Abstract
A new concept for simultaneous detection of two model proteases based on immobilized fluorescently labelled peptides was developed and evaluated. Each probe was composed of a carrier modified by poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) chains, a specifically cleavable linker, and a fluorescent dye incorporated in the peptide tail. Based on a single excitation–double emission fluorescence response of liberated fluorophores caused by enzymatic cleavage, the presence of a single or both proteases in a mixture was unambiguously determined in an experimentally established concentration range. Among the tested solid supports, Rink Amide PEGA resin was recognized as the most suitable choice from the perspective of on-resin enzyme assays.
1. Introduction
Proteases play an unprecedented role in our everyday lives by enabling and facilitating numerous essential biochemical processes. Beside human metabolic pathways, where three main proteases including trypsin, chymotrypsin, and pepsin are produced, they are also indispensable in immune functions, as well as cell division, blood clotting, and protein recycling processes [1]. By monitoring their activities, some complex biochemical actions inside the cells have been clarified and explained.
As the functionalities of particular proteases are usually interconnected, simultaneous detection of more than one enzyme species might be necessary for the unambiguous elucidation of some metabolic mechanisms or the detection of known processes connected with proteolytic cascades [2,3,4]. Although a broad scope of tools and applications [5,6] for sensitive and selective in vitro, as well as in vivo detection of different proteases has already been reported, individual techniques could be rarely combined for the purpose of synchronous detection of diverse enzymes. Various uptakes due to different pH of media, incubation parameters, as well as mutual undesired interactions causing spectral interferences are just a few of the potential drawbacks that one might frequently have faced.
Even though, some fluorescence based sensing techniques (e.g., Förster resonance energy transfer—FRET) enable detection of more than one enzyme species at the same time, they have mostly been used for single enzyme screening [7,8,9]. Consequently, only a few examples of multi-dye fluorescent probes for simultaneous monitoring of various caspases [10,11], caspases in combination with metalloproteinases [12,13], or various proteases [14] have been reported until now.
While soluble protease probes are predominant in assay kits, as well as abundantly described in the literature, their immobilized analogues have been reported only sporadically. Two such studies, dealing with fluorescently labelled proteins covalently bound to a solid support, were published by Trzcinska et al. [15,16]. Although, the authors highlighted efficiency, simplicity, and potential versatility of developed sensors, they were constructed in a way to monitor only one protease at a time.
Considering various surfaces suitable for the attachment of peptide probes, superficial modification of carriers with poly(ethylene glycol) spacers seems to be one of the primary choices [17]. On the other hand, different materials including gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) have been used as solid supports as well. Despite the fact that reported AuNP based sensors [18,19] enable simultaneous sensing of different proteases, the availability of materials for flat applications with respect to reasonable price remains challenging.
Immobilized peptides were also used as protease substrates in assay kits comprised of liquid crystals. The enzymatic disruption of the peptide chains resulted in a homeotropic orientation of LCs, and a consequent change of optical signals. Although the authors demonstrated very low detectable concentrations of trypsin and chymotrypsin, the system was unable to distinguish between both proteases [20].
Notwithstanding the above-mentioned examples of the solid support-based multi-enzyme detection, the complexity and sophistication of some of the already established conceptual models could partially or even completely suppress their larger adoption and practical implementation. Therefore, the idea of immobilized probes aimed at simultaneous detection of various proteases still requires fundamental innovations and further development.
Here we report a new concept for synchronous detection of two model proteases in a relatively wide concentration range. Our main focus was to develop a robust and reliable methodology that is simple to use and requires no advanced equipment, skills, or techniques. Due to its flexibility, availability, and scalability, the presented sensor herein might be of great added value in various scientific fields including biochemistry, biology, pharmacy, and medicine.
2. Materials and Methods
Solid-phase synthesis was performed on four different resins including Rink Amide PEGA resin (0.35 mmol/g, Novabiochem, Germany), TentaGel XV RAM resin (0.22 mmol/g, Rapp Polymere GmbH, Tübingen, Germany), H-Rink amide ChemMatrix resin (0.40–0.60 mmol/g, Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany) and Polystyrene Wang resin (0.9 mmol/g, AAPPTec, Louisville, KY, USA). The chemicals and solvents were obtained from the available commercial sources. 7-Diethylaminocoumarin-3-carboxylic acid (DEAC) was synthesized according to a literature procedure [21].
2.1. Synthesis and Evaluation of Immobilized Peptides
The appropriate solid support was first placed into 5 or 10 mL plastic syringe (B. Braun Melsungen AG, Melsungen, Germany) equipped with a sintered plastic filter (Torviq, Tucson, AZ, USA), then prewashed with dichloromethane (5 times), and subsequently reacted with suitable reagents. Resins with Rink linker were pretreated with 50% piperidine in DMF before the first reaction step. The transformations were carried out on a Titer Plate Shaker (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA), while after completion of the reactions, the resins were washed with dimethylformamide (10 times) and dichloromethane (10 times), using a Domino Block (Torviq, Niles, MI, USA) and a vacuum pump (KNF Neuberger Inc., Trenton, NJ, USA). The complete synthetic pathway is presented in the Supplementary Materials (Figures S1 and S2).
After each reaction step, a small portion of embedded peptide was chemically cleaved from the carrier using 50% trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) in dichloromethane (DCM). Volatile liquids were evaporated under a stream of nitrogen, while the resulting sticky residue was treated with acetonitrile, then diluted with ultrapure water (Mili-Q Water Purification System, Progard T3, Merck Millipore, Darmstadt, Germany), filtered, and subsequently analyzed by LC-MS carried out on an UHPLC chromatograph (Acquity), using X-select C-18 column (Waters, Borehamwood, UK). Ten millimolar ammonium acetate in ultrapure water and acetonitrile (gradient 20–80% during the first 3 min) was used as a mobile phase, while its flowrate was set to 600 µL/min. Detection was performed by a photodiode array detector (Waters, UK) and a single-quadrupole mass spectrometer (Waters, UK). Characterization of the intermediates can be found in the Supplementary Materials (Figures S3–S12).
2.2. Loading, Yield Determination, and Storage (Rink Amide PEGA Resin)
After the first reaction step (binding of PEG spacer), the precisely weighed amount of approximately 100 mg of the resin was treated with 50% TFA in dichloromethane (5 × 5 mL). Fractions of the cleaved compound were joined and the volatile liquids were evaporated under a stream of nitrogen. The sticky residue was dissolved in deuterated DMSO and an NMR spectrum using an internal standard (2-propanol) was measured for the purpose of compound quantification. The residual solid support left over after TFA cleavage was intensively washed with DCM (10 times) and diethyl ether (10 times), subsequently dried under a stream of nitrogen, and finally weighed. Taking into account the quantity of cleaved compound, as well as the mass of dried resin, a loading of 0.20 mmol/g was established.
The final trypsin and chymotrypsin probes anchored to Rink Amide PEGA resin were also subjected to the above described procedure of loading determination. Considering a final loading of 0.11 mmol/g for the former and 0.15 mmol/g for the latter, the corresponding probes were synthesized in good to very good overall yields of 55% and 75% after 11 and 13 reaction steps, respectively (Figures S1 and S2). The probable cause of the considerably lower yield for the trypsin linker in comparison with the chymotrypsin could potentially have originated from the use of fluorinated chemicals during removal of the 4-methyltrityl protecting group from the lysine sidechain, and consequent damage of solid support.
The final resin-anchored probes were intensively washed with DCM (5 times), then dried under a stream of nitrogen until constant weight, and finally stored at −80 °C.
2.3. Characterization of the Probes
For the purpose of characterization, the trypsin probe TP (substrate for trypsin) was synthesized on Polystyrene Wang resin, while TentaGel XV RAM resin was utilized for the chymotrypsin probe CP (substrate for chymotrypsin) preparation. The individual compounds were then chemically cleaved from the solid support using a few portions (5 × 5 mL) of 50% trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) in DCM. The obtained fractions were combined and the volatile liquids were evaporated under a stream of nitrogen, providing sticky residue that was further dissolved in acetonitrile (4 mL), diluted with ultrapure water (6 mL), and filtered through a syringe filter (0.22 µm, HPST, Prague, Czech Republic). The resulting sample (10 mL) was purified on reverse-phase C-18 semi-preparative HPLC column (YMC—Actus Pro 12 mm S—5 µm 100 × 20 mm, Kyoto, Japan) with a gradient of 10 mM solution of ammonium acetate in ultrapure water and acetonitrile, using a flowrate of 15 mL/min. The collected fractions were combined and concentrated in vacuo using a rotary evaporator (Buchi R-215 Rotavapor, Marshall Scientific, Flawil, Switzerland), while the aqueous solution of ammonium acetate was removed by freeze-drying on lyophilizer (ScanVac Coolsafe 110-4, LaboGene, Lillerød, Denmark). The obtained dry colorful powder was characterized using LC-MS, NMR (ECX500, JEOL Resonance, Tokyo, Japan) and HRMS (Dionex Ultimate 3000, Orbitrap Elite high-resolution mass spectrometer, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) analyses. Because of stability reasons, the isolated compounds were kept in a freezer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) at −80 °C.
The quantum yields of the synthesized probes (Figures S13 and S16) were calculated by the standard procedure (Recording Fluorescence Quantum Yields—HORIBA Scientific) using fluorescein in 0.1 M NaOH and Rhodamine B in distilled water as references for the trypsin probe (TP) and the chymotrypsin probe (CP), respectively. The fluorescence measurements were performed with a Cary Eclipse Fluorescence Spectrophotometer (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA).
2.4. Biological Testing
2.4.1. Reconstitution of Enzymes
Both, trypsin (bovine pancreas, TPCK treated, ≥10,000 BAEE units/mg protein) and α-chymotrypsin (bovine pancreas, TLCK treated, type VII, ≥40 units/mg protein) were ordered from Sigma-Aldrich (Steinheim, Germany) in the form of lyophilized white powders. The appropriate amount of individual enzyme was weighed into a 1.5 mL Eppendorf safe-lock plastic tube (Hamburg, Germany), reconstituted in 1 mM HCl in ultrapure water, properly aliquoted, and stored at −80 °C. The content of a particular Eppendorf tube with reconstituted enzyme was used within a few hours after its first defrosting.
2.4.2. In-Solution Enzyme Assays
Isolated probe was dissolved in 0.1 M Tris-HCl buffer (1.8 mL, pH = 8.0), and then the appropriate aliquot of the corresponding enzyme reconstituted in 1 mM HCl (200 µL) was added. The enzymatic cleavage was monitored by LC-MS. In all cases, the corresponding masses of cleaved fragments were unambiguously confirmed (Figures S19–S22).
2.4.3. On-Resin Enzyme Assays
The process of on-resin enzyme testing is presented in Figure 1. The corresponding dried resin (2.0–2.1 mg) was weighed into 2 mL Eppendorf safe-lock plastic tubes using an analytical balance (XPE26, Mettler Toledo, Maharashtra, India). Afterwards, the appropriate volume (900 µL for the dye releasing studies; 800 µL for all other experiments) of Tris-HCl buffer was added (Figure 1A) and a solid support was mechanically crushed into smaller bits using a spatula (Figure 1B). In the next step, a suitable volume (100 µL for the dye releasing studies; 200 µL for all other experiments) of 1 mM HCl in ultrapure water, with or without enzyme was added (Figure 1C). The obtained heterogeneous system was shaken (ν = 210 min−1) on a horizontal shaker (Benchmark Scientific, Sayreville, NJ, USA) during the incubation in the incubator (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) at 37 °C (Figure 1D). After incubation was completed, the content of an Eppendorf tube was sucked up into a syringe (Figure 1E), and subsequently filtered into a single-use plastic fluorimeter cuvette (Sigma-Aldrich, Milano, Italy) (Figure 1F). Finally, the fluorescence response of the sample prepared in this way was measured with a Cary Eclipse Fluorescence Spectrophotometer (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA).
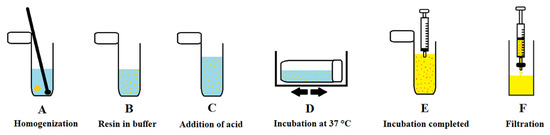
Figure 1.
On-resin enzyme testing.
All fluorescence data were obtained in three independent parallels, while for each individual set of measurements, an average value as well as the standard deviation were calculated and are graphically presented.
2.5. Stability Testing of Resin-Anchored Probes
To examine the stability of freshly synthesized materials, suitable dried resin (2.0−2.1 mg) was weighed into several Eppendorf tubes. Some parallels were stored at −80 °C, while the others were kept at laboratory temperature in darkness. After the appropriate time period, Tris-HCl buffer (800 μL) and 1 mM HCl (200 μL) were added to the individual tubes and the samples obtained in this way were then incubated at 37 °C for 15 min. After completion of the incubation process, the residual solid support was filtered out and the fluorescence response of the released fluorophore in the resulting filtrate was measured.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis and Evaluation of Target Probes
The developed sensor for the simultaneous detection of two model proteases consists of two separate selectively cleavable peptide linkers anchored to a solid support (ITP—immobilized substrate for trypsin and ICP—immobilized substrate for chymotrypsin). Considering the recently published data [22], sequences of Ala-Lys-Ala and Ala-Phe-Ala were confirmed as suitable recognizable sites for trypsin and chymotrypsin, respectively. In addition, two poly(ethylene glycol) spacers, one between the resin and the cleavage site, and another between the cleavage site and the corresponding fluorescent dye, were introduced to both probes to improve the efficiency of the enzymatic cleavage (Figure 2A). Both, the trypsin and chymotrypsin specific building block sequences were capped with the fluorophores at their ends. While for the former DEAC was utilized, Rhodamine B was chosen in the case of the latter (Figure 2A).
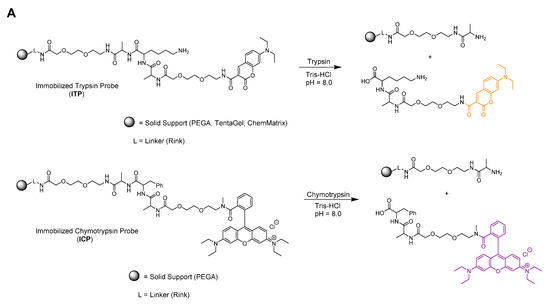
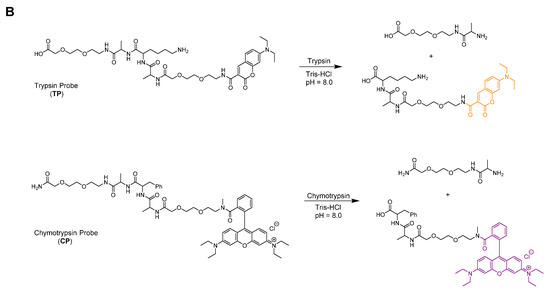
Figure 2.
On-resin (A) and in-solution (B) enzymatic cleavage.
Before on-resin enzyme experiments were carried out, detailed analyses and unambiguous characterization of the unanchored final probes TP (Figure 2B and Figures S13–S15) and CP (Figure 2B and Figures S16–S18), as well as their susceptibility to enzymatic cleavage were studied. For this purpose, the target compounds were synthesized on relatively accessible and inexpensive solid supports, and finally chemically cleaved from the matrices. According to expectations, in-solution enzymatic cleavage of TP and CP monitored by LC-MS analyses resulted in interruption of the trypsin specific linker at the C-terminus of lysine, while the chymotrypsin linker was snipped at the C-terminus of phenylalanine (Figure 2B and Figures S19–S22).
3.2. Fluorescence Spectra of TP and CP Probes
On-resin enzymatic cleavage was tracked by fluorescence spectroscopy. Considering the fluorescence spectra of TP and CP probes (Figure 3), excitation wavelengths of 410 nm and 554 nm were utilized for the initial studies on the trypsin probe (ITP) and chymotrypsin probe (ICP), respectively.
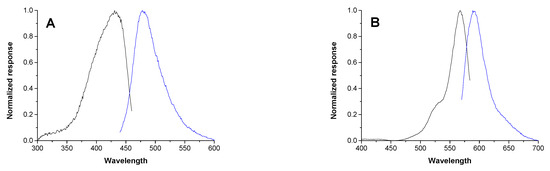
Figure 3.
Normalized excitation (black line) and emission (blue line) spectra of 10–5 M trypsin probe (A) and 10–6 M chymotrypsin probe (B) in Tris-HCl buffer (pH = 8.0) measured at 37 °C.
3.3. Solid Supports for On-Resin Enzymatic Cleavage
As the core of this study was enzyme detection in an on-resin manner, the establishment of the appropriate matrix predestined for enzymatic cleavage in aqueous solution was an important task. To compare the suitability of different resins, the trypsin probe (ITP) was synthesized on three different poly(ethylene glycol) based carriers including TentaGel XV RAM resin, H-Rink amide ChemMatrix resin, and Rink Amide PEGA resin. In all three cases, the purity of the final ITP probe exceeded 90% according to LC-MS.
After successful preparation of the resin-anchored probes, the time dependent spontaneous release of fluorophore into neat buffer was monitored via fluorescence measuring in the presence (yellow dots) and absence (blue dots) of trypsin (Figure 4). The differences in responses were barely distinguishable in the case of TentaGel XV RAM resin (Figure 4A, Table S1). While the value for the blank after 15 min was relatively low (45 on average); quite a similar value (62 in average) was obtained after the same time of incubation with trypsin in high concentration (25 μg/mL), indicating low trypsin activity towards the probe bound to TentaGel XV RAM resin. In the case of H-Rink amide ChemMatrix resin (Figure 4B, Table S2), the responses for blank as well as those for trypsin solution (25 μg/mL) were significantly higher. Although the resulting gap in fluorescence intensities between blank samples and those treated with trypsin seems to be sufficient for unambiguous detection of trypsin in high concentrations, potential distinguishability problems might arise for diluted samples. Finally, Rink Amide PEGA resin (Figure 4C, Table S3) was evaluated. Taking into account the modest increase in fluorescence intensity for the blanks, as well as the most significant difference between the average responses for samples treated with and without trypsin (25 μg/mL), Rink Amide PEGA resin was identified as the most promising carrier for on-resin enzyme testing among all three of the studied solid supports.
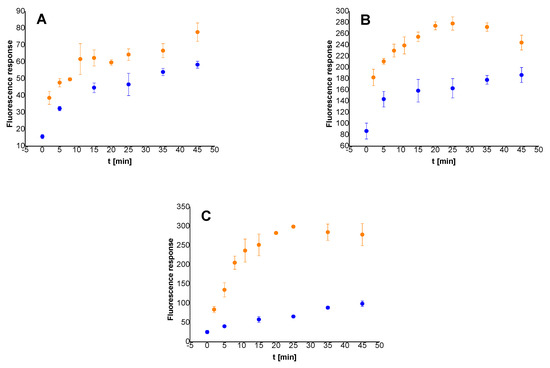
Figure 4.
Time dependent fluorescence response of dissolved released fragment from the ITP bound to TentaGel XV RAM resin (A), H-Rink amide ChemMatrix resin (B) and Rink Amide PEGA resin (C) in the presence (yellow dots) and absence (blue dots) of trypsin (25 μg/mL). The probe (2.0–2.1 mg) was dispersed in Tris-HCl buffer (0.1 M; 1 mL). Fluorescence emission was measured at 480 nm after excitation at 410 nm. Detector voltage was set to 600 V.
The discrepancies in the fluorescence responses for blank samples could be attributed to the different types of utilized solid supports (Figure 4A–C), their manufacturing processes, and the consequent stabilities of the matrices-bound linkers. In addition, the overall resistance of the studied resins to chemicals and reaction conditions used for probe preparation may also play an important role.
Considering the results of enzyme assays on the immobilized trypsin probe (ITP), the chymotrypsin linker was synthesized on Rink Amide PEGA resin as well, to obtain the immobilized probe ICT. To avoid pH dependent Rhodamine B framework closure, and consequent spirolactam formation resulting in fluorescence quenching, Mitsunobu methylation of the deprotected amino group was performed just before the fluorophore was introduced into the molecule. The fluorescence response of the N-methylated probe treated with chymotrypsin (250 µg/mL) (yellow dots) was satisfactory (Figure 5, Table S4) and clearly distinguishable from the corresponding blank reference values (blue dots).
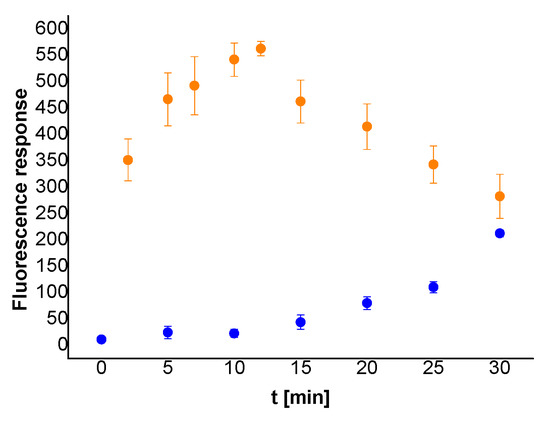
Figure 5.
Time dependent fluorescence response of the dissolved released fragment from the ICT bound to Rink Amide PEGA resin in the presence (yellow dots) and absence (blue dots) of chymotrypsin (250 μg/mL). The probe (2.0–2.1 mg) was dispersed in Tris-HCl buffer (0.1 M; 1 mL). Fluorescence emission was measured at 595 nm after excitation at 554 nm. Detector voltage was set to 500 V.
As demonstrated in Figure 4B,C and Figure 5, a considerable decline in fluorescence response for samples treated with trypsin longer than 25 min or chymotrypsin longer than 12 min was detected. The observed trend could be presumably caused by electrostatic interactions between the released dye and functional groups on the surface of the solid support [17]. As the resin with immobilized dye-labelled peptide is dispersed into the buffer and subjected to enzyme activity, the fluorophore bound to the residual peptide is released into solution. Simultaneously, part of the liberated dye-carrying peptide fragments is adsorbed back to the carrier surface. Throughout the first few minutes of the experiment, enzymatic cleavage is a predominant process over adhesion and the overall fluorescence response increases within the time. However, at some particular point in time, the equilibrium between fluorophore release and its adsorption is moved towards the latter, and the overall fluorescence intensity starts to decline.
3.4. The Lowest Detectable Concentration of Trypsin and Chymotrypsin
In the next step, the determination of the lowest detectable enzyme concentration for trypsin and chymotrypsin was carried out (Figure 6). First, fluorescence emission responses for the ITP and ICP probes were measured after their excitation at the characteristic excitation wavelengths, 410 nm for ITP and 554 nm for ICP. Due to a significantly higher fluorescence response of the chymotrypsin probe in comparison to the trypsin probe, the fluorescence measurements for the former were carried out at reduced sensitivity of the detector (500 V). In an attempt to unify experimental parameters, the emission intensities for ICP were measured also after its excitation at 410 nm. Although the responses obtained after excitation at 554 nm were expectedly higher than those acquired after excitation at 410 nm, no significant effect on the lowest detectable concentration of chymotrypsin was detected. While the presence of trypsin was unambiguously confirmed at a concentration of at least 0.5 µg/mL (Figure 6A, Table S5), the lowest detectable concentration for chymotrypsin was 10 times higher (5 µg/mL) (Figure 6B, Table S6).
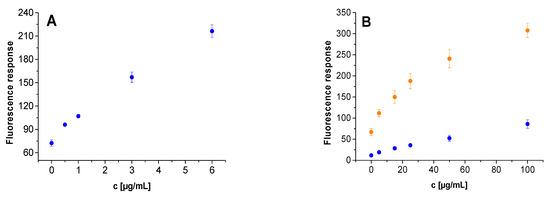
Figure 6.
The dependence of fluorescence intensity on trypsin and chymotrypsin concentration after application of ITP (A) and ICP (B) anchored to Rink Amide PEGA resin. Immobilized probes (2.0−2.1 mg) were dispersed in Tris-HCl buffer (0.1 M; 1 mL) and incubated for 15 min at 37 °C. Fluorescence emission was measured at 480 nm (ITP) and 595 nm (ICP) after excitation at 410 nm (blue dots) and 554 nm (yellow dots). Detector voltage was set either to 600 V (λEXC = 410 nm) or 500 V (λEXC = 554 nm).
3.5. Simultaneous Detection of Both Proteases
By applying a uniform excitation wavelength (410 nm), as well as the previously determined lowest detectable concentrations for both enzymes, a model for simultaneous detection of trypsin and chymotrypsin at various concentration combinations was developed. First, the average fluorescence response for blank samples was established. Then, both immobilized probes were synchronously treated either with a single protease, or with both enzymes at the same time. While a trypsin concentration of 0.5 µg/mL always resulted in clear distinguishability from the blank parallels, a chymotrypsin concentration of 5 µg/mL was found insufficient for its unambiguous evaluation in combination with trypsin. As a result, a new minimal clearly distinguishable concentration for chymotrypsin (15 µg/mL) was experimentally validated (Table S7).
In Figure 7, fluorescence responses for various concentrations of both proteases are plotted to X-Y coordinates. In the absence of enzymes, the fluorescence response with the average point [83,21] is charted in the white area. The values of individual measurements never exceed 90 and 25 on the X- and Y-axis, respectively. The solitary presence of chymotrypsin in concentrations of 15 µg/mL or higher is characterized by points in the green area, as the average X-value (referring to trypsin) remains under 90, while numbers on the Y-axis (referring to chymotrypsin) exceed 50. Conversely, when only trypsin (0.5 µg/mL or higher) is present, the average X-value surpasses 95, while Y-values always persist below 25 (blue area). In the presence of both proteases, both X- and Y-values exceed 100 and 30, respectively (ochre area).
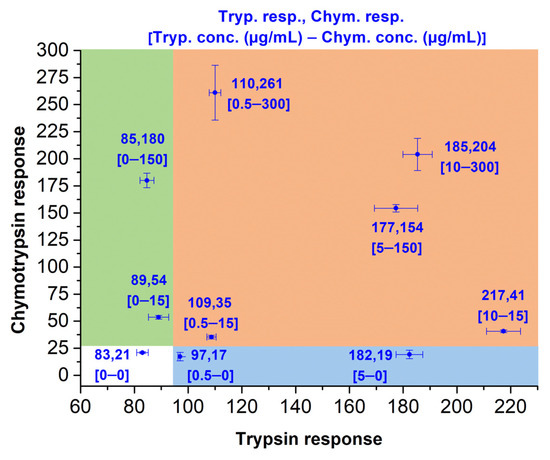
Figure 7.
Simultaneous fluorescence-based detection of the trypsin–chymotrypsin pair in various concentration combinations with synchronous usage of ITP and ICP bound to Rink Amide PEGA resin. The immobilized probes (2.0–2.1 mg) were dispersed in Tris-HCl buffer (0.1 M; 1 mL) and incubated for 15 min at 37 °C. Fluorescence emission was measured at 480 nm (ITP) and 595 nm (ICP) after excitation at 410 nm. Detector voltage was set to 600 V.
To ensure that the selection of a single-excitation wavelength (410 nm) does not negatively affect the sensitivity of the assay, ITP and ICP were synchronously incubated with the recently established lowest detectable concentrations of trypsin (0.5 µg/mL) and chymotrypsin (15 µg/mL), as well as in the absence of both proteases. Subsequently, the emission intensities measured at 595 nm, after excitations at 410 nm and 554 nm were compared. While the ratios of the average emission responses for the samples incubated in the presence of the enzymes to those incubated in the absence of proteases were very comparable in the case of both excitation wavelengths, considerably lower standard deviations for the measurements performed using uniform excitation at 410 nm were observed (Table S8). Consequently, utilization of a single-excitation wavelength (410 nm) was found advantageous for our system, as all measurements could be carried out at a consistent instrument set-up, and consequently the continuous adjustment of various parameters including slit width or detector voltage could be effectively avoided.
3.6. Stability of the Immobilized Probes
Due to the spontaneous liberation of fluorophores into buffer solution within the time, stability testing of the freshly synthesized resin-anchored probes was performed. As can be seen in Figure 8, the stability of the trypsin probe (Figure 8A, Table S9) stored at room temperature is relatively low, as the fluorescence responses were raised tremendously during the first few days of the experiment (yellow dots). In contrast, no increase in fluorescence was detected for samples stored at −80 °C (blue dots) throughout the first 30 days. The stability of the chymotrypsin probe (Figure 8B, Table S10) seems to be much higher. An increase of fluorescence intensity for samples stored at laboratory temperature (yellow dots) was observable, however it was still significantly lower than in the case of the trypsin probe. As expected, no worth-mentioning changes in fluorescence responses for the chymotrypsin probe stored at −80 °C (blue dots) were detected during the first 28 days of the experiment. Even though, the main reason for higher instability of the immobilized trypsin probe was not clearly identified, partial damage of the resin caused by chemicals or reaction conditions could potentially have led to its faster degradation at laboratory temperature, and consequent spontaneous release of the fluorophore.
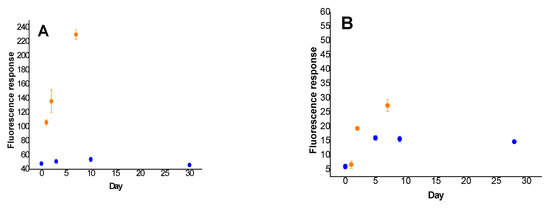
Figure 8.
Fluorescence-based stability testing of ITP (A) and ICP (B) anchored to Rink Amide PEGA resin stored at room temperature (yellow dots) and at −80 °C (blue dots) for defined number of days. Immobilized probes (2.0–2.1 mg) were dispersed in Tris-HCl buffer (0.1 M; 1 mL) and incubated for 15 min at 37 °C. Fluorescence emission was measured at 480 nm (ITP) and 595 nm (ICP) after excitation at 410 nm. Detector voltage was set to 600 V.
According to the presented facts herein, repeating freezing and defrosting of resin-embedded probes, as well as their storage at room temperature can negatively affect their stability. The issue could be efficiently circumvented by immediate aliquoting of the whole amount of freshly synthesized material, continuous storage of the resulting aliquots at −80 °C, and their prompt utilization after first defrosting.
4. Conclusions
In conclusion, a methodology for synchronous detection of two model proteases, namely trypsin and chymotrypsin, based on single excitation–double emission fluorescence-monitored enzymatic cleavage of target resin-bound peptides, was successfully established and verified. Among all the examined solid supports, Rink Amide PEGA resin was recognized as the best matrix for probe immobilization and subsequent implementation of on-resin biological assays. The developed methodology was found reliable for unambiguous detection of a single or both enzymes in a mixture, throughout the specified concentration range. Taking into account the simple and relatively inexpensive multi-step synthesis as well as the high purity (>90%) of the final materials, the presented approach, herein, could be easily scaled-up, potentially verified by simple modification of the amino acid sequences, and finally applied to selective detection of different proteases.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/chemosensors9060119/s1, Figure S1: On-resin synthesis of trypsin linker (yield: 55%). Figure S2: On-resin synthesis of chymotrypsin linker (yield: 75%). Figure S3: LC-MS analysis of chemically cleaved compound from Resin 1. Figure S4: LC-MS analysis of chemically cleaved compound from Resin 2. Figure S5: LC-MS analysis of chemically cleaved compound from Resin T3. Figure S6: LC-MS analysis of chemically cleaved compound from Resin T4. Figure S7: LC-MS analysis of chemically cleaved compound from Resin T5. Figure S8: LC-MS analysis of chemically cleaved compound from Resin C3. Figure S9: LC-MS analysis of chemically cleaved compound from Resin C4. Figure S10: LC-MS analysis of chemically cleaved compound from Resin C5. Figure S11: LC-MS analysis of chemically cleaved compound from Resin C7. Figure S12: LC-MS analysis of chemically cleaved compound from Resin T7. Figure S13: Trypsin probe (chemically cleaved from Polystyrene Wang resin). Figure S14: LC-MS analysis of purified trypsin probe. Figure S15: 1H NMR spectrum of purified trypsin probe. Figure S16: Chymotrypsin probe (chemically cleaved from TentaGel XV RAM resin). Figure S17: LC-MS analysis of purified chymotrypsin probe. Figure S18: 1H NMR spectrum of purified chymotrypsin probe. Figure S19: Enzymatically cleaved fragment from the trypsin probe. Figure S20: LC-MS analysis of enzymatically cleaved fragment from the trypsin probe. Figure S21: Enzymatically cleaved fragment from the chymotrypsin probe. Figure S22: LC-MS analysis of enzymatically cleaved fragment from the chymotrypsin probe. Table S1: Time-dependent fluorescence response of trypsin linker (TentaGel XV RAM resin). Table S2: Time-dependent fluorescence response of trypsin linker (H-Rink amide ChemMatrix resin). Table S3: Time-dependent fluorescence response of trypsin linker (Rink Amide PEGA resin). Table S4: Time-dependent fluorescence response of chymotrypsin linker (Rink Amide PEGA resin). Table S5: Fluorescence response—determination of the lowest detectable concentration of trypsin. Table S6: Fluorescence response—determination of the lowest detectable concentration of chymotrypsin. Table S7: Fluorescence response—simultaneous detection of trypsin and chymotrypsin. Table S8: Fluorescence response—the lowest detectable concentration of chymotrypsin at different wavelengths. Table S9: Stability of Rink Amide PEGA resin-anchored trypsin linker. Table S10: Stability of Rink Amide PEGA resin-anchored chymotrypsin linker.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization and methodology, D.M. and J.H.; investigation, D.M.; writing—original draft preparation, D.M. and J.H.; writing—review and editing, D.M. and J.H.; funding acquisition: J.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Czech Science Foundation (GACR project 19-23972S).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available in Supplementary Materials.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Mótyán, J.; Tóth, F.; Tőzsér, J. Research Applications of Proteolytic Enzymes in Molecular Biology. Biomolecules 2013, 3, 923–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulus, J.K.; Kourelis, J.; Ramasubramanian, S.; Homma, F.; Godson, A.; Hörger, A.C.; Hong, T.N.; Krahn, D.; Ossorio Carballo, L.; Wang, S.; et al. Extracellular proteolytic cascade in tomato activates immune protease Rcr3. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 17409–17417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mason, S.D.; Joyce, J.A. Proteolytic networks in cancer. Trends Cell Biol. 2011, 21, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulus, J.K.; Van Der Hoorn, R.A.L. Do proteolytic cascades exist in plants? J. Exp. Bot. 2019, 70, 1997–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, I.L.H.; Yang, K.L. Recent developments in protease activity assays and sensors. Analyst 2017, 142, 1867–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Wu, G.; Tian, X.; Liu, Z. Smart fluorescent probes for in situ imaging of enzyme activity: Design strategies and applications. Future Med. Chem. 2018, 10, 2729–2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.S.; Ackerley, D.F.; Calcott, M.J. High-Throughput Screening for Inhibitors of the SARS-CoV-2 Protease Using a FRET-Biosensor. Molecules 2020, 25, 4666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ripp, S.; Turunen, P.; Minot, E.D.; Rowan, A.E.; Blank, K.G. Deciphering Design Principles of Förster Resonance Energy Transfer-Based Protease Substrates: Thermolysin-Like Protease from Geobacillus stearothermophilus as a Test Case. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 4148–4156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lossi, L.; Cocito, C.; Alasia, S.; Merighi, A. Ex vivo imaging of active caspase 3 by a FRET-based molecular probe demonstrates the cellular dynamics and localization of the protease in cerebellar granule cells and its regulation by the apoptosis-inhibiting protein survivin. Mol. Neurodegener. 2016, 11, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Simone, J.; Hewgill, D.; Siegel, R.; Lipsky, P.E.; He, L. Measurement of two caspase activities simultaneously in living cells by a novel dual FRET fluorescent indicator probe. Cytom. Part A 2006, 69, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kominami, K.; Nagai, T.; Sawasaki, T.; Tsujimura, Y.; Yashima, K.; Sunaga, Y.; Tsuchimochi, M.; Nishimura, J.; Chiba, K.; Nakabayashi, J.; et al. In Vivo Imaging of Hierarchical Spatiotemporal Activation of Caspase-8 during Apoptosis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e50218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.Y.; Liu, L.H.; Cheng, H.; Li, B.; Qiu, W.X.; Zhang, X.Z. A dual-FRET-based fluorescence probe for the sequential detection of MMP-2 and caspase-3. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 14520–14523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.; Li, S.Y.; Zheng, H.R.; Li, C.X.; Xie, B.R.; Chen, K.W.; Li, B.; Zhang, X.Z. Multi-Förster Resonance Energy Transfer-Based Fluorescent Probe for Spatiotemporal Matrix Metalloproteinase-2 and Caspase-3 Imaging. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 4349–4354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Fang, L.; Shi, M.; Huang, Y.; Yao, L.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, L.; Liang, H. A peptide-based four-color fluorescent polydopamine nanoprobe for multiplexed sensing and imaging of proteases in living cells. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 1651–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trzcinska, R.; Suder, P.; Bodzon-Kulakowska, A.; Skalska, M.; Marcinkowski, A.; Kubacki, J.; Pedrys, R.; Silberring, J.; Dworak, A.; Trzebicka, B. Synthesis and characterisation of PEG-peptide surfaces for proteolytic enzyme detection. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 9049–9059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trzcinska, R.; Balin, K.; Kubacki, J.; Marzec, M.E.; Pedrys, R.; Szade, J.; Silberring, J.; Dworak, A.; Trzebicka, B. Relevance of the poly (ethylene glycol) linkers in peptide surfaces for proteases assays. Langmuir 2014, 30, 5015–5025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goddard, J.M.; Hotchkiss, J.H. Polymer surface modification for the attachment of bioactive compounds. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2007, 32, 698–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Geng, J.; Miyoshi, D.; Ren, J.; Sugimoto, N.; Qu, X. A rapid and sensitive add-mix-measure assay for multiple proteinases based on one gold nanoparticle-peptide-fluorophore conjugate. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 26, 743–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, R.P.; Tian, X.C.; Qiu, P.; Qiu, J.D. Multiplexed electrochemical detection of trypsin and chymotrypsin based on distinguishable signal nanoprobes. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 9256–9263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.H.; Yang, K.L. Oligopeptide immobilization strategy for improving stability and sensitivity of liquid-crystal protease assays. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 204, 734–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.; Guo, D.; He, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, X.; Duan, C. A color-tunable europium complex emitting three primary colors and white light. Angew. Chem.—Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 6132–6135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okorochenkova, Y.; Porubský, M.; Benická, S.; Hlaváč, J. A novel three-fluorophore system as a ratiometric sensor for multiple protease detection. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 7589–7592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).