York, NY, USA) | Completed (for 10 patients) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rigante, D.; Veredice, C. Neuroinflammation as a Novel Therapeutic Frontier for Sanfilippo Syndrome. Children 2025, 12, 1530. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12111530
Rigante D, Veredice C. Neuroinflammation as a Novel Therapeutic Frontier for Sanfilippo Syndrome. Children. 2025; 12(11):1530. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12111530
Chicago/Turabian StyleRigante, Donato, and Chiara Veredice. 2025. "Neuroinflammation as a Novel Therapeutic Frontier for Sanfilippo Syndrome" Children 12, no. 11: 1530. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12111530
APA StyleRigante, D., & Veredice, C. (2025). Neuroinflammation as a Novel Therapeutic Frontier for Sanfilippo Syndrome. Children, 12(11), 1530. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12111530







