Nobiletin in Cancer Therapy: How This Plant Derived-Natural Compound Targets Various Oncogene and Onco-Suppressor Pathways
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Sources of NOB
3. Bioavailability of NOB
4. Therapeutic and Biological Activities of NOB
5. Potential Role of NOB in Human Malignancies
5.1. Nobiletin and Chemotherapy
5.2. Relation between NOB and Metastasis
5.3. Head and Neck Cancers
5.4. Thoracic Cancers
5.5. Gynecological Cancers
5.6. Urological Cancers
5.7. Gastrointestinal Cancers
5.8. Hematological Cancers
5.9. Anti-angiogenesis Effect
6. Conclusion and Remarks
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Gupta, B.; Sadaria, D.; Warrier, V.U.; Kirtonia, A.; Kant, R.; Awasthi, A.; Baligar, P.; Pal, J.K.; Yuba, E.; Sethi, G.; et al. Plant lectins and their usage in preparing targeted nanovaccines for cancer immunotherapy. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2020. (In press) [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, H.-Y.; Wu, J.-R.; Gao, W.-Y.; Lin, H.-R.; Chen, P.-Y.; Chen, C.-I.; Wu, M.-J.; Yen, J.-H. The Cholesterol-Modulating Effect of Methanol Extract of Pigeon Pea (Cajanus cajan (L.) Millsp.) Leaves on Regulating LDLR and PCSK9 Expression in HepG2 Cells. Molecules 2019, 24, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banik, K.; Ranaware, A.M.; Harsha, C.; Nitesh, T.; Girisa, S.; Deshpande, V.; Fan, L.; Nalawade, S.P.; Sethi, G.; Kunnumakkara, A.B. Piceatannol: A natural stilbene for the prevention and treatment of cancer. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 153, 104635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.F.; Weng, C.J.; Sethi, G.; Hu, D.N. Natural bioactives and phytochemicals serve in cancer treatment and prevention. Evid. Based Complement Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 698190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, S.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Kumar, A.P.; Yap, C.T.; Sethi, G.; Bishayee, A. Targeting autophagy using natural compounds for cancer prevention and therapy. Cancer 2019, 125, 1228–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashyap, D.; Tuli, H.S.; Yerer, M.B.; Sharma, A.; Sak, K.; Srivastava, S.; Pandey, A.; Garg, V.K.; Sethi, G.; Bishayee, A. Natural product-based nanoformulations for cancer therapy: Opportunities and challenges. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2019. (In press) [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarla, N.S.; Bishayee, A.; Sethi, G.; Reddanna, P.; Kalle, A.M.; Dhananjaya, B.L.; Dowluru, K.S.; Chintala, R.; Duddukuri, G.R. Targeting arachidonic acid pathway by natural products for cancer prevention and therapy. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2016, 40, 48–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishayee, A.; Sethi, G. Bioactive natural products in cancer prevention and therapy: Progress and promise. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2016, 40, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashrafizadeh, M.; Javanmardi, S.; Moradi-Ozarlou, M.; Mohammadinejad, R.; Farkhondeh, T.; Samarghandian, S.; Garg, M. Natural products and phytochemical nanoformulations targeting mitochondria in oncotherapy: An updated review on resveratrol. Biosci. Rep. 2020, 40, BSR20200257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, C.D.; Rangappa, S.; Preetham, H.D.; Chandra Nayak, S.; Gupta, V.K.; Basappa, S.; Sethi, G.; Rangappa, K.S. Targeting STAT3 signaling pathway in cancer by agents derived from Mother Nature. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2020. (In press)
- Wang, H.; Ahn, K.S.; Alharbi, S.A.; Shair, O.H.M.; Arfuso, F.; Sethi, G.; Chinnathambi, A.; Tang, F.R. Celastrol Alleviates Gamma Irradiation-Induced Damage by Modulating Diverse Inflammatory Mediators. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.H.; Jung, S.H.; Chinnathambi, A.; Alahmadi, T.A.; Alharbi, S.A.; Sethi, G.; Ahn, K.S. Attenuation of STAT3 Signaling Cascade by Daidzin Can Enhance the Apoptotic Potential of Bortezomib against Multiple Myeloma. Biomolecules 2019, 10, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanmugam, M.K.; Kannaiyan, R.; Sethi, G. Targeting cell signaling and apoptotic pathways by dietary agents: Role in the prevention and treatment of cancer. Nutr. Cancer 2011, 63, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasannan, R.; Kalesh, K.A.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Nachiyappan, A.; Ramachandran, L.; Nguyen, A.H.; Kumar, A.P.; Lakshmanan, M.; Ahn, K.S.; Sethi, G. Key cell signaling pathways modulated by zerumbone: Role in the prevention and treatment of cancer. Biochem. Pharm. 2012, 84, 1268–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, S.; Verma, S.S.; Rai, V.; Awasthee, N.; Chava, S.; Hui, K.M.; Kumar, A.P.; Challagundla, K.B.; Sethi, G.; Gupta, S.C. Long non-coding RNAs are emerging targets of phytochemicals for cancer and other chronic diseases. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2019, 76, 1947–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethi, G.; Ahn, K.S.; Sung, B.; Aggarwal, B.B. Pinitol targets nuclear factor-κB activation pathway leading to inhibition of gene products associated with proliferation, apoptosis, invasion, and angiogenesis. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2008, 7, 1604–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, L.; Manu, K.A.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Li, F.; Siveen, K.S.; Vali, S.; Kapoor, S.; Abbasi, T.; Surana, R.; Smoot, D.T.; et al. Isorhamnetin inhibits proliferation and invasion and induces apoptosis through the modulation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma activation pathway in gastric cancer. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 38028–38040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siveen, K.S.; Mustafa, N.; Li, F.; Kannaiyan, R.; Ahn, K.S.; Kumar, A.P.; Chng, W.J.; Sethi, G. Thymoquinone overcomes chemoresistance and enhances the anticancer effects of bortezomib through abrogation of NF-kappaB regulated gene products in multiple myeloma xenograft mouse model. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 634–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, P.; Li, F.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Vali, S.; Abbasi, T.; Kapoor, S.; Ahn, K.S.; Kumar, A.P.; Sethi, G. Honokiol inhibits signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 signaling, proliferation, and survival of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via the protein tyrosine phosphatase SHP-1. J. Cell Physiol. 2012, 227, 2184–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.M.; Li, F.; Rajendran, P.; Kumar, A.P.; Hui, K.M.; Sethi, G. Identification of beta-escin as a novel inhibitor of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3/Janus-activated kinase 2 signaling pathway that suppresses proliferation and induces apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. J. Pharm. Exp. 2010, 334, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Li, L.; Shi, W.; Liu, H.; Yang, J.; Yuan, X.; Wu, L. The multifunctional effects of nobiletin and its metabolites in vivo and in vitro. Evid. Based Complementary Altern. Med. 2016, 2016, 2918796. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Cai, D.; Pearce, K.; Sun, P.Y.; Roberts, A.C.; Glanzman, D.L. Reinstatement of long-term memory following erasure of its behavioral and synaptic expression in Aplysia. Elife 2014, 3, e03896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uckoo, R.M.; Jayaprakasha, G.; Vikram, A.; Patil, B.S. Polymethoxyflavones isolated from the peel of Miaray Mandarin (Citrus miaray) have biofilm inhibitory activity in Vibrio harveyi. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 7180–7189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itoh, N.; Iwata, C.; Toda, H. Molecular cloning and characterization of a flavonoid-O-methyltransferase with broad substrate specificity and regioselectivity from Citrus depressa. BMC Plant Biol. 2016, 16, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.-H.; Charles, A.L.; Kung, H.-F.; Ho, C.-T.; Huang, T.-C. Extraction of nobiletin and tangeretin from Citrus depressa Hayata by supercritical carbon dioxide with ethanol as modifier. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2010, 31, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohno, H.; Yoshitani, S.-i.; Tsukio, Y.; Murakami, A.; Koshimizu, K.; Yano, M.; Tokuda, H.; Nishino, H.; Ohigashi, H.; Tanaka, T. Dietary administration of citrus nobiletin inhibits azoxymethane-induced colonic aberrant crypt foci in rats. Life Sci. 2001, 69, 901–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, A.; Nakamura, Y.; Torikai, K.; Tanaka, T.; Koshiba, T.; Koshimizu, K.; Kuwahara, S.; Takahashi, Y.; Ogawa, K.; Yano, M. Inhibitory effect of citrus nobiletin on phorbol ester-induced skin inflammation, oxidative stress, and tumor promotion in mice. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 5059–5066. [Google Scholar]
- Uckoo, R.M.; Jayaprakasha, G.K.; Patil, B.S. Rapid separation method of polymethoxyflavones from citrus using flash chromatography. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2011, 81, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaii, S.; Tomono, Y.; Katase, E.; Ogawa, K.; Yano, M. Quantitation of flavonoid constituents in citrus fruits. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1999, 47, 3565–3571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukayama, M.; Ichikawa, R.; Yamamoto, K.; Sasaki, T.; Kawamura, Y. Microwave-assisted rapid extraction of polymethoxyflavones from dried peels of Citrus yuko Hort. ex Tanaka. Nippon Shokuhin Kagaku Kogaku Kaish J. Jpn. Soc. Food Sci. Technol. 2009, 56, 359–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Silva, I.; Estrada, M.F.V.; Pereira, C.; da Silva, A.B.; Bronze, M.R.; Alves, P.M.; Duarte, C.M.; Brito, C.; Serra, A.T. Polymethoxylated flavones from orange peels inhibit cell proliferation in a 3D cell model of human colorectal cancer. Nutr. Cancer 2018, 70, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, H.-C.; Jang, M.-G.; Kang, C.-H.; Lee, N.-H.; Kang, S.-I.; Lee, S.-R.; Park, D.-B.; Kim, S.-J. Preparation of a polymethoxyflavone-rich fraction (PRF) of Citrus sunki Hort. ex Tanaka and its antiproliferative effects. Food Chem. 2010, 123, 484–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asakawa, T.; Hiza, A.; Nakayama, M.; Inai, M.; Oyama, D.; Koide, H.; Shimizu, K.; Wakimoto, T.; Harada, N.; Tsukada, H. PET imaging of nobiletin based on a practical total synthesis. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 2868–2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshigai, E.; Machida, T.; Okuyama, T.; Mori, M.; Murase, H.; Yamanishi, R.; Okumura, T.; Ikeya, Y.; Nishino, H.; Nishizawa, M. Citrus nobiletin suppresses inducible nitric oxide synthase gene expression in interleukin-1β-treated hepatocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 439, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noguchi, S.; Atsumi, H.; Iwao, Y.; Kan, T.; Itai, S. Nobiletin: A citrus flavonoid displaying potent physiological activity. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. C Struct. Chem. 2016, 72, 124–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onoue, S.; Nakamura, T.; Uchida, A.; Ogawa, K.; Yuminoki, K.; Hashimoto, N.; Hiza, A.; Tsukaguchi, Y.; Asakawa, T.; Kan, T. Physicochemical and biopharmaceutical characterization of amorphous solid dispersion of nobiletin, a citrus polymethoxylated flavone, with improved hepatoprotective effects. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 49, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Bi, J.; Johnson, D.; Sun, Y.; Song, M.; Qiu, P.; Dong, P.; Decker, E.; Xiao, H. Analysis of 10 metabolites of polymethoxyflavones with high sensitivity by electrochemical detection in high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Song, M.; Dong, P.; Qiu, P.; Guo, S.; Zhong, Z.; Li, S.; Ho, C.T.; Xiao, H. Identification of novel bioactive metabolites of 5-demethylnobiletin in mice. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2013, 57, 1999–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, Z.; Sang, S.; Huang, M.T.; Ho, C.T. Identification of nobiletin metabolites in mouse urine. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2006, 50, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, T.; Yoshimura, Y.; Yabuki, H.; Nakazawa, T.; Ohsawa, K.; Mimaki, Y.; Sashida, Y. Urinary metabolites of nobiletin orally administered to rats. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2003, 51, 1426–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Song, M.; Wang, M.; Zheng, J.; Gao, Z.; Xu, F.; Zhang, G.; Xiao, H. Chemopreventive effects of nobiletin and its colonic metabolites on colon carcinogenesis. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2015, 59, 2383–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, S.; Jonca, M.; Lambros, T.; Ferguson, S.; Goodnow, R.; Ho, C.T. Comparison of supercritical fluid chromatography and liquid chromatography for the separation of urinary metabolites of nobiletin with chiral and non-chiral stationary phases. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2006, 20, 1206–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koga, N.; Ohta, C.; Kato, Y.; Haraguchi, K.; Endo, T.; Ogawa, K.; Ohta, H.; Yano, M. In vitro metabolism of nobiletin, a polymethoxy-flavonoid, by human liver microsomes and cytochrome P450. Xenobiotica 2011, 41, 927–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M. Biotransformation of Polymethoxyflavones and Its Implication on Biological Activities. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Massachusetts, Amherst, MA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hattori, T.; Tagawa, H.; Inai, M.; Kan, T.; Kimura, S.I.; Itai, S.; Mitragotri, S.; Iwao, Y. Transdermal delivery of nobiletin using ionic liquids. Sci Rep 2019, 9, 20191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Liang, Y.; Pei, Y.; Li, B.; Liang, H. Plant exine capsules based encapsulation strategy: A high loading and long-term effective delivery system for nobiletin. Food Res. Int. 2020, 127, 108691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, W.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, T.; Sun, S.; Ye, J.; Li, Z.; Mao, L.; Ren, J. Enhancement of Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Nobiletin in Macrophages by a Nano-Emulsion Preparation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xie, J.; Ai, Z.; Su, J. Nobiletin-loaded micelles reduce ovariectomy-induced bone loss by suppressing osteoclastogenesis. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 7839–7849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshtkar, S.; Kaviani, M.; Jabbarpour, Z.; Geramizadeh, B.; Motevaseli, E.; Nikeghbalian, S.; Shamsaeefar, A.; Motazedian, N.; Al-Abdullah, I.H.; Ghahremani, M.H.; et al. Protective effect of nobiletin on isolated human islets survival and function against hypoxia and oxidative stress-induced apoptosis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.F.; Jiang, H.; Chen, J.; Guo, X.; Li, Y.; Hu, Q.; Yang, S. Nobiletin ameliorates myocardial ischemia and reperfusion injury by attenuating endoplasmic reticulum stress-associated apoptosis through regulation of the PI3K/AKT signal pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 73, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Wu, D.; Huang, L.; Jiang, C.; Pan, T.; Kang, X.; Pan, J. Nobiletin Inhibits IL-1beta-Induced Inflammation in Chondrocytes via Suppression of NF-kappaB Signaling and Attenuates Osteoarthritis in Mice. Front. Pharm. 2019, 10, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuboi, T.; Lu, R.; Yonezawa, T.; Watanabe, A.; Woo, J.T.; Abe-Dohmae, S.; Yokoyama, S. Molecular mechanism for nobiletin to enhance ABCA1/G1 expression in mouse macrophages. Atherosclerosis 2020, 297, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuk, T.; Kim, Y.; Yang, J.; Sung, J.; Jeong, H.S.; Lee, J. Nobiletin Inhibits Hepatic Lipogenesis via Activation of AMP-Activated Protein Kinase. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 2018, 7420265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, H.; Du, Y.; Liu, P.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Shen, H.; Xing, L.; Xue, X.; Chen, J.; et al. Long noncoding RNA TP53TG1 promotes pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma development by acting as a molecular sponge of microRNA-96. Cancer Sci. 2019, 110, 2760–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneda, H.; Otomo, R.; Sasaki, N.; Omi, T.; Sato, T.; Kaneda, T. Endothelium-independent vasodilator effects of nobiletin in rat aorta. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 140, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youn, K.; Lee, S.; Jun, M. Discovery of Nobiletin from Citrus Peel as a Potent Inhibitor of beta-Amyloid Peptide Toxicity. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nohara, K.; Mallampalli, V.; Nemkov, T.; Wirianto, M.; Yang, J.; Ye, Y.; Sun, Y.; Han, L.; Esser, K.A.; Mileykovskaya, E.; et al. Nobiletin fortifies mitochondrial respiration in skeletal muscle to promote healthy aging against metabolic challenge. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.A.; Sun, Q.; Li, Y.C.; Weng, R.X.; Wu, R.; Zhang, H.H.; Xu, G.Y. Overexpression of Purinergic P2X4 Receptors in Hippocampus Rescues Memory Impairment in Rats with Type 2 Diabetes. Neurosci. Bull. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josefs, T.; Barrett, T.J.; Brown, E.J.; Quezada, A.; Wu, X.; Voisin, M.; Amengual, J.; Fisher, E.A. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps (NETs) promote macrophage inflammation and impair atherosclerosis resolution in mice with diabetes. Jci Insight 2020. (In press) [CrossRef]
- Nguyen-Ngo, C.; Salomon, C.; Quak, S.; Lai, A.; Willcox, J.C.; Lappas, M. Nobiletin exerts anti-diabetic and anti-inflammatory effects in an in vitro human model and in vivo murine model of gestational diabetes. Clin. Sci. 2020, 134, 571–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brissot, P.; Ropert, M.; Le Lan, C.; Loréal, O. Non-transferrin bound iron: A key role in iron overload and iron toxicity. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta Bba Gen. Subj. 2012, 1820, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudjoncik, A.; Guenancia, C.; Zeller, M.; Cottin, Y.; Vergely, C.; Rochette, L. Iron, oxidative stress, and redox signaling in the cardiovascular system. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2014, 58, 1721–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finazzi, D.; Arosio, P. Biology of ferritin in mammals: An update on iron storage, oxidative damage and neurodegeneration. Arch. Toxicol. 2014, 88, 1787–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gammella, E.; Recalcati, S.; Rybinska, I.; Buratti, P.; Cairo, G. Iron-induced damage in cardiomyopathy: Oxidative-dependent and independent mechanisms. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2015, 2015, 230182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, Y.; He, H.; Zhang, Z.; Liao, Z.; Yin, D.; Liu, D.; Yi, B.; He, M. Long-term sodium ferulate supplementation scavenges oxygen radicals and reverses liver damage induced by iron overloading. Molecules 2016, 21, 1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, L.; Li, X. LncRNA TUG1 promoted viability and associated with gemcitabine resistant in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 137, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; He, H.; Yin, D.; Que, A.; Tang, L.; Liao, Z.; Huang, Q.; He, M. Mechanism of chronic dietary iron overload-induced liver damage in mice. Mol. Med. Rep. 2013, 7, 1173–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, D.; Yi, B.; Liao, Z.; Tang, L.; Yin, D.; He, M. Taurine supplementation reduces oxidative stress and protects the liver in an iron-overload murine model. Mol. Med. Rep. 2014, 10, 2255–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, B.; Chen, X.; Zhou, Q.; Li, H.; Chen, S.; Yin, D.; He, H.; He, M. Nobiletin Regulates ROS/ADMA/DDAHII/eNOS/NO Pathway and Alleviates Vascular Endothelium Injury by Iron Overload. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2020. (In press) [CrossRef]
- Lebre, M.C.; Vieira, P.L.; Tang, M.W.; Aarrass, S.; Helder, B.; Newsom-Davis, T.; Tak, P.P.; Screaton, G.R. Synovial IL-21/TNF-producing CD4+ T cells induce joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis by inducing matrix metalloproteinase production by fibroblast-like synoviocytes. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2017, 101, 775–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, R.; Jin, Y.; Sun, L.; Yang, L.; Li, C.; Li, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhao, J. Interleukin-21 induces migration and invasion of fibroblast-like synoviocytes from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2016, 184, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Guo, S.; Dong, Q. Nobiletin suppresses IL-21/IL-21 receptor-mediated inflammatory response in MH7A fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS): An implication in rheumatoid arthritis. Eur. J. Pharm. 2020, 875, 172939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrow, N.M.; Burke, A.C.; Samsoondar, J.P.; Seigel, K.E.; Wang, A.; Telford, D.E.; Sutherland, B.G.; O’Dwyer, C.; Steinberg, G.R.; Fullerton, M.D.; et al. The citrus flavonoid nobiletin confers protection from metabolic dysregulation in high-fat-fed mice independent of AMPK. J. Lipid Res. 2020, 61, 387–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Wang, H.; Li, T.; Chen, L.; Zheng, B.; Liu, R.H. Nobiletin Delays Aging and Enhances Stress Resistance of Caenorhabditis elegans. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guvenc, M.; Cellat, M.; Gokcek, I.; Ozkan, H.; Arkali, G.; Yakan, A.; Yurdagul Ozsoy, S.; Aksakal, M. Nobiletin attenuates acetaminophen-induced hepatorenal toxicity in rats. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2020, 34, e22427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishiuchi, N.; Nakashima, A.; Doi, S.; Yoshida, K.; Maeda, S.; Kanai, R.; Yamada, Y.; Ike, T.; Doi, T.; Kato, Y.; et al. Hypoxia-preconditioned mesenchymal stem cells prevent renal fibrosis and inflammation in ischemia-reperfusion rats. Stem Cell Res. 2020, 11, 130. [Google Scholar]
- Guvenc, M.; Cellat, M.; Uyar, A.; Ozkan, H.; Gokcek, I.; Isler, C.T.; Yakan, A. Nobiletin Protects from Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Rats by Suppressing Inflammatory Cytokines and Regulating iNOS-eNOS Expressions. Inflammation 2020, 43, 336–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Wang, F.; Yu, L.; Li, Z. Nobiletin alleviates cerebral ischemic-reperfusion injury via MAPK signaling pathway. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2019, 11, 5967–5977. [Google Scholar]
- Nohara, K.; Nemkov, T.; D’Alessandro, A.; Yoo, S.H.; Chen, Z. Coordinate Regulation of Cholesterol and Bile Acid Metabolism by the Clock Modifier Nobiletin in Metabolically Challenged Old Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, J.-H.; Lin, C.-Y.; Chuang, C.-H.; Chin, H.-K.; Wu, M.-J.; Chen, P.-Y. Nobiletin Promotes Megakaryocytic Differentiation through the MAPK/ERK-Dependent EGR1 Expression and Exerts Anti-Leukemic Effects in Human Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML) K562 Cells. Cells 2020, 9, 877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermawan, A.; Putri, H. Bioinformatics Studies Provide Insight into Possible Target and Mechanisms of Action of Nobiletin against Cancer Stem Cells. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2020, 21, 611–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Q.; Liang, X.; Wu, Y.; Lu, Y. Nobiletin protects against myocardial injury and myocardial apoptosis following coronary microembolization via activating PI3K/Akt pathway in rats. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2019, 392, 1121–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, T.; Wang, C.; Chi, Q.; Shi, J.; Zhu, P.; Dong, N. Nobiletin exhibits potent inhibition on tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced calcification of human aortic valve interstitial cells via targeting ABCG2 and AKR1B1. Phytother. Res. 2019, 33, 1717–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Lu, X. Nobiletin suppresses oxidative stress and apoptosis in H9c2 cardiomyocytes following hypoxia/reoxygenation injury. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 854, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, G.; Mi, Y.; Fan, R.; Li, R.; Liu, Z.; Liu, X. Nobiletin Protects against systemic inflammation-stimulated memory impairment via MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 5122–5134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, L.; Xie, H.; Chen, C.; Tao, Z.; Zhang, C.; Cai, L. Inhibiting the PI3K/AKT/NF-κB signal pathway with nobiletin for attenuating the development of osteoarthritis: In vitro and in vivo studies. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 2161–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potue, P.; Wunpathe, C.; Maneesai, P.; Kukongviriyapan, U.; Prachaney, P.; Pakdeechote, P. Nobiletin alleviates vascular alterations through modulation of Nrf-2/HO-1 and MMP pathways in l-NAME induced hypertensive rats. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 1880–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Han, Y.; Zhao, F.; Zhao, Z.; Tian, J.; Jia, K. Nobiletin suppresses high-glucose–induced inflammation and ECM accumulation in human mesangial cells through STAT3/NF-κB pathway. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 3467–3473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.P.; Shen, Q.Q.; Wen, M.; Zou, J.Q.; Wang, Y.; Yang, J.X.; Hu, L.Z.; Zheng, X.L.; Chen, Y.S.; Su, H.; et al. Nobiletin reduces LPL-mediated lipid accumulation and pro-in fl ammatory cytokine secretion through upregulation of miR-590 expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2019, 508, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dusabimana, T.; Kim, S.R.; Kim, H.J.; Park, S.W.; Kim, H. Nobiletin ameliorates hepatic ischemia and reperfusion injury through the activation of SIRT-1/FOXO3a-mediated autophagy and mitochondrial biogenesis. Exp. Mol. Med. 2019, 51, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfarouk, K.O.; Stock, C.-M.; Taylor, S.; Walsh, M.; Muddathir, A.K.; Verduzco, D.; Bashir, A.H.; Mohammed, O.Y.; Elhassan, G.O.; Harguindey, S. Resistance to cancer chemotherapy: Failure in drug response from ADME to P-gp. Cancer Cell Int. 2015, 15, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshimali, Y.I.; Wu, Y.; Khaddour, H.; Wu, Y.; Gradinaru, D.; Sukhija, H.; Chung, S.S.; Vadgama, J.V. Optimization of cancer treatment through overcoming drug resistance. J. Cancer Res. Oncobiol. 2018, 1, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamioka, H.; Tomono, T.; Fujita, A.; Onozato, R.; Iijima, M.; Tsuchida, S.; Arai, T.; Fujita, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yano, K.; et al. Moesin-Mediated P-Glycoprotein Activation during Snail-Induced Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Lung Cancer Cells. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020. (In press) [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.W.; Law, B.Y.K.; Qu, S.L.Q.; Hamdoun, S.; Chen, J.; Zhang, W.; Guo, J.R.; Wu, A.G.; Mok, S.W.F.; Zhang, D.W.; et al. SERCA and P-glycoprotein inhibition and ATP depletion are necessary for celastrol-induced autophagic cell death and collateral sensitivity in multidrug-resistant tumor cells. Pharm. Res. 2020, 153, 104660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.; Qin, Z.; Zhang, W.D.; Cheng, G.; Yehuda, A.G.; Ashby, C.R., Jr.; Chen, Z.S.; Cheng, X.D.; Qin, J.J. Medicinal chemistry strategies to discover P-glycoprotein inhibitors: An update. Drug Resist Updat 2020, 49, 100681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, S.-L.; Tian, Y.; Huo, S.; Qu, B.; Liu, R.-M.; Xu, P.; Li, Y.-Z.; Xie, Y. Nobiletin and its derivatives overcome multidrug resistance (MDR) in cancer: Total synthesis and discovery of potent MDR reversal agents. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2020, 10, 327–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesołowska, O.; Wiśniewski, J.; Środa-Pomianek, K.; Bielawska-Pohl, A.; Paprocka, M.; Duś, D.; Duarte, N.l.; Ferreira, M.-J.U.; Michalak, K. Multidrug resistance reversal and apoptosis induction in human colon cancer cells by some flavonoids present in citrus plants. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 1896–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, D.P.; Pojo, M.; Pinto, A.T.; Leite, V.; Serra, A.T.; Cavaco, B.M. Nobiletin Alone or in Combination with Cisplatin Decreases the Viability of Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer Cell Lines. Nutr. Cancer 2020, 72, 352–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, S.K.; Kulkarni, N.S.; Farrales, P.; Kanabar, D.D.; Parvathaneni, V.; Kunda, N.K.; Muth, A.; Gupta, V. Sorafenib Loaded Inhalable Polymeric Nanocarriers against Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Pharm. Res. 2020, 37, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leineweber, C.G.; Pietzner, A.; Zhang, I.W.; Blessin, U.B.; Rothe, M.; Schott, E.; Schebb, N.H.; Weylandt, K.H. Assessment of the Effect of Sorafenib on Omega-6 and Omega-3 Epoxyeicosanoid Formation in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guney Eskiler, G.; Deveci, A.O.; Bilir, C.; Kaleli, S. Synergistic effects of nobiletin and sorafenib combination on metastatic prostate cancer cells. Nutr. Cancer 2019, 71, 1299–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, S.P.; Bhardwaj, G.; Gerlach, J.H.; Mackie, J.E.; Grant, C.E.; Almquist, K.C.; Stewart, A.J.; Kurz, E.U.; Duncan, A.M.; Deeley, R.G. Overexpression of a transporter gene in a multidrug-resistant human lung cancer cell line. Science 1992, 258, 1650–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, S.P. Targeting multidrug resistance protein 1 (MRP1, ABCC1): Past, present, and future. Annu. Rev. Pharm. Toxicol. 2014, 54, 95–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manohar, C.F.; Bray, J.A.; Salwen, H.R.; Madafiglio, J.; Cheng, A.; Flemming, C.; Marshall, G.M.; Norris, M.D.; Haber, M.; Cohn, S.L. MYCN-mediated regulation of the MRP1 promoter in human neuroblastoma. Oncogene 2004, 23, 753–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scotto, K.W. Transcriptional regulation of ABC drug transporters. Oncogene 2003, 22, 7496–7511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, M.; Wang, J.; Ren, Y.; Li, L.; He, W.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, T.; Li, Z. Over-expression of FSIP1 promotes breast cancer progression and confers resistance to docetaxel via MRP1 stabilization. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, T.; Ding, J.; Li, W. miR-7 Reverses Breast Cancer Resistance to Chemotherapy by Targeting MRP1 and BCL2. Onco Targets 2019, 12, 11097–11105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, J.Y.; Hung, M.; Van, L.; Unno, T.; Cho, S.K. Nobiletin Enhances Chemosensitivity to Adriamycin through Modulation of the Akt/GSK3β/β–Catenin/MYCN/MRP1 Signaling Pathway in A549 Human Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Cells. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, P.K.; Naik, P.P.; Praharaj, P.P.; Meher, B.R.; Gupta, P.K.; Verma, R.S.; Maiti, T.K.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Chinnathambi, A.; Alharbi, S.A.; et al. Abrus agglutinin stimulates BMP-2-dependent differentiation through autophagic degradation of beta-catenin in colon cancer stem cells. Mol. Carcinog. 2018, 57, 664–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuvanalakshmi, G.; Rangappa, K.S.; Dharmarajan, A.; Sethi, G.; Kumar, A.P.; Warrier, S. Breast Cancer Stem-Like Cells Are Inhibited by Diosgenin, a Steroidal Saponin, by the Attenuation of the Wnt beta-Catenin Signaling via the Wnt Antagonist Secreted Frizzled Related Protein-4. Front. Pharm. 2017, 8, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuvanalakshmi, G.; Gamit, N.; Patil, M.; Arfuso, F.; Sethi, G.; Dharmarajan, A.; Kumar, A.P.; Warrier, S. Stemness, Pluripotentiality, and Wnt Antagonism: sFRP4, a Wnt antagonist Mediates Pluripotency and Stemness in Glioblastoma. Cancers 2018, 11, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Gong, L.; Lvzi, X.; Qiu, K.; Zhang, Z.; Wan, L. Echinacoside inhibits breast cancer cells by suppressing the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020. (In press) [CrossRef]
- Luo, J. Glycogen synthase kinase 3beta (GSK3beta) in tumorigenesis and cancer chemotherapy. Cancer Lett. 2009, 273, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, P.S.; Wang, L.Z.; Dai, X.; Tseng, S.H.; Loo, S.J.; Sethi, G. Judicious Toggling of mTOR Activity to Combat Insulin Resistance and Cancer: Current Evidence and Perspectives. Front. Pharm. 2016, 7, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, C.D.; Srinivasa, V.; Rangappa, S.; Mervin, L.; Mohan, S.; Paricharak, S.; Baday, S.; Li, F.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Chinnathambi, A.; et al. Trisubstituted-Imidazoles Induce Apoptosis in Human Breast Cancer Cells by Targeting the Oncogenic PI3K/Akt/mTOR Signaling Pathway. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, S.H.; Ko, J.H.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, C.; Lee, H.; Nam, D.; Lee, J.; Lee, S.G.; Yang, W.M.; Um, J.Y.; et al. Ginkgolic Acid Inhibits Invasion and Migration and TGF-beta-Induced EMT of Lung Cancer Cells through PI3K/Akt/mTOR Inactivation. J. Cell Physiol. 2017, 232, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, C.; Um, J.Y.; Sethi, G.; Ahn, K.S. Casticin-Induced Inhibition of Cell Growth and Survival Are Mediated through the Dual Modulation of Akt/mTOR Signaling Cascade. Cancers 2019, 11, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.S.; Yap, W.N.; Arfuso, F.; Kar, S.; Wang, C.; Cai, W.; Dharmarajan, A.M.; Sethi, G.; Kumar, A.P. Targeting the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in gastric carcinoma: A reality for personalized medicine? World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 12261–12273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, H.; Guo, Q.; Liu, T.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, M.; Zeng, K.; Tu, P. Cucurbitacin E Inhibits Huh7 Hepatoma Carcinoma Cell Proliferation and Metastasis via Suppressing MAPKs and JAK/STAT3 Pathways. Molecules 2020, 25, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, Y.S.; Seo, K.I.; Sanggenol, L. Induces Apoptosis and Cell Cycle Arrest via Activation of p53 and Suppression of PI3K/Akt/mTOR Signaling in Human Prostate Cancer Cells. Nutrients 2020, 12, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, T.; Shen, H.; Huang, H.; Yang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, G. Cholesterol-lowering drug pitavastatin targets lung cancer and angiogenesis via suppressing prenylation-dependent Ras/Raf/MEK and PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling. Anticancer Drugs 2020, 31, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, G.; Sun, H.; Yu, D. Nobiletin sensitizes colorectal cancer cells to oxaliplatin by PI3K/Akt/MTOR pathway. Front. Biosci. 2019, 24, 303–312. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, W.; Feng, S.; Yao, X.; Yuan, Z.; Liu, L.; Xie, Y. Nobiletin enhances the efficacy of chemotherapeutic agents in ABCB1 overexpression cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 18789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravn, S.; Heide-Jorgensen, U.; Christiansen, C.F.; Verwaal, V.J.; Hagemann-Madsen, R.H.; Iversen, L.H. Overall risk and risk factors for metachronous peritoneal metastasis after colorectal cancer surgery: A nationwide cohort study. Bjs Open 2020, 4, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.Y.; Tang, M.L.; Ning, J.F.; Hao, Y.P.; Zhou, L.; Sun, X. Novel octapeptide-DTX prodrugs targeting MMP-7 as effective agents for the treatment of colorectal cancer with lower systemic toxicity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 193, 112194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.I.; Kil, J.H.; Yu, G.H.; Karadeniz, F.; Oh, J.H.; Seo, Y.; Kong, C.S. 3,5-Dicaffeoyl-epi-quinic acid inhibits the PMA-stimulated activation and expression of MMP-9 but not MMP-2 via downregulation of MAPK pathway. Z. Naturforsch. C. J. Biosci. 2020. (In press) [CrossRef]
- O’Reilly, M.S.; Wiederschain, D.; Stetler-Stevenson, W.G.; Folkman, J.; Moses, M.A. Regulation of angiostatin production by matrix metalloproteinase-2 in a model of concomitant resistance. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 29568–29571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, C.Y.; Ho, Y.C.; Lin, C.W.; Yang, W.E.; Yu, Y.L.; Tsai, M.C.; Yang, S.F.; Su, S.C. Salvianolic acid A suppresses MMP-2 expression and restrains cancer cell invasion through ERK signaling in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 252, 112601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Hao, Y.; Wan, X.; He, J.; Tong, Y. Baicalein inhibits cell development, metastasis and EMT and induces apoptosis by regulating ERK signaling pathway in osteosarcoma. J. Recept. Signal Transduct. Res. 2020, 40, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanai, T.; Kondo, N.; Okada, M.; Sano, H.; Okumura, G.; Kijima, Y.; Ogose, A.; Kawashima, H.; Endo, N. The JNK pathway represents a novel target in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis through the suppression of MMP-3. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2020, 15, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, S.H.; Kwon, K.M.; Park, J.Y.; Abekura, F.; Lee, Y.C.; Chung, T.W.; Ha, K.T.; Chang, H.W.; Cho, S.H.; Kim, J.S.; et al. Esculentoside H inhibits colon cancer cell migration and growth through suppression of MMP-9 gene expression via NF-kB signaling pathway. J. Cell Biochem. 2019, 120, 9810–9819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.L.; Hsieh, M.J.; Yang, J.S.; Lin, C.W.; Lue, K.H.; Lu, K.H.; Yang, S.F. Nobiletin inhibits human osteosarcoma cells metastasis by blocking ERK and JNK-mediated MMPs expression. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 35208–35223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.O.; Khan, F.A.; Galindo-Campos, M.A.; Yelamos, J. Understanding specific functions of PARP-2: New lessons for cancer therapy. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2016, 6, 1842–1863. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Megnin-Chanet, F.; Bollet, M.A.; Hall, J. Targeting poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase activity for cancer therapy. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2010, 67, 3649–3662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vida, A.; Marton, J.; Miko, E.; Bai, P. Metabolic roles of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerases. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2017, 63, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, P.; Jiao, Y.; Hao, M.; Tang, X. microRNA-383 suppresses the PI3K-AKT-MTOR signaling pathway to inhibit development of cervical cancer via down-regulating PARP2. J. Cell Biochem. 2018, 119, 5243–5252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.D.; Hu, P.J.; Chao, Y.X.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, X.J.; Chen, B.Z.; Yu, X.Y.; Cai, Y. Nobiletin induces growth inhibition and apoptosis in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma C666-1 cells through regulating PARP-2/SIRT1/AMPK signaling pathway. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 7, 1104–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Gu, C.; Yao, X.; Guo, W.; Wang, H.; Lin, T.; Li, F.; Chen, D.; Wu, J.; Ye, G.; et al. CD73 promotes tumor metastasis by modulating RICS/RhoA signaling and EMT in gastric cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, R.; Chatterjee, J. ROS and oncogenesis with special reference to EMT and stemness. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2020, 99, 151073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, T.W. Dependence and Guidance Receptors-DCC and Neogenin-In Partial EMT and the Actions of Serine Proteases. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhao, X.; Zheng, X.; Zheng, Y.; Dong, X.; Zhao, N.; Liao, S.; Sun, B. The EMT transcription factor, Twist1, as a novel therapeutic target for pulmonary sarcomatoid carcinomas. Int. J. Oncol. 2020, 56, 750–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zheng, K.; Li, C.; Zhao, Y.; Li, H.; Liu, X.; Long, Y.; Yao, J. Nobiletin inhibits invasion via inhibiting AKT/GSK3β/β-catenin signaling pathway in Slug-expressing glioma cells. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 37, 2847–2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Han, Y.; Song, M.; Charoensinphon, N.; Zheng, J.; Qiu, P.; Wu, X.; Xiao, H. Inhibitory effects of nobiletin and its major metabolites on lung tumorigenesis. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 7444–7452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabeshima, K.; Inoue, T.; Shimao, Y.; Sameshima, T. Matrix metalloproteinases in tumor invasion: Role for cell migration. Pathol. Int. 2002, 52, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Wang, S.; Tian, S.; He, Y.; Lou, H.; Yang, Z.; Kong, Y.; Cao, X. Nobiletin inhibits breast cancer via p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase, nuclear transcription factor-kappaB, and nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 pathways in MCF-7 cells. Food Nutr. Res. 2018, 21, 62. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, N.; Wang, M.M.; Wang, Y.H.; Zhang, Z.N.; Cao, H.R.; Lv, Y.H.; Yang, Y.; Fan, P.H.; Qiu, F.; Gao, X.M. Tetrahydrocurcumin induces G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis involving p38 MAPK activation in human breast cancer cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 67, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubo, M.; Gotoh, K.; Eguchi, H.; Kobayashi, S.; Iwagami, Y.; Tomimaru, Y.; Akita, H.; Asaoka, T.; Noda, T.; Takeda, Y.; et al. Impact of CD36 on Chemoresistance in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2020, 27, 610–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Li, K.; Huang, X.; Zhao, C.; Mei, Y.; Li, X.; Jiao, L.; Yang, H. lncRNA SLC7A11-AS1 Promotes Chemoresistance by Blocking SCF(beta-TRCP)-Mediated Degradation of NRF2 in Pancreatic Cancer. Mol. Nucleic Acids 2020, 19, 974–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, M.; Cai, X.; Long, L.; Xie, L.; Ma, H.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, S.; Zeng, C. CD36 promotes the epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis in cervical cancer by interacting with TGF-beta. J. Transl. Med. 2019, 17, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurai, K.; Tomihara, K.; Yamazaki, M.; Heshiki, W.; Moniruzzaman, R.; Sekido, K.; Tachinami, H.; Ikeda, A.; Imaue, S.; Fujiwara, K.; et al. CD36 expression on oral squamous cell carcinoma cells correlates with enhanced proliferation and migratory activity. Oral Dis. 2019, 26, 745–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoumi-Dehghi, S.; Babashah, S.; Sadeghizadeh, M. microRNA-141-3p-containing small extracellular vesicles derived from epithelial ovarian cancer cells promote endothelial cell angiogenesis through activating the JAK/STAT3 and NF-kappaB signaling pathways. J. Cell Commun. Signal 2020. (In press) [CrossRef]
- Sp, N.; Kang, D.Y.; Kim, D.H.; Park, J.H.; Lee, H.G.; Kim, H.J.; Darvin, P.; Park, Y.-M.; Yang, Y.M. Nobiletin inhibits CD36-dependent tumor angiogenesis, migration, invasion, and sphere formation through the Cd36/Stat3/Nf-Κb signaling axis. Nutrients 2018, 10, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Androutsopoulos, V.P.; Tsatsakis, A.M. Benzo [a] pyrene sensitizes MCF7 breast cancer cells to induction of G1 arrest by the natural flavonoid eupatorin-5-methyl ether, via activation of cell signaling proteins and CYP1-mediated metabolism. Toxicol. Lett. 2014, 230, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surichan, S.; Androutsopoulos, V.P.; Sifakis, S.; Koutala, E.; Tsatsakis, A.; Arroo, R.R.; Boarder, M.R. Bioactivation of the citrus flavonoid nobiletin by CYP1 enzymes in MCF7 breast adenocarcinoma cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 3320–3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surichan, S.; Arroo, R.R.; Ruparelia, K.; Tsatsakis, A.M.; Androutsopoulos, V.P. Nobiletin bioactivation in MDA-MB-468 breast cancer cells by cytochrome P450 CYP1 enzymes. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 113, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, J.D.; Thompson, L.U. Mammalian lignans and genistein decrease the activities of aromatase and 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase in MCF-7 cells. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2005, 94, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, Y.H.; Doerge, D.R.; Woodling, K.A.; Hartman, J.A.; Kwak, J.; Helferich, W.G. Dietary genistein negates the inhibitory effect of letrozole on the growth of aromatase-expressing estrogen-dependent human breast cancer cells (MCF-7Ca) in vivo. Carcinogenesis 2008, 29, 2162–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, L.; Chan, F.L.; Chen, S.; Leung, L.K. The citrus flavonone hesperetin inhibits growth of aromatase-expressing MCF-7 tumor in ovariectomized athymic mice. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2012, 23, 1230–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Gho, W.M.; Chan, F.L.; Chen, S.; Leung, L.K. Dietary administration of the licorice flavonoid isoliquiritigenin deters the growth of MCF-7 cells overexpressing aromatase. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 124, 1028–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahideh, S.T.; Keramatipour, M.; Nourbakhsh, M.; Koohdani, F.; Hoseini, M.; Talebi, S.; Shidfar, F. Comparison of the effects of nobiletin and letrozole on the activity and expression of aromatase in the MCF-7 breast cancer cell line. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2017, 95, 468–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.H.; Lee, J.H.; Ko, J.H.; Jung, S.H.; Sethi, G.; Ahn, K.S. Brassinin Represses Invasive Potential of Lung Carcinoma Cells through Deactivation of PI3K/Akt/mTOR Signaling Cascade. Molecules 2019, 24, 1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Chinnathambi, A.; Alharbi, S.A.; Shair, O.H.M.; Sethi, G.; Ahn, K.S. Farnesol abrogates epithelial to mesenchymal transition process through regulating Akt/mTOR pathway. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 150, 104504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, C.Y.; Chai, J.Y.; Tang, T.F.; Wong, W.F.; Sethi, G.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Chong, P.P.; Looi, C.Y. The E-Cadherin and N-Cadherin Switch in Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition: Signaling, Therapeutic Implications, and Challenges. Cells 2019, 8, 1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.T.; Wang, L.; Wang, H.; Tang, F.R.; Cai, W.Q.; Sethi, G.; Xin, H.W.; Ma, Z. Insights into Biological Role of LncRNAs in Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. Cells 2019, 8, 1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, X.; Ahn, K.S.; Wang, L.Z.; Kim, C.; Deivasigamni, A.; Arfuso, F.; Um, J.-Y.; Kumar, A.P.; Chang, Y.-C.; Kumar, D. Ascochlorin enhances the sensitivity of doxorubicin leading to the reversal of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2016, 15, 2966–2976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, H. Geraniin inhibits TGF-beta1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and suppresses A549 lung cancer migration, invasion and anoikis resistance. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 3529–3534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhan, Y.; Liu, K.; Wang, R. Nobiletin inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition of human non-small cell lung cancer cells by antagonizing the TGF-beta1/Smad3 signaling pathway. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 35, 2767–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Huang, C.; Hu, G.; Ma, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, J.; Huang, Y.; Zheng, J.; Xue, W.; Xu, Y.; et al. Tumor-educated B cells promote renal cancer metastasis via inducing the IL-1beta/HIF-2alpha/Notch1 signals. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, N.N.; Jiao, J.; Meng, X.; An, Y.; Han, C.; Huang, S. Abnormal overexpression of G9a in melanoma cells promotes cancer progression via upregulation of the Notch1 signaling pathway. Aging 2020, 12, 2393–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.J.; Liu, J.W.; Zhang, Q.G.; Zhang, J.J.; Xu, H.T.; Liu, H.J. Nobiletin inhibited hypoxia-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition of lung cancer cells by inactivating of Notch-1 signaling and switching on miR-200b. Pharmazie 2015, 70, 256–262. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Guan, B.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Z.; He, S.; Zhan, Y.; Su, B.; Han, H.; Zhang, X.; Wang, B.; et al. MicroRNA-200b is downregulated and suppresses metastasis by targeting LAMA4 in renal cell carcinoma. EBioMedicine 2019, 44, 439–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Chen, S.; Huang, Y.; Xu, S.; Song, H.; Zhang, W.; Sun, N. LINC00667 promotes Wilms’ tumor metastasis and stemness by sponging miR-200b/c/429 family to regulate IKK-beta. Cell Biol. Int. 2020. (In press) [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.D.; Lai, T.Y.; Chien, C.T.; Yu, H.J. Activating Nrf-2 signaling depresses unilateral ureteral obstruction-evoked mitochondrial stress-related autophagy, apoptosis and pyroptosis in kidney. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, 47299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, S.J.F.; Marchi, S.; Petroni, G.; Kroemer, G.; Galluzzi, L.; Pervaiz, S. Noncanonical Cell Fate Regulation by Bcl-2 Proteins. Trends Cell Biol. 2020. (In press) [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazari, Y.; Bravo-San Pedro, J.M.; Hetz, C.; Galluzzi, L.; Kroemer, G. Autophagy in hepatic adaptation to stress. J. Hepatol. 2020, 72, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buqué, A.; Rodriguez-Ruiz, M.E.; Fucikova, J.; Galluzzi, L. Apoptotic caspases cut down the immunogenicity of radiation. OncoImmunology 2019, 8, e1655364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yin, B.; Li, D.; Wang, G.; Han, X.; Sun, X. GSDME mediates caspase-3-dependent pyroptosis in gastric cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 495, 1418–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Chen, J.; Mao, L.; Guo, Y.; Hao, Y.; Deng, Y.; Han, X.; Li, Q.; Liao, W.; Yuan, M. Nobiletin Triggers Reactive Oxygen Species-Mediated Pyroptosis through Regulating Autophagy in Ovarian Cancer Cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 1326–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, C.Y. LncRNA SNHG7 enhances chemoresistance in neuroblastoma through cisplatin-induced autophagy by regulating miR-329-3p/MYO10 axis. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 3805–3817. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.; Ren, H.; Li, J.; Hao, M.; Hao, J.; Ren, H.; Guo, L.; Liu, R. TIPE2 suppressed cisplatin resistance by inducing autophagy via mTOR signalling pathway. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2020, 113, 104367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, P.; Xu, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, D.; Peng, P.; Zheng, C.; Meng, Q.J.; Yang, L.; Luo, Z. Knockdown of cytokeratin 8 overcomes chemoresistance of chordoma cells by aggravating endoplasmic reticulum stress through PERK/eIF2alpha arm of unfolded protein response and blocking autophagy. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Chen, E.; Tang, Y.; Mao, J.; Shen, J.; Zheng, X.; Xie, S.; Zhang, S.; Wu, Y.; Liu, H.; et al. miR-223 overexpression inhibits doxorubicin-induced autophagy by targeting FOXO3a and reverses chemoresistance in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Qi, W.; Liu, S.; Sun, L.; Ding, A.; Yu, G.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Qiu, W.; Lv, J. TSPAN9 suppresses the chemosensitivity of gastric cancer to 5-fluorouracil by promoting autophagy. Cancer Cell Int. 2020, 20, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Q.; Jing, F.J.; Xu, W.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Sun, J.L.; Xing, X.M.; Zhou, C.K.; Jing, F.B. Ubenimex induces autophagy inhibition and EMT suppression to overcome cisplatin resistance in GC cells by perturbing the CD13/EMP3/PI3K/AKT/NF-kappaB axis. Aging 2019, 12, 80–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, H.; Li, T.; Qiu, W.; Zhu, Z. Claudin-1 silencing increases sensitivity of liver cancer HepG2 cells to 5-fluorouracil by inhibiting autophagy. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 18, 5709–5716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.-P.; Guo, H.; Wang, X.-B. Nobiletin (NOB) suppresses autophagic degradation via over-expressing AKT pathway and enhances apoptosis in multidrug-resistant SKOV3/TAX ovarian cancer cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 103, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeda, K.; Kaisho, T.; Akira, S. Toll-like receptors. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 21, 335–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, F.; Zhang, D. Toll-like receptors and prostate cancer. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, L.A.; Bowie, A.G. The family of five: TIR-domain-containing adaptors in Toll-like receptor signalling. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 7, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deveci Ozkan, A. Anti-inflammatory effects of nobiletin on TLR4/TRIF/IRF3 and TLR9/IRF7 signaling pathways in prostate cancer cells. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2020, 42, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denicourt, C.; Dowdy, S.F. Targeting apoptotic pathways in cancer cells. Science 2004, 305, 1411–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.-T.; Chang, J.T.-C.; Wang, H.-M.; Ng, S.-H.; Hsueh, C.; Lee, L.-Y.; Lin, C.-H.; Chen, I.-H.; Huang, S.-F.; Cheng, A.-J. Analysis of risk factors of predictive local tumor control in oral cavity cancer. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2008, 15, 915–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarante-Mendes, G.P.; Naekyung Kim, C.; Liu, L.; Huang, Y.; Perkins, C.L.; Green, D.R.; Bhalla, K. Bcr-Abl exerts its antiapoptotic effect against diverse apoptotic stimuli through blockage of mitochondrial release of cytochrome C and activation of caspase-3. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 1998, 91, 1700–1705. [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson, D.W.; Thornberry, N.A. Life and death decisions. Science 2003, 299, 214–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- RV, E.H.; Bredesen, D. Coupling endoplasmic reticulum stress to the cell death program. Cell Death Differ. 2004, 11, 372380Rodrgue. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Huang, J.; Yu, C.; Xiang, L.; Li, L.; Shi, D.; Lin, F. Quercetin Enhanced Paclitaxel Therapeutic Effects Towards PC-3 Prostate Cancer Through ER Stress Induction and ROS Production. Onco. Targets 2020, 13, 513–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeyashiki, C.; Melhem, H.; Hering, L.; Baebler, K.; Cosin-Roger, J.; Schefer, F.; Weder, B.; Hausmann, M.; Scharl, M.; Rogler, G.; et al. Activation of pH-Sensing Receptor OGR1 (GPR68) Induces ER Stress Via the IRE1alpha/JNK Pathway in an Intestinal Epithelial Cell Model. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Tian, J. FNDC3B is associated with ER stress and poor prognosis in cervical cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 19, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, G.; Xu, Z.; Chen, X.; Pan, H.; Wang, Y.; Jin, B. CDCA5 functions as a tumor promoter in bladder cancer by dysregulating mitochondria-mediated apoptosis, cell cycle regulation and PI3k/AKT/mTOR pathway activation. J. Cancer 2020, 11, 2408–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goan, Y.G.; Wu, W.T.; Liu, C.I.; Neoh, C.A.; Wu, Y.J. Involvement of Mitochondrial Dysfunction, Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress, and the PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathway in Nobiletin-Induced Apoptosis of Human Bladder Cancer Cells. Molecules 2019, 24, 2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Cho, S.K.; Kapoor, S.; Kumar, A.; Vali, S.; Abbasi, T.; Kim, S.H.; Sethi, G.; Ahn, K.S. beta-Caryophyllene oxide inhibits constitutive and inducible STAT3 signaling pathway through induction of the SHP-1 protein tyrosine phosphatase. Mol. Carcinog. 2014, 53, 793–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, C.D.; Bharathkumar, H.; Bulusu, K.C.; Pandey, V.; Rangappa, S.; Fuchs, J.E.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Dai, X.; Li, F.; Deivasigamani, A.; et al. Development of a novel azaspirane that targets the Janus kinase-signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma in vitro and in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 34296–34307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, A.L.A.; Hirpara, J.L.; Pervaiz, S.; Eu, J.Q.; Sethi, G.; Goh, B.C. Do STAT3 inhibitors have potential in the future for cancer therapy? Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2017, 26, 883–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.; Hirpara, J.L.; Eu, J.Q.; Sethi, G.; Wang, L.; Goh, B.C.; Wong, A.L. Targeting STAT3 and oxidative phosphorylation in oncogene-addicted tumors. Redox Biol. 2019, 25, 101073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, Y.J.; Lin, Y.M.; Huang, Y.C.; Shi, B.; Yeh, K.T.; Gong, Z.; Lu, J.W. Prognostic significance of high YY1AP1 and PCNA expression in colon adenocarcinoma. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 494, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, S. STAT3-induced upregulation of circCCDC66 facilitates the progression of non-small cell lung cancer by targeting miR-33a-5p/KPNA4 axis. Biomed. Pharm. 2020, 126, 110019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, H.; Zhang, X.; Su, Y.; Jia, C.; Dai, C. GNAS promotes inflammation-related hepatocellular carcinoma progression by promoting STAT3 activation. Cell Mol. Biol. Lett. 2020, 25, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.; Zhang, G.; Zhu, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Yan, F.; Pan, C.; Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Wang, F.; Meng, P.; et al. Nobiletin Inhibits Cell Viability via the SRC/AKT/STAT3/YY1AP1 Pathway in Human Renal Carcinoma Cells. Front. Pharm. 2019, 10, 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melendez-Rodriguez, F.; Roche, O.; Sanchez-Prieto, R.; Aragones, J. Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 2-Dependent Pathways Driving Von Hippel-Lindau-Deficient Renal Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, C.M.; Poon, B.P.K.; Kano, Y.; Pluthero, F.G.; Kahr, W.H.A.; Ohh, M. A Hypoxia-Inducible HIF1-GAL3ST1-Sulfatide Axis Enhances ccRCC Immune Evasion via Increased Tumor Cell-Platelet Binding. Mol. Cancer Res. 2019, 17, 2306–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimoto, S.; Tanaka, F.; Morita, H.; Hiraki, A.; Hashimoto, S. Hypoxia-induced HIF-1alpha and ZEB1 are critical for the malignant transformation of ameloblastoma via TGF-beta-dependent EMT. Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 7822–7832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Xiong, W.; Zhou, R.; Song, N.; Liu, L.; Qian, J. Dexmedetomidine protects H9C2 against hypoxia/reoxygenation injury through miR-208b-3p/Med13/Wnt signaling pathway axis. Biomed. Pharm. 2020, 125, 110001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Anazi, A.; Parhar, R.; Saleh, S.; Al-Hijailan, R.; Inglis, A.; Al-Jufan, M.; Bazzi, M.; Hashmi, S.; Conca, W.; Collison, K.; et al. Data on hypoxia-induced VEGF, leptin and NF-kB p65 expression. Data Brief 2018, 21, 2395–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asgarova, A.; Asgarov, K.; Godet, Y.; Peixoto, P.; Nadaradjane, A.; Boyer-Guittaut, M.; Galaine, J.; Guenat, D.; Mougey, V.; Perrard, J.; et al. PD-L1 expression is regulated by both DNA methylation and NF-kB during EMT signaling in non-small cell lung carcinoma. Oncoimmunology 2018, 7, e1423170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, L.; Zhai, R.; Chen, T.; Gao, C.; Xue, R.; Wang, N.; Wang, J.; Xu, Y.; Gui, D. Panax Notoginseng Ameliorates Podocyte EMT by Targeting the Wnt/beta-Catenin Signaling Pathway in STZ-Induced Diabetic Rats. Drug Des. Devel. 2020, 14, 527–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Zhang, S.; Yin, M.; Guo, L.; Xu, M.; Wang, Y. Nobiletin inhibits hypoxia-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in renal cell carcinoma cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 2039–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics 2017. Ca Cancer J. Clin. 2017, 67, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernstein, C.N.; Blanchard, J.F.; Kliewer, E.; Wajda, A. Cancer risk in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: A population-based study. Cancer 2001, 91, 854–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, D.C.; Shaker, A.; Levin, M.S. Chronic intestinal inflammation: Inflammatory bowel disease and colitis-associated colon cancer. Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, J.X.H.; Tan, L.T.; Goh, J.K.; Chan, K.G.; Pusparajah, P.; Lee, L.H.; Goh, B.H. Nobiletin and Derivatives: Functional Compounds from Citrus Fruit Peel for Colon Cancer Chemoprevention. Cancers 2019, 11, 867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Song, M.; Qiu, P.; Li, F.; Wang, M.; Zheng, J.; Wang, Q.; Xu, F.; Xiao, H. A metabolite of nobiletin, 4′-demethylnobiletin and atorvastatin synergistically inhibits human colon cancer cell growth by inducing G0/G1 cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Song, M.; Qiu, P.; Rakariyatham, K.; Li, F.; Gao, Z.; Cai, X.; Wang, M.; Xu, F.; Zheng, J.; et al. Synergistic chemopreventive effects of nobiletin and atorvastatin on colon carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis 2017, 38, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neurath, M.F. Cytokines in inflammatory bowel disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 329–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, M.; Liu, B.; Song, H.; Yu, R.; Zou, D.; Chen, Y.; Ma, Y.; Lv, F.; Xu, L.; Zhang, Z.; et al. beta-Elemene inhibits the metastasis of multidrug-resistant gastric cancer cells through miR-1323/Cbl-b/EGFR pathway. Phytomedicine 2020, 69, 153184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Guo, H.; Zhu, L.; Xu, L.; Pei, Q.; Cao, Y. LINC00152 Knock-down Suppresses Esophageal Cancer by EGFR Signaling Pathway. Open Med. 2020, 15, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Q.; Peng, X.; Zhang, Y. Cytotoxicity of amide-linked local anesthetics on melanoma cells via inhibition of Ras and RhoA signaling independent of sodium channel blockade. BMC Anesth. 2020, 20, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Hong, D.; Lou, Z.; Tu, X.; Jin, L. Lupeol inhibits migration and invasion of colorectal cancer cells by suppressing RhoA-ROCK1 signaling pathway. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2020. (In press) [CrossRef]
- Shan, C.; Hui, W.; Li, H.; Wang, Z.; Guo, C.; Peng, R.; Gu, J.; Chen, Y.; Ouyang, Q. Discovery of Novel Autophagy Inhibitors and Their Sensitization Abilities for Vincristine-Resistant Esophageal Cancer Cell Line Eca109/VCR. ChemMedChem 2020. (In press) [CrossRef]
- Moon, J.Y.; Cho, S.K. Nobiletin Induces Protective Autophagy Accompanied by ER-Stress Mediated Apoptosis in Human Gastric Cancer SNU-16 Cells. Molecules 2016, 21, 914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.H.; Lin, Y.T.; Liang, C.M.; Liang, S.M. A novel c-Kit/phospho-prohibitin axis enhances ovarian cancer stemness and chemoresistance via Notch3-PBX1 and beta-catenin-ABCG2 signaling. J. Biomed. Sci. 2020, 27, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, M.; Nagata, Y.; Kanojia, D.; Mayakonda, A.; Yoshida, K.; Haridas Keloth, S.; Zang, Z.J.; Okuno, Y.; Shiraishi, Y.; Chiba, K.; et al. Profiling of somatic mutations in acute myeloid leukemia with FLT3-ITD at diagnosis and relapse. Blood 2015, 126, 2491–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, M.K.; Mashima, T.; Seimiya, H. Tankyrase Inhibitors Target Colorectal Cancer Stem Cells via AXIN-Dependent Downregulation of c-KIT Tyrosine Kinase. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 765–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, M.; Ou, R.; Zhang, Q.; Lin, F.; Li, X.; Wang, K.; Xu, Y. MicroRNA-664 suppresses the growth of cervical cancer cells via targeting c-Kit. Drug Des. Devel. 2019, 13, 2371–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.-Y.; Chen, Y.-T.; Gao, W.-Y.; Wu, M.-J.; Yen, J.-H. Nobiletin Down-Regulates c-KIT Gene Expression and Exerts Antileukemic Effects on Human Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 13423–13434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leone, P.; Buonavoglia, A.; Fasano, R.; Solimando, A.G.; De Re, V.; Cicco, S.; Vacca, A.; Racanelli, V. Insights into the Regulation of Tumor Angiogenesis by Micro-RNAs. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cui, J.; Si, T. Endostar blocks the metastasis, invasion and angiogenesis of ovarian cancer cells. Neoplasma 2020. (In press) [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danielsen, T.; Rofstad, E.K. VEGF, bFGF and EGF in the angiogenesis of human melanoma xenografts. Int. J. Cancer 1998, 76, 836–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieg, D.J.; Hauck, C.R.; Ilic, D.; Klingbeil, C.K.; Schaefer, E.; Damsky, C.H.; Schlaepfer, D.D. FAK integrates growth-factor and integrin signals to promote cell migration. Nat. Cell Biol. 2000, 2, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roskoski, R., Jr. Src protein-tyrosine kinase structure and regulation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 324, 1155–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, G.; Wright, K.L.; Huang, M.; Song, L.; Haura, E.; Turkson, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, T.; Sinibaldi, D.; Coppola, D.; et al. Constitutive Stat3 activity up-regulates VEGF expression and tumor angiogenesis. Oncogene 2002, 21, 2000–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Han, Z.C. STAT3: A critical transcription activator in angiogenesis. Med. Res. Rev. 2008, 28, 185–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ahn, K.S.; Kim, C.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Siveen, K.S.; Arfuso, F.; Samym, R.P.; Deivasigamanim, A.; Lim, L.H.; Wang, L.; et al. Nimbolide-Induced Oxidative Stress Abrogates STAT3 Signaling Cascade and Inhibits Tumor Growth in Transgenic Adenocarcinoma of Mouse Prostate Model. Antioxid. Redox. Signal 2016, 24, 575–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, C.; Sethi, G.; Ahn, K.S. Brassinin inhibits STAT3 signaling pathway through modulation of PIAS-3 and SOCS-3 expression and sensitizes human lung cancer xenograft in nude mice to paclitaxel. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 6386–6405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Chiang, S.Y.; Nam, D.; Chung, W.S.; Lee, J.; Na, Y.S.; Sethi, G.; Ahn, K.S. Capillarisin inhibits constitutive and inducible STAT3 activation through induction of SHP-1 and SHP-2 tyrosine phosphatases. Cancer Lett. 2014, 345, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Chen, L.; Chatterjee, S.; Basha, J.; Kumar, A.P.; Kundu, T.K.; Sethi, G. Garcinol, a polyisoprenylated benzophenone modulates multiple proinflammatory signaling cascades leading to the suppression of growth and survival of head and neck carcinoma. Cancer Prev. Res. 2013, 6, 843–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sp, N.; Kang, D.Y.; Joung, Y.H.; Park, J.H.; Kim, W.S.; Lee, H.K.; Song, K.D.; Park, Y.M.; Yang, Y.M. Nobiletin Inhibits Angiogenesis by Regulating Src/FAK/STAT3-Mediated Signaling through PXN in ER(+) Breast Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, S.H.; Kim, S.M.; Nam, D.; Lee, J.H.; Ahn, K.S.; Choi, S.H.; Kim, S.H.; Shim, B.S.; Chang, I.M.; Ahn, K.S. Antimetastatic effect of nobiletin through the down-regulation of CXC chemokine receptor type 4 and matrix metallopeptidase-9. Pharm. Biol. 2012, 50, 1210–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morley, K.L.; Ferguson, P.J.; Koropatnick, J. Tangeretin and nobiletin induce G1 cell cycle arrest but not apoptosis in human breast and colon cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2007, 251, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Ono, M.; Takeshima, M.; Nakano, S. Antiproliferative and apoptosis-inducing activity of nobiletin against three subtypes of human breast cancer cell lines. Anticancer Res. 2014, 34, 1785–1792. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.; Jin, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wan, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, L. Inhibitory effects of nobiletin on hepatocellular carcinoma in vitro and in vivo. Phytother. Res. PTR 2014, 28, 560–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.D.; Liao, Y.C.; Shih, Y.W.; Tsai, L.Y. Nobiletin attenuates metastasis via both ERK and PI3K/Akt pathways in HGF-treated liver cancer HepG2 cells. Phytomedicine 2013, 20, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemoto, K.; Ikeda, A.; Yoshida, C.; Kimura, J.; Mori, J.; Fujiwara, H.; Yokosuka, A.; Mimaki, Y.; Ohizumi, Y.; Degawa, M. Characteristics of nobiletin-mediated alteration of gene expression in cultured cell lines. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 431, 530–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimizu, N.; Otani, Y.; Saikawa, Y.; Kubota, T.; Yoshida, M.; Furukawa, T.; Kumai, K.; Kameyama, K.; Fujii, M.; Yano, M.; et al. Anti-tumour effects of nobiletin, a citrus flavonoid, on gastric cancer include: Antiproliferative effects, induction of apoptosis and cell cycle deregulation. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2004, 20, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, J.Y.; Cho, M.; Ahn, K.S.; Cho, S.K. Nobiletin induces apoptosis and potentiates the effects of the anticancer drug 5-fluorouracil in p53-mutated SNU-16 human gastric cancer cells. Nutr. Cancer 2013, 65, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.C.; Cheng, T.H.; Lee, J.S.; Chen, J.H.; Liao, Y.C.; Fong, Y.; Wu, C.H.; Shih, Y.W. Nobiletin, a citrus flavonoid, suppresses invasion and migration involving FAK/PI3K/Akt and small GTPase signals in human gastric adenocarcinoma AGS cells. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2011, 347, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lien, L.M.; Wang, M.J.; Chen, R.J.; Chiu, H.C.; Wu, J.L.; Shen, M.Y.; Chou, D.S.; Sheu, J.R.; Lin, K.H.; Lu, W.J. Nobiletin, a polymethoxylated flavone, inhibits glioma cell growth and migration via arresting cell cycle and suppressing MAPK and Akt pathways. Phytother. Res. 2016, 30, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uesato, S.; Yamashita, H.; Maeda, R.; Hirata, Y.; Yamamoto, M.; Matsue, S.; Nagaoka, Y.; Shibano, M.; Taniguchi, M.; Baba, K.; et al. Synergistic antitumor effect of a combination of paclitaxel and carboplatin with nobiletin from Citrus depressa on non-small-cell lung cancer cell lines. Planta Med. 2014, 80, 452–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, S.Y.; Hsieh, M.J.; Chen, C.J.; Yang, S.F.; Chen, M.K. Nobiletin inhibits invasion and migration of human nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell lines by involving ERK1/2 and transcriptional inhibition of MMP-2. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2015, 19, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chen, A.Y.; Huang, H.; Ye, X.; Rollyson, W.D.; Perry, H.E.; Brown, K.C.; Rojanasakul, Y.; Rankin, G.O.; Dasgupta, P.; et al. The flavonoid nobiletin inhibits tumor growth and angiogenesis of ovarian cancers via the Akt pathway. Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 46, 2629–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Creed, A.; Chen, A.Y.; Huang, H.; Li, Z.; Rankin, G.O.; Ye, X.; Xu, G.; Chen, Y.C. Nobiletin suppresses cell viability through AKT pathways in PC-3 and DU-145 prostate cancer cells. BMC Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2014, 15, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, S.Y.; Hsieh, M.J.; Chen, C.J.; Yang, S.F.; Chen, M.K. A citrus polymethoxyflavonoid, nobiletin, is a novel MEK inhibitor that exhibits antitumor metastasis in human fibrosarcoma HT-1080 cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 366, 168–173. [Google Scholar]
- Miyata, Y.; Sato, T.; Yano, M.; Ito, A. Activation of protein kinase C βII/ε-c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase pathway and inhibition of mitogen-activated protein/extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 phosphorylation in antitumor invasive activity induced by the polymethoxy flavonoid, nobiletin. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2004, 3, 839–847. [Google Scholar]
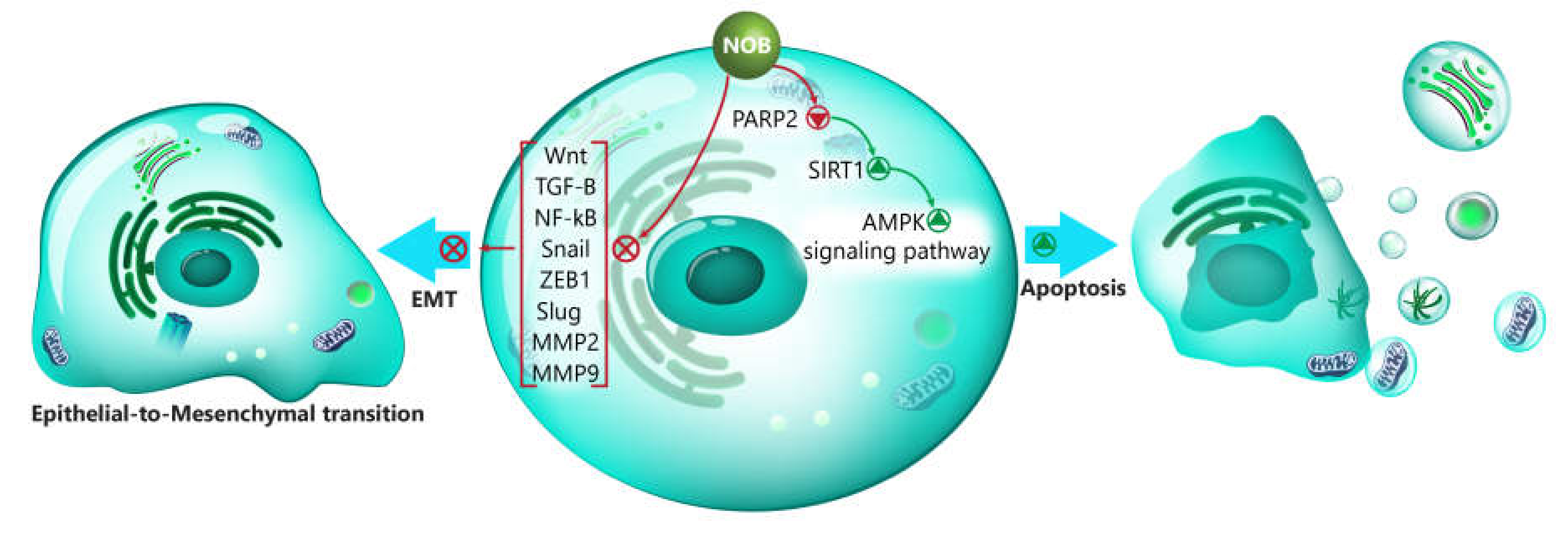
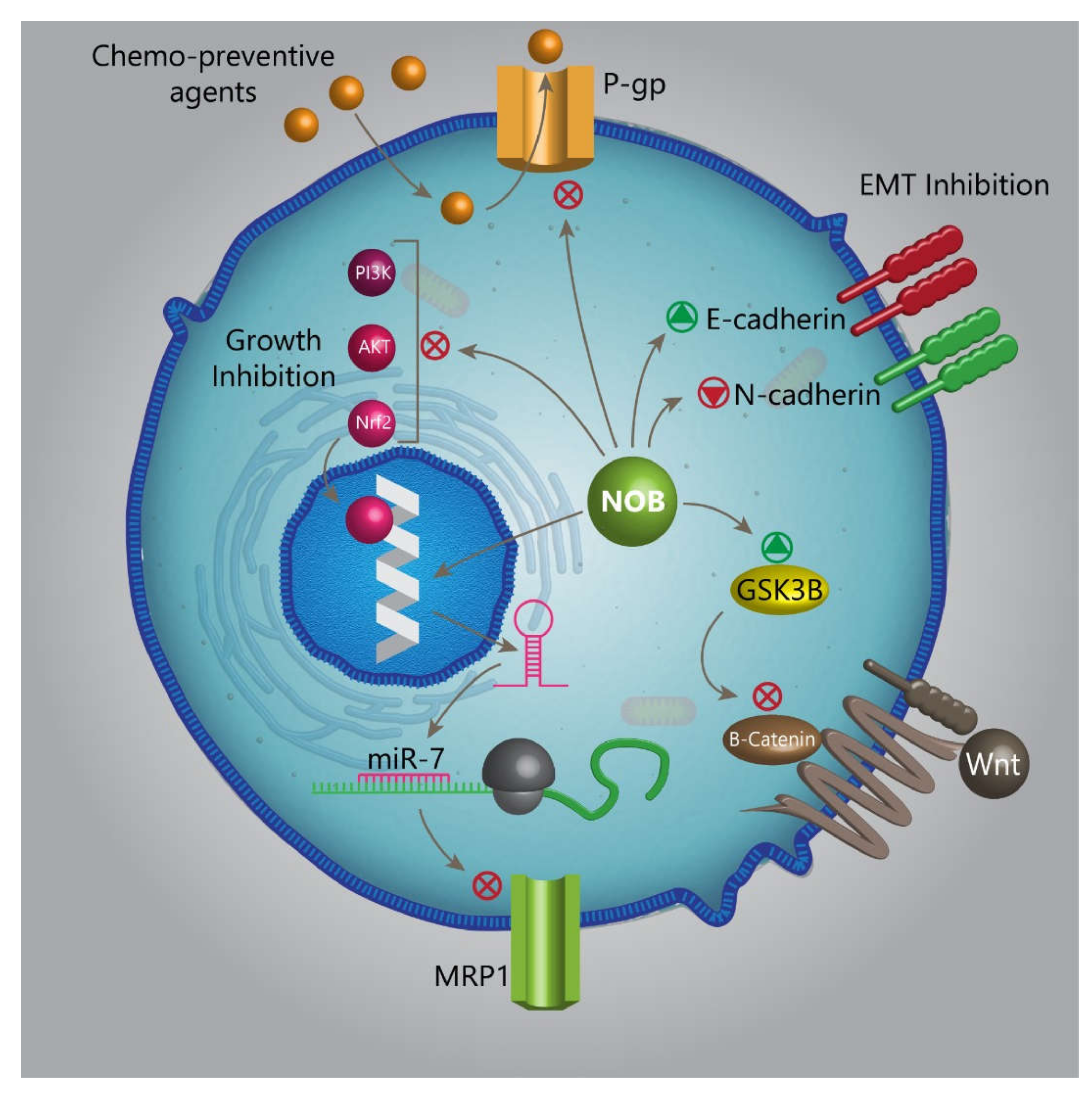
| Disease/Protective Effect | In Vitro/In Vivo | Dose | Duration of Experiment | Administration Route | Results | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cardioprotective | In vivo (rat) | 15 mg/kg | Before coronary microembolization | Tail vein | Downregulation of apoptosis and protecting against myocardial injury by induction of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. | [82] |
| Cardioprotective | In vitro (human aortic valves) | 10, 20, and 50 μM | 24 and 48 h | - | By activation of ABCG2 and AKR1B1, NOB suppresses tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-mediated calcification of the human aortic valve. | [83] |
| Cardioprotective | In vitro (H9c2 cardiomyocytes) | 12.5, 25, 50, and 100 μM | 24 h | - | Reducing apoptosis and oxidative stress after ischemic/reperfusion (I/R) injury via the stimulation of Akt/GSK-3β. | [84] |
| Neuroprotective | In vivo (mice) | 100 mg/kg/day | 6 weeks | Oral gavage | Decreasing the levels of anti-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and interleukin (IL)-1β by downregulation of the NF-κB signaling pathway and, also, inhibition of microglial activation. | [85] |
| Osteoarthritis | In vitro (primary human chondrocytes) In vivo (mice model of osteoarthritis) | 20, 40, and 80 μM 20 mg/kg | 2 h 8 weeks | Gavage | Alleviation of osteoarthritis by downregulation of PI3K/Akt/NF-κB pathway and reducing inflammatory factors. | [86] |
| Antihypertensive | In vivo (rat) | 20 and 40 mg/kg | 2 weeks | - | Attenuation of vascular changes, induction of antihypertensive effect, inhibition of matrix metalloproteinases (MMP)-2 and -9, and reducing oxidative stress through Nrf2 activation. | [87] |
| Anti-inflammation | In vitro (human mesangial cells) | 5, 10, 20, and 30 μM | 24 h | - | By inhibition of STAT3, NOB downregulates the expression of NF-κB to decrease the levels of TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β. | [88] |
| Anti-inflammation | In vitro (macrophages) | 0, 10, 20, 40, and 80 μM | 24 h | - | NOB enhances the expression of miR-590 to decrease the levels of proinflammatory cytokines. | [89] |
| I/R injury | In vivo (mice) | 5 mg/kg | At the start of reperfusion | Intraperitoneal | Alleviation of hepatic I/R injury by stimulation of autophagy and mitochondrial biogenesis via the SIRT1/FOXO3a axis. | [90] |
| Cancer Type | Cell Line | In Vitro/In Vivo | Dose | Duration of Experiment | Administration Route | Results | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Breast cancer | Human breast carcinoma MDA-MB-231 cells | In vitro | 0, 10, 30, and 50 μM | 24 h | - | Significantly decreasing the expressions of genes related to the malignant behavior of cancer cells such as CXCR4, MMP-9, NF-κB, and MAPK. | [247] |
| Breast cancer Colon cancer | MDA-MB-435, MCF-7 (human ductal breast carcinoma and adenocarcinoma, respectively), and HT-29 (human colorectal adenocarcinoma) cell lines | In vitro | 0, 50, 100, 150, and 200 μM | 12, 24, 48, 72, and 96 h | - | Induction of the G1 cell cycle arrest not apoptosis in cancer cells. | [248] |
| Breast cancer | MCF7 cells | In vitro | 0, 1, 5, and 10 μM | 0, 3, 6, 9, and 24 h | - | The CYP1A1 induces the bioactivation of NOB in breast cancer cells, resulting in cell cycle arrest at the G1 phase. | [154] |
| Breast cancer | Three subtypes of breast cancer cell lines, including hormone receptor (ER/PR)-positive MCF-7, hormone receptor-negative but HER2-positive SK-BR-3, and triple-negative MDA-MB-468 | In vitro | 100 μM | 0, 2, 6, 12, and 24 h | - | The stimulation of apoptosis and cell cycle arrest via the downregulation of Bcl-XL, ERK1/2, cyclin D1, Akt, and mTOR and upregulation of p21 and Bax. | [249] |
| Hepatocellular carcinoma | SMMC-7721 cells | In vitro In vivo | 2-128 mg/L 125, 250, and 500 mg/kg | 48 h 11 days | Intragastric gavage | Stimulation of the G2 cell cycle arrest, downregulation of Bcl-2 and COX-2, upregulation of Bax and caspase-3, and triggering apoptosis. | [250] |
| Liver cancer | HepG2 cells | In vitro | 0.5, 1, and 2.5 μM | 12 h | - | Suppressing the invasion and migration of cancer cells via the downregulation of ERK and the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. | [251] |
| Hepatocellular carcinoma Neuroblastoma cells | HuH-7 human hepatocarcinoma cells and SK-N-SH human neuroblastoma cells | In vitro | 100 μM | 24 h | - | Increasing the levels of genes related to the endoplasmic reticulum, such as CHOP, Ddit3, Trib3, and Asns, and decreasing the levels of genes related to cell cyclins, such as Ccna2, Ccne2, and E2f8. | [252] |
| Gastric cancer | Four human gastric cancer cell lines, including TMK-1, MKN-74, KATO-III, and MKN-45 | In vitro | 0, 50, 100, 150, 200, and 250 μM | 24 h | - | Induction of apoptosis and the cell cycle arrest and enhancing the chemotherapy efficacy of cisplatin. | [253] |
| Gastric cancer | AGS, MKN-45, SNU-1, and SNU-16 cells | In vitro | 0, 12.5, 25, 50, 100, and 200 μM | 48 h | - | Stimulation of the G1 cell cycle arrest and apoptosis via enhancing the levels of the Bax/Bcl-2 ratio, caspase-3, caspase-9, and PARP. | [254] |
| Gastric carcinoma | Human AGS gastric adenocarcinoma cell line | In vitro | 0, 1, 1.5, and 2 μM | 24 and 48 h | - | Stimulation of a diminution in the invasion and migration of gastric cancer cells via the inhibition of a small GTPase signal and FAK/PI3K/Akt. | [255] |
| Glioma | Human U87 and Hs683 glioma cell lines | In vitro | 20, 50, and 100 μM | 24 and 48 h | - | Suppressing the migration, invasion, and proliferation of cancer cells by induction of the cell cycle arrest (downregulation of cyclin D1 and cyclin-dependent kinase-2) and inhibition of the MAPK and Akt signaling pathways. | [256] |
| Lung cancer | A549 and H460 cell lines | In vitro In vivo | 20, 40, and 80 μM 600 μg | 24 h 30 days | Intraperitoneal | Induction of the G1 cell cycle arrest and subsequent sensitivity of cancer cells to paclitaxel and carboplatin. | [257] |
| Nasopharyngeal carcinoma | HONE-1 and NPC-BM, human NPC cells lines | In vitro | 0, 10, 20, and 40 μM | 12 and 24 h | - | Reducing the expression of MMP-2 and suppressing the phosphorylation of ERK1/2 mediate the antitumor activity of NOB against cancer cells. | [258] |
| Ovarian cancer | Human ovarian cancer cell lines, OVCAR-3 and A2780/CP70 | In vitro | 0, 5, 10, 20, 40, 80, and 160 μM | 16 h | - | Simultaneously reducing the levels of HIF-1α, Akt, and NF-κB, leading to the downregulation of VEGF and the subsequent inhibition of angiogenesis. | [259] |
| Prostate cancer | PC-3 cells | In vitro | 0, 5, 10, 20, 40, 80, and 160 μM | 24 h | - | The downregulation of Akt by NOB impairs the proliferation and growth of cancer cells. By the inhibition of Akt, the expression of HIF-1α as a downstream target undergoes a decrease. | [260] |
| Fibrosarcoma | Human fibrosarcoma HT-1080 cells | In vitro | 16, 34, and 64 μM | 24 h | - | Inhibiting the metastasis and migration of cancer cells through the downregulation of MEK. | [261] |
| Fibrosarcoma | Human fibrosarcoma HT-1080 cells | In vitro | 64 μmol/L | 12 h | - | Reducing the expression of pro-MMPs and enhancing the expression of the tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 1. Suppressing the activity of MEK1/2 and inducting the phosphorylation of JNK. | [262] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ashrafizadeh, M.; Zarrabi, A.; Saberifar, S.; Hashemi, F.; Hushmandi, K.; Hashemi, F.; Moghadam, E.R.; Mohammadinejad, R.; Najafi, M.; Garg, M. Nobiletin in Cancer Therapy: How This Plant Derived-Natural Compound Targets Various Oncogene and Onco-Suppressor Pathways. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 110. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8050110
Ashrafizadeh M, Zarrabi A, Saberifar S, Hashemi F, Hushmandi K, Hashemi F, Moghadam ER, Mohammadinejad R, Najafi M, Garg M. Nobiletin in Cancer Therapy: How This Plant Derived-Natural Compound Targets Various Oncogene and Onco-Suppressor Pathways. Biomedicines. 2020; 8(5):110. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8050110
Chicago/Turabian StyleAshrafizadeh, Milad, Ali Zarrabi, Sedigheh Saberifar, Farid Hashemi, Kiavash Hushmandi, Fardin Hashemi, Ebrahim Rahmani Moghadam, Reza Mohammadinejad, Masoud Najafi, and Manoj Garg. 2020. "Nobiletin in Cancer Therapy: How This Plant Derived-Natural Compound Targets Various Oncogene and Onco-Suppressor Pathways" Biomedicines 8, no. 5: 110. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8050110
APA StyleAshrafizadeh, M., Zarrabi, A., Saberifar, S., Hashemi, F., Hushmandi, K., Hashemi, F., Moghadam, E. R., Mohammadinejad, R., Najafi, M., & Garg, M. (2020). Nobiletin in Cancer Therapy: How This Plant Derived-Natural Compound Targets Various Oncogene and Onco-Suppressor Pathways. Biomedicines, 8(5), 110. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8050110






