A Bibliometric Analysis of Physical Literacy Studies in Relation to Health of Children and Adolescents
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design and Data
2.2. Data Analysis
3. Results
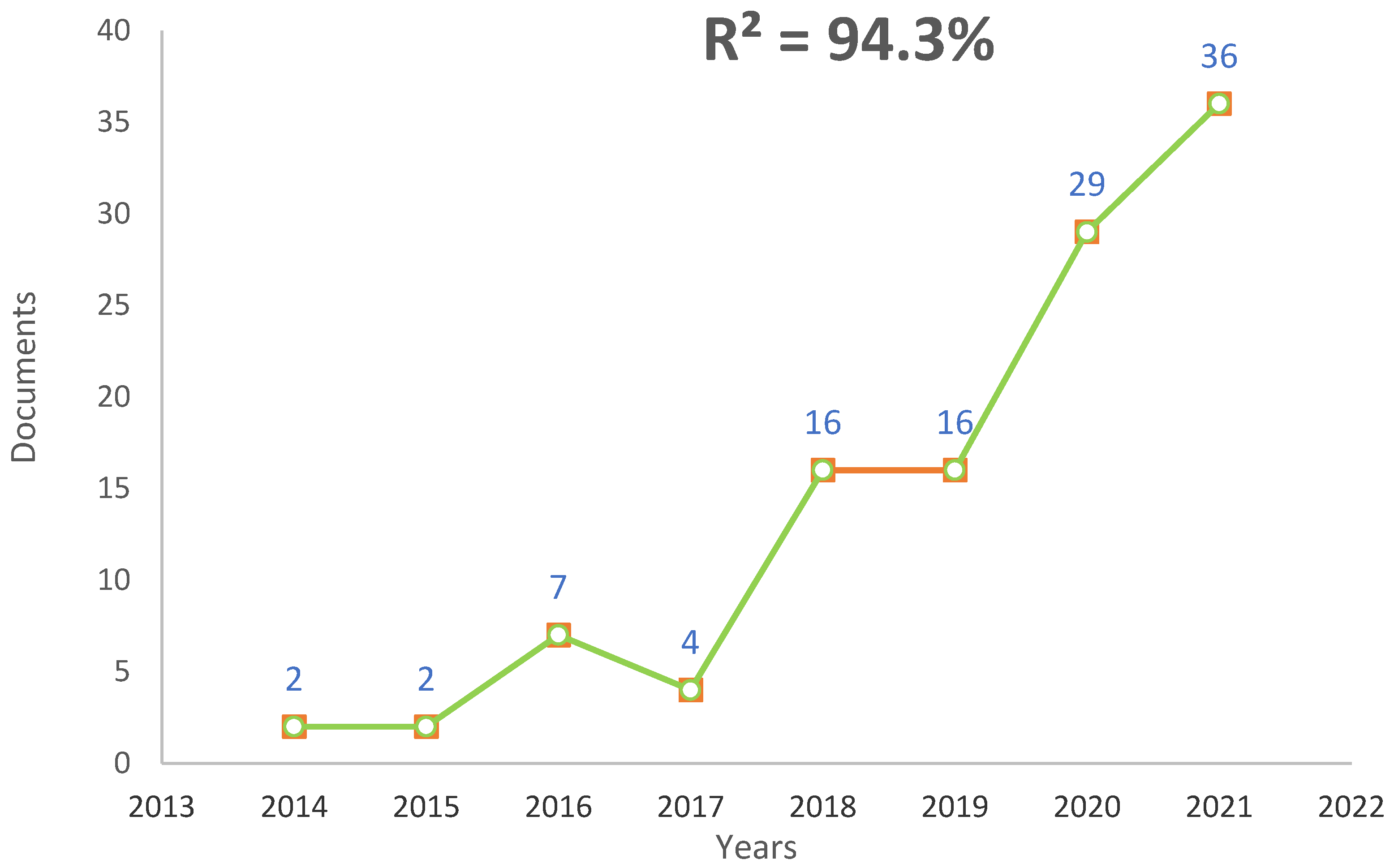
3.1. Annual Publications Trend
3.2. WoS Categories
3.3. Publications Titles
3.4. Prolific and Influential Co-Authors
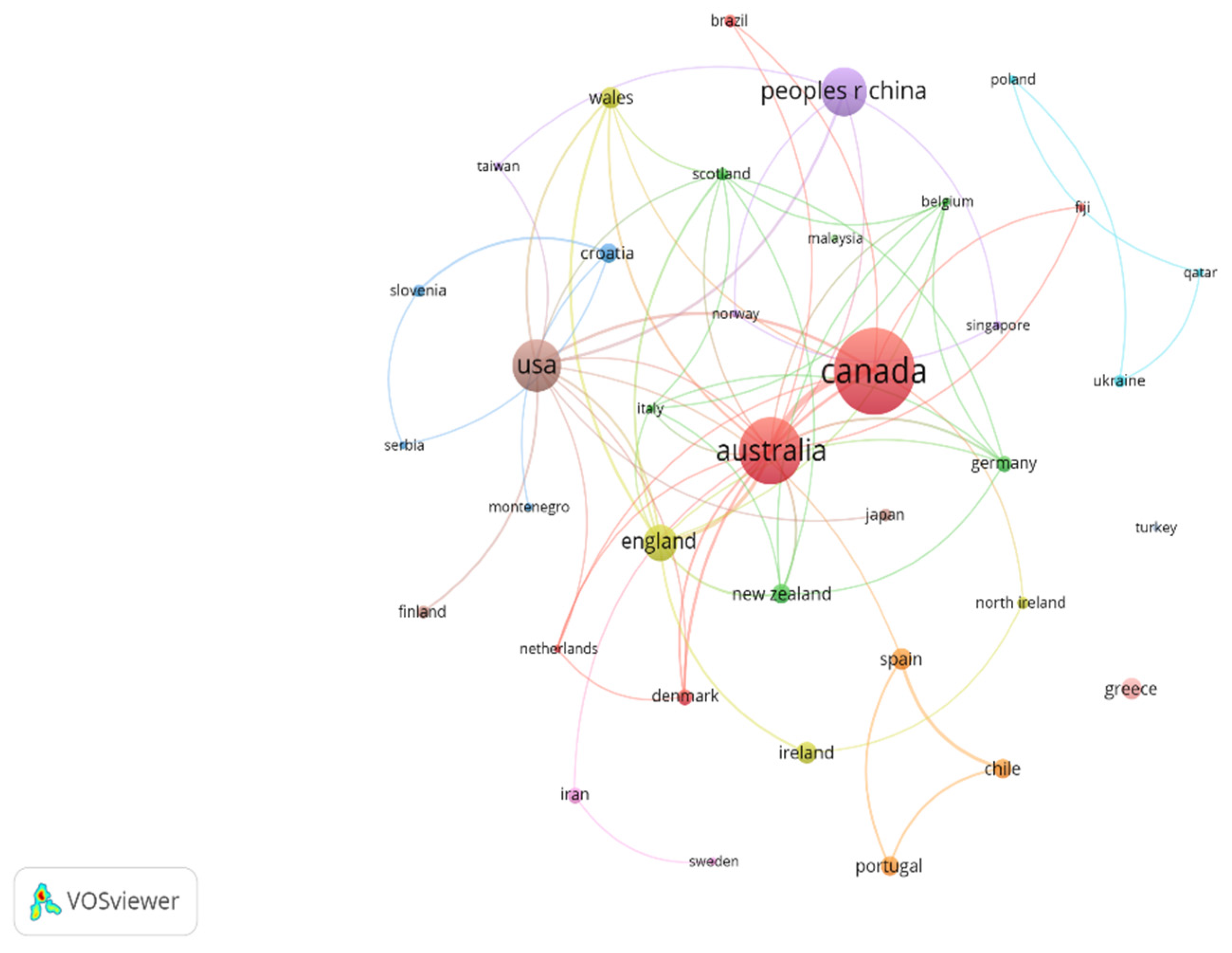
3.5. Countries/Regions
3.6. Author Keywords
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Warburton, D.E.; Nicol, C.W.; Bredin, S.S. Health benefits of physical activity: The evidence. CMAJ 2006, 174, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Physical Activity. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/physical-activity (accessed on 1 December 2022).
- Lautenschlager, N.T.; Almeida, O.P.; Flicker, L.; Janca, A. Can physical activity improve the mental health of older adults? Ann. Gen. Psychiatry 2004, 3, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.Y.; Han, L.H.; Zhang, J.H.; Luo, S.; Hu, J.W.; Sun, K. The influence of physical activity, sedentary behavior on health-related quality of life among the general population of children and adolescents: A systematic review. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0187668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perales, F.; Del Pozo-Cruz, J.; Del Pozo-Cruz, B. Impact of physical activity on psychological distress: A prospective analysis of an Australian national sample. Am. J. Public Health 2014, 104, e91–e97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macera, C.A.; Hootman, J.M.; Sniezek, J.E. Major public health benefits of physical activity. Arthritis Care Res. 2003, 49, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irandoust, K.; Taheri, M.; H’mida, C.; Neto, G.R.; Trabelsi, K.; Ammar, A.; Souissi, N.; Chtourou, H.; Nikolaidis, P.T.; Rosemann, T.; et al. Exergaming and aquatic exercises affect lung function and weight loss in obese children. Int. J. Sports Med. 2021, 42, 566–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, M. Effect of running training on white blood cells and platelets count and red blood cells distribution width in untrained middle-aged men. Int. J. Sport Stud. Health 2019, 2, e89513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loprinzi, P.D.; Cardinal, B.J.; Loprinzi, K.L.; Lee, H. Benefits and environmental determinants of physical activity in children and adolescents. Obes. Facts 2012, 5, 597–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hills, A.P.; Street, S.J.; Byrne, N.M. Physical activity and health: “What is old is new again”. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2015, 75, 77–95. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Telama, R.; Yang, X.; Laakso, L.; Viikari, J. Physical activity in childhood and adolescence as predictor of physical activity in young adulthood. Am. J. Prev. Med. 1997, 13, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, S.; Rajmil, L. Advertising, obesity and child health: The case of Spain. BMJ Paediatr. Open 2022, 6, e001482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owen, N.; Healy, G.N.; Matthews, C.E.; Dunstan, D.W. Too much sitting: The population-health science of sedentary behavior. Exerc. Sport Sci. Rev. 2010, 38, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahoo, K.; Sahoo, B.; Choudhury, A.K.; Sofi, N.Y.; Kumar, R.; Bhadoria, A.S. Childhood obesity: Causes and consequences. J. Fam. Med. Prim. Care 2015, 4, 187. [Google Scholar]
- Hallal, P.C.; Andersen, L.B.; Bull, F.C.; Guthold, R.; Haskell, W.; Ekelund, U.; Lancet Physical Activity Series Working Group. Global physical activity levels: Surveillance progress, pitfalls, and prospects. Lancet 2012, 380, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Physical Activity in Adolescents; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016.
- WHO Obesity. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/obesity#tab=tab_1 (accessed on 1 December 2022).
- de Bont, J.; Bennett, M.; León-Muñoz, L.M.; Duarte-Salles, T. The prevalence and incidence rate of overweight and obesity among 2.5 million children and adolescents in Spain. Rev. Esp. Cardiol. 2022, 75, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spinelli, A.; Buoncristiano, M.; Nardone, P.; Starc, G.; Hejgaard, T.; Júlíusson, P.B.; Fismen, A.S.; Weghuber, D.; Musić Milanović, S.; García-Solano, M. Thinness, overweight, and obesity in 6-to 9-year-old children from 36 countries: The World Health Organization European Childhood Obesity Surveillance Initiative—COSI 2015–2017. Obes. Rev. 2021, 22, e13214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunez-Cortés, M. Relation of obesity and cardiovascular risk in Spain. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. 2006, 76, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Ullevig, S.L.; Sosa, E.; Liang, Y.; Olmstead, T.; Howard, J.T.; Errisuriz, V.L.; Estrada, V.M.; Martinez, C.E.; He, M. Study protocol for a cluster randomized controlled trial to test “¡ Míranos! Look at Us, We Are Healthy!”—An early childhood obesity prevention program. BMC Pediatr. 2019, 19, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toussaint, N.; Streppel, M.T.; Mul, S.; Schreurs, A.; Balledux, M.; van Drongelen, K.; Janssen, M.; Fukkink, R.G.; Weijs, P.J. A preschool-based intervention for Early Childhood Education and Care (ECEC) teachers in promoting healthy eating and physical activity in toddlers: Study protocol of the cluster randomized controlled trial PreSchool@ HealthyWeight. BMC Public Health 2019, 19, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, W.; Belton, S.; Issartel, J. Promoting physical literacy in Irish adolescent youth: The youth-physical activity towards health (Y-PATH) intervention. MOJ Public Health 2015, 2, 168–173. [Google Scholar]
- Mendoza-Muñoz, M.; Carlos-Vivas, J.; Villafaina, S.; Parraca, J.A.; Vega-Muñoz, A.; Contreras-Barraza, N.; Raimundo, A. Effects of a Physical Literacy Breaks (PLBreaks) Program on Physical Literacy and Body Composition in Portuguese Schoolchildren: A Study Protocol. Biology 2022, 11, 910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabadán-Diehl, C.; Safdie, M.; Rodin, R. Colaboración trilateral entre Canadá, Estados Unidos y México en torno a la Iniciativa contra la Obesidad Infantil. RPSP 2016, 40, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gába, A.; Rubín, L.; Badura, P.; Roubalová, E.; Sigmund, E.; Kudláček, M.; Sigmundová, D.; Dygrýn, J.; Hamrik, Z. Health, Results from the Czech Republic’s 2018 report card on physical activity for children and youth. J. Exerc. Sci. Fit. 2018, 15, S338–S340. [Google Scholar]
- de Balazs, A.C.R.; de D’Amico, R.L.; Cedeño, J.J.M. Alfabetización física: Una percepción reflexiva. J. Dialógica Rev. Multidiscip. 2017, 14, 87–102. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, D.M.; Dudley, D.A.; Cairney, J. Physical literacy profiles are associated with differences in children’s physical activity participation: A latent profile analysis approach. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2020, 23, 1062–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cairney, J.; Dudley, D.; Kwan, M.; Bulten, R.; Kriellaars, D. Physical literacy, physical activity and health: Toward an evidence-informed conceptual model. Sports Med. 2019, 49, 371–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza-Muñoz, M.; Barrios-Fernández, S.; Adsuar, J.C.; Pastor-Cisneros, R.; Risco-Gil, M.; García-Gordillo, M.Á.; Carlos-Vivas, J. Influence of body composition on physical literacy in Spanish children. Biology 2021, 10, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldwell, H.A.; Di Cristofaro, N.A.; Cairney, J.; Bray, S.R.; MacDonald, M.J.; Timmons, B.W. Physical literacy, physical activity, and health indicators in school-age children. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coyne, P.; Vandenborn, E.; Santarossa, S.; Milne, M.M.; Milne, K.J.; Woodruff, S.J. Physical literacy improves with the Run Jump Throw Wheel program among students in grades 4–6 in southwestern Ontario. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2019, 44, 645–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kriellaars, D.J.; Cairney, J.; Bortoleto, M.A.; Kiez, T.K.; Dudley, D.; Aubertin, P. The impact of circus arts instruction in physical education on the physical literacy of children in grades 4 and 5. J. Teach. Phys. Educ. 2019, 38, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza-Muñoz, M.; Calle-Guisado, V.; Pastor-Cisneros, R.; Barrios-Fernandez, S.; Rojo-Ramos, J.; Vega-Muñoz, A.; Contreras-Barraza, N.; Carlos-Vivas, J. Effects of Active Breaks on Physical Literacy: A Cross-Sectional Pilot Study in a Region of Spain. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 7597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandigo, J.; Lodewyk, K.; Tredway, J. Examining the impact of a teaching games for understanding approach on the development of physical literacy using the passport for life assessment tool. J. Teach. Phys. Educ. 2019, 38, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bremer, E.; Graham, J.D.; Cairney, J. Outcomes and feasibility of a 12-week physical literacy intervention for children in an afterschool program. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwan, M.Y.; Graham, J.D.; Bedard, C.; Bremer, E.; Healey, C.; Cairney, J. Examining the effectiveness of a pilot physical literacy–based intervention targeting first-year university students: The PLUS program. J. Sage Open 2019, 9, 2158244019850248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holler, P.; Jaunig, J.; Moser, O.; Tuttner, S.; Simi, H.; Wallner, D.; Amort, F.M.; van Poppel, M. Primary Care and Physical Literacy: A Non-Randomized Controlled Pilot Study to Combat the High Prevalence of Physically Inactive Adults in Austria. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 8593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza-Muñoz, M.; Vega-Muñoz, A.; Carlos-Vivas, J.; Denche-Zamorano, Á.; Adsuar, J.C.; Raimundo, A.; Salazar-Sepúlveda, G.; Contreras-Barraza, N.; Muñoz-Urtubia, N. The Bibliometric Analysis of Studies on Physical Literacy for a Healthy Life. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 15211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.-C.; Liu, F.-H.; Liu, C.-M.; Yu, C.-H.; Chang, Y.-C. Bibliometric analysis of top-cited articles in Journal of Dental Sciences. J. Dent. Sci. 2023, 18, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denche-Zamorano, Á.; Pereira-Payo, D.; Franco-García, J.M.; Pastor-Cisneros, R.; Salazar-Sepúlveda, G.; Castillo, D.; Marín-Gil, M.; Barrios-Fernandez, S. Mapping the scientific research on suicide and physical activity: A bibliometric analysis. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 16413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalantari, A.; Kamsin, A.; Kamaruddin, H.S.; Ale Ebrahim, N.; Gani, A.; Ebrahimi, A.; Shamshirband, S. A bibliometric approach to tracking big data research trends. J. Big Data 2017, 4, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, N.S.; Malik, A.A.; Shahbaz, M.Q. Bibliometric analysis of statistics journals indexed in web of science under emerging source citation index. Sage Open 2021, 11, 2158244020988870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Solla Price, D. A general theory of bibliometric and other cumulative advantage processes. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. 1976, 27, 292–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zipf, G.K. Selected studies of the principle of relative frequency in language. In Selected Studies of the Principle of Relative Frequency in Language; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bulick, S. Book use as a Bradford-Zipf phenomenon. Coll. Res. Libr. 1978, 39, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morse, P.M.; Leimkuhler, F.F. Exact solution for the Bradford distribution and its use in modeling informational data. Oper. Res. 1979, 27, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotka, A.J. The frequency distribution of scientific productivity. J. Wash. Acad. Sci. 1926, 16, 317–323. [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch, J.E. An index to quantify an individual’s scientific research output. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 16569–16572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perianes-Rodriguez, A.; Waltman, L.; Van Eck, N.J. Constructing bibliometric networks: A comparison between full and fractional counting. J. Inf. 2016, 10, 1178–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waltman, L.; Van Eck, N.J.; Noyons, E.C. A unified approach to mapping and clustering of bibliometric networks. J. Informetr. 2010, 4, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longmuir, P.E.; Boyer, C.; Lloyd, M.; Yang, Y.; Boiarskaia, E.; Zhu, W.; Tremblay, M.S. The Canadian assessment of physical literacy: Methods for children in grades 4 to 6 (8 to 12 years). BMC Public Health 2015, 15, 767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, C.E.; Longmuir, P.E.; Boyer, C.; Andersen, L.B.; Barnes, J.D.; Boiarskaia, E.; Cairney, J.; Faigenbaum, A.D.; Faulkner, G.; Hands, B.P. The Canadian assessment of physical literacy: Development of a model of children’s capacity for a healthy, active lifestyle through a Delphi process. J. Phys. Act. Health 2016, 13, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belanger, K.; Barnes, J.D.; Longmuir, P.E.; Anderson, K.D.; Bruner, B.; Copeland, J.L.; Gregg, M.J.; Hall, N.; Kolen, A.M.; Lane, K.N. The relationship between physical literacy scores and adherence to Canadian physical activity and sedentary behaviour guidelines. BMC Public Health 2018, 18, 1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, L.M.; Dudley, D.A.; Telford, R.D.; Lubans, D.R.; Bryant, A.S.; Roberts, W.M.; Morgan, P.J.; Schranz, N.K.; Weissensteiner, J.R.; Vella, S.A. Guidelines for the selection of physical literacy measures in physical education in Australia. J. Teach. Phys. Educ. 2019, 38, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremblay, M.S.; Longmuir, P.E.; Barnes, J.D.; Belanger, K.; Anderson, K.D.; Bruner, B.; Copeland, J.L.; Nyström, C.D.; Gregg, M.J.; Hall, N. Physical literacy levels of Canadian children aged 8–12 years: Descriptive and normative results from the RBC Learn to Play–CAPL project. BMC Public Health 2018, 18, 1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornish, K.; Fox, G.; Fyfe, T.; Koopmans, E.; Pousette, A.; Pelletier, C.A. Understanding physical literacy in the context of health: A rapid scoping review. J. BMC Public Health 2020, 20, 1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, L.; O’Connor, J.; Alfrey, L. Mapping the physical literacy controversy: An analysis of key actors within scholarly literature. J. Phys. Educ. 2021, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cairney, J.; Veldhuizen, S.; Graham, J.D.; Rodriguez, C.; Bedard, C.; Bremer, E.; Kriellaars, D. A Construct Validation Study of PLAYfun. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2018, 50, 855–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, S. Physical literacy in children and adolescents: Definitions, assessments, and interventions. Eur. Phys. Educ. Rev. 2021, 27, 96–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodewyk, K.R.; Mandigo, J.L. Early validation evidence of a Canadian practitioner-based assessment of physical literacy in physical education: Passport for Life. Phys. Educ. 2017, 74, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jupiter4 The Tools. Available online: https://fms.60minkidsclub.org/?page_id¼270 (accessed on 1 December 2022).
- Lane, C.; Carson, V.; Morton, K.; Reno, K.; Wright, C.; Predy, M.; Naylor, P.-J. A real-world feasibility study of the PLAYshop: A brief intervention to facilitate parent engagement in developing their child’s physical literacy. Pilot Feasibility Stud. 2021, 7, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jean de Dieu, H.; Zhou, K. Physical Literacy Assessment Tools: A Systematic Literature Review for Why, What, Who, and How. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 7954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Do, J.; Blais, A.; Feldman, B.; Brandão, L.R.; Lougheed, J.; Pohl, D.; Klaassen, R.J.; Johnston, D.L.; De Laat, D.; Roth, J. Characterization of physical literacy in children with chronic medical conditions compared with healthy controls: A cross-sectional study. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2021, 46, 1073–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohl, H.W., 3rd; Craig, C.L.; Lambert, E.V.; Inoue, S.; Alkandari, J.R.; Leetongin, G.; Kahlmeier, S.; Lancet Physical Activity Series Working Group. The pandemic of physical inactivity: Global action for public health. Lancet 2012, 380, 294–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, G.; Laddu, D.R.; Phillips, S.A.; Lavie, C.J.; Arena, R. A tale of two pandemics: How will COVID-19 and global trends in physical inactivity and sedentary behavior affect one another? Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2021, 64, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudley, D.; Cairney, J.; Wainwright, N.; Kriellaars, D.; Mitchell, D. Critical considerations for physical literacy policy in public health, recreation, sport, and education agencies. Quest 2017, 69, 436–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesic, M.G.; Peric, M.; Gilic, B.; Manojlovic, M.; Drid, P.; Modric, T.; Znidaric, Z.; Zenic, N.; Pajtler, A. Are Health Literacy and Physical Literacy Independent Concepts? A Gender-Stratified Analysis in Medical School Students from Croatia. Children 2022, 9, 1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesic, M.G.; Savicevic, A.J.; Peric, M.; Gilic, B.; Zenic, N. Specificity of the Associations between Indices of Cardiovascular Health with Health Literacy and Physical Literacy; A Cross-Sectional Study in Older Adolescents. Medicina 2022, 58, 1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakkalbasi, N.; Bauer, K.; Glover, J.; Wang, L. Three options for citation tracking: Google Scholar, Scopus and Web of Science. Biomed. Digit. Libr. 2006, 3, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadegani, A.A.; Salehi, H.; Yunus, M.M.; Farhadi, H.; Fooladi, M.; Farhadi, M.; Ebrahim, N.A. A comparison between two main academic literature collections: Web of Science and Scopus databases. Asian Soc. Sci. 2013, 9, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falagas, M.E.; Pitsouni, E.I.; Malietzis, G.A.; Pappas, G. Comparison of PubMed, Scopus, web of science, and Google scholar: Strengths and weaknesses. FASEB J. 2008, 22, 338–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harzing, A.-W.; Alakangas, S. Google Scholar, Scopus and the Web of Science: A longitudinal and cross-disciplinary comparison. Scientometrics 2016, 106, 787–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| WoS Categories | Doc. | Prolific Journals | Doc. | Prolific Publishers | Doc. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Public Environmental Occupational Health | 43 | BMC Public Health | 20 | Springer Nature | 29 |
| Sport Sciences | 41 | International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health | 14 | MDPI | 24 |
| Education Educational Research | 39 | Physical Education and Sport Pedagogy | 7 | Taylor & Francis | 23 |
| Environmental Sciences | 14 | Journal of Teaching in Physical Education | 6 | Elsevier | 11 |
| Hospitality Leisure Sport Tourism | 13 | European Physical Education Review | 5 | Human Kinetics Publ Inc | 10 |
| Bradford’s Zone | Journals | Doc. | %Doc. | Cit. * | JIF | Q. | %O.A | Cumulative Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CORE | BMC Public Health | 19 | 13.77% | 437 | 4.135 | Q2 | 99.59% | 13.77% |
| International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health | 14 | 10.14% | 84 | 4.614 | Q1 | 96.11% | 23.91% | |
| Physical Education and Sport Pedagogy | 7 | 5.07% | 28 | 4.638 | Q1 | 19.16% | 28.99% | |
| Journal of Teaching in Physical Education | 6 | 4.35% | 102 | 2.66 | Q2 | 1.74% | 33.33% | |
| ZONE 1 | European Physical Education Review | 5 | 3.62% | 38 | 3.675 | Q1 | 16.67% | 3.62% |
| Applied Physiology Nutrition and Metabolism | 4 | 2.90% | 22 | 3.016 | Q2 | 7.89% | 6.52% | |
| Biology-Basel | 3 | 2.17% | 9 | 5.168 | Q1 | 94.78% | 8.70% | |
| Children-Basel | 3 | 2.17% | 12 | 2.835 | Q2 | 95.35% | 10.87% | |
| Curriculum studies in Health and Physical Education | 3 | 2.17% | 15 | N/A | N/A | 14.29% | 13.04% | |
| Frontiers in Public Health | 3 | 2.17% | 22 | 6.461 | Q1 | 99.17% | 15.22% | |
| Journal of Exercise Science & Fitness | 3 | 2.17% | 28 | 3.465 | Q2 | 100.00% | 17.39% | |
| Journal of Physical Activity & Health | 3 | 2.17% | 69 | 3 | Q2 | 0.64% | 19.57% | |
| Psychology of Sport and Exercise | 3 | 2.17% | 3 | 5.118 | Q1 | 7.47% | 21.74% | |
| Frontiers in Sports and Active Living | 2 | 1.45% | 0 | N/A | N/A | 98.51% | 23.19% | |
| Journal of Physical Education Recreation and Dance | 2 | 1.45% | 2 | N/A | N/A | 0.00% | 24.64% | |
| Journal of Science and Medicine in Sport | 2 | 1.45% | 8 | 4.597 | Q1 | 8.42% | 26.09% | |
| Physical Educator-Us | 2 | 1.45% | 21 | N/A | N/A | 0.00% | 27.54% | |
| Quest | 2 | 1.45% | 88 | 2.891 | Q2 | 4.44% | 28.99% | |
| Revista de Psicologia del Deporte | 2 | 1.45% | 3 | 0.936 | Q4 | 0% | 30.43% | |
| Science of Gymnastics Journal | 2 | 1.45% | 4 | N/A | N/A | 0% | 31.88% | |
| Sport Education and Society | 2 | 1.45% | 5 | 3.586 | Q1 | 14.92% | 33.33% | |
| Sports Medicine | 2 | 1.45% | 247 | 11.928 | Q1 | 31.33% | 34.78% | |
| Sports Medicine—Open | 2 | 1.45% | 10 | 6.766 | Q1 | 100% | 36.23% |
| Authors | Affiliation | Country/Region | Doc. | Cit. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Longmuir, Patricia E. | University of Ottawa | Canada | 16 | 494 |
| Cairney, John | University of Queensland | Australia | 15 | 403 |
| Tremblay, Mark S. | Children’s Hospital Eastern Ontario Research Institute | Canada | 14 | 479 |
| Sum, Raymond Kim Wai | Chinese University of Hong Kong | China | 11 | 75 |
| Barnes, Joel D. | Children’s Hospital Eastern Ontario Research Institute | Canada | 9 | 284 |
| Li, Ming Hui | Chinese University of Hong Kong | China | 8 | 32 |
| Dudley, Dean | Macquaire University | Australia | 7 | 284 |
| Belanger, Kevin | Children’s Hospital Eastern Ontario Research Institute | Canada | 6 | 145 |
| Ha, Amy S. | Chinese University of Hong Kong | China | 6 | 27 |
| Kriellaars, Dean | University of Manitoba | Canada | 6 | 275 |
| Woodruff, Sarah J. | University of Windsor | Canada | 6 | 153 |
| Barnett, Lisa M. | Deakin University | Australia | 5 | 29 |
| Kaioglou, Vasiliki | National & Kapodistrian University Athens | Greece | 5 | 23 |
| Ma, Rui-Si | Jinan University | China | 5 | 16 |
| Sheehan, Dwayne | Mount Royal Uni, Fac. of Health, Community, and Education | Canada | 5 | 108 |
| Sit, Cindy Hui Ping | Chinese University of Hong Kong | China | 5 | 22 |
| Stone, Michelle R. | Dalhousie University | Canada | 5 | 117 |
| Venetsanou, Fotini | National and Kapodistrian University Athens | Greece | 5 | 23 |
| Author(s) | Total Documents | Documents in H-Index 21 | Most-Cited Document | Times Cited * |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Longmuir, Patricia E. | 16 | 7 | The Canadian Assessment of Physical Literacy: methods for children in grades 4 to 6 (8 to 12 years) [52] | 101 |
| Tremblay, Mark S. | 14 | 8 | ||
| Cairney, John | 15 | 5 | Physical Literacy, Physical Activity and Health: Toward an Evidence-Informed Conceptual Model [29] | 147 |
| Dudley, Dean | 7 | 3 | ||
| Kriellaars, Dean | 6 | 4 | ||
| Barnes, Joel D. | 9 | 5 | The Canadian Assessment of Physical Literacy: Development of a Model of Children’s Capacity for a Healthy, Active Lifestyle Through a Delphi Process [53] | 65 |
| Belanger, Kevin | 6 | 3 | The relationship between physical literacy scores and adherence to Canadian physical activity and sedentary behaviour guidelines [54] | 47 |
| Woodruff, Sarah J. | 6 | 3 | ||
| Sheehan, Dwayne | 5 | 2 | ||
| Barnett, Lisa M. | 5 | 1 | Guidelines for the Selection of Physical Literacy Measures in Physical Education in Australia [55] | 21 |
| Stone, Michelle R. | 5 | 1 | Physical literacy levels of Canadian children aged 8–12 years: descriptive and normative results from the RBC Learn to Play-CAPL project [56] | 44 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Urbano-Mairena, J.; Castillo-Paredes, A.; Muñoz-Bermejo, L.; Denche-Zamorano, Á.; Rojo-Ramos, J.; Pastor-Cisneros, R.; Mendoza-Muñoz, M. A Bibliometric Analysis of Physical Literacy Studies in Relation to Health of Children and Adolescents. Children 2023, 10, 660. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10040660
Urbano-Mairena J, Castillo-Paredes A, Muñoz-Bermejo L, Denche-Zamorano Á, Rojo-Ramos J, Pastor-Cisneros R, Mendoza-Muñoz M. A Bibliometric Analysis of Physical Literacy Studies in Relation to Health of Children and Adolescents. Children. 2023; 10(4):660. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10040660
Chicago/Turabian StyleUrbano-Mairena, Javier, Antonio Castillo-Paredes, Laura Muñoz-Bermejo, Ángel Denche-Zamorano, Jorge Rojo-Ramos, Raquel Pastor-Cisneros, and María Mendoza-Muñoz. 2023. "A Bibliometric Analysis of Physical Literacy Studies in Relation to Health of Children and Adolescents" Children 10, no. 4: 660. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10040660
APA StyleUrbano-Mairena, J., Castillo-Paredes, A., Muñoz-Bermejo, L., Denche-Zamorano, Á., Rojo-Ramos, J., Pastor-Cisneros, R., & Mendoza-Muñoz, M. (2023). A Bibliometric Analysis of Physical Literacy Studies in Relation to Health of Children and Adolescents. Children, 10(4), 660. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10040660










