Hematologic Risk Factors for the Development of Retinopathy of Prematurity—A Retrospective Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wood, E.H.; Chang, E.Y.; Beck, K.; Hadfield, B.R.; Quinn, A.R.; Harper, C.A., 3rd. 80 Years of vision: Preventing blindness from retinopathy of prematurity. J. Perinatol. 2021, 41, 1216–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.J.; Port, A.D.; Swan, R.; Campbell, J.P.; Chan, R.V.P.; Chiang, M.F. Retinopathy of prematurity: A review of risk factors and their clinical significance. Surv. Ophthalmol. 2018, 63, 618–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grottenberg, B.G.; Korseth, K.M.; Follestad, T.; Stensvold, H.J.; Støen, R.; Austeng, D. Stable incidence but regional differences in retinopathy of prematurity in Norway from 2009 to 2017. Acta Ophthalmol. 2021, 99, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerull, R.; Brauer, V.; Bassler, D.; Laubscher, B.; Pfister, R.E.; Nelle, M.; Muller, B.; Gerth-Kahlert, C.; Adams, M.; Swiss Neonatal Network and Follow-up Group. Incidence of retinopathy of prematurity (ROP) and ROP treatment in Switzerland 2006–2015: A population-based analysis. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2018, 103, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, P.P.; Müller, A.; Lagrèze, W.A.; Holz, F.G.; Stahl, A.; Krohne, T.U. Incidence of retinopathy of prematurity in Germany: Evaluation of current screening criteria. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2021, 106, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoogerwerf, A.; Schalij-Delfos, N.E.; van Schooneveld, M.J.; Termote, J.U. Incidence of retinopathy of prematurity over the last decade in the Central Netherlands. Neonatology 2010, 98, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daruich, A.; Bremond-Gignac, D.; Behar-Cohen, F.; Kermorvant, E. [Retinopathy of prematurity: From prevention to treatment]. Med. Sci. 2020, 36, 900–907. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, J.W. Risk factor analysis for the development and progression of retinopathy of prematurity. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swan, R.; Kim, S.J.; Campbell, J.P.; Paul Chan, R.V.; Sonmez, K.; Taylor, K.D.; Li, X.; Chen, Y.-D.I.; Rotter, J.I.; Simmons, C.; et al. The genetics of retinopathy of prematurity: A model for neovascular retinal disease. Ophthalmol. Retina 2018, 2, 949–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartnett, M.E.; Penn, J.S. Mechanisms and management of retinopathy of prematurity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 2515–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramshekar, A.; Hartnett, M.E. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Signaling in Models of Oxygen-Induced Retinopathy: Insights Into Mechanisms of Pathology in Retinopathy of Prematurity. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9, 96143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, C.; Webster, K.A.; Bhatt, A.; Tian, H.; Su, G.; Li, W. Concurrent Physiological and Pathological Angiogenesis in Retinopathy of Prematurity and Emerging Therapies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.; Li, B.; Wang, Z.; Zou, J.; Jia, Y.; Yoshida, S.; Zhou, Y. Novel Potential Biomarkers for Retinopathy of Prematurity. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 840030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özkaya, D. The Role of Thrombocyte Parameters in Retinopathy of Prematurity Development. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2022, 2022, 7518533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korkmaz, L.; Baştuğ, O.; Özdemir, A.; Korkut, S.; Karaca, Ç.; Akın, M.A.; Ozturk, M.A. Platelet mass index can be a reliable marker in predicting the prognosis of retinopathy of prematurity in very preterm infants. Pediatr. Neonatol. 2018, 59, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Dong, Y.; Lu, C.W.; Yang, W.; Li, Q. Relationship between mean platelet volume and retinopathy of prematurity. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2015, 253, 1791–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şahinoğlu Keşkek, N.; Gülcan, H.; Yılmaz, G.; Akkoyun, İ. Impact of Platelet Count in Retinopathy of Prematurity. Turk. J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 50, 351–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dammann, O.; Hartnett, M.E.; Stahl, A. Retinopathy of prematurity. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2022. early view. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bancalari, A.; Schade, R. Update in the Treatment of Retinopathy of Prematurity. Am. J. Perinatol. 2022, 39, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Zeng, X.; Chen, M.; Fan, Z.; Zheng, L.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, S.; He, J.C.; Zhang, G. Refractive and biometrical characteristics of children with retinopathy of prematurity who received laser photocoagulation or intravitreal ranibizumab injection. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2022, 260, 3213–3219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popovic, M.M.; Nichani, P.; Muni, R.H.; Mireskandari, K.; Tehrani, N.N.; Kertes, P.J. Intravitreal antivascular endothelial growth factor injection versus laser photocoagulation for retinopathy of prematurity: A meta-analysis of 3701 eyes. Surv. Ophthalmol. 2021, 66, 572–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sankar, M.J.; Sankar, J.; Chandra, P. Anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) drugs for treatment of retinopathy of prematurity. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 1, Cd009734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartnett, M.E. Retinopathy of Prematurity: Evolving Treatment with Anti-Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 218, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VanderVeen, D.K.; Cataltepe, S.U. Anti-vascular endothelial growth factor intravitreal therapy for retinopathy of prematurity. Semin. Perinatol. 2019, 43, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, M.F.; Quinn, G.E.; Fielder, A.R.; Ostmo, S.R.; Paul Chan, R.V.; Berrocal, A.; Binenbaum, G.; Blair, M.; Campbell, J.P.; Capone, A., Jr.; et al. International Classification of Retinopathy of Prematurity, 3rd Edition. Ophthalmology 2021, 128, e51–e68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, A.; Dhindsa, Y.; Sim, M.S.; Altendahl, M.; Tsui, I. Prenatal intrauterine growth restriction and risk of retinopathy of prematurity. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinov, V.G.; Koleva-Georgieva, D.N.; Sivkova, N.P.; Krasteva, M.B. The 5-minute Apgar Score as a Prognostic Factor for Development and Progression of Retinopathy of Prematurity. Folia Med. 2017, 59, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, A.; Dammann, C.; Nielsen, H.C.; Volpe, M.V. A Pathogenic Relationship of Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia and Retinopathy of Prematurity A Review of Angiogenic Mediators in Both Diseases. Front. Pediatr. 2018, 6, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Procianoy, R.S.; Garcia-Prats, J.A.; Hittner, H.M.; Adams, J.M.; Rudolph, A.J. An association between retinopathy of prematurity and intraventricular hemorrhage in very low birth weight infants. Acta Paediatr. Scand. 1981, 70, 473–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aly, H.; Othman, H.F.; Munster, C.; Das, A.; Sears, J. The U.S. National Trend for Retinopathy of Prematurity. Am. J. Perinatol. 2022, 29, 1569–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmo, F.R.; Alves, E.A.R.; Moreira, R.A.A.; Severino, V.O.; Rocha, L.P.; Monteiro, M.L.G.D.R.; Reis, M.A.D.; Etchebehere, R.M.; Machado, J.R.; Correa, R.R.M. Intrauterine infection, immune system and premature birth. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2018, 31, 1227–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, A.; Sonnie, C.; Worley, S.; Sharma, A.; Howard, D.; Moore, J.; Rodriguez, R.J.; Hoppe, G.; Sears, J.E. Comparison of Biphasic vs. Static Oxygen Saturation Targets Among Infants with Retinopathy of Prematurity. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2019, 137, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phelps, D.; Lindblad, A.; Bradford, J.D.; Wood, N.E. Supplemental Therapeutic Oxygen for Prethreshold Retinopathy Of Prematurity (STOP-ROP), a randomized, controlled trial. I: Primary outcomes. Pediatrics 2000, 105, 295–310. [Google Scholar]
- Askie, L.M.; Henderson-Smart, D.J.; Irwig, L.; Simpson, J.M. Oxygen-saturation targets and outcomes in extremely preterm infants. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 349, 959–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Hua, X.; Yu, Y.; Zhu, P.; Hong, K.; Ke, Y. Effect of red blood cell transfusion on the development of retinopathy of prematurity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0234266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Parameter | Group 1 (with ROP, n = 59 Patients) | Group 2 (without ROP, n = 90 Patients) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gestational age at birth, weeks (mean ± SD) | 27.97 ± 2.50 | 29.83 ± 1.71 | <0.001 |
| Birth weight, grams (mean ± SD) | 1102.8 ± 379.52 | 1366.83 ± 319.92 | <0.001 |
| Newborns’ gender (n/%) | Male = 30 (50.8%) Female = 29 (49.2%) | Male = 56 (62.2%) Female = 34 (37.8%) | 0.16 |
| Apgar score at 1 min (mean ± SD) | 4.49 ± 1.66 | 5.42 ± 1.59 | <0.001 |
| Apgar score at 5 min (mean ± SD) | 5.64 ± 1.39 | 6.47 ± 1.30 | <0.001 |
| Antenatal corticosteroid administration (n/%) | Yes = 12 (20.3%) | Yes = 13 (14.4%) | 0.37 |
| Neonatal Comorbidities | Group 1 (with ROP, n = 59 Patients) | Group 2 (without ROP, n = 90 Patients) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| NEC (n/%) | Yes = 11 (18.6%) | Yes = 12 (13.3%) | 0.30 |
| IUGR (n/%) | Yes = 14 (23.7%) | Yes = 10 (11.1%) | 0.04 |
| Mild BPD (n/%) | Yes = 10 (16.9%) | Yes = 4 (4.4%) | 0.01 |
| Moderate BPD (n/%) | Yes = 5 (8.5%) | Yes = 4 (4.4%) | 0.31 |
| Severe BPD (n/%) | Yes = 3 (5.1%) | Yes = 2 (2.2%) | 0.34 |
| Systemic infection (n/%) | Yes = 18 (30.5%) | Yes = 4 (4.4%) | <0.001 |
| IVH (n/%) | Yes = 28 (47.5%) | Yes = 22 (24.4%) | 0.004 |
| Therapeutic Interventions | Group 1 (with ROP, n = 59 Patients) | Group 2 (without ROP, n = 90 Patients) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| FiO2 in delivery room (mean ± SD) | 0.42 ± 0.22 | 0.39 ± 0.19 | 0.16 |
| High-flow oxygen therapy, days (mean ± SD) | 11.83 ± 20.01 | 2.87 ± 8.54 | <0.001 |
| CPAP, days (mean ± SD) | 8.80 ± 8.59 | 4.10 ± 4.51 | <0.001 |
| CPAP FiO2 > 30%, days (mean ± SD) | 0.46 ± 2.02 | 0.04 ± 0.20 | <0.001 |
| CPAP FiO2: 25–30%, days (mean ± SD) | 0.93 ± 1.57 | 0.33 ± 1.06 | <0.001 |
| CPAP FiO2: 21–25%, days (mean ± SD) | 7.32 ± 7.85 | 3.74 ± 3.87 | <0.001 |
| Mechanical ventilation, days (mean ± SD) | 14.34 ± 22.87 | 2.82 ± 6.53 | <0.001 |
| Transfusion of packed red blood cells <7 days (n/%) | Yes = 23 (39%) | Yes = 11 (12.2%) | <0.001 |
| Transfusion of packed red blood cells days 7–28 (n/%) | Yes = 27 (45.8%) | Yes = 19 (21.1%) | 0.001 |
| Transfusion of packed red blood cells >28 days (n/%) | Yes = 38 (64.4%) | Yes = 34 (37.8%) | 0.001 |
| Erythropoietin administration (n/%) | Yes = 55 (42%) | Yes = 76 (58%) | 0.10 |
| Oral iron administration | Yes = 59 (100%) | Yes = 82 (91.1%) | 0.019 |
| Hematological Parameter | Subgroup 1 (Stage 1, n = 35) | Subgroup 2 (Stage 2, n = 18) | Subgroup 3 (Stage 3, n = 6) | Control Group (n = 90) | Mean Squares between Groups | F Score | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hb, number ×106/mm3, day 1 (mean ± SD) | 15.33 ± 3.19 | 15 ± 2.82 | 14.51 ± 3.86 | 16.38 ± 2.22 | 19.40 | 2.82 | 0.041 |
| Ht, %, day 1 (mean ± SD) | 48.31 ± 10.14 | 47.05 ± 8.22 | 45.65 ± 11.49 | 51.78 ± 6.84 | 217.751 | 3.329 | 0.021 |
| PLT, number/mm3 (mean ± SD) | 246.628 ± 100.699 | 248.666 ± 107.182 | 340.666 ± 171.011 | 235.122 ± 73.8692 | 21,260.477 | 2.630 | 0.052 |
| MPV, fL, day 1 (mean ± SD) | 6.44 ± 1.11 | 5.97 ± 0.83 | 6.88 ± 1.65 | 6.33 ± 1.20 | 1.50 | 1.11 | 0.347 |
| PMI, fL*nL−1, day 1 (mean ± SD) | 1546.82 ± 615.66 | 1448.16 ± 589.68 | 2148.2 ± 791.36 | 1460.04 ± 466.55 | 927,678.04 | 3.25 | 0.023 |
| Hb, number ×106/mm3, day 7 (mean ± SD) | 14.02 ± 2.70 | 14.14 ± 2.74 | 13.6 ± 4.03 | 15.35 ± 2.30 | 21.660 | 3.369 | 0.020 |
| Ht, %, day 7 (mean ± SD) | 43.56 ± 8.45 | 44.38 ± 7.91 | 43.25 ± 13.03 | 48.56 ± 6.97 | 274.203 | 4.581 | 0.004 |
| PLT day 7, number/mm3 (mean ± SD) | 236.314 ± 99.170 | 263.277 ± 123.695 | 306.666 ± 143.960 | 235.533 ± 83.622 | 12,711.481 | 1.396 | 0.246 |
| MPV, fL, day 7 (mean ± SD) | 6.92 ± 1.52 | 6.76 ± 1.26 | 7.13 ± 3.27 | 6.49 ± 1.24 | 2.129 | 1.038 | 0.378 |
| PMI, fL*nL−1, day 7 (mean ± SD) | 1563.45 ± 556.35 | 1677.75 ± 696.29 | 1894.91 ± 569.40 | 1502.09 ± 553.85 | 406,212.909 | 1.235 | 0.299 |
| Hb, number ×106/mm3, day 10 (mean ± SD) | 13.28 ± 2.27 | 12.92 ± 2.70 | 11.25 ± 2.56 | 14.52 ± 2.21 | 35.853 | 6.740 | <0.001 |
| Ht, %, day 10 (mean ± SD) | 40.91 ± 7.04 | 40.39 ± 8.18 | 35.31 ± 8.24 | 45.18 ± 6.65 | 350.064 | 7.140 | <0.001 |
| PLT day 10, number/mm3 (mean ± SD) | 310.228 ± 120.888 | 311.28 ± 167.19 | 243.33 ± 98.22 | 308.09 ± 107.35 | 8354.098 | 0.592 | 0.621 |
| MPV, fL, day 10 (mean ± SD) | 7.43 ± 1.58 | 7.84 ± 2.07 | 7.63 ± 2.58 | 7.39 ± 1.45 | 1.068 | 0.407 | 0.748 |
| PMI, fL*nL−1, day 10 (mean ± SD) | 2273.29 ± 957.03 | 2332.27 ± 1214.06 | 1671.51 ± 460.78 | 2252.51 ± 843.05 | 714,409.469 | 0.860 | 0.464 |
| Hb, number ×106/mm3, week 32 (mean ± SD) | 10.89 ± 2.45 | 10.51 ± 2.04 | 10.16 ± 1.29 | 11.06 ± 2.43 | 2.808 | 0.502 | 0.682 |
| Ht, %, week 32 (mean ± SD) | 33.96 ± 7.62 | 32.60 ± 6.46 | 31.80 ± 4.68 | 37.23 ± 26.29 | 193.581 | 0.436 | 0.727 |
| PLT week 32, number/mm3 (mean ± SD) | 397.81 ± 152.65 | 394.55 ± 164.39 | 421.33 ± 243.62 | 418.51 ± 125.37 | 5555.259 | 0.273 | 0.845 |
| MPV, fL, week 32 (mean ± SD) | 6.94 ± 1.09 | 7.26 ± 1.66 | 7.33 ± 1.99 | 7.17 ± 1.73 | 0.678 | 0.262 | 0.853 |
| PMI, fL*nL−1, week 32 (mean ± SD) | 2711.19 ± 1017.06 | 2731.77 ± 1022.69 | 3289.08 ± 2369.87 | 2951.12 ± 959.16 | 950,540.143 | 0.846 | 0.471 |
| Hb, number ×106/mm3, week 33 (mean ± SD) | 10.62 ± 2.67 | 10.14 ± 1.49 | 8.11 ± 4.11 | 10.53 ± 2.08 | 11.910 | 2.296 | 0.080 |
| Ht, %, week 33 (mean ± SD) | 33.06 ± 7.98 | 31.75 ± 3.99 | 26.40 ± 13.86 | 32.91 ± 6.44 | 86.426 | 1.767 | 0.156 |
| PLT week 33, number/mm3 (mean ± SD) | 354.74 ± 133.31 | 356.06 ± 139.80 | 324.33 ± 235.03 | 392.61 ± 114.43 | 21,260.173 | 1.296 | 0.278 |
| MPV, fL, week 33 (mean ± SD) | 6.87 ± 1.72 | 6.66 ± 1.14 | 5.78 ± 3.07 | 6.83 ± 1.30 | 2.265 | 1.018 | 0.387 |
| PMI, fL*nL−1, week 33 (mean ± SD) | 2474.70 ± 908.27 | 2339.45 ± 880.26 | 2262.20 ± 1637.63 | 2626.48 ± 760 | 669,691.404 | 0.916 | 0.435 |
| Hb, number ×106/mm3, week 34 (mean ± SD) | 9.56 ± 3.29 | 9.29 ± 2.80 | 6.88 ± 5.59 | 10.04 ± 2.20 | 20.526 | 2.729 | 0.046 |
| Ht, %, week 34 (mean ± SD) | 29.46 ± 9.94 | 29.25 ± 8.77 | 21.31 ± 17.26 | 31.46 ± 6.85 | 216.777 | 3.038 | 0.031 |
| PLT week 34, number/mm3 (mean ± SD) | 331.40 ± 148.02 | 310.56 ± 129.10 | 281.50 ± 264.17 | 374.70 ± 128.60 | 40,603.549 | 2.066 | 0.107 |
| MPV, fL, week 34 (mean ± SD) | 6.49 ± 2.22 | 5.98 ± 1.77 | 4.93 ± 4.00 | 6.64 ± 2.02 | 6.989 | 1.521 | 0.212 |
| PMI, fL*nL−1, week 34 (mean ± SD) | 2312.79 ± 973.83 | 1923.92 ± 795.28 | 2180.01 ± 2268.03 | 2474.78 ± 905.95 | 1,626,865.633 | 1.664 | 0.177 |
| Hematological Parameter | Odds Ratio | 95%CI Lower Limit | 95%CI Upper Limit | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hb day 1 | 0.40 | 0.14 | 1.15 | 0.093 |
| Hb day 7 | 1.32 | 0.95 | 1.84 | 0.090 |
| Hb day 10 | 0.99 | 0.95 | 1.03 | 0.703 |
| Hb week 32 | 0.97 | 0.21 | 4.51 | 0.975 |
| Hb week 33 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 0.649 |
| Hb week 34 | 3.36 | 0.84 | 13.38 | 0.085 |
| Ht day 1 | 0.64 | 0.42 | 1.00 | 0.051 |
| Ht day 7 | 1.01 | 0.98 | 1.05 | 0.314 |
| Ht day 10 | 2.57 | 0.85 | 7.75 | 0.092 |
| Ht week 32 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 0.347 |
| Ht week 33 | 2.32 | 0.68 | 7.84 | 0.174 |
| Ht week 34 | 0.70 | 0.46 | 1.06 | 0.093 |
| PLT day 1 | 0.98 | 0.96 | 1.00 | 0.216 |
| PLT day 7 | 0.43 | 0.16 | 1.14 | 0.090 |
| PLT day 10 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 0.216 |
| PLT week 32 | 1.15 | 0.74 | 1.78 | 0.518 |
| PLT week 33 | 0.98 | 0.87 | 1.10 | 0.812 |
| PLT week 34 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 1.02 | 0.351 |
| MPV day 1 | 0.92 | 0.31 | 2.72 | 0.890 |
| MPV day 7 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 0.253 |
| MPV day 10 | 1.28 | 0.26 | 6.34 | 0.755 |
| MPV week 32 | 0.95 | 0.56 | 1.59 | 0.852 |
| MPV week 33 | 1.00 | 0.98 | 1.01 | 0.851 |
| MPV week 34 | 1.188 | 0.55 | 2.56 | 0.658 |
| PMI day 1 | 4.151 | 1.39 | 7.50 | 0.032 |
| PMI day 7 | 3.57 | 0.65 | 10.05 | 0.023 |
| PMI day 10 | 3.72 | 0.46 | 8.13 | 0.018 |
| PMI week 32 | 0.99 | 0.98 | 1.01 | 0.839 |
| PMI week 33 | 1.11 | 0.58 | 2.12 | 0.743 |
| PMI week 34 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 0.594 |
| Hematological Parameter | Odds Ratio | 95%CI Lower Limit | 95%CI Upper Limit | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hb day 1 | 2.93 | 0.79 | 10.83 | 0.107 |
| Hb day 7 | 1.05 | 0.33 | 3.32 | 0.932 |
| Hb day 10 | 0.71 | 0.15 | 3.32 | 0.671 |
| Hb week 32 | 2.90 | 0.67 | 4.12 | 0.089 |
| Hb week 33 | 0.21 | 0.01 | 2.46 | 0.216 |
| Hb week 34 | 0.21 | 0.01 | 3.00 | 0.252 |
| Ht day 1 | 0.66 | 0.42 | 1.03 | 0.073 |
| Ht day 7 | 1.01 | 0.69 | 1.49 | 0.930 |
| Ht day 10 | 1.06 | 0.62 | 1.80 | 0.831 |
| Ht week 32 | 0.44 | 0.17 | 1.11 | 0.083 |
| Ht week 33 | 1.54 | 0.70 | 3.36 | 0.276 |
| Ht week 34 | 1.72 | 0.72 | 4.08 | 0.215 |
| PLT day 1 | 0.96 | 0.89 | 1.04 | 0.411 |
| PLT day 7 | 1.04 | 0.97 | 1.11 | 0.213 |
| PLT day 10 | 1.03 | 0.97 | 1.08 | 0.251 |
| PLT week 32 | 1.01 | 0.98 | 1.03 | 0.297 |
| PLT week 33 | 0.99 | 0.96 | 1.01 | 0.556 |
| PLT week 34 | 1.02 | 0.99 | 1.05 | 0.116 |
| MPV day 1 | 0.02 | 0.005 | 1.18 | 0.061 |
| MPV day 7 | 1.79 | 0.50 | 6.04 | 0.174 |
| MPV day 10 | 2.78 | 0.97 | 7.96 | 0.056 |
| MPV week 32 | 2.09 | 0.63 | 6.89 | 0.222 |
| MPV week 33 | 1.43 | 0.39 | 5.22 | 0.587 |
| MPV week 34 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 1.01 | 0.450 |
| PMI day 1 | 7.67 | 1.87 | 16.48 | 0.036 |
| PMI day 7 | 0.99 | 0.98 | 1.00 | 0.270 |
| PMI day 10 | 0.99 | 0.98 | 1.00 | 0.307 |
| PMI week 32 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 0.385 |
| PMI week 33 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 0.958 |
| PMI week 34 | 0.99 | 0.98 | 1.00 | 0.067 |
| Hematological Parameter | Odds Ratio | 95%CI Lower Limit | 95%CI Upper Limit | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hb day 1 | 0.84 | 0.64 | 1.09 | 0.201 |
| Hb day 7 | 0.83 | 0.61 | 1.13 | 0.240 |
| Hb day 10 | 0.57 | 0.38 | 0.87 | 0.069 |
| Hb week 32 | 0.84 | 0.56 | 1.26 | 0.423 |
| Hb week 33 | 0.84 | 0.59 | 1.19 | 0.333 |
| Hb week 34 | 0.87 | 0.65 | 1.17 | 0.363 |
| Ht day 1 | 1.06 | 0.89 | 1.26 | 0.479 |
| Ht day 7 | 1.12 | 0.94 | 1.34 | 0.189 |
| Ht day 10 | 0.77 | 0.61 | 0.97 | 0.061 |
| Ht week 32 | 0.97 | 0.82 | 1.14 | 0.751 |
| Ht week 33 | 0.97 | 0.86 | 1.08 | 0.630 |
| Ht week 34 | 0.94 | 0.85 | 1.04 | 0.259 |
| PLT day 1 | 0.91 | 0.89 | 2.03 | 0.430 |
| PLT day 7 | 1.01 | 0.99 | 1.02 | 0.090 |
| PLT day 10 | 0.97 | 0.95 | 1.99 | 0.314 |
| PLT week 32 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 1.01 | 0.651 |
| PLT week 33 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 1.01 | 0.726 |
| PLT week 34 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 1.01 | 0.694 |
| MPV day 1 | 0.75 | 0.12 | 4.59 | 0.759 |
| MPV day 7 | 1.62 | 0.27 | 9.70 | 0.595 |
| MPV day 10 | 0.94 | 0.30 | 2.92 | 0.924 |
| MPV week 32 | 0.58 | 0.19 | 1.71 | 0.326 |
| MPV week 33 | 0.51 | 0.18 | 1.44 | 0.209 |
| MPV week 34 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 0.078 |
| PMI day 1 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 0.153 |
| PMI day 7 | 0.99 | 0.98 | 1.00 | 0.050 |
| PMI day 10 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 0.375 |
| PMI week 32 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 0.662 |
| PMI week 33 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 0.148 |
| PMI week 34 | 0.84 | 0.64 | 1.09 | 0.201 |
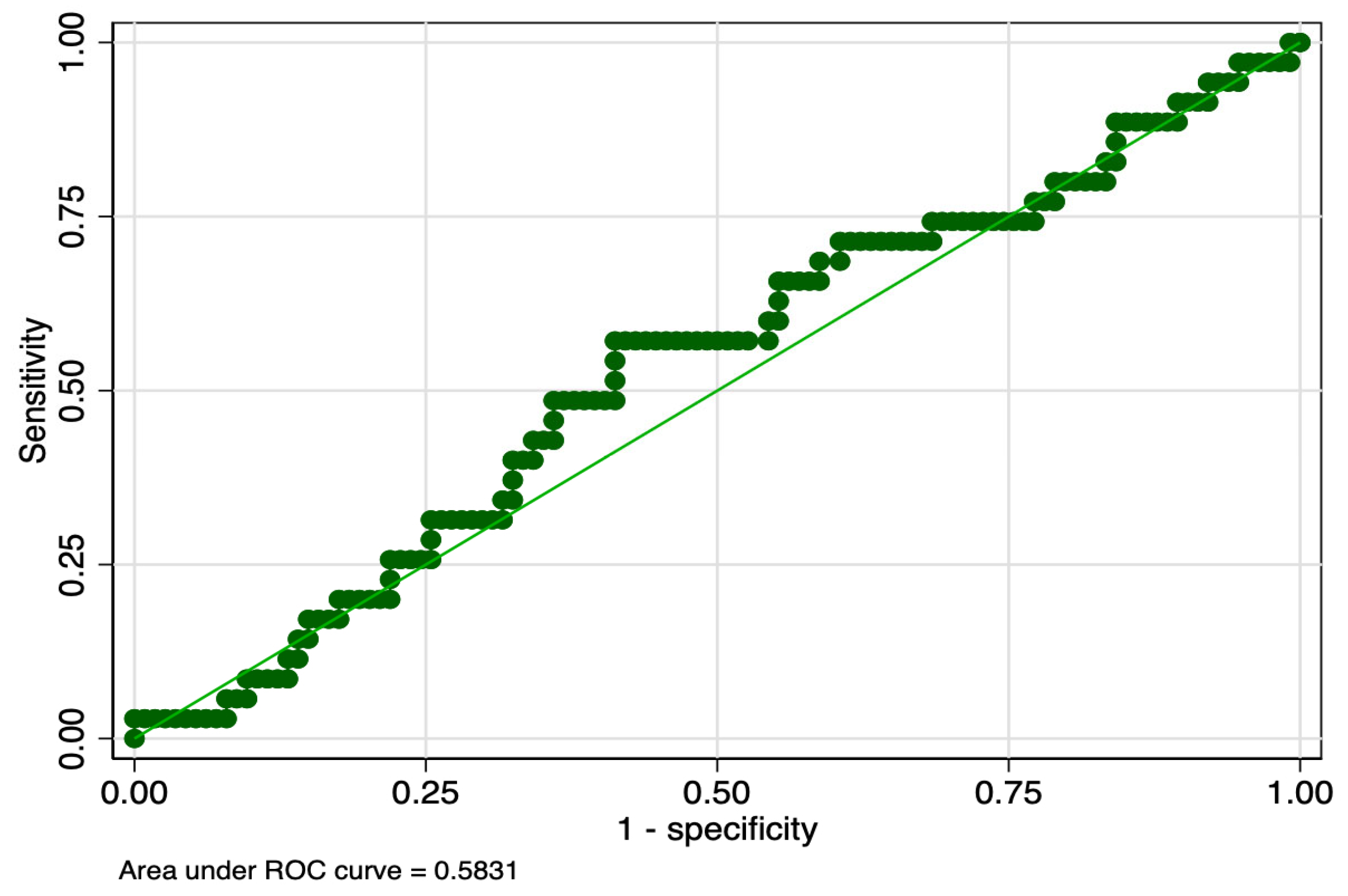
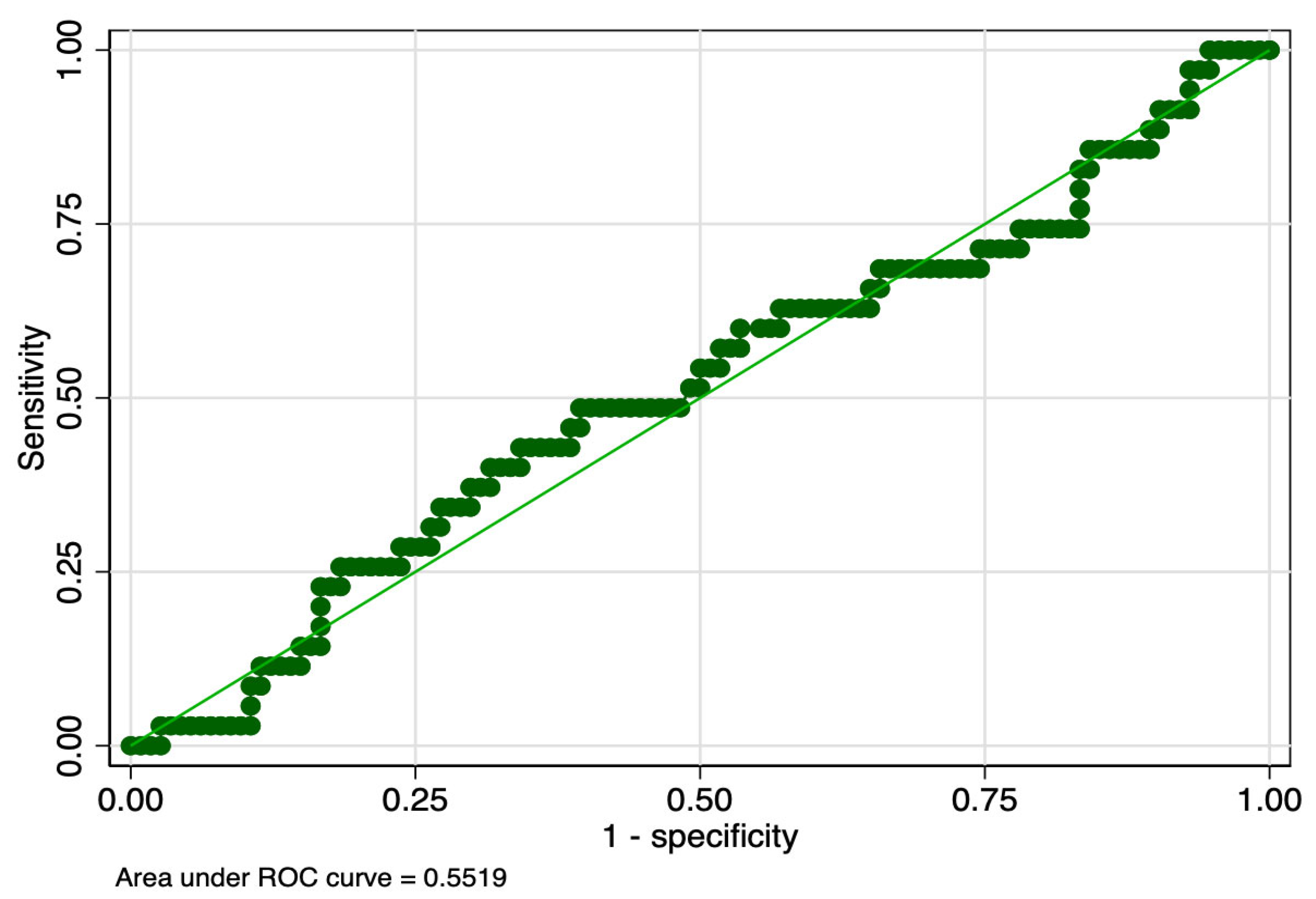
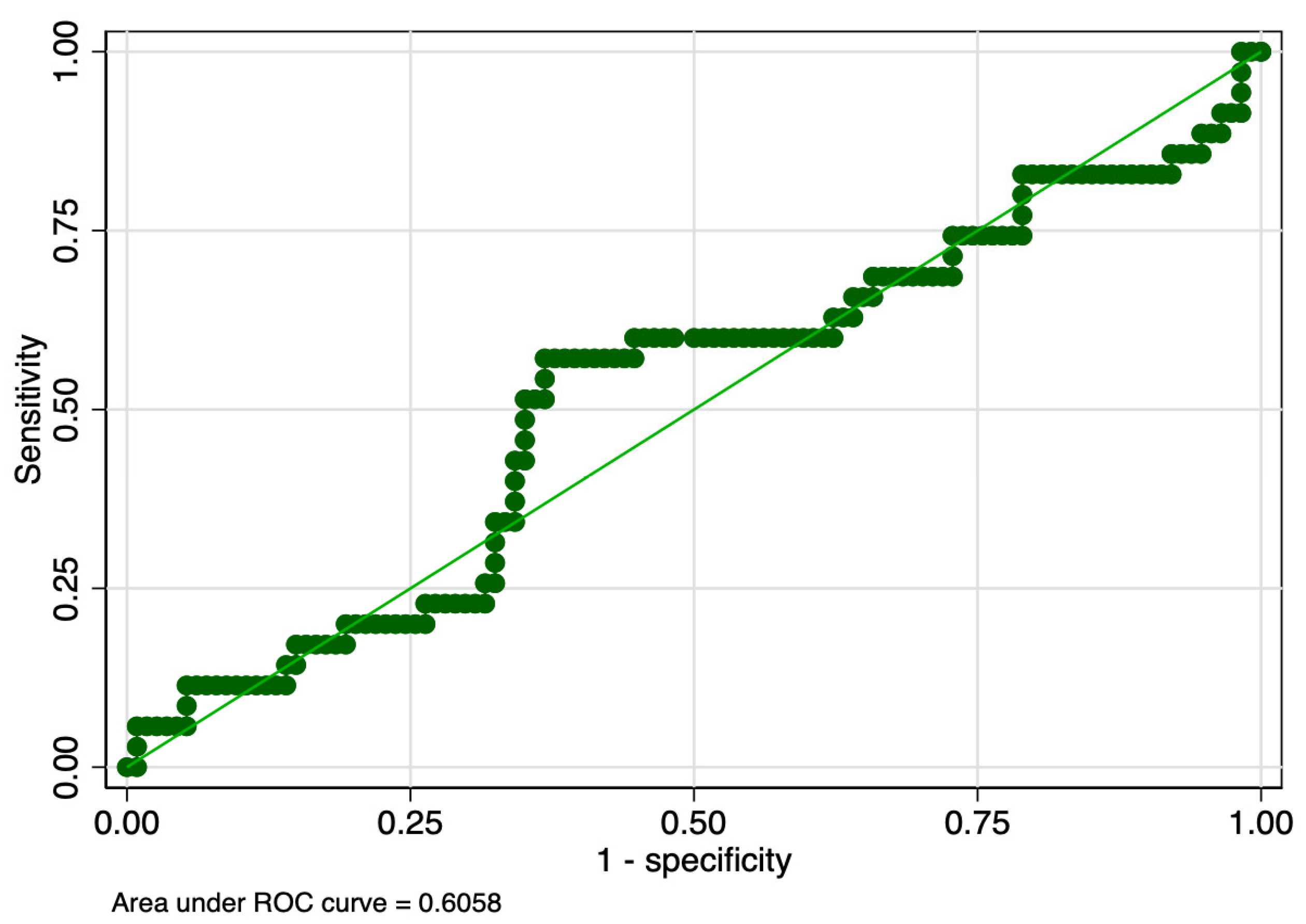
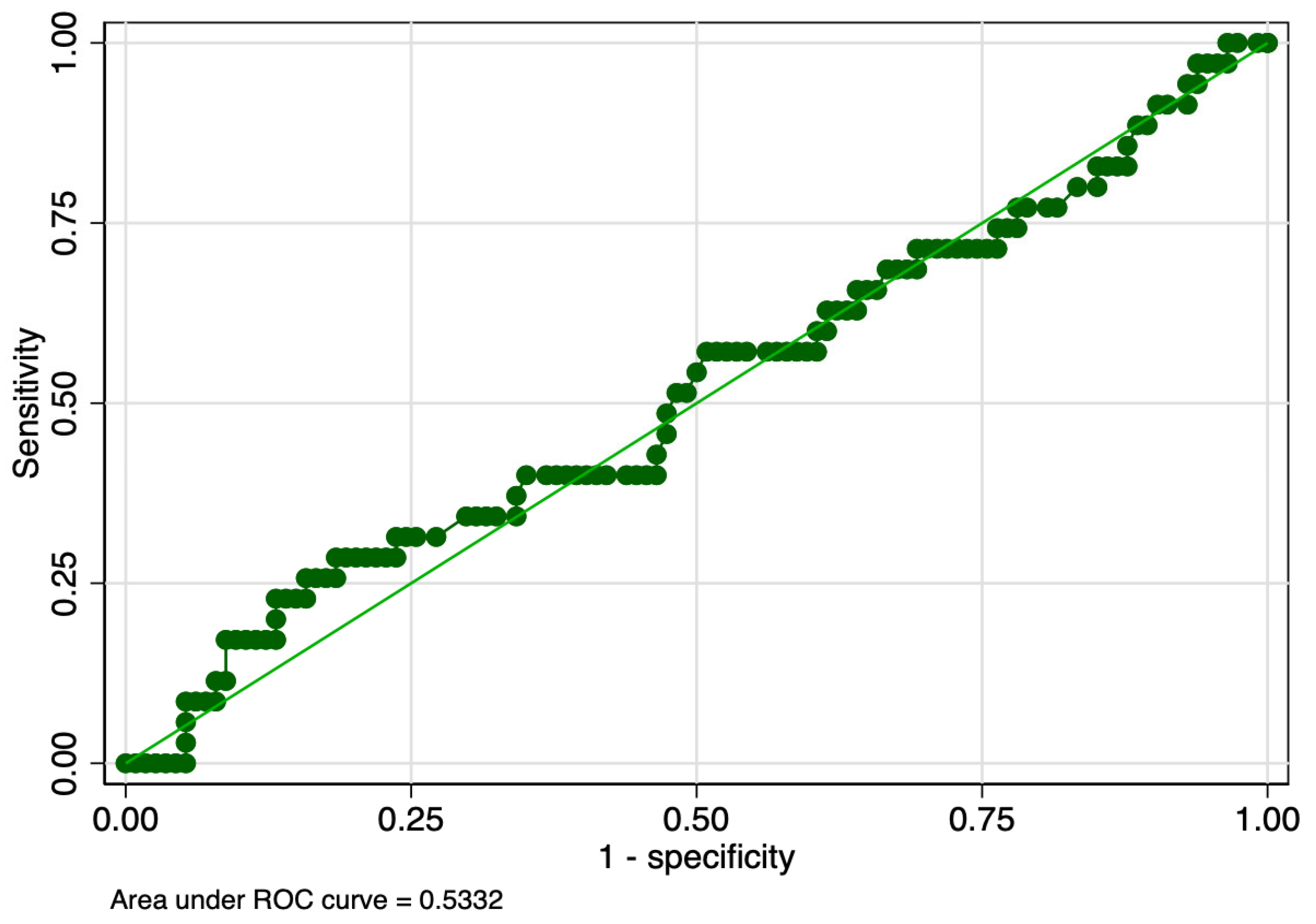
| ROP Stage | Hematological Parameter | Cut-Off (fL*nL−1) | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | ROC Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | PMI day 1 | 1514.3 | 57 | 59 | 0.58 |
| PMI day 7 | 1627.6 | 49 | 61 | 0.55 | |
| PMI day 10 | 2321.8 | 57 | 63 | 0.60 | |
| 2 | PMI day 1 | 1570.4 | 44 | 61 | 0.53 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zonda, G.I.; Mogos, R.; Melinte-Popescu, A.-S.; Adam, A.-M.; Harabor, V.; Nemescu, D.; Socolov, D.; Harabor, A.; Melinte-Popescu, M.; Hincu, M.A.; et al. Hematologic Risk Factors for the Development of Retinopathy of Prematurity—A Retrospective Study. Children 2023, 10, 567. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10030567
Zonda GI, Mogos R, Melinte-Popescu A-S, Adam A-M, Harabor V, Nemescu D, Socolov D, Harabor A, Melinte-Popescu M, Hincu MA, et al. Hematologic Risk Factors for the Development of Retinopathy of Prematurity—A Retrospective Study. Children. 2023; 10(3):567. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10030567
Chicago/Turabian StyleZonda, Gabriela Ildiko, Raluca Mogos, Alina-Sînziana Melinte-Popescu, Ana-Maria Adam, Valeriu Harabor, Dragos Nemescu, Demetra Socolov, Anamaria Harabor, Marian Melinte-Popescu, Maura Adelina Hincu, and et al. 2023. "Hematologic Risk Factors for the Development of Retinopathy of Prematurity—A Retrospective Study" Children 10, no. 3: 567. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10030567
APA StyleZonda, G. I., Mogos, R., Melinte-Popescu, A.-S., Adam, A.-M., Harabor, V., Nemescu, D., Socolov, D., Harabor, A., Melinte-Popescu, M., Hincu, M. A., Vasilache, I.-A., Carauleanu, A., Adam, G., & Paduraru, L. (2023). Hematologic Risk Factors for the Development of Retinopathy of Prematurity—A Retrospective Study. Children, 10(3), 567. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10030567







