A Practical Update on Pediatric Eosinophilic Esophagitis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Epidemiology
3. Pathogenesis
4. Diagnosis
4.1. Clinical Features and Heterogeneity of EoE
4.2. Endoscopic and Histological Features
- Edema (E), i.e., the loss of vascular markings (present 1, absent 0);
- Rings (R) or esophageal trachealization (none 0, mild 1, moderate 2, severe 3);
- Exudates (E) or white plaques (none 0, mild 1, severe 2);
- Furrows (F) or vertical lines (none 0, mild 1, severe 2);
- Strictures (S) (present 1, absent 0).
5. Therapy
5.1. Pharmacological Therapy
5.1.1. Topical Corticosteroids
5.1.2. Proton Pump Inhibitors
5.1.3. Biologic Therapies
5.2. Diet Therapies
5.2.1. Elemental Diet
5.2.2. Empirical Food Elimination Diet (FED)
5.2.3. Allergy-Test-Directed Elimination Diet
6. EoE Follow-Up
6.1. Nutritional Issues and Assessment
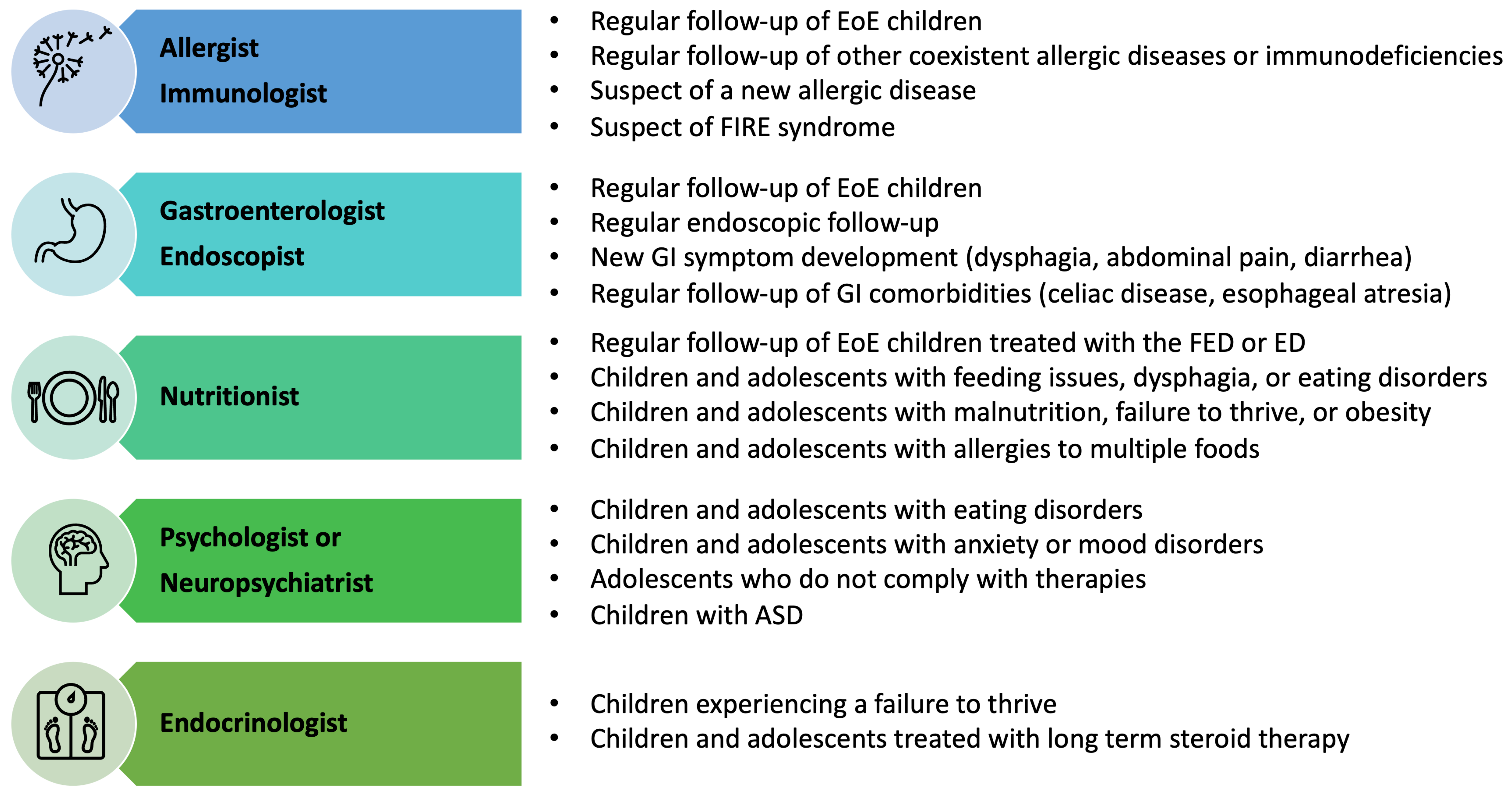
6.2. Multidisciplinary Assessment
7. Conclusions
- Personalize treatments according to the molecular profile and clinical features of patients.
- Assess the long-term effects of currently available therapies.
- Identify noninvasive biomarkers and new molecular therapeutic targets.
- Implement the use of less invasive tools to assess disease activity.
- Improve the diagnostic process to identify the disease and prevent potential complications early.
- Define international guidelines for long-term pediatric EoE management, focusing on the central role of a multidisciplinary approach.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Licari, A.; Votto, M.; D’Auria, E.; Castagnoli, R.; Caimmi, S.M.E.; Marseglia, G.L. Eosinophilic Gastrointestinal Diseases in Children: A Practical Review. Curr. Pediatr. Rev. 2020, 16, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landres, R.T.; Kuster, G.G.; Strum, W.B. Eosinophilic esophagitis in a patient with vigorous achalasia. Gastroenterology 1978, 74, 1298–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winter, H.S.; Madara, J.L.; Stafford, R.J.; Grand, R.J.; Quinlan, J.E.; Goldman, H. Intraepithelial eosinophils: A new diagnostic criterion for reflux esophagitis. Gastroenterology 1982, 83, 818–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attwood, S.E.; Smyrk, T.C.; Demeester, T.R.; Jones, J.B. Esophageal eosinophilia with dysphagia. A distinct clinicopathologic syndrome. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1993, 38, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Straumann, A.; Spichtin, H.P.; Bernoulli, R.; Loosli, J.; Vögtlin, J. Idiopathic eosinophilic esophagitis: A frequently overlooked disease with typical clinical aspects and discrete endoscopic findings. Schweiz. Med. Wochenschr. 1994, 124, 1419–1429. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dellon, E.S.; Hirano, I. Epidemiology and Natural History of Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Rooij, W.E.; Barendsen, M.E.; Warners, M.J.; van Rhijn, B.D.; Verheij, J.; Bruggink, A.H.; Bredenoord, A.J. Emerging incidence trends of eosinophilic esophagitis over 25 years: Results of a nationwide register-based pathology cohort. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2021, 33, e14072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Votto, M.; Raffaele, A.; De Filippo, M.; Caimmi, S.; Brunero, M.; Riccipetitoni, G.; Marseglia, G.L.; Licari, A. Eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders in children and adolescents: A single-center experience. Dig. Liver Dis. 2022, 54, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, P.; Arias, Á.; Arias-González, L.; Laserna-Mendieta, E.J.; Ruiz-Ponce, M.; Lucendo, A.J. Systematic review with meta-analysis: The growing incidence and prevalence of eosinophilic oesophagitis in children and adults in population-based studies. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 49, 1116–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allin, K.H.; Poulsen, G.; Melgaard, D.; Frandsen, L.T.; Jess, T.; Krarup, A.L. Eosinophilic oesophagitis in Denmark: Population-based incidence and prevalence in a nationwide study from 2008 to 2018. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2022, 10, 640–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, Á.; Lucendo, A.J. Incidence and prevalence of eosinophilic oesophagitis increase continiously in adults and children in Central Spain: A 12-year population-based study. Dig. Liver Dis. 2019, 51, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, G.A.; Alexander, J.A.; Schleck, C.D.; Zinsmeister, A.R.; Smyrk, T.C.; Elias, R.M.; Locke III, G.R.; Talley, N.J. Epidemiology of eosinophilic esophagitis over three decades in Olmsted County, Minnesota. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2009, 7, 1055–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hruz, P.; Straumann, A.; Bussmann, C.; Heer, P.; Simon, H.U.; Zwahlen, M.; Beglinger, C.; Schoepfer, A.M. Escalating incidence of eosinophilic esophagitis: A 20-year prospective, population-based study in Olten County, Switzerland. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 128, 1349–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Rhijn, B.D.; Verheij, J.; Smout, A.J.; Bredenoord, A.J. Rapidly increasing incidence of eosinophilic esophagitis in a large cohort. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2013, 25, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapel, R.C.; Miller, J.K.; Torres, C.; Aksoy, S.; Lash, R.; Katzka, D.A. Eosinophilic esophagitis: A prevalent disease in the United States that affects all age groups. Gastroenterology 2008, 134, 1316–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, S.F. Epidemiology and natural history of atopic diseases. Eur. Clin. Respir. J. 2015, 2, 24642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, C.; Pearce, N.; Douwes, J. The hygiene hypothesis in allergy and asthma: An update. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 13, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Votto, M.; Marseglia, G.L.; De Filippo, M.; Brambilla, I.; Caimmi, S.M.E.; Licari, A. Early Life Risk Factors in Pediatric EoE: Could We Prevent This Modern Disease? Front. Pediatr. 2020, 8, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celebi Sozener, Z.; Ozdel Ozturk, B.; Cerci, P.; Turk, M.; Gorgulu Akin, B.; Akdis, M.; Altiner, S.; Ozbey, U.; Ogulur, I.; Mitamura, Y.; et al. Epithelial barrier hypothesis: Effect of the external exposome on the microbiome and epithelial barriers in allergic disease. Allergy 2022, 77, 1418–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhernov, Y.V.; Vysochanskaya, S.O.; Sukhov, V.A.; Zaostrovtseva, O.K.; Gorshenin, D.S.; Sidorova, E.A.; Mitrokhin, O.V. Molecular Mechanisms of Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruffner, M.A.; Kennedy, K.; Cianferoni, A. Pathophysiology of eosinophilic esophagitis: Recent advances and their clinical implications. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2019, 15, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liacouras, C.A.; Spergel, J.M.; Ruchelli, E.; Verma, R.; Mascarenhas, M.; Semeao, E.; Flick, J.; Kelly, J.; Brown-Whitehorn, T.; Mamula, P.; et al. Eosinophilic esophagitis: A 10-year experience in 381 children. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2005, 3, 1198–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansoor, E.; Cooper, G.S. The 2010–2015 Prevalence of Eosinophilic Esophagitis in the USA: A Population-Based Study. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2016, 61, 2928–2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen-Brady, K.; Firszt, R.; Fang, J.C.; Wong, J.; Smith, K.R.; Peterson, K.A. Population-based familial aggregation of eosinophilic esophagitis suggests a genetic contribution. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 140, 1138–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, E.S.; Martin, L.J.; Collins, M.H.; Kottyan, L.C.; Sucharew, H.; He, H.; Mukkada, V.A.; Succop, P.A.; Abonia, J.P.; Foote, H.; et al. Twin and family studies reveal strong environmental and weaker genetic cues explaining heritability of eosinophilic esophagitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 134, 1084–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, E.T.; Kappelman, M.D.; Kim, H.P.; Ringel-Kulka, T.; Dellon, E.S. Early life exposures as risk factors for pediatric eosinophilic esophagitis. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2013, 57, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radano, M.C.; Yuan, Q.; Katz, A.; Fleming, J.T.; Kubala, S.; Shreffler, W.; Keet, C.A. Cesarean section and antibiotic use found to be associated with eosinophilic esophagitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2014, 2, 475–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, E.T.; Kuhl, J.T.; Martin, L.J.; Rothenberg, M.E.; Dellon, E.S. Prenatal, intrapartum, and postnatal factors are associated with pediatric eosinophilic esophagitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, E.T.; Gupta, S.K. Early Life Factors and Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Building the Evidence. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2018, 67, 549–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witmer, C.P.; Susi, A.; Min, S.B.; Nylund, C.M. Early Infant Risk Factors for Pediatric Eosinophilic Esophagitis. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2018, 67, 610–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Shea, K.M.; Aceves, S.S.; Dellon, E.S.; Gupta, S.K.; Spergel, J.M.; Furuta, G.T.; Rothenberg, M.E. Pathophysiology of Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 333–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kottyan, L.C.; Rothenberg, M.E. Genetics of eosinophilic esophagitis. Mucosal Immunol. 2017, 10, 580–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, X.; March, M.; Mentch, F.; Nguyen, K.; Glessner, J.; Qu, H.; Liu, Y.; Furuta, G.; Aceves, S.; Gonsalves, N.; et al. A genome-wide association meta-analysis identifies new eosinophilic esophagitis loci. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2022, 149, 988–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleiman, P.M.; Wang, M.L.; Cianferoni, A.; Aceves, S.; Gonsalves, N.; Nadeau, K.; Bredenoord, A.J.; Furuta, G.T.; Spergel, J.M.; Hakonarson, H. GWAS identifies four novel eosinophilic esophagitis loci. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.W.; Jensen, E.T.; Dellon, E.S. Nature with Nurture: The Role of Intrinsic Genetic and Extrinsic Environmental Factors on Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2022, 22, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, C.M.; Lenti, M.V.; Merli, S.; Licari, A.; Votto, M.; Marseglia, G.L.; Di Sabatino, A. Primary eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders and allergy: Clinical and therapeutic implications. Clin. Transl. Allergy 2022, 12, e12146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capucilli, P.; Hill, D.A. Allergic Comorbidity in Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Mechanistic Relevance and Clinical Implications. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2019, 57, 111–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchard, C.; Mingler, M.K.; McBride, M.; Putnam, P.E.; Collins, M.H.; Chang, G.; Stringer, K.; Abonia, J.P.; Molkentin, J.D.; Rothenberg, M.E. Periostin facilitates eosinophil tissue infiltration in allergic lung and esophageal responses. Mucosal Immunol. 2008, 1, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, M.; Bagi, P.; Strongin, A.; Heimall, J.; Zhao, X.; Lawrence, M.G.; Trivedi, A.; Henderson, C.; Hsu, A.; Quezado, M.; et al. Gastrointestinal Manifestations of STAT3-Deficient Hyper-IgE Syndrome. J. Clin. Immunol. 2017, 37, 695–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paluel-Marmont, C.; Bellon, N.; Barbet, P.; Leclerc-Mercier, S.; Hadj-Rabia, S.; Dupont, C.; Bodemer, C. Eosinophilic esophagitis and colonic mucosal eosinophilia in Netherton syndrome. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 139, 2003–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoda, T.; Wen, T.; Aceves, S.S.; Abonia, J.P.; Atkins, D.; Bonis, P.A.; Caldwell, J.M.; Capocelli, K.E.; Carpenter, C.L.; Collins, M.H.; et al. Eosinophilic oesophagitis endotype classification by molecular, clinical, and histopathological analyses: A cross-sectional study. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 3, 477–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keely, S.; Talley, N.J. Endophenotyping eosinophilic oesophagitis: A new era for management? Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 3, 449–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellon, E.S.; Liacouras, C.A.; Molina-Infante, J.; Furuta, G.T.; Spergel, J.M.; Zevit, N.; Spechler, S.J.; Attwood, S.E.; Straumann, A.; Aceves, S.S.; et al. Updated International Consensus Diagnostic Criteria for Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Proceedings of the AGREE Conference. Gastroenterology 2018, 155, 1022–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Votto, M.; De Filippo, M.; Castagnoli, R.; Delle Cave, F.; Giffoni, F.; Santi, V.; Vergani, M.; Caffarelli, C.; De Amici, M.; Marseglia, G.L.; et al. Noninvasive biomarkers of eosinophilic esophagitis. Acta Biomed. 2021, 92, e2021530. [Google Scholar]
- Grueso-Navarro, E.; Navarro, P.; Laserna-Mendieta, E.J.; Lucendo, A.J.; Arias-González, L. Blood-Based Biomarkers for Eosinophilic Esophagitis and Concomitant Atopic Diseases: A Look into the Potential of Extracellular Vesicles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Votto, M.; Lenti, M.V.; De Silvestri, A.; Bertaina, F.; Bertozzi, M.; Caimmi, S.; Cereda, E.; De Filippo, M.; Di Sabatino, A.; Klersy, C.; et al. Evaluation of diagnostic time in pediatric patients with eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders according to their clinical features. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2023, 49, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muir, A.B.; Brown-Whitehorn, T.; Godwin, B.; Cianferoni, A. Eosinophilic esophagitis: Early diagnosis is the key. Clin. Exp. Gastroenterol. 2019, 12, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruffner, M.A.; Cianferoni, A. Phenotypes and endotypes in eosinophilic esophagitis. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2020, 124, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, I.; Sharaf, R.; Stollman, N.; Wang, K.; Falck-Ytter, Y.; Chan, E.; Rank, M.; Stukus, D.; Greenhawt, M. Spotlight: Treatment of Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE). Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinbach, E.C.; Hernandez, M.; Dellon, E.S. Eosinophilic Esophagitis and the Eosinophilic Gastrointestinal Diseases: Approach to Diagnosis and Management. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2018, 6, 1483–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaheen, N.J.; Mukkada, V.; Eichinger, C.S.; Schofield, H.; Todorova, L.; Falk, G.W. Natural history of eosinophilic esophagitis: A systematic review of epidemiology and disease course. Dis. Esophagus 2018, 31, doy015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capucilli, P.; Cianferoni, A.; Grundmeier, R.W.; Spergel, J.M. Comparison of comorbid diagnoses in children with and without eosinophilic esophagitis in a large population. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2018, 121, 711–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Cervera, J.; Arias, Á.; Redondo-González, O.; Cano-Mollinedo, M.M.; Terreehorst, I.; Lucendo, A.J. Association between atopic manifestations and eosinophilic esophagitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2017, 118, 582–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, D.A.; Dudley, J.W.; Spergel, J.M. The Prevalence of Eosinophilic Esophagitis in Pediatric Patients with IgE-Mediated Food Allergy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2017, 5, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, D.A.; Grundmeier, R.W.; Ramos, M.; Spergel, J.M. Eosinophilic Esophagitis Is a Late Manifestation of the Allergic March. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2018, 6, 1528–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talathi, S.; Knight, T.; Dimmitt, R.; Mestre, J.; Jester, T. Concurrent eosinophilic esophagitis in pediatric patients with inflammatory bowel disease: A case series. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2019, 123, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abonia, J.P.; Wen, T.; Stucke, E.M.; Grotjan, T.; Griffith, M.S.; Kemme, K.A.; Collins, M.H.; Putnam, P.E.; Franciosi, J.P.; von Tiehl, K.F.; et al. High prevalence of eosinophilic esophagitis in patients with inherited connective tissue disorders. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 132, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Votto, M.; Naso, M.; Brambilla, I.; Caimmi, S.; De Filippo, M.; Licari, A.; Marseglia, G.L.; Castagnoli, R. Eosinophilic Gastrointestinal Diseases in Inborn Errors of Immunity. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Votto, M.; Fasola, S.; Cilluffo, G.; Ferrante, G.; La Grutta, S.; Marseglia, G.L.; Licari, A. Cluster analysis of clinical data reveals three pediatric eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorder phenotypes. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2022, 33, e13746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biedermann, L.; Holbreich, M.; Atkins, D.; Chehade, M.; Dellon, E.S.; Furuta, G.T.; Hirano, I.; Gonsalves, N.; Greuter, T.; Gupta, S.; et al. Food-induced immediate response of the esophagus-A newly identified syndrome in patients with eosinophilic esophagitis. Allergy 2021, 76, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holbreich, M.; Straumann, A. Features of food-induced immediate response in the esophagus (FIRE) in a series of adult patients with eosinophilic esophagitis. Allergy 2021, 76, 2893–2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vott, M.; Naso, M.; De Filippo, M.; Marseglia, A.; Raffaele, A.; Marseglia, G.L.; Licari, A. Food-induced immediate response of the esophagus: A first report in the pediatric age. Allergy 2022, 77, 711–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirano, I.; Moy, N.; Heckman, M.G.; Thomas, C.S.; Gonsalves, N.; Achem, S.R. Endoscopic assessment of the oesophageal features of eosinophilic oesophagitis: Validation of a novel classification and grading system. Gut 2013, 62, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatesh, R.D.; Leinwand, K.; Nguyen, N. Pediatric Unsedated Transnasal Endoscopy. Gastrointest. Endosc. Clin. N. Am. 2023, 33, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, M.H.; Martin, L.J.; Alexander, E.S.; Boyd, J.T.; Sheridan, R.; He, H.; Pentiuk, S.; Putnam, P.E.; Abonia, J.P.; Mukkada, V.A.; et al. Newly developed and validated eosinophilic esophagitis histology scoring system and evidence that it outperforms peak eosinophil count for disease diagnosis and monitoring. Dis. Esophagus 2017, 30, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biedermann, L.; Straumann, A.; Greuter, T.; Schreiner, P. Eosinophilic esophagitis-established facts and new horizons. Semin. Immunopathol. 2021, 43, 319–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murali, A.R.; Gupta, A.; Attar, B.M.; Ravi, V.; Koduru, P. Topical steroids in eosinophilic esophagitis: Systematic review and meta-analysis of placebo-controlled randomized clinical trials. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 31, 1111–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawla, P.; Sunkara, T.; Thandra, K.C.; Gaduputi, V. Efficacy and Safety of Budesonide in the Treatment of Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized and Non-Randomized Studies. Drugs R D 2018, 18, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellon, E.S.; Sheikh, A.; Speck, O.; Woodward, K.; Whitlow, A.B.; Hores, J.M.; Ivanovic, M.; Chau, A.; Woosley, J.T.; Madanick, R.D.; et al. Viscous topical is more effective than nebulized steroid therapy for patients with eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastroenterology 2012, 143, 321–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aceves, S.S.; Newbury, R.O.; Chen, D.; Mueller, J.; Dohil, R.; Hoffman, H.; Bastian, J.F.; Broide, D.H. Resolution of remodeling in eosinophilic esophagitis correlates with epithelial response to topical corticosteroids. Allergy 2010, 65, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eluri, S.; Runge, T.M.; Hansen, J.; Kochar, B.; Reed, C.C.; Robey, B.S.; Woosley, J.T.; Shaheen, N.J.; Dellon, E.S. Diminishing Effectiveness of Long-Term Maintenance Topical Steroid Therapy in PPI Non-Responsive Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2017, 8, e97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, C.A.; Palmquist, J.; Proudfoot, J.A.; Qian, A.; Wangberg, H.; Khosh-Hemmat, E.; Khosh-Hemmat, E.; Dohil, R.; Aceves, S.S. Evaluation of long-term course in children with eosinophilic esophagitis reveals distinct histologic patterns and clinical characteristics. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 144, 1050–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cianferoni, A. Eosinophilic esophagitis and other eosinophilic disorders of the gastrointestinal tract. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2020, 31 (Suppl. S24), 25–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, E.T.; Huang, K.Z.; Chen, H.X.; Landes, L.E.; McConnell, K.A.; Almond, M.A.; Safta, A.M.; Johnston, D.T.; Durban, R.; Jobe, L.; et al. Longitudinal Growth Outcomes Following First-line Treatment for Pediatric Patients with Eosinophilic Esophagitis. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2019, 68, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucendo, A.J.; Arias, Á.; Molina-Infante, J. Efficacy of Proton Pump Inhibitor Drugs for Inducing Clinical and Histologic Remission in Patients with Symptomatic Esophageal Eosinophilia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 14, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, T.; Dellon, E.S.; Moawad, F.J.; Furuta, G.T.; Aceves, S.S.; Rothenberg, M.E. Transcriptome analysis of proton pump inhibitor-responsive esophageal eosinophilia reveals proton pump inhibitor-reversible allergic inflammation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 135, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Cheng, E.; Huo, X.; Yu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Pham, T.H.; Wang, D.H.; Spechler, S.J.; Souza, R.F. Omeprazole blocks STAT6 binding to the eotaxin-3 promoter in eosinophilic esophagitis cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e50037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straumann, A.; Conus, S.; Grzonka, P.; Kita, H.; Kephart, G.; Bussmann, C.; Beglinger, C.; Smith, D.A.; Patel, J.; Byrne, M.; et al. Anti-interleukin-5 antibody treatment (mepolizumab) in active eosinophilic oesophagitis: A randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial. Gut 2010, 59, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spergel, J.M.; Rothenberg, M.E.; Collins, M.H.; Furuta, G.T.; Markowitz, J.E.; Fuchs, G., 3rd; O’Gorman, M.A.; Abonia, J.P.; Young, J.; Henkel, T.; et al. Reslizumab in children and adolescents with eosinophilic esophagitis: Results of a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 129, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biedermann, L.; Straumann, A. Mechanisms and clinical management of eosinophilic oesophagitis: An overview. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 20, 101–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassani, M.; Koenderman, L. Immunological and hematological effects of IL-5(Rα)-targeted therapy: An overview. Allergy 2018, 73, 1979–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothenberg, M.E.; Wen, T.; Greenberg, A.; Alpan, O.; Enav, B.; Hirano, I.; Nadeau, K.; Kaiser, S.; Peters, T.; Perez, A.; et al. Intravenous anti-IL-13 mAb QAX576 for the treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 135, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirano, I.; Collins, M.H.; Assouline-Dayan, Y.; Larry, E.; Gupta, S.K.; Straumann, A.; Safroneeva, E.; Grimm, M.; Smith, H.; Tompkins, C.A.; et al. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of a novel recombinant, humanized, anti-interleukin-13 monoclonal antibody (RPC4046) in patients with active eosinophilic esophagitis: Results of the HEROES study. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2016, 4, A1–A156. [Google Scholar]
- Licari, A.; Castagnoli, R.; Marseglia, A.; Olivero, F.; Votto, M.; Ciprandi, G.; Marseglia, G.L. Dupilumab to Treat Type 2 Inflammatory Diseases in Children and Adolescents. Paediatr. Drugs 2020, 22, 295–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, K.J.; Lazenby, A.J.; Rowe, P.C.; Yardley, J.H.; Perman, J.A.; Sampson, H.A. Eosinophilic esophagitis attributed to gastroesophageal reflux: Improvement with an amino acid-based formula. Gastroenterology 1995, 109, 1503–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucendo, A.J.; Molina-Infante, J.; Arias, Á.; von Arnim, U.; Bredenoord, A.J.; Bussmann, C.; Amil Dias, J.; Bove, M.; González-Cervera, J.; Larsson, H.; et al. Guidelines on eosinophilic esophagitis: Evidence-based statements and recommendations for diagnosis and management in children and adults. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2017, 5, 335–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bortoli, N.; Penagini, R.; Savarino, E.; Marchi, S. Eosinophilic esophagitis: Update in diagnosis and management. Position paper by the Italian Society of Gastroenterology and Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (SIGE). Dig. Liver Dis. 2017, 49, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Infante, J.; Lucendo, A.J. Dietary therapy for eosinophilic esophagitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 142, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chehade, M.; Aceves, S.S. Treatment of Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Diet or Medication? J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2021, 9, 3249–3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, C.J.; Abonia, J.P.; King, E.C.; Putnam, P.E.; Collins, M.H.; Franciosi, J.P.; Rothenberg, M.E. Comparative dietary therapy effectiveness in remission of pediatric eosinophilic esophagitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 129, 1570–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markowitz, J.E.; Spergel, J.M.; Ruchelli, E.; Liacouras, C.A. Elemental diet is an effective treatment for eosinophilic esophagitis in children and adolescents. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2003, 98, 777–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warners, M.J.; Vlieg-Boerstra, B.J.; Verheij, J.; van Rhijn, B.D.; Van Ampting, M.T.; Harthoorn, L.F.; de Jonge, W.J.; Smout, A.J.; Bredenoord, A.J. Elemental diet decreases inflammation and improves symptoms in adult eosinophilic oesophagitis patients. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 45, 777–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, K.A.; Byrne, K.R.; Vinson, L.A.; Ying, J.; Boynton, K.K.; Fang, J.C.; Gleich, G.J.; Adler, D.G.; Clayton, F. Elemental diet induces histologic response in adult eosinophilic esophagitis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 108, 759–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cianferoni, A.; Shuker, M.; Brown-Whitehorn, T.; Hunter, H.; Venter, C.; Spergel, J.M. Food avoidance strategies in eosinophilic oesophagitis. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2019, 49, 269–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visaggi, P.; Mariani, L.; Pardi, V.; Rosi, E.M.; Pugno, C.; Bellini, M.; Bellini, M.; Zingone, F.; Ghisa, M.; Marabotto, E.; et al. Dietary Management of Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Tailoring the Approach. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Votto, M.; Castagnoli, R.; De Filippo, M.; Brambilla, I.; Cuppari, C.; Marseglia, G.L.; Licari, A. Behavioral issues and quality of life in children with eosinophilic esophagitis. Minerva Pediatr. 2020, 72, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagalwalla, A.F.; Sentongo, T.A.; Ritz, S.; Hess, T.; Nelson, S.P.; Emerick, K.M.; Melin-Aldana, H.; Li, B.U. Effect of six-food elimination diet on clinical and histologic outcomes in eosinophilic esophagitis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2006, 4, 1097–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, A.; González-Cervera, J.; Tenias, J.M.; Lucendo, A.J. Efficacy of dietary interventions for inducing histologic remission in patients with eosinophilic esophagitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastroenterology 2014, 146, 1639–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagalwalla, A.F.; Wechsler, J.B.; Amsden, K.; Schwartz, S.; Makhija, M.; Olive, A.; Davis, C.M.; Manuel-Rubio, M.; Marcus, S.; Shaykin, R.; et al. Efficacy of a 4-Food Elimination Diet for Children with Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 15, 1698–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Infante, J.; Arias, A.; Barrio, J.; Rodríguez-Sánchez, J.; Sanchez-Cazalilla, M.; Lucendo, A.J. Four-food group elimination diet for adult eosinophilic esophagitis: A prospective multicenter study. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 134, 1093–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Infante, J.; Arias, Á.; Alcedo, J.; Garcia-Romero, R.; Casabona-Frances, S.; Prieto-Garcia, A.; Modolell, I.; Gonzalez-Cordero, P.L.; Perez-Martinez, I.; Martin-Lorente, J.L.; et al. Step-up empiric elimination diet for pediatric and adult eosinophilic esophagitis: The 2-4-6 study. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 1365–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirano, I.; Chan, E.S.; Rank, M.A.; Sharaf, R.N.; Stollman, N.H.; Stukus, D.R.; Wang, K.; Greenhawt, M.; Falck-Ytter, Y.T.; Chachu, K.A.; et al. AGA Institute and the Joint Task Force on Allergy-Immunology Practice Parameters Clinical Guidelines for the Management of Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1776–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greuter, T.; Alexander, J.A.; Straumann, A.; Katzka, D.A. Diagnostic and Therapeutic Long-term Management of Eosinophilic Esophagitis- Current Concepts and Perspectives for Steroid Use. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2018, 9, e212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucendo, A.J. Meta-Analysis-Based Guidance for Dietary Management in Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2015, 17, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliva, S.; Volpe, D.; Russo, G.; Veraldi, S.; Papoff, P.; Giordano, C.; Ruggiero, C.; Trovato, C.M.; Terrin, G.; Rossetti, D.; et al. Maintenance Therapy with the Lowest Effective Dose of Oral Viscous Budesonide in Children with Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 20, 2905–2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Votto, M.; De Filippo, M.; Olivero, F.; Raffaele, A.; Cereda, E.; De Amici, M.; Testa, G.; Marseglia, G.L.; Licari, A. Malnutrition in Eosinophilic Gastrointestinal Disorders. Nutrients 2020, 13, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, H.; Groetch, M.; Wang, J. Growth and nutritional concerns in children with food allergy. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 13, 275–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colson, D.; Kalach, N.; Soulaines, P.; Vannerom, Y.; Campeotto, F.; Talbotec, C.; Chatenoud, L.; Hankard, R.; Dupont, C. The impact of dietary therapy on clinical and biologic parameters of pediatric patients with eosinophilic esophagitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2014, 2, 587–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, P.; Furuta, G.T.; Brennan, T.; Henry, M.L.; Maune, N.C.; Sundaram, S.S.; Menard-Katcher, C.; Atkins, D.; Takurukura, F.; Giffen, S.; et al. Nutritional State and Feeding Behaviors of Children with Eosinophilic Esophagitis and Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2018, 66, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groetch, M.; Venter, C.; Skypala, I.; Vlieg-Boerstra, B.; Grimshaw, K.; Durban, R.; Cassin, A.; Henry, M.; Kliewer, K.; Kabbash, L.; et al. Dietary Therapy and Nutrition Management of Eosinophilic Esophagitis: A Work Group Report of the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2017, 5, 312–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Votto, M.; De Filippo, M.; Lenti, M.V.; Rossi, C.M.; Di Sabatino, A.; Marseglia, G.L.; Licari, A. Diet Therapy in Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Focus on a Personalized Approach. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 9, 820192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Infants and Young Children | Older Children | Adolescents |
|---|---|---|
| Regurgitation that does not recover with formula thickening, splitting of feedings, or acid suppressants. | GERD-like symptoms that do not recover with acid suppressants. | GERD-like symptoms that do not recover with acid suppressants. |
| Young children who prefer creamy or smoothed foods, soups, or liquids and avoid solid meals. | Children with selective feeding (avoiding more solid foods like meat and crusty bread). | Dysphagia for solids, then for liquids |
| Toddlers with speech delay | Children who drink a lot during meals to help food bolus progression. | Food impaction episodes |
| Young children with failure to thrive not related to more common diseases (food allergy, celiac disease, recurrent infections, or other chronic conditions) | Children who eat slowly compared to their siblings or friends. | Eating disorders |
| Non-surgical causes of recurrent vomiting | Epigastric/abdominal pain that is not responsive to conventional therapies for functional gastrointestinal disorders. | Selective feeding, avoidance of solid food or pills |
| Non-neurological dysphagia | Episodes of food impaction | Anxiety about eating in public places |
| Recurrent cough/wheezing | Non-neurological dysphagia for solid food | Adolescents eat slowly compared to their siblings or friends. |
| Gagging or coughing with feeding | FIRE symptoms | FIRE symptoms |
| Recurrent cough | Heartburn or chest pain episodes |
| Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs) | Slurry Budesonide | Swallowed Fluticasone | Dupilumab | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dose | Children: 1 mg/kg/day. Adolescents: 20–40 mg/day. | <10 years: 1 mg/day. >10 years: 2 mg/day. | <10 years: 440 mcg twice daily. >10 years: 880 mcg twice daily. | >12 years (weight > 40 kg): 300 mg/weekly. |
| Specific instructions | Twice daily. 30 min before meals. | Mixed with sucralose (5 g of sucralose), honey, or 2.5 mL aminoacidic formula per mg of budesonide to make a total volume of 8–12 mL. | Do not use the spacer. Do not inhale. | Pre-filled syringe or pre-filled pen for home administration. |
| General considerations | Initial treatment of 8–12 weeks. Effective in 54% of children. | Second dose administered at bedtime. Avoid eating/drinking 30 min after use. Safe and well tolerated. | Before beginning:
| |
| Long-term maintenance therapy | PPIs are generally safe. The response is sustained in inflammatory phenotype (70%). | Esophageal candidiasis 4–5%. Consider periodic monitoring for adrenal insufficiency, bone metabolism, and growth. The strategy is to decrease the dose to the lowest adequate level. Limited data on optimal dosage and side effects of long-term use | No long-term data. The most common side effects include injection site reactions, upper respiratory tract infections, cold sores in the mouth or on lips, and joint pain (arthralgia). | |
| NCT Number | Intervention | Population | Status | Phase |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT04394351 | Dupilumab vs. placebo | 1–11 years old | Active—not recruiting | Phase 3 |
| NCT05247866 | Dupilumab in food reintroduction | 6–25 years old | Recruiting | Phase 4 |
| NCT04991935 | Cendakimab vs. placebo | 12–75 years old | Recruiting | Phase 3 |
| NCT04753697 | Cendakimab | 12–75 years old | Recruiting | Phase 3 |
| NCT05583227 | Tezepelumab vs. placebo | 12–80 years old | Recruiting | Phase 3 |
| Diet Therapy | Rationale | Indications | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Elemental diet (ED) | Exclusive administration of aminoacidic-based formula. Modified ED: one or two less-allergenic foods (vegetables or fruits) are permitted. | Toddlers or young children with severe active EoE. Severe cases. Rescue therapy in severe/refractory cases or temporary solutions. | Rapid remission in 2 weeks. Higher compliance in infants and toddlers. Pediatric amino-acid-based formulas are almost nutritionally complete. | Poor palatability. Low compliance among children and adolescents. Feeding skill regression may be observed in children with NG or G-tube. Amino-acid-based formulas are expensive and not covered by insurance. Less effective in patients with stricturing EoE. |
| Empiric food elimination diet (FED) | Step-up approach (From 1–2-FED to 6-FED) | Pediatric patients. Moderate symptoms. A diet rich in milk and wheat. | Early identification of trigger food. Short diagnostic process. Avoid unnecessary diet restrictions. | Less effective. |
| Top-down approach (From 6-FED to 1–2-FED) | Adults and adolescents with normal or high BMI. Severe symptoms. Baseline diet rich in fruits and vegetables. There is much time to prepare alternative meals and high financial resources. | More effective. | Up to 7 endoscopies, one after every single food reintroduction. Several diet restrictions. Low compliance. Risk of nutritional deficiencies. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Votto, M.; De Filippo, M.; Caimmi, S.; Indolfi, C.; Raffaele, A.; Tosca, M.A.; Marseglia, G.L.; Licari, A. A Practical Update on Pediatric Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Children 2023, 10, 1620. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10101620
Votto M, De Filippo M, Caimmi S, Indolfi C, Raffaele A, Tosca MA, Marseglia GL, Licari A. A Practical Update on Pediatric Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Children. 2023; 10(10):1620. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10101620
Chicago/Turabian StyleVotto, Martina, Maria De Filippo, Silvia Caimmi, Cristiana Indolfi, Alessandro Raffaele, Maria Angela Tosca, Gian Luigi Marseglia, and Amelia Licari. 2023. "A Practical Update on Pediatric Eosinophilic Esophagitis" Children 10, no. 10: 1620. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10101620
APA StyleVotto, M., De Filippo, M., Caimmi, S., Indolfi, C., Raffaele, A., Tosca, M. A., Marseglia, G. L., & Licari, A. (2023). A Practical Update on Pediatric Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Children, 10(10), 1620. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10101620









