The Rating of Perceived Exertion—Pediatric (RPE-P) Scale: Preliminary Validation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Procedure
- (1)
- Familiarization to ratings of perceived exertion and muscle pain scales.
- (2)
- Paper and pencil questionnaires (described below).
- (3)
- Yoga pose (Warrior II) held for three, 1 min iterations (with a 30 s break after minutes 1 and 2).
2.3. Measures
2.3.1. Rating of Perceived Exertion—Pediatric (RPE-P) Scale
2.3.2. Borg Scale 6–20 Category Scale of Perceived Exertion
2.3.3. Ratings of Concurrent Muscle Pain
2.3.4. Physical Activity Questionnaire for Adolescents (PAQ-A)
2.3.5. Current Pain
2.3.6. Fear of Pain Questionnaire-Child (FOPQ-C)
2.3.7. Adolescent Sleep-Wake Scale—Short Form (ASWS)
2.3.8. Meal Nutritional Quality
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Participants
3.2. Psychometric Properties—Whole Sample
3.3. Concurrent Validity
3.4. Convergent Validity
3.5. Discriminant Validity
3.6. Cross-Sectional Construct Validity—Known-Groups Validity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anderson, E.; Durstine, J.L. Physical activity, exercise, and chronic diseases: A brief review. Sports Med. Health Sci. 2019, 1, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paley, C.A.; Johnson, M.I. Physical Activity to Reduce Systemic Inflammation Associated with Chronic Pain and Obesity: A Narrative Review. Clin. J. Pain 2016, 32, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabbitts, J.A.; Holley, A.L.; Karlson, C.W.; Palermo, T.M. Bidirectional associations between pain and physical activity in adolescents. Clin. J. Pain 2014, 30, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simons, L.E.; Kaczynski, K.J. The Fear Avoidance model of chronic pain: Examination for pediatric application. J. Pain 2012, 13, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, M.; Murtaugh, T.; Pantaleao, A.; Zempsky, W.T.; Guite, J.W. Chronic Pain and Obesity Within a Pediatric Interdisciplinary Pain Clinic Setting: A Preliminary Examination of Current Relationships and Future Directions. Clin. J. Pain 2017, 33, 738–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, A.C.; Drinkard, B.; McDuffie, J.R.; Ghorbani, S.; Yanoff, L.B.; Yanovski, J.A. Influence of excess adiposity on exercise fitness and performance in overweight children and adolescents. Pediatrics 2005, 115, e690–e696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eston, R.; Evans, H.; Faulkner, J.; Lambrick, D.; Al-Rahamneh, H.; Parfitt, G. A perceptually regulated, graded exercise test predicts peak oxygen uptake during treadmill exercise in active and sedentary participants. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2012, 112, 3459–3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasai, D.; Tsiros, M.D.; Eston, R.; Parfitt, G. Ratings of perceived exertion from a submaximal 20-m shuttle run test predict peak oxygen uptake in children and the test feels better. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2023, 123, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pind, R.; Purge, P.; Mäestu, E.; Vahtra, E.; Hofmann, P.; Mäestu, J. Session Rating of Perceived Exertion Is Different for Similar Intensity and Duration Prescribed Low-Intensity Sessions and Has a Different Effect on Performance in Young Cross-Country Skiers. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2023, 37, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temm, D.A.; Standing, R.J.; Best, R. Training, Wellbeing and Recovery Load Monitoring in Female Youth Athletes. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 11463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasai, D.; Parfitt, G.; Tarca, B.; Eston, R.; Tsiros, M.D. The Use of Ratings of Perceived Exertion in Children and Adolescents: A Scoping Review. Sports Med. 2021, 51, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racil, G.; Chelly, M.S.; Coquart, J.; Padulo, J.; Teodor, D.F.; Russo, L. Long- and Short-Term High-Intensity Interval Training on Lipid Profile and Cardiovascular Disorders in Obese Male Adolescents. Children 2023, 10, 1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolusso, D.V.; Dobbs, W.C.; Esco, M.R. The predictability of peak oxygen consumption using submaximal ratings of perceived exertion in adolescents. Int. J. Exerc. Sci. 2018, 11, 1173. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Laurent, C.M.; Green, J.M.; Davis, J.-K.; Geary, C.L.; Voth, N.R. Differentiated ratings of perceived exertion between overweight and non-overweight children during submaximal cycling. Int. J. Health Sci. 2019, 13, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, P.K.; Leung, R.W.; Liu, J.D.; Quach, B.; Zhao, Y. Exercise regulation during cycle ergometry using Cantonese version of the CERT and Borg’s RPE. J. Phys. Educ. Sport 2013, 13, 170–176. [Google Scholar]
- Reinke, M.; Schmitz, G.; Living, A. Children can rate perceived effort but do not follow intensity instructions during soccer training. Front. Sports Act. Living 2023, 5, 1251585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naidu, S.A.; Fanchini, M.; Cox, A.; Smeaton, J.; Hopkins, W.G.; Serpiello, F.R. Validity of session rating of perceived exertion assessed via the cr100 scale to track internal load in elite youth football players. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2019, 14, 403–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrington, J.W.; Anguiano-Hernandez, J.G.; Kingston, D.C. Muscle activation and rating of perceived exertion of typically developing children during DRY and aquatic treadmill walking. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2023, 68, 102737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halouani, J.; H’Mida, C.; Trabelsi, K.; Clark, C.C.T.; Glenn, J.M.; Chtourou, H. Physiological responses of small-sided vs. regular games in youth volleyball players. Biol. Sport 2023, 40, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupo, C.; Tessitore, A.; Gasperi, L.; Gomez, M. Session-RPE for quantifying the load of different youth basketball training sessions. Biol. Sport 2017, 34, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, D.P.; Carling, C.; Chaouachi, A.; Dellal, A.; Castagna, C.; Chamari, K.; Behm, D.G.; Research, C. Estimation of oxygen uptake from heart rate and ratings of perceived exertion in young soccer players. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2011, 25, 1983–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamb, K.L. Exercise regulation during cycle ergometry using the children’s effort rating table (CERT) and rating of perceived exertion (RPE) scales. Pediatr. Exerc. Sci. 1996, 8, 337–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borg, G. Borg’s Perceived Exertion and PAIN Scales; Human kinetics: Champaign, IL, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- McManus, A.; Armstrong, N.; Welsman, J.; Kirby, B.; Welsman, J. Ratings of Perceived Exertion in Prepubescent GIRLS and Boys; Chapman and Hall: London, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, L.L.; Lemanek, K.; Blount, R.L.; Dahlquist, L.M.; Lim, C.S.; Palermo, T.M.; McKenna, K.D.; Weiss, K.E. Evidence-based assessment of pediatric pain. J. Pediatr. Psychol. 2008, 33, 939–955; discussion 937–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, A.C.; Samuelson, B.; Palermo, T.M. Obesity in children and adolescents with chronic pain: Associations with pain and activity limitations. Clin. J. Pain 2010, 26, 705–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holley, A.L.; Zhou, C.; Wilson, A.C.; Hainsworth, K.; Palermo, T.M. The CALI-9: A brief measure for assessing activity limitations in children and adolescents with chronic pain. Pain 2018, 159, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, R.J.; Goss, F.L.; Aaron, D.J.; Nagle, E.F.; Gallagher, M., Jr.; Kane, I.R.; Tessmer, K.A.; Schafer, M.A.; Hunt, S.E. Concurrent muscle hurt and perceived exertion of children during resistance exercise. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2009, 41, 1146–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, R.J.; Goss, F.L.; Boer, N.F.; Peoples, J.A.; Foreman, A.J.; Dabayebeh, I.M.; Millich, N.B.; Balasekaran, G.; Riechman, S.E.; Gallagher, J.D.; et al. Children’s OMNI scale of perceived exertion: Mixed gender and race validation. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2000, 32, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, A.C.; Palermo, T.M. Physical activity and function in adolescents with chronic pain: A controlled study using actigraphy. J. Pain 2012, 13, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hainsworth, K.R.; Davies, W.H.; Khan, K.A.; Weisman, S.J. Co-occurring chronic pain and obesity in children and adolescents: The impact on health-related quality of life. Clin. J. Pain 2009, 25, 715–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netemeyer, R.G.; Bearden, W.O.; Sharma, S. Scaling Procedures: Issues and Applications; Sage Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Raff, H.; Phillips, J.M.; Simpson, P.M.; Weisman, S.J.; Hainsworth, K.R. Serum soluble urokinase plasminogen activator receptor in adolescents: Interaction of chronic pain and obesity. Pain Rep. 2020, 5, e836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuczmarski, R.J.; Ogden, C.L.; Grummer-Strawn, L.M.; Flegal, K.M.; Guo, S.S.; Wei, R.; Mei, Z.; Curtin, L.R.; Roche, A.F.; Johnson, C.L. CDC growth charts: United States. Adv. Data 2000, 314, 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Castarlenas, E.; Jensen, M.P.; von Baeyer, C.L.; Miró, J. Psychometric Properties of the Numerical Rating Scale to Assess Self-Reported Pain Intensity in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review. Clin. J. Pain 2017, 33, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Baeyer, C.L.; Spagrud, L.J.; McCormick, J.C.; Choo, E.; Neville, K.; Connelly, M.A. Three new datasets supporting use of the Numerical Rating Scale (NRS-11) for children’s self-reports of pain intensity. Pain 2009, 143, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfeiffer, K.A.; Pivarnik, J.M.; Womack, C.J.; Reeves, M.J.; Malina, R.M. Reliability and validity of the Borg and OMNI rating of perceived exertion scales in adolescent girls. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2002, 34, 2057–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voss, C.; Ogunleye, A.A.; Sandercock, G.R. Physical Activity Questionnaire for children and adolescents: English norms and cut-off points. Pediatr. Int. Off. J. Jpn. Pediatr. Soc. 2013, 55, 498–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essner, B.; Noel, M.; Myrvik, M.; Palermo, T. Examination of the Factor Structure of the Adolescent Sleep-Wake Scale (ASWS). Behav. Sleep Med. 2015, 13, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruening, M.; MacLehose, R.; Loth, K.; Story, M.; Neumark-Sztainer, D. Feeding a family in a recession: Food insecurity among Minnesota parents. Am. J. Public Health 2012, 102, 520–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Cunha Ribeiro, R.P.; Franco, T.C.; Pinto, A.J.; Pontes Filho, M.A.G.; Domiciano, D.S.; de Sá Pinto, A.L.; Lima, F.R.; Roschel, H.; Gualano, B. Prescribed Versus Preferred Intensity Resistance Exercise in Fibromyalgia Pain. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homann, D.; Stefanello, J.M.; Góes, S.M.; Leite, N. Impaired functional capacity and exacerbation of pain and exertion during the 6-minute walk test in women with fibromyalgia. Rev. Bras. Fisioter. 2011, 15, 474–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narouze, S.; Souzdalnitski, D. Obesity and chronic pain: Systematic review of prevalence and implications for pain practice. Reg. Anesth. Pain Med. 2015, 40, 91–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kung, S.M.; Fink, P.W.; Legg, S.J.; Ali, A.; Shultz, S.P. Age-Related Differences in Perceived Exertion While Walking and Running Near the Preferred Transition Speed. Pediatr. Exerc. Sci. 2020, 32, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bardin, J.; Maciejewski, H.; Diry, A.; Droit-Volet, S.; Thomas, C.; Ratel, S. Sex- and age-related differences in the rating of perceived exertion after high-intensity rowing exercise during childhood and adolescence. Psychophysiology 2023, 60, e14296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greer, B.K.; Young, P.R.; Thompson, B.; Rickert, B.J.; Moran, M.F. Impact of Direction of Unloading Influence on Template Rate of Perceived Exertion. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2018, 32, 3398–3404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Negro, J.; Yanci, J. Which instructional models influence more on perceived exertion, affective valence, physical activity level, and class time in physical education? Educ. Psychol. 2020, 40, 608–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Sun, C.; Sun, B.; Chen, X.; Tan, Z. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Relationship between Actual Exercise Intensity and Rating of Perceived Exertion in the Overweight and Obese Population. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 12912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stolzman, S.; Danduran, M.; Hunter, S.K.; Bement, M.H. Pain Response after Maximal Aerobic Exercise in Adolescents across Weight Status. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2015, 47, 2431–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoner, A.M.; Jastrowski Mano, K.E.; Weisman, S.J.; Hainsworth, K.R. Obesity impedes functional improvement in youth with chronic pain: An initial investigation. Eur. J. Pain 2017, 21, 1495–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birnie, K.A.; Hundert, A.S.; Lalloo, C.; Nguyen, C.; Stinson, J.N. Recommendations for selection of self-report pain intensity measures in children and adolescents: A systematic review and quality assessment of measurement properties. Pain 2019, 160, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brellenthin, A.G.; Crombie, K.M.; Cook, D.B.; Sehgal, N.; Koltyn, K.F. Psychosocial Influences on Exercise-Induced Hypoalgesia. Pain Med. 2017, 18, 538–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutin, I. In BMI We Trust: Reframing the Body Mass Index as a Measure of Health. Soc. Theory Health STH 2018, 16, 256–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Group | Combined N = 157 | HC n = 40 | CPHW n = 40 | O n = 40 | CPO n = 37 | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 0.286 | |||||
| Mdn | 15.00 | 15.00 | 15.00 | 14.00 | 15.00 | |
| IQR | 14.00–16.00 | 14.00–16.00 | 13.25–16.00 | 13.00–15.75 | 14.00–16.00 | |
| Sex, n (%) | 0.980 | |||||
| Female | 80 (51.0) | 20 (50.0) | 20 (50.0) | 20 (50.0) | 20 (54.1) | |
| Male | 77 (49.0) | 20 (50.0) | 20 (50.0) | 20 (50.0) | 17 (45.9) | |
| Race, n (%) | 0.005 | |||||
| White | 133 (84.7) | 38 (95.0) | 35 (87.5) | 35 (87.5) | 25 (67.6) | |
| Black | 10 (6.4) | 0 (0.0) | 4 (10.0) | 0 (0.0) | 6 (16.2) * | |
| Asian/Pacific Islander | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | |
| American Native | 2 (1.3) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 2 (5.4) † | |
| Native Hawaiian | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | |
| More than One Race | 12 (7.6) | 2 (5.0) | 1 (2.5) | 5 (12.5) | 4 (10.8) | |
| Ethnicity, n (%) | 0.191 | |||||
| Not Hispanic or Latino | 135 (86.0) | 37 (92.5) | 33 (82.5) | 36 (90.0) | 29 (78.4) | |
| Hispanic or Latino | 19 (12.1) | 2 (5.0) | 5 (12.5) | 4 (10.0) | 8 (21.6) | |
| Prefer not to Answer | 3 (1.9) | 1 (2.5) | 2 (5.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | |
| BMI Percentile | <0.001 | |||||
| Mdn | 84.59 | 55.76 | 55.95 | 96.95 | 98.63 | |
| IQR | 55.40–97.40 | 37.12–70.65 | 36.85–73.20 | 95.26–98.32 | 96.37–99.52 | |
| Physical Activity | <0.001 | |||||
| M | 2.43 | 2.87 | 2.22 | 2.39 | 2.22 | |
| SD | 0.69 | 0.52 | 0.67 | 0.72 | 0.66 | |
| Pain Type, n (%) § | N/A ‡ | N/A ‡ | 0.041 | |||
| Headache/Migraine | 58 (75.3) | 25 (62.5) | 33 (89.2) | |||
| Trunk | 5 (6.5) | 4 (10.0) | 1 (2.7) | |||
| Extremities | 6 (7.8) | 6 (15.0) | 0 (0.0) | |||
| Abdomen | 7 (9.1) | 4 (10.0) | 3 (8.1) | |||
| Other | 1 (1.3) | 1 (2.5) | 0 (0.0) | |||
| How many days in the past 2 weeks had pain | <0.001 | |||||
| Mdn | 3.00 | 1.00 | 6.00 | 2.00 | 7.00 | |
| IQR | 1.00–7.00 | 0.00–2.00 | 4.00–13.75 | 0.00–3.00 | 3.00–12.50 | |
| Current Pain on Day of Appointment | ||||||
| Mdn | 0.00 | 0.00 | 2.00 | 0.00 | 2.00 | |
| IQR | 0.00–2.00 | 0.00–1.00 | 0.00–4.00 | 0.00–0.00 | 0.00–5.00 |
| Group | Combined N = 157 | CP Subgroup n = 77 |
|---|---|---|
| FOPQ-C Total | ||
| M (SD) | 24.03 (20.38) | 37.34 (19.51) |
| Mdn (IQR) | 22.00 (6.00–38.00) | 37.00 (24.00–46.50) |
| FOPQ-C Avoidance | ||
| M (SD) | 11. 40 (9.91) | 18.38 (8.99) |
| Mdn (IQR) | 9.00 (2.50–18.50) | 18.00 (12.00–24.00) |
| FOPQ-C Fear of Pain | ||
| M (SD) | 12.62 (11.47) | 18.96 (11.87) |
| Mdn (IQR) | 10.00 (3.00–20.00) | 18.00 (10.00–27.00) |
| ASWS Total | ||
| M (SD) | 4.19 (0.82) | 3.82 (0.90) |
| Mdn (IQR) | 4.30 (3.80–4.80) | 3.90 (3.10–4.45) |
| Current Pain | ||
| M (SD) | 1.38 (1.98) | 2.40 (2.28) |
| Mdn (IQR) | 0.00 (0.00–2.00) | 2.00 (0.00–4.50) |
| Mean RPE-P | ||
| M (SD) | 3.26 (1.97) | 3.73 (2.10) |
| Mdn (IQR) | 3.00 (1.75–4.67) | 3.67 (2.08–5.17) |
| Mean Borg | ||
| M (SD) | 9.75 (2.61) | 10.15 (2.90) |
| Mdn (IQR) | 9.33 (7.50–11.92) | 10.00 (7.42–12.50) |
| Mean MP | ||
| M (SD) | 2.61 (1.90) | 3.17 (2.01) |
| Mdn (IQR) | 2.33 (1.00–3.92) | 2.83 (1.75–4.75) |
| Group | Combined N = 157 | HC n = 40 | CPHW n = 40 | O n = 40 | CPO n = 37 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RPE-p Minute 1 | |||||
| Mdn | 2.50 | 2.50 | 3.00 | 2.00 | 4.0 |
| IQR | 2.0–4.0 | 1.6–3.5 | 1.3–4.9 | 1.3–3.0 | 2.0–5.0 |
| RPE-P Minute 2 | |||||
| Mdn | 3.00 | 3.00 | 2.50 | 2.00 | 4.50 |
| IQR | 2.0–4.5 | 2.0–4.0 | 21.5–5.0 | 1.0–3.0 | 3.0–5.0 |
| RPE-P Minute 3 | |||||
| Mdn | 3.50 | 3.50 | 3.25 | 3.00 | 4.50 |
| IQR | 2.0–5.0 | 2.0–5.0 | 2.0–5.5 | 1.1–4.0 | 3.0–6.0 |
| RPE-P All Mins. | |||||
| Mdn | 3.00 | 3.00 | 2.92 | 2.33 | 4.33 |
| IQR | 1.75–4.67 | 1.8–4.3 | 1.7–5.1 | 1.3–3.63 | 2.6–5.3 |
| Borg Minute 1 | |||||
| Mdn | 8.5 | 8.75 | 8.50 | 8.00 | 10.50 |
| IQR | 7.0–11.0 | 7.0–10.4 | 7.0–11.5 | 7.0–9.9 | 7.0–12.0 |
| Borg Minute 2 | |||||
| Mdn | 9.50 | 9.50 | 9.25 | 8.8 | 11.00 |
| IQR | 7.5–12.0 | 7.6–11.5 | 7.5–12.5 | 7.0–11.4 | 7.8–12.8 |
| Borg Minute 3 | |||||
| Mdn | 10.50 | 11.00 | 9.00 | 9.25 | 11.50 |
| IQR | 8.0–12.5 | 8.6–12.5 | 7.1–13.4 | 7.0–12.0 | 7.8–13.8 |
| Borg All Mins. | |||||
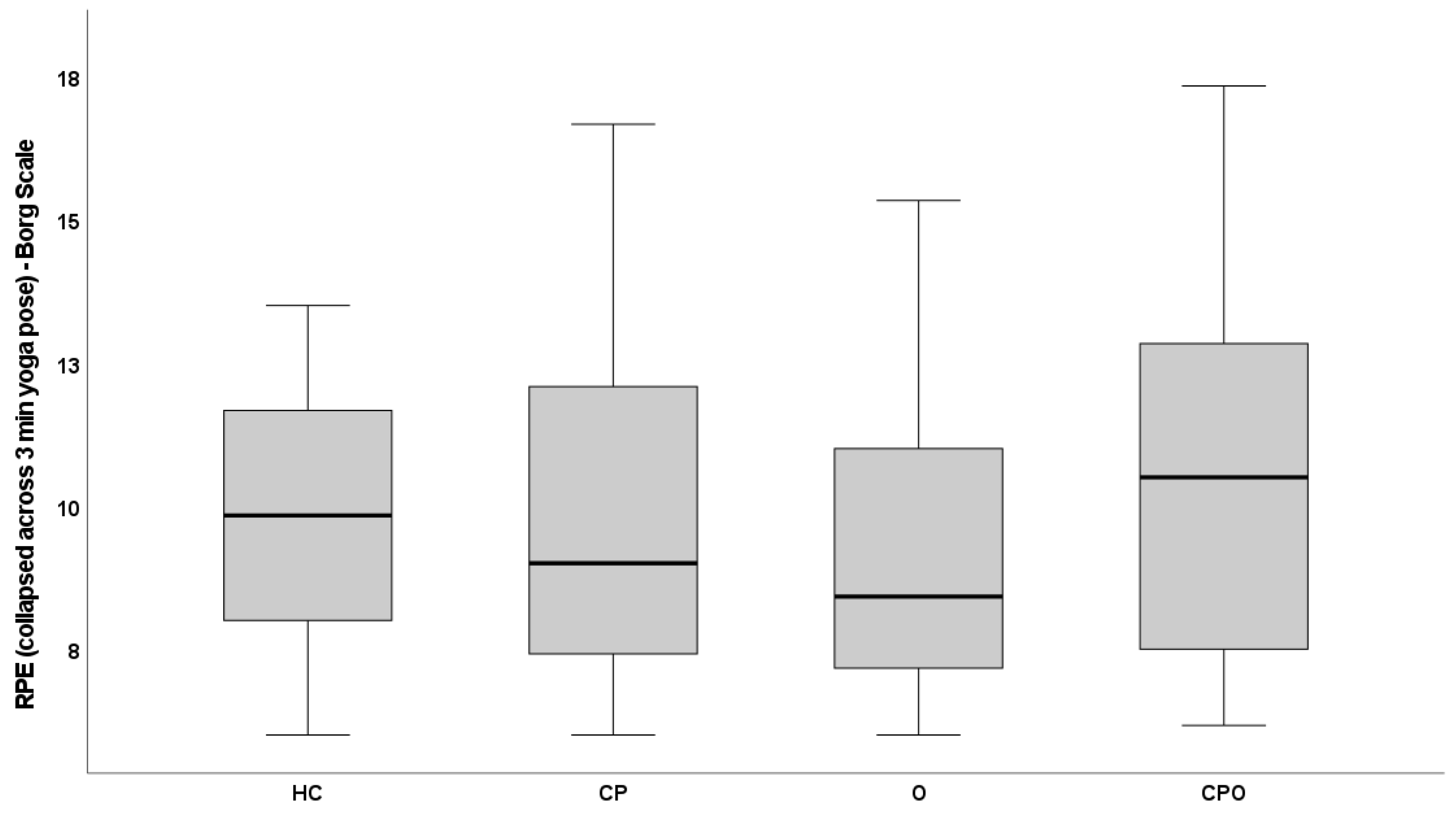
| Mdn | 9.33 | 9.83 | 9.00 | 8.42 | 10.50 |
| IQR | 7.5–11.9 | 8.0–11.8 | 7.4–12.1 | 7.2–11.1 | 7.4–12.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
LiaBraaten, B.; Stolzman, S.; Simpson, P.M.; Zhang, L.; Brockman, T.; Linneman, N.; Weisman, S.J.; Hainsworth, K.R. The Rating of Perceived Exertion—Pediatric (RPE-P) Scale: Preliminary Validation. Children 2023, 10, 1906. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10121906
LiaBraaten B, Stolzman S, Simpson PM, Zhang L, Brockman T, Linneman N, Weisman SJ, Hainsworth KR. The Rating of Perceived Exertion—Pediatric (RPE-P) Scale: Preliminary Validation. Children. 2023; 10(12):1906. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10121906
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiaBraaten, Brynn, Stacy Stolzman, Pippa M. Simpson, Liyun Zhang, Taylor Brockman, Nina Linneman, Steven J. Weisman, and Keri R. Hainsworth. 2023. "The Rating of Perceived Exertion—Pediatric (RPE-P) Scale: Preliminary Validation" Children 10, no. 12: 1906. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10121906
APA StyleLiaBraaten, B., Stolzman, S., Simpson, P. M., Zhang, L., Brockman, T., Linneman, N., Weisman, S. J., & Hainsworth, K. R. (2023). The Rating of Perceived Exertion—Pediatric (RPE-P) Scale: Preliminary Validation. Children, 10(12), 1906. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10121906





