Novel Prostate Cancer Biomarkers: Aetiology, Clinical Performance and Sensing Applications
Abstract
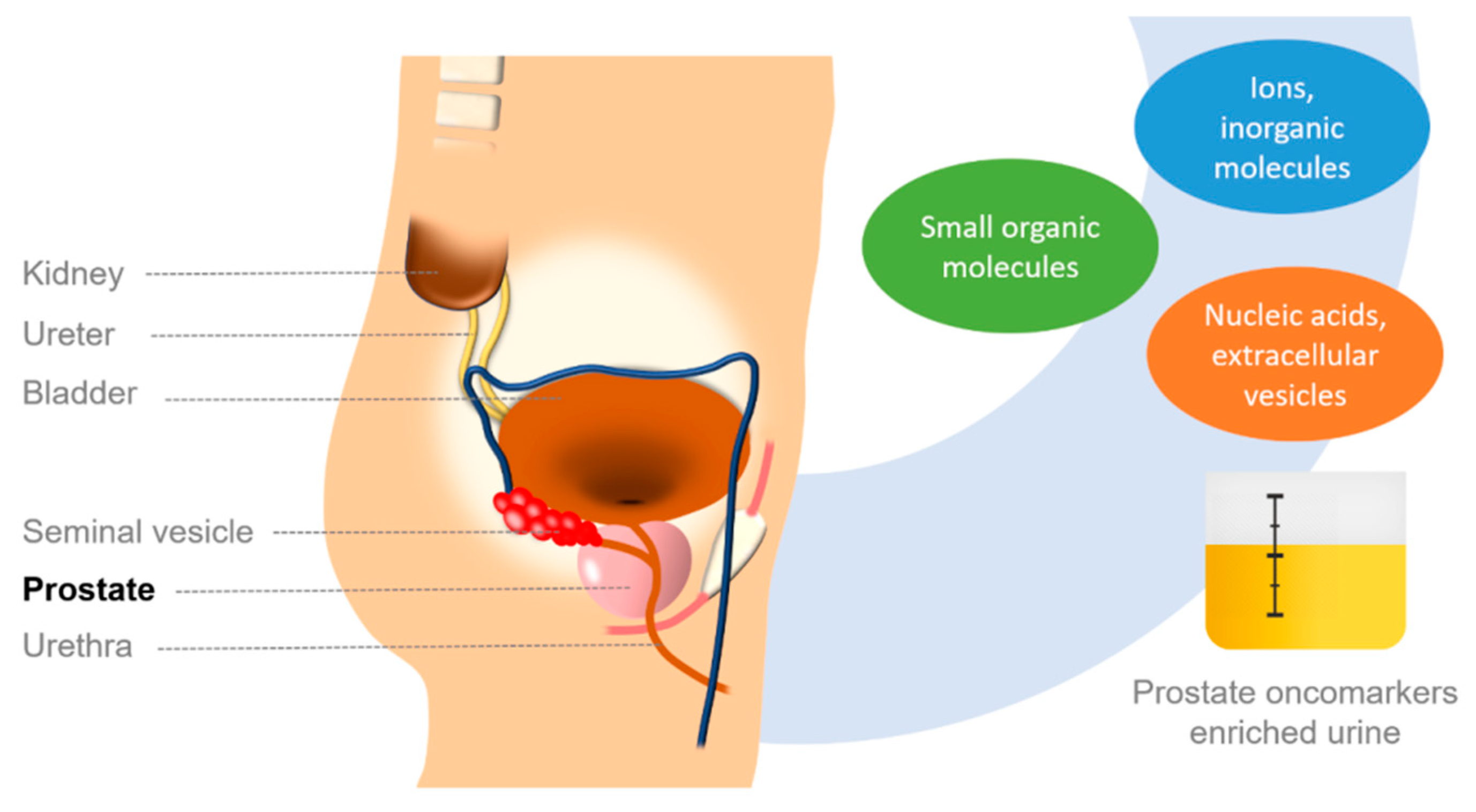
1. Prostate Cancer
2. Ions and Small Molecules as PCa Biomarkers
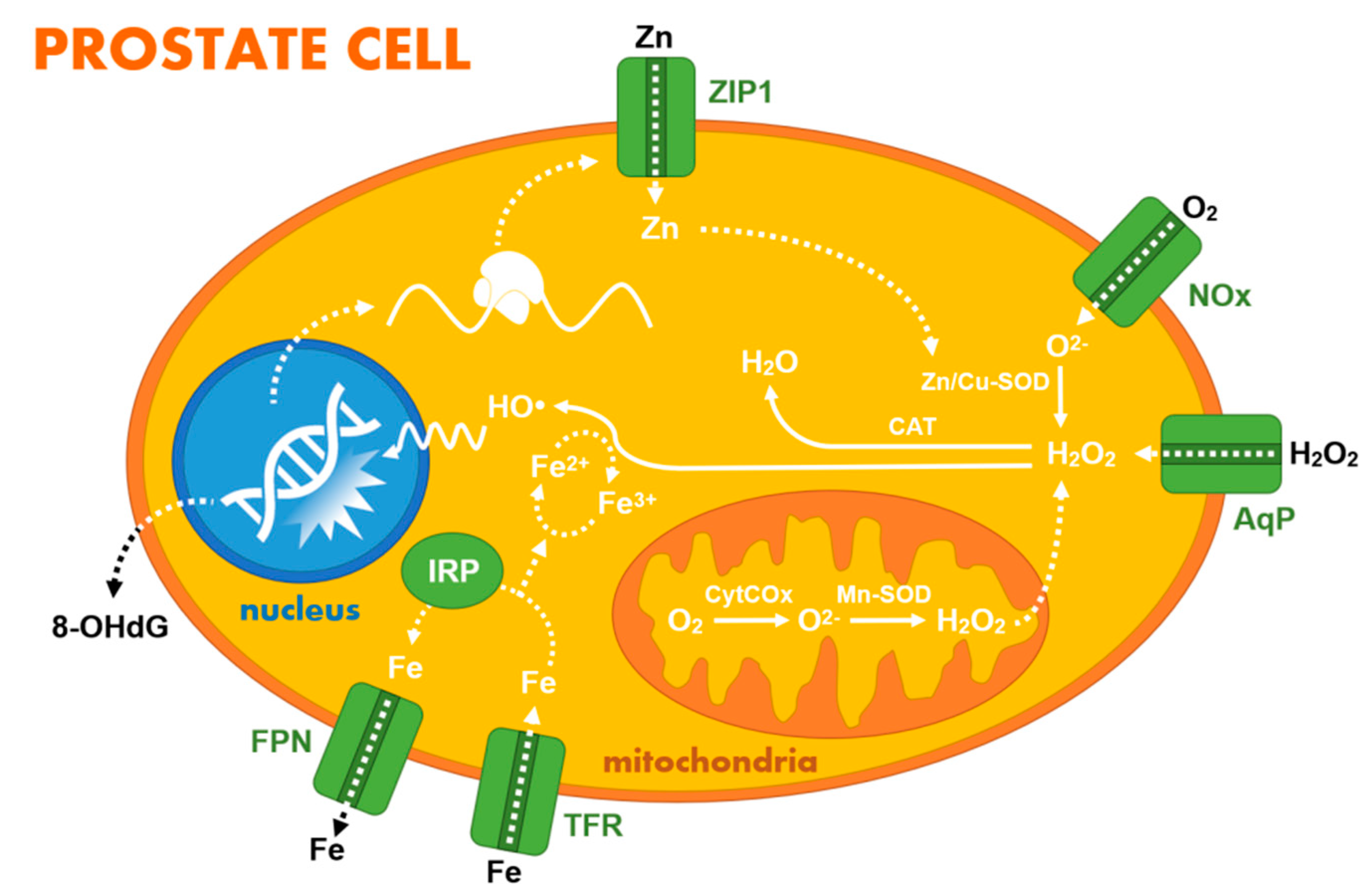
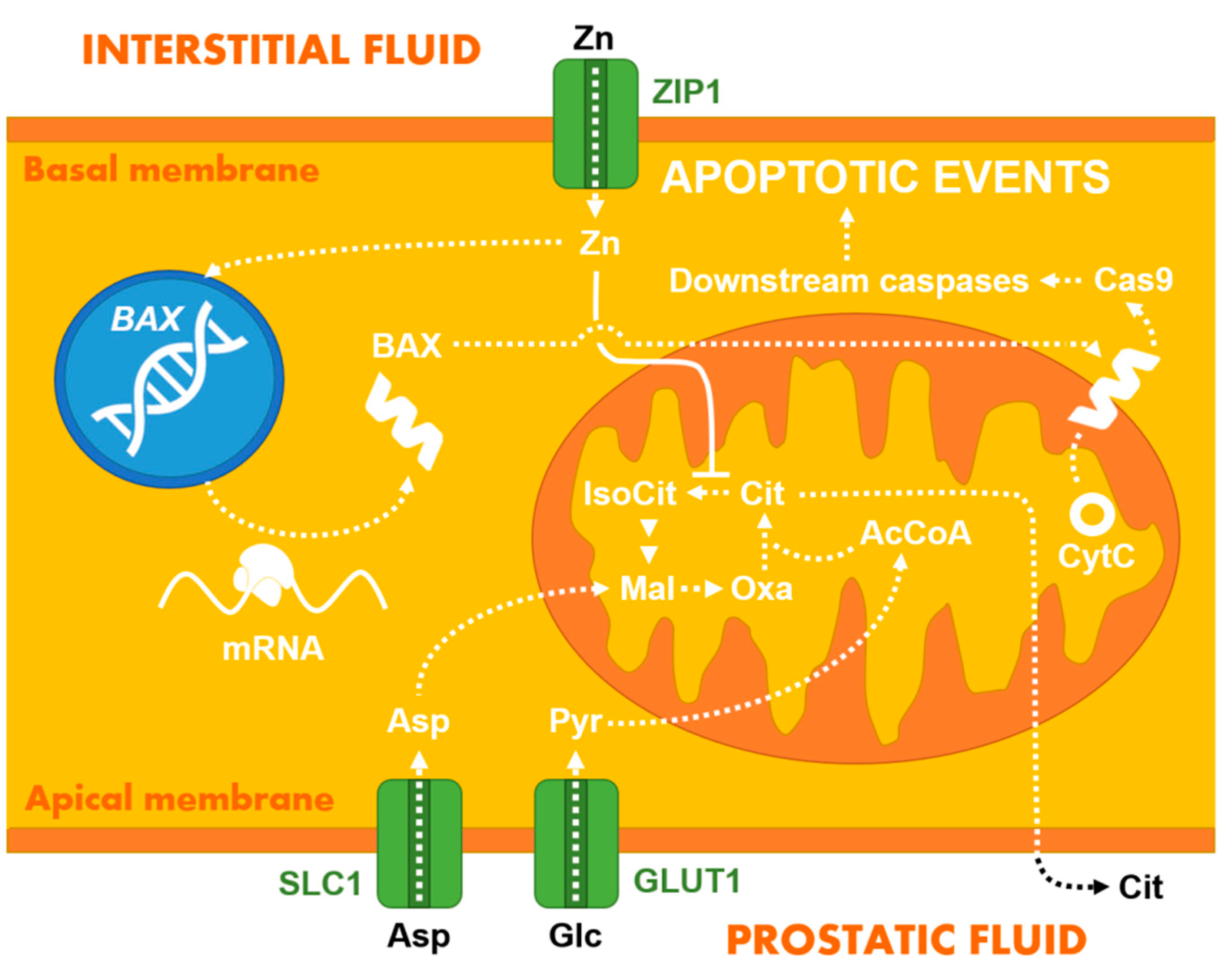
2.1. Zinc Homeostasis and Its Diagnostic Value
2.2. Other Ions, Hydrogen Peroxide, and Small Organic Molecules
| Detection | Surface Modification | LOD (nM) | Linear Range (µM) | RT (s) | Stability (h) | Application | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amper. | PVA-Ag/AnNPs-pphTEOS-SOX/GE | 500 | 0.5–7.5 | 17 | - | Aq. media | [66] |
| Amper. | SOX/EDC/NHS/Au/ZnONPs/SPEs | 16 | 0.01–0.1 | - | 60 d | Synth. urine | [50] |
| Amper. | SOX/CHIT/CuNPs/cMWCNT/AuE | 0.0001 | 0.1–100 | 2 | 180 d | Serum | [67] |
| Amper. | SOXNPs/AuE | 10 | 0.1–100 | 2 | 180 | Urine | [68] |
| Amper. | SOX/Pt@ZIF8/GCE | 1060 | 5–30 | - | 3 | Aq. media | [69] |
| Amper. | Nafion-SOX/Pt/AAO | 50 | 0.05–100 | - | - | Aq. media | [70] |
| Amper. | SOX/Pt/OIHMMP/GCE | 130 | 1–70 | - | - | Serum | [71] |
| Amper. | SOX/PAA/GCE | 0.4 | 0.001–0.05 | - | 15 d | Urine | [72] |
| Amper. | SOX/Pt-Fe3O4@C/GCE | 430 | 0.5–60 | - | - | Serum | [73] |
| Amper. | SOX/chitosan/Ti3C2TX/GCE | 18 | 0.036–7.8 | 2 | - | Synth. urine | [44] |
| Amper. | Fe3O4@ZIF-8@MIP/AuE | 0.0004 | 0.000001–0.0001 | - | 5 w | Urine | [74] |
| Potent. | MIP-based sensor | 0.14 | 0.001–10 | <120 | >5 m | Aq. media | [75] |
| Potent. | GO based nanocomposite | 3.3 | 0.01–100 | 60 | 3–4 m | Aq. media | [76] |
| Potent. | Non-GO based nanocomposite | 0.005 | 0.001–10 | 60 | 3–4 m | Aq. media | [76] |
| Imped. | MIP/AuNPs/SPCE | 8.5 | 0.011–17.9 | - | ~7 d | Aq. media | [77] |
| Color. | PdNPs based sensing platform | 5.0 | 0.01–50 | - | - | Urine | [78] |
| Color. | NQS/GO/GCE | 730 | 6.2–26.3 | - | - | Aq. media | [79] |
| Fluor. | Nanomaghemite/AuNPs/QD/peptide | 0.05 | 0.005–0.05 | - | - | Urine, cells | [80] |
| Fluor. | ssDNA aptamer-based sensor | 55 | 0.1–2 | - | - | Urine | [81] |
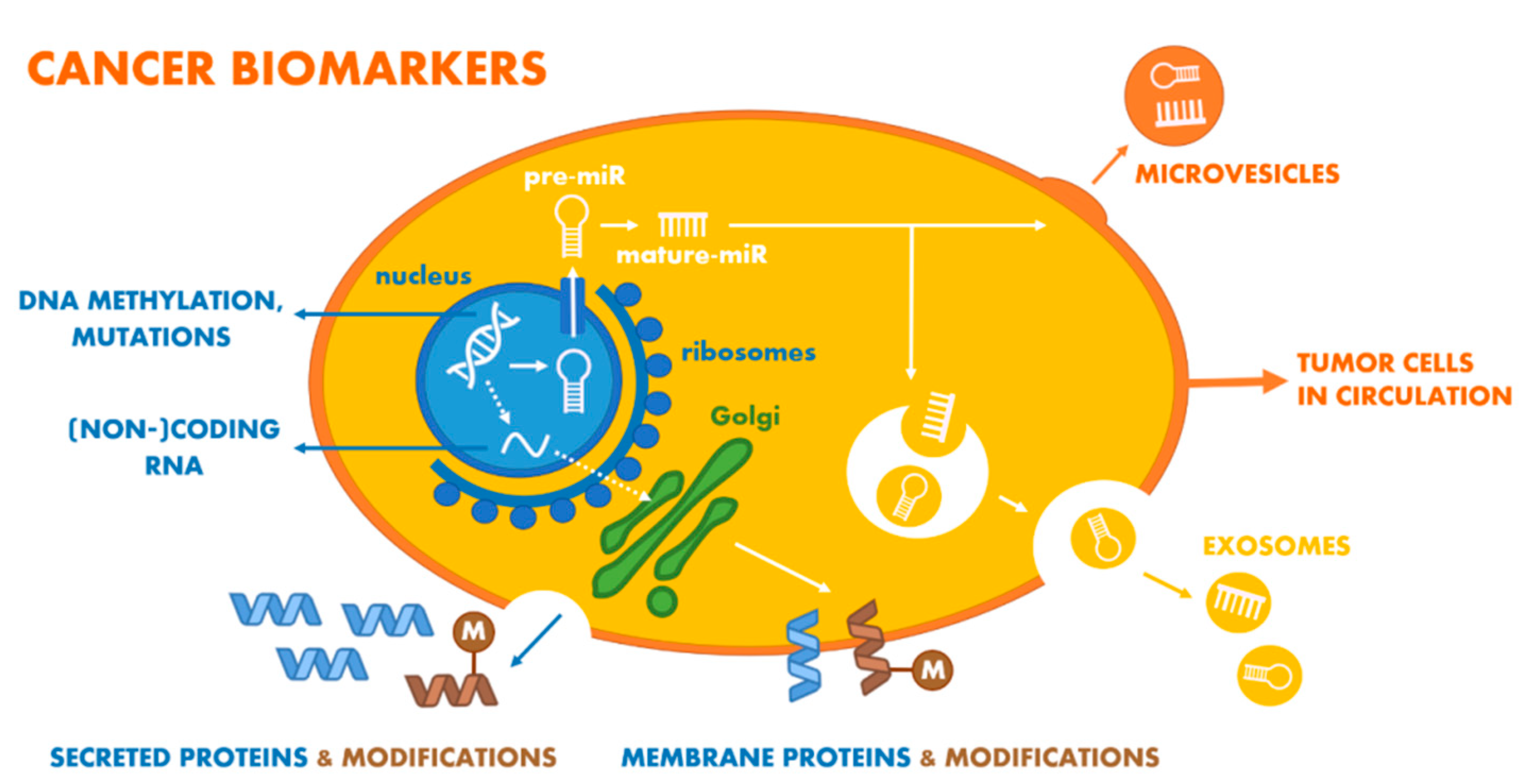
3. Nucleic Acid-Based PCa Biomarkers
3.1. PCA3 Gene RNA Product
3.2. miRNA PCa Biomarkers
3.3. Changes in DNA Level (DNA-Based and Derived Oncomarkers)
4. Protein-Based PCa Biomarkers
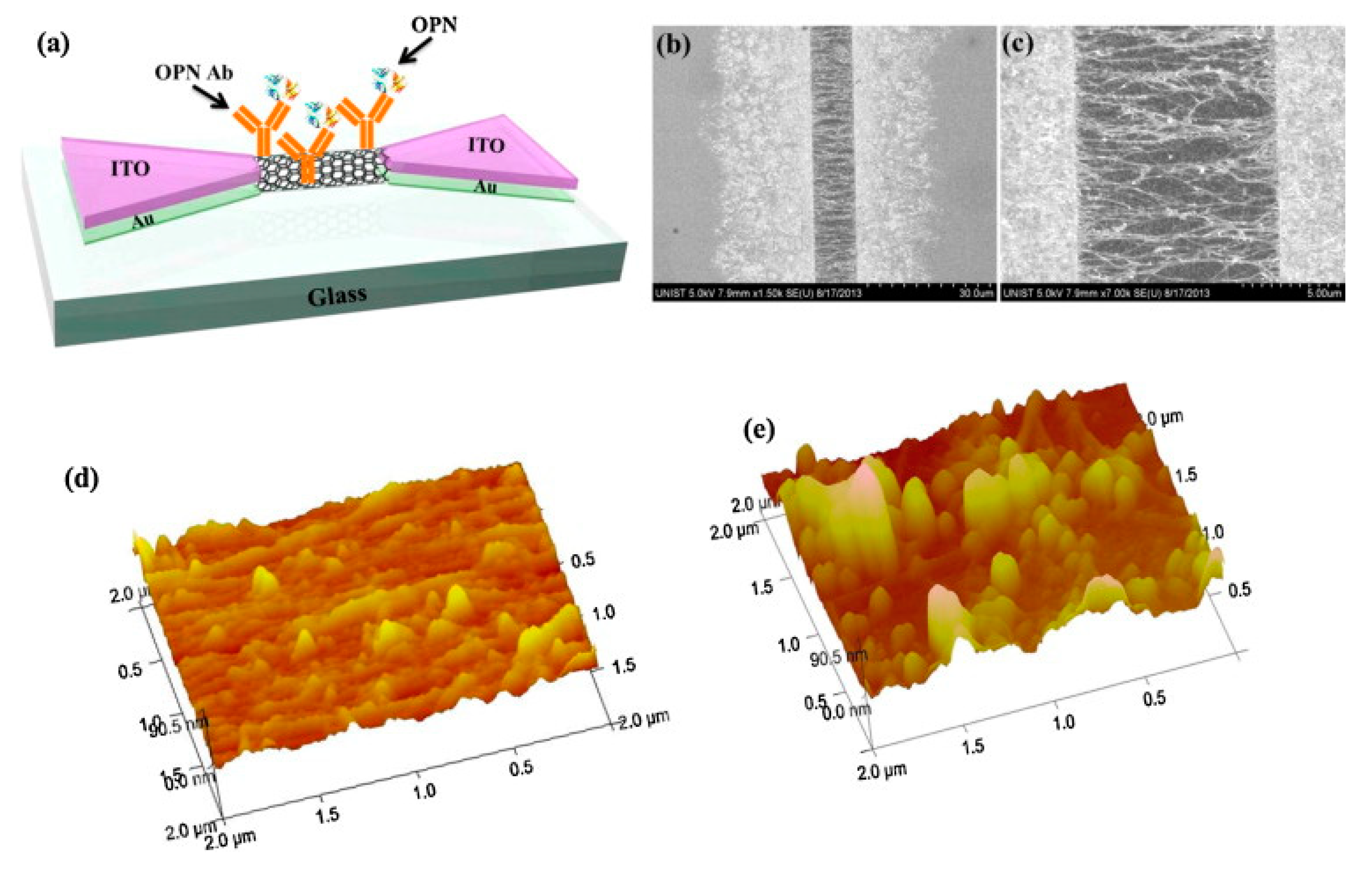
4.1. Osteopontin
4.2. Engrailed-2 Protein (EN2)
4.3. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR)
4.4. Alpha-Methylacyl-CoA Racemase (AMACR)
4.5. Prostatic Acid Phosphatase (PAP)
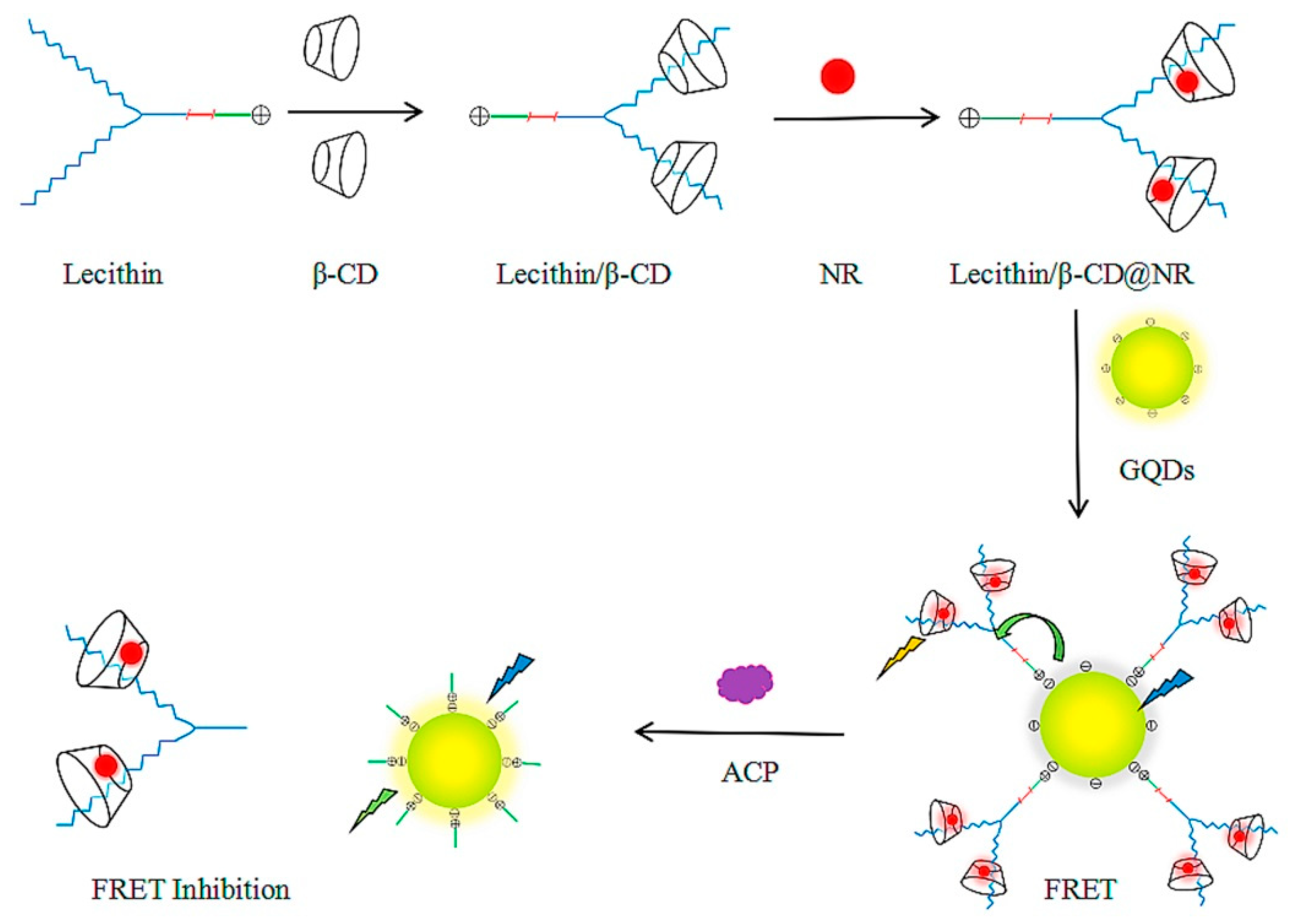
4.6. Acid Phosphatase (ACP)
4.7. Spondin-2 (SPON2)
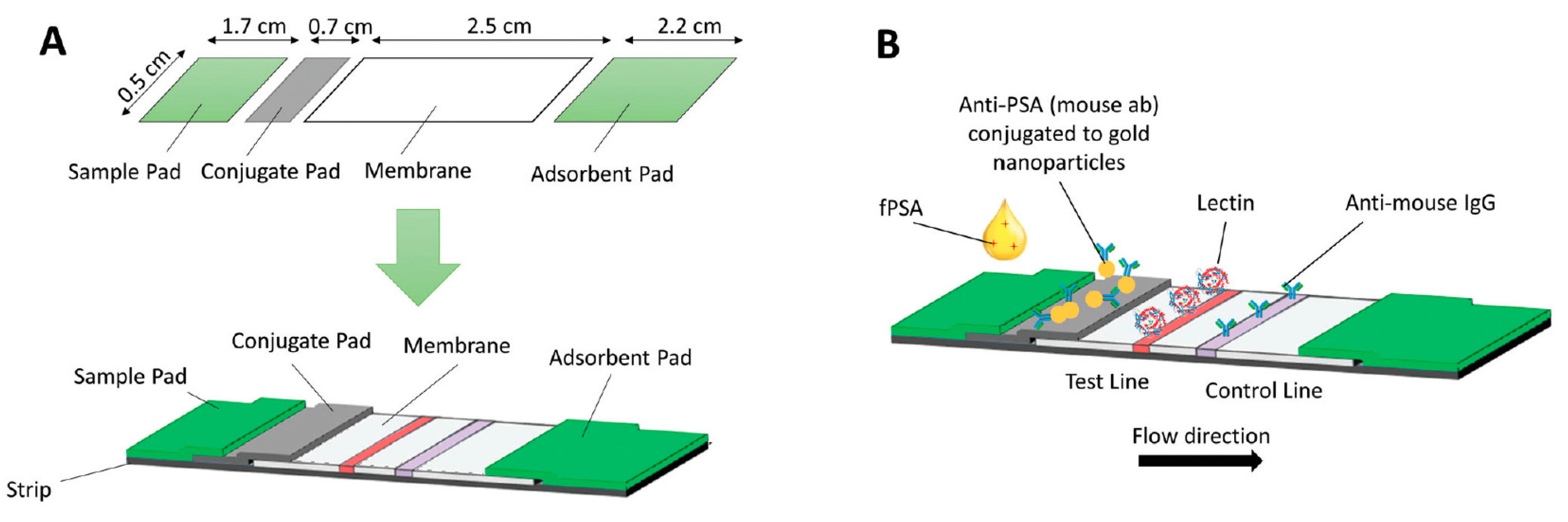
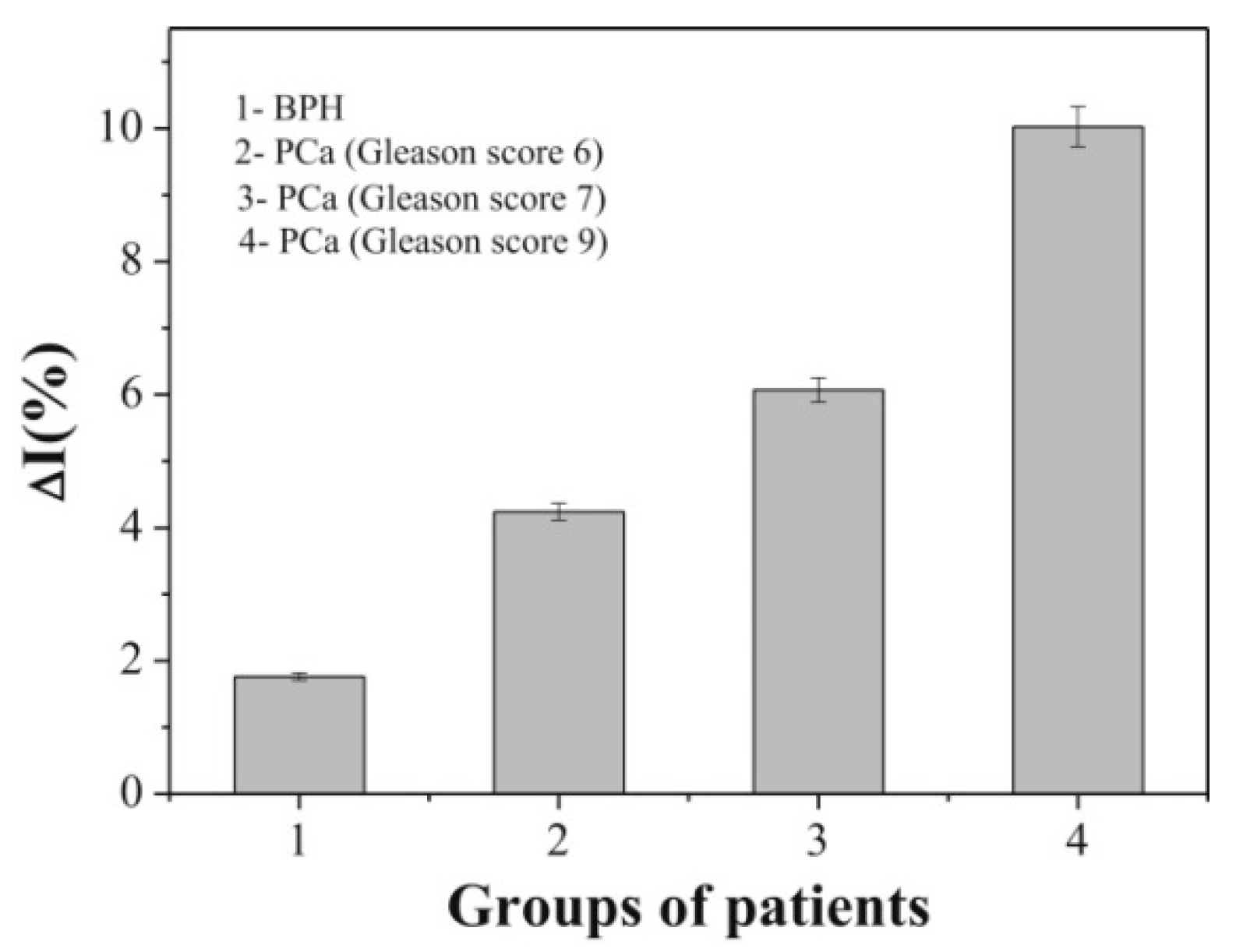
4.8. Prostate Membrane-Specific Antigen (PSMA)
4.9. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF)
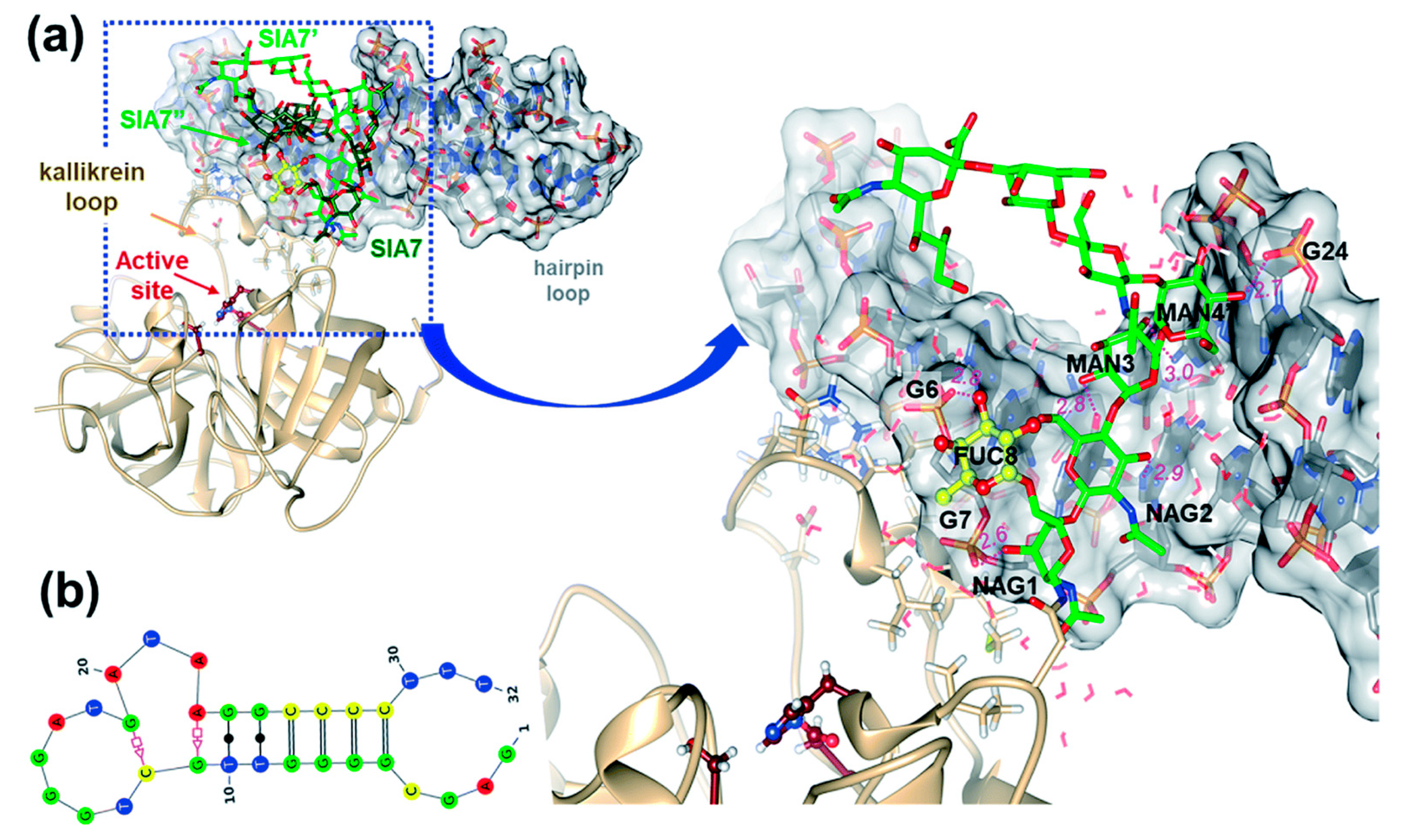
5. Glycan-Based PCa Biomarkers
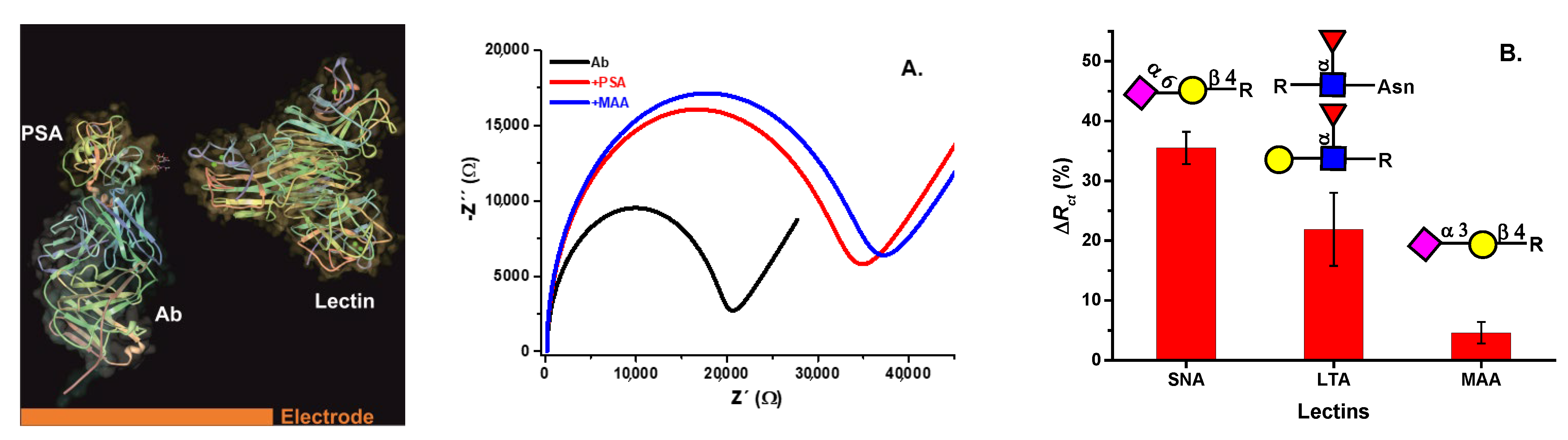
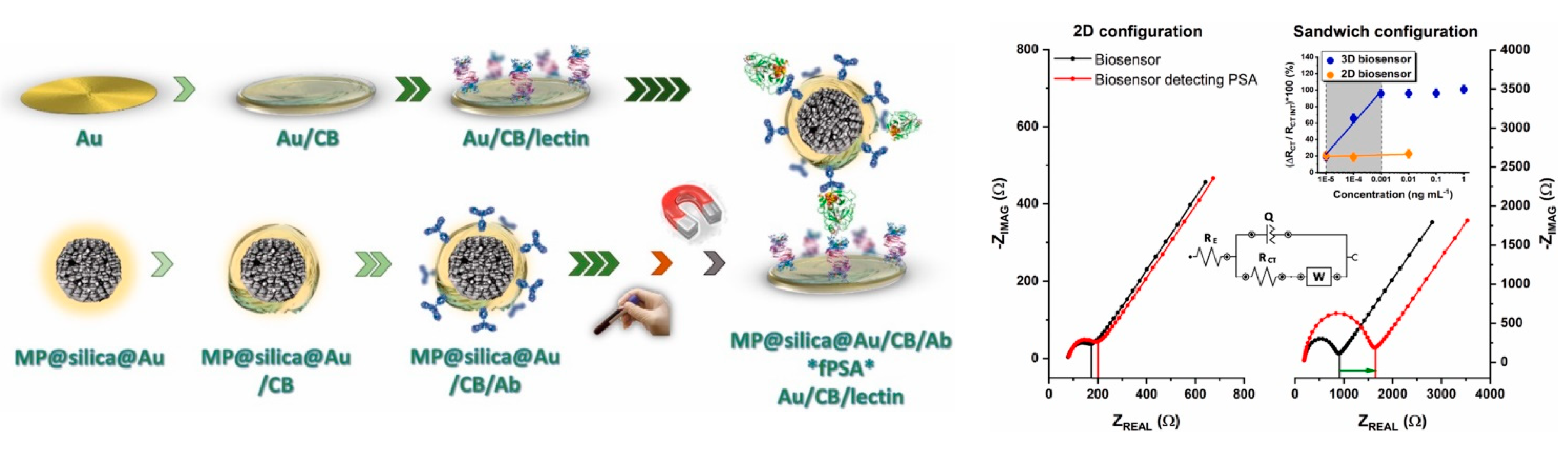
5.1. Lectin-Based Glycan Analysis
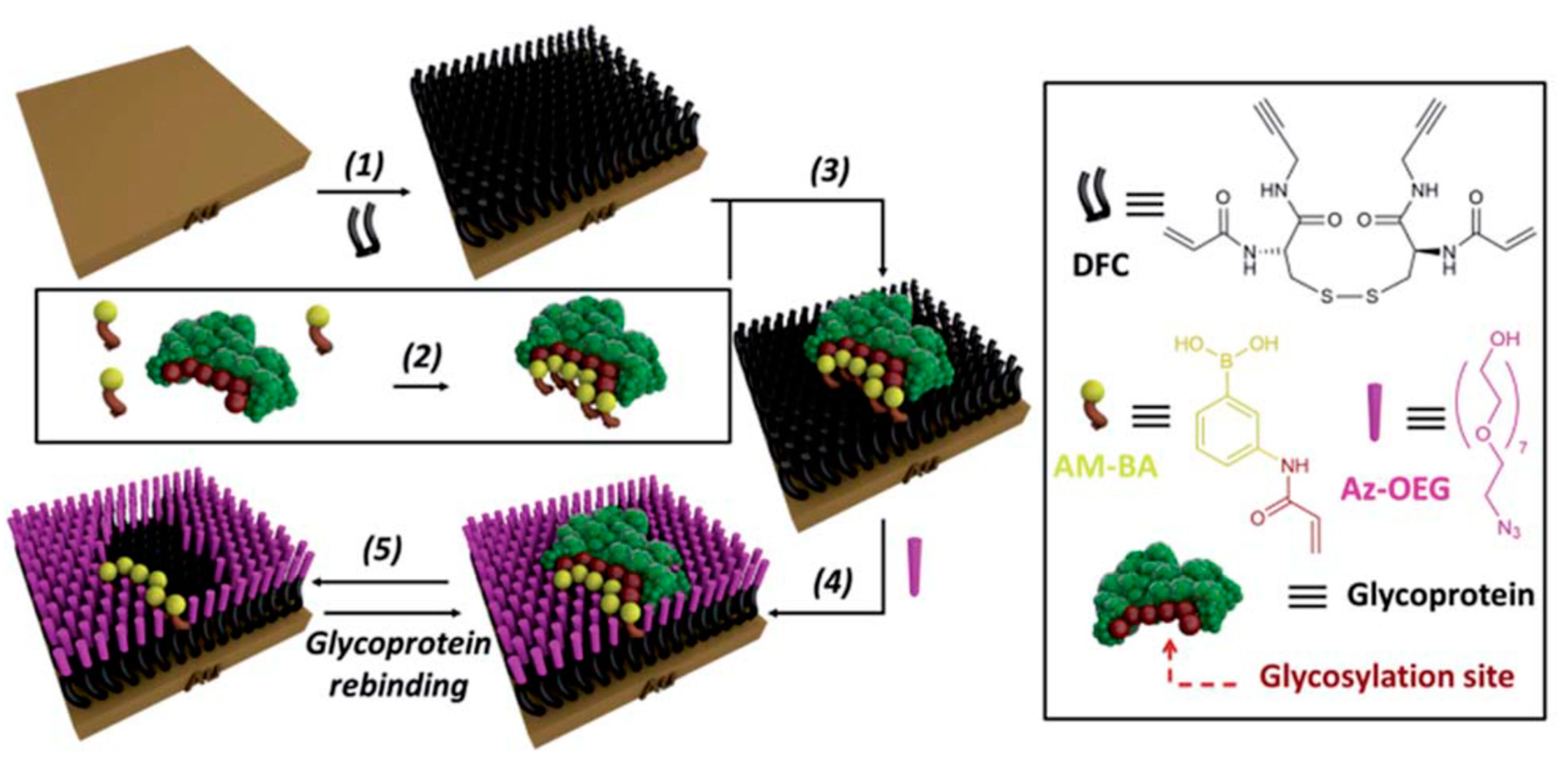
5.2. Molecularly-Imprinted Polymers (MIPs) for Glycan Analysis
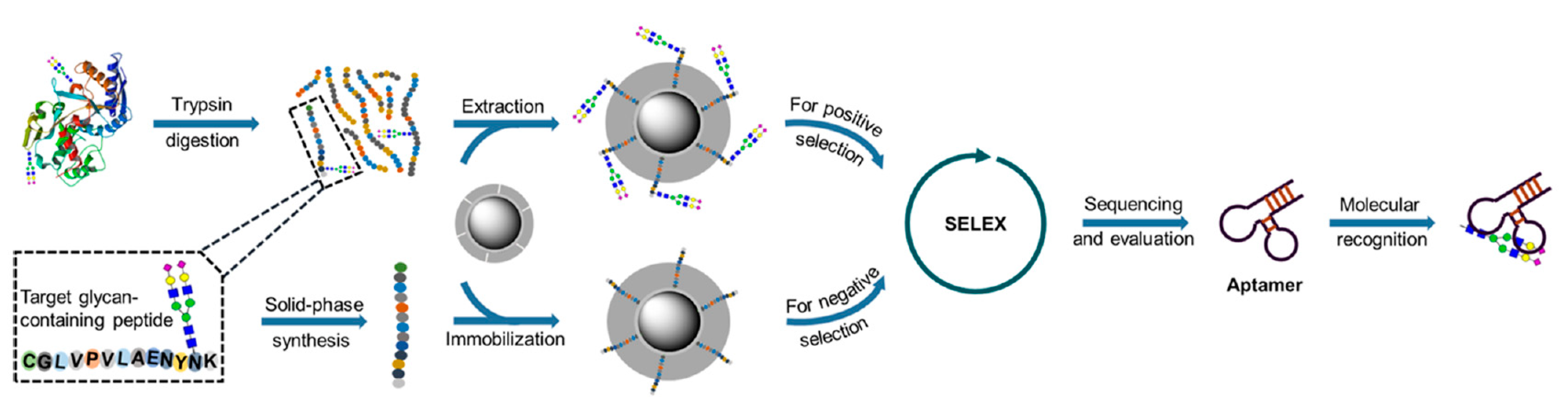
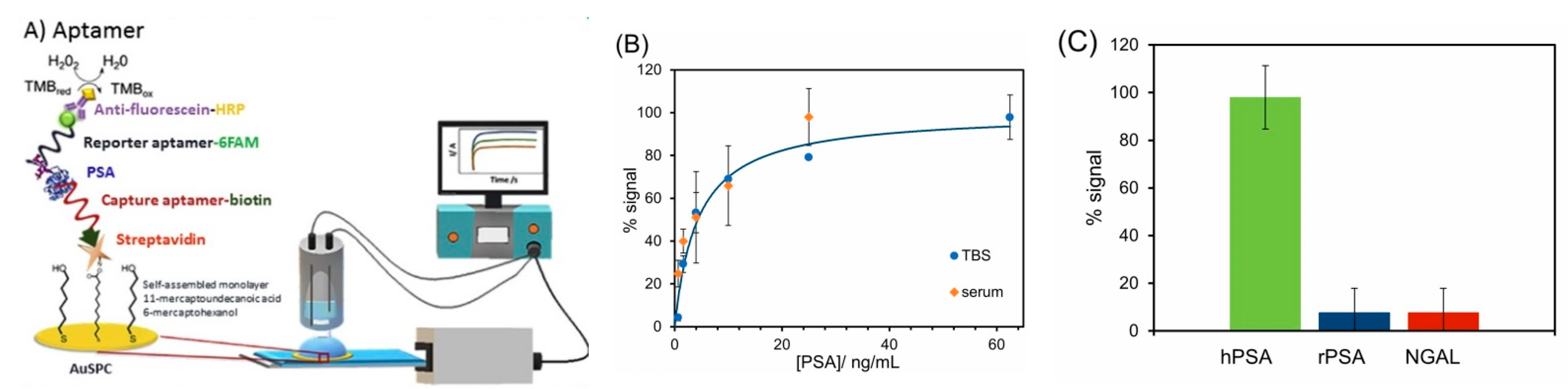
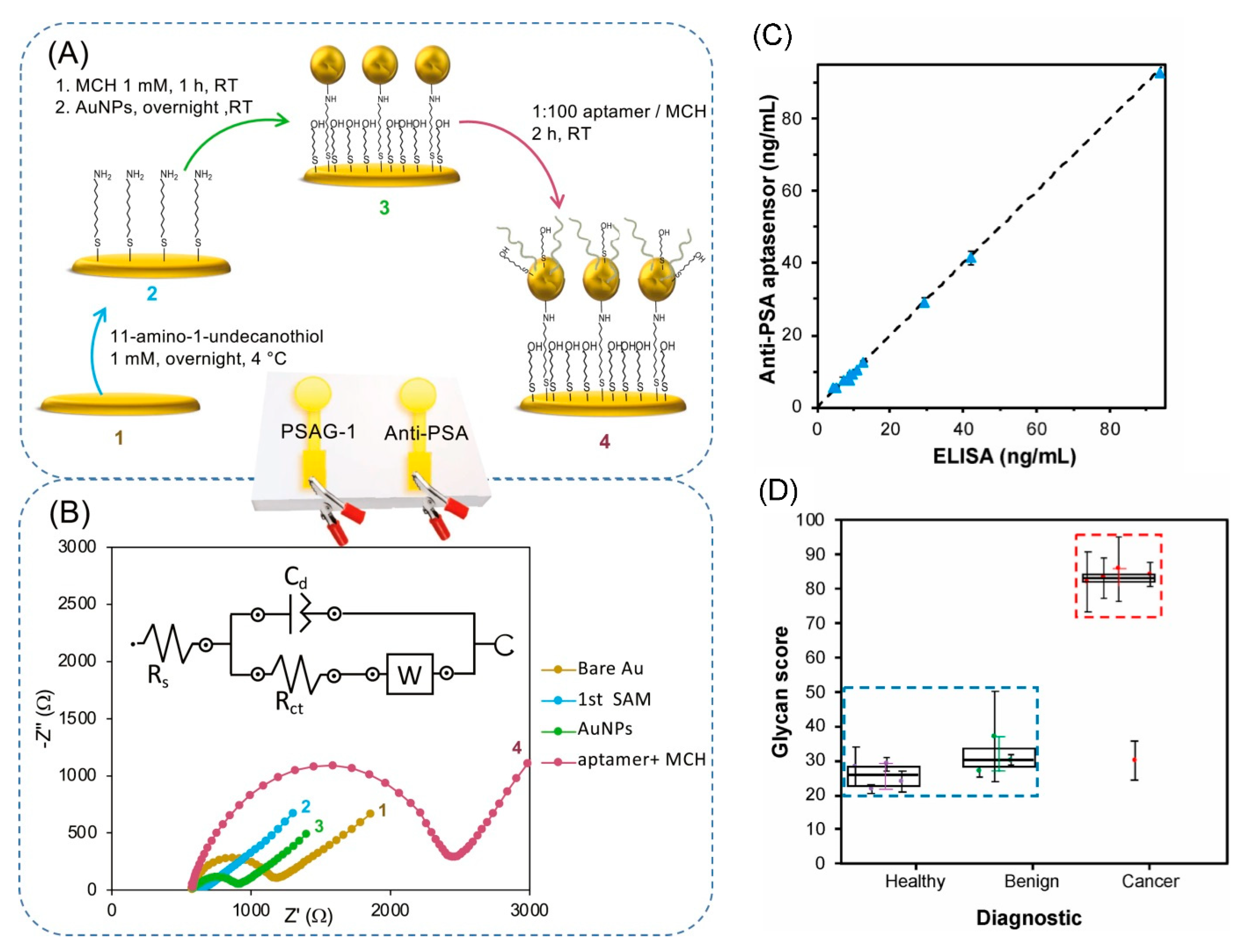
5.3. Detection of Glycoproteins Using Specific Aptamers
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawla, P. Epidemiology of Prostate Cancer. World J. Oncol. 2019, 10, 63–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kensler, K.H.; Pernar, C.H.; Mahal, B.A.; Nguyen, P.L.; Trinh, Q.-D.; Kibel, A.S.; Rebbeck, T.R. Racial/ethnic variation in PSA testing and prostate cancer incidence following the 2012 U.S.P.S.T.F. recommendation. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, J.A.; Moser, R.P.; Ellison, G.L.; Martin, D.N. Associations of Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) Testing in the US Population: Results from a National Cross-Sectional Survey. J. Community Health 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkac, J.; Gajdosova, V.; Hroncekova, S.; Bertok, T.; Hires, M.; Jane, E.; Lorencova, L.; Kasak, P. Prostate-specific antigen glycoprofiling as diagnostic and prognostic biomarker of prostate cancer. Interface Focus 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattox, A.K.; Bettegowda, C.; Zhou, S.; Papadopoulos, N.; Kinzler, K.W.; Vogelstein, B. Applications of liquid biopsies for cancer. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, eaay1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkac, J.; Bertok, T.; Hires, M.; Jane, E.; Lorencova, L.; Kasak, P. Glycomics of prostate cancer: Updates. Exp. Rev. Proteom. 2019, 16, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gratacós-Mulleras, A.; Duran, A.; Asadi Shehni, A.; Ferrer-Batallé, M.; Ramírez, M.; Comet, J.; de Llorens, R.; Saldova, R.; Llop, E.; Peracaula, R. Characterisation of the main PSA glycoforms in aggressive prostate cancer. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertok, T.; Jane, E.; Bertokova, A.; Lorencova, L.; Zvara, P.; Smolkova, B.; Kucera, R.; Klocker, H.; Tkac, J. Validating fPSA Glycoprofile as a Prostate Cancer Biomarker to Avoid Unnecessary Biopsies and Re-Biopsies. Cancers 2020, 12, 2988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, N.P.; Fuentealba, C.; Reyes, E.; Lopez, M.A.; Salazar, A.; Minzer, S.; Munoz, L.; Orrego, S.; Guzman, E.; Arzeno, L. Predictive Value of Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio in the Diagnosis of Significant Prostate Cancer at Initial Biopsy: A Comparison with Free Percent Prostate Specific Antigen, Prostate Specific Antigen Density and Primary Circulating Prostate Cells. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2019, 20, 3385–3389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawahara, T.; Fukui, S.; Sakamaki, K.; Ito, Y.; Ito, H.; Kobayashi, N.; Izumi, K.; Yokomizo, Y.; Miyoshi, Y.; Makiyama, K.; et al. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio predicts prostatic carcinoma in men undergoing needle biopsy. Oncotarget 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejous, C.; Krishnan, U.M. Sensors for diagnosis of prostate cancer: Looking beyond the prostate specific antigen. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 173, 112790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Zapatero-Rodríguez, J.; O’Kennedy, R. Prostate cancer diagnostics: Clinical challenges and the ongoing need for disruptive and effective diagnostic tools. Biotechnol. Adv. 2017, 35, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodson, R. Small organ, big reach. Nature 2015, 528, S118–S119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2015, 65, 5–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNally, C.J.; Ruddock, M.W.; Moore, T.; McKenna, D.J. Biomarkers That Differentiate Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia from Prostate Cancer: A Literature Review. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 5225–5241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, H. Laboratory measurement of urine albumin and urine total protein in screening for proteinuria in chronic kidney disease. Clin. Biochem. Rev. 2011, 32, 97–102. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, M.M.; Calixto, J.D.; Sousa, A.C.A.; Pereira, B.J.; Lima, Á.S.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Freire, M.G. Towards the differential diagnosis of prostate cancer by the pre-treatment of human urine using ionic liquids. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maywald, M.; Wessels, I.; Rink, L. Zinc Signals and Immunity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessels, I.; Maywald, M.; Rink, L. Zinc as a Gatekeeper of Immune Function. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kambe, T.; Matsunaga, M.; Takeda, T.-A. Understanding the Contribution of Zinc Transporters in the Function of the Early Secretory Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Stovall, D.B.; Wang, W.; Sui, G. Advances of Zinc Signaling Studies in Prostate Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costello, L.C.; Franklin, R.B. A comprehensive review of the role of zinc in normal prostate function and metabolism; and its implications in prostate cancer. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2016, 611, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wu, Q.; Hu, X.; Dong, X.; Wang, L.; Liu, Q.; Long, Z.; Li, L. Comparative study of serum zinc concentrations in benign and malignant prostate disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hupe, M.C.; Philippi, C.; Roth, D.; Kümpers, C.; Ribbat-Idel, J.; Becker, F.; Joerg, V.; Duensing, S.; Lubczyk, V.H.; Kirfel, J.; et al. Expression of Prostate-Specific Membrane Antigen (PSMA) on Biopsies Is an Independent Risk Stratifier of Prostate Cancer Patients at Time of Initial Diagnosis. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wüstemann, T.; Haberkorn, U.; Babich, J.; Mier, W. Targeting prostate cancer: Prostate-specific membrane antigen based diagnosis and therapy. Med. Res. Rev. 2019, 39, 40–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, K.; Nonomura, N. Role of Androgen Receptor in Prostate Cancer: A Review. World J. Men Health 2019, 37, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Wan, X.; Du, C.; Wang, H.; Zhou, J.; Wang, Z. A novel fluorescent probe for the early detection of prostate cancer based on endogenous zinc sensing. Prostate 2019, 79, 1378–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.; Chang, W.; Wang, W.; Wu, H.; Pu, K.; Wu, A.; Qin, Z.; Tao, Y.; Yue, Z.; Wang, P.; et al. A novel tetrapeptide fluorescence sensor for early diagnosis of prostate cancer based on imaging Zn(2+) in healthy versus cancerous cells. J. Adv. Res. 2020, 24, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, J.M.; Wang, F.; Sessler, C.D.; Vogler, N.W.; Zhang, D.Y.; Loucks, W.H.; Tzounopoulos, T.; Lippard, S.J. Photoactivatable Sensors for Detecting Mobile Zinc. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 2020–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Y.; Singh, C.K.; Sadak, O.; Ahmad, N.; Gunasekaran, S. Electrochemical detection of mobile zinc ions for early diagnosis of prostate cancer. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2019, 833, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarafanov, A.G.; Todorov, T.I.; Centeno, J.A.; Macias, V.; Gao, W.; Liang, W.M.; Beam, C.; Gray, M.A.; Kajdacsy-Balla, A.A. Prostate cancer outcome and tissue levels of metal ions. Prostate 2011, 71, 1231–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, J.T.; Tan, Y.Q.; Valeri, L.; Lee, J.; Geok, P.P.; Chia, S.E.; Ong, C.N.; Seow, W.J. Association between serum heavy metals and prostate cancer risk—A multiple metal analysis. Environ. Int. 2019, 132, 105109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vela, D. Iron Metabolism in Prostate Cancer; From Basic Science to New Therapeutic Strategies. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stelling, M.P.; Motta, J.M.; Mashid, M.; Johnson, W.E.; Pavão, M.S.; Farrell, N.P. Metal ions and the extracellular matrix in tumor migration. FEBS J. 2019, 286, 2950–2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serhan, M.; Jackemeyer, D.; Long, M.; Sprowls, M.; Diez Perez, I.; Maret, W.; Chen, F.; Tao, N.; Forzani, E. Total Iron Measurement in Human Serum with a Novel Smartphone-Based Assay. IEEE J. Trans. Eng. Health Med. 2020, 8, 2800309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshin, O.; Kireev, D.; Hlukhova, H.; Idachaba, F.; Akinwande, D.; Atayero, A. Graphene-Based Biosensor for Early Detection of Iron Deficiency. Sensors 2020, 20, 3688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.D.; Sun, C.; Lambeth, J.D.; Marshall, F.; Amin, M.; Chung, L.; Petros, J.A.; Arnold, R.S. Increased Nox1 and hydrogen peroxide in prostate cancer. Prostate 2005, 62, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, C.; Wang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Chen, S.; Han, Y.; Li, L.; Wang, M.; Jin, X. Roles of Reactive Oxygen Species in Biological Behaviors of Prostate Cancer. Biomed. Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 1269624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimalasena, S.; Gothard, L.; Anbalagan, S.; Allen, S.; Sinnett, V.; Mohammed, K.; Kothari, G.; Musallam, A.; Lucy, C.; Yu, S.; et al. Intratumoral Hydrogen Peroxide with Radiation Therapy in Locally Advanced Breast Cancer: Results from a Phase 1 Clinical Trial. Int. J. Rad. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2020, 108, 1019–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crulhas, B.P.; Ramos, N.P.; Castro, G.R.; Pedrosa, V.A. Detection of hydrogen peroxide releasing from prostate cancer cell using a biosensor. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2016, 20, 2427–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Cheng, K.; Wang, W.; Yang, L.; Xie, Y.; Feng, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Sun, H. A pyrene-based ratiometric fluorescent probe with a large Stokes shift for selective detection of hydrogen peroxide in living cells. J. Pharm. Anal. 2020, 10, 490–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorencova, L.; Bertok, T.; Dosekova, E.; Holazova, A.; Paprckova, D.; Vikartovska, A.; Sasinkova, V.; Filip, J.; Kasak, P.; Jerigova, M.; et al. Electrochemical performance of Ti(3)C(2)T(x) MXene in aqueous media: Towards ultrasensitive H2O2 sensing. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 235, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hroncekova, S.; Bertok, T.; Hires, M.; Jane, E.; Lorencova, L.; Vikartovska, A.; Tanvir, A.; Kasak, P.; Tkac, J. Ultrasensitive Ti3C2TX MXene/Chitosan Nanocomposite-Based Amperometric Biosensor for Detection of Potential Prostate Cancer Marker in Urine Samples. Processes 2020, 8, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strmiska, V.; Michalek, P.; Lackova, Z.; Guran, R.; Krizkova, S.; Vanickova, L.; Zitka, O.; Stiborova, M.; Eckschlager, T.; Klejdus, B.; et al. Sarcosine is a prostate epigenetic modifier that elicits aberrant methylation patterns through the SAMe-Dnmts axis. Mol. Oncol. 2019, 13, 1002–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreekumar, A.; Poisson, L.M.; Rajendiran, T.M.; Khan, A.P.; Cao, Q.; Yu, J.; Laxman, B.; Mehra, R.; Lonigro, R.J.; Li, Y.; et al. Metabolomic profiles delineate potential role for sarcosine in prostate cancer progression. Nature 2009, 457, 910–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cernei, N.; Heger, Z.; Gumulec, J.; Zitka, O.; Masarik, M.; Babula, P.; Eckschlager, T.; Stiborova, M.; Kizek, R.; Adam, V. Sarcosine as a potential prostate cancer biomarker—A review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 13893–13908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jornet-Martínez, N.; Henderson, C.J.; Campíns-Falcó, P.; Daly, R.; Hall, E.A.H. Towards sarcosine determination in urine for prostatic carcinoma detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 287, 380–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heger, Z.; Merlos Rodrigo, M.A.; Michalek, P.; Polanska, H.; Masarik, M.; Vit, V.; Plevova, M.; Pacik, D.; Eckschlager, T.; Stiborova, M.; et al. Sarcosine Up-Regulates Expression of Genes Involved in Cell Cycle Progression of Metastatic Models of Prostate Cancer. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebelo, T.S.; Pereira, C.M.; Sales, M.G.; Noronha, J.P.; Costa-Rodrigues, J.; Silva, F.; Fernandes, M.H. Sarcosine oxidase composite screen-printed electrode for sarcosine determination in biological samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 2014, 850, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Struys, E.A.; Heijboer, A.C.; van Moorselaar, J.; Jakobs, C.; Blankenstein, M.A. Serum sarcosine is not a marker for prostate cancer. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2010, 47, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ankerst, D.P.; Liss, M.; Zapata, D.; Hoefler, J.; Thompson, I.M.; Leach, R.J. A case control study of sarcosine as an early prostate cancer detection biomarker. BMC Urol. 2015, 15, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zou, L.; Liang, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, D.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, F.; Liu, M. The Urinary Sarcosine/Creatinine Ratio is a Potential Diagnostic and Prognostic Marker in Prostate Cancer. Med. Sci. Monit. 2018, 24, 3034–3041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkotsos, G.; Virgiliou, C.; Lagoudaki, I.; Sardeli, C.; Raikos, N.; Theodoridis, G.; Dimitriadis, G. The Role of Sarcosine, Uracil, and Kynurenic Acid Metabolism in Urine for Diagnosis and Progression Monitoring of Prostate Cancer. Metabolites 2017, 7, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kdadra, M.; Höckner, S.; Leung, H.; Kremer, W.; Schiffer, E. Metabolomics Biomarkers of Prostate Cancer: A Systematic Review. Diagnostics 2019, 9, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spur, E.-M.; Decelle, E.A.; Cheng, L.L. Metabolomic imaging of prostate cancer with magnetic resonance spectroscopy and mass spectrometry. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2013, 40, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, A.R.; Bastos, M.d.L.; Carvalho, M.; Guedes de Pinho, P. Biomarker Discovery in Human Prostate Cancer: An Update in Metabolomics Studies. Transl. Oncol. 2016, 9, 357–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzakos, V.; Slätis, K.; Djureinovic, T.; Helleday, T.; Hunt, M.C. N-acyl taurines are anti-proliferative in prostate cancer cells. Lipids 2012, 47, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Peralbo, M.A.; Gómez-Gómez, E.; Calderón-Santiago, M.; Carrasco-Valiente, J.; Ruiz-García, J.; Requena-Tapia, M.J.; Luque de Castro, M.D.; Priego-Capote, F. Prostate Cancer Patients–Negative Biopsy Controls Discrimination by Untargeted Metabolomics Analysis of Urine by LC-QTOF: Upstream Information on Other Omics. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dereziński, P.; Klupczynska, A.; Sawicki, W.; Pałka, J.A.; Kokot, Z.J. Amino Acid Profiles of Serum and Urine in Search for Prostate Cancer Biomarkers: A Pilot Study. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2017, 14, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giskeødegård, G.F.; Hansen, A.F.; Bertilsson, H.; Gonzalez, S.V.; Kristiansen, K.A.; Bruheim, P.; Mjøs, S.A.; Angelsen, A.; Bathen, T.F.; Tessem, M.B. Metabolic markers in blood can separate prostate cancer from benign prostatic hyperplasia. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 113, 1712–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, J.A.; Fensom, G.K.; Rinaldi, S.; Scalbert, A.; Appleby, P.N.; Achaintre, D.; Gicquiau, A.; Gunter, M.J.; Ferrari, P.; Kaaks, R.; et al. Pre-diagnostic metabolite concentrations and prostate cancer risk in 1077 cases and 1077 matched controls in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition. BMC Med. 2017, 15, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stabler, S.; Koyama, T.; Zhao, Z.; Martinez-Ferrer, M.; Allen, R.H.; Luka, Z.; Loukachevitch, L.V.; Clark, P.E.; Wagner, C.; Bhowmick, N.A. Serum methionine metabolites are risk factors for metastatic prostate cancer progression. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, D.M.; Nanni, C.; Fanti, S. Evaluation of Prostate Cancer with Radiolabeled Amino Acid Analogs. J. Nucl. Med. 2016, 57, 61s–66s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kobus, T.; Wright, A.J.; Weiland, E.; Heerschap, A.; Scheenen, T.W.J. Metabolite ratios in 1H MR spectroscopic imaging of the prostate. Magn. Res. Med. 2015, 73, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lad, U.; Kale, G.M.; Bryaskova, R. Sarcosine Oxidase Encapsulated Polyvinyl Alcohol-Silica-AuNP Hybrid Films for Sarcosine Sensing Electrochemical Bioelectrode. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2014, 161, B98–B101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narwal, V.; Kumar, P.; Joon, P.; Pundir, C.S. Fabrication of an amperometric sarcosine biosensor based on sarcosine oxidase/chitosan/CuNPs/c-MWCNT/Au electrode for detection of prostate cancer. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2018, 113, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Narwal, V.; Jaiwal, R.; Pundir, C.S. Construction and application of amperometric sarcosine biosensor based on SOxNPs/AuE for determination of prostate cancer. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 122, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Wang, J.; Yang, C.; Zhao, X.; Xie, S.; Ge, Z. Nano Pt@ZIF8 Modified Electrode and Its Application to Detect Sarcosine. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2018, 165, H247–H250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Wei, W.; Ke, S.; Zeng, X.; Lin, P. A novel and sensitive sarcosine biosensor based on organic electrochemical transistor. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 307, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, Q.; Du, D.; Yang, H.; Lin, Y. Amperometric sarcosine biosensor with strong anti-interference capabilities based on mesoporous organic-inorganic hybrid materials. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 141, 111431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ma, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; He, G. An amperometric biosensor for the assay of sarcosine based on the cross coupled chemical and electrochemical reactions with practical applications. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2019, 833, 568–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Li, N.; Li, Q.; Chen, S.; Wang, H.-L.; Yang, H. Amperometric sarcosine biosensor based on hollow magnetic Pt–Fe3O4@C nanospheres. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1078, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, P.; Wang, Y.; He, F. Electrochemical sensor based on super-magnetic metal–organic framework@molecularly imprinted polymer for Sarcosine detection in urine. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2020, 24, 620–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özkütük, E.B.; Diltemiz, S.E.; Avcı, Ş.; Uğurağ, D.; Aykanat, R.B.; Ersöz, A.; Say, R. Potentiometric sensor fabrication having 2D sarcosine memories and analytical features. Mat. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 69, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altunkök, N.; Biçen Ünlüer, Ö.; Birlik Özkütük, E.; Ersöz, A. Development of potentıometrıc bıosensor for dıagnosıs of prostate cancer. Mat. Sci. Eng. B 2021, 263, 114789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguy, T.P.; Van Phi, T.; Tram, D.T.N.; Eersels, K.; Wagner, P.; Lien, T.T.N. Development of an impedimetric sensor for the label-free detection of the amino acid sarcosine with molecularly imprinted polymer receptors. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2017, 246, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, J.; Xu, W.; Wan, Q.; Zhang, X.; Lin, J.; Chen, J.; Chen, J. Colorimetric determination of sarcosine in urine samples of prostatic carcinoma by mimic enzyme palladium nanoparticles. Anal. Chim. Acta 2014, 825, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Z.; Yin, B.; Wang, H.; Li, M.; Rao, H.; Liu, X.; Zhou, X.; Lu, X. An organic indicator functionalized graphene oxide nanocomposite-based colorimetric assay for the detection of sarcosine. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 5488–5496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heger, Z.; Cernei, N.; Krizkova, S.; Masarik, M.; Kopel, P.; Hodek, P.; Zitka, O.; Adam, V.; Kizek, R. Paramagnetic Nanoparticles as a Platform for FRET-Based Sarcosine Picomolar Detection. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, L.; Gao, T.; Pei, R. In vitro selection of DNA aptamers for the development of fluorescent aptasensor for sarcosine detection. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2018, 276, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornu, J.-N.; Cancel-Tassin, G.; Ondet, V.; Girardet, C.; Cussenot, O. Olfactory Detection of Prostate Cancer by Dogs Sniffing Urine: A Step Forward in Early Diagnosis. Eur. Urol. 2011, 59, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascual, L.; Campos, I.; Vivancos, J.-L.; Quintás, G.; Loras, A.; Martínez-Bisbal, M.C.; Martínez-Máñez, R.; Boronat, F.; Ruiz-Cerdà, J.L. Detection of prostate cancer using a voltammetric electronic tongue. Analyst 2016, 141, 4562–4567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, K.; Liu, T.; Chen, J.; Lv, W.; Yang, W.; Xu, S.; Wang, X.; Li, L. Decreased glucose bioavailability and elevated aspartate metabolism in prostate cancer cells undergoing epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020, 235, 5602–5612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Shen, Y.; Wen, Y.; Campbell, R.E. High-Performance Intensiometric Direct- and Inverse-Response Genetically Encoded Biosensors for Citrate. ACS Cent. Sci. 2020, 6, 1441–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abarghoei, S.; Fakhri, N.; Borghei, Y.S.; Hosseini, M.; Ganjali, M.R. A colorimetric paper sensor for citrate as biomarker for early stage detection of prostate cancer based on peroxidase-like activity of cysteine-capped gold nanoclusters. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2019, 210, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, H.; Liu, B.; Liu, D.; Zhu, X.; Wei, X.; Yu, L.; Shen, Q.; Qu, P.; Xu, M. Lanthanide coordination polymer-based biosensor for citrate detection in urine. Anal. Methods 2019, 11, 1405–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoi, T.H.; Chan, C.F.; Chan, W.L.; Chiu, K.F.; Wong, W.T.; Ng, C.F.; Wong, K.L. Urinary Polyamines: A Pilot Study on Their Roles as Prostate Cancer Detection Biomarkers. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Feng, Z.; Chen, N. Spermidine as a target for cancer therapy. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 159, 104943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, R.R.; Debnath, S.; Das, S.; Wakchaure, P.; Ganguly, B.; Chatterjee, P.B. A Highly Selective Turn-On Biosensor for Measuring Spermine/Spermidine in Human Urine and Blood. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2019, 2, 2374–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstein, S.J.; Mackrain, K.; Stolzenberg-Solomon, R.Z.; Selhub, J.; Virtamo, J.; Albanes, D. Serum creatinine and prostate cancer risk in a prospective study. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2009, 18, 2643–2649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pundir, C.S.; Kumar, P.; Jaiwal, R. Biosensing methods for determination of creatinine: A review. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 126, 707–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rule, A.D.; Jacobson, D.J.; Roberts, R.O.; Girman, C.J.; McGree, M.E.; Lieber, M.M.; Jacobsen, S.J. The association between benign prostatic hyperplasia and chronic kidney disease in community-dwelling men. Kidney Int. 2005, 67, 2376–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura-Melo, S.; Miranda-Castro, R.; de-Los-Santos-Álvarez, N.; Miranda-Ordieres, A.J.; Dos Santos Junior, J.R.; da Silva Fonseca, R.A.; Lobo-Castañón, M.J. A Quantitative PCR-Electrochemical Genosensor Test for the Screening of Biotech Crops. Sensors 2017, 17, 881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosario, R.; Mutharasan, R. Nucleic acid electrochemical and electromechanical biosensors: A review of techniques and developments. Rev. Anal. Chem 2014, 33, 213–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marks, L.S.; Bostwick, D.G. Prostate Cancer Specificity of PCA3 Gene Testing: Examples from Clinical Practice. Rev. Urol. 2008, 10, 175–181. [Google Scholar]
- Merola, R.; Tomao, L.; Antenucci, A.; Sperduti, I.; Sentinelli, S.; Masi, S.; Mandoj, C.; Orlandi, G.; Papalia, R.; Guaglianone, S.; et al. PCA3 in prostate cancer and tumor aggressiveness detection on 407 high-risk patients: A National Cancer Institute experience. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 34, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbera, M.; Pepe, P.; Paola, Q.; Aragona, F. PCA3 score accuracy in diagnosing prostate cancer at repeat biopsy: Our experience in 177 patients. Arch. Ital. Urol. Androl. 2012, 84, 227–229. [Google Scholar]
- Marks, L.S.; Fradet, Y.; Deras, I.L.; Blase, A.; Mathis, J.; Aubin, S.M.; Cancio, A.T.; Desaulniers, M.; Ellis, W.J.; Rittenhouse, H.; et al. PCA3 molecular urine assay for prostate cancer in men undergoing repeat biopsy. Urology 2007, 69, 532–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Yao, J.; Xu, L.; Xu, Z.; Ge, Y.; Zhou, L.; Zhao, F.; Jia, R. Diagnosis accuracy of PCA3 level in patients with prostate cancer: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Int. Braz. J. Urol. 2020, 46, 691–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Qu, X.; Jiang, J.; Gao, P.; Zhao, D.; Lian, X.; Li, X. Diagnostic significance of urinary long non-coding PCA3 RNA in prostate cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 58577–58586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, J.C.; Soares, A.C.; Rodrigues, V.C.; Melendez, M.E.; Santos, A.C.; Faria, E.F.; Reis, R.M.; Carvalho, A.L.; Oliveira, O.N. Detection of the Prostate Cancer Biomarker PCA3 with Electrochemical and Impedance-Based Biosensors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interf. 2019, 11, 46645–46650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertok, T.; Lorencova, L.; Chocholova, E.; Jane, E.; Vikartovska, A.; Kasak, P.; Tkac, J. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy Based Biosensors: Mechanistic Principles, Analytical Examples and Challenges towards Commercialization for Assays of Protein Cancer Biomarkers. ChemElectroChem 2019, 6, 989–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajdosova, V.P.; Lorencova, L.; Blsakova, A.; Kasak, P.; Bertok, T.; Tkac, J. Challenges for impedimetric affinity sensors targeting proteins detection. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2021, 28, 100717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, V.C.; Soares, J.C.; Soares, A.C.; Braz, D.C.; Melendez, M.E.; Ribas, L.C.; Scabini, L.F.S.; Bruno, O.M.; Carvalho, A.L.; Reis, R.M.; et al. Electrochemical and optical detection and machine learning applied to images of genosensors for diagnosis of prostate cancer with the biomarker PCA3. Talanta 2021, 222, 121444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Wen, J.; Li, J.; Lin, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhuang, X.; Tian, C.; Chen, L. Highly sensitive detection of prostate cancer specific PCA3 mimic DNA using SERS-based competitive lateral flow assay. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 15530–15536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilela, P.; El-Sagheer, A.; Millar, T.M.; Brown, T.; Muskens, O.L.; Kanaras, A.G. Graphene Oxide-Upconversion Nanoparticle Based Optical Sensors for Targeted Detection of mRNA Biomarkers Present in Alzheimer’s Disease and Prostate Cancer. ACS Sens. 2017, 2, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamkamon, V.; Htoo, K.P.P.; Yainoy, S.; Suksrichavalit, T.; Tangchaikeeree, T.; Eiamphungporn, W. Urinary PCA3 detection in prostate cancer by magnetic nanoparticles coupled with colorimetric enzyme-linked oligonucleotide assay. EXCLI J. 2020, 19, 501–513. [Google Scholar]
- Ashrafizadeh, M.; Hushmandi, K.; Rahmani Moghadam, E.; Zarrin, V.; Hosseinzadeh Kashani, S.; Bokaie, S.; Najafi, M.; Tavakol, S.; Mohammadinejad, R.; Nabavi, N.; et al. Progress in Delivery of siRNA-Based Therapeutics Employing Nano-Vehicles for Treatment of Prostate Cancer. Bioengineering 2020, 7, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavallaie, R.; De Almeida, S.R.; Gooding, J.J. Toward biosensors for the detection of circulating microRNA as a cancer biomarker: An overview of the challenges and successes. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2015, 7, 580–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.T.; Kim, W.-J. MicroRNAs in prostate cancer. Prostate Int. 2013, 1, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Agata, R.; Spoto, G. Advanced methods for microRNA biosensing: A problem-solving perspective. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 4425–4444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasomva, K.; Sen, A.; Paulraj, M.G.; Sailo, S.; Raphael, V.; Puro, K.-U.; Assumi, S.R.; Ignacimuthu, S. Roles of microRNA in prostate cancer cell metabolism. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2018, 102, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mompeón, A.; Ortega-Paz, L.; Vidal-Gómez, X.; Costa, T.J.; Pérez-Cremades, D.; Garcia-Blas, S.; Brugaletta, S.; Sanchis, J.; Sabate, M.; Novella, S.; et al. Disparate miRNA expression in serum and plasma of patients with acute myocardial infarction: A systematic and paired comparative analysis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabahi, A.; Salahandish, R.; Ghaffarinejad, A.; Omidinia, E. Electrochemical nano-genosensor for highly sensitive detection of miR-21 biomarker based on SWCNT-grafted dendritic Au nanostructure for early detection of prostate cancer. Talanta 2020, 209, 120595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.A.; Newbury, L.J.; Drago, G.; Bowen, T.; Redman, J.E. Electrochemical detection of urinary microRNAs via sulfonamide-bound antisense hybridisation. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 253, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, N.H.; Abdellateif, M.S.; Thabet, G.; Kassem, S.H.; El-Salam, M.A.; El-Leithy, A.A.; Selim, M.M. Combining PHI and miRNAs as Biomarkers in Prostate Cancer Diagnosis and Prognosis. Clin. Lab. 2019, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidarra, D.; Constâncio, V.; Barros-Silva, D.; Ramalho-Carvalho, J.; Moreira-Barbosa, C.; Antunes, L.; Maurício, J.; Oliveira, J.; Henrique, R.; Jerónimo, C. Circulating MicroRNAs as Biomarkers for Prostate Cancer Detection and Metastasis Development Prediction. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.C.N.; Xie, W.; Yang, M.; Hsieh, C.-L.; Drouin, S.; Lee, G.-S.M.; Kantoff, P.W. Expression differences of circulating microRNAs in metastatic castration resistant prostate cancer and low-risk, localized prostate cancer. Prostate 2013, 73, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, A.; Jung, M.; Mollenkopf, H.-J.; Wagner, I.; Stephan, C.; Jentzmik, F.; Miller, K.; Lein, M.; Kristiansen, G.; Jung, K. Diagnostic and prognostic implications of microRNA profiling in prostate carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 126, 1166–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, R.J.; Pawlowski, T.; Catto, J.W.F.; Marsden, G.; Vessella, R.L.; Rhees, B.; Kuslich, C.; Visakorpi, T.; Hamdy, F.C. Changes in circulating microRNA levels associated with prostate cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2012, 106, 768–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, R.M.; Zauli, D.A.G.; Neto, B.S.; Brum, I.S. Urinary microRNAs expression in prostate cancer diagnosis: A systematic review. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2020, 22, 2061–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredsøe, J.; Rasmussen, A.K.I.; Thomsen, A.R.; Mouritzen, P.; Høyer, S.; Borre, M.; Ørntoft, T.F.; Sørensen, K.D. Diagnostic and Prognostic MicroRNA Biomarkers for Prostate Cancer in Cell-free Urine. Eur. Urol. Focus 2018, 4, 825–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Dou, B.; Shi, K.; Chai, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Yuan, R. Multiplexed and Amplified Electronic Sensor for the Detection of MicroRNAs from Cancer Cells. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 11913–11918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Aamri, M.; Yammouri, G.; Mohammadi, H.; Amine, A.; Korri-Youssoufi, H. Electrochemical Biosensors for Detection of MicroRNA as a Cancer Biomarker: Pros and Cons. Biosensors 2020, 10, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanov, Y.; Pleshakova, T.; Malsagova, K.; Kurbatov, L.; Popov, V.; Glukhov, A.; Smirnov, A.; Enikeev, D.; Potoldykova, N.; Alekseev, B.; et al. Detection of Marker miRNAs, Associated with Prostate Cancer, in Plasma Using SOI-NW Biosensor in Direct and Inversion Modes. Sensors 2019, 19, 5248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Yang, R.; Shi, M.; Wu, C.; Fang, X.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Tan, W. Rationally designed molecular beacons for bioanalytical and biomedical applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 3036–3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolly, P.; Batistuti, M.R.; Miodek, A.; Zhurauski, P.; Mulato, M.; Lindsay, M.A.; Estrela, P. Highly sensitive dual mode electrochemical platform for microRNA detection. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mucci, L.A.; Hjelmborg, J.B.; Harris, J.R.; Czene, K.; Havelick, D.J.; Scheike, T.; Graff, R.E.; Holst, K.; Möller, S.; Unger, R.H.; et al. Familial Risk and Heritability of Cancer Among Twins in Nordic Countries. JAMA 2016, 315, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benafif, S.; Kote-Jarai, Z.; Eeles, R.A. A Review of Prostate Cancer Genome-Wide Association Studies (GWAS). Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2018, 27, 845–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumacher, F.R.; Al Olama, A.A.; Berndt, S.I.; Benlloch, S.; Ahmed, M.; Saunders, E.J.; Dadaev, T.; Leongamornlert, D.; Anokian, E.; Cieza-Borrella, C.; et al. Association analyses of more than 140,000 men identify 63 new prostate cancer susceptibility loci. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 928–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhao, D.; Spring, D.J.; DePinho, R.A. Genetics and biology of prostate cancer. Genes Dev. 2018, 32, 1105–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ewing, C.M.; Ray, A.M.; Lange, E.M.; Zuhlke, K.A.; Robbins, C.M.; Tembe, W.D.; Wiley, K.E.; Isaacs, S.D.; Johng, D.; Wang, Y.; et al. Germline Mutations in HOXB13 and Prostate-Cancer Risk. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eftekhari-Sis, B.; Karaminejad, S.; Karimi, F. A Nano-Biosensor for the Detection of 185delAG Mutation in BRCA1 Gene, Leading to Breast Cancer. Cancer Investig. 2016, 34, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filippidou, M.K.; Loukas, C.M.; Kaprou, G.; Tegou, E.; Petrou, P.; Kakabakos, S.; Tserepi, A.; Chatzandroulis, S. Detection of BRCA1 gene on partially reduced graphene oxide biosensors. Microelectron. Eng. 2019, 216, 111093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Su, J.; He, G.; Xu, Y.; Wang, C.; Zheng, M.; Qian, Q.; Mi, X. Electrochemical DNA Sensor for Sensitive BRCA1 Detection Based on DNA Tetrahedral-Structured Probe and Poly-Adenine Mediated Gold Nanoparticles. Biosensors 2020, 10, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Hu, Q.; Zhi, F.; Zhang, S.; Mao, D.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, H. Significance of the TMPRSS2:ERG gene fusion in prostate cancer. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 5450–5458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Løvf, M.; Totland Carm, K.; Cathrine Bakken, A.; Hoff, A.M.; Skotheim, R.I. Novel transcription-induced fusion RNAs in prostate cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Yu, L.; Wang, Z. PCA3 and TMPRSS2-ERG gene fusions as diagnostic biomarkers for prostate cancer. Chin. J. Cancer Res. 2016, 28, 65–71. [Google Scholar]
- Koo, K.M.; Wee, E.J.H.; Mainwaring, P.N.; Trau, M. A simple, rapid, low-cost technique for naked-eye detection of urine-isolated TMPRSS2:ERG gene fusion RNA. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocedi, A.; Noce, A.; Marrone, G.; Noce, G.; Cattani, G.; Gambardella, G.; Di Lauro, M.; Di Daniele, N.; Ricci, G. Glutathione Transferase P1-1 an Enzyme Useful in Biomedicine and as Biomarker in Clinical Practice and in Environmental Pollution. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pljesa-Ercegovac, M.; Savic-Radojevic, A.; Matic, M.; Coric, V.; Djukic, T.; Radic, T.; Simic, T. Glutathione Transferases: Potential Targets to Overcome Chemoresistance in Solid Tumors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanwal, R.; Pandey, M.; Bhaskaran, N.; Maclennan, G.T.; Fu, P.; Ponsky, L.E.; Gupta, S. Protection against oxidative DNA damage and stress in human prostate by glutathione S-transferase P1. Mol. Carcinog. 2014, 53, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurioli, G.; Martignano, F.; Salvi, S.; Costantini, M.; Gunelli, R.; Casadio, V. GSTP1 methylation in cancer: A liquid biopsy biomarker? Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2018, 56, 702–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Shukla, G.C.; Gupta, S. MicroRNA Regulating Glutathione S-Transferase P1 in Prostate Cancer. Curr. Pharm. Rep. 2015, 1, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topkaya, S.N.; Ozkan-Ariksoysal, D.; Kosova, B.; Ozel, R.; Ozsoz, M. Electrochemical DNA biosensor for detecting cancer biomarker related to glutathione S-transferase P1 (GSTP1) hypermethylation in real samples. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 31, 516–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nur Topkaya, S.; Ozkan-Ariksoysal, D. Prostate Cancer Biomarker Detection with Carbon Nanotubes Modified Screen Printed Electrodes. Electroanal 2016, 28, 1077–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiou, C.C.; Chang, P.Y.; Chan, E.C.; Wu, T.L.; Tsao, K.C.; Wu, J.T. Urinary 8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine and its analogs as DNA marker of oxidative stress: Development of an ELISA and measurement in both bladder and prostate cancers. Clin. Chim. Acta 2003, 334, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sova, H.; Jukkola-Vuorinen, A.; Puistola, U.; Kauppila, S.; Karihtala, P. 8-Hydroxydeoxyguanosine: A new potential independent prognostic factor in breast cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2010, 102, 1018–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtake, S.; Kawahara, T.; Ishiguro, Y.; Takeshima, T.; Kuroda, S.; Izumi, K.; Miyamoto, H.; Uemura, H. Oxidative stress marker 8-hydroxyguanosine is more highly expressed in prostate cancer than in benign prostatic hyperplasia. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 9, 302–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosy Goyal, R.N. Determination of 8-Hydroxydeoxyguanosine: A potential biomarker of oxidative stress, using carbon-allotropic nanomaterials modified glassy carbon sensor. Talanta 2016, 161, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.; Oyama, M.; Goyal, R.N. Electrochemical investigations of 8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine and its determination at an edge plane pyrolytic graphite electrode. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 1722–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Rosy Goyal, R.N. A melamine based molecularly imprinted sensor for the determination of 8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine in human urine. Talanta 2017, 166, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, G.V.; Tavares, A.P.M.; Fortunato, E.; Sales, M.G.F. Paper-Based Sensing Device for Electrochemical Detection of Oxidative Stress Biomarker 8-Hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG) in Point-of-Care. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Azmi, M.A.; Tehrani, Z.; Lewis, R.P.; Walker, K.A.D.; Jones, D.R.; Daniels, D.R.; Doak, S.H.; Guy, O.J. Highly sensitive covalently functionalised integrated silicon nanowire biosensor devices for detection of cancer risk biomarker. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 52, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, E.; Hu, Y.; Hussein, A.; Yu, C.-Y.; Tang, H.; Mechref, Y. Characterization of the Glycosylation Site of Human PSA Prompted by Missense Mutation using LC–MS/MS. J. Proteome Res. 2015, 14, 2872–2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popovics, P.; Awadallah, W.N.; Kohrt, S.E.; Case, T.C.; Miller, N.L.; Ricke, E.A.; Huang, W.; Ramirez-Solano, M.; Liu, Q.; Vezina, C.M.; et al. Prostatic osteopontin expression is associated with symptomatic benign prostatic hyperplasia. Prostate 2020, 80, 731–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajdosova, V.; Lorencova, L.; Kasak, P.; Tkac, J. Electrochemical Nanobiosensors for Detection of Breast Cancer Biomarkers. Sensors 2020, 20, 4022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodavirdi, A.C.; Song, Z.; Yang, S.; Zhong, C.; Wang, S.; Wu, H.; Pritchard, C.; Nelson, P.S.; Roy-Burman, P. Increased Expression of Osteopontin Contributes to the Progression of Prostate Cancer. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 883–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moorman, H.R.; Poschel, D.; Klement, J.D.; Lu, C.; Redd, P.S.; Liu, K. Osteopontin: A Key Regulator of Tumor Progression and Immunomodulation. Cancers 2020, 12, 3379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.; Hong, S.; Singh, R.; Jang, J. Single-walled carbon nanotube based transparent immunosensor for detection of a prostate cancer biomarker osteopontin. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 869, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Shi, Y.; Sa, R.; Hao, J.; Hu, J.; Xiao, M.; Wang, C.; Yan, L.; Qiao, B.; Chen, G. Altered staining patterns and expression level of Engrailed-2 in benign prostatic hyperplasia and prostate Cancer predict prostatic disease progression. BMC Cancer 2020, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Killick, E.; Morgan, R.; Launchbury, F.; Bancroft, E.; Page, E.; Castro, E.; Kote-Jarai, Z.; Aprikian, A.; Blanco, I.; Clowes, V.; et al. Role of Engrailed-2 (EN2) as a prostate cancer detection biomarker in genetically high risk men. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marszałł, M.P.; Sroka, W.; Adamowski, M.; Słupski, P.; Jarzemski, P.; Siódmiak, J.; Odrowąż-Sypniewska, G. Engrailed-2 protein as a potential urinary prostate cancer biomarker: A comparison study before and after digital rectal examination. Eur. J. Cancer Prev. 2015, 24, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punia, N.; Primon, M.; Simpson, G.R.; Pandha, H.S.; Morgan, R. Membrane insertion and secretion of the Engrailed-2 (EN2) transcription factor by prostate cancer cells may induce antiviral activity in the stroma. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Jo, H.; Her, J.; Lee, H.Y.; Ban, C. Ultrasensitive electrochemical detection of engrailed-2 based on homeodomain-specific DNA probe recognition for the diagnosis of prostate cancer. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 66, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiragun, T.; Yanase, Y.; Kose, K.; Kawaguchi, T.; Uchida, K.; Tanaka, S.; Hide, M. Surface plasmon resonance-biosensor detects the diversity of responses against epidermal growth factor in various carcinoma cell lines. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 32, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, Z.; Feng, L.; Ji, D.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, W.; Dai, Y.; Janyasupab, M.; Li, X.; Wen, W.; Liu, C.-C. Phase-Regulated Sensing Mechanism of MoS2 Based Nanohybrids toward Point-of-Care Prostate Cancer Diagnosis. Small 2020, 16, 2000307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.Y.; Cheng, K.L.; McGuffin-Cawley, J.D.; Shieu, F.S.; Samia, A.C.; Gupta, S.; Cooney, M.; Thompson, C.L.; Liu, C.C. Detection of Alpha-Methylacyl-CoA Racemase (AMACR), a Biomarker of Prostate Cancer, in Patient Blood Samples Using a Nanoparticle Electrochemical Biosensor. Biosensors 2012, 2, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolly, P.; Miodek, A.; Yang, D.-K.; Chen, L.-C.; Lloyd, M.D.; Estrela, P. Electro-Engineered Polymeric Films for the Development of Sensitive Aptasensors for Prostate Cancer Marker Detection. ACS Sens. 2016, 1, 1308–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, F.C.B.; Bueno, P.R. Optimized electrochemical biosensor for human prostatic acid phosphatase. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2017, 253, 1106–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamel, A.H.; Galal, H.R.; Hanna, A.A. Novel planar chip biosensors for potentiometric immunoassay of acid phosphatase activity based on the use of ion association complexes as novel electroactive materials. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2014, 9, 5776–5787. [Google Scholar]
- Na, W.; Liu, Q.; Sui, B.; Hu, T.; Su, X. Highly sensitive detection of acid phosphatase by using a graphene quantum dots-based förster resonance energy transfer. Talanta 2016, 161, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parra-Cabrera, C.; Samitier, J.; Homs-Corbera, A. Multiple biomarkers biosensor with just-in-time functionalization: Application to prostate cancer detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 77, 1192–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Kim, M.; Kim, D.; Kang, S.H.; Lee, K.H.; Jeong, Y. Interfacial charge regulation of protein blocking layers in transistor biosensor for direct measurement in serum. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 147, 111737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.-W.; Wei, K.-C.; Liao, S.-s.; Huang, C.-Y.; Sun, C.-L.; Wu, P.-J.; Lu, Y.-J.; Yang, H.-W.; Ma, C.-C.M. A reusable magnetic graphene oxide-modified biosensor for vascular endothelial growth factor detection in cancer diagnosis. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 67, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, J.; Mendes, R.G.; Bachmatiuk, A.; Zhao, L.; Ta, H.Q.; Gemming, T.; Liu, H.; Liu, Z.; Rummeli, M.H. Applications of 2D MXenes in energy conversion and storage systems. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 72–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crulhas, B.P.; Karpik, A.E.; Delella, F.K.; Castro, G.R.; Pedrosa, V.A. Electrochemical aptamer-based biosensor developed to monitor PSA and VEGF released by prostate cancer cells. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409, 6771–6780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pihikova, D.; Pakanova, Z.; Nemcovic, M.; Barath, P.; Belicky, S.; Bertok, T.; Kasak, P.; Mucha, J.; Tkac, J. Sweet characterisation of prostate specific antigen using electrochemical lectin-based immunosensor assay and MALDI TOF/TOF analysis: Focus on sialic acid. Proteomics 2016, 16, 3085–3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pihikova, D.; Kasak, P.; Kubanikova, P.; Sokol, R.; Tkac, J. Aberrant sialylation of a prostate-specific antigen: Electrochemical label-free glycoprofiling in prostate cancer serum samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 934, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belicky, S.; Damborsky, P.; Zapatero-Rodriguez, J.; O’Kennedy, R.; Tkac, J. Full-length antibodies versus single-chain antibody fragments for a selective impedimetric lectin-based glycoprofiling of prostate specific antigen. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 246, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pihíková, D.; Belicky, Š.; Kasák, P.; Bertok, T.; Tkac, J. Sensitive detection and glycoprofiling of a prostate specific antigen using impedimetric assays. Analyst 2016, 141, 1044–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belicky, S.; Cernocka, H.; Bertok, T.; Holazova, A.; Reblova, K.; Palecek, E.; Tkac, J.; Ostatna, V. Label-free chronopotentiometric glycoprofiling of prostate specific antigen using sialic acid recognizing lectins. Bioelectrochemistry 2017, 117, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, T.; Kaneko, T.; Kojima, S.; Nakamura, Y.; Ide, Y.; Ishida, K.; Suda, Y.; Yamashita, K. High-Sensitivity Immunoassay with Surface Plasmon Field-Enhanced Fluorescence Spectroscopy Using a Plastic Sensor Chip: Application to Quantitative Analysis of Total Prostate-Specific Antigen and GaINAc beta 1-4GIcNAc-Linked Prostate-Specific Antigen for Prostate Cancer Diagnosis. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 1797–1803. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Haga, Y.; Uemura, M.; Baba, S.; Inamura, K.; Takeuchi, K.; Nonomura, N.; Ueda, K. Identification of Multisialylated LacdiNAc Structures as Highly Prostate Cancer Specific Glycan Signatures on PSA. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 2247–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertokova, A.; Bertok, T.; Jane, E.; Hires, M.; Ďubjaková, P.; Novotná, O.; Belan, V.; Fillo, J.; Tkac, J. Detection of N, N-diacetyllactosamine (LacdiNAc) containing free prostate-specific antigen for early stage prostate cancer diagnostics and for identification of castration-resistant prostate cancer patients. Biorg. Med. Chem. 2021, 116156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertok, T.; Lorencova, L.; Hroncekova, S.; Gajdosova, V.; Jane, E.; Hires, M.; Kasak, P.; Kaman, O.; Sokol, R.; Bella, V.; et al. Advanced impedimetric biosensor configuration and assay protocol for glycoprofiling of a prostate oncomarker using Au nanoshells with a magnetic core. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 131, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertok, T.; Lorencova, L.; Hroncekova, S.; Gajdosova, V.; Jane, E.; Hires, M.; Kasak, P.; Kaman, O.; Sokol, R.; Bella, V.; et al. Synthesis and characterization of Au nanoshells with a magnetic core and betaine derivatives. Methodsx 2019, 6, 1999–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jolly, P.; Damborsky, P.; Madaboosi, N.; Soares, R.R.G.; Chu, V.; Conde, J.P.; Katrlik, J.; Estrela, P. DNA aptamer-based sandwich microfluidic assays for dual quantification and multi-glycan profiling of cancer biomarkers. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 79, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damborsky, P.; Koczula, K.M.; Gallotta, A.; Katrlik, J. Lectin-based lateral flow assay: Proof-of-concept. Analyst 2016, 141, 6444–6448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, P.M.S.; Lima, A.L.R.; Silva, B.V.M.; Coelho, L.; Dutra, R.F.; Correia, M.T.S. Cratylia mollis lectin nanoelectrode for differential diagnostic of prostate cancer and benign prostatic hyperplasia based on label-free detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 85, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephenson-Brown, A.; Acton, A.L.; Preece, J.A.; Fossey, J.S.; Mendes, P.M. Selective glycoprotein detection through covalent templating and allosteric click-imprinting. Chem. Sci. 2015, 6, 5114–5119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Wang, Y.; Xing, R.; Chen, J.; Liu, J.; Li, W.; Liu, Z. Orthogonal dual molecularly imprinted polymer-based plasmonic immunosandwich assay: A double characteristic recognition strategy for specific detection of glycoproteins. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 145, 111729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, R.; Peng, C.; Sun, L.; Zhang, L.-X.; Bai, C.-C.; Dong, L.-Y.; Wang, X.-H. Integrating boronate affinity controllable-oriented surface imprinting nylon wire and pH-triggered allochroic-graphene oxide for ultrasensitive detection of glycoprotein. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2021, 330, 129310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tommasone, S.; Tagger, Y.K.; Mendes, P.M. Targeting Oligosaccharides and Glycoconjugates Using Superselective Binding Scaffolds. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2002298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, H.; Sunayama, H.; Kitayama, Y.; Takano, E.; Takeuchi, T. Site-specific post-imprinting modification of molecularly imprinted polymer nanocavities with a modifiable functional monomer for prostate cancer biomarker recognition. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2019, 20, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tommasone, S.; Allabush, F.; Tagger, Y.K.; Norman, J.; Kopf, M.; Tucker, J.H.R.; Mendes, P.M. The challenges of glycan recognition with natural and artificial receptors. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 5488–5505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Ma, Y.Y.; Guo, Z.C.; Xing, R.R.; Liu, Z. Efficient Screening of Glycan-Specific Aptamers Using a Glycosylated Peptide as a Scaffold. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 956–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz-Fernandez, A.; Miranda-Castro, R.; Diaz, N.; Suarez, D.; de-los-Santos-Alvarez, N.; Jesus Lobo-Castanon, M. Aptamers targeting protein-specific glycosylation in tumor biomarkers: General selection, characterization and structural modeling. Chem. Sci. 2020, 11, 9402–9413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz-Fernandez, A.; Miranda-Castro, R.; de-los-Santos-Alvarez, N.; Rodriguez, E.F.; Lobo-Castanon, M.J. Focusing aptamer selection on the glycan structure of prostate-specific antigen: Toward more specific detection of prostate cancer. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 128, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz-Fernandez, A.; Miranda-Castro, R.; de-los-Santos-Alvarez, N.; Lobo-Castanon, M.J.; Estrela, P. Impedimetric aptamer-based glycan PSA score for discrimination of prostate cancer from other prostate diseases. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 175, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz-Fernandez, A.; Lorenzo-Gomez, R.; Miranda-Castro, R.; de-los-Santos-Alvarez, N.; Lobo-Castanon, M.J. Electrochemical aptasensors for cancer diagnosis in biological fluids—A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1124, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bertok, T.; Bertokova, A.; Hroncekova, S.; Chocholova, E.; Svecova, N.; Lorencova, L.; Kasak, P.; Tkac, J. Novel Prostate Cancer Biomarkers: Aetiology, Clinical Performance and Sensing Applications. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 205. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9080205
Bertok T, Bertokova A, Hroncekova S, Chocholova E, Svecova N, Lorencova L, Kasak P, Tkac J. Novel Prostate Cancer Biomarkers: Aetiology, Clinical Performance and Sensing Applications. Chemosensors. 2021; 9(8):205. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9080205
Chicago/Turabian StyleBertok, Tomas, Aniko Bertokova, Stefania Hroncekova, Erika Chocholova, Natalia Svecova, Lenka Lorencova, Peter Kasak, and Jan Tkac. 2021. "Novel Prostate Cancer Biomarkers: Aetiology, Clinical Performance and Sensing Applications" Chemosensors 9, no. 8: 205. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9080205
APA StyleBertok, T., Bertokova, A., Hroncekova, S., Chocholova, E., Svecova, N., Lorencova, L., Kasak, P., & Tkac, J. (2021). Novel Prostate Cancer Biomarkers: Aetiology, Clinical Performance and Sensing Applications. Chemosensors, 9(8), 205. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9080205






