Analysis of the Influence of IL-6 and the Activation of the Jak/Stat3 Pathway in Fibromyalgia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Induction of Fibromyalgia
2.3. IL-6 Ab Administration
2.4. Experimental Groups
2.5. Behavioral Analyses
2.5.1. Von Frey Hair Test
2.5.2. Hot-Plate Test
2.5.3. Tail-Flick Warm-Water Test
2.6. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
2.7. Western-Blot Analysis
2.8. Immunohistochemical Analysis
2.9. ELISA Analysis
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
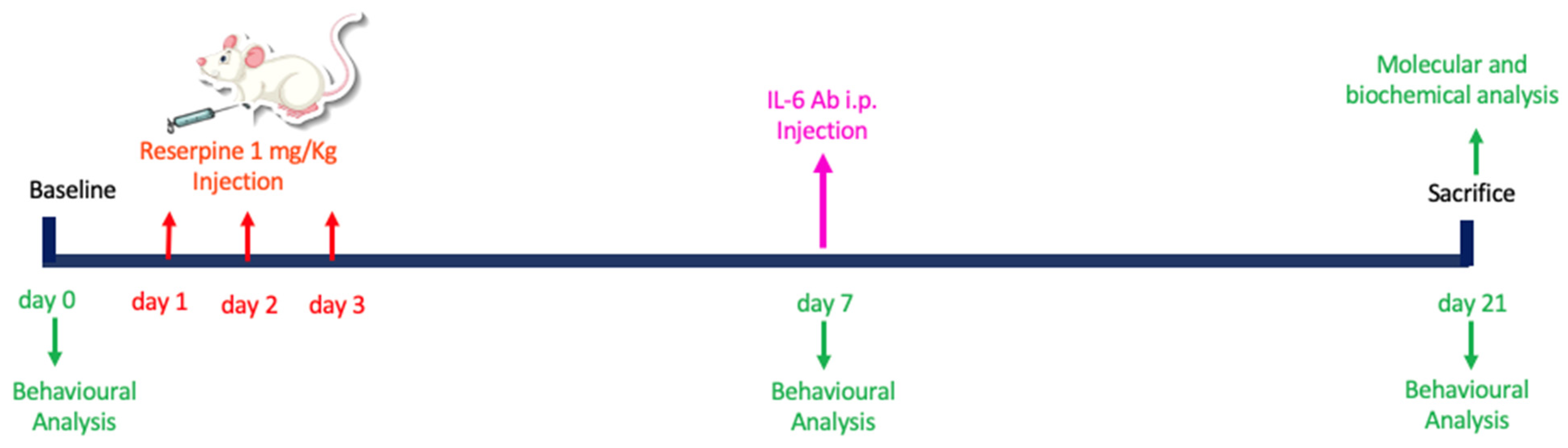
3.1. Experimental Timeline
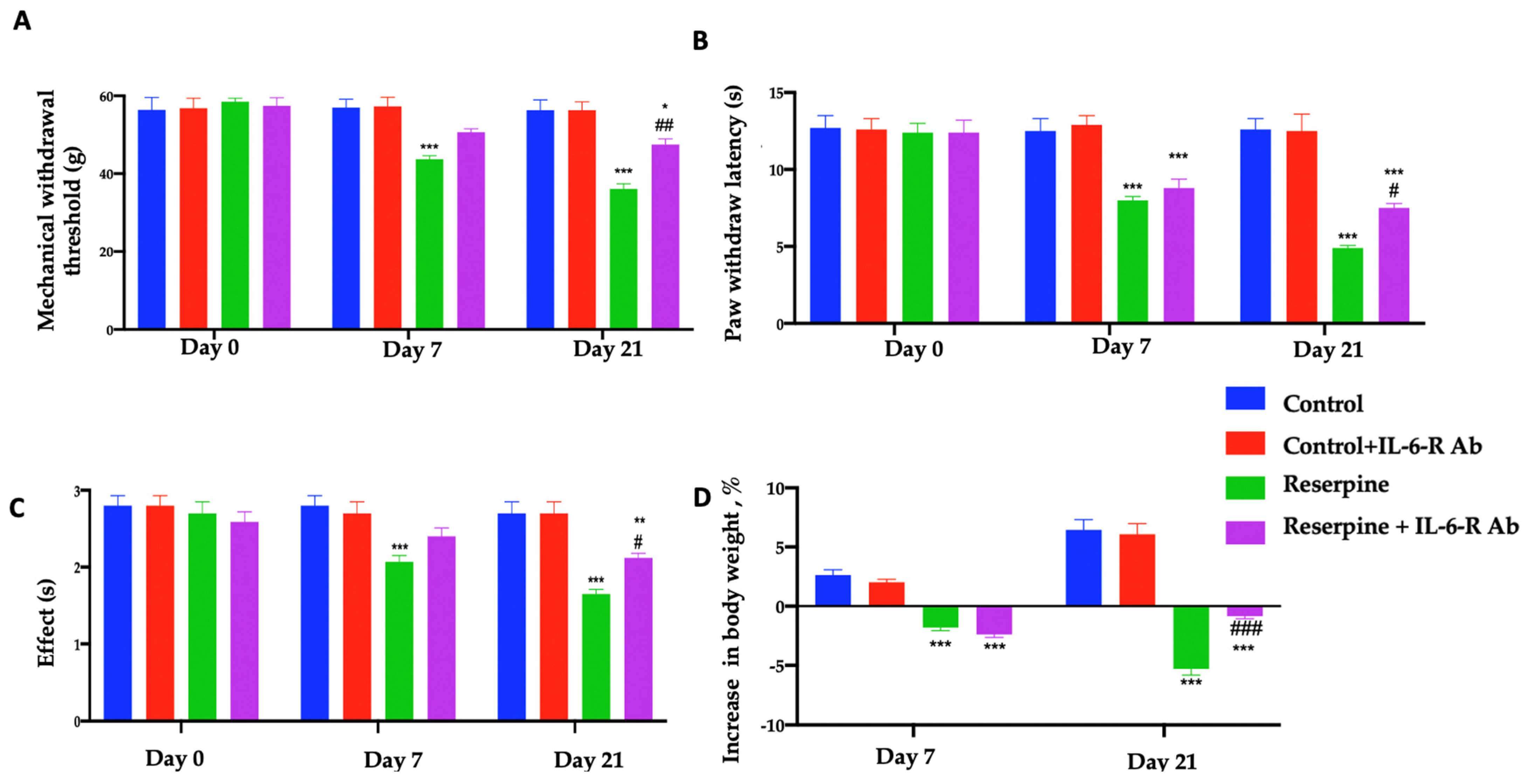
3.2. Analysis of Pain-like Behaviours
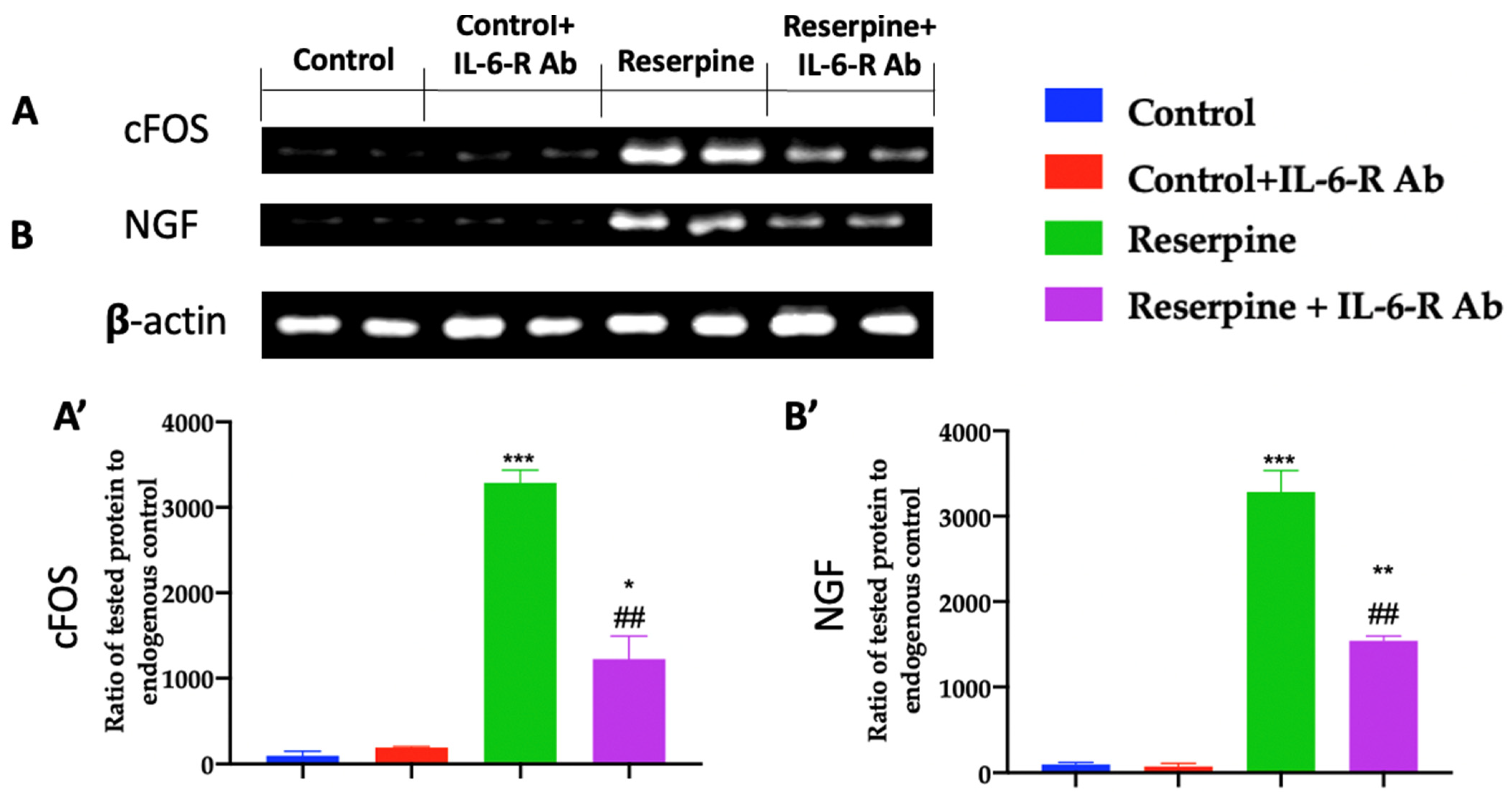
3.3. Analysis of Pain-Related Mediators
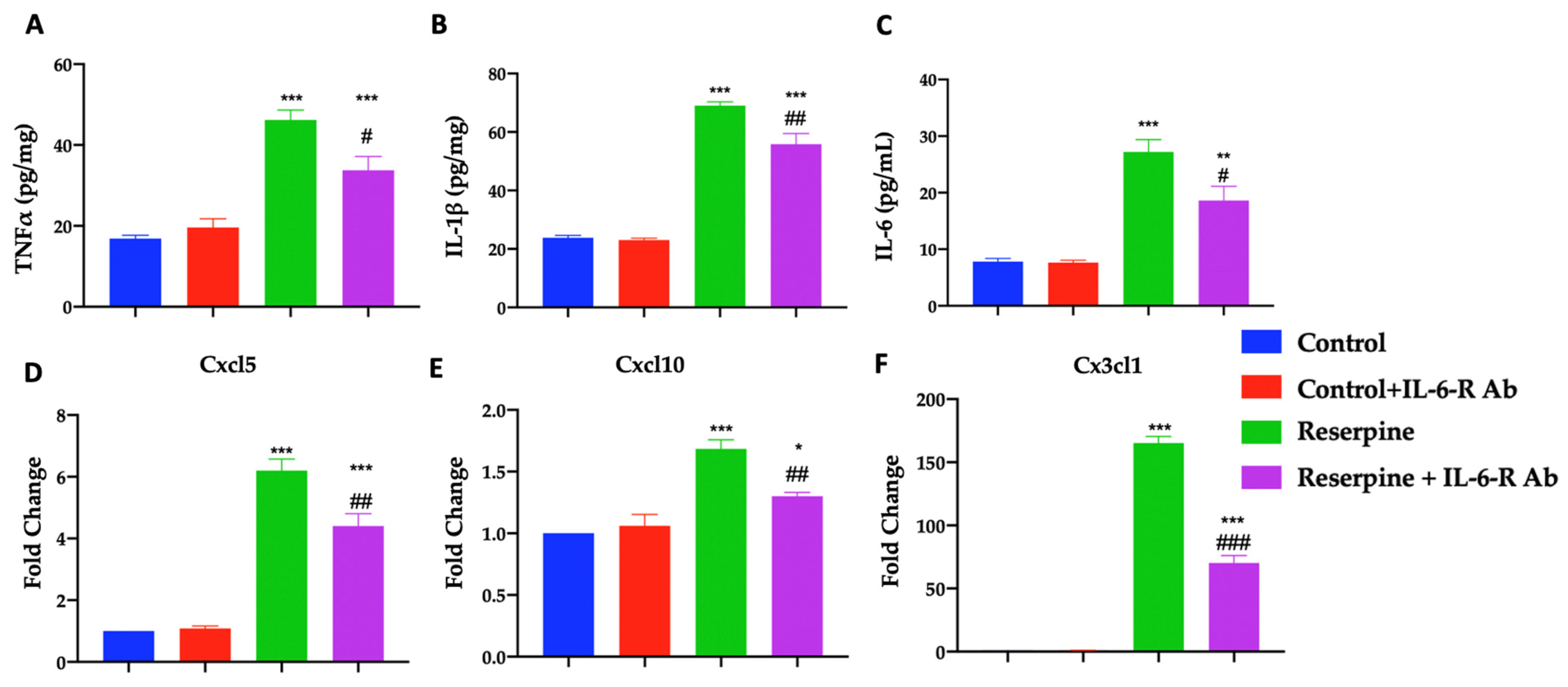
3.4. Analysis of Pro-Inflammatory Mediators
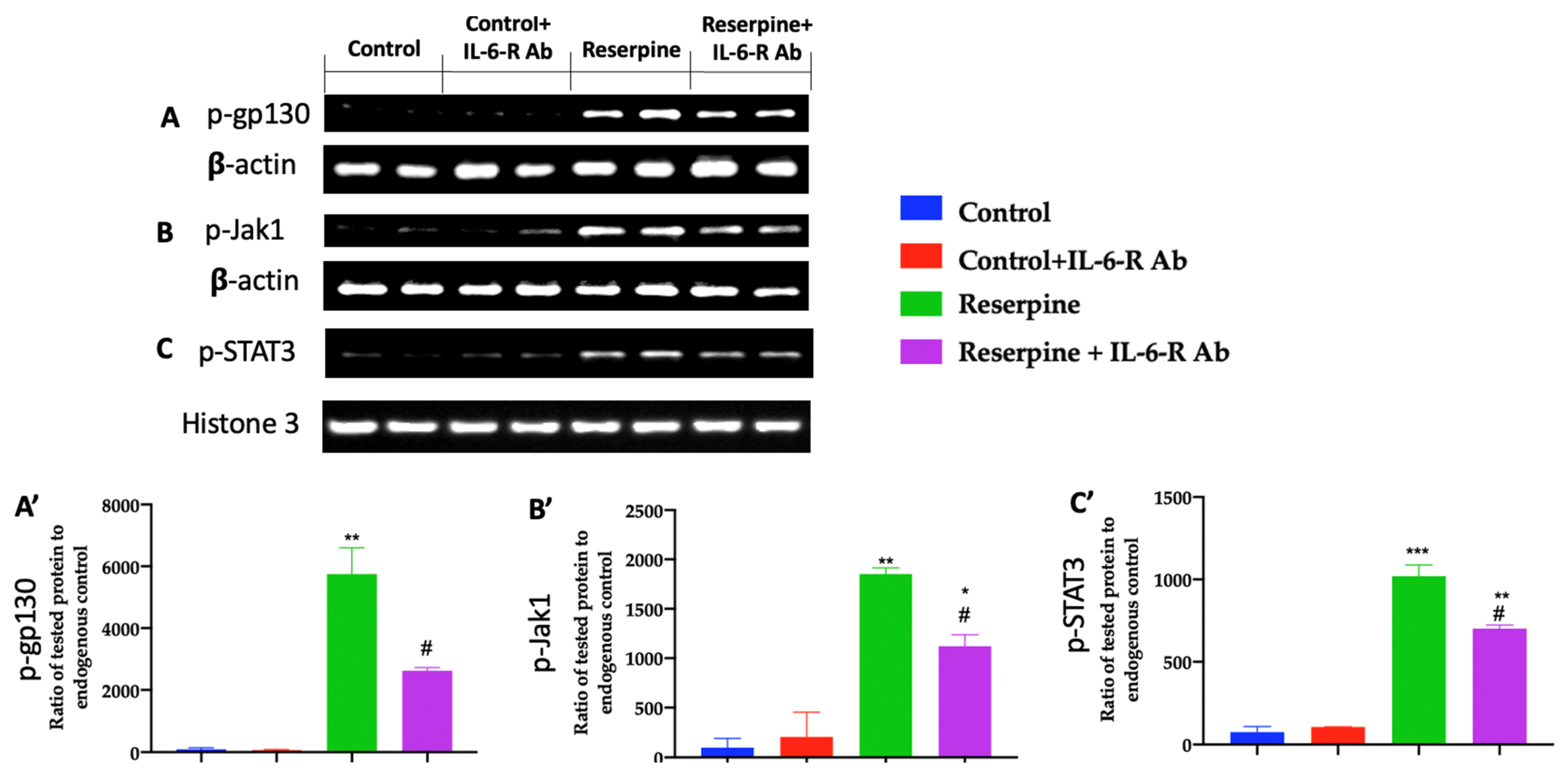
3.5. Analysis of the Jak/Stat Pathway
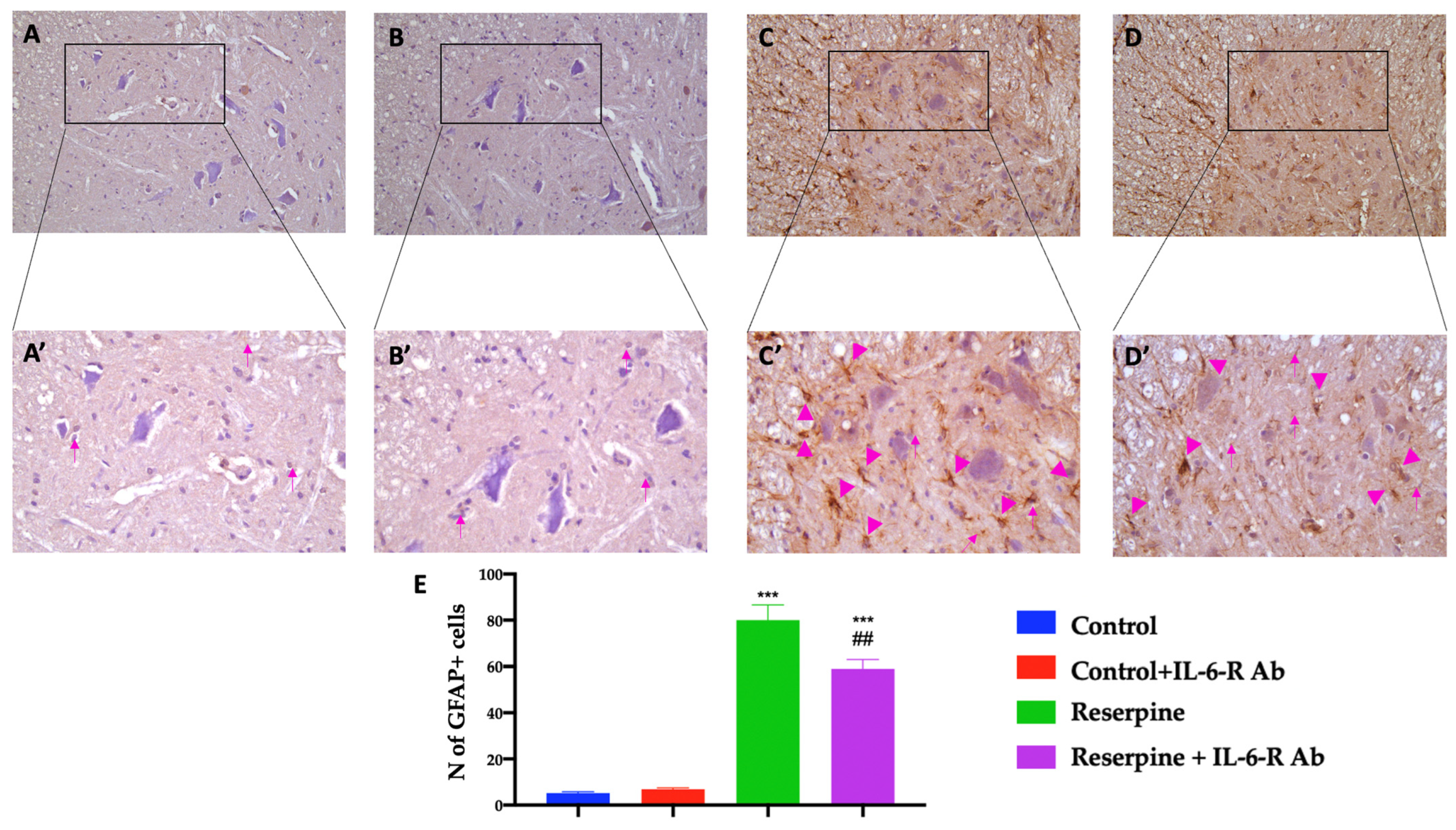
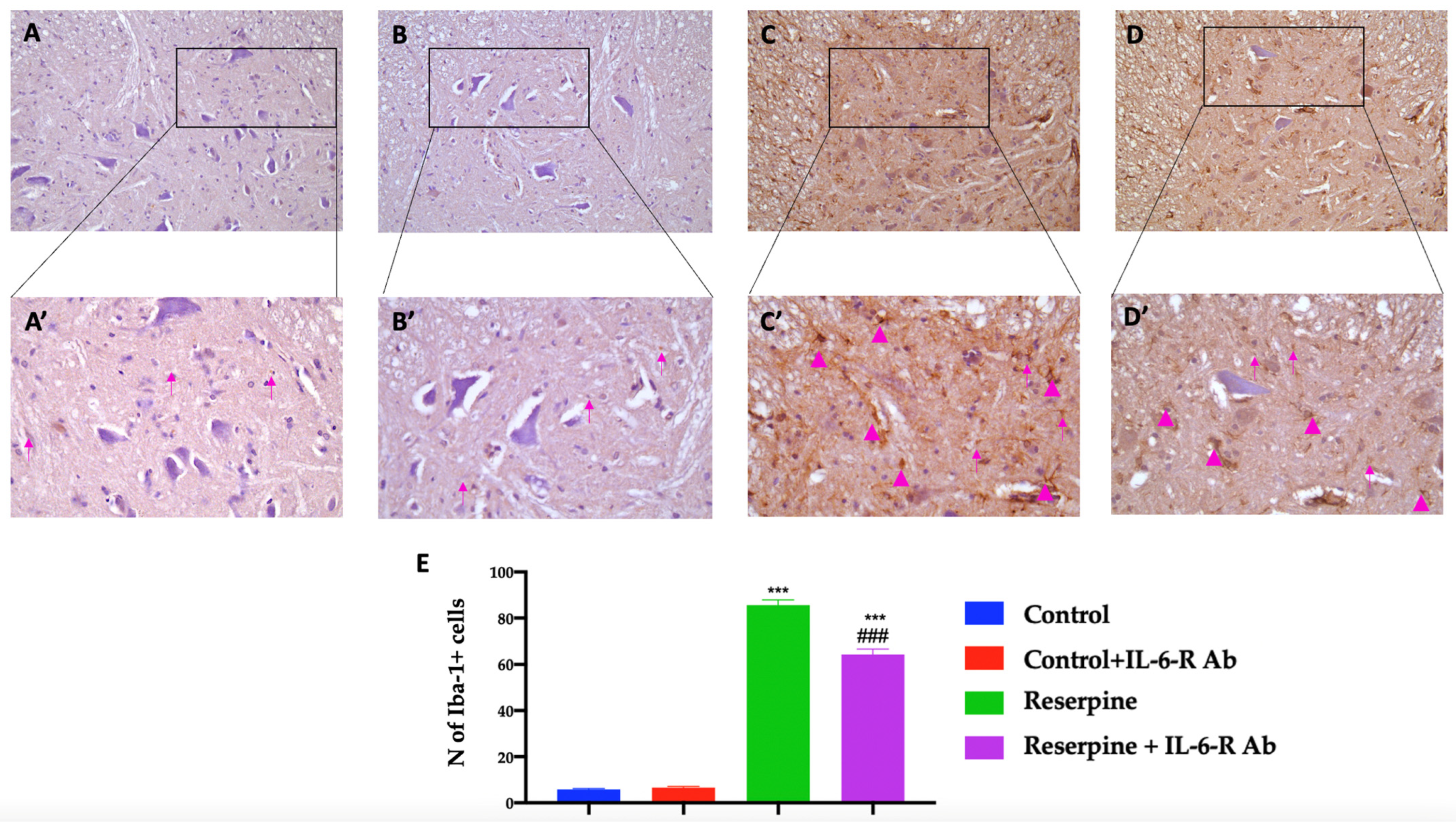
3.6. Analysis of Glial Activation
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maffei, M.E. Fibromyalgia: Recent Advances in Diagnosis, Classification, Pharmacotherapy and Alternative Remedies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, A.G.; Jha, S.K.; Iskander, J.; Avanthika, C.; Jhaveri, S.; Patel, V.H.; Rasagna Potini, B.; Talha Azam, A. Diagnostic Challenges and Management of Fibromyalgia. Cureus 2021, 13, e18692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia Rodriguez, D.F.; Abud Mendoza, C. Physiopathology of fibromyalgia. Reumatol. Clin. 2020, 16, 191–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Agnelli, S.; Arendt-Nielsen, L.; Gerra, M.C.; Zatorri, K.; Boggiani, L.; Baciarello, M.; Bignami, E. Fibromyalgia: Genetics and epigenetics insights may provide the basis for the development of diagnostic biomarkers. Mol. Pain 2019, 15, 1744806918819944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarzi-Puttini, P.; Giorgi, V.; Marotto, D.; Atzeni, F. Fibromyalgia: An update on clinical characteristics, aetiopathogenesis and treatment. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2020, 16, 645–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latremoliere, A.; Woolf, C.J. Central sensitization: A generator of pain hypersensitivity by central neural plasticity. J. Pain 2009, 10, 895–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bair, M.J.; Krebs, E.E. Fibromyalgia. Ann. Intern. Med. 2020, 172, ITC33–ITC48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolf, C.J.; Ma, Q. Nociceptors—Noxious stimulus detectors. Neuron 2007, 55, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, R.-R.; Kohno, T.; Moore, K.A.; Woolf, C.J. Central sensitization and LTP: Do pain and memory share similar mechanisms? Trends Neurosci. 2003, 26, 696–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolf, C.J.; Salter, M.W. Neuronal plasticity: Increasing the gain in pain. Science 2000, 288, 1765–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hucho, T.; Levine, J.D. Signaling pathways in sensitization: Toward a nociceptor cell biology. Neuron 2007, 55, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellato, E.; Marini, E.; Castoldi, F.; Barbasetti, N.; Mattei, L.; Bonasia, D.E.; Blonna, D. Fibromyalgia syndrome: Etiology, pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment. Pain Res. Treat. 2012, 2012, 426130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzies, V.; Lyon, D.E.; Elswick, R.K., Jr.; Montpetit, A.J.; McCain, N.L. Psychoneuroimmunological relationships in women with fibromyalgia. Biol. Res. Nurs. 2013, 15, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradley, L.A. Pathophysiology of fibromyalgia. Am. J. Med. 2009, 122, S22–S30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, J.J.; Cidoncha, A.; Bote, M.E.; Hinchado, M.D.; Ortega, E. Altered profile of chemokines in fibromyalgia patients. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2014, 51, 576–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behm, F.G.; Gavin, I.M.; Karpenko, O.; Lindgren, V.; Gaitonde, S.; Gashkoff, P.A.; Gillis, B.S. Unique immunologic patterns in fibromyalgia. BMC Clin. Pathol. 2012, 12, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Pinto, I.; Agmon-Levin, N.; Howard, A.; Shoenfeld, Y. Fibromyalgia and cytokines. Immunol. Lett. 2014, 161, 200–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coskun Benlidayi, I. Role of inflammation in the pathogenesis and treatment of fibromyalgia. Rheumatol. Int. 2019, 39, 781–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theoharides, T.C.; Tsilioni, I.; Bawazeer, M. Mast Cells, Neuroinflammation and Pain in Fibromyalgia Syndrome. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uceyler, N.; Rogausch, J.P.; Toyka, K.V.; Sommer, C. Differential expression of cytokines in painful and painless neuropathies. Neurology 2007, 69, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genevay, S.; Finckh, A.; Zufferey, P.; Viatte, S.; Balague, F.; Gabay, C. Adalimumab in acute sciatica reduces the long-term need for surgery: A 3-year follow-up of a randomised double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2012, 71, 560–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, G.M.; Peterlin, B.L.; Perreault, M.J.; Grothusen, J.R.; Schwartzman, R.J. Changes in plasma cytokines and their soluble receptors in complex regional pain syndrome. J. Pain 2012, 13, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conti, P.; Gallenga, C.E.; Caraffa, A.; Ronconi, G.; Kritas, S.K. Impact of mast cells in fibromyalgia and low-grade chronic inflammation: Can IL-37 play a role? Dermatol. Ther. 2020, 33, e13191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLeo, J.A.; Rutkowski, M.D.; Stalder, A.K.; Campbell, I.L. Transgenic expression of TNF by astrocytes increases mechanical allodynia in a mouse neuropathy model. Neuroreport 2000, 11, 599–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatashita, S.; Sekiguchi, M.; Kobayashi, H.; Konno, S.; Kikuchi, S. Contralateral neuropathic pain and neuropathology in dorsal root ganglion and spinal cord following hemilateral nerve injury in rats. Spine 2008, 33, 1344–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordaro, M.; Siracusa, R.; D’Amico, R.; Genovese, T.; Franco, G.; Marino, Y.; Di Paola, D.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Impellizzeri, D.; Di Paola, R.; et al. Role of Etanercept and Infliximab on Nociceptive Changes Induced by the Experimental Model of Fibromyalgia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, C.; Galbraith, J.A.; Heckman, H.M.; Myers, R.R. Pathology of experimental compression neuropathy producing hyperesthesia. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 1993, 52, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, K.; Tsuda, M.; Tozaki-Saitoh, H. Modification of neuropathic pain sensation through microglial ATP receptors. Purinergic Signal. 2007, 3, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, J.E.; Nico, L.; VandeVord, P.; Skoff, A.M. Modulation of neuropathic pain by a glial-derived factor. Pain Med. 2009, 10, 1229–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, A.; Beggs, S.; Vega-Avelaira, D.; Costigan, M.; Hathway, G.J.; Salter, M.W.; Fitzgerald, M. Spinal microglia and neuropathic pain in young rats. Pain 2007, 128, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thacker, M.A.; Clark, A.K.; Bishop, T.; Grist, J.; Yip, P.K.; Moon, L.D.; Thompson, S.W.; Marchand, F.; McMahon, S.B. CCL2 is a key mediator of microglia activation in neuropathic pain states. Eur. J. Pain 2009, 13, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofroniew, M.V.; Howe, C.L.; Mobley, W.C. Nerve growth factor signaling, neuroprotection, and neural repair. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2001, 24, 1217–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watkins, L.R.; Maier, S.F.; Goehler, L.E. Cytokine-to-brain communication: A review & analysis of alternative mechanisms. Life Sci. 1995, 57, 1011–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milligan, E.D.; Watkins, L.R. Pathological and protective roles of glia in chronic pain. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2009, 10, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.Q.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Z.H.; Chen, S.P.; Li, M.; Shahveranov, A.; Ye, D.W.; Tian, Y.K. Interleukin-6: An emerging regulator of pathological pain. J. Neuroinflamm. 2016, 13, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blum-Degen, D.; Muller, T.; Kuhn, W.; Gerlach, M.; Przuntek, H.; Riederer, P. Interleukin-1 beta and interleukin-6 are elevated in the cerebrospinal fluid of Alzheimer’s and de novo Parkinson’s disease patients. Neurosci. Lett. 1995, 202, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodroofe, M.N.; Cuzner, M.L. Cytokine mRNA expression in inflammatory multiple sclerosis lesions: Detection by non-radioactive in situ hybridization. Cytokine 1993, 5, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, T.; Yasukawa, K.; Harada, H.; Taga, T.; Watanabe, Y.; Matsuda, T.; Kashiwamura, S.; Nakajima, K.; Koyama, K.; Iwamatsu, A.; et al. Complementary DNA for a novel human interleukin (BSF-2) that induces B lymphocytes to produce immunoglobulin. Nature 1986, 324, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheller, J.; Garbers, C.; Rose-John, S. Interleukin-6: From basic biology to selective blockade of pro-inflammatory activities. Semin. Immunol. 2014, 26, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Kishimoto, T. The biology and medical implications of interleukin-6. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2014, 2, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulanger, M.J.; Chow, D.C.; Brevnova, E.E.; Garcia, K.C. Hexameric structure and assembly of the interleukin-6/IL-6 alpha-receptor/gp130 complex. Science 2003, 300, 2101–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishimoto, T. Interleukin-6: From basic science to medicine--40 years in immunology. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 23, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinrich, P.C.; Behrmann, I.; Haan, S.; Hermanns, H.M.; Muller-Newen, G.; Schaper, F. Principles of interleukin (IL)-6-type cytokine signalling and its regulation. Biochem. J. 2003, 374, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, A.L.; Hayes, K.C.; Dekaban, G.A. Clinical correlates of elevated serum concentrations of cytokines and autoantibodies in patients with spinal cord injury. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2007, 88, 1384–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detloff, M.R.; Fisher, L.C.; McGaughy, V.; Longbrake, E.E.; Popovich, P.G.; Basso, D.M. Remote activation of microglia and pro-inflammatory cytokines predict the onset and severity of below-level neuropathic pain after spinal cord injury in rats. Exp. Neurol. 2008, 212, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corominas, H.; Alegre, C.; Narvaez, J.; Fernandez-Cid, C.M.; Torrente-Segarra, V.; Gomez, M.R.; Pan, F.M.; Morla, R.M.; Martinez, F.J.R.; Gomez-Centeno, A.; et al. Correlation of fatigue with other disease related and psychosocial factors in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with tocilizumab: ACT-AXIS study. Medicine 2019, 98, e15947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guptarak, J.; Wanchoo, S.; Durham-Lee, J.; Wu, Y.; Zivadinovic, D.; Paulucci-Holthauzen, A.; Nesic, O. Inhibition of IL-6 signaling: A novel therapeutic approach to treating spinal cord injury pain. Pain 2013, 154, 1115–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Mao-Ying, Q.L.; Chen, J.W.; Yang, C.J.; Wang, Y.Q.; Tan, Z.M. Involvement of EphB1 receptor/ephrinB1 ligand in bone cancer pain. Neurosci. Lett. 2011, 496, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nightingale, S. The neuropathic pain market. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2012, 11, 101–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeLeo, J.A.; Colburn, R.W.; Nichols, M.; Malhotra, A. Interleukin-6-mediated hyperalgesia/allodynia and increased spinal IL-6 expression in a rat mononeuropathy model. J. Interferon. Cytokine Res. 1996, 16, 695–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miltenburg, N.C.; Boogerd, W. Chemotherapy-induced neuropathy: A comprehensive survey. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2014, 40, 872–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millan, M.J. The induction of pain: An integrative review. Prog. Neurobiol. 1999, 57, 1–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolfe, F.; Smythe, H.A.; Yunus, M.B.; Bennett, R.M.; Bombardier, C.; Goldenberg, D.L.; Tugwell, P.; Campbell, S.M.; Abeles, M.; Clark, P.; et al. The American College of Rheumatology 1990 Criteria for the Classification of Fibromyalgia. Report of the Multicenter Criteria Committee. Arthritis Rheum. 1990, 33, 160–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vierck, C.J., Jr. Mechanisms underlying development of spatially distributed chronic pain (fibromyalgia). Pain 2006, 124, 242–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koroschetz, J.; Rehm, S.E.; Gockel, U.; Brosz, M.; Freynhagen, R.; Tolle, T.R.; Baron, R. Fibromyalgia and neuropathic pain--differences and similarities. A comparison of 3057 patients with diabetic painful neuropathy and fibromyalgia. BMC Neurol. 2011, 11, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melemedjian, O.K.; Asiedu, M.N.; Tillu, D.V.; Peebles, K.A.; Yan, J.; Ertz, N.; Dussor, G.O.; Price, T.J. IL-6- and NGF-induced rapid control of protein synthesis and nociceptive plasticity via convergent signaling to the eIF4F complex. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 15113–15123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melemedjian, O.K.; Tillu, D.V.; Moy, J.K.; Asiedu, M.N.; Mandell, E.K.; Ghosh, S.; Dussor, G.; Price, T.J. Local translation and retrograde axonal transport of CREB regulates IL-6-induced nociceptive plasticity. Mol. Pain 2014, 10, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenn, D.; Richter, F.; Schaible, H.G. Sensitization of unmyelinated sensory fibers of the joint nerve to mechanical stimuli by interleukin-6 in the rat: An inflammatory mechanism of joint pain. Arthritis Rheum. 2007, 56, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obreja, O.; Schmelz, M.; Poole, S.; Kress, M. Interleukin-6 in combination with its soluble IL-6 receptor sensitises rat skin nociceptors to heat, in vivo. Pain 2002, 96, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, F.Q.; Poole, S.; Lorenzetti, B.B.; Ferreira, S.H. The pivotal role of tumour necrosis factor alpha in the development of inflammatory hyperalgesia. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1992, 107, 660–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendieta, D.; De la Cruz-Aguilera, D.L.; Barrera-Villalpando, M.I.; Becerril-Villanueva, E.; Arreola, R.; Hernandez-Ferreira, E.; Perez-Tapia, S.M.; Perez-Sanchez, G.; Garces-Alvarez, M.E.; Aguirre-Cruz, L.; et al. IL-8 and IL-6 primarily mediate the inflammatory response in fibromyalgia patients. J. Neuroimmunol. 2016, 290, 22–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Mahony, L.F.; Srivastava, A.; Mehta, P.; Ciurtin, C. Is fibromyalgia associated with a unique cytokine profile? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Rheumatology 2021, 60, 2602–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagakura, Y.; Takahashi, M.; Noto, T.; Sekizawa, T.; Oe, T.; Yoshimi, E.; Tamaki, K.; Shimizu, Y. Different pathophysiology underlying animal models of fibromyalgia and neuropathic pain: Comparison of reserpine-induced myalgia and chronic constriction injury rats. Behav. Brain Res. 2012, 226, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Perez, B.; Deulofeu, M.; Homs, J.; Merlos, M.; Vela, J.M.; Verdu, E.; Boadas-Vaello, P. Long-lasting reflexive and nonreflexive pain responses in two mouse models of fibromyalgia-like condition. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 9719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagakura, Y.; Oe, T.; Aoki, T.; Matsuoka, N. Biogenic amine depletion causes chronic muscular pain and tactile allodynia accompanied by depression: A putative animal model of fibromyalgia. Pain 2009, 146, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taguchi, T.; Katanosaka, K.; Yasui, M.; Hayashi, K.; Yamashita, M.; Wakatsuki, K.; Kiyama, H.; Yamanaka, A.; Mizumura, K. Peripheral and spinal mechanisms of nociception in a rat reserpine-induced pain model. Pain 2015, 156, 415–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, V.; Kuhad, A.; Tiwari, V.; Chopra, K. Curcumin ameliorates reserpine-induced pain-depression dyad: Behavioural, biochemical, neurochemical and molecular evidences. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2011, 36, 1570–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusco, R.; Siracusa, R.; D’Amico, R.; Peritore, A.F.; Cordaro, M.; Gugliandolo, E.; Crupi, R.; Impellizzeri, D.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Di Paola, R. Melatonin Plus Folic Acid Treatment Ameliorates Reserpine-Induced Fibromyalgia: An Evaluation of Pain, Oxidative Stress, and Inflammation. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Impellizzeri, D.; Siracusa, R.; Cordaro, M.; Peritore, A.F.; Gugliandolo, E.; D’Amico, R.; Fusco, R.; Crupi, R.; Rizzarelli, E.; Cuzzocrea, S.; et al. Protective effect of a new hyaluronic acid -carnosine conjugate on the modulation of the inflammatory response in mice subjected to collagen-induced arthritis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 125, 110023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Amico, R.; Fusco, R.; Siracusa, R.; Impellizzeri, D.; Peritore, A.F.; Gugliandolo, E.; Interdonato, L.; Sforza, A.M.; Crupi, R.; Cuzzocrea, S.; et al. Inhibition of P2X7 Purinergic Receptor Ameliorates Fibromyalgia Syndrome by Suppressing NLRP3 Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Paola, R.; Fusco, R.; Gugliandolo, E.; Crupi, R.; Evangelista, M.; Granese, R.; Cuzzocrea, S. Co-micronized Palmitoylethanolamide/Polydatin Treatment Causes Endometriotic Lesion Regression in a Rodent Model of Surgically Induced Endometriosis. Front. Pharmacol. 2016, 7, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Paola, D.; Capparucci, F.; Lanteri, G.; Crupi, R.; Marino, Y.; Franco, G.A.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Spano, N.; Gugliandolo, E.; Peritore, A.F. Environmental Toxicity Assessment of Sodium Fluoride and Platinum-Derived Drugs Co-Exposure on Aquatic Organisms. Toxics 2022, 10, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crupi, R.; Palma, E.; Siracusa, R.; Fusco, R.; Gugliandolo, E.; Cordaro, M.; Impellizzeri, D.; De Caro, C.; Calzetta, L.; Cuzzocrea, S.; et al. Protective Effect of Hydroxytyrosol Against Oxidative Stress Induced by the Ochratoxin in Kidney Cells: In vitro and in vivo Study. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messina, L.; Bruno, F.; Licata, P.; Paola, D.D.; Franco, G.; Marino, Y.; Peritore, A.F.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Gugliandolo, E.; Crupi, R. Snail Mucus Filtrate Reduces Inflammation in Canine Progenitor Epidermal Keratinocytes (CPEK). Animals 2022, 12, 1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordaro, M.; Fusco, R.; D’Amico, R.; Siracusa, R.; Peritore, A.F.; Gugliandolo, E.; Genovese, T.; Crupi, R.; Mandalari, G.; Cuzzocrea, S.; et al. Cashew (Anacardium occidentale L.) Nuts Modulate the Nrf2 and NLRP3 Pathways in Pancreas and Lung after Induction of Acute Pancreatitis by Cerulein. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusco, R.; Cordaro, M.; Siracusa, R.; Peritore, A.F.; Gugliandolo, E.; Genovese, T.; D’Amico, R.; Crupi, R.; Smeriglio, A.; Mandalari, G.; et al. Consumption of Anacardium occidentale L. (Cashew Nuts) Inhibits Oxidative Stress through Modulation of the Nrf2/HO-1 and NF-kB Pathways. Molecules 2020, 25, 4426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peritore, A.F.; D’Amico, R.; Siracusa, R.; Cordaro, M.; Fusco, R.; Gugliandolo, E.; Genovese, T.; Crupi, R.; Di Paola, R.; Cuzzocrea, S.; et al. Management of Acute Lung Injury: Palmitoylethanolamide as a New Approach. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Paola, D.; Abbate, J.M.; Iaria, C.; Cordaro, M.; Crupi, R.; Siracusa, R.; D’Amico, R.; Fusco, R.; Impellizzeri, D.; Cuzzocrea, S.; et al. Environmental Risk Assessment of Dexamethasone Sodium Phosphate and Tocilizumab Mixture in Zebrafish Early Life Stage (Danio rerio). Toxics 2022, 10, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fusco, R.; Salinaro, A.T.; Siracusa, R.; D’Amico, R.; Impellizzeri, D.; Scuto, M.; Ontario, M.L.; Crea, R.; Cordaro, M.; Cuzzocrea, S.; et al. Hidrox((R)) Counteracts Cyclophosphamide-Induced Male Infertility through NRF2 Pathways in a Mouse Model. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusco, R.; Gugliandolo, E.; Campolo, M.; Evangelista, M.; Di Paola, R.; Cuzzocrea, S. Effect of a new formulation of micronized and ultramicronized N-palmitoylethanolamine in a tibia fracture mouse model of complex regional pain syndrome. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Paola, D.; Natale, S.; Iaria, C.; Cordaro, M.; Crupi, R.; Siracusa, R.; D’Amico, R.; Fusco, R.; Impellizzeri, D.; Cuzzocrea, S.; et al. Intestinal Disorder in Zebrafish Larvae (Danio rerio): The Protective Action of N-Palmitoylethanolamide-oxazoline. Life 2022, 12, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peritore, A.F.; Crupi, R.; Scuto, M.; Gugliandolo, E.; Siracusa, R.; Impellizzeri, D.; Cordaro, M.; D’Amico, R.; Fusco, R.; Di Paola, R.; et al. The Role of Annexin A1 and Formyl Peptide Receptor 2/3 Signaling in Chronic Corticosterone-Induced Depression-Like behaviors and Impairment in Hippocampal-Dependent Memory. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2020, 19, 27–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Lavin, M. Centralized nociplastic pain causing fibromyalgia: An emperor with no cloths? Clin. Rheumatol. 2022, 41, 3915–3917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeSantana, J.M.; da Cruz, K.M.; Sluka, K.A. Animal models of fibromyalgia. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2013, 15, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peritore, A.F.; Siracusa, R.; Fusco, R.; Gugliandolo, E.; D’Amico, R.; Cordaro, M.; Crupi, R.; Genovese, T.; Impellizzeri, D.; Cuzzocrea, S.; et al. Ultramicronized Palmitoylethanolamide and Paracetamol, a New Association to Relieve Hyperalgesia and Pain in a Sciatic Nerve Injury Model in Rat. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohr, J.B.; Kuczenski, R.; Niculescu, A.B. Oxidative mechanisms and tardive dyskinesia. CNS Drugs 2003, 17, 47–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilska, A.; Dubiel, M.; Sokołowska-Jez, M.; Lorenc-Koci, E.; Włodek, L. Alpha-lipoic acid differently affects the reserpine-induced oxidative stress in the striatum and prefrontal cortex of rat brain. Neuroscience 2007, 146, 1758–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagis, S.; Tamer, L.; Sahin, G.; Bilgin, R.; Guler, H.; Ercan, B.; Erdogan, C. Free radicals and antioxidants in primary fibromyalgia: An oxidative stress disorder? Rheumatol. Int. 2005, 25, 188–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pall, M.L. Nitric oxide synthase partial uncoupling as a key switching mechanism for the NO/ONOO–cycle. Med. Hypotheses 2007, 69, 821–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Littlejohn, G.; Guymer, E. Neurogenic inflammation in fibromyalgia. Semin. Immunopathol. 2018, 40, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backryd, E.; Tanum, L.; Lind, A.L.; Larsson, A.; Gordh, T. Evidence of both systemic inflammation and neuroinflammation in fibromyalgia patients, as assessed by a multiplex protein panel applied to the cerebrospinal fluid and to plasma. J. Pain Res. 2017, 10, 515–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rus, A.; Lopez-Sanchez, J.A.; Garcia-Rios, M.C.; Tapia-Haro, R.M.; Casas-Barragan, A.; Correa-Rodriguez, M.; Aguilar-Ferrandiz, M.E. Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide, Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor, and Clinical Manifestations in Women With Fibromyalgia. Nurs. Res. 2023, 72, E1–E7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.K.; Kim, K.S.; Lee, Y.S.; Park, S.H.; Choe, J.Y. Arterial stiffness and proinflammatory cytokines in fibromyalgia syndrome. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2010, 28, S71–S77. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Heinrich, P.C.; Behrmann, I.; Muller-Newen, G.; Schaper, F.; Graeve, L. Interleukin-6-type cytokine signalling through the gp130/Jak/STAT pathway. Biochem. J. 1998, 334 Pt 2, 297–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.; Liu, Y.; Li, P.K.; Li, C.; Lin, J. LLL12 inhibits endogenous and exogenous interleukin-6-induced STAT3 phosphorylation in human pancreatic cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 2011, 31, 2029–2035. [Google Scholar]
- Popiolek-Barczyk, K.; Kolosowska, N.; Piotrowska, A.; Makuch, W.; Rojewska, E.; Jurga, A.M.; Pilat, D.; Mika, J. Parthenolide Relieves Pain and Promotes M2 Microglia/Macrophage Polarization in Rat Model of Neuropathy. Neural Plast. 2015, 2015, 676473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez, E.; Rivat, C.; Pommier, B.; Mauborgne, A.; Pohl, M. JAK/STAT3 pathway is activated in spinal cord microglia after peripheral nerve injury and contributes to neuropathic pain development in rat. J. Neurochem. 2008, 107, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przanowski, P.; Dabrowski, M.; Ellert-Miklaszewska, A.; Kloss, M.; Mieczkowski, J.; Kaza, B.; Ronowicz, A.; Hu, F.; Piotrowski, A.; Kettenmann, H.; et al. The signal transducers Stat1 and Stat3 and their novel target Jmjd3 drive the expression of inflammatory genes in microglia. J. Mol. Med. 2014, 92, 239–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Tian, Y.; Lu, N.; Gin, T.; Cheng, C.H.; Chan, M.T. Stat3 inhibition attenuates mechanical allodynia through transcriptional regulation of chemokine expression in spinal astrocytes. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuda, M.; Kohro, Y.; Yano, T.; Tsujikawa, T.; Kitano, J.; Tozaki-Saitoh, H.; Koyanagi, S.; Ohdo, S.; Ji, R.-R.; Salter, M.W. JAK-STAT3 pathway regulates spinal astrocyte proliferation and neuropathic pain maintenance in rats. Brain 2011, 134, 1127–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofroniew, M.V.; Vinters, H.V. Astrocytes: Biology and pathology. Acta Neuropathol. 2010, 119, 7–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholz, J.; Woolf, C.J. The neuropathic pain triad: Neurons, immune cells and glia. Nat. Neurosci. 2007, 10, 1361–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peck, M.M.; Maram, R.; Mohamed, A.; Ochoa Crespo, D.; Kaur, G.; Ashraf, I.; Malik, B.H. The Influence of Pro-inflammatory Cytokines and Genetic Variants in the Development of Fibromyalgia: A Traditional Review. Cureus 2020, 12, e10276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, V.H.; Grewal, J.; Hackshaw, K.V.; Mongiovi, P.C.; Stino, A.M. Fibromyalgia syndrome and small fiber, early or mild sensory polyneuropathy. Muscle Nerve 2018, 58, 625–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, J.; Herrmann, D.; Stanton, M.; Barbano, R.; Logigian, E. Painful small-fiber neuropathy in Sjögren syndrome. Neurology 2005, 65, 925–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meares, G.P.; Ma, X.; Qin, H.; Benveniste, E.N. Regulation of CCL20 expression in astrocytes by IL-6 and IL-17. Glia 2012, 60, 771–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ubogu, E.E.; Cossoy, M.B.; Ransohoff, R.M. The expression and function of chemokines involved in CNS inflammation. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2006, 27, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, F.A.; Jung, H.; Miller, R.J. Chemokines and the pathophysiology of neuropathic pain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 20151–20158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marino, Y.; Arangia, A.; Cordaro, M.; Siracusa, R.; D’Amico, R.; Impellizzeri, D.; Cupi, R.; Peritore, A.F.; Gugliandolo, E.; Fusco, R.; et al. Analysis of the Influence of IL-6 and the Activation of the Jak/Stat3 Pathway in Fibromyalgia. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 792. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11030792
Marino Y, Arangia A, Cordaro M, Siracusa R, D’Amico R, Impellizzeri D, Cupi R, Peritore AF, Gugliandolo E, Fusco R, et al. Analysis of the Influence of IL-6 and the Activation of the Jak/Stat3 Pathway in Fibromyalgia. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(3):792. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11030792
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarino, Ylenia, Alessia Arangia, Marika Cordaro, Rosalba Siracusa, Ramona D’Amico, Daniela Impellizzeri, Rosalia Cupi, Alessio Filippo Peritore, Enrico Gugliandolo, Roberta Fusco, and et al. 2023. "Analysis of the Influence of IL-6 and the Activation of the Jak/Stat3 Pathway in Fibromyalgia" Biomedicines 11, no. 3: 792. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11030792
APA StyleMarino, Y., Arangia, A., Cordaro, M., Siracusa, R., D’Amico, R., Impellizzeri, D., Cupi, R., Peritore, A. F., Gugliandolo, E., Fusco, R., Cuzzocrea, S., & Di Paola, R. (2023). Analysis of the Influence of IL-6 and the Activation of the Jak/Stat3 Pathway in Fibromyalgia. Biomedicines, 11(3), 792. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11030792










