In Vitro Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Selected Green Leafy Vegetables
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Reagents
2.3. Preparation of Crude Extracts
2.4. Membrane Lysis Assay
2.4.1. Preparation of Erythrocyte Suspension
2.4.2. Heat-Induced Hemolysis
2.4.3. Effect on Protein Denaturation
2.4.4. Proteinase Inhibitory Activity
2.5. Lipoxygenase Inhibition Assay
2.6. Determination of Polyphenols, Flavonoids, and Carotenoids
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
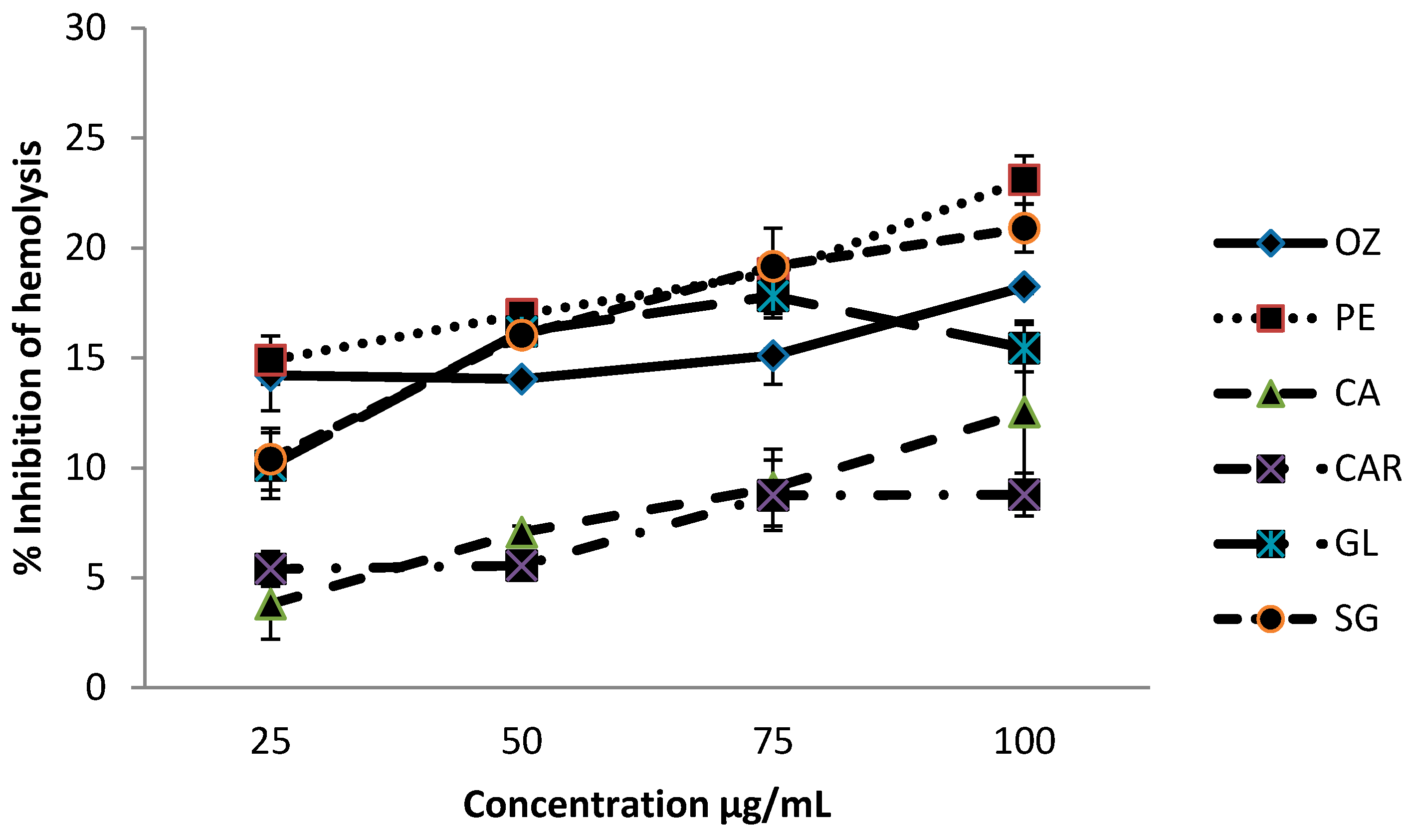
3.1. Effect on Hemolysis
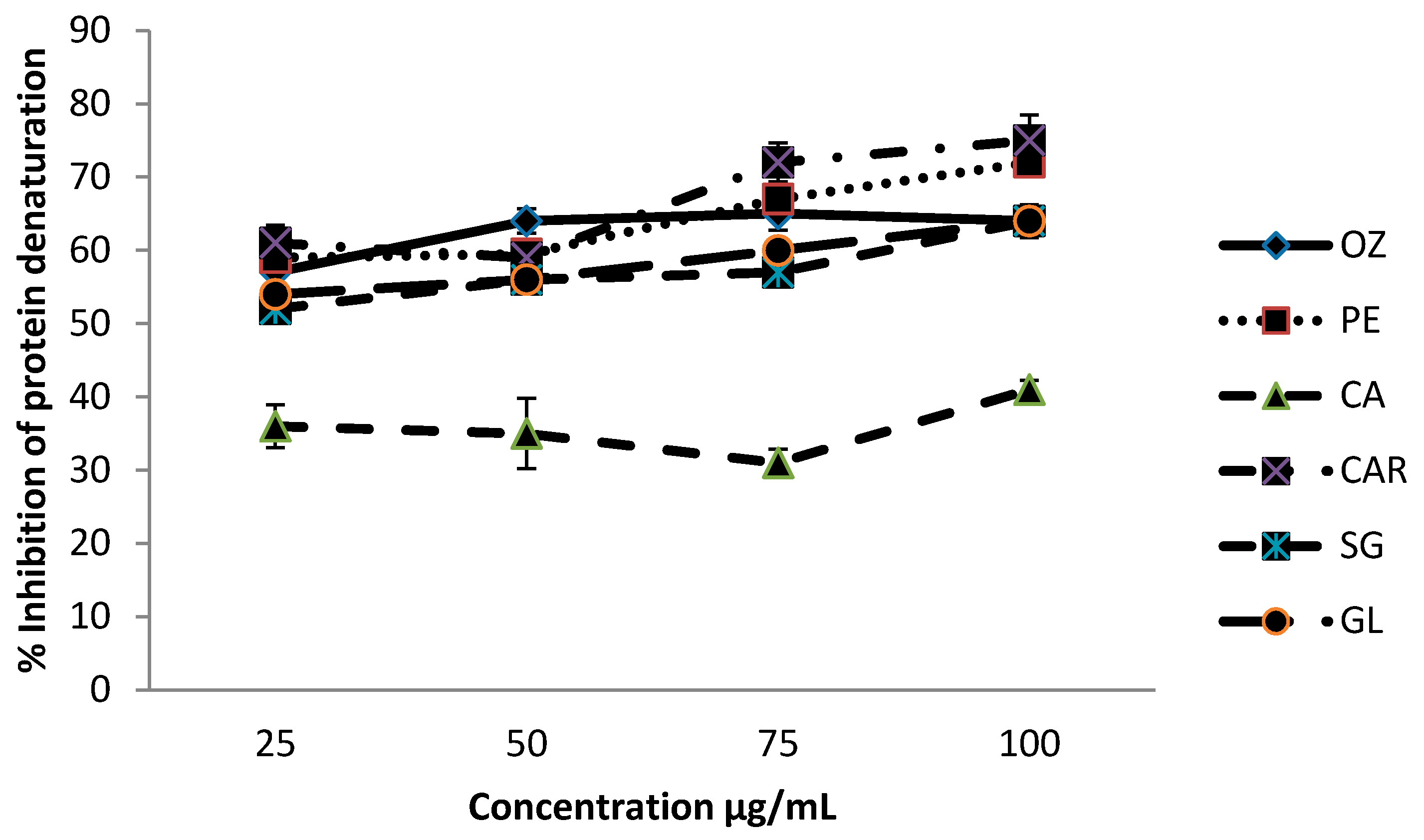
3.2. Effect of Protein Denaturation
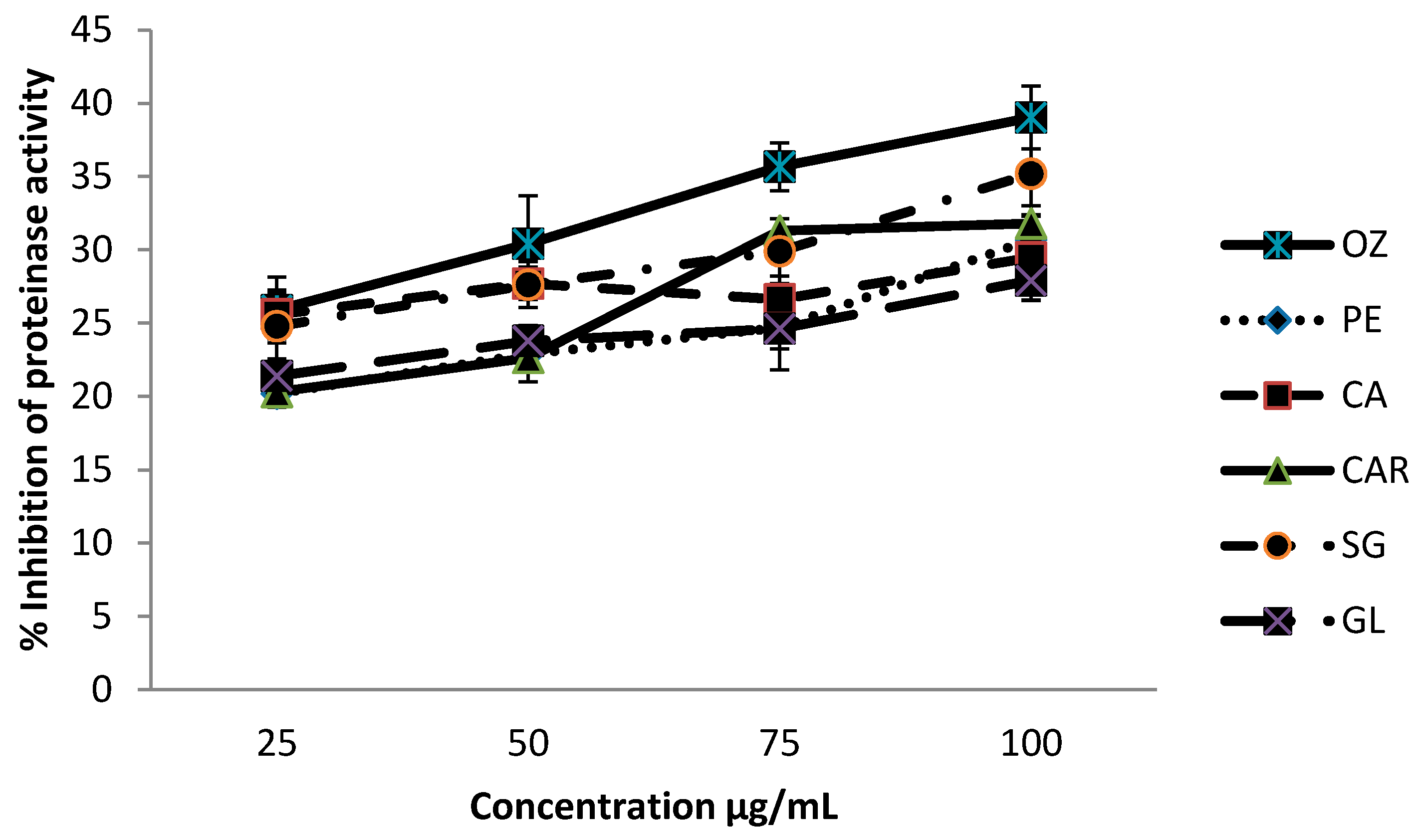
3.3. Proteinase Inhibitory Activities
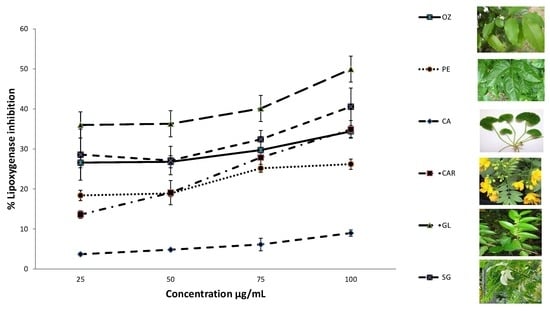
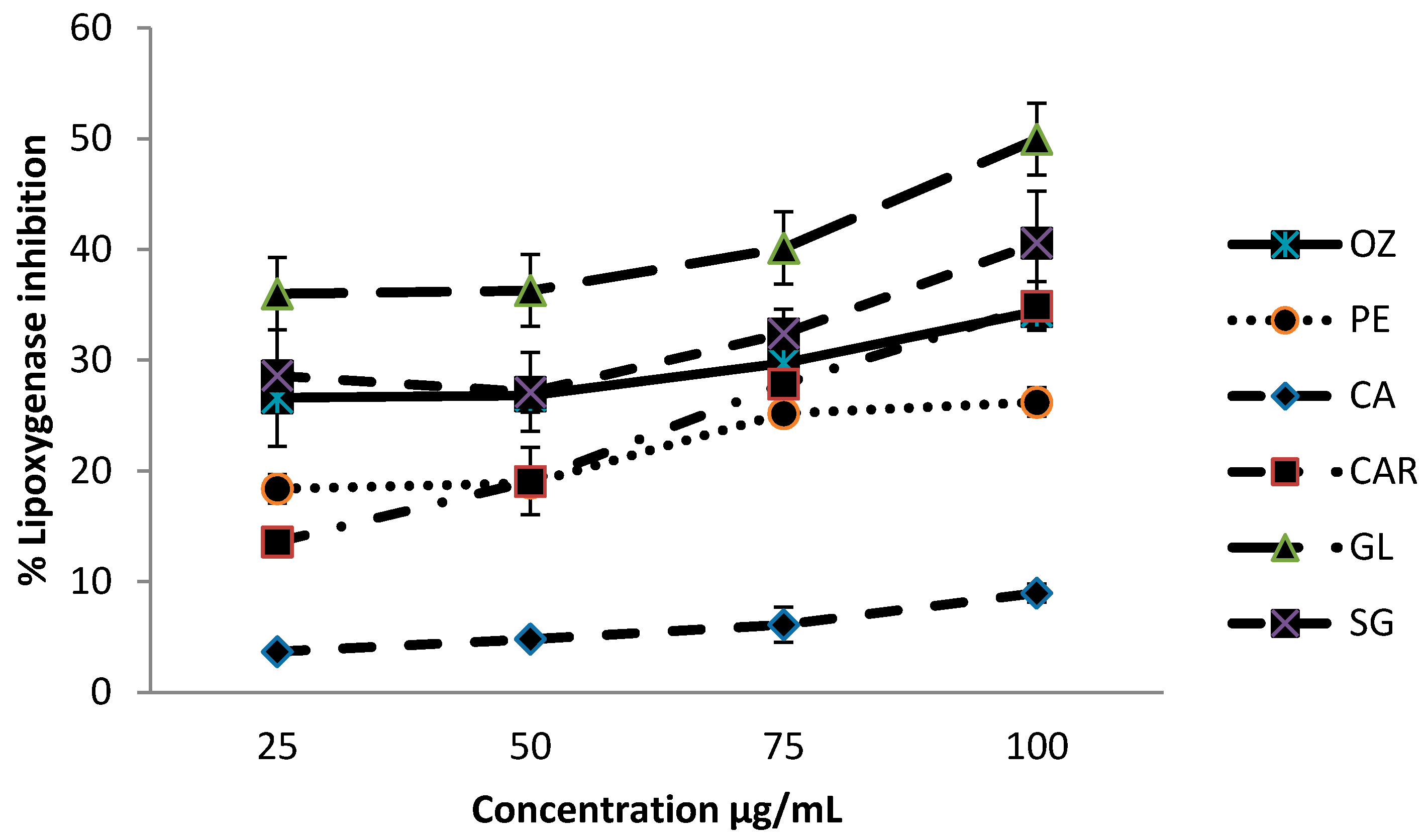
3.4. Lipoxygenase Inhibition Activity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferrero-Millani, L.; Nelsen, O.H.; Anderson, P.S.; Girardin, S.E. Chronic inflammation: Importance of NOD2 and NALP3 in interleukin-1 beta generation. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2007, 147, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandra, S.; Chatterjee, P.; Dey, P.; Bhattacharya, S. Evaluation of in vitro anti-inflammatory activity of coffee against the denaturation of the protein. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2012, 2, 178–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollman, P.C.H. Absorption, bioavailability and metabolism of flavonoids. Pharm. Biol. 2004, 42, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leelaprakash, G.; Dass, S.M. In vitro anti-inflammatory activity of methanol extract of Enicostemma axillare. Int. J. Drug Dev. Res. 2011, 3, 189–196. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, M.H.; Lai, C.S.; Ho, C.T. Anti-inflammatory activity of natural dietary flavonoids. Food Funct. 2010, 1, 15–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, M.H.; Lai, C.S.; Dushenkov, S.; Ho, C.T. Modulation of inflammatory genes by natural dietary bioactive compounds. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 4467–4477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Lafuente, A.; Guillamón, E.; Villares, A.; Rostagno, M.A.; Martínez, J.A. Flavonoids as anti-inflammatory agents: Implications in cancer and cardiovascular disease. Inflamm. Res. 2009, 58, 537–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunathilake, K.D.P.P.; Ranaweera, K.K.D.S. Antioxidative properties of 34 green leafy vegetables. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 26, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunathilake, K.D.P.P.; Ranaweera, K.K.D.S.; Rupasinghe, H.P.V. Analysis of rutin, β-carotene, and lutein content and evaluation of antioxidant activities of six edible leaves on free radicals and reactive oxygenspecies. J. Food Biochem. 2018, 42, e12579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chippada, S.C.; Vangalapati, M. Antioxidant, an anti-inflammatory and anti-arthritic activity of Centellaasiatica extracts. J. Chem. Biol. Phys. Sci. 2011, 1, 260–269. [Google Scholar]
- Shinde, U.A.; Phadke, A.S.; Nari, A.M.; Mungantiwar, A.A.; Dikshit, V.J.; Saraf, M.N. Membrane stabilization activity—A possible mechanism of action for the anti-inflammatory activity of Cedrusdeodora wood oil. Fitoterapia 1999, 70, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okoli, C.O.; Akah, P.A.; Onuoha, N.J.; Okoye, T.C.; Nwoye, A.C.; Nworu, C.S. Acanthus montanus: An experimental evaluation of the antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory and immunological properties of a traditional remedy for furuncles. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2008, 8, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunathilake, K.D.P.P.; Ranaweera, K.K.D.S.; Rupasinghe, H.P.V. Influence of boiling, steaming and frying of selected leafy vegetables on the in vitro anti-inflammation associated biological activities. Plants 2018, 7, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gambhire, M.; Juvekar, A.; Wankhede, S. Evaluation of the anti-inflammatory activity of methanol extract of Barleria cristata leaves by in vivo and in vitro methods. Int. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 7, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Sakat, S.; Juvekar, A.R.; Gambhire, M.N. In vitro antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity of methanol extract of Oxalis corniculata Linn. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 2, 146–155. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H. Affecting the activity of soybean lipoxygenase-1. J. Mol. Graph. 1996, 14, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunathilake, K.D.P.P. A Fruit-Based Functional Beverage Designed to Reduce the Risk of Cardiovascular Disease. Master’s Thesis, Dalhousie University, Halifax, NS, Canada, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Gunathilake, K.D.P.P.; Ranaweera, K.K.D.S.; Rupasinghe, H.P.V.; Perera, O.D.A.N.; Jayaweera, H.P.S. Response surface optimization of extraction of polyphenols and carotenoids from Sesbania grandiflora leaves with ethanol-water system. Asian J. Biotechnol. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 2, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunathilake, K.D.P.P.; Ranaweera, K.K.D.S.; Rupasinghe, H.P.V. Optimization of phenolics and carotenoids extraction from leaves of Passiflora edulis using response surface methods. Asian J. Biotechnol. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 1, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunathilake, K.D.P.P.; Ranaweera, K.K.D.S.; Rupasinghe, H.P.V. Change of phenolics, carotenoids, and antioxidant capacity following simulated gastrointestinal digestion and dialysis of selected edible green leaves. Food Chem. 2018, 245, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umapathy, E.; Ndebia, E.J.; Meeme, A.; Adam, B.; Menziwa, P.; Nkeh-Chungag, B.N.; Iputo, J.E. An experimental evaluation of Albuca setosa aqueous extract on membrane stabilization, protein denaturation and white blood cell migration during acute inflammation. J. Med. Plants Res. 2010, 4, 789–795. [Google Scholar]
- Benincá, J.P.; Montanher, A.B.; Zucolotto, S.M.; Schenkel, E.P.; Fröde, T.S. Evaluation of the anti-inflammatory efficacy of Passiflora edulis. Food Chem. 2007, 104, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyedepo, F.A.J. Anti-protease and membrane stabilizing activities of extracts of Fagra zanthoxiloides, Olax subscorpioides and Tetrapleura tetraptera. Int. J. Pharm. 1995, 33, 65–69. [Google Scholar]
- Aitadafoun, M.; Mounieri, C.; Heyman, S.F.; Binitisc, C.; Bon, C. 4-alkoxy benzamides as new potent phospholipase A2 inhibitors. J. Biochem. Pharm. 1996, 51, 737–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizushima, Y. Inhibition of protein denaturation by antirheumatic or antiphlogistic agents. Arch. Int. Pharmacodyn. Ther. 1964, 149, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.N.; Bevara, G.B.; Laxmikoteswramma, K.; Malla, R.R. Antioxidant, cytoprotective and anti-inflammatory activities of stem bark extract of Semecarpus anacardium. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2013, 6, 213–219. [Google Scholar]
- Govindappa, M.; Naga, S.S.; Poojashri, M.N.; Sadananda, T.S.; Chandrappa, C.P. Antimicrobial, antioxidant and in vitro anti-inflammatory activity of ethanol extract and active phytochemical screening of Wedelia trilobata (L.) Hitchc. J. Pharmacogn. Phytother. 2011, 3, 43–51. [Google Scholar]
- Chou, C.T. The antiinflammatory effect of an extract of Tripterygium wilfordii hook F on adjuvant-induced paw oedema in rats and inflammatory mediators release. Phytother. Res. 1997, 11, 152–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.N.; Chatterjee, S. Long-term toxicity study of ART-400. Indian Indig. Med. 1995, 16, 117–123. [Google Scholar]
- Rackova, L.; Oblozinsky, M.; Kastalova, D.; Kettmann, V.; Bezakova, L. Free radical scavenging activity and lipoxygenase inhibition of Mahonia aquafolium extract and isoquinoline alkaloids. J. Inflamm. 2007, 4, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akinwunmi, K.F.; Oyedapo, O.O. In vitro anti-inflammatory evaluation of African nutmeg (Monodora myristica) seeds. Eur. J. Med. Plants 2015, 8, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khasawneh, M.A.; Elwy, H.M.; Hamza, A.A.; Fawzi, N.M.; Hassan, A.H. Antioxidant, anti-lipoxygenase and cytotoxic activity of Leptadenia pyrotechnica (Forssk.) Decne polyphenolic constituents. Molecules 2011, 16, 7510–7521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trouillas, P.; Calliste, C.A.; Allais, D.P.; Simon, A.; Marfak, A.; Delage, C.; Duroux, J.L. Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and antiproliferative properties of sixteen water plant extract used in the Limousin countryside as herbal teas. Food Chem. 2003, 80, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Correlation | r | p |
|---|---|---|
| Phenolics versus protein denaturation | 0.741 | 0.001 |
| Phenolics versus hemolysis | 0.731 | 0.001 |
| Phenolics versus lipoxygenase activity | 0.531 | 0.024 |
| Phenolics versus proteinase activity | 0.903 | 0.001 |
| Flavonoids versus protein denaturation | 0.842 | 0.000 |
| Flavonoids versus hemolysis | 0.454 | 0.054 |
| Flavonoids versus lipoxygenase activity | 0.388 | 0.001 |
| Flavonoids versus proteinase activity | 0.712 | 0.001 |
| Carotenoids versus protein denaturation | 0.735 | 0.001 |
| Carotenoids versus hemolysis | 0.387 | 0.112 |
| Carotenoids versus lipoxygenase activity | 0.688 | 0.002 |
| Carotenoids versus proteinase activity | 0.639 | 0.004 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gunathilake, K.D.P.P.; Ranaweera, K.K.D.S.; Rupasinghe, H.P.V. In Vitro Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Selected Green Leafy Vegetables. Biomedicines 2018, 6, 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines6040107
Gunathilake KDPP, Ranaweera KKDS, Rupasinghe HPV. In Vitro Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Selected Green Leafy Vegetables. Biomedicines. 2018; 6(4):107. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines6040107
Chicago/Turabian StyleGunathilake, K. D. P. P., K. K. D. S. Ranaweera, and H. P. Vasantha Rupasinghe. 2018. "In Vitro Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Selected Green Leafy Vegetables" Biomedicines 6, no. 4: 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines6040107
APA StyleGunathilake, K. D. P. P., Ranaweera, K. K. D. S., & Rupasinghe, H. P. V. (2018). In Vitro Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Selected Green Leafy Vegetables. Biomedicines, 6(4), 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines6040107