Integrated Single-Cell Transcriptome Analysis Reveals Novel Insights into the Role of Opioid Signaling in the Pathophysiology of Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Single-Cell Transcriptome Sequence Data
2.2. Quality Control and Removing Doublets
2.3. Cell Clustering, Annotating, and Proportion Calculation
2.4. Opioid Signaling Evaluating and Function Enrichment Analysis
2.5. Cell Communication Speculating
2.6. Cell Pseudotime Analysis
2.7. Cell Transcription Factor Analysis
2.8. Chip Transcriptome Sequence Analysis and Clinical Prediction Model Building
2.9. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
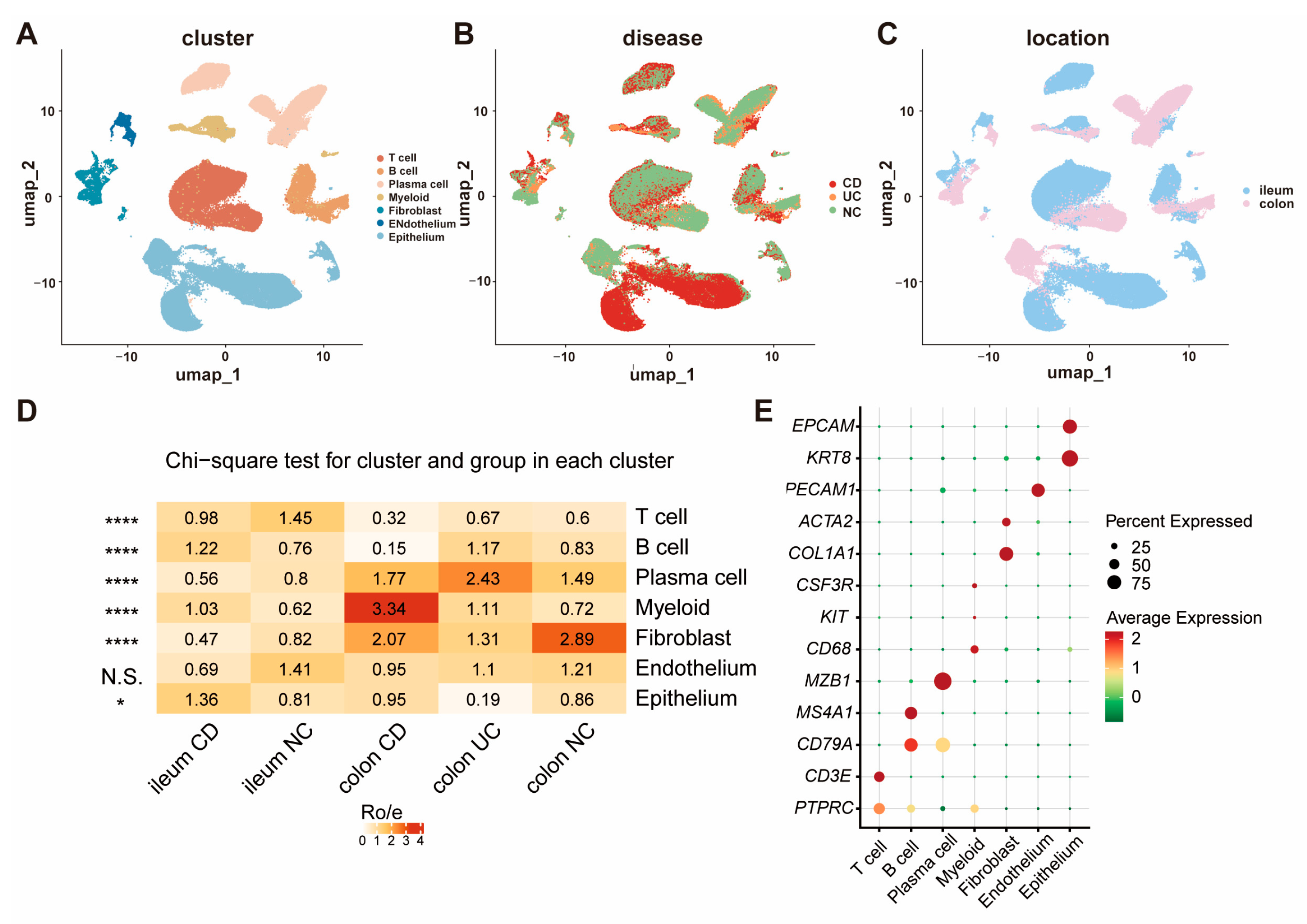
3.1. The Cellular Landscape of IBD Identified by scRNA-seq
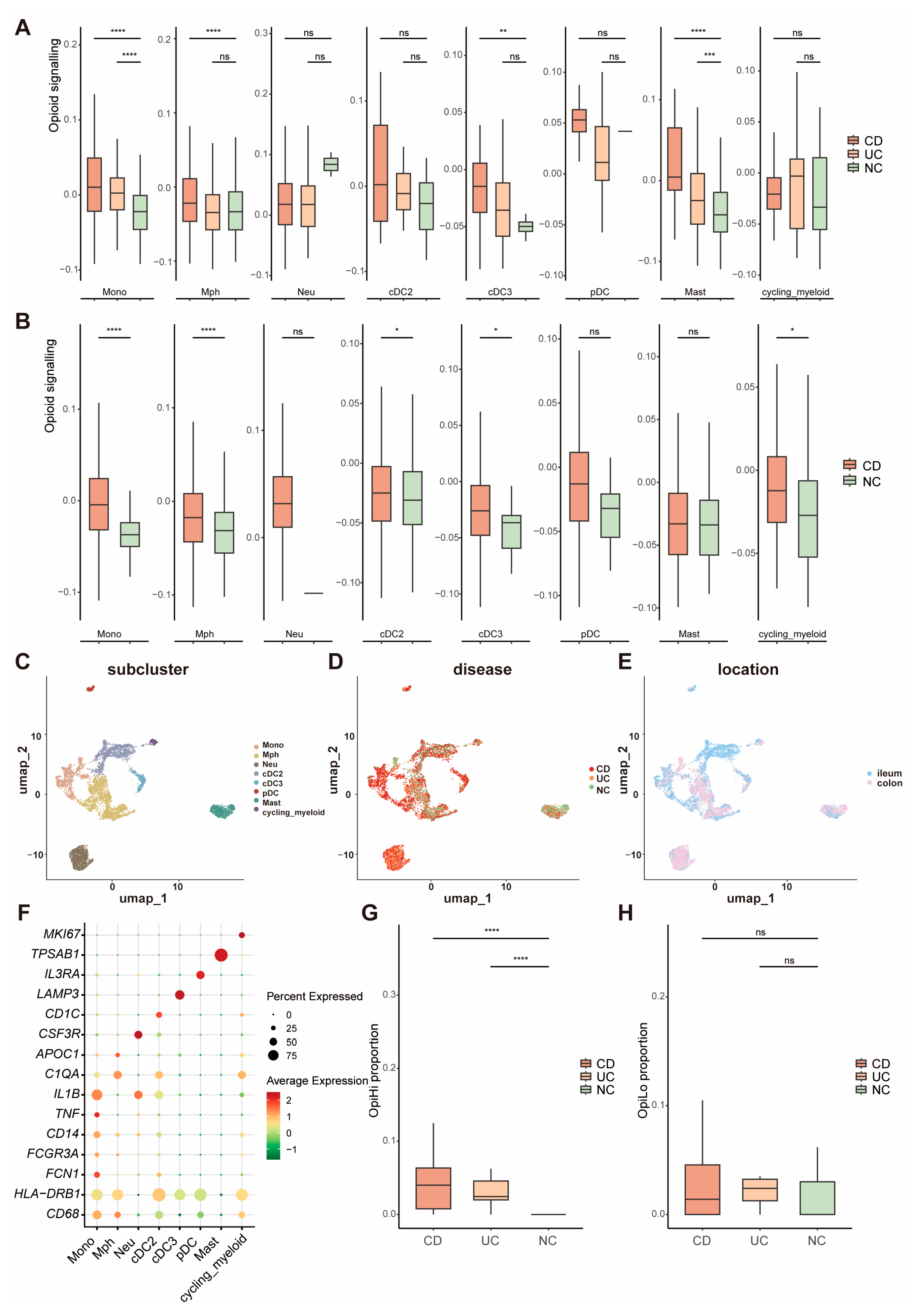
3.2. The Expression of Opioid Signaling-Related Gene Is Significantly Increased in Monocytes from IBD Tissues
3.3. TNF-Related Signaling Pathway Is Significantly Upregulated in OpiHi Monocytes
3.4. The Inflammatory Microenvironment in IBD Tissues Drives the Generation of OpiHi Monocytes
3.5. OpiHi Monocytes Signature Gene Can Predict the Response of Anti-TNF Therapy
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IBD | Inflammatory Bowel Disease |
| CD | Crohn’s Disease |
| UC | Ulcerative Colitis |
| OpiHi monocytes | Monocytes with high expression level of opioid signaling-related genes |
| OpiLo monocytes | Monocytes with low expression level of opioid signaling-related genes |
| NC | Normal Controls |
| scRNA-seq | Single-cell Transcriptomics |
| DC | Dendritic Cell |
| TNF | Tumor Necrosis Factor |
| AUC | The Area Under the Curve |
| GEO | Gene Expression Omnibus |
| ssGSEA | Single Sample Gene Set Enrichment Analysis |
| DEG | Differentially Expressed Gene |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| ROC | Receiver Operating Characteristic |
References
- Roda, G.; Chien Ng, S.; Kotze, P.G.; Argollo, M.; Panaccione, R.; Spinelli, A.; Kaser, A.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L.; Danese, S. Crohn’s disease. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2020, 6, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, T.; Siegmund, B.; Le Berre, C.; Wei, S.C.; Ferrante, M.; Shen, B.; Bernstein, C.N.; Danese, S.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L.; Hibi, T. Ulcerative colitis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2020, 6, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, M.; Allin, K.H.; Petralia, F.; Colombel, J.F.; Jess, T. Multiomics to elucidate inflammatory bowel disease risk factors and pathways. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 19, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeshi, K.; Jamtsho, T.; Wangchuk, P. Current Treatments, Emerging Therapeutics, and Natural Remedies for Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Molecules 2024, 29, 3954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stalgis, C.; Deepak, P.; Mehandru, S.; Colombel, J.F. Rational Combination Therapy to Overcome the Plateau of Drug Efficacy in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Gastroenterology 2021, 161, 394–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norton, C.; Czuber-Dochan, W.; Artom, M.; Sweeney, L.; Hart, A. Systematic review: Interventions for abdominal pain management in inflammatory bowel disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 46, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coates, M.D.; Johri, A.; Gorrepati, V.S.; Maheshwari, P.; Dalessio, S.; Walter, V.; Stuart, A.; Koltun, W.; Bernasko, N.; Tinsley, A.; et al. Abdominal pain in quiescent inflammatory bowel disease. Int. J. Color. Dis. 2021, 36, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nørgård, B.M.; Thorarinsson, C.T.; Nielsen, J.; Dalal, R.S.; Andersen, M.L.; Lund, K.; Friedman, S.; Knudsen, T.; Kjeldsen, J. Predictors for Chronic Opioid Use in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Population-Based Cohort Study. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Li, S.; Ma, X.; Chen, X.; Tian, X.; Li, X.; Chen, L.; Kang, Q.; Wang, X.; Jin, P.; et al. Immunomodulatory effects of fentanyl and morphine on DSS- and TNBS-induced colitis. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2022, 44, 1044–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philippe, D.; Dubuquoy, L.; Groux, H.; Brun, V.; Chuoï-Mariot, M.T.; Gaveriaux-Ruff, C.; Colombel, J.F.; Kieffer, B.L.; Desreumaux, P. Anti-inflammatory properties of the mu opioid receptor support its use in the treatment of colon inflammation. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 111, 1329–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alley, K.; Singla, A.; Afzali, A. Opioid Use Is Associated With Higher Health Care Costs and Emergency Encounters in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2019, 25, 1990–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Khan, S.; Akerman, M.; Sultan, K. Analysis of the clinical indications for opiate use in inflammatory bowel disease. Intest. Res. 2017, 15, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burr, N.E.; Smith, C.; West, R.; Hull, M.A.; Subramanian, V. Increasing Prescription of Opiates and Mortality in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Diseases in England. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Off. Clin. Pract. J. Am. Gastroenterol. Assoc. 2018, 16, 534–541.e536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riggott, C.; Fairbrass, K.M.; Selinger, C.P.; Gracie, D.J.; Ford, A.C. Impact of Opioid Use on the Natural History of Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Prospective Longitudinal Follow-up Study. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2024, 30, 1724–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagata, K.; Nagase, H.; Okuzumi, A.; Nishiyama, C. Delta Opioid Receptor Agonists Ameliorate Colonic Inflammation by Modulating Immune Responses. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 730706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymaszkiewicz, A.; Mierzejewski, M.; Januszkiewicz, E.; Machelak, W.; Talar, M.; Włodarczyk, J.; Świerczyński, M.; Kordek, R.; Fichna, J.; Zielińska, M. The role of bidirectional communication between the adipokines and the endogenous opioid system in an experimental mouse model of colitis-associated colorectal cancer. Pharmacol. Rep. 2024, 76, 112–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, J.C.; Chang, C.; Boschetti, G.; Ungaro, R.; Giri, M.; Grout, J.A.; Gettler, K.; Chuang, L.S.; Nayar, S.; Greenstein, A.J.; et al. Single-Cell Analysis of Crohn’s Disease Lesions Identifies a Pathogenic Cellular Module Associated with Resistance to Anti-TNF Therapy. Cell 2019, 178, 1493–1508.e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddipatla, S.C.; Kolachala, V.L.; Venkateswaran, S.; Dodd, A.F.; Pelia, R.S.; Geem, D.; Yin, H.; Sun, Y.; Xu, C.; Mo, A.; et al. Assessing Cellular and Transcriptional Diversity of Ileal Mucosa Among Treatment-Naïve and Treated Crohn’s Disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2023, 29, 274–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido-Trigo, A.; Corraliza, A.M.; Veny, M.; Dotti, I.; Melón-Ardanaz, E.; Rill, A.; Crowell, H.L.; Corbí, Á.; Gudiño, V.; Esteller, M.; et al. Macrophage and neutrophil heterogeneity at single-cell spatial resolution in human inflammatory bowel disease. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 4506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Lu, J.; Fan, T.; Niu, M.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, F.; et al. Selective oxidative protection leads to tissue topological changes orchestrated by macrophage during ulcerative colitis. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 3675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Hao, S.; Andersen-Nissen, E.; Mauck, W.M., 3rd; Zheng, S.; Butler, A.; Lee, M.J.; Wilk, A.J.; Darby, C.; Zager, M.; et al. Integrated analysis of multimodal single-cell data. Cell 2021, 184, 3573–3587.e29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wickham, H.; Averick, M.; Bryan, J.; Chang, W.; McGowan, L.; François, R.; Grolemund, G.; Hayes, A.; Henry, L.; Hester, J.; et al. Welcome to the Tidyverse. J. Open Source Softw. 2019, 4, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milacic, M.; Beavers, D.; Conley, P.; Gong, C.; Gillespie, M.; Griss, J.; Haw, R.; Jassal, B.; Matthews, L.; May, B.; et al. The Reactome Pathway Knowledgebase 2024. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, D672–D678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Hu, E.; Xu, S.; Chen, M.; Guo, P.; Dai, Z.; Feng, T.; Zhou, L.; Tang, W.; Zhan, L.; et al. clusterProfiler 4.0: A universal enrichment tool for interpreting omics data. Innovation 2021, 2, 100141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, S.; Guerrero-Juarez, C.F.; Zhang, L.; Chang, I.; Ramos, R.; Kuan, C.H.; Myung, P.; Plikus, M.V.; Nie, Q. Inference and analysis of cell-cell communication using CellChat. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trapnell, C.; Cacchiarelli, D.; Grimsby, J.; Pokharel, P.; Li, S.; Morse, M.; Lennon, N.J.; Livak, K.J.; Mikkelsen, T.S.; Rinn, J.L. The dynamics and regulators of cell fate decisions are revealed by pseudotemporal ordering of single cells. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badia, I.M.P.; Vélez Santiago, J.; Braunger, J.; Geiss, C.; Dimitrov, D.; Müller-Dott, S.; Taus, P.; Dugourd, A.; Holland, C.H.; Ramirez Flores, R.O.; et al. decoupleR: Ensemble of computational methods to infer biological activities from omics data. Bioinform. Adv. 2022, 2, vbac016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arijs, I.; Li, K.; Toedter, G.; Quintens, R.; Van Lommel, L.; Van Steen, K.; Leemans, P.; De Hertogh, G.; Lemaire, K.; Ferrante, M.; et al. Mucosal gene signatures to predict response to infliximab in patients with ulcerative colitis. Gut 2009, 58, 1612–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arijs, I.; De Hertogh, G.; Lemaire, K.; Quintens, R.; Van Lommel, L.; Van Steen, K.; Leemans, P.; Cleynen, I.; Van Assche, G.; Vermeire, S.; et al. Mucosal gene expression of antimicrobial peptides in inflammatory bowel disease before and after first infliximab treatment. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toedter, G.; Li, K.; Marano, C.; Ma, K.; Sague, S.; Huang, C.C.; Song, X.Y.; Rutgeerts, P.; Baribaud, F. Gene expression profiling and response signatures associated with differential responses to infliximab treatment in ulcerative colitis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 106, 1272–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, A.; Tamayo, P.; Mootha, V.K.; Mukherjee, S.; Ebert, B.L.; Gillette, M.A.; Paulovich, A.; Pomeroy, S.L.; Golub, T.R.; Lander, E.S.; et al. Gene set enrichment analysis: A knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 15545–15550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robin, X.; Turck, N.; Hainard, A.; Tiberti, N.; Lisacek, F.; Sanchez, J.C.; Müller, M. pROC: An open-source package for R and S+ to analyze and compare ROC curves. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabeza-Cabrerizo, M.; Cardoso, A.; Minutti, C.M.; Pereira da Costa, M.; Reis e Sousa, C. Dendritic Cells Revisited. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2021, 39, 131–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heras-Murillo, I.; Adán-Barrientos, I.; Galán, M.; Wculek, S.K.; Sancho, D. Dendritic cells as orchestrators of anticancer immunity and immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 21, 257–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, Y.; Chow, K.V.; Soo, P.; Xu, Z.; Brady, J.L.; Lawlor, K.E.; Masters, S.L.; O’Keeffe, M.; Shortman, K.; Zhang, J.G.; et al. Plasmacytoid dendritic cells are short-lived: Reappraising the influence of migration, genetic factors and activation on estimation of lifespan. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.; Cai, Y.; Lv, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yang, H.; Liu, Q.; Hong, M.; Teng, Y.; Tang, W.; Ma, R.; et al. Single-cell RNA sequencing unveils the communications between malignant T and myeloid cells contributing to tumor growth and immunosuppression in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Cancer Lett. 2022, 551, 215972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boden, E.K.; Kongala, R.; Hindmarch, D.C.; Shows, D.M.; Juarez, J.G.; Lord, J.D. Vedolizumab Efficacy Is Associated with Decreased Intracolonic Dendritic Cells, Not Memory T Cells. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2024, 30, 704–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarazi, D.; Maynes, J.T. Impact of Opioids on Cellular Metabolism: Implications for Metabolic Pathways Involved in Cancer. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lashgari, N.A.; Roudsari, N.M.; Zandi, N.; Pazoki, B.; Rezaei, A.; Hashemi, M.; Momtaz, S.; Rahimi, R.; Shayan, M.; Dehpour, A.R.; et al. Current overview of opioids in progression of inflammatory bowel disease; pharmacological and clinical considerations. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2021, 48, 855–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuitavi, J.; Torres-Pérez, J.V.; Lorente, J.D.; Campos-Jurado, Y.; Andrés-Herrera, P.; Polache, A.; Agustín-Pavón, C.; Hipólito, L. Crosstalk between Mu-Opioid receptors and neuroinflammation: Consequences for drug addiction and pain. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2023, 145, 105011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamberts, J.T.; Traynor, J.R. Opioid receptor interacting proteins and the control of opioid signaling. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2013, 19, 7333–7347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rullo, L.; Morosini, C.; Lacorte, A.; Cristani, M.; Coluzzi, F.; Candeletti, S.; Romualdi, P. Opioid system and related ligands: From the past to future perspectives. J. Anesth. Analg. Crit. Care 2024, 4, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones-Hall, Y.L.; Nakatsu, C.H. The Intersection of TNF, IBD and the Microbiome. Gut Microbes 2016, 7, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neurath, M.F. Strategies for targeting cytokines in inflammatory bowel disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2024, 24, 559–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Murugesan, S.; Ibrahim, N.; Elawad, M.; Al Khodor, S. Predictive biomarkers for anti-TNF alpha therapy in IBD patients. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 22, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, M.; Xie, Z.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, G. Integrated Single-Cell Transcriptome Analysis Reveals Novel Insights into the Role of Opioid Signaling in the Pathophysiology of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1398. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061398
Zhang M, Xie Z, Zhang S, Zhou G. Integrated Single-Cell Transcriptome Analysis Reveals Novel Insights into the Role of Opioid Signaling in the Pathophysiology of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(6):1398. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061398
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Mudan, Zhuo Xie, Shenghong Zhang, and Gaoshi Zhou. 2025. "Integrated Single-Cell Transcriptome Analysis Reveals Novel Insights into the Role of Opioid Signaling in the Pathophysiology of Inflammatory Bowel Disease" Biomedicines 13, no. 6: 1398. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061398
APA StyleZhang, M., Xie, Z., Zhang, S., & Zhou, G. (2025). Integrated Single-Cell Transcriptome Analysis Reveals Novel Insights into the Role of Opioid Signaling in the Pathophysiology of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Biomedicines, 13(6), 1398. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061398





