Reliability and Validity of the HBSC Physical Activity Questionnaire in Japanese Adolescents
Abstract
Highlights
- The Japanese version of the WHO Health Behaviour in School-aged Children physical activity questionnaire (HBSC-J) had an acceptable reliability and validity for evaluating moderate-to-vigorous intensity physical activity (MVPA) in Japa-nese adolescents of both sexes.
- Duration, but not frequency, of vigorous physical activity as measured by the questionnaire was related to the accelerometer measurement in both sexes.
- The HBSC-J questionnaire is acceptable for evaluating daily MVPA in Japanese adolescents.
- An MVPA of 60 min per day as measured by an accelerometer corresponded to 3.6 days with 60 min per day measured by the questionnaire.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Anthropometry
2.3. Physical Activity Measurements
2.4. Self-Report Questionnaire
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Participant Characteristics
3.2. Reliability and Validity of the PA Questions in the HBSC-J Questionnaire
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PA | Physical activity |
| HBSC | The WHO Health Behaviour in School-aged Children physical activity |
| HBSC-J | The Japanese version of the WHO Health Behaviour in School-aged Children physical activity |
| ICCs | Intraclass correlation coefficients |
| MVPA | Moderate-to-vigorous physical activity |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| VPA | Vigorous physical activity |
| METs | Metabolic equivalents |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| SD | Standard deviation |
References
- Guthold, R.; Stevens, G.A.; Riley, L.M.; Bull, F.C. Global trends in insufficient physical activity among adolescents. Lancet Child. Adolesc. Health 2020, 4, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokyo Metropolitan Board of Education. The Summary of the Step Counts in the Tokyo Metropolitan Board and Education Survey. 2012. Available online: https://www.kyoiku.metro.tokyo.lg.jp/documents/d/kyoiku/07_45 (accessed on 15 September 2025).
- Japan Sports Agency. The Report of FY2019 Survey on Physical Strength and Athletic Performance. Available online: https://www.mext.go.jp/sports/content/20201015-spt_kensport01-000010432_6.pdf (accessed on 21 August 2025).
- Spruijtenburg, G.E.; van Abswoude, F.; Adams, I.L.J.; Platvoet, S.W.J.; de Niet, M.; Steenbergen, B. Change in general and domain-specific physical activity during the transition from primary to secondary education: A systematic review. BMC Public Health 2024, 24, 1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corder, K.; Winpenny, E.; Love, R.; Brown, H.E.; White, M.; van Sluijs, E. Change in physical activity from adolescence to early adulthood: A systematic review and meta-analysis of longitudinal cohort studies. Br. J. Sports Med. 2019, 53, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallal, P.C.; Andersen, L.B.; Bull, F.C.; Guthold, R.; Haskell, W.; Ekelund, U.; Lancet Physical Activity Series Working Group. Global physical activity levels: Surveillance progress, pitfalls, and prospects. Lancet 2012, 380, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.; Stolk, R.P.; Sauer, P.J.; Sijtsma, A.; Wiersma, R.; Huang, G.; Corpeleijn, E. Factors of physical activity among Chinese children and adolescents: A systematic review. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2017, 14, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morseth, B.; Jørgensen, L.; Emaus, N.; Jacobsen, B.K.; Wilsgaard, T. Tracking of leisure time physical activity during 28 yr in adults: The Tromsø study. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2011, 43, 1229–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, M.; Tynjälä, J.; Lv, Y.; Villberg, J.; Zhang, Z.; Kannas, L. Test-retest reliability of selected items of Health Behaviour in School-aged Children (HBSC) survey questionnaire in Beijing, China. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2010, 10, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, S.T.; Hong, J.T.; Wang, H. Is the Health Behavior in School-Aged Survey Questionnaire Reliable and Valid in Assessing Physical Activity and Sedentary Behavior in Young Populations? A Systematic Review. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 729641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohoutek, J.; Maráček, M.; Ng, K.; Hamrik, Z. Test-retest reliability of selected HBSC items in Vietnam: Well-being, physical and sedentary activities, and eating behaviours. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2022, 22, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, C.; Kyan, A.; Takakura, M.; Olds, T.; Schranz, N.; Tanaka, S. Validation of the Physical Activity Questions in the World Health Organization Health Behavior in School-Aged Children Survey Using Accelerometer Data in Japanese Children and Adolescents. J. Phys. Act. Health 2021, 18, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, M.L.; Okely, A.D.; Chey, T.; Bauman, A. The reliability and validity of the physical activity questions in the WHO health behaviour in school-children (HBSC) survey: A population study. Br. J. Sports Med. 2001, 35, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangul, V.; Holmen, T.L.; Kurtze, N.; Cuypers, K.; Midthjell, K. Reliability and validity of two frequently used self-administered physical activity questionnaires in adolescents. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2008, 8, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology. Health Checkup Manual for School Children (2015 Revision); Japanese Society of School Health: Tokyo, Japan, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ohkawara, K.; Oshima, Y.; Hikihara, Y.; Ishikawa-Takata, K.; Tabata, I.; Tanaka, S. Real-time estimation of daily physical activity intensity by a triaxial accelerometer and a gravity-removal classification algorithm. Br. J. Nutr. 2011, 105, 1681–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trost, S.G. State of the art reviews: Measurement of physical activity in children and adolescents. Am. J. Lifestyle Med. 2007, 1, 299–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mâsse, L.C.; Fuemmeler, B.F.; Anderson, C.B.; Matthews, C.E.; Trost, S.G.; Catellier, D.J.; Treuth, M. Accelerometer data reduction: A comparison of four reduction algorithms on select outcome variables. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2005, 37 (Suppl. S11), S544–S554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Japan Physical Activity Research Platform: JPARP. Available online: https://paplatform.umin.jp/ (accessed on 21 August 2025).
- Currie, C.; Inchley, J.; Molcho, M.; Lenzi, M.; Veselska, Z.; Wild, F. (Eds.) . Health Behaviour in School-Aged Children (HBSC) Study Protocol: Background, Methodology and Mandatory Items for the 2013/14 Survey; CAHRU: St Andrews, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, C.; Kyan, A.; Takakura, M.; Olds, T.; Schranz, N.; Tanaka, S. The validity of the Japanese version of physical activity questions in the WHO Health Behaviour in School-aged Children (HBSC) survey. Res. Exerc. Epidemiol. 2017, 19, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Health Behaviour in School-Aged Children (HBSC) Study. Available online: https://www.who.int/europe/initiatives/health-behaviour-in-school-aged-children-(hbsc)-study (accessed on 15 September 2025).
- Koo, T.K.; Li, M.Y. A guideline of selecting and reporting intraclass correlation coefficients for reliability research. J. Chiropr. Med. 2016, 15, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubert, S.; Barnes, J.D.; Demchenko, I.; Hawthorne, M.; Abdeta, C.; Abi Nader, P.; Adsuar Sala, J.C.; Aguilar-Farias, N.; Aznar, S.; Bakalár, P.; et al. Global Matrix 4.0 Physical Activity Report Card Grades for Children and Adolescents: Results and Analyses From 57 Countries. J. Phys. Act. Health 2022, 19, 700–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosselli, M.; Ermini, E.; Tosi, B.; Boddi, M.; Stefani, L.; Toncelli, L.; Modesti, P.A. Gender differences in barriers to physical activity among adolescents. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2020, 30, 1582–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohl, H.W.; Fulton, J.E.; Caspersen, C.J. Assessment of Physical Activity among Children and Adolescents: A Review and Synthesis. Prev. Med. 2000, 31, S54–S76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallis, J.F.; Buono, M.J.; Roby, J.J.; Micale, F.G.; Nelson, J.A. Seven-day recall and other physical activity self-reports in children and adolescents. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1993, 25, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasakawa Sports Foundation. Available online: https://www.ssf.or.jp/publication/ssf_books/index.html (accessed on 15 September 2025). (In Japanese).
- Chinapaw, M.J.; Mokkink, L.B.; van Poppel, M.N.; van Mechelen, W.; Terwee, C.B. Physical activity questionnaires for youth: A systematic review of measurement properties. Sports Med. 2010, 40, 539–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattler, M.C.; Jaunig, J.; Tösch, C.; Watson, E.D.; Mokkink, L.B.; Dietz, P.; van Poppel, M.N.M. Current Evidence of Measurement Properties of Physical Activity Questionnaires for Older Adults: An Updated Systematic Review. Sports Med. 2020, 50, 1271–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sember, V.; Meh, K.; Sorić, M.; Starc, G.; Rocha, P.; Jurak, G. Validity and Reliability of International Physical Activity Questionnaires for Adults across EU Countries: Systematic Review and Meta Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| All (n = 215) | Girls (n = 93) | Boys (n = 122) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | ± | SD | Mean | ± | SD | Mean | ± | SD | |
| Age (years) | 16.7 | ± | 0.8 | 16.8 | ± | 0.8 | 16.7 | ± | 0.9 |
| Height (cm) * | 165.1 | ± | 8.3 | 158.2 | ± | 5.4 | 170.4 | ± | 5.8 |
| Weight (kg) * | 55.9 | ± | 8.7 | 50.2 | ± | 5.7 | 60.2 | ± | 8.1 |
| Body Mass Index (kg/m2) * | 20.5 | ± | 2.4 | 20.1 | ± | 2.0 | 20.7 | ± | 2.6 |
| Relative Weight (%) * | −1.3 | ± | 11.8 | −3.5 | ± | 9.9 | 0.4 | ± | 12.9 |
| Daily Physical Activity by Questionnaire | At Baseline | Follow-Up | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All (n = 215) | Girls (n = 93) | Boys (n = 122) | All (n = 215) | Girls (n = 93) | Boys (n = 122) | |||||||
| n | (%) | n | (%) | n | (%) | n | (%) | n | (%) | n | (%) | |
| Days of MVPA at least 60 min/day | ||||||||||||
| 0 (day/week) | 14 | (6.5) | 7 | (7.5) | 7 | (5.7) | 16 | (7.4) | 6 | (6.5) | 10 | (8.2) |
| 1 (day/week) | 10 | (4.7) | 7 | (7.5) | 3 | (2.5) | 8 | (3.7) | 4 | (4.3) | 4 | (3.3) |
| 2 (day/week) | 32 | (14.9) | 18 | (19.4) | 14 | (11.5) | 29 | (13.5) | 20 | (21.5) | 9 | (7.4) |
| 3 (day/week) | 33 | (15.3) | 10 | (10.8) | 23 | (18.9) | 36 | (16.7) | 15 | (16.1) | 21 | (17.2) |
| 4 (day/week) | 21 | (9.8) | 11 | (11.8) | 10 | (8.2) | 18 | (8.4) | 7 | (7.5) | 11 | (9.0) |
| 5 (day/week) | 36 | (16.7) | 19 | (20.4) | 17 | (13.9) | 32 | (14.9) | 16 | (17.2) | 16 | (13.1) |
| 6 (day/week) | 26 | (12.1) | 8 | (8.6) | 18 | (14.8) | 30 | (14.0) | 10 | (10.8) | 20 | (16.4) |
| 7 (day/week) | 43 | (20.0) | 13 | (14.0) | 30 | (24.6) | 46 | (21.4) | 15 | (16.1) | 31 | (25.4) |
| Frequency of VPA by questionnaire | ||||||||||||
| Every day | 24 | (11.2) | 15 | (16.1) | 9 | (7.4) | 24 | (11.2) | 16 | (17.2) | 8 | (6.6) |
| 4 to 6 times a week | 10 | (4.7) | 7 | (7.5) | 3 | (2.5) | 11 | (5.1) | 6 | (6.5) | 5 | (4.1) |
| 2 to 3 times a week | 11 | (5.1) | 4 | (4.3) | 7 | (5.7) | 12 | (5.6) | 2 | (2.2) | 10 | (8.2) |
| Once a week | 32 | (14.9) | 16 | (17.2) | 16 | (13.1) | 22 | (10.2) | 8 | (8.6) | 14 | (11.5) |
| Once a month | 42 | (19.5) | 16 | (17.2) | 26 | (21.3) | 43 | (20.0) | 24 | (25.8) | 19 | (15.6) |
| Less than once a month | 60 | (27.9) | 26 | (28.0) | 34 | (27.9) | 72 | (33.5) | 27 | (29.0) | 45 | (36.9) |
| Never | 36 | (16.7) | 9 | (9.7) | 27 | (22.1) | 31 | (14.4) | 10 | (10.8) | 21 | (17.2) |
| Duration of VPA by questionnaire | ||||||||||||
| None | 41 | (19.1) | 26 | (28.0) | 15 | (12.3) | 40 | (18.6) | 21 | (22.6) | 19 | (15.6) |
| About half an hour | 44 | (20.5) | 23 | (24.7) | 21 | (17.2) | 30 | (14.0) | 11 | (11.8) | 19 | (15.6) |
| About 1 h | 38 | (17.7) | 11 | (11.8) | 27 | (22.1) | 40 | (18.6) | 20 | (21.5) | 20 | (16.4) |
| About 2 to 3 h | 37 | (17.2) | 13 | (14.0) | 24 | (19.7) | 40 | (18.6) | 20 | (21.5) | 20 | (16.4) |
| About 4 to 6 h | 24 | (11.2) | 10 | (10.8) | 14 | (11.5) | 25 | (11.6) | 12 | (12.9) | 13 | (10.7) |
| About 7 h or more | 31 | (14.4) | 10 | (10.8) | 21 | (17.2) | 40 | (18.6) | 9 | (9.7) | 31 | (25.4) |
| All (n = 154) | Girls (n = 78) | Boys (n = 76) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | ± | SD | Mean | ± | SD | Mean | ± | SD | |
| Age (years) | 16.8 | ± | 0.9 | 16.8 | ± | 0.9 | 16.7 | ± | 0.9 |
| Height (cm) * | 164.2 | ± | 8.4 | 158.0 | ± | 5.4 | 170.6 | ± | 5.7 |
| Weight (kg) * | 55.4 | ± | 8.5 | 50.2 | ± | 5.5 | 60.8 | ± | 7.7 |
| Body Mass Index (kg/m2) * | 20.5 | ± | 2.4 | 20.1 | ± | 2.0 | 20.9 | ± | 2.6 |
| Relative Weight (%) * | −1.3 | ± | 11.4 | −3.5 | ± | 9.6 | 1.0 | ± | 12.8 |
| Daily Physical Activity by Accelerometer | All (n = 154) | Girls (n = 78) | Boys (n = 76) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | ± | SD | Mean | ± | SD | Mean | ± | SD | |
| Time in more than 3 METs (min/day) * | 89.9 | ± | 41.0 | 77.0 | ± | 29.3 | 103.2 | ± | 47.0 |
| Time in more than 6 METs (min/day) * | 5.5 | ± | 8.1 | 2.5 | ± | 3.1 | 8.7 | ± | 10.2 |
| Daily physical activity by questionnaire | |||||||||
| Days of MVPA at least 60 min/day | n | (%) | n | (%) | n | (%) | |||
| 0 (day/week) | 7 | (4.5) | 5 | (6.4) | 2 | (2.6) | |||
| 1 (day/week) | 6 | (3.9) | 5 | (6.4) | 1 | (1.3) | |||
| 2 (day/week) | 24 | (15.6) | 16 | (20.5) | 8 | (10.5) | |||
| 3 (day/week) | 25 | (16.2) | 10 | (12.8) | 15 | (19.7) | |||
| 4 (day/week) | 14 | (9.1) | 9 | (11.5) | 5 | (6.6) | |||
| 5 (day/week) | 28 | (18.2) | 14 | (17.9) | 14 | (18.4) | |||
| 6 (day/week) | 17 | (11.0) | 6 | (7.7) | 11 | (14.5) | |||
| 7 (day/week) | 33 | (21.4) | 13 | (16.7) | 20 | (26.3) | |||
| Frequency of VPA by questionnaire | |||||||||
| Every day | 17 | (11.0) | 13 | (16.7) | 4 | (5.3) | |||
| 4 to 6 times a week | 10 | (6.5) | 8 | (10.3) | 2 | (2.6) | |||
| 2 to 3 times a week | 8 | (5.2) | 4 | (5.1) | 4 | (5.3) | |||
| Once a week | 27 | (17.5) | 14 | (17.9) | 13 | (17.1) | |||
| Once a month | 28 | (18.2) | 13 | (16.7) | 15 | (19.7) | |||
| Less than once a month | 41 | (26.6) | 20 | (25.6) | 21 | (27.6) | |||
| Never | 23 | (14.9) | 6 | (7.7) | 17 | (22.4) | |||
| Duration of VPA by questionnaire | |||||||||
| None | 35 | (22.7) | 25 | (32.1) | 10 | (13.2) | |||
| About half an hour | 30 | (19.5) | 17 | (21.8) | 13 | (17.1) | |||
| About 1 h | 26 | (16.9) | 8 | (10.3) | 18 | (23.7) | |||
| About 2 to 3 h | 26 | (16.9) | 11 | (14.1) | 15 | (19.7) | |||
| About 4 to 6 h | 17 | (11.0) | 9 | (11.5) | 8 | (10.5) | |||
| About 7 h or more | 20 | (13.0) | 8 | (10.3) | 12 | (15.8) | |||
| All (n = 215) | Girls (n = 93) | Boys (n = 122) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ICC [95% CI] | ICC [95% CI] | ICC [95% CI] | |
| Days of at least 60 min/day MVPA (days/week) | 0.74 [0.68–0.80] | 0.63 [0.49–0.74] | 0.82 [0.75–0.87] |
| Frequency of VPA (days/week) | 0.71 [0.64–0.77] | 0.72 [0.60–0.80] | 0.69 [0.58–0.77] |
| Duration of VPA (hours/week) | 0.64 [0.55–0.83] | 0.64 [0.50–0.75] | 0.62 [0.50–0.72] |
| By Accelerometer (min/day) | All (n = 154) | Girls (n = 78) | Boys (n = 76) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MVPA [95% CI] | VPA [95% CI] | MVPA [95% CI] | VPA [95% CI] | MVPA [95% CI] | VPA [95% CI] | |
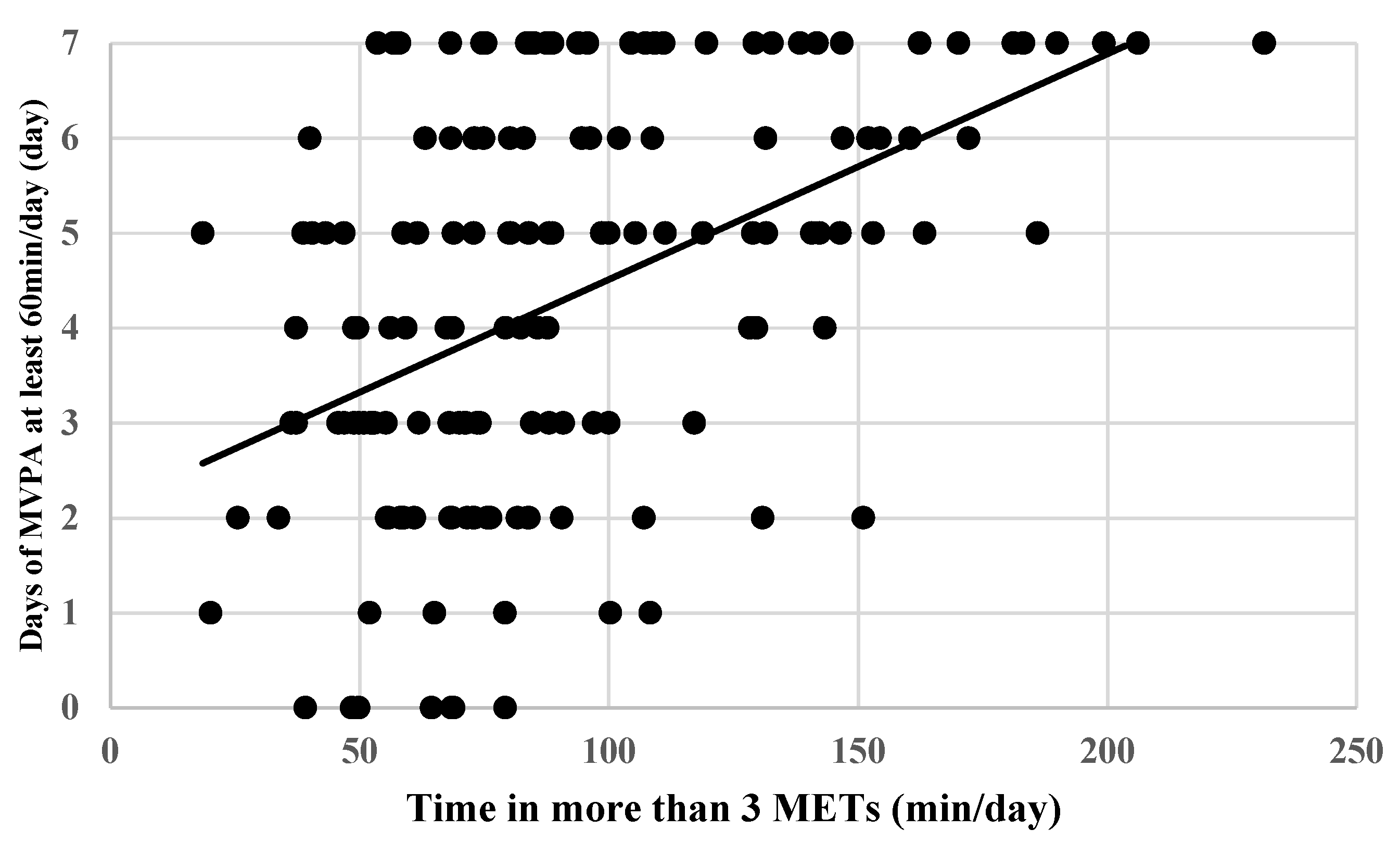
| Days of at least 60 min/day MVPA (days/week) | 0.44 [0.30–0.56] | 0.41 [0.21–0.58] | 0.48 [0.28–0.64] | |||
| p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | ||||
| Frequency of VPA (days/week) | −0.19 [−0.34–−0.03] | −0.26 [−0.46–−0.04] | −0.23 [−0.44–−0.01] | |||
| p = 0.017 | p = 0.021 | p = 0.053 | ||||
| Duration of VPA (hours/week) | 0.24 [0.08–0.38] | 0.40 [0.19–0.57] | 0.24 [0.02–0.43] | |||
| p = 0.003 | p < 0.001 | p = 0.040 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tanaka, C.; Watanabe, M.; Oishi, K.; Reilly, J.J.; Ishii, K.; Tanaka, S. Reliability and Validity of the HBSC Physical Activity Questionnaire in Japanese Adolescents. Children 2025, 12, 1360. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12101360
Tanaka C, Watanabe M, Oishi K, Reilly JJ, Ishii K, Tanaka S. Reliability and Validity of the HBSC Physical Activity Questionnaire in Japanese Adolescents. Children. 2025; 12(10):1360. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12101360
Chicago/Turabian StyleTanaka, Chiaki, Masashi Watanabe, Kan Oishi, John J. Reilly, Kojiro Ishii, and Shigeho Tanaka. 2025. "Reliability and Validity of the HBSC Physical Activity Questionnaire in Japanese Adolescents" Children 12, no. 10: 1360. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12101360
APA StyleTanaka, C., Watanabe, M., Oishi, K., Reilly, J. J., Ishii, K., & Tanaka, S. (2025). Reliability and Validity of the HBSC Physical Activity Questionnaire in Japanese Adolescents. Children, 12(10), 1360. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12101360







