Saliva Free Light Chains in Patients with Neuro-Sjögren
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Saliva Sample Collection
2.3. Analytical Procedures
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Patients
3.2. Comparison of Patients with SS and Controls
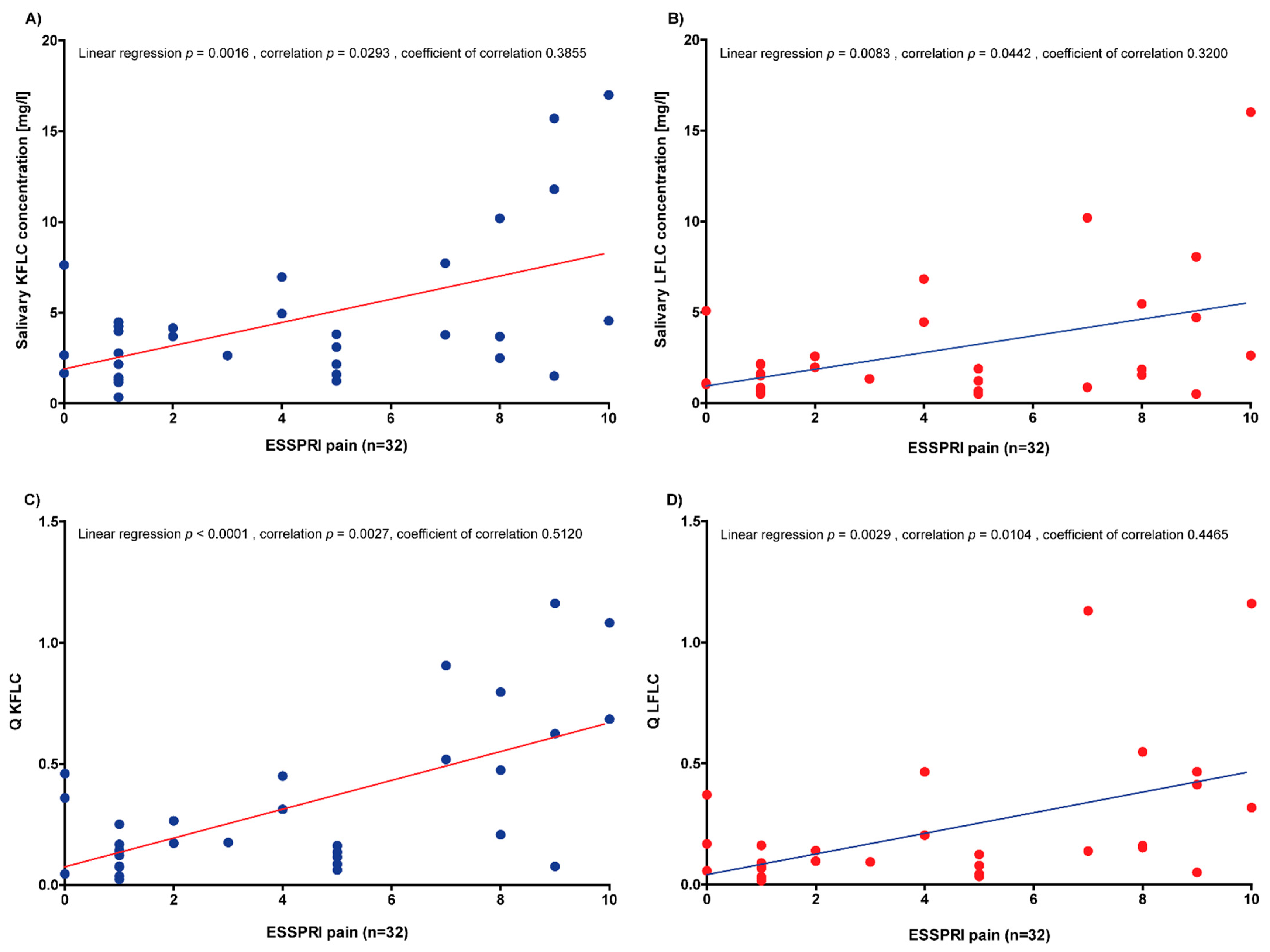
3.3. Correlation of Serum and Saliva Protein Concentrations with Severity of Xerostomia
3.4. Correlation of Serum and Saliva Protein Concentrations with Disease Activity
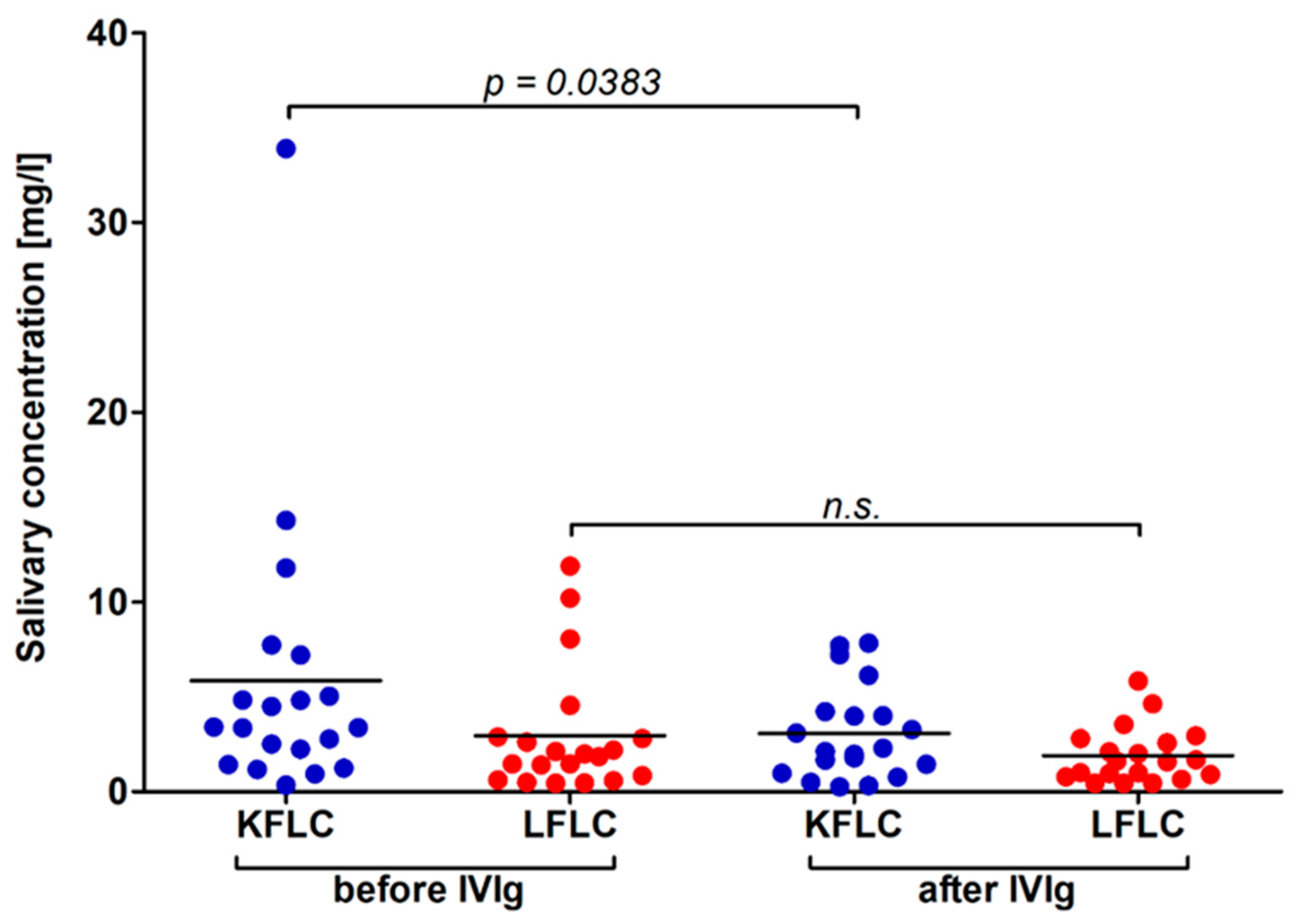
3.5. Influence of IVIg Application and Longitudinal Subgroup Analysis of 20 Patients Benefitting from IVIG Treatment
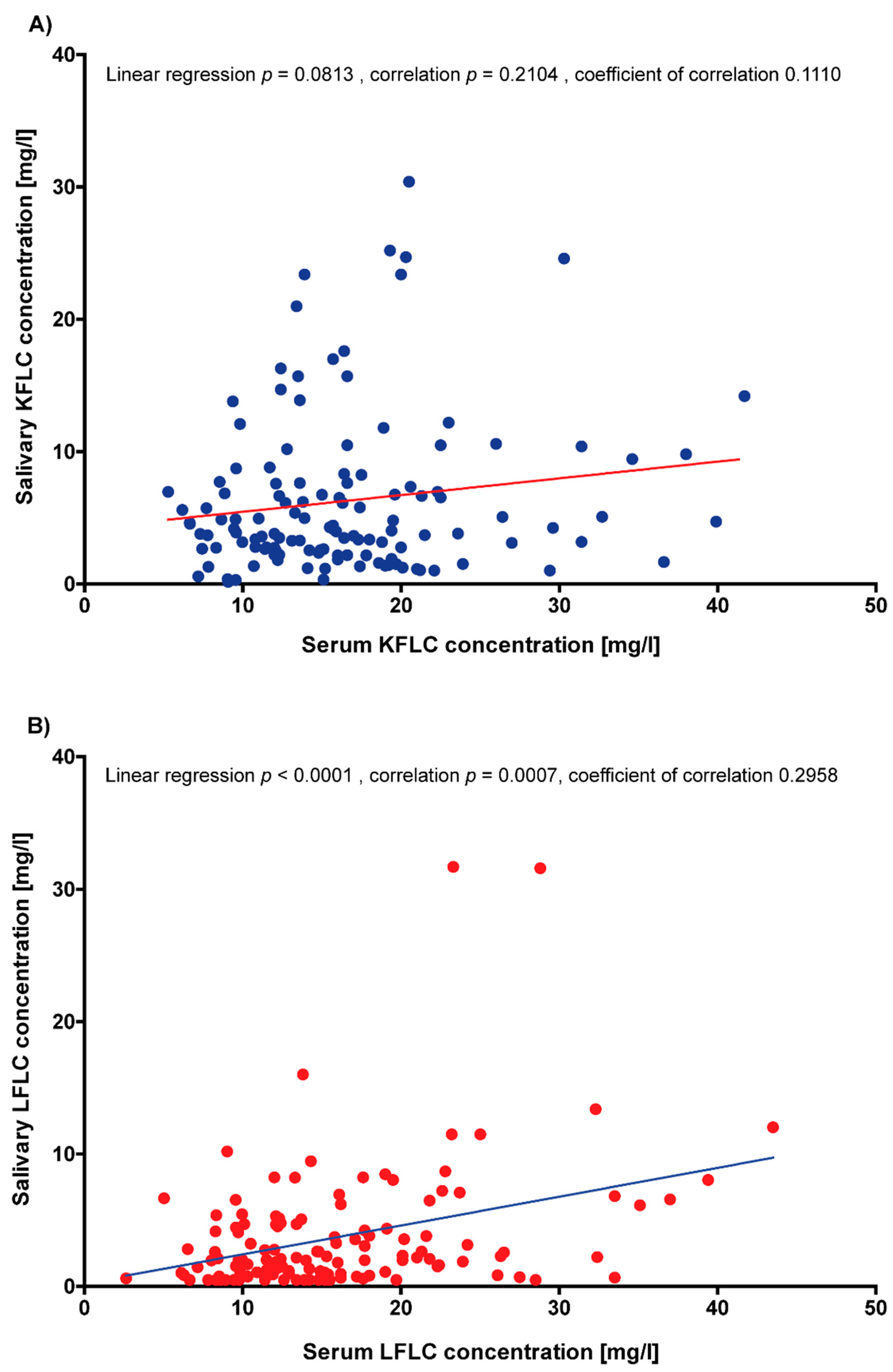
3.6. Correlation of Serum and Saliva FLC Concentrations
3.7. Correlation of Saliva FLC Concentrations with Renal Function
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sjögren, H. Zur Kenntnis der keratoconjunctivitis sicca. Acta Ophthalmol. 1933, 13, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, R.I. Sjögren’s syndrome. Lancet 2005, 366, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, E.; Seeliger, T.; Skripuletz, T.; Gödecke, V.; Beider, S.; Jablonka, A.; Witte, T.; Ernst, D. Multimodal Assessment and Characterization of Sicca Syndrome. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 777599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seeliger, T.; Bönig, L.; Gingele, S.; Prenzler, N.K.; Thiele, T.; Ernst, D.; Witte, T.; Stangel, M.; Skripuletz, T.; Körner, S. Nerve ultrasound findings in Sjögren’s syndrome-associated neuropathy. J. Neuroimaging 2021, 31, 1156–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seeliger, T.; Bönig, L.; Witte, T.; Thiele, T.; Lesinski-Schiedat, A.; Stangel, M.; Lenarz, T.; Prenzler, N.C.; Skripuletz, T. Hearing dysfunction in patients with Neuro-Sjögren: A cross-sectional study. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sogkas, G.; Hirsch, S.; Olsson, K.M.; Hinrichs, J.B.; Thiele, T.; Seeliger, T.; Skripuletz, T.; Schmidt, R.E.; Witte, T.; Jablonka, A.; et al. Lung Involvement in Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome-An Under-Diagnosed Entity. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butryn, M.; Neumann, J.; Rolfes, L.; Bartels, C.; Wattjes, M.P.; Mahmoudi, N.; Seeliger, T.; Konen, F.F.; Thiele, T.; Witte, T.; et al. Clinical, Radiological, and Laboratory Features of Spinal Cord Involvement in Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiboski, C.H.; Shiboski, S.C.; Seror, R.; Criswell, L.A.; Labetoulle, M.; Lietman, T.M.; Rasmussen, A.; Scofield, H.; Vitali, C.; Bowman, S.J.; et al. 2016 American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism classification criteria for primary Sjögren’s syndrome: A consensus and data-driven methodology involving three international patient cohorts. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, K.; Iijima, M.; Koike, H.; Hattori, N.; Tanaka, F.; Watanabe, H.; Katsuno, M.; Fujita, A.; Aiba, I.; Ogata, A.; et al. The wide spectrum of clinical manifestations in Sjögren’s syndrome-associated neuropathy. Brain 2005, 128, 2518–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, T.E.; Cox, D.; Shiboski, C.H.; Schiødt, M.; Wu, A.; Lanfranchi, H.; Umehara, H.; Zhao, Y.; Challacombe, S.; Lam, M.Y.; et al. Associations between salivary gland histopathologic diagnoses and phenotypic features of Sjögren’s syndrome among 1726 registry participants. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 63, 2021–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nocturne, G.; Mariette, X. B cells in the pathogenesis of primary Sjögren syndrome. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2018, 14, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottenberg, J.E.; Seror, R.; Miceli-Richard, C.; Benessiano, J.; Devauchelle-Pensec, V.; Dieude, P.; Dubost, J.J.; Fauchais, A.L.; Goeb, V.; Hachulla, E.; et al. Serum levels of beta2-microglobulin and free light chains of immunoglobulins are associated with systemic disease activity in primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Data at enrollment in the prospective ASSESS cohort. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jülich, M.; Kanne, A.M.; Sehnert, B.; Budweiser, S.; Voll, R.E.; Kollert, F. Serological lymphocytic activity and patient-reported outcomes in Sjögren. s syndrome. Clin. Rheumatol. 2018, 37, 2361–2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, K.; Chipeta, C.; Parker, A.; Harding, S.; Cockell, S.J.; Gillespie, C.S.; Hallinan, J.; Barone, F.; Bowman, S.J.; Ng, W.F.; et al. B-cell activity markers are associated with different disease activity domains in primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Rheumatology 2018, 57, 1222–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verstappen, G.M.; Moerman, R.V.; van Nimwegen, J.F.; van Ginkel, M.S.; Bijzet, J.; Mossel, E.; Vissink, A.; Hazenberg, B.P.C.; Arends, S.; Kroese, F.G.M.; et al. Serum immunoglobulin free light chains are sensitive biomarkers for monitoring disease activity and treatment response in primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Rheumatology 2018, 57, 1812–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandhya, P.; Christudoss, P.; Kabeerdoss, J.; Mandal, S.K.; Aithala, R.; Mahasampath, G.; Job, V.; Danda, D. Diagnostic accuracy of salivary and serum-free light chain assays in primary Sjögren’s syndrome: A pilot study. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 20, 760–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhya, P.; Kabeerdoss, J.; Christudoss, P.; Arulraj, R.; Mandal, S.K.; Janardana, R.; Chebbi, P.P.; Ganesan, M.P.; Mahasampath, G.; Danda, D. Salivary free light chains and salivary immunoglobulins as potential non-invasive biomarkers in primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2022, 25, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pars, K.; Pul, R.; Schwenkenbecher, P.; Sühs, K.W.; Wurster, U.; Witte, T.; Bronzlik, P.; Stangel, M.; Skripuletz, T. Cerebrospinal Fluid Findings in Neurological Diseases Associated with Sjögren’s Syndrome. Eur. Neurol. 2017, 77, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konen, F.F.; Schwenkenbecher, P.; Jendretzky, K.F.; Gingele, S.; Sühs, K.W.; Tumani, H.; Süße, M.; Skripuletz, T. The Increasing Role of Kappa Free Light Chains in the Diagnosis of Multiple Sclerosis. Cells 2021, 10, 3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwenkenbecher, P.; Konen, F.F.; Wurster, U.; Witte, T.; Gingele, S.; Sühs, K.W.; Stangel, M.; Skripuletz, T. Reiber's Diagram for Kappa Free Light Chains: The New Standard for Assessing Intrathecal Synthesis? Diagnostics 2019, 9, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwenkenbecher, P.; Konen, F.F.; Wurster, U.; Jendretzky, K.F.; Gingele, S.; Sühs, K.W.; Pul, R.; Witte, T.; Stangel, M.; Skripuletz, T. The Persisting Significance of Oligoclonal Bands in the Dawning Era of Kappa Free Light Chains for the Diagnosis of Multiple Sclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moutsopoulos, H.M.; Steinberg, A.D.; Fauci, A.S.; Lane, H.C.; Papadopoulos, N.M. High incidence of free monoclonal lambda light chains in the sera of patients with Sjogren’s syndrome. J. Immunol. 1983, 130, 2663–2665. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Seror, R.; Ravaud, P.; Bowman, S.J.; Baron, G.; Tzioufas, A.; Theander, E.; Gottenberg, J.E.; Bootsma, H.; Mariette, X.; Vitali, C.; et al. EULAR Sjogren’s syndrome disease activity index: Development of a consensus systemic disease activity index for primary Sjogren’s syndrome. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2010, 69, 1103–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seror, R.; Ravaud, P.; Mariette, X.; Bootsma, H.; Theander, E.; Hansen, A.; Ramos-Casals, M.; Dörner, T.; Bombardieri, S.; Hachulla, E.; et al. EULAR Sjogren’s Syndrome Patient Reported Index (ESSPRI): Development of a consensus patient index for primary Sjogren’s syndrome. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2011, 70, 968–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seeliger, T.; Prenzler, N.K.; Gingele, S.; Seeliger, B.; Körner, S.; Thiele, T.; Bönig, L.; Sühs, K.W.; Witte, T.; Stangel, M.; et al. Neuro-Sjögren: Peripheral Neuropathy with Limb Weakness in Sjögren’s Syndrome. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeliger, T.; Gingele, S.; Bönig, L.; Konen, F.F.; Körner, S.; Prenzler, N.; Thiele, T.; Ernst, D.; Witte, T.; Stangel, M.; et al. CIDP associated with Sjögren’s syndrome. J. Neurol. 2021, 268, 2908–2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito-Zerón, P.; Retamozo, S.; Gandía, M.; Akasbi, M.; Pérez-De-Lis, M.; Diaz-Lagares, C.; Bosch, X.; Bové, A.; Pérez-Alvarez, R.; Soto-Cárdenas, M.J.; et al. Monoclonal gammopathy related to Sjögren syndrome: A key marker of disease prognosis and outcomes. J. Autoimmun. 2012, 39, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levey, A.S.; Stevens, L.A.; Schmid, C.H.; Zhang, Y.L.; Castro, A.F., 3rd; Feldman, H.I.; Kusek, J.W.; Eggers, P.; Van Lente, F.; Greene, T.; et al. A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 150, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeliger, T.; Gehlhaar, M.A.; Oluwatoba-Popoola, I.; Konen, F.F.; Haar, M.; Donicova, E.; Wachsmann, M.; Pielen, A.; Gingele, S.; Prenzler, N.K.; et al. Trigeminal Nerve Affection in Patients with Neuro-Sjögren Detected by Corneal Confocal Microscopy. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 4484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeliger, T.; Jacobsen, L.; Hendel, M.; Bönig, L.; Prenzler, N.K.; Thiele, T.; Ernst, D.; Witte, T.; Stangel, M.; Kopp, B.; et al. Cognitive impairment in patients with Neuro-Sjögren. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2020, 7, 1352–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konen, F.F.; Schwenkenbecher, P.; Jendretzky, K.F.; Gingele, S.; Witte, T.; Sühs, K.W.; Grothe, M.; Hannich, M.J.; Süße, M.; Skripuletz, T. Kappa Free Light Chains in Cerebrospinal Fluid in Inflammatory and Non-Inflammatory Neurological Diseases. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konen, F.F.; Schwenkenbecher, P.; Wurster, U.; Jendretzky, K.F.; Möhn, N.; Gingele, S.; Sühs, K.W.; Hannich, M.J.; Grothe, M.; Witte, T.; et al. The Influence of Renal Function Impairment on Kappa Free Light Chains in Cerebrospinal Fluid. J. Cent. Nerv. Syst. Dis. 2021, 13, 11795735211042166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seror, R.; Gottenberg, J.E.; Devauchelle-Pensec, V.; Dubost, J.J.; Le Guern, V.; Hayem, G.; Fauchais, A.L.; Goeb, V.; Hachulla, E.; Hatron, P.Y.; et al. European League Against Rheumatism Sjögren’s Syndrome Disease Activity Index and European League Against Rheumatism Sjögren’s Syndrome Patient-Reported Index: A complete picture of primary Sjögren’s syndrome patients. Arthritis Care Res. 2013, 65, 1358–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoval-Flores, M.G.; Chan-Campos, I.; Hernández-Molina, G. Factors influencing the EULAR Sjögren’s Syndrome Patient-Reported Index in primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2021, 39, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lackner, A.; Bosch, P.; Zenz, S.; Horwath-Winter, J.; Rabensteiner, D.F.; Hermann, J.; Graninger, W.; Stradner, M.H. Go Ask Your Patients! PSS-QoL Reported Perception of Dryness Correlates with Lacrimal and Salivary Flow in Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 660580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konen, F.F.; Wurster, U.; Witte, T.; Jendretzky, K.F.; Gingele, S.; Tumani, H.; Sühs, K.W.; Stangel, M.; Schwenkenbecher, P.; Skripuletz, T. The Impact of Immunomodulatory Treatment on Kappa Free Light Chains as Biomarker in Neuroinflammation. Cells 2020, 9, 842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Characteristic | Sjögren’s Syndrome (n = 50) | Control Group (n = 80) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age [years], median (min–max) | 60 (40–84) | 54 (18–82) | 0.0030 |
| Female/male—ratio | 0.5 | 0.9 | 0.1473 |
| Clinical features | |||
| Objectifiable ocular sicca-syptoms, n (%) | 38 (76%) | 24 (30%) | <0.0001 |
| Objectifiable oral sicca-syptoms, n (%) | 30 (60%) | 30 (38%) | 0.0184 |
| Pathological focus score in minor salivary gland biopsy, n (%) | 34 (68%) | 0 | <0.0001 |
| Ro-antibody positivity, n (%) | 26 (52%) | 0 | <0.0001 |
| La-antibody positivity, n (%) | 3 (6%) | 0 | 0.1583 |
| Rheumatoid factor positivity, n (%) | 7 (14%) | 4 (5%) | 0.1045 |
| ESSDAI total score, median (min–max) | 17 (0–42) | ND | ND |
| ESSPRI total score, median (min–max) * | 4.5 (0–9) | ND | ND |
| ESSPRI sicca score, median (min–max) * | 4 (1–9) | ND | ND |
| ESSPRI fatigue score, median (min–max) * | 6.5 (0–10) | ND | ND |
| ESSPRI pain score, median (min–max) * | 4 (0–10) | ND | ND |
| Treatment | |||
| Untreated patients, n (%) | 17 (34%) | 37 (46%) | 0.5779 |
| Treated with IVIg, n (%) | 22 (44%) | 30 (38%) | 0.8074 |
| Treated with oral azathioprine or prednisolon, n (%) | 6 (12%) | 11 (14%) | 0.5809 |
| Treated with cyclophosphamide, rituximab or ocrelizumab, n (%) | 5 (10%) | 2 (2%) | 0.2285 |
| Characteristic | Sjögren’s Syndrome (n = 50) | Control Group (n = 80) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Serum albumin concentration [g/L], mean (min–max) | 40 (27–58) | 42 (31–51) | 0.1262 |
| Serum IgG concentration [g/L], mean (min–max) | 13 (0.4–49) | 12 (4–32) | 0.8991 |
| Serum IgA concentration [g/L], mean (min–max) | 2 (0.1–5.1) | 2 (0.5–8.8) | 0.6153 |
| Serum IgM concentration [g/L], mean (min–max) | 1.2 (0.03–7.7) | 1.2 (0.28–9.6) | 0.1538 |
| Serum KFLC concentration [mg/L], mean (min–max) | 19 (5–124) | 17 (7–42) | 0.4023 |
| Serum LFLC concentration [mg/L], mean (min–max) | 14 (3–131) | 15 (7–172) | 0.8802 |
| Salivary KFLC concentration [mg/L], mean (min–max) | 7 (0.4–30) | 7 (0.2–60) | 0.8183 |
| Salivary LFLC concentration [mg/L], mean (min–max) | 4 (0.5–32) | 3 (0.5–32) | 0.4934 |
| Saliva/serum KFLC quotient, mean (min–max) | 0.5 (0.02–1.7) | 0.4 (0.02–2.4) | 0.8764 |
| Saliva/serum LFLC quotient, mean (min–max) | 0.3 (0.02–1.3) | 0.2 (0.01–1.4) | 0.3983 |
| eGFR [mL/min/1.73 m2], mean (min–max) | 82 (51–118) | 87 (39–134) | 0.1372 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Konen, F.F.; Seeliger, T.; Schwenkenbecher, P.; Gingele, S.; Jendretzky, K.F.; Sühs, K.-W.; Ernst, D.; Witte, T.; Skripuletz, T. Saliva Free Light Chains in Patients with Neuro-Sjögren. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2470. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10102470
Konen FF, Seeliger T, Schwenkenbecher P, Gingele S, Jendretzky KF, Sühs K-W, Ernst D, Witte T, Skripuletz T. Saliva Free Light Chains in Patients with Neuro-Sjögren. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(10):2470. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10102470
Chicago/Turabian StyleKonen, Franz Felix, Tabea Seeliger, Philipp Schwenkenbecher, Stefan Gingele, Konstantin Fritz Jendretzky, Kurt-Wolfram Sühs, Diana Ernst, Torsten Witte, and Thomas Skripuletz. 2022. "Saliva Free Light Chains in Patients with Neuro-Sjögren" Biomedicines 10, no. 10: 2470. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10102470
APA StyleKonen, F. F., Seeliger, T., Schwenkenbecher, P., Gingele, S., Jendretzky, K. F., Sühs, K.-W., Ernst, D., Witte, T., & Skripuletz, T. (2022). Saliva Free Light Chains in Patients with Neuro-Sjögren. Biomedicines, 10(10), 2470. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10102470






