Decoding Cuproptosis-Sphingolipid-Immune Crosstalk in Atopic Dermatitis: A Multi-Omics Network Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
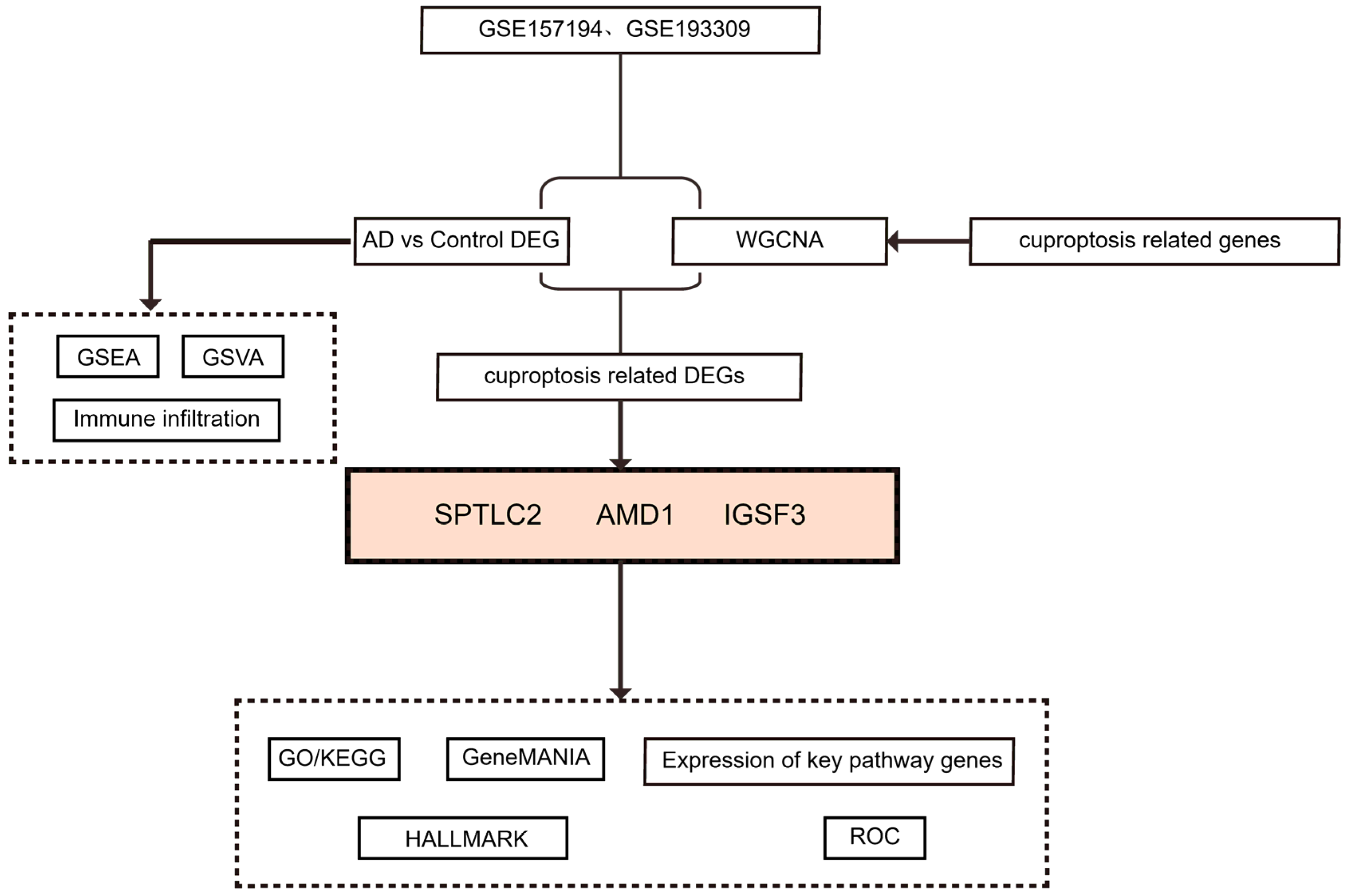
2. Methods
2.1. Data Acquisition and Preprocessing
2.2. Analysis of AD-Related Differences
2.3. Enrichment Analysis of GSEA and GSVA
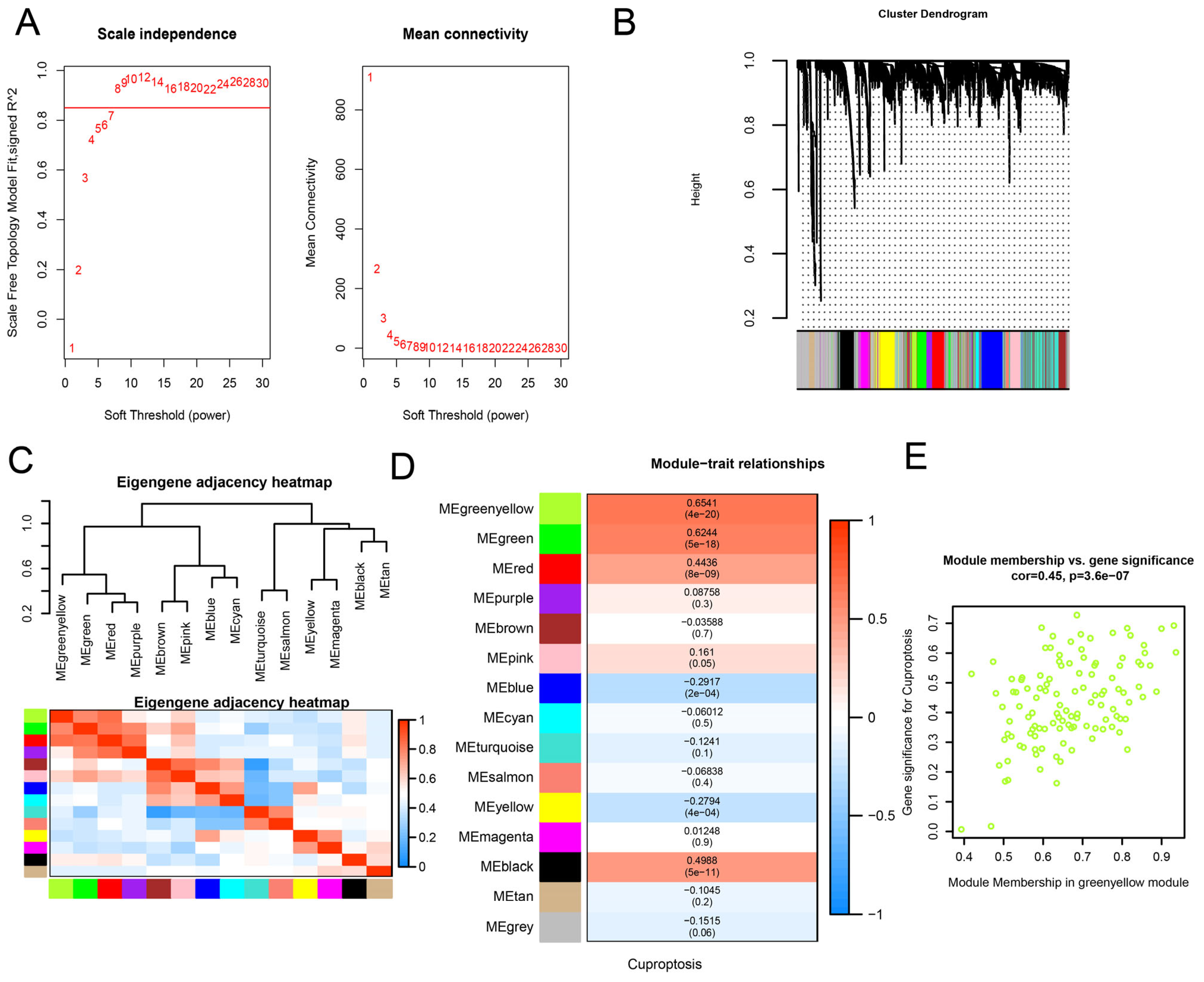
2.4. WGCNA Analysis and Identification of Significant Modules
2.5. GO and KEGG Analysis
2.6. GeneMANIA
2.7. The ROC Curve
2.8. Immune Cell Infiltration and Correlation Analysis
2.9. Construction of RBP-mRNA Network
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
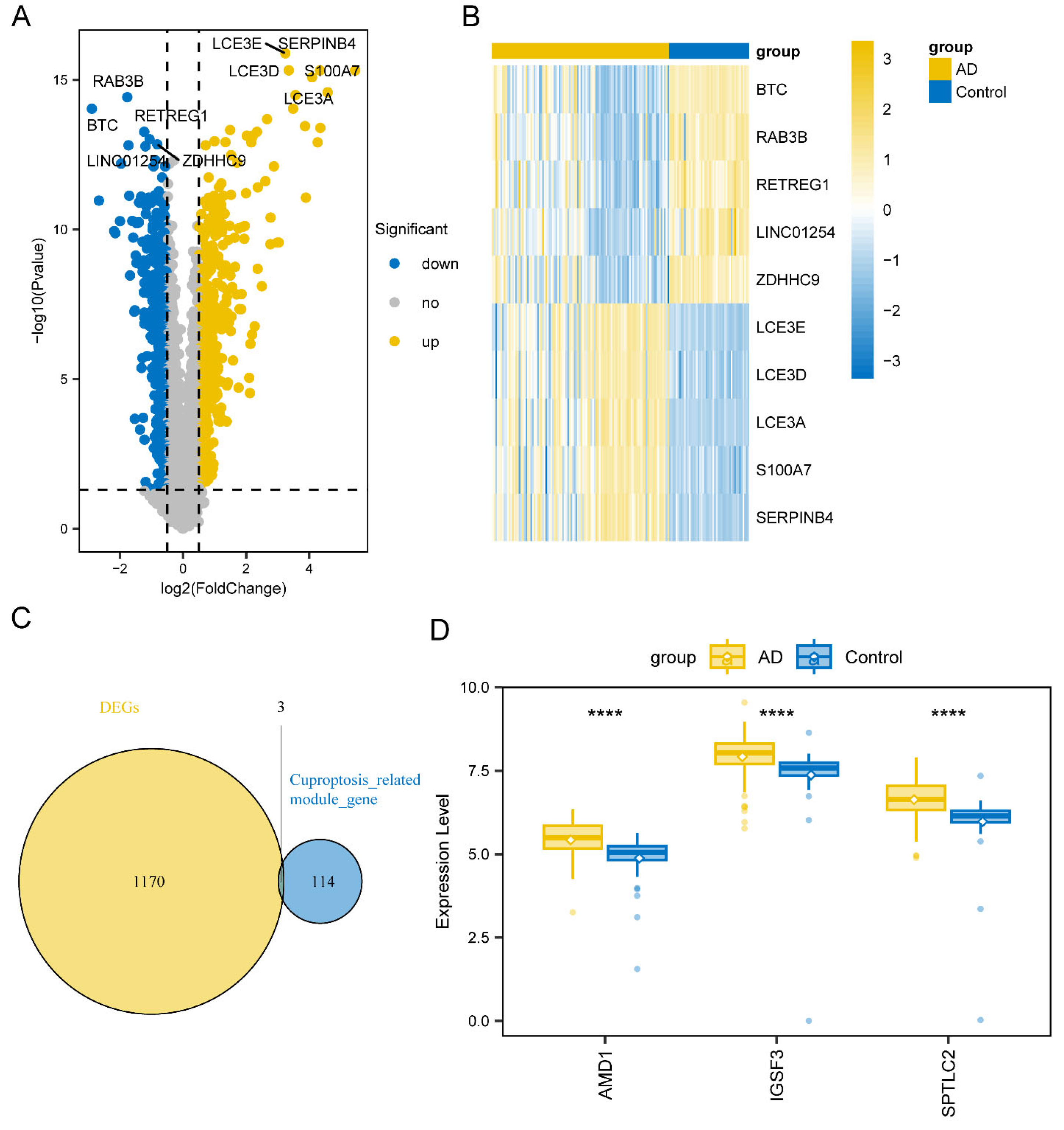
3.1. Identification of Key WGCNA Module and DEGs
3.2. AD-Related Differentially Expressed Genes
3.3. GSEA Analysis
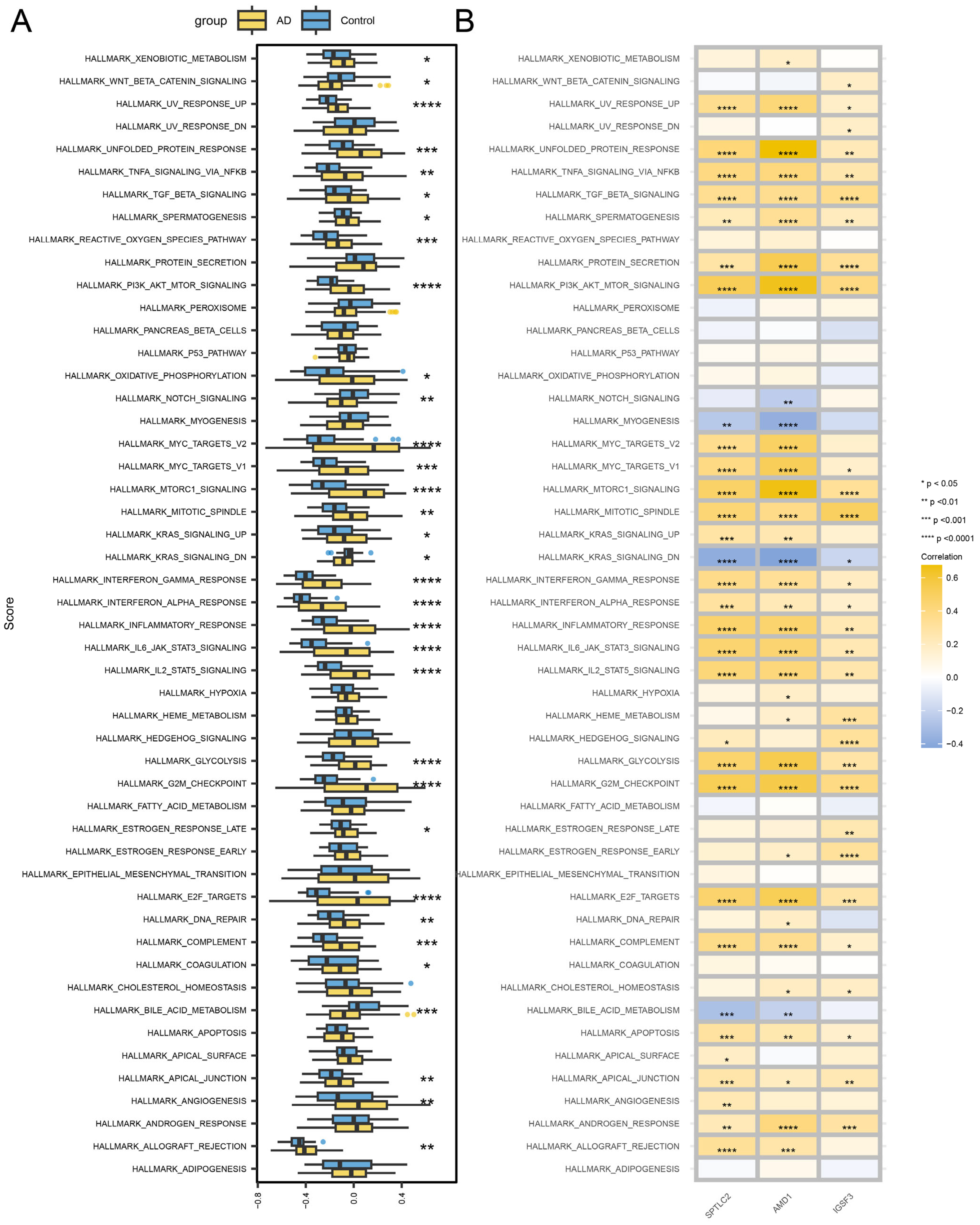
3.4. GSVA Analysis
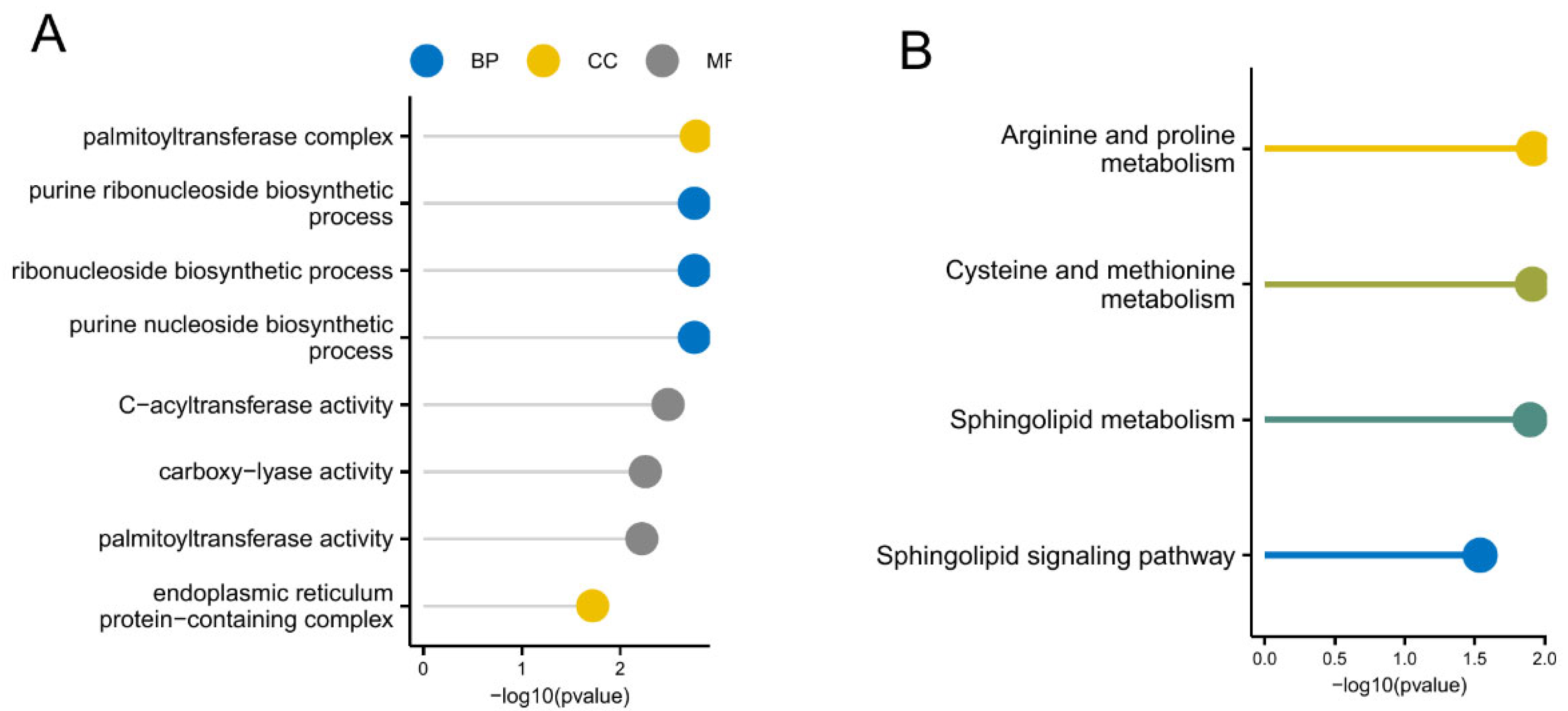
3.5. GO and KEGG Analysis
3.6. Hub Gene Interaction Analysis
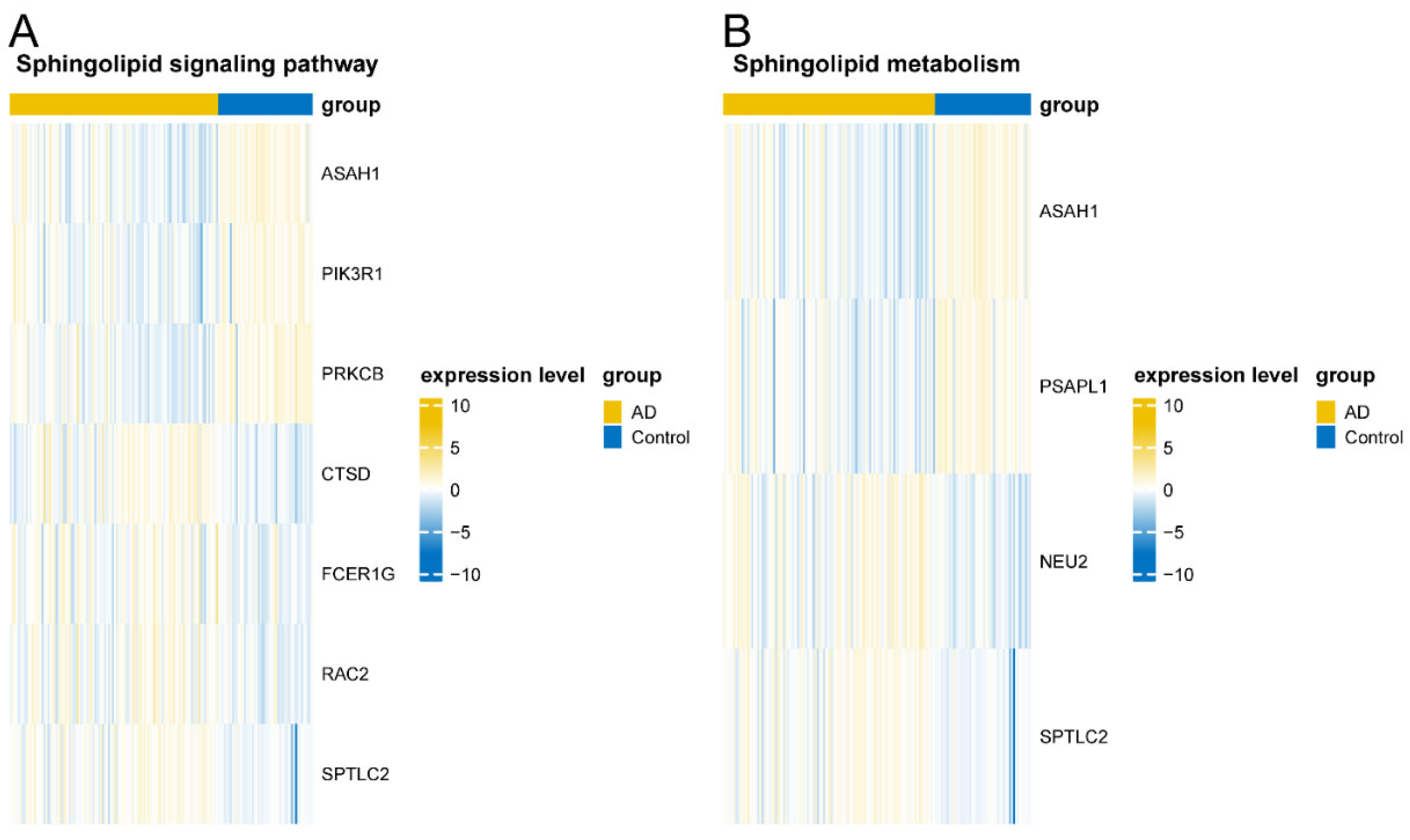
3.7. Validation of Key Pathway Gene Sets
3.8. Immune Infiltration Analysis
3.9. Hub Gene-Related Signaling Pathways
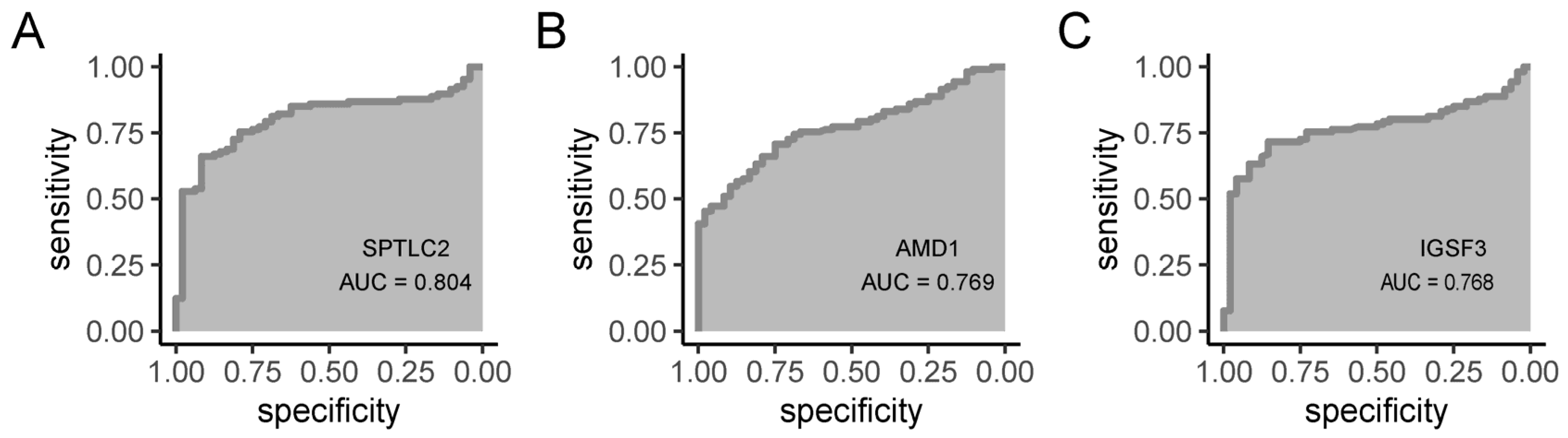
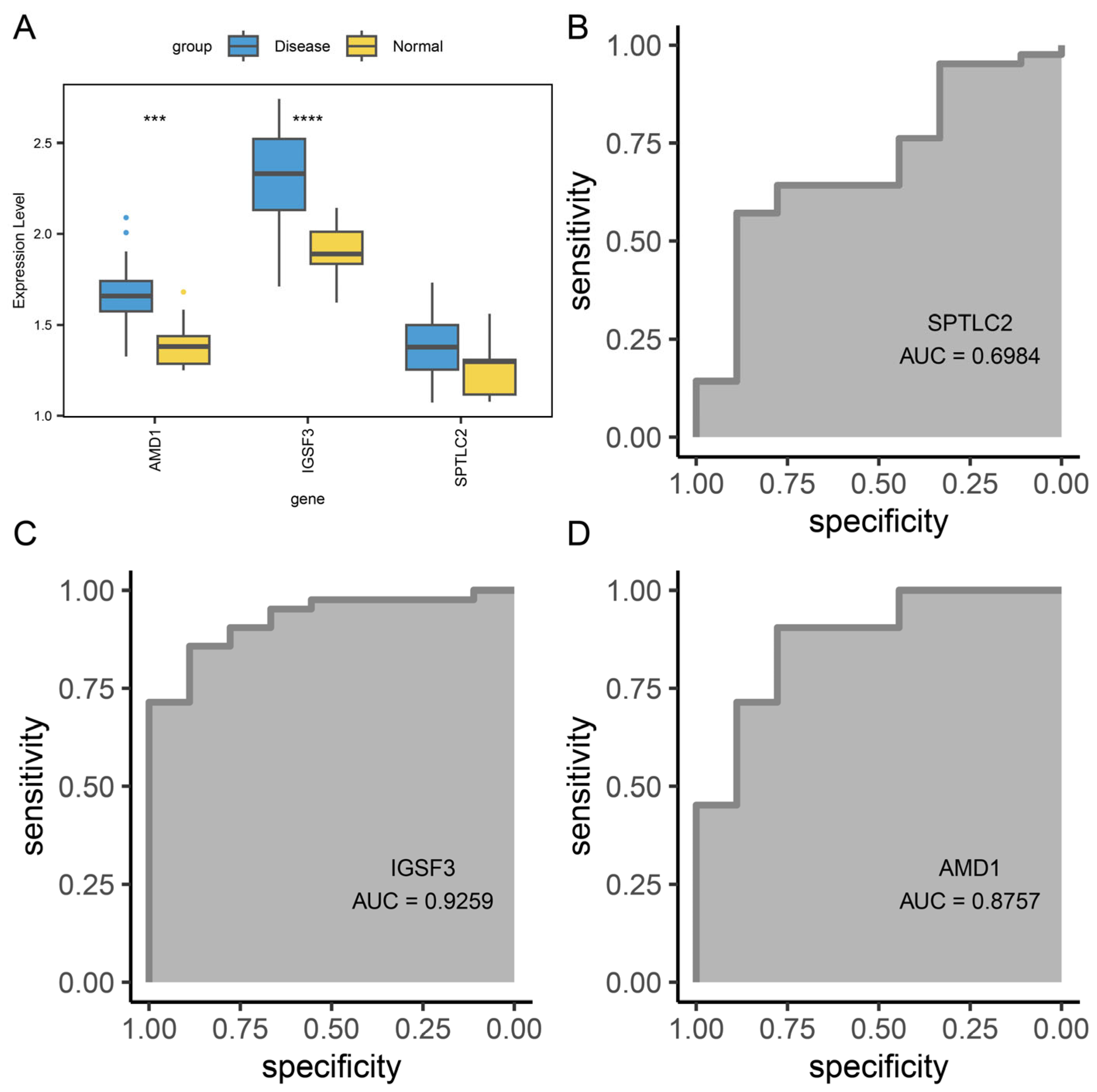
3.10. Diagnostic Value of Hub Gene
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weidinger, S.; Beck, L.A.; Bieber, T.; Kabashima, K.; Irvine, A.D. Atopic dermatitis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2018, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langan, S.M.; Irvine, A.D.; Weidinger, S. Atopic dermatitis. Lancet 2020, 396, 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, K.; Penn, R.B.; Rattan, S.; Panettieri, R.A.; Voight, B.F.; An, S.S. Mendelian Randomization Analysis Reveals a Complex Genetic Interplay among Atopic Dermatitis, Asthma, and Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2023, 207, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ständer, S. Atopic Dermatitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1136–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, D.; Jamil, A.; Nor, N.M.; Ibrahim, S.B.K.; Poh, B.K. Food restriction, nutrition status, and growth in toddlers with atopic dermatitis. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2020, 37, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bawany, F.; Northcott, C.A.; Beck, L.A.; Pigeon, W.R. Sleep Disturbances and Atopic Dermatitis: Relationships, Methods for Assessment, and Therapies. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2021, 9, 1488–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, H.-J.; Shin, M.K.; Seo, J.-K.; Jeong, S.J.; Cho, A.R.; Choi, S.-H.; Lew, B.-L. Cross-sectional study of psychiatric comorbidities in patients with atopic dermatitis and nonatopic eczema, urticaria, and psoriasis. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2019, 15, 1469–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidinger, S.; Novak, N. Atopic dermatitis. Lancet 2016, 387, 1109–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustin, M.; Langenbruch, A.; Blome, C.; Gutknecht, M.; Werfel, T.; Ständer, S.; Steinke, S.; Kirsten, N.; Silva, N.; Sommer, R. Characterizing treatment-related patient needs in atopic eczema: Insights for personalized goal orientation. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. JEADV 2020, 34, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, E.L.; Guttman-Yassky, E.; Margolis, D.J.; Feldman, S.R.; Qureshi, A.; Hata, T.; Mastey, V.; Wei, W.; Eckert, L.; Chao, J.; et al. Association of Inadequately Controlled Disease and Disease Severity with Patient-Reported Disease Burden in Adults with Atopic Dermatitis. JAMA Dermatol. 2018, 154, 903–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunner, P.M.; Leung, D.Y.M.; Guttman-Yassky, E. Immunologic, microbial, and epithelial interactions in atopic dermatitis. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 2018, 120, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubo, A.; Nagao, K.; Amagai, M. Epidermal barrier dysfunction and cutaneous sensitization in atopic diseases. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Sánchez, A.; Miranda-Díaz, A.G.; Cardona-Muñoz, E.G. The Role of Oxidative Stress in Physiopathology and Pharmacological Treatment with Pro- and Antioxidant Properties in Chronic Diseases. Oxidative Med. Cell Longev. 2020, 2020, 2082145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Li, X.K. Oxidative Stress in Atopic Dermatitis. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 2721469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solier, S.; Müller, S.; Cañeque, T.; Versini, A.; Mansart, A.; Sindikubwabo, F.; Baron, L.; Emam, L.; Gestraud, P.; Pantoș, G.D.; et al. A druggable copper-signalling pathway that drives inflammation. Nature 2023, 617, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- el-Kholy, M.S.; Gas Allah, M.A.; el-Shimi, S.; el-Baz, F.; el-Tayeb, H.; Abdel-Hamid, M.S. Zinc and copper status in children with bronchial asthma and atopic dermatitis. J. Egypt. Public Health Assoc. 1990, 65, 657–668. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Di Toro, R.; Galdo Capotorti, G.; Gialanella, G.; Miraglia del Giudice, M.; Moro, R.; Perrone, L. Zinc and copper status of allergic children. Acta Paediatr. Scand. 1987, 76, 612–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stelmach, I.; Grzelewski, T.; Bobrowska-Korzeniowska, M.; Kopka, M.; Majak, P.; Jerzynska, J.; Stelmach, W.; Polańska, K.; Sobala, W.; Gromadzińska, J.; et al. The role of zinc, copper, plasma glutathione peroxidase enzyme, and vitamins in the development of allergic diseases in early childhood: The Polish mother and child cohort study. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2014, 35, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Yin, J.; Hong, X.; Liu, R. Exposure to Heavy Metals and Allergic Outcomes in Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Biol. Trace Element Res. 2022, 200, 4615–4631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsvetkov, P.; Coy, S.; Petrova, B.; Dreishpoon, M.; Verma, A.; Abdusamad, M.; Rossen, J.; Joesch-Cohen, L.; Humeidi, R.; Spangler, R.D.; et al. Copper induces cell death by targeting lipoylated TCA cycle proteins. Science 2022, 375, 1254–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsvetkov, P.; Detappe, A.; Cai, K.; Keys, H.R.; Brune, Z.; Ying, W.; Thiru, P.; Reidy, M.; Kugener, G.; Rossen, J.; et al. Mitochondrial metabolism promotes adaptation to proteotoxic stress. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2019, 15, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, P.-Y.; Yen, H.-H.; Yang, T.-H.; Su, C.-C. Tetrathiomolybdate, a copper chelator inhibited imiquimod-induced skin inflammation in mice. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2018, 92, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Dong, Z.; Li, M.; Liu, L.; Luo, H.; Wang, P.; Zhang, D.; Yang, X.; Zhou, K.; Lei, S. Graphene Oxide/Copper Nanoderivatives-Modified Chitosan/Hyaluronic Acid Dressings for Facilitating Wound Healing in Infected Full-Thickness Skin Defects. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 8231–8247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Li, Y.; Du, C.; Sang, L.; Liu, L.; Li, Y.; Wang, F.; Fan, W.; Tang, P.; Zhang, S.; et al. Evidence of pyroptosis and ferroptosis extensively involved in autoimmune diseases at the single-cell transcriptome level. J. Transl. Med. 2022, 20, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Li, D.; Liang, Q.; Yang, M.; Pan, Y.; Li, H. Cross-talk between cuproptosis and ferroptosis regulators defines the tumor microenvironment for the prediction of prognosis and therapies in lung adenocarcinoma. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1029092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Lu, K.; Jiang, X.; Wei, Q.; Zhu, L.; Wang, X.; Jin, H.; Feng, L. Ferroptosis inducers enhanced cuproptosis induced by copper ionophores in primary liver cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. CR 2023, 42, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Zhou, C.; Ren, X.; Jing, Q.; Gao, Y.; Yang, C.; Shen, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Hu, W.; Jin, F.; et al. Inhibiting the compensatory elevation of xCT collaborates with disulfiram/copper-induced GSH consumption for cascade ferroptosis and cuproptosis. Redox Biol. 2024, 69, 103007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, M.E.; Phipson, B.; Wu, D.; Hu, Y.; Law, C.W.; Shi, W.; Smyth, G.K. limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, A.; Tamayo, P.; Mootha, V.K.; Mukherjee, S.; Ebert, B.L.; Gillette, M.A.; Paulovich, A.; Pomeroy, S.L.; Golub, T.R.; Lander, E.S.; et al. Gene set enrichment analysis: A knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 15545–15550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberzon, A.; Birger, C.; Thorvaldsdóttir, H.; Ghandi, M.; Mesirov, J.P.; Tamayo, P. The Molecular Signatures Database (MSigDB) hallmark gene set collection. Cell Syst. 2015, 1, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberzon, A.; Subramanian, A.; Pinchback, R.; Thorvaldsdóttir, H.; Tamayo, P.; Mesirov, J.P. Molecular signatures database (MSigDB) 3.0. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 1739–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langfelder, P.; Horvath, S. WGCNA: An R package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Wang, L.-G.; Han, Y.; He, Q.-Y. clusterProfiler: An R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters. OMICS J. Integr. Biol. 2012, 16, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S. KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warde-Farley, D.; Donaldson, S.L.; Comes, O.; Zuberi, K.; Badrawi, R.; Chao, P.; Franz, M.; Grouios, C.; Kazi, F.; Lopes, C.T.; et al. The GeneMANIA prediction server: Biological network integration for gene prioritization and predicting gene function. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, W214–W220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Robin, X.; Turck, N.; Hainard, A.; Tiberti, N.; Lisacek, F.; Sanchez, J.-C.; Müller, M. pROC: An open-source package for R and S+ to analyze and compare ROC curves. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Lv, X.; Li, Y.; Gao, X.; Ma, Z.; Fu, X.; Li, Y. Integrated Machine Learning and Single-Sample Gene Set Enrichment Analysis Identifies a TGF-Beta Signaling Pathway Derived Score in Headneck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Oncol. 2022, 2022, 3140263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, K.; Murphy, D. Application of ggplot2 to Pharmacometric Graphics. CPT Pharmacomet. Syst. Pharmacol. 2013, 2, e79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowowiejska, J.; Baran, A.; Flisiak, I. Lipid Alterations and Metabolism Disturbances in Selected Inflammatory Skin Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Min, J.; Wang, F. Copper homeostasis and cuproptosis in health and disease. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Zhuang, H.; Shao, S.; Zeng, X.; Xue, P.; Bai, T.; Wang, X.; Shangguan, S.; Chen, Y.; Yan, S.; et al. Mitochondrial-Targeted Copper Delivery for Cuproptosis-Based Synergistic Cancer Therapy. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2024, 13, e2304522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Hua, M.; Han, Y.; Yang, L.; Huang, Z.; Ran, J.; Wang, H.; Ren, F.; Yang, C.; Li, Z. Hijacking endogenous iron to amplify lysosomal-mitochondrial cascade damage for boosting anti-tumor immunotherapy. Biomaterials 2025, 316, 122983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sroka-Tomaszewska, J.; Trzeciak, M. Molecular Mechanisms of Atopic Dermatitis Pathogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, Y.; Park, K. Ceramides in Skin Health and Disease: An Update. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2021, 22, 853–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Sassa, T.; Kihara, A. Comparison of skin barrier abnormalities and epidermal ceramide profiles among three ω-O-acylceramide synthesis-deficient mouse strains. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2023, 113, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Yang, X.; Fan, Q.; Liu, B.; Hu, W.; Cui, Y. Transcriptomic profiling identifies differentially expressed genes and related pathways associated with wound healing and cuproptosis-related genes in Ganxi goats. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1149333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Fu, M.; Li, N.; Ye, M. Identification of immune infiltration and cuproptosis-related subgroups in Crohn’s disease. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1074271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Kang, R.; Tang, D. HMGB1 is a mediator of cuproptosis-related sterile inflammation. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 996307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, J.T.; Chang, C.; Higgs, R.E.; Engle, S.M.; Liu, Y.; Sissons, S.E.; Rodgers, G.H.; Simpson, E.L.; Silverberg, J.I.; Forman, S.B.; et al. Insights into adult atopic dermatitis heterogeneity derived from circulating biomarker profiling in patients with moderate-to-severe disease. Exp. Dermatol. 2021, 30, 1650–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafei-Shamsabadi, D.A.; Klose, C.S.N.; Halim, T.Y.F.; Tanriver, Y.; Jakob, T. Context Dependent Role of Type 2 Innate Lymphoid Cells in Allergic Skin Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, P.R.; Seminario-Vidal, L.; Abe, B.; Ghobadi, C.; Sims, J.T. Cytokines and Epidermal Lipid Abnormalities in Atopic Dermatitis: A Systematic Review. Cells 2023, 12, 2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujii, M. Current Understanding of Pathophysiological Mechanisms of Atopic Dermatitis: Interactions among Skin Barrier Dysfunction, Immune Abnormalities and Pruritus. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2020, 43, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutaria, N.; Adawi, W.; Goldberg, R.; Roh, Y.S.; Choi, J.; Kwatra, S.G. Itch: Pathogenesis and treatment. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2022, 86, 17–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wen, X.; Jia, S.; Wu, J.; Wang, S.; Yu, T.; Xu, H. Decoding Cuproptosis-Sphingolipid-Immune Crosstalk in Atopic Dermatitis: A Multi-Omics Network Analysis. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1349. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061349
Wen X, Jia S, Wu J, Wang S, Yu T, Xu H. Decoding Cuproptosis-Sphingolipid-Immune Crosstalk in Atopic Dermatitis: A Multi-Omics Network Analysis. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(6):1349. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061349
Chicago/Turabian StyleWen, Xiaowen, Shulin Jia, Jing Wu, Suitian Wang, Teng Yu, and Haoyou Xu. 2025. "Decoding Cuproptosis-Sphingolipid-Immune Crosstalk in Atopic Dermatitis: A Multi-Omics Network Analysis" Biomedicines 13, no. 6: 1349. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061349
APA StyleWen, X., Jia, S., Wu, J., Wang, S., Yu, T., & Xu, H. (2025). Decoding Cuproptosis-Sphingolipid-Immune Crosstalk in Atopic Dermatitis: A Multi-Omics Network Analysis. Biomedicines, 13(6), 1349. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061349





