The Role of Regulatory B Lymphocytes in Allergic Diseases
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. B-Cell Development, Activation and Differentiation
3. Regulatory B Cells
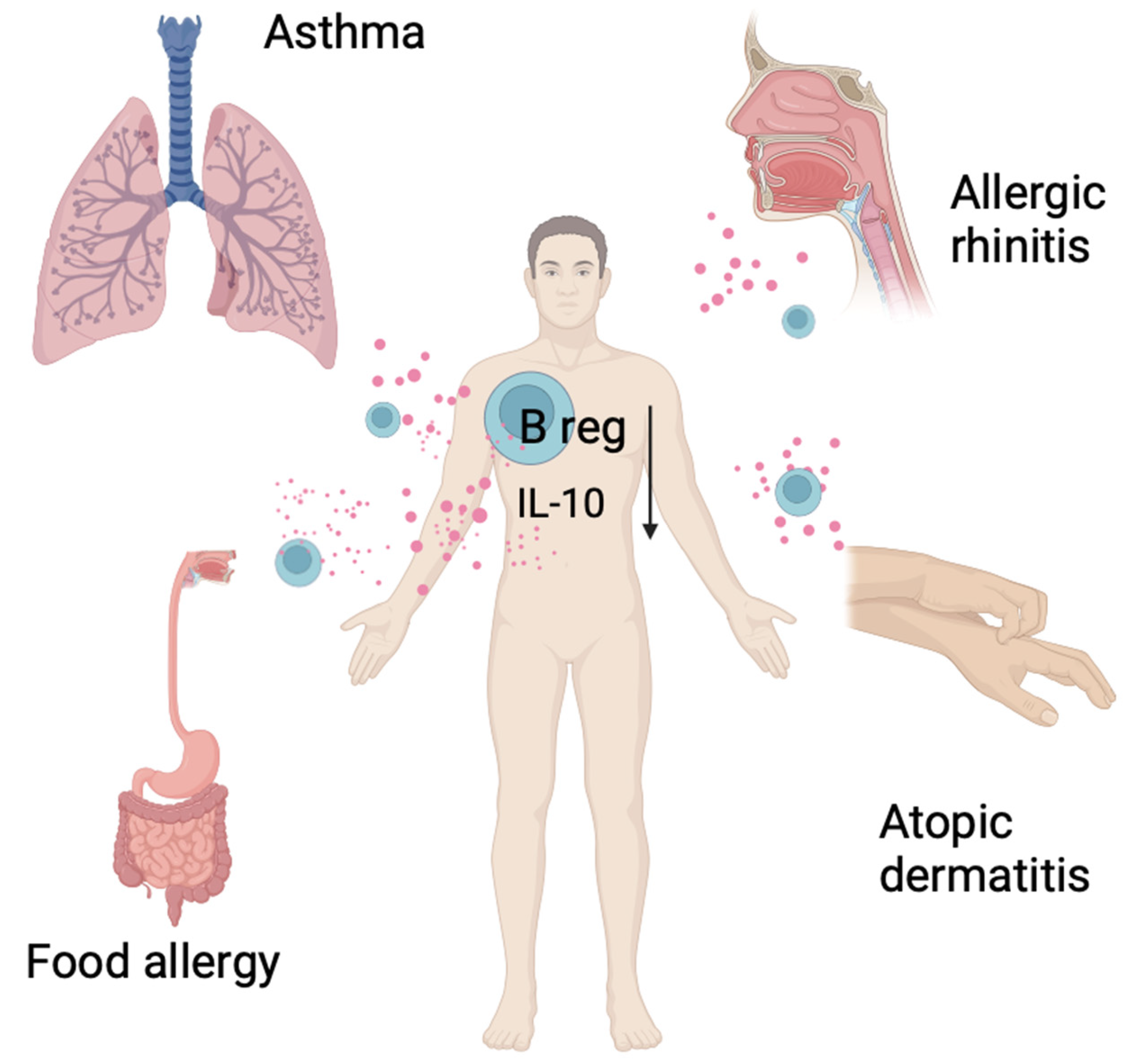
4. The Role of Regulatory B Cells in Allergic Diseases in Humans
5. Asthma
6. Atopic Dermatitis
7. Allergic Rhinitis
8. Food Allergy
9. Allergen Immunotherapy
10. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dang, M.; Yu, J.; Galant-Swafford, J.; Karam, S.D. The dichotomy of regulatory B cells in cancer versus allergic disease. Mol. Carcinog. 2024, 63, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Matsumura, Y.; Watanabe, R.; Fujimoto, M. Suppressive mechanisms of regulatory B cells in mice and humans. Int. Immunol. 2023, 35, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rosser, E.C.; Mauri, C. Regulatory B cells: Origin, phenotype, and function. Immunity 2015, 42, 607–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veh, J.; Ludwig, C.; Schrezenmeier, H.; Jahrsdörfer, B. Regulatory B Cells-Immunopathological and Prognostic Potential in Humans. Cells 2024, 13, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chekol Abebe, E.; Asmamaw Dejenie, T.; Mengie Ayele, T.; Dagnew Baye, N.; Agegnehu Teshome, A.; Tilahun Muche, Z. The role of regulatory B cells in health and diseases: A systemic review. J. Inflamm. Res. 2021, 14, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mickael, M.E.; Bieńkowska, I.; Sacharczuk, M. An Update on the Evolutionary History of Bregs. Genes 2022, 13, 890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tsai, D.Y.; Hung, K.H.; Chang, C.W.; Lin, K.I. Regulatory mechanisms of B cell responses and the implication in B cell-related diseases. J. Biomed. Sci. 2019, 26, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Patton, D.T.; Plumb, A.W.; Redpath, S.A.; Osborne, L.C.; Perona-Wright, G.; Abraham, N. The development and survival but not function of follicular B cells is dependent on IL-7Rα Tyr449 signaling. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88771, Erratum in PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e93316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wentink, M.W.J.; Kalina, T.; Perez-Andres, M.; Del Pino Molina, L.; IJspeert, H.; Kavelaars, F.G.; Lankester, A.C.; Lecrevisse, Q.; van Dongen, J.J.M.; Orfao, A.; et al. Delineating Human B Cell Precursor Development with Genetically Identified PID Cases as a Model. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Martin, V.G.; Wu, Y.B.; Townsend, C.L.; Lu, G.H.; O’Hare, J.S.; Mozeika, A.; Coolen, A.C.; Kipling, D.; Fraternali, F.; Dunn-Walters, D.K. Transitional B Cells in Early Human B Cell Development—Time to Revisit the Paradigm? Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Winkler, T.H.; Mårtensson, I.L. The Role of the Pre-B Cell Receptor in B Cell Development, Repertoire Selection, and Tolerance. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chung, J.B.; Silverman, M.; Monroe, J.G. Transitional B cells: Step by step towards immune competence. Trends Immunol. 2003, 24, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahaf, G.; Zisman-Rozen, S.; Benhamou, D.; Melamed, D.; Mehr, R. B Cell Development in the Bone Marrow Is Regulated by Homeostatic Feedback Exerted by Mature B Cells. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Noviski, M.; Mueller, J.L.; Satterthwaite, A.; Garrett-Sinha, L.A.; Brombacher, F.; Zikherman, J. IgM and IgD B cell receptors differentially respond to endogenous antigens and control B cell fate. eLife 2018, 7, e35074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kliem, C.V.; Schaub, B. The role of regulatory B cells in immune regulation and childhood allergic asthma. Mol. Cell Pediatr. 2024, 11, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Katz, S.I.; Parker, D.; Turk, J.L. B-cell suppression of delayed hypersensitivity reactions. Nature 1974, 251, 550–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, S.D.; Dittel, B.N.; Hardardottir, F.; Janeway, C.A., Jr. Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis induction in genetically B cell-deficient mice. J. Exp. Med. 1996, 184, 2271–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mizoguchi, A.; Mizoguchi, E.; Takedatsu, H.; Blumberg, R.S.; Bhan, A.K. Chronic intestinal inflammatory condition generates IL-10-producing regulatory B cell subset characterized by CD1d upregulation. Immunity 2002, 16, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clatworthy, M.R.; Watson, C.J.; Plotnek, G.; Bardsley, V.; Chaudhry, A.N.; Bradley, J.A.; Smith, K.G. B-cell-depleting induction therapy and acute cellular rejection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 2683–2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Guidelli, G.M.; Fioravanti, A.; Rubegni, P.; Feci, L. Induced psoriasis after rituximab therapy for rheumatoid arthritis: A case report and review of the literature. Rheumatol. Int. 2013, 33, 2927–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goetz, M.; Atreya, R.; Ghalibafian, M.; Galle, P.R.; Neurath, M.F. Exacerbation of ulcerative colitis after rituximab salvage therapy. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2007, 13, 1365–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dass, S.; Vital, E.M.; Emery, P. Development of psoriasis after B cell depletion with rituximab. Arthritis Rheum. 2007, 56, 2715–2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akdis, C.A.; Blesken, T.; Akdis, M.; Wüthrich, B.; Blaser, K. Role of interleukin 10 in specific immunotherapy. J. Clin. Investig. 1998, 102, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Shen, P.; Roch, T.; Lampropoulou, V.; O’Connor, R.A.; Stervbo, U.; Hilgenberg, E.; Ries, S.; Dang, V.D.; Jaimes, Y.; Daridon, C.; et al. IL-35-producing B cells are critical regulators of immunity during autoimmune and infectious diseases. Nature 2014, 507, 366–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mielle, J.; Audo, R.; Hahne, M.; Macia, L.; Combe, B.; Morel, J.; Daien, C. IL-10 Producing B Cells Ability to Induce Regulatory T Cells Is Maintained in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lindner, S.; Dahlke, K.; Sontheimer, K.; Hagn, M.; Kaltenmeier, C.; Barth, T.F.; Beyer, T.; Reister, F.; Fabricius, D.; Lotfi, R.; et al. Interleukin 21-induced granzyme B-expressing B cells infiltrate tumors and regulate T cells. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 2468–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nouël, A.; Pochard, P.; Simon, Q.; Ségalen, I.; Le Meur, Y.; Pers, J.O.; Hillion, S. B-Cells induce regulatory T cells through TGF-β/IDO production in A CTLA-4 dependent manner. J. Autoimmun. 2015, 59, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catalán, D.; Mansilla, M.A.; Ferrier, A.; Soto, L.; Oleinika, K.; Aguillón, J.C.; Aravena, O. Immunosuppressive Mechanisms of Regulatory B Cells. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 611795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Eiza, N.; Zuckerman, E.; Carlebach, M.; Rainis, T.; Goldberg, Y.; Vadasz, Z. Increased killer B cells in chronic HCV infection may lead to autoimmunity and increased viral load. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2018, 193, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Jansen, K.; Cevhertas, L.; Ma, S.; Satitsuksanoa, P.; Akdis, M.; van de Veen, W. Regulatory B cells, A to, Z. Allergy 2021, 76, 2699–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosser, E.C.; Mauri, C. The emerging field of regulatory B cell immunometabolism. Cell Metab. 2021, 33, 1088–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neves, P.; Lampropoulou, V.; Calderon-Gomez, E.; Roch, T.; Stervbo, U.; Shen, P.; Kühl, A.A.; Loddenkemper, C.; Haury, M.; Nedospasov, S.A.; et al. Signaling via the MyD88 adaptor protein in B cells suppresses protective immunity during Salmonella typhimurium infection. Immunity 2010, 33, 777–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blair, P.A.; Noreña, L.Y.; Flores-Borja, F.; Rawlings, D.J.; Isenberg, D.A.; Ehrenstein, M.R.; Mauri, C. CD19(+)CD24(hi)CD38(hi) B cells exhibit regulatory capacity in healthy individuals but are functionally impaired in systemic Lupus Erythematosus patients. Immunity 2010, 32, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosma, A.; Abdel-Gadir, A.; Isenberg, D.A.; Jury, E.C.; Mauri, C. Lipid-antigen presentation by CD1d(+) B cells is essential for the maintenance of invariant natural killer T cells. Immunity 2012, 36, 477–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Das, A.; Ellis, G.; Pallant, C.; Lopes, A.R.; Khanna, P.; Peppa, D.; Chen, A.; Blair, P.; Dusheiko, G.; Gill, U.; et al. IL-10-producing regulatory B cells in the pathogenesis of chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 3925–3935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Flores-Borja, F.; Bosma, A.; Ng, D.; Reddy, V.; Ehrenstein, M.R.; Isenberg, D.A.; Mauri, C. CD19+CD24hiCD38hi B cells maintain regulatory T cells while limiting TH1 and TH17 differentiation. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5, 173ra23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Cheng, L.S.; Wu, S.D.; Wang, S.Q.; Li, L.; She, W.M.; Li, J.; Wang, J.Y.; Jiang, W. IL-10-producing regulatory B-cells suppressed effector T-cells but enhanced regulatory T-cells in chronic HBV infection. Clin. Sci. 2016, 130, 907–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menon, M.; Blair, P.A.; Isenberg, D.A.; Mauri, C. A Regulatory Feedback between Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells and Regulatory B Cells Is Aberrant in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Immunity 2016, 44, 683–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Oleinika, K.; Rosser, E.C.; Matei, D.E.; Nistala, K.; Bosma, A.; Drozdov, I.; Mauri, C. CD1d-dependent immune suppression mediated by regulatory B cells through modulations of iNKT cells. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Khan, A.R.; Hams, E.; Floudas, A.; Sparwasser, T.; Weaver, C.T.; Fallon, P.G. PD-L1hi B cells are critical regulators of humoral immunity. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 5997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fehres, C.M.; van Uden, N.O.; Yeremenko, N.G.; Fernandez, L.; Franco Salinas, G.; van Duivenvoorde, L.M.; Huard, B.; Morel, J.; Spits, H.; Hahne, M.; et al. APRIL Induces a Novel Subset of IgA+ Regulatory B Cells That Suppress Inflammation via Expression of IL-10 and PD-L1. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sun, X.; Zhang, T.; Li, M.; Yin, L.; Xue, J. Immunosuppressive B cells expressing PD-1/PD-L1 in solid tumors: A mini review. QJM Int. J. Med. 2022, 115, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brosseau, C.; Durand, M.; Colas, L.; Durand, E.; Foureau, A.; Cheminant, M.A.; Bouchaud, G.; Castan, L.; Klein, M.; Magnan, A.; et al. CD9+ Regulatory B Cells Induce T Cell Apoptosis via IL-10 and Are Reduced in Severe Asthmatic Patients. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Matsumoto, M.; Baba, A.; Yokota, T.; Nishikawa, H.; Ohkawa, Y.; Kayama, H.; Kallies, A.; Nutt, S.L.; Sakaguchi, S.; Takeda, K.; et al. Interleukin-10-producing plasmablasts exert regulatory function in autoimmune inflammation. Immunity 2014, 41, 1040–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Masson, A.; Bouaziz, J.D.; Le Buanec, H.; Robin, M.; O’Meara, A.; Parquet, N.; Rybojad, M.; Hau, E.; Monfort, J.B.; Branchtein, M.; et al. CD24(hi)CD27+ and plasmablast-like regulatory B cells in human chronic graft-versus-host disease. Blood 2015, 125, 1830–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shalapour, S.; Font-Burgada, J.; Di Caro, G.; Zhong, Z.; Sanchez-Lopez, E.; Dhar, D.; Willimsky, G.; Ammirante, M.; Strasner, A.; Hansel, D.E.; et al. Immunosuppressive plasma cells impede T-cell-dependent immunogenic chemotherapy. Nature 2015, 521, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mao, H.; Pan, F.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, P.; Gou, M.; Dai, G. CD19loCD27hi Plasmablasts Suppress Harmful Th17 Inflammation Through Interleukin 10 Pathway in Colorectal Cancer. DNA Cell Biol. 2017, 36, 870–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fillatreau, S. Natural regulatory plasma cells. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2018, 55, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- van de Veen, W.; Stanic, B.; Yaman, G.; Wawrzyniak, M.; Söllner, S.; Akdis, D.G.; Rückert, B.; Akdis, C.A.; Akdis, M. IgG4 production is confined to human IL-10-producing regulatory B cells that suppress antigen-specific immune responses. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 131, 1204–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Q.; Yeung, M.; Camirand, G.; Zeng, Q.; Akiba, H.; Yagita, H.; Chalasani, G.; Sayegh, M.H.; Najafian, N.; Rothstein, D.M. Regulatory B cells are identified by expression of TIM-1 and can be induced through TIM-1 ligation to promote tolerance in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 3645–3656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Xiao, S.; Brooks, C.R.; Zhu, C.; Wu, C.; Sweere, J.M.; Petecka, S.; Yeste, A.; Quintana, F.J.; Ichimura, T.; Sobel, R.A.; et al. Defect in regulatory B-cell function and development of systemic autoimmunity in T-cell Ig mucin 1 (Tim-1) mucin domain-mutant mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 12105–12110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Xiao, S.; Brooks, C.R.; Sobel, R.A.; Kuchroo, V.K. Tim-1 is essential for induction and maintenance of IL-10 in regulatory B cells and their regulation of tissue inflammation. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 1602–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Aravena, O.; Ferrier, A.; Menon, M.; Mauri, C.; Aguillón, J.C.; Soto, L.; Catalán, D. TIM-1 defines a human regulatory B cell population that is altered in frequency and function in systemic sclerosis patients. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2017, 19, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gu, X.L.; He, H.; Lin, L.; Luo, G.X.; Wen, Y.F.; Xiang, D.C.; Qiu, J. Tim-1+ B cells suppress T cell interferon-gamma production and promote Foxp3 expression, but have impaired regulatory function in coronary artery disease. Apmis 2017, 125, 872–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, S.; Bod, L.; Pochet, N.; Kota, S.B.; Hu, D.; Madi, A.; Kilpatrick, J.; Shi, J.; Ho, A.; Zhang, H.; et al. Checkpoint Receptor TIGIT Expressed on Tim-1+ B Cells Regulates Tissue Inflammation. Cell Rep. 2020, 32, 107892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Iwata, Y.; Matsushita, T.; Horikawa, M.; Dilillo, D.J.; Yanaba, K.; Venturi, G.M.; Szabolcs, P.M.; Bernstein, S.H.; Magro, C.M.; Williams, A.D.; et al. Characterization of a rare IL-10-competent B-cell subset in humans that parallels mouse regulatory B10 cells. Blood 2011, 117, 530–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yanaba, K.; Bouaziz, J.D.; Haas, K.M.; Poe, J.C.; Fujimoto, M.; Tedder, T.F. A regulatory B cell subset with a unique CD1dhiCD5+ phenotype controls T cell-dependent inflammatory responses. Immunity 2008, 28, 639–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, J.R.; Quan, S.; Soliven, B. IL-10 derived from CD1dhiCD5+ B cells regulates experimental autoimmune myasthenia gravis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2015, 289, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chien, C.H.; Chiang, B.L. Regulatory T cells induced by B cells: A novel subpopulation of regulatory T cells. J. Biomed. Sci. 2017, 24, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Murakami, Y.; Saito, H.; Shimizu, S.; Kono, Y.; Shishido, Y.; Miyatani, K.; Matsunaga, T.; Fukumoto, Y.; Ashida, K.; Sakabe, T.; et al. Increased regulatory B cells are involved in immune evasion in patients with gastric cancer. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Daïen, C.I.; Tan, J.; Audo, R.; Mielle, J.; Quek, L.E.; Krycer, J.R.; Angelatos, A.; Duraes, M.; Pinget, G.; Ni, D.; et al. Gut-derived acetate promotes B10 cells with antiinflammatory effects. JCI Insight 2021, 6, e144156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Meng, X.; Grötsch, B.; Luo, Y.; Knaup, K.X.; Wiesener, M.S.; Chen, X.X.; Jantsch, J.; Fillatreau, S.; Schett, G.; Bozec, A. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α is a critical transcription factor for IL-10-producing B cells in autoimmune disease. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Piper, C.J.M.; Rosser, E.C.; Oleinika, K.; Nistala, K.; Krausgruber, T.; Rendeiro, A.F.; Banos, A.; Drozdov, I.; Villa, M.; Thomson, S.; et al. Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Contributes to the Transcriptional Program of IL-10-Producing Regulatory B Cells. Cell Rep. 2019, 29, 1878–1892.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hagn, M.; Schwesinger, E.; Ebel, V.; Sontheimer, K.; Maier, J.; Beyer, T.; Syrovets, T.; Laumonnier, Y.; Fabricius, D.; Simmet, T.; et al. Human B cells secrete granzyme B when recognizing viral antigens in the context of the acute phase cytokine IL-21. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 1838–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahrsdörfer, B.; Blackwell, S.E.; Wooldridge, J.E.; Huang, J.; Andreski, M.W.; Jacobus, L.S.; Taylor, C.M.; Weiner, G.J. B-chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells and other B cells can produce granzyme B and gain cytotoxic potential after interleukin-21-based activation. Blood 2006, 108, 2712–2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chesneau, M.; Michel, L.; Dugast, E.; Chenouard, A.; Baron, D.; Pallier, A.; Durand, J.; Braza, F.; Guerif, P.; Laplaud, D.A.; et al. Tolerant Kidney Transplant Patients Produce B Cells with Regulatory Properties. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 26, 2588–2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kaltenmeier, C.; Gawanbacht, A.; Beyer, T.; Lindner, S.; Trzaska, T.; van der Merwe, J.A.; Härter, G.; Grüner, B.; Fabricius, D.; Lotfi, R.; et al. CD4+ T cell-derived IL-21 and deprivation of CD40 signaling favor the in vivo development of granzyme B-expressing regulatory B cells in HIV patients. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 3768–3777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagn, M.; Ebel, V.; Sontheimer, K.; Schwesinger, E.; Lunov, O.; Beyer, T.; Fabricius, D.; Barth, T.F.; Viardot, A.; Stilgenbauer, S.; et al. CD5+ B cells from individuals with systemic lupus erythematosus express granzyme, B. Eur. J. Immunol. 2010, 40, 2060–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Zhu, X.; Liu, H.; Zeng, M.; Graner, M.W.; Zhou, B.; Chen, X. CD19(+)CD1d(+)CD5(+) B cell frequencies are increased in patients with tuberculosis and suppress Th17 responses. Cell Immunol. 2012, 274, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Zeng, G.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, X.; Chen, Q.; Suthakaran, P.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, Q.; Liu, H.; et al. Anti-tuberculosis treatment enhances the production of IL-22 through reducing the frequencies of regulatory B cell. Tuberculosis 2014, 94, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimura, S.; Manabe, I.; Takaki, S.; Nagasaki, M.; Otsu, M.; Yamashita, H.; Sugita, J.; Yoshimura, K.; Eto, K.; Komuro, I.; et al. Adipose Natural Regulatory B Cells Negatively Control Adipose Tissue Inflammation. Cell Metab. 2013, 18, 759–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Hernández, M.H.; Rodríguez-Varela, E.; García-Jacobo, R.E.; Hernández-De la Torre, M.; Uresti-Rivera, E.E.; González-Amaro, R.; Portales-Pérez, D.P. Frequency of regulatory B cells in adipose tissue and peripheral blood from individuals with overweight, obesity and normal-weight. Obes. Res. Clin. Pract. 2018, 12, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saze, Z.; Schuler, P.J.; Hong, C.S.; Cheng, D.; Jackson, E.K.; Whiteside, T.L. Adenosine production by human B cells and B cell-mediated suppression of activated T cells. Blood 2013, 122, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kaku, H.; Cheng, K.F.; Al-Abed, Y.; Rothstein, T.L. A novel mechanism of B cell-mediated immune suppression through CD73 expression and adenosine production. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 5904–5913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ma, S.; Satitsuksanoa, P.; Jansen, K.; Cevhertas, L.; van de Veen, W.; Akdis, M. B regulatory cells in allergy. Immunol. Rev. 2021, 299, 10–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castagnoli, R.; Brambilla, I.; Giovannini, M.; Marseglia, G.L.; Licari, A. New approaches in childhood asthma treatment. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2023, 23, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- van der Vlugt, L.E.; Mlejnek, E.; Ozir-Fazalalikhan, A.; Janssen Bonas, M.; Dijksman, T.R.; Labuda, L.A.; Schot, R.; Guigas, B.; Möller, G.M.; Hiemstra, P.S.; et al. CD24(hi)CD27(+) B cells from patients with allergic asthma have impaired regulatory activity in response to lipopolysaccharide. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2014, 44, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, K.; Jin, L.; Yu, S. Roles of regulatory B cells in the pathogenesis of allergic rhinitis. Allergol. Immunopathol. 2022, 50, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lommatzsch, M.; Dost, M.; Jaishankar, N.; Weise, M.; Stoll, P.; Virchow, J.C.; Bratke, K. Dupilumab treatment increases transitional B cells in severe asthma. Allergy 2023, 78, 2055–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, G.; Jiang, W.; Sun, D.; Sun, Z.; Chen, A.; Fang, H.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Yin, Z.; Wei, H.; et al. B-cell-derived IL-10 promotes allergic sensitization in asthma regulated by Bcl-3. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2023, 20, 1313–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Miyajima, S.; Shigehara, K.; Kamekura, R.; Takaki, H.; Yabe, H.; Ikegami, I.; Asai, Y.; Nishikiori, H.; Chiba, H.; Uno, E.; et al. Activated circulating T follicular helper cells and skewing of T follicular helper 2 cells are down-regulated by treatment including an inhaled corticosteroid in patients with allergic asthma. Allergol. Int. 2020, 69, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wirz, O.F.; Głobińska, A.; Ochsner, U.; van de Veen, W.; Eller, E.; Christiansen, E.S.; Halken, S.; Nielsen, C.; Bindslev-Jensen, C.; Antó, J.M.; et al. Comparison of regulatory B cells in asthma and allergic rhinitis. Allergy 2019, 74, 815–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braza, F.; Chesne, J.; Castagnet, S.; Magnan, A.; Brouard, S. Regulatory functions of B cells in allergic diseases. Allergy 2014, 69, 1454–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mota, I.; Martins, C.; Borrego, L.M. Regulatory B Cells and Allergy: Uncovering the Link. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2024, 27, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhivaki, D.; Lemoine, S.; Lim, A.; Morva, A.; Vidalain, P.O.; Schandene, L.; Casartelli, N.; Rameix-Welti, M.A.; Hervé, P.L.; Dériaud, E.; et al. Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infects Regulatory B Cells in Human Neonates via Chemokine Receptor CX3CR1 and Promotes Lung Disease Severity. Immunity 2017, 46, 301–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sheehan, W.J.; Maghzian, N.; Rastogi, D.; Bollard, C.M.; Lin, A.A. Decreased regulatory B cells in pediatric patients with asthma. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2023, 131, 120–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mei-Yen Yong, A.; Tay, Y.K. Atopic Dermatitis: Racial and Ethnic Differences. Dermatol. Clin. 2017, 35, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshihara, Y.; Ishiuji, Y.; Yoshizaki, A.; Kurita, M.; Hayashi, M.; Ishiji, T.; Nakagawa, H.; Asahina, A.; Yanaba, K. IL-10-Producing Regulatory B Cells Are Decreased in Patients with Atopic Dermatitis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2019, 139, 475–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.; Jo, M.G.; Min, K.Y.; Choi, M.Y.; Kim, Y.M.; Kim, H.S.; Choi, W.S. IL-10+ regulatory B cells mitigate atopic dermatitis by suppressing eosinophil activation. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 18164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Čelakovská, J.; Čermáková, E.; Boudková, P.; Andrýs, C.; Krejsek, J. Evaluation of Leukocytes, B and T Lymphocytes, and expression of CD200 and CD23 on B lymphocytes in Patients with Atopic Dermatitis on Dupilumab Therapy-Pilot Study. Dermatol. Ther. 2023, 13, 1171–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Siddiqui, Z.A.; Walker, A.; Pirwani, M.M.; Tahiri, M.; Syed, I. Allergic rhinitis: Diagnosis and management. Br. J. Hosp. Med. 2022, 83, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, A.S.; Doherty, T.A.; Karta, M.R.; Das, S.; Baum, R.; Rosenthal, P.; Beppu, A.; Miller, M.; Kurten, R.; Broide, D.H. Regulatory B cells and T follicular helper cells are reduced in allergic rhinitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 138, 1192–1195.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Luo, J.; Guo, H.; Liu, Z.; Peng, T.; Hu, X.; Han, M.; Yang, X.; Zhou, X.; Li, H. Analysis of Peripheral B Cell Subsets in Patients With Allergic Rhinitis. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2018, 10, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kamekura, R.; Shigehara, K.; Miyajima, S.; Jitsukawa, S.; Kawata, K.; Yamashita, K.; Nagaya, T.; Kumagai, A.; Sato, A.; Matsumiya, H.; et al. Alteration of circulating type 2 follicular helper T cells and regulatory B cells underlies the comorbid association of allergic rhinitis with bronchial asthma. Clin. Immunol. 2015, 158, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamji, M.H.; Kappen, J.; Abubakar-Waziri, H.; Zhang, J.; Steveling, E.; Watchman, S.; Kouser, L.; Eifan, A.; Switzer, A.; Varricchi, G.; et al. Nasal allergen-neutralizing IgG4 antibodies block IgE-mediated responses: Novel biomarker of subcutaneous grass pollen immunotherapy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 143, 1067–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, R.L.; Krawiec, M.; Koplin, J.J.; Santos, A.F. Update on food allergy. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2021, 32, 647–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhang, S.; Sicherer, S.; Berin, M.C.; Agyemang, A. Pathophysiology of Non-IgE-Mediated Food Allergy. Immunotargets Ther. 2021, 10, 431–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Noh, J.; Lee, J.H.; Noh, G.; Bang, S.Y.; Kim, H.S.; Choi, W.S.; Cho, S.; Lee, S.S. Characterisation of allergen-specific responses of IL-10-producing regulatory B cells (Br1) in Cow Milk Allergy. Cell Immunol. 2010, 264, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noh, J.; Noh, G.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, A.R.; Choi, W.S. Allergen-specific responses of CD19(+)CD5(+)Foxp3(+) regulatory B cells (Bregs) and CD4(+)Foxp3(+) regulatory T cell (Tregs) in immune tolerance of cow milk allergy of late eczematous reactions. Cell Immunol. 2012, 274, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Noh, J.; Noh, G.; Choi, W.S.; Cho, S.; Lee, S.S. Allergen-specific transforming growth factor-β-producing CD19+CD5+ regulatory B-cell (Br3) responses in human late eczematous allergic reactions to cow’s milk. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2011, 31, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, G.G. The global burden of IBD: From 2015 to 2025. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 12, 720–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Guo, C.; Zhao, F.; Zhu, J.; Xu, Y.; Liu, Z.Q.; Yang, G.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Gu, X.; Xiao, L.; et al. Vasoactive intestinal peptide stabilizes intestinal immune homeostasis through maintaining interleukin-10 expression in regulatory B cells. Theranostics 2019, 9, 2800–2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Durham, S.R.; Shamji, M.H. Allergen immunotherapy: Past, present and future. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2023, 23, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- van de Veen, W.; Akdis, M. Role of IgG4 in IgE-mediated allergic responses. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 138, 1434–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boonpiyathad, T.; van de Veen, W.; Wirz, O.; Sokolowska, M.; Rückert, B.; Tan, G.; Sangasapaviliya, A.; Pradubpongsa, P.; Fuengthong, R.; Thantiworasit, P.; et al. Role of Der p 1-specific B cells in immune tolerance during 2 years of house dust mite-specific immunotherapy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 143, 1077–1086.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharif, H.; Singh, I.; Kouser, L.; Mösges, R.; Bonny, M.A.; Karamani, A.; Parkin, R.V.; Bovy, N.; Kishore, U.; Robb, A.; et al. Immunologic mechanisms of a short-course of Lolium perenne peptide immunotherapy: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 144, 738–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cierzniak, A.; Kaliszewski, K.; Małodobra-Mazur, M. The Preliminary Evaluation of Epigenetic Modifications Regulating the Expression of IL10 in Insulin-Resistant Adipocytes. Genes 2022, 13, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Boonpiyathad, T.; Meyer, N.; Moniuszko, M.; Sokolowska, M.; Eljaszewicz, A.; Wirz, O.F.; Tomasiak-Lozowska, M.M.; Bodzenta-Lukaszyk, A.; Ruxrungtham, K.; van de Veen, W. High-dose bee venom exposure induces similar tolerogenic B-cell responses in allergic patients and healthy beekeepers. Allergy 2017, 72, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiest, M.; Upchurch, K.; Hasan, M.M.; Cardenas, J.; Lanier, B.; Millard, M.; Turner, J.; Oh, S.; Joo, H. Phenotypic and functional alterations of regulatory B cell subsets in adult allergic asthma patients. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2019, 49, 1214–1224, Erratum in Clin. Exp. Allergy 2019, 49, 1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampath, V.; Sindher, S.B.; Alvarez Pinzon, A.M.; Nadeau, K.C. Can food allergy be cured? What are the future prospects? Allergy 2020, 75, 1316–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| A Type of Regulatory B Cell | Location | Phenotype | Immunosuppressive Molecules | Author/Year | Mouse Equivalent |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Immature transitional B cell | Peripheral blood, liver | CD19+CD24hi CD38hi CD1dhi | IL-10, CD80/86 | Blair et al., 2010, Bosma et al., 2012, Das et al., 2012, Flores-Borja et al., 2013, Liu et al., 2016, Menon et al., 2016, Oleinika et al., 2018 [33,34,35,36,37,38,39] | No |
| PD-L1 hi B cells | Solid tumors, spleen | CD19+PD-L1hi | PD-L1, IgA, IL-10 | Khan et al., 2015, Feres et al., 2019, Sun et al., 2019 [40,41,42] | Yes |
| CD9+ B cells | Peripheral blood, spleen | CD19+CD9+ | IL-10 | Brosseau et al., 2018 [43] | Yes |
| Plasmablasts | Peripheral blood, lymph nodes, spleen | CD19+CD24hi CD27int CD38+CD138+IgA+PD-L1− IL-10+ | IL-10, TGF-β | Matsumoto et al., 2014, de Masson et al., 2015, Shalapour et al., 2015, Mao et al., 2017, Fillatreau et al., 2018, Fehres et al., 2019 [41,44,45,46,47,48] | Yes |
| Br1 cells | Peripheral blood | CD19+CD25+CD71hi CD73lo | IL-10, IgG4 | Van de Veen et al., 2013 [49] | No |
| Tim1+ B cells | Peripheral blood, spleen | CD19+Tim-1+ | IL-10 | Ding et al., 2011, Xiao et al., 2012, Xiao et al., 2015, Aravena et al., 2017, Gu et al., 2017, Xiao et al., 2020 [50,51,52,53,54,55] | Yes |
| B10 B cells | Peripheral blood, spleen, astric mucosa, stomach cancer | CD19+CD24hi CD27+ | IL-10 | Iwata et al., 2011, Yanaba et al., 2008, Sheng et al., 2015, Chien et al., 2017, Murakami et al., 2019, Daien et al., 2021, Meng et al., 2018, Piper et al., 2019 [56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63] | Yes |
| Granzyme B+ lymphocytes (GraB cells) | Peripheral blood, solid tumors | CD19+CD20+GrB+CD86+CD147+, IDO+, (CD38±CD25±CD27+CD1d±CD5±CD10+IgM±) | Granzyme B, IDO, CD25 | Hagn et al., 2009, Lindner et al., 2013, Jahrsdorfer et al., 2006, Chesneau et al., 2015, Kaltenmeier et al., 2015 [26,64,65,66,67] | No |
| CD5+ B cells | Peripheral blood | CD19+CD5+GrB+ CD1dhi | Granzyme B, IL-10 | Hagn et al., 2010, Zhang et al., 2012, Zhang et al., 2014 [68,69,70] | Yes |
| Adipose tissue B lymphocytes | Adipose tissue | CD19+ CD27+CD38hi | IL-10 | Nishimura et al., 2013, Garcia-Hernandez et al., 2018 [71,72] | Yes |
| CD39+CD73+ B cells | Peripheral blood, spleen | CD19+CD39+ CD73+ | AMP/Adenosine | Saze 2013, Kaku 2014 [73,74] | Yes |
| Disease or Therapy | Feature of Regulatory B Cells | Author/Year |
|---|---|---|
| Asthma | Reduced ability of CD24++CD27+ regulatory B cells to produce IL-10 in response to LPS94 stimulation | Van der Vlugt et al., 2014 [77] |
| Reduced ability of B regs to produce IL-10 in response to CpG95 stimulation | Wirz et al., 2019 [82] | |
| Reduced number of CD5+ and CD1d+CD5+ B lymphocytes | Wiest et al., 2019 [109] | |
| CD9+ regulatory B lymphocytes induce apoptosis of CD3+CD4+CD25+ effector T lymphocytes | Braza et al., 2014, Brosseau et al., 2018 [43,83] | |
| The number of regulatory B cells infected with RSV is proportional to the viremia and to the reduced number of Th1 lymphocytes in the serum | Zhiyaki et al., 2017 [85] | |
| Reduced number of B regs in children and adolescents with bronchial asthma | Sheehan et al., 2023 [86] | |
| Lower absolute number and percentage of B regs in asthma patients compared to the healthy group | Miyaijma et al., 2020 [81] | |
| Atopic dermatitis | The occurrence of regulatory B cells of the CD24hiCD38hi type is reduced, and the severity of the disease is inversely proportional to the number of this type of regulatory B cells. The ability of regulatory B cells to produce IL-10 is lower in response to IL-6 stimulation | Yoshihara et al., 2019 [88] |
| B regs, through the secretion of IL-10, inhibit eosinophil activation, including degranulation and EPO secretion. | Lee et al., 2024 [89] | |
| Allergic rhinitis | Increased number of regulatory B lymphocytes of the CD19+CD24hi CD27+ type, decreased number of CD19+CD24hi CD38hi, CD19+CD25+CD71+CD73 and CD19+CD5hiCD1d+ lymphocytes | Kim et al., 2016, Luo et al., 2018 [92,93] |
| The occurrence of CD19+CD25+CD71+ regulatory B cells producing IL-10 after TLR9 stimulation is reduced | Wirz et al., 2019 [82] | |
| Lower percentage of IL-10 secreting Bregs of the CD19+CD24hiCD38hi and CD19+CD5hiCD1d+ type in patients with seasonal ANN compared to the control group. Increased concentration of both above-mentioned Bregs types in patients after treatment with allergen immunotherapy (SCIT, subcutaneous immunotherapy) | Shamji 2019 [95] | |
| Food allergies | The number of CD19+CD5+ regulatory B cells is reduced in patients with milk allergy compared to the control group | Noh et al., 2010 [98] |
| CD19+CD25+CD71+CD73- regulatory B cells have reduced ability to secrete IL-10. Proliferation of CD4+CD25+ regulatory B cells is increased in patients with ulcerative colitis | Sun et al., 2019 [102] | |
| The number of TGF-β+CD19+CD5+ and CD19+CD5+Foxp3+ regulatory B cells is reduced in patients with cow’s milk allergy | Sun et al., 2019, Sampath 2020 [102,110] | |
| CD19+CD25+CD71+ regulatory B cells secrete reduced amounts of IL-10 | Kaplan 2015 [101] | |
| Allergen immunotherapy | Increased number of IL-0+ and/or IL-1RA+ regulatory B cells in patients using AIT with house dust mite allergens | Boonpiyathad et al., 2019 [105] |
| Allergen immunotherapy induces the development of IL-35+ and IL-10+ regulatory T lymphocytes and regulatory B lymphocytes | Sharif 2019 [106] | |
| During the allergy season, the number of IL-10 regulatory B cells is increased in people who are allergic to a given alergen | Shamji et al., 2019 [95] | |
| In beekeepers and patients after AIT, an increase in the number of D73-CD25+CD71+IL-10+ BR1 lymphocytes is observed | Boonpiyathad et al., 2017 [108] | |
| The percentage of IL-10 regulatory B cells specific for bee venom allergens is increased compared to nonspecific B cells. Naïve CD27- regulatory B cells are characterized by increased selective IgG4 production compared to IL-10-naïve cells | Van de Veen et al., 2013 [49] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lipińska-Opałka, A.; Leszczyńska-Pilich, M.; Będzichowska, A.; Tomaszewska, A.; Rustecka, A.; Kalicki, B. The Role of Regulatory B Lymphocytes in Allergic Diseases. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2721. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122721
Lipińska-Opałka A, Leszczyńska-Pilich M, Będzichowska A, Tomaszewska A, Rustecka A, Kalicki B. The Role of Regulatory B Lymphocytes in Allergic Diseases. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(12):2721. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122721
Chicago/Turabian StyleLipińska-Opałka, Agnieszka, Michalina Leszczyńska-Pilich, Agata Będzichowska, Agata Tomaszewska, Agnieszka Rustecka, and Bolesław Kalicki. 2024. "The Role of Regulatory B Lymphocytes in Allergic Diseases" Biomedicines 12, no. 12: 2721. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122721
APA StyleLipińska-Opałka, A., Leszczyńska-Pilich, M., Będzichowska, A., Tomaszewska, A., Rustecka, A., & Kalicki, B. (2024). The Role of Regulatory B Lymphocytes in Allergic Diseases. Biomedicines, 12(12), 2721. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122721






