Does Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw Influence the Quality of Life of Cancer Patients?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ruggiero, S.L.; Dodson, T.B.; Assael, L.A.; Landesberg, R.; Marx, R.E.; Mehrotra, B. American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons Position Paper on Bisphosphonate-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaws—2009 Update. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2009, 67, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggiero, S.L.; Dodson, T.B.; Fantasia, J.; Goodday, R.; Aghaloo, T.; Mehrotra, B.; O’Ryan, F. American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons Position Paper on Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw—2014 Update. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2014, 72, 1938–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarom, N.; Shapiro, C.L.; Peterson, D.E.; Van Poznak, C.H.; Bohlke, K.; Ruggiero, S.L.; Migliorati, C.A.; Khan, A.; Morrison, A.; Anderson, H.; et al. Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw: MASCC/ISOO/ASCO Clinical Practice Guideline. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 2270–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Fede, O.; Panzarella, V.; Mauceri, R.; Fusco, V.; Bedogni, A.; Muzio, L.L.; Board, S.O.; Campisi, G. The Dental Management of Patients at Risk of Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw: New Paradigm of Primary Prevention. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 2684924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Hamadeh, I.S.; Song, S.; Katz, J.; Moreb, J.S.; Langaee, T.Y.; Lesko, L.J.; Gong, Y. Osteonecrosis of the Jaw in the United States Food and Drug Administration’s Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS). J. Bone Miner. Res. 2016, 31, 336–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahtinen, S.; Koivunen, P.; Ala-Kokko, T.; Laurila, P.; Kaarela, O.; Liisanantti, J.H. Quality of life after free flap surgery for cancer of the head and neck in patients with or without postoperative complications. Eur. Arch. Oto Rhino Laryngol. 2018, 275, 2575–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momeni, A.; Kim, R.Y.; Kattan, A.; Lee, G.K. Microsurgical head and neck reconstruction after oncologic ablation: A study analyzing health-related quality of life. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2013, 70, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeo, U.; Galanakis, A.; Marias, C.; Vecchio, A.D.; Tenore, G.; Palaia, G.; Vescovi, P.; Polimeni, A. Observation of Pain Control in Patients with Bisphosphonate-Induced Osteonecrosis Using Low Level Laser Therapy: Preliminary Results. Photomed. Laser Surg. 2011, 29, 447–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vescovi, P.; Merigo, E.; Meleti, M.; Fornaini, C.; Namour, S.; Manfredi, M. Nd: YAG laser biostimulation of bisphosphonate-associated necrosis of the jawbone with and without surgical treatment. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2007, 45, 628–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGowan, K.; McGowan, T.; Ivanovski, S. Risk factors for medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaws: A systematic review. Oral Dis. 2017, 24, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arraras, J.I.; De La Vega, F.A.; Asin, G.; Rico, M.; Zarandona, U.; Eito, C.; Cambra, K.; Barrondo, M.; Errasti, M.; Verdún, J.; et al. The EORTC QLQ-C15-PAL questionnaire: validation study for Spanish bone metastases patients. Qual. Life Res. 2014, 23, 849–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caissie, A.; Zeng, L.; Nguyen, J.; Zhang, L.; Jon, F.; Dennis, K.; Holden, L.; Culleton, S.; Koo, K.; Tsao, M.; et al. Assessment of Health-related Quality of Life with the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer QLQ-C15-PAL after Palliative Radiotherapy of Bone Metastases. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 24, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groenvold, M.; Petersen, M.A.; Aaronson, N.K.; Arraras, J.I.; Blazeby, J.M.; Bottomley, A.; Fayers, P.M.; de Graeff, A.; Hammerlid, E.; Kaasa, S.; et al. The development of the EORTC QLQ-C15-PAL: A shortened questionnaire for cancer patients in palliative care. Eur. J. Cancer 2006, 42, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soelver, L.; Oestergaard, B.; Rydahl-Hansen, S.; Wagner, L. Advanced cancer patients’ self-assessed physical and emotional problems on admission and discharge from hospital general wards—A questionnaire study. Eur. J. Cancer Care 2012, 21, 667–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Murphy, J.; Mannion, C. Medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaws and quality of life: review and structured analysis. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagell, P.; Westergren, A.; Årestedt, K. Beware of the origin of numbers: Standard scoring of the SF-12 and SF-36 summary measures distorts measurement and score interpretations. Res. Nurs. Health 2017, 40, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capocci, M.; Romeo, U.; Guerra, F.; Mannocci, A.; Tenore, G.; Annibali, S.; Ottolenghi, L. Medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaws (MRONJ) and quality of life evaluation: a pilot study. Clin. Ter. 2017, 168, e253–e257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassoni, A.; Romeo, U.; Terenzi, V.; Della Monaca, M.; Rajabtork Zadeh, O.; Raponi, I.; Fadda, M.T.; Polimeni, A.; Valentini, V. Adalimumab: Another Medication Related to Osteonecrosis of the Jaws? Case Rep. Dent. 2016, 2016, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, M.R.; Burr, D.B. The Pathogenesis of Bisphosphonate-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw: So Many Hypotheses, So Few Data. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2009, 67 (Suppl. 5), 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosella, D.; Papi, P.; Giardino, R.; Cicalini, E.; Piccoli, L.; Pompa, G. Medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw: Clinical and practical guidelines. J. Int. Soc. Prev. Community Dent. 2016, 6, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marx, R.E. Oral and Intravenous Bisphosphonate-Induced Osteonecrosis of the Jaws, History, Etiology, Prevention, and Treatment; Quintessence Publishing Company: Batavia, IL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Stanton, D.C.; Balasanian, E. Outcome of Surgical Management of Bisphosphonate-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaws: Review of 33 Surgical Cases. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2009, 67, 943–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freiberger, J.; Padilla-Burgos, R.; McGraw, T.; Suliman, H.B.; Kraft, K.H.; Stolp, B.W.; Moon, R.E.; Piantadosi, C.A. Utility of hyperbaric oxygen in treatment of bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaws. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2012, 70, 1573–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Felice, F.; De Vincentiis, M.; Valentini, V.; Musio, D.; Mezi, S.; Lo Mele, L.; Terenzi, V.; D’Aguanno, V.; Cassoni, A.; Di Brino, M.; et al. Follow-up program in head and neck cancer. Crit. Rev. Oncol. 2017, 113, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Felice, F.; De Vincentiis, M.; Valentini, V.; Musio, D.; Mezi, S.; Lo Mele, L.; Della Monaca, M.; D’Aguanno, V.; Terenzi, V.; Di Brino, M.; et al. Management of salivary gland malignant tumor: the Policlinico Umberto I, “Sapienza” University of Rome Head and Neck Unit clinical recommendations. Crit. Rev. Oncol. 2017, 120, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamb, B.W.; Brown, K.F.; Nagpal, K.; Vincent, C.; Green, J.S.; Sevdalis, N. Quality of Care Management Decisions by Multidisciplinary Cancer Teams: A Systematic Review. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2011, 18, 2116–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller-Nordhorn, J.; Roll, S.; Willich, S.N. Comparison of the short form (SF)-12 health status instrument with the SF-36 in patients with coronary heart disease. Heart 2004, 90, 523–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, G.; Adams, R.; Wilson, D. Results from several population studies show that recommended scoring methods of the SF-36 and the SF-12 may lead to incorrect conclusions and subsequent health decisions. Qual. Life Res. 2014, 23, 2195–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miksad, R.A.; Lai, K.C.; Dodson, T.B.; Woo, S.B.; Treister, N.S.; Akinyemi, O.; Bihrle, M.; Maytal, G.; August, M.; Gazelle, G.S.; et al. Quality of Life Implications of Bisphosphonate-Associated Osteonecrosis of the Jaw. Oncologist 2011, 16, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeo, U.; Tenore, G.; Cassoni, A.; Rocchetti, F.; Mohsen, A.; Pompa, G.; Valentini, V.; Polimeni, A. A multidisciplinary team for the management of oral cancer: A project called MoMax. Ann. Stomatol. 2018, 9, 134–140. [Google Scholar]
- Nortvedt, M.W.; Riise, T.; Myhr, K.-M.; Nyland, H.I. Performance of the SF-36, SF-12, and RAND-36 Summary Scales in a Multiple Sclerosis Population. Med. Care 2000, 38, 1022–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickard, A.S.; Johnson, J.A.; Penn, A.; Lau, F.; Noseworthy, T. Replicability of SF-36 summary scores by the SF-12 in stroke patients. Stroke 1999, 30, 1213–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ware, J.; Kosinski, M.; Keller, S.D. A 12-Item Short-Form Health Survey: Construction of scales and preliminary tests of reliability and validity. Med. Care 1996, 34, 220–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busija, L.; Pausenberger, E.; Haines, T.P.; Haymes, S.; Buchbinder, R.; Osborne, R.H. Adult measures of general health and health-related quality of life: Medical Outcomes Study Short Form 36-Item (SF-36) and Short Form 12-Item (SF-12) Health Surveys, Nottingham Health Profile (NHP), Sickness Impact Profile (SIP), Medical Outcomes Study Short Form 6D (SF-6D), Health Utilities Index Mark 3 (HUI3), Quality of Well-Being Scale (QWB), and Assessment of Quality of Life (AQoL). Arthritis Care Res. 2011, 63 (Suppl. 11), S383–S412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Characteristics | Distribution (%) |
|---|---|
| Age | |
| Under 60 | 4 (20%) |
| Over 60 | 16 (80%) |
| Gender | |
| Male | 8 (40%) |
| Female | 12 (60%) |
| Marital status | |
| Single | 5 (25%) |
| Married | 14 (70%) |
| Tumor | |
| Cancer | 8 (40%) |
| Cancer with bone metastasis | 12 (60%) |
| Anti-resorptive medication timing | |
| Past | 15 (75%) |
| Current | 5 (25%) |
| Active principle | |
| Zoledronic acid | 9 (45%) |
| Clodronic acid | 1 (5%) |
| Alendronic acid | 1 (5%) |
| Denosumab (one dose every month) | 3 (15%) |
| Adalimumab | 1 (5%) |
| Combination | 5 (25%) |
| Method of administration | |
| I.V | 11 (55%) |
| I.M/S.C | 5 (25%) |
| Oral | 1 (5%) |
| Association | 3 (15%) |
| Anti-resorptive medications duration | |
| <3 years | 8 (40%) |
| >3 years | 12 (60%) |
| I.V. < 8 infusions | 2 (10%) |
| I.V. + 8 infusions | 12 (60%) |
| MRONJ stage | |
| 0 | 6 (30%) |
| I | 2 (10%) |
| II | 11 (55%) |
| III | 1 (5%) |
| Localization | |
| Maxilla | 3 (15%) |
| Mandible | 12 (60%) |
| Both | 5 (25%) |
| Variable | n | Score of PCS-12 Median (min–max) | p-Value | Score of MCS-12 Median (max–min) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
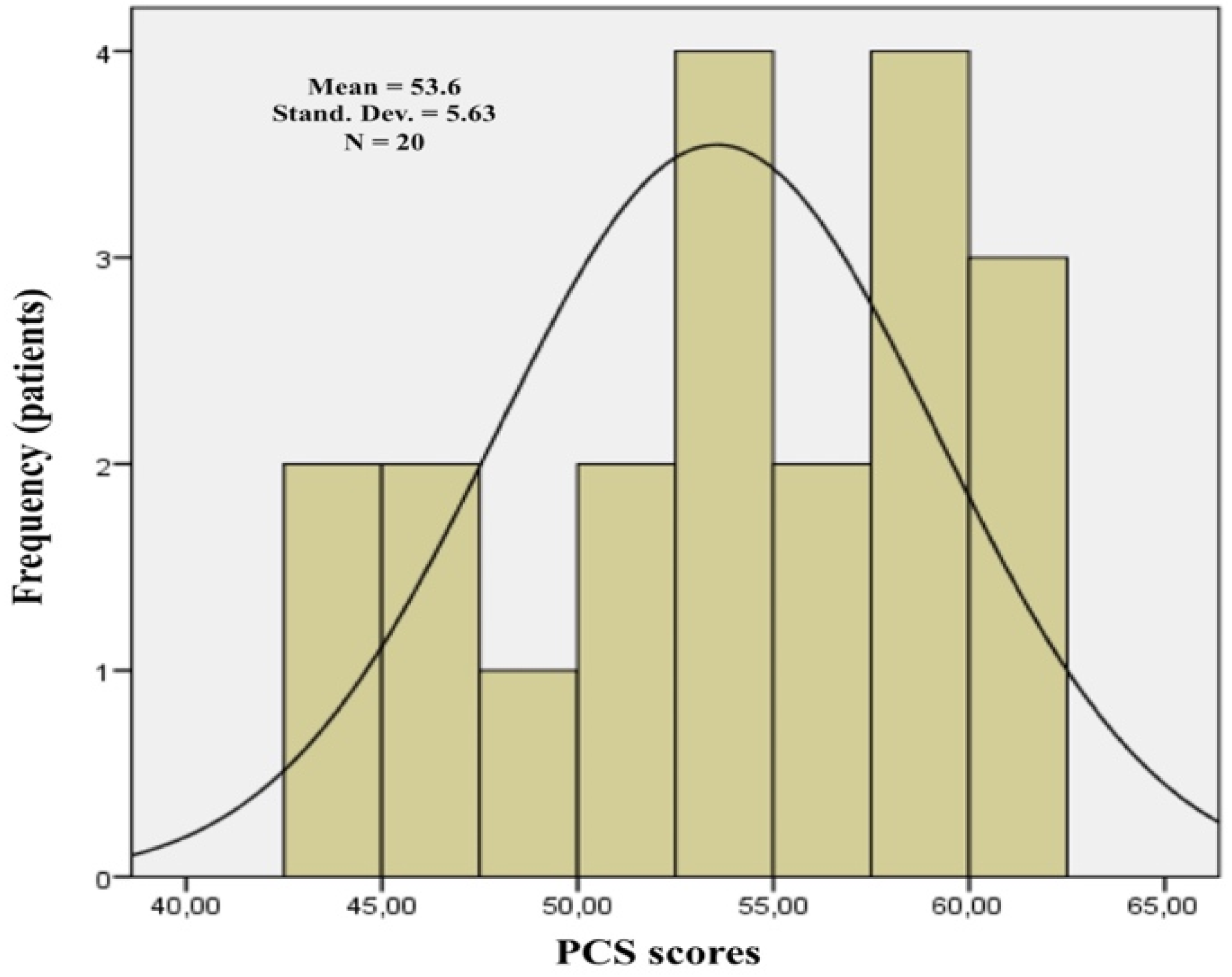
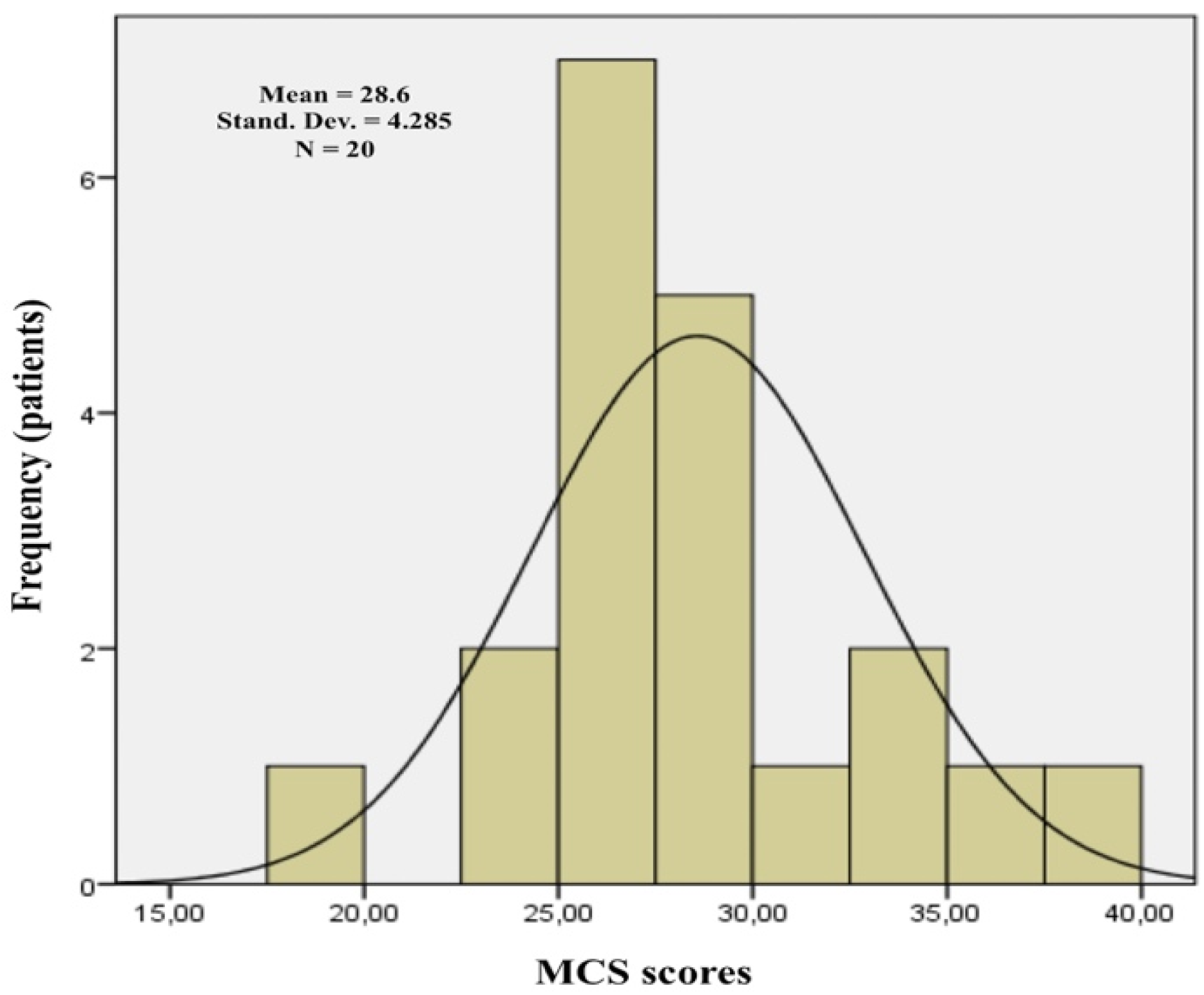
| All the sample | 20 | 53.6 (43.7–60.6) | 28.6 (19.6–37.9) | ||
| Age | 0.06 | 0.018 | |||
| Under 60 | 4 | 48.8 (44.5–53.4) | 31.9 (29.9–35.2) | ||
| Over 60 | 16 | 56.2 (43.7–60.6) | 27.4 (19.6–37.97) | ||
| Gender | 0.70 | 0.22 | |||
| Male | 8 | 54.02 (43.7–60.3) | 28.789 (26.2–37.97) | ||
| Female | 12 | 54.5 (44.5–60.6) | 27.4 (19.6–35.2) | ||
| Marital status | 0.71 | 0.58 | |||
| Single | 5 | 54.7 (43.8–60.1) | 27.5 (25.4–37.97) | ||
| Married | 14 | 54.5 (44.5–60.6) | 27.7 (19.6–35.2) | ||
| Not declared | 1 | 53.4 | 30.8 | ||
| Tumor | 0.28 | 0.68 | |||
| Cancer | 8 | 57.4 (50.2–60.1) | 27.7 (24.4–29.7) | ||
| Cancer with bone metastasis | 12 | 52.96 (44.5–60.6) | 28.6 (19.6–37.97) | ||
| Anti-resorptive medication timing | 0.86 | 0.73 | |||
| Past | 15 | 53.5 (43.7–60.6) | 27.9 (19.6–37.97) | ||
| Current | 5 | 57.1 (45–60.1) | 27.4 (25.4–35.2) | ||
| Active principle | 0.57 | 0.54 | |||
| Zoledronic acid | 9 | 54.7 (43.7–60.6) | 27.5 (19.6–37.97) | ||
| Clodronic acid | 1 | 57.1 | 28.8 | ||
| Alendronic acid | 1 | 60.1 | 25.4 | ||
| Denosumab (one dose every month) | 3 | 57.8 (50.8–60.3) | 27.9 (26.5–29.8) | ||
| Adalimumab | 1 | 53.5 | 23.6 | ||
| Combination | 5 | 50.2 (45–59.4) | 29.7 (26.3–35.2) | ||
| Method of administration | 0.38 | 0.38 | |||
| I.V | 11 | 53.4 (43.7–60.6) | 27.5 (19.6–37.97) | ||
| I.M/S.C | 5 | 57.1 (50.8–60.3) | 27.9 (23.6–29.8) | ||
| Oral | 1 | 60.1 | 25.4 | ||
| Association | 3 | 52.6 (45–59.4) | 32.99 (27.4–35.2) | ||
| Anti-resorptive medications duration | 0.25 | 0.45 | |||
| <3 years | 8 | 57.1 (50.2–60.3) | 29.3 (26.6–37.97) | ||
| >3 years | 12 | 51.7 (47.7–60.6) | 28.1 (19.6–35.2) | ||
| I.V < 8 infusions | 2 | 57.4 (55.4–59.4) | 25.9 (24.4–27.4) | ||
| I.V + 8 infusions | 12 | 51.4 (43.7–60.6) | 29.8 (19.6–37.97) | ||
| MRONJ stage | 0.85 | 0.15 | |||
| 0 | 6 | 53.4 (46.8–60.1) | 27.5 (23.6–30.8) | ||
| I | 2 | 51.4 (45–57.7) | 31.4 (27.5–35.2) | ||
| II | 11 | 55.4 (43.7–60.6) | 27.4 (19.6–34.5) | ||
| III | 1 | 54.7 | 37.97 | ||
| Localization | 0.47 | 1.00 | |||
| Maxilla | 3 | 54.1 (43.7–60.3) | 27.438 (23.6–37.97) | ||
| Mandible | 12 | 57.8 (45–60.6) | 27.9 (19.6–35.2) | ||
| Both | 5 | 54.3 (46.8–60.1) | 28.2 (25.4–30.8) | ||
| Variable | PCS-12 | MCS-12 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| β | p-Value | β | p-Value | |
| Age | −0.188 | 0.55 | −0.123 | 0.77 |
| Gender | 0.632 | 0.15 | −0.633 | 0.25 |
| Marital status | 0.320 | 0.37 | −0.136 | 0.76 |
| Anti-resorptive medication timing | −0.830 | 0.08 | 1.018 | 0.09 |
| Anti-resorptive medications duration | −1.137 | 0.03 | 0.471 | 0.32 |
| Number of infusions | 0.715 | 0.10 | −0.652 | 0.21 |
| MRONJ stage | −0.007 | 0.98 | 0.410 | 0.31 |
| Localization | 0.729 | 0.09 | −0.643 | 0.21 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tenore, G.; Mohsen, A.; Rossi, A.F.; Palaia, G.; Rocchetti, F.; Cassoni, A.; Valentini, V.; Ottolenghi, L.; Polimeni, A.; Romeo, U. Does Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw Influence the Quality of Life of Cancer Patients? Biomedicines 2020, 8, 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8040095
Tenore G, Mohsen A, Rossi AF, Palaia G, Rocchetti F, Cassoni A, Valentini V, Ottolenghi L, Polimeni A, Romeo U. Does Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw Influence the Quality of Life of Cancer Patients? Biomedicines. 2020; 8(4):95. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8040095
Chicago/Turabian StyleTenore, Gianluca, Ahmed Mohsen, Antonella Francesca Rossi, Gaspare Palaia, Federica Rocchetti, Andrea Cassoni, Valentino Valentini, Livia Ottolenghi, Antonella Polimeni, and Umberto Romeo. 2020. "Does Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw Influence the Quality of Life of Cancer Patients?" Biomedicines 8, no. 4: 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8040095
APA StyleTenore, G., Mohsen, A., Rossi, A. F., Palaia, G., Rocchetti, F., Cassoni, A., Valentini, V., Ottolenghi, L., Polimeni, A., & Romeo, U. (2020). Does Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw Influence the Quality of Life of Cancer Patients? Biomedicines, 8(4), 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8040095












