Risk Factors for Postoperative Pulmonary Compromise in a Pediatric Population: A Retrospective Review of a Single Institution Cohort
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
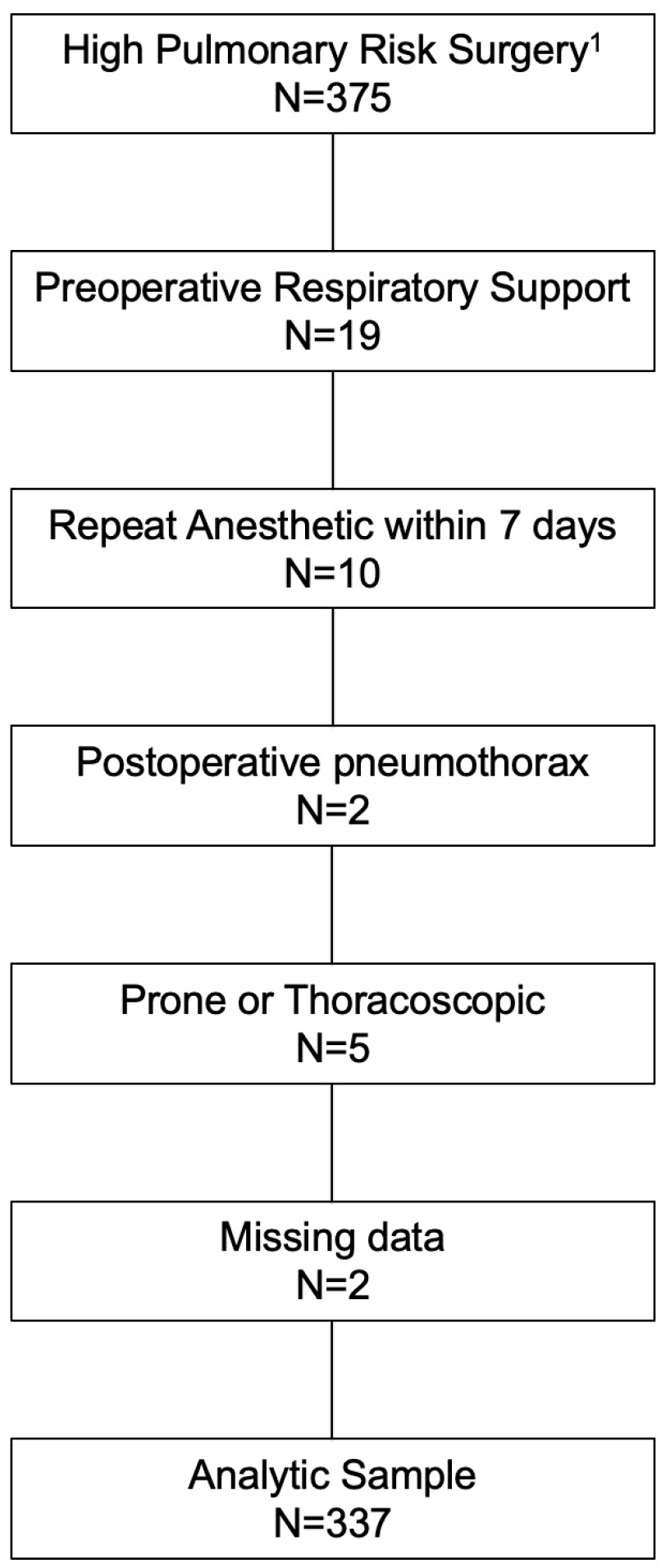
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Outcomes
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
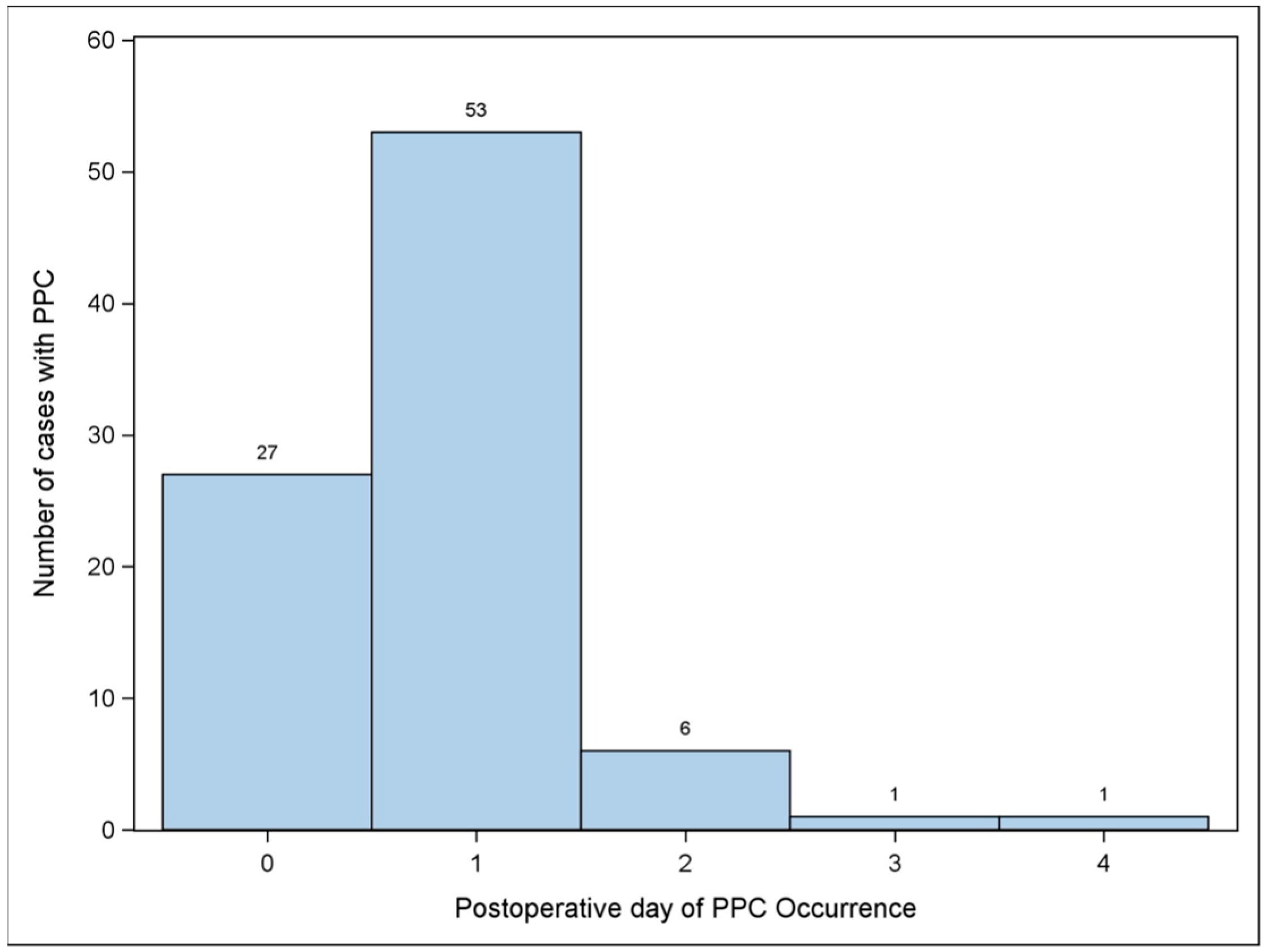
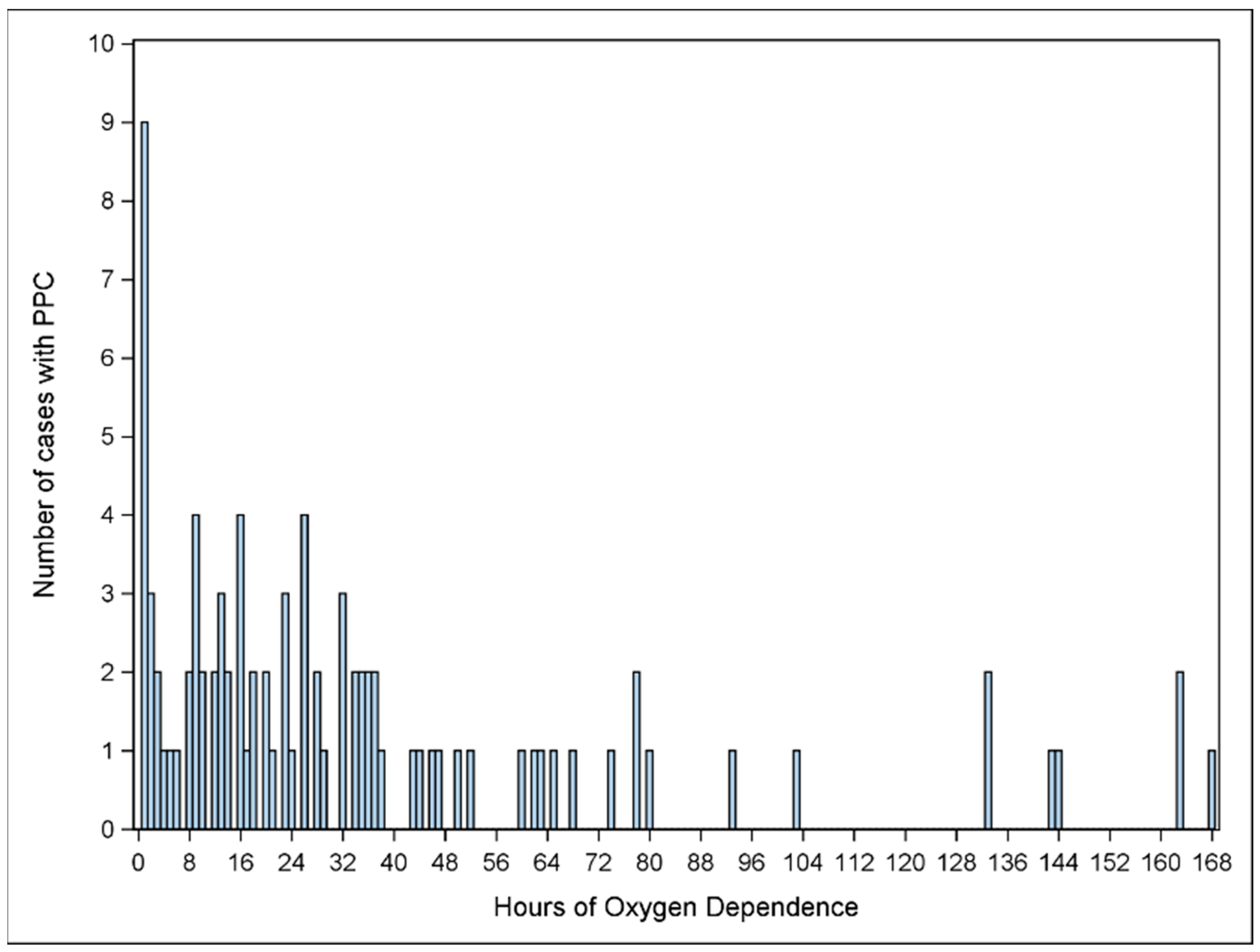
3.1. Primary Outcome
3.2. Secondary Outcome
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ASA | American Society of Anesthesiologists |
| CI | confidence interval |
| IRB | institutional review board |
| LOS | length of stay |
| OR | operating room |
| PPC | postoperative pulmonary complication |
References
- Oofuvong, M.; Geater, A.F.; Chongsuvivatwong, V.; Chanchayanon, T.; Sriyanaluk, B.; Saefung, B.; Nuanjun, K. Excess costs and length of hospital stay attributable to perioperative respiratory events in children. Anesth. Analg. 2015, 120, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheon, E.C.; Palac, H.L.; Paik, K.H.; Hajduk, J.; De Oliveira, G.S.; Jagannathan, N.; Suresh, S. Unplanned, Postoperative Intubation in Pediatric Surgical Patients: Development and Validation of a Multivariable Prediction Model. Anesthesiology 2016, 125, 914–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karalapillai, D.; Weinberg, L.; Peyton, P.; Ellard, L.; Hu, R.; Pearce, B.; Tan, C.O.; Story, D.; O’Donnell, M.; Hamilton, P.; et al. Effect of Intraoperative Low Tidal Volume vs Conventional Tidal Volume on Postoperative Pulmonary Complications in Patients Undergoing Major Surgery: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2020, 324, 848–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Futier, E.; Constantin, J.-M.; Paugam-Burtz, C.; Pascal, J.; Eurin, M.; Neuschwander, A.; Marret, E.; Beaussier, M.; Gutton, C.; Lefrant, J.-Y.; et al. A trial of intraoperative low-tidal-volume ventilation in abdominal surgery. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 428–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Y.; Liu, J.; Nie, X.; Liu, L.; Fu, W.; Zhao, X.; Zheng, T.; Xu, Z.; Cai, J.; Wang, F.; et al. Association of tidal volume during mechanical ventilation with postoperative pulmonary complications in pediatric patients undergoing major scoliosis surgery. Paediatr. Anaesth. 2020, 30, 806–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheon, E.C.; Ballard, H.A.; Burjek, N.E.; Phillips, M.; Robles, A.; Raval, M.V. Identifying a pediatric cohort to prospectively evaluate ventilation strategies to mitigate postoperative pulmonary complications. Paediatr. Anaesth. 2022, 32, 1368–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenberg, J.; Ullstad, T.; Larsen, P.N.; Moesgaard, F.; Kehlet, H. Continuous assessment of oxygen saturation and subcutaneous oxygen tension after abdominal operations. Acta Chir. Scand. 1990, 156, 585–590. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg, J.; Ullstad, T.; Rasmussen, J.; Hjorne, F.P.; Poulsen, N.J.; Goldman, M.D. Time course of postoperative hypoxaemia. Eur. J. Surg. 1994, 160, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenberg, J.; Wildschiodtz, G.; Pedersen, M.H.; von Jessen, F.; Kehlet, H. Late postoperative nocturnal episodic hypoxaemia and associated sleep pattern. Br. J. Anaesth. 1994, 72, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaminski, P.N.; Forgiarini, L.A.; Andrade, C.F., Jr. Early respiratory therapy reduces postoperative atelectasis in children undergoing lung resection. Respir. Care 2013, 58, 805–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Ji, S.H.; Jang, Y.E.; Kim, E.H.; Kim, J.T.; Kim, H.S. Application of a High-Flow Nasal Cannula for Prevention of Postextubation Atelectasis in Children Undergoing Surgery: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Anesth. Analg. 2021, 133, 474–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felcar, J.M.; Guitti, J.C.; Marson, A.C.; Cardoso, J.R. Preoperative physiotherapy in prevention of pulmonary complications in pediatric cardiac surgery. Rev. Bras. Cir. Cardiovasc. 2008, 23, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisler, L.D.; Hua, M.; Li, G.; Sun, L.S.; Kim, M. A Multivariable Model Predictive of Unplanned Postoperative Intubation in Infant Surgical Patients. Anesth. Analg. 2019, 129, 1645–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramanyam, R.; Yeramaneni, S.; Hossain, M.M.; Anneken, A.M.; Varughese, A.M. Perioperative Respiratory Adverse Events in Pediatric Ambulatory Anesthesia: Development and Validation of a Risk Prediction Tool. Anesth. Analg. 2016, 122, 1578–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, S.L.; Monsour, A.; Barrowman, N.; Hoey, L.; Bromwich, M.; Momoli, F.; Chan, T.; Goldberg, R.; Patel, A.; Yin, L.; et al. Predictors of postoperative respiratory complications in children undergoing adenotonsillectomy. J. Clin. Sleep. Med. 2020, 16, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guay, J.; Ochroch, E.A.; Kopp, S. Intraoperative use of low volume ventilation to decrease postoperative mortality, mechanical ventilation, lengths of stay and lung injury in adults without acute lung injury. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018, 7, CD011151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludbrook, G.L. The Hidden Pandemic: The Cost of Postoperative Complications. Curr. Anesthesiol. Rep. 2022, 12, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Delivery Type | N (%) |
|---|---|
| Nasal Cannula | 79 (67.5) |
| Simple Mask | 3 (2.6) |
| Blow By | 14 (12.0) |
| High Flow Nasal Cannula | 9 (7.7) |
| Non-Rebreather | 4 (3.4) |
| Non-Invasive Positive Pressure Ventilation | 2 (1.7) |
| Endotracheal Tube | 6 (5.1) |
| Mean ± SD/N (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | No Postoperative Oxygen Dependence (N = 248) | Postoperative Oxygen Dependence (N = 89) | Unadjusted OR (95% CI) | p-Value |
| Age (y) | 1.93 ± 1.82 | 2.32 ± 1.99 | 1.11 (0.98, 1.26) | 0.0931 |
| Sex | ||||
| Male | 118 (47.58) | 49 (55.06) | 1.35 (0.83, 2.19) | 0.2270 |
| Female | 130 (52.42) | 40 (44.94) | 1 | REF |
| Height (cm) | 92.92 ± 19.48 | 95.62 ± 17.16 | 1.01 (0.99, 1.02) | 0.2473 |
| Actual Body Weight (kg) | 11.31 ± 6.69 | 11.05 ± 5.57 | 0.99 (0.96, 1.03) | 0.7401 |
| ASA Physical Status | ||||
| I | 16 (6.45) | 2 (2.25) | 1 | REF |
| II | 97 (39.11) | 18 (20.22) | 1.48 (0.31, 7.02) | 0.6184 |
| III | 132 (53.23) | 62 (69.66) | 3.76 (0.84, 16.84) | 0.08384 |
| IV | 3 (1.21) | 7 (7.87) | 18.66 (2.53, 137.5) | 0.00409 |
| Case type | ||||
| Laparoscopic | 41 (16.53) | 9 (10.11) | 1 | REF |
| Open | 191 (77.02) | 77 (86.52) | 1.84 (0.85, 3.96) | 0.12104 |
| Operative time (min) | 219.71 ± 111.64 | 323.35 ± 154.71 | 1.06 (1.04, 1.08) | <0.0001 |
| Emergency | 42 (16.94) | 10 (11.24) | 0.62 (0.30, 1.30) | 0.2048 |
| Regional Anesthesia | 94 (37.90) | 45 (50.56) | 1.68 (1.03, 2.73) | 0.0383 |
| Cyanotic Heart Disease | 2 (0.81) | 3 (3.37) | 4.29 (0.71, 26.11) | 0.1140 |
| CNS Tumor | 3 (1.21) | 0 (0) | 0.39 (0.01, 12.10) | 0.5928 |
| Impaired Cognition/Delayed | 26 (10.48) | 18 (20.22) | 2.17 (1.12, 4.18) | 0.0214 |
| History of Cancer | 50 (20.16) | 12 (13.48) | 0.61 (0.31, 1.21) | 0.1616 |
| History of Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia | 1 (0.40) | 4 (4.49) | 11.62 (1.28, 105.35) | 0.0292 |
| Neuraxial | ||||
| None | 153 (61.69) | 44 (49.44) | 1 | REF |
| Fascial plane block | 39 (15.73) | 27 (30.34) | 2.41 (1.33, 4.36) | 0.00376 |
| Neuraxial | 56 (22.58) | 18 (20.22) | 1.12 (0.60, 2.09) | 0.7284 |
| Mean ± SD/N (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | No Postoperative Oxygen Dependence (N = 248) | Postoperative Oxygen Dependence (N = 89) | Adjusted OR (95% CI) | p-Value |
| Age (y) | 1.93 ± 1.82 | 2.32 ± 1.99 | 1.01 (0.87, 1.18) | 0.85092 |
| ASA Physical Status | ||||
| I | 16 (6.45) | 2 (2.25) | 1 | REF |
| II | 97 (39.11) | 18 (20.22) | 0.95 (0.19, 4.69) | 0.95167 |
| III | 132 (53.23) | 62 (69.66) | 1.61 (0.34, 7.65) | 0.54603 |
| IV | 3 (1.21) | 7 (7.87) | 9.86 (1.22, 79.9) | 0.03202 |
| Operative time (min) | 219.71 ± 111.64 | 323.35 ± 154.71 | 1.05 (1.03, 1.08) | 0.00001 |
| Impaired Cognition/Delayed | 26 (10.48) | 18 (20.22) | 1.84 (0.88, 3.86) | 0.10546 |
| History of Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia | 1 (0.40) | 4 (4.49) | 4.74 (0.47, 47.68) | 0.1869 |
| Neuraxial | ||||
| None | 153 (61.69) | 44 (49.44) | 1 | REF |
| Fascial plane block | 39 (15.73) | 27 (30.34) | 1.11 (0.53, 2.29) | 0.78678 |
| Neuraxial | 56 (22.58) | 18 (20.22) | 0.69 (0.34, 1.4) | 0.30278 |
| Outcomes | Mean ± SD | Unadjusted Model | Adjusted Model | ||||
| Total Sample | Group | Geometric Mean Ratio (95% CI) | p value | Geometric Mean Ratio (95% CI) | p value | ||
| N = 337 | No Postoperative Oxygen Dependence | Postoperative Oxygen Dependence | |||||
| N = 248 (73.59%) | N = 89 (26.41%) | ||||||
| Postoperative Length of Stay | 11.51 ± 15.44 | 9.91 ± 14.65 | 15.98 ± 16.73 | 1.95 (1.55–2.45) | <0.0001 | 1.39 (1.10–1.75) | 0.0062 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Robles, A.; Raval, M.V.; Wu, C.; Ballard, H.A.; Phillips, M.; Burjek, N.E.; Cheon, E.C. Risk Factors for Postoperative Pulmonary Compromise in a Pediatric Population: A Retrospective Review of a Single Institution Cohort. Children 2025, 12, 1403. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12101403
Robles A, Raval MV, Wu C, Ballard HA, Phillips M, Burjek NE, Cheon EC. Risk Factors for Postoperative Pulmonary Compromise in a Pediatric Population: A Retrospective Review of a Single Institution Cohort. Children. 2025; 12(10):1403. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12101403
Chicago/Turabian StyleRobles, Alison, Mehul V. Raval, Chunyi Wu, Heather A. Ballard, Mitchell Phillips, Nicholas E. Burjek, and Eric C. Cheon. 2025. "Risk Factors for Postoperative Pulmonary Compromise in a Pediatric Population: A Retrospective Review of a Single Institution Cohort" Children 12, no. 10: 1403. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12101403
APA StyleRobles, A., Raval, M. V., Wu, C., Ballard, H. A., Phillips, M., Burjek, N. E., & Cheon, E. C. (2025). Risk Factors for Postoperative Pulmonary Compromise in a Pediatric Population: A Retrospective Review of a Single Institution Cohort. Children, 12(10), 1403. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12101403






