Echocardiographic Determination of Umbilical Catheter Tip Location Mitigates Complications: A Randomized, Controlled Trial
Highlights
- Umbilical catheter position has been correlated with the incidence of catheter-related infection.
- PoCUS can identify the location of the umbilical catheter more accurately and imme-diately than traditional radiography.
- PoCUS should be considered as a standard tool for umbilical catheter placement.
- The use of PoCUS for catheter localization should be promoted in all NICUs.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| UVCs | Umbilical venous catheters |
| UACs | Umbilical artery catheters |
| CLABSI | Central line-associated bloodstream infection |
| PoCUS | Point-of-care ultrasound |
| PICCs | Peripherally inserted central catheters |
References
- Levit, O.L.; Shabanova, V.; Bizzarro, M.J. Umbilical catheter-associated complications in a level IV neonatal intensive care unit. J. Perinatol. 2020, 40, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M’Hamdi, K.; Kabiri, M.; Karboubi, L.; Ghanimi, Z.; Barkat, A. Neonatal liver abscess after umbilical venous catheter. Arch. Pediatr. 2013, 20, 196–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, H.; Ferrara, A. Rapid estimation of insertional length of umbilical catheters in newborns. Am. J. Dis. Child. 1986, 140, 786–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, F.; Brevaut-Malaty, V.; Pasquali, R.; Thomachot, L.; Vialet, R.; Hassid, S.; Nicaise, C.; Martin, C.; Panuel, M. Comparison of ultrasound and X-ray in determining the position of umbilical venous catheters. Resuscitation 2012, 83, 705–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.Q.; Xie, C.X.; Liao, J.F.; Xu, F.D.; Du, B.; Zhong, B.M.; He, X.G.; Li, N. Point-of-care ultrasound for monitoring catheter tip location during umbilical vein catheterization in neonates: A prospective study. Front. Pediatr. 2023, 11, 1225087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubortone, S.A.; Costa, S.; Perri, A.; D’Andrea, V.; Vento, G.; Barone, G. Real-time ultrasound for tip location of umbilical venous catheter in neonates: A pre/post intervention study. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2021, 47, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.T.; Huang, H.C.; Liu, Y.C.; Chang, H.Y.; Ou-Yang, M.C.; Chen, C.C.; Chen, F.S.; Chung, M.Y.; Chen, I.L. The appropriate frequency of dressing for percutaneous central venous catheters in preventing catheter-related blood stream infection in NICU—A randomized controlled trial. Pediatr. Neonatol. 2021, 62, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, S.J.; Broer, S.D.L.; Hemels, M.A.C.; Visser, D.H.; Antonius, T.A.J.; Heijting, I.E.; Bergman, K.A.; Termote, J.U.M.; Hutten, M.C.; van der Sluijs, J.P.F.; et al. Central-line-associated bloodstream infection burden among Dutch neonatal intensive care units. J. Hosp. Infect. 2024, 144, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Andrea, V.; Prontera, G.; Rubortone, S.A.; Pezza, L.; Pinna, G.; Barone, G.; Pittiruti, M.; Vento, G. Umbilical venous catheter update: A narrative review including ultrasound and training. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9, 774705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.J.; Yoo, S.Y.; Jeon, T.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, Y.J. Imaging of umbilical venous catheter-related hepatic complications in neonates. J. Korean Soc. Radiol. 2023, 84, 586–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumpa, V.; Avulakunta, I.D. Umbilical Artery Catheterization. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025; Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK559111/ (accessed on 10 April 2023).
- Huang, H.C.; Su, L.T.; Liu, Y.C.; Chang, H.Y.; Ou-Yang, M.C.; Chung, M.Y.; Chen, F.S.; Chen, C.C.; Chen, I.L. The role of ultrasonography for detecting tip location of percutaneous central venous catheters in neonates—A single-center, prospective cohort study. Pediatr. Neonatol. 2021, 62, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.S.; Huang, H.C.; Liu, Y.C.; Chen, I.L. Echocardiographic determination of percutaneous central venous catheters in the superior vena cava: A prospective sohort tudy. Children 2022, 9, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maki, D.G.; Weise, C.E.; Sarafin, H.W. A semiquantitative culture method for identifying intravenous-catheter-related infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 1977, 296, 1305–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddadin, Y.; Annamaraju, P.; Regunath, H. Central Line–Associated Blood Stream Infections. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022; Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK430891/ (accessed on 26 November 2022).
- Rossi, S.; Jogeesvaran, K.H.; Matu, E.; Khan, H.; Grande, E.; Meau-Petit, V. Point-of-care ultrasound for neonatal central catheter positioning: Impact on X-rays and line tip position accuracy. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2022, 181, 2097–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponin, L.; Ruangkit, C.; Ruangwattanapaisarn, N.; Nuntnarumit, P. Real-time ultrasound to assess the umbilical catheter position in neonates: A randomized, controlled trial. J. Perinatol. 2025, 45, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. WHO Recommendations on Postnatal Care of the Mother and Newborn; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Quattrin, R.; Iacobucci, K.; De Tina, A.L.; Gallina, L.; Pittini, C.; Brusaferro, S. 70% Alcohol versus dry cord care in the umbilical cord care: A case-control study in Italy. Medicine 2016, 95, e3207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gislason-Lee, A.J. Patient X-ray exposure and ALARA in the neonatal intensive care unit: Global patterns. Pediatr. Neonatol. 2021, 62, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tapio, S.; Little, M.P.; Kaiser, J.C.; Impens, N.; Hamada, N.; Georgakilas, A.G.; Simar, D.; Salomaa, S. Ionizing radiation-induced circulatory and metabolic diseases. Environ. Int. 2021, 146, 106235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domina, E.A.; Kopylenko, O.L.; Chekhun, V.F. Evaluation of current factors of radiation-associated carcinogenesis. Exp. Oncol. 2023, 45, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karber, B.C.; Nielsen, J.C.; Balsam, D.; Messina, C.; Davidson, D. Optimal radiologic position of an umbilical venous catheter tip as determined by echocardiography in very low birth weight newborns. J. Neonatal Perinatal Med. 2017, 10, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulickal, A.S.; Charlagorla, P.K.; Tume, S.C.; Chhabra, M.; Narula, P.; Nadroo, A.M. Superiority of targeted neonatal echocardiography for umbilical venous catheter tip localization: Accuracy of a clinician performance model. J. Perinatol. 2013, 33, 950–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
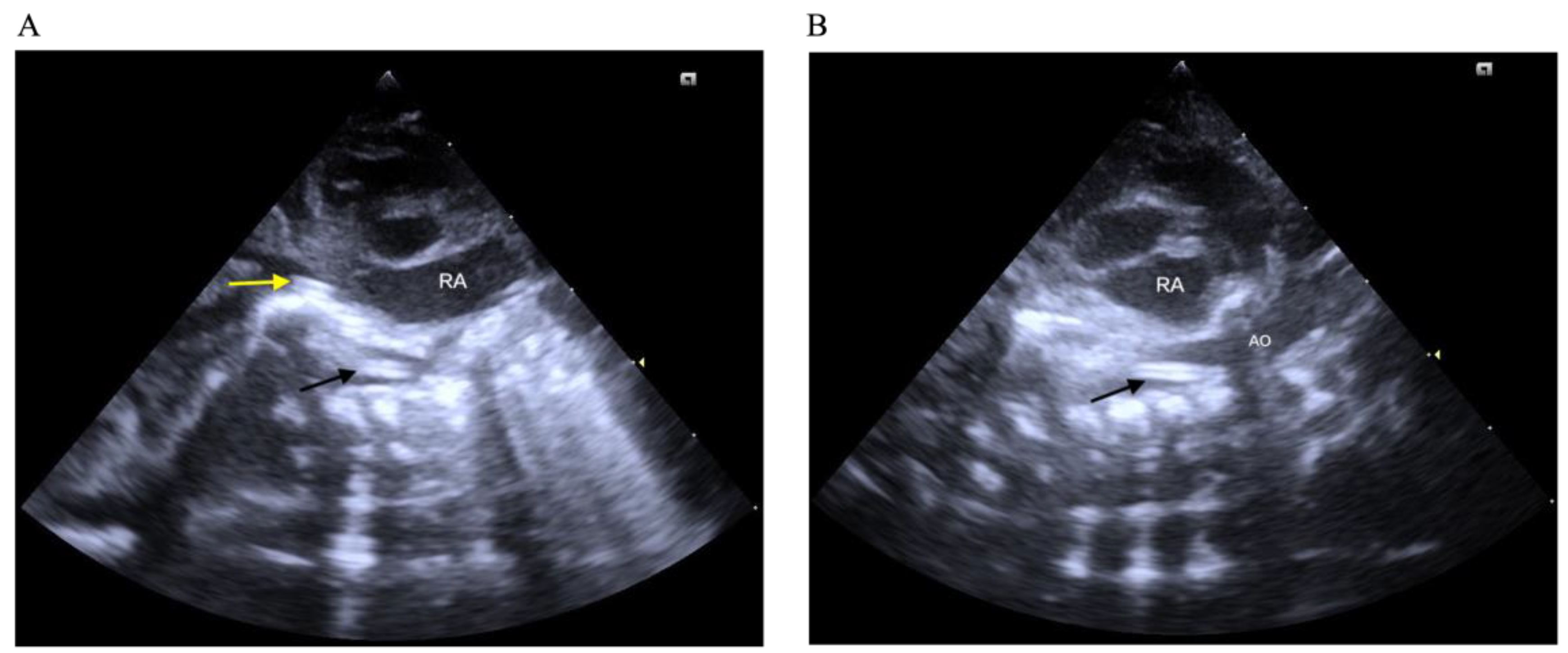
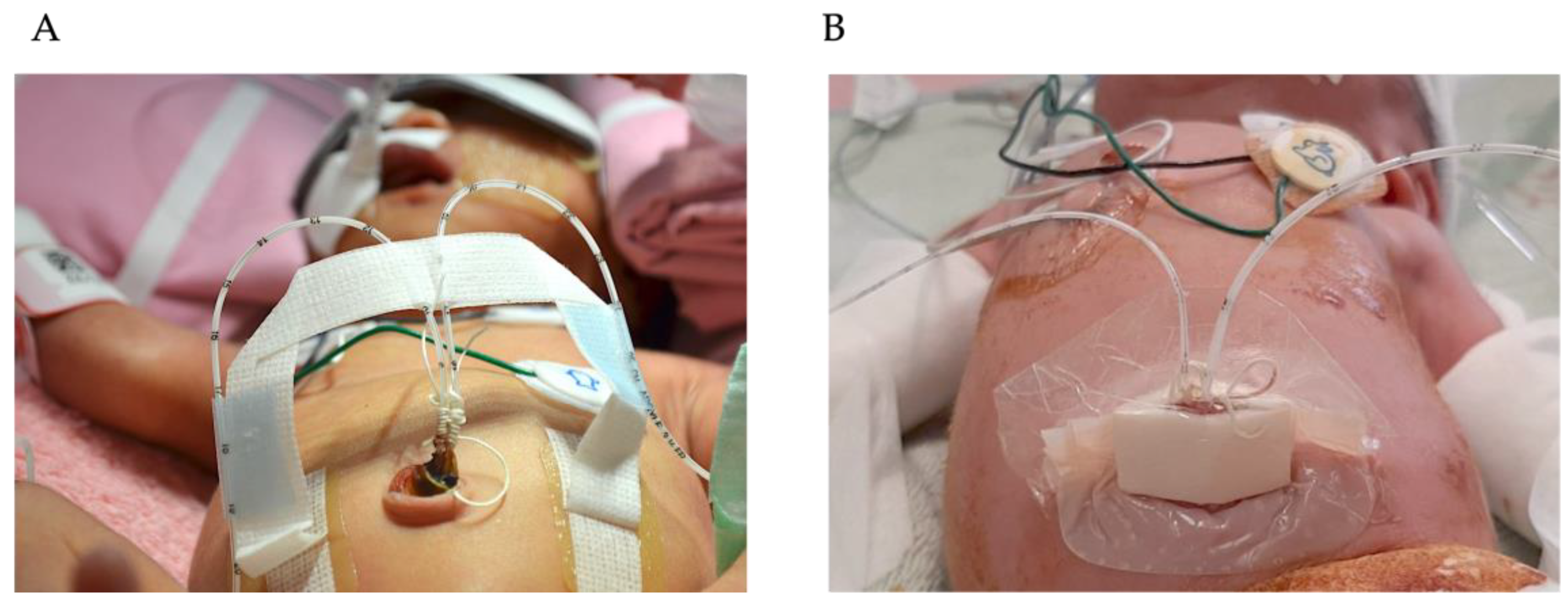
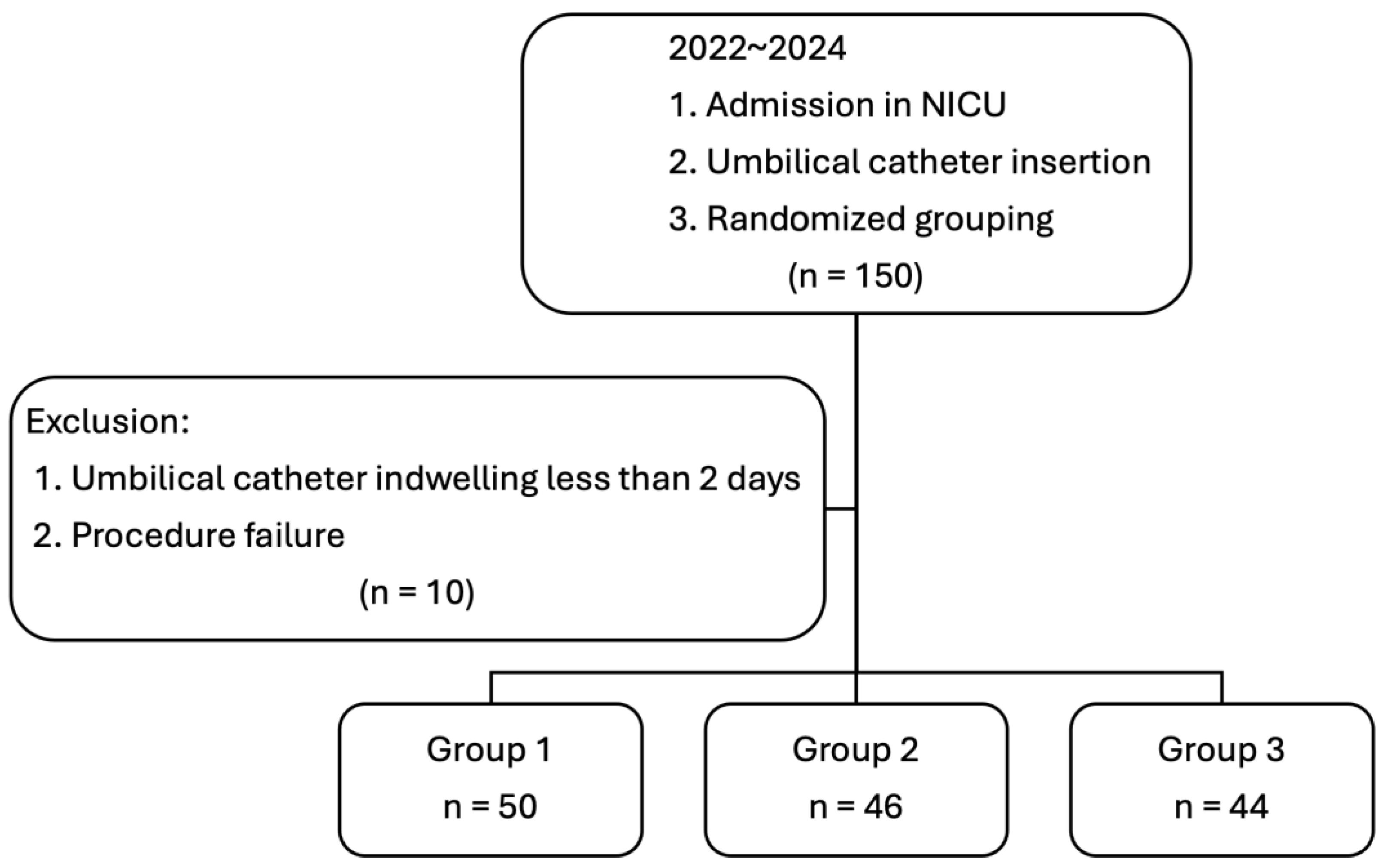
| Variable | Group 1 (n = 50) | Group 2 (n = 46) | Group 3 (n = 44) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Birth weight (g) | 1675.3 ± 923.07 | 1685.0 ± 824.8 | 1788.6 ± 903.4 | 0.795 |
| Sex (F/M) | 28/22 | 22/24 | 22/22 | 0.774 |
| Gestational age (week) | 31.44 ± 4.79 | 32.22 ± 4.38 | 32.91 ± 4.80 | 0.314 |
| Preterm delivery (n, %) | 41 (82) | 36 (78.3) | 31 (70.5) | 0.495 |
| Apgar score at 1 min | 5.24 ± 2.64 | 5.52 ± 2.25 | 5.59 ± 2.39 | 0.749 |
| Apgar score at 5 min | 7.20 ± 2.24 | 7.41 ± 2.09 | 7.43 ± 2.16 | 0.837 |
| Cesarean section delivery | 30 (60) | 35 (76) | 29 (66) | 0.208 |
| Maternal fever | 10 (20) | 5 (10.9) | 5 (11.4) | 0.281 |
| Premature rupture of membranes | 10 (20) | 7 (15.2) | 12 (27.3) | 0.347 |
| Chorioamnionitis | 11 (22) | 5 (10.8) | 12 (27.2) | 0.132 |
| Antenatal steroid | 26 (52) | 23 (50) | 23 (52.3) | 0.809 |
| Antenatal magnesium | 32 (64) | 24 (52.1) | 19 (43.2) | 0.222 |
| Antenatal antibiotics | 42 (84) | 42 (91.3) | 24 (54.5) | 0.001 |
| Both UAC and UVC insertion | 21 (42.0) | 27 (58.7) | 27 (61.4) | 0.167 |
| Duration of indwelling umbilical catheters (days) | 4.76 ± 3.17 | 4.72 ± 2.12 | 4.25 ± 1.93 | 0.557 |
| Duration of confirmed tip location (minutes) | 102.12 ± 116.9 | 23.72 ± 39.4 | 11.63 ± 9.82 | <0.001 |
| Malposition (n, %) | 25 (50) | 10 (21.7) | 8 (18.2) | 0.001 |
| Neonatal antibiotic use | 50 (100) | 46 (100) | 44 (100) | - |
| Catheter colonization (n, %) | 15 (30) | 5 (10.9) | 3 (6.8) | 0.006 |
| Catheter related bloodstream infection (n, %) | 4 (8) | 0 | 0 | 0.026 |
| Multiple Regression Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group 2 vs. Group 1 | Group 3 vs. Group 1 | |||
| p Value | Odds Ratio (95% CI) | p Value | Odds Ratio (95% CI) | |
| Birth weight | 0.078 | 0.998 (0.996–1.000) | 0.147 | 0.999 (0.997–1.001) |
| Sex (F/M) | 0.479 | 1.510 (0.482–4.732) | 0.613 | 1.399 (0.381–5.144) |
| Gestational age | 0.144 | 1.265 (0.923–1.733) | 0.166 | 1.270 (0.906–1.779) |
| Preterm delivery | 0.195 | 0.202 (0.018–2.267) | 0.264 | 0.239 (0.019–2.939) |
| Apgar score at 1 min | 0.937 | 1.020 (0.625–1.666) | 0.591 | 1.162 (0.671–2.012) |
| Apgar score at 5 min | 0.821 | 1.065 (0.616–1.843) | 0.919 | 0.969 (0.530–1.771) |
| Antenatal antibiotics | 0.360 | 1.955 (0.466–8.204) | 0.008 | 0.240 (0.084–0.688) |
| Duration of indwelling umbilical catheters | 0.292 | 1.177 (0.869–1.596) | 0.280 | 1.212 (0.855–1.720) |
| Duration of confirmed tip location | <0.001 | 0.970 (0.954–0.986) | <0.001 | 0.923 (0.889–0.960) |
| Malposition | 0.030 | 0.253 (0.073–0.874) | 0.005 | 0.131 (0.032–0.533) |
| Catheter colonization | 0.578 | 0.651 (0.143–2.955) | 0.347 | 0.404 (0.061–2.675) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, Y.-J.; Liu, Y.-C.; Huang, H.-C.; Wang, Y.-S.; Wu, H.-S.; Su, Y.-H.; Hsu, Y.-C.; Chen, I.-L. Echocardiographic Determination of Umbilical Catheter Tip Location Mitigates Complications: A Randomized, Controlled Trial. Children 2025, 12, 1509. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12111509
Lin Y-J, Liu Y-C, Huang H-C, Wang Y-S, Wu H-S, Su Y-H, Hsu Y-C, Chen I-L. Echocardiographic Determination of Umbilical Catheter Tip Location Mitigates Complications: A Randomized, Controlled Trial. Children. 2025; 12(11):1509. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12111509
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Yi-Jhen, Yu-Chen Liu, Hsin-Chun Huang, Yao-Sheng Wang, Hwa-Shiu Wu, Yu-Han Su, Yu-Chen Hsu, and I-Lun Chen. 2025. "Echocardiographic Determination of Umbilical Catheter Tip Location Mitigates Complications: A Randomized, Controlled Trial" Children 12, no. 11: 1509. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12111509
APA StyleLin, Y.-J., Liu, Y.-C., Huang, H.-C., Wang, Y.-S., Wu, H.-S., Su, Y.-H., Hsu, Y.-C., & Chen, I.-L. (2025). Echocardiographic Determination of Umbilical Catheter Tip Location Mitigates Complications: A Randomized, Controlled Trial. Children, 12(11), 1509. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12111509






