Potentiometric Electronic Tongue for Pharmaceutical Analytics: Determination of Ascorbic Acid Based on Electropolymerized Films
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
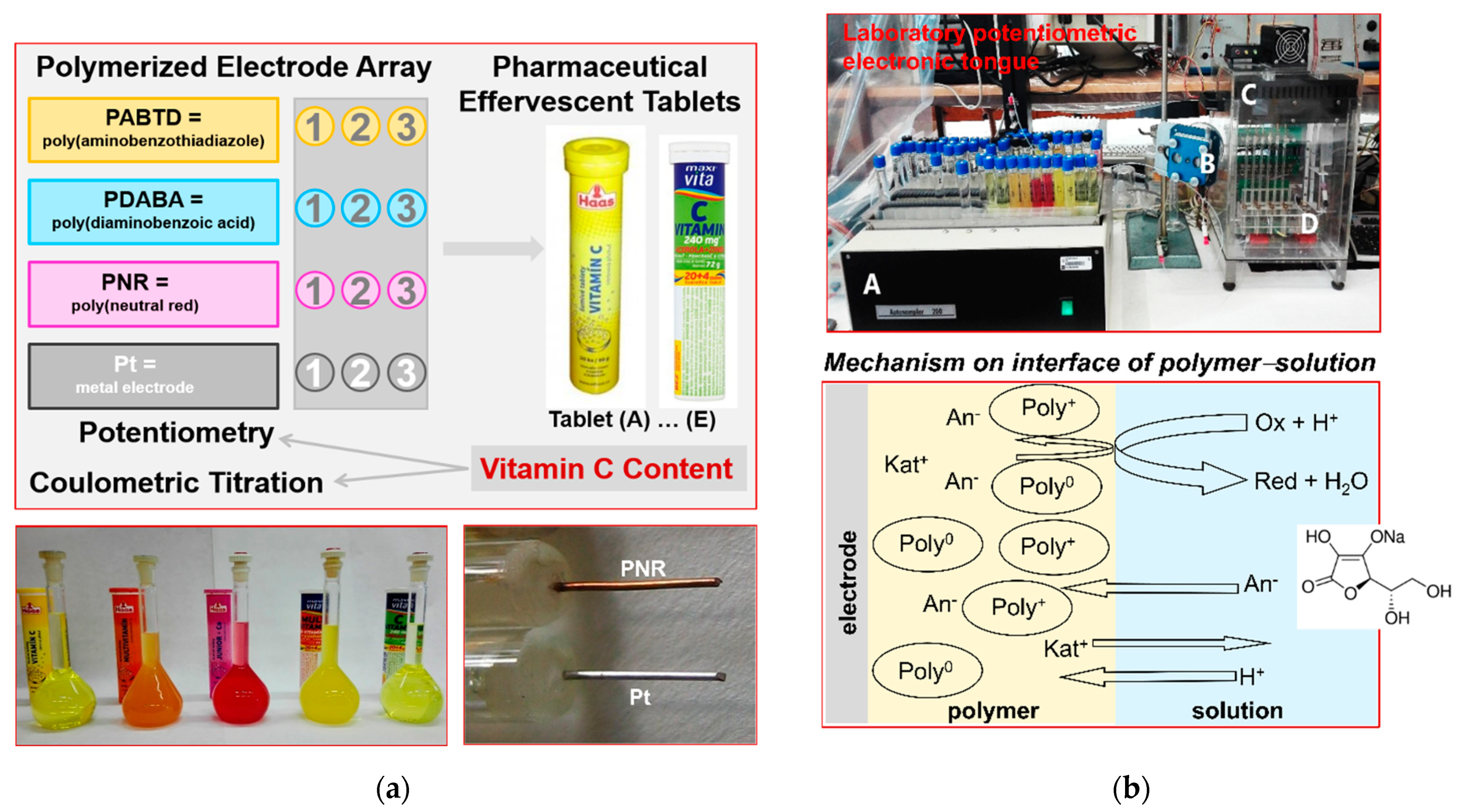
2.2. Preparation of Polymerized Film Electrodes for Electronic Tongue
2.3. Potentiometric Measurements with Electrode Array
2.4. Analysis of Commercial Samples of Effervescent Tablets Containing Vitamin C Dissolved in Acetate Buffer or Distilled Water
2.5. Data Processing
2.6. Coulometric Titration
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Type of Polymericized Films for Electrode Array
3.2. Potentiometric Characterization of Electrode Array
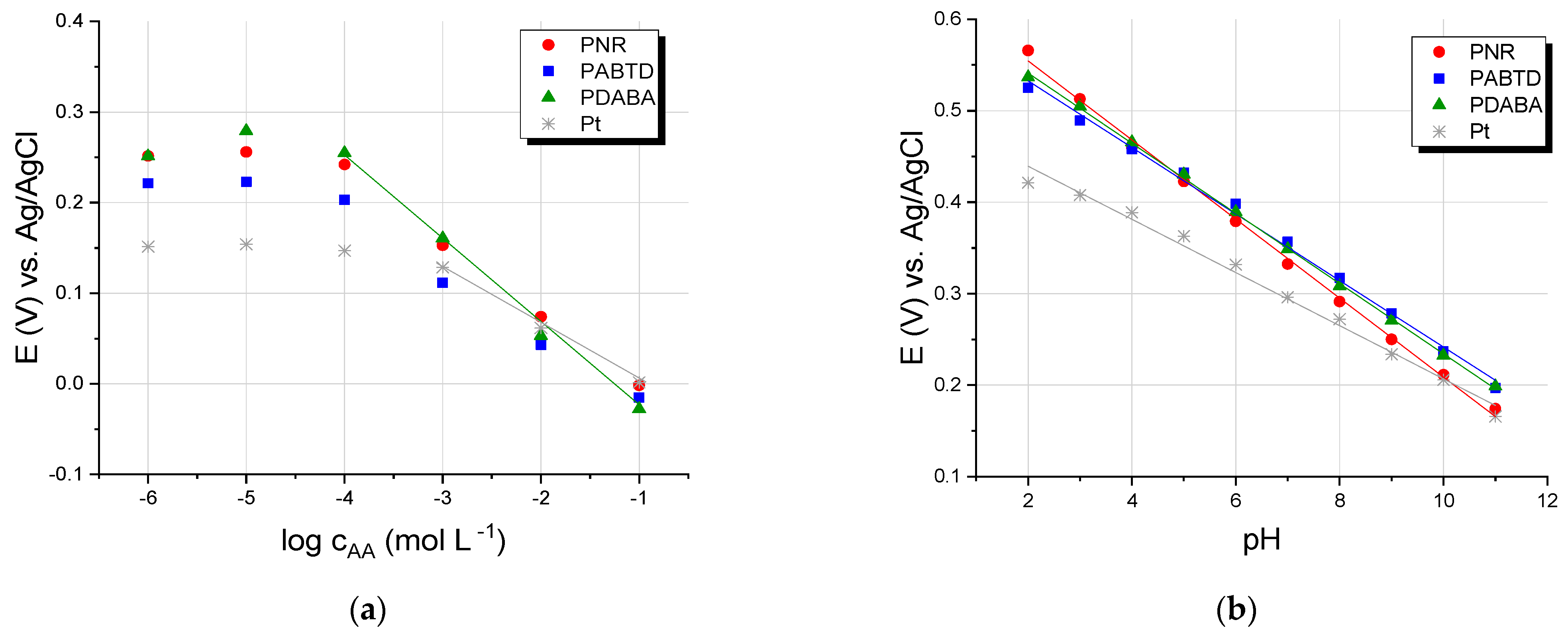
3.2.1. Response to Ascorbic Acid and pH
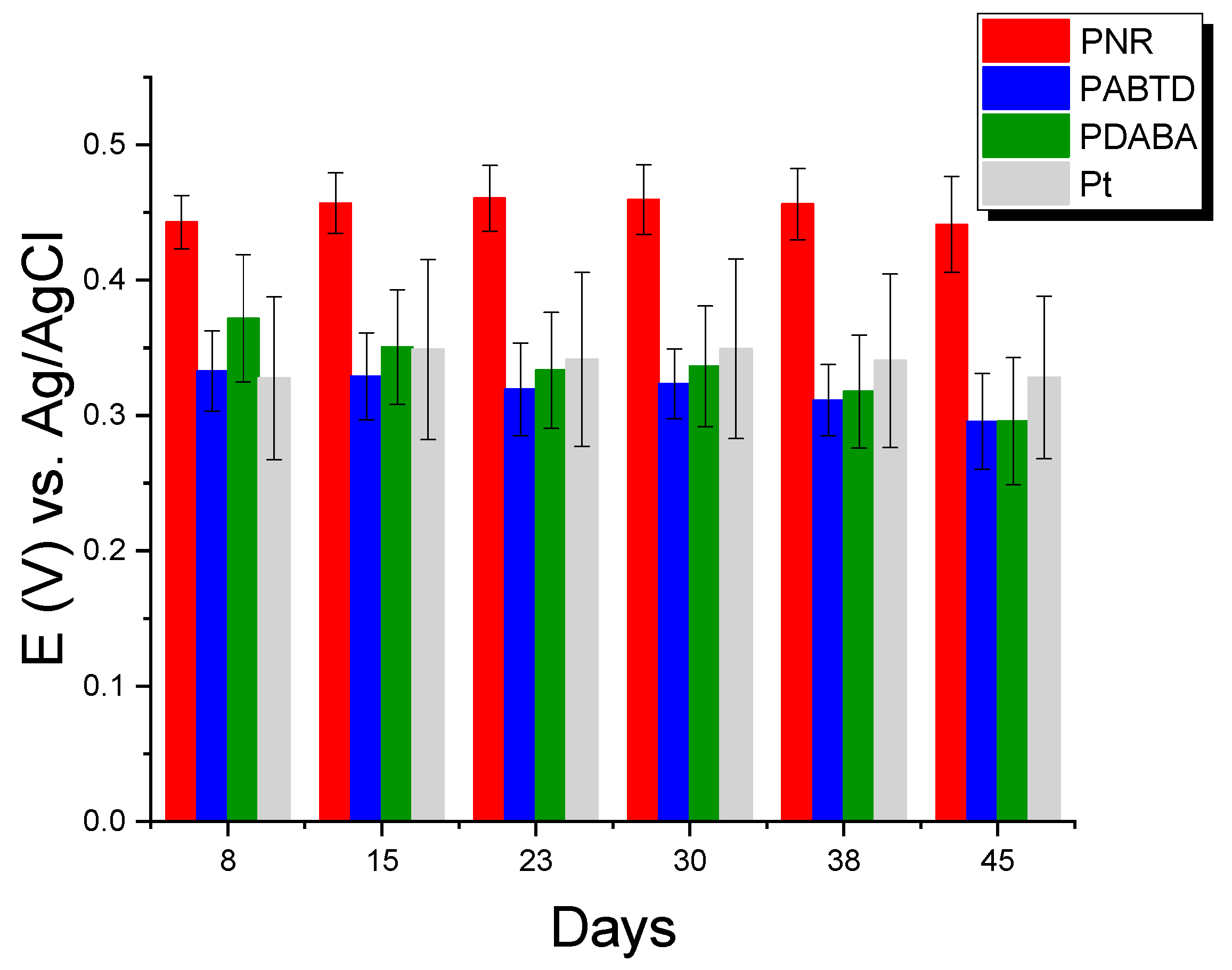
3.2.2. Stability of Potentiometric Signal
3.3. Pattern Recognition of Effervescent Tablets Dissolved in Acetate Buffer Using an Electronic Tongue
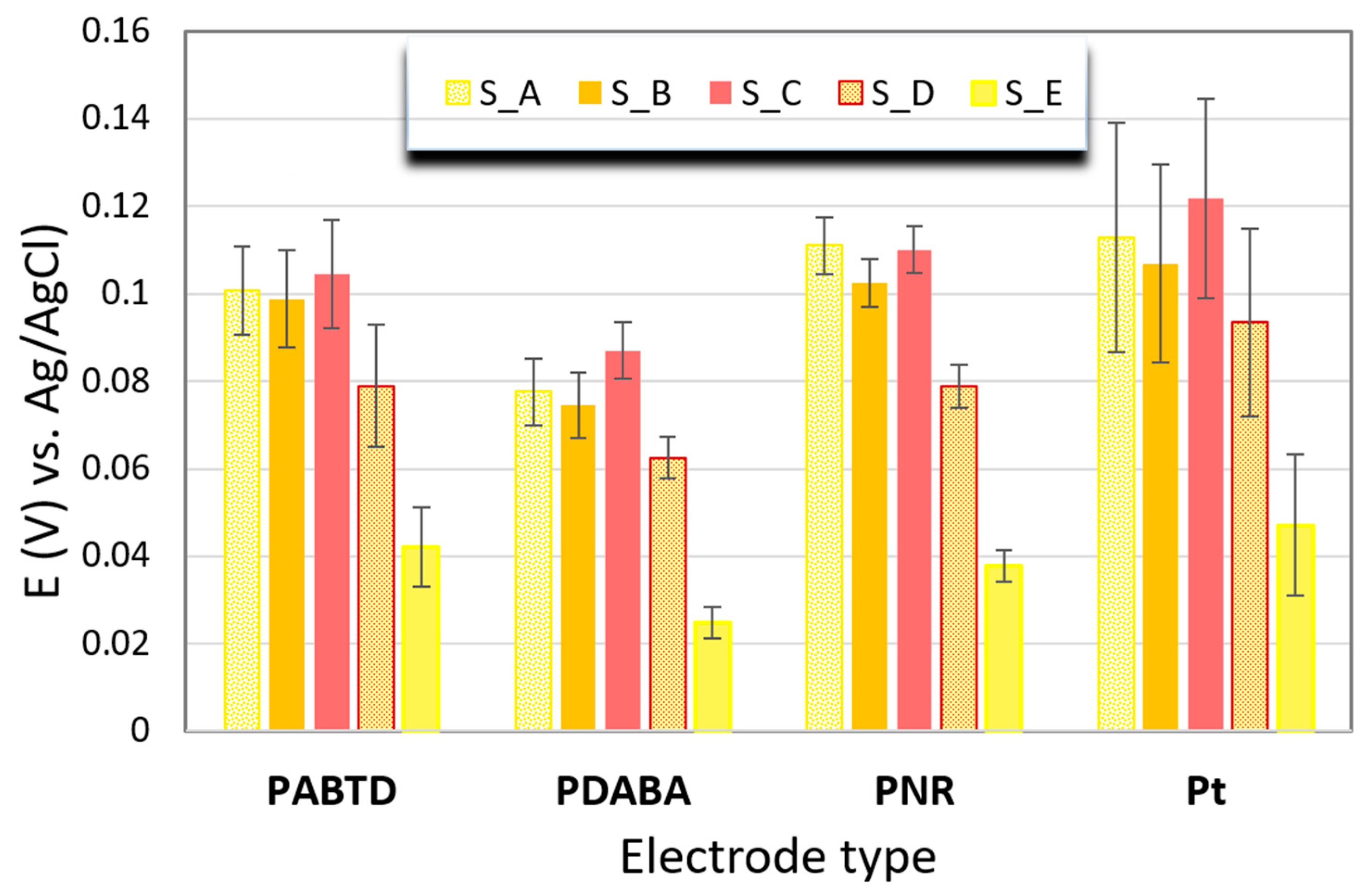
3.3.1. Analysis/Measurements of Effervescent Tablets
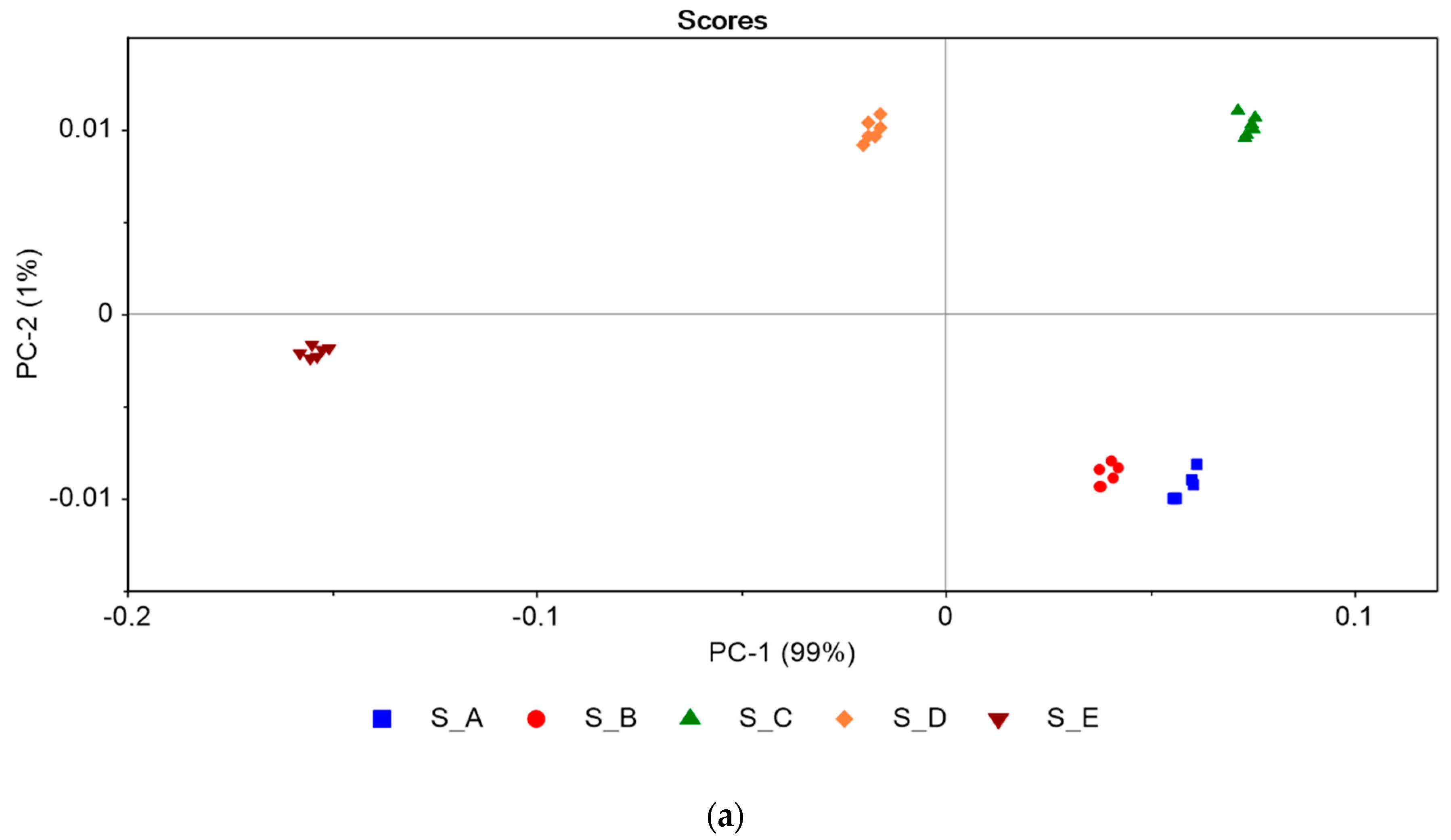
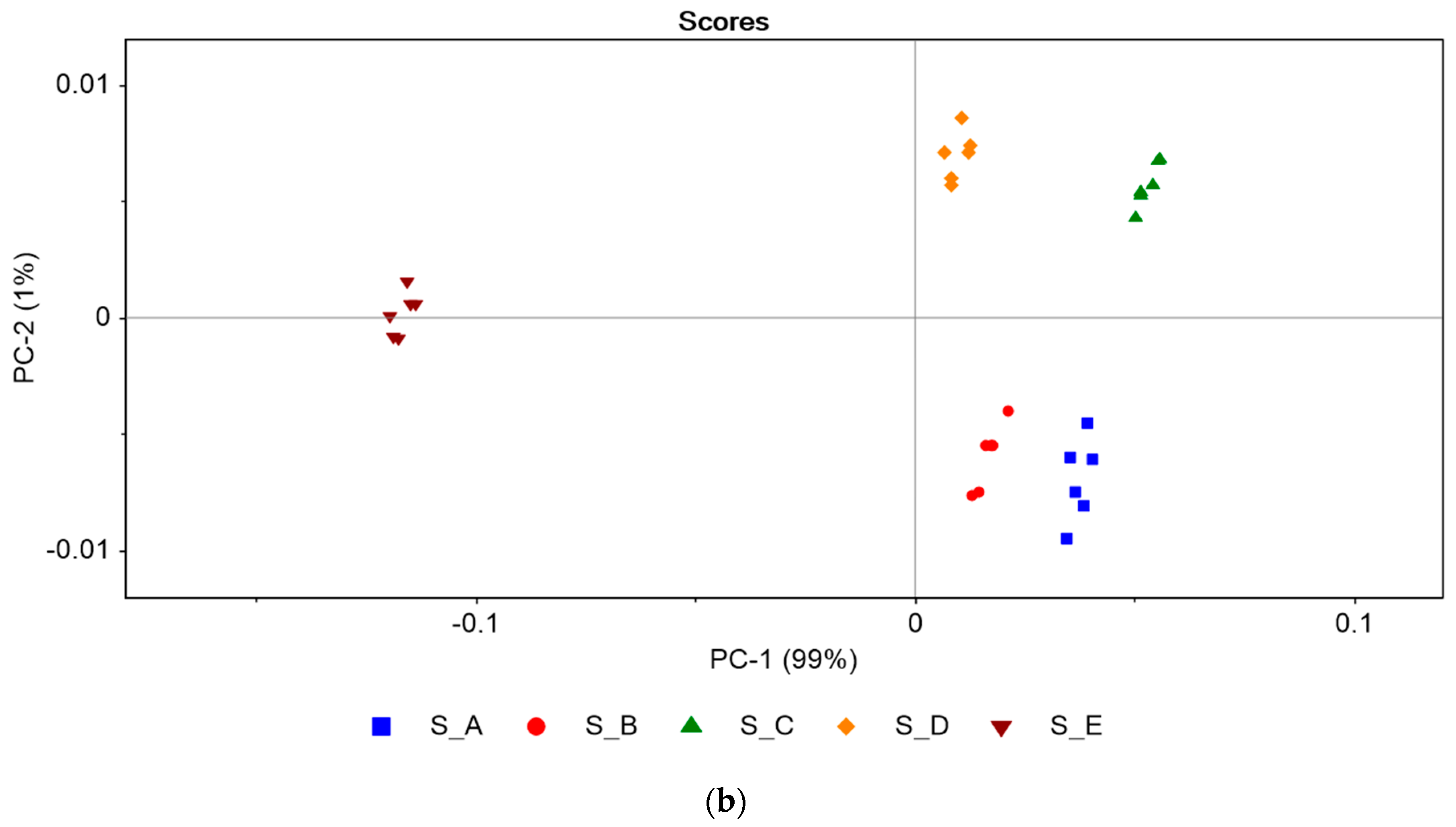
3.3.2. PCA Processing of the Potentiometric Data—Recognition of Effervescent Tablets
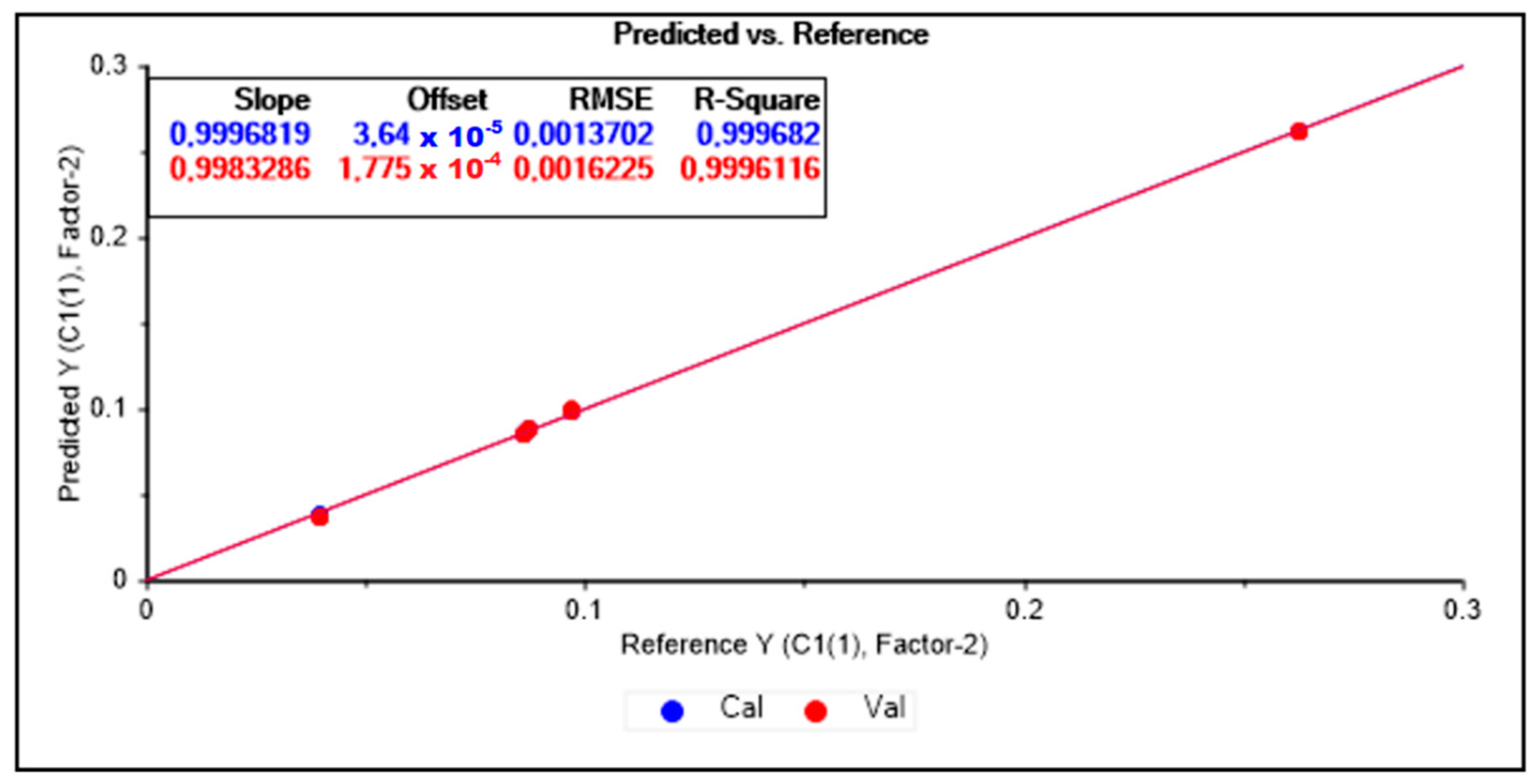
3.3.3. Prediction Models
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ciosek, P.; Wroblewski, W. Sensor arrays for liquid sensing—Electronic tongue systems. Analyst 2007, 132, 963–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woertz, K.; Tissen, C.; Kleinebudde, P.; Breitkreutz, J. Taste sensing systems (electronic tongues) for pharmaceutical applications. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 417, 256–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Habara, M.; Ikezazki, H.; Chen, R.; Naito, Y.; Toko, K. Advanced taste sensors based on artificial lipids with global selectivity to basic taste qualities and high correlation to sensory scores. Sensors 2010, 10, 3411–3443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krejzová, E.; Bělohlav, Z. Masking the Taste of Active Substances in Orally Dispersible Tablets. Chem. Listy 2004, 108, 17–24. [Google Scholar]
- Sohi, H.; Sultana, Y.; Khar, R.K. Taste masking technologies in oral pharmaceuticals: Recent developments and approaches. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2004, 30, 429–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayenew, Z.; Puri, V.; Kumar, L.; Bansal, A.K. Trends in pharmaceutical taste masking technologies: A patent review. Recent Pat. Drug Deliv. Formul. 2009, 3, 26–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagh, D.V.; Ghadlinge, S.V. Taste Masking Methods and Techniques in Oral Pharmaceuticals: Current Perspectives. J. Pharm. Res. 2009, 2, 1049–1054. [Google Scholar]
- Shishkanova, T.V.; Broncová, G.; Skálová, A.; Prokopec, V.; Člupek, M.; Král, V. Potentiometric electronic tongue for taste assessment of ibuprofen based pharmaceuticals. Electroanalysis 2019, 31, 2024–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.-H.; Lu, S.H.; Lai, Y.H.; Lai, G.-H.; Dizon, G.V.; Yang, T.I.; Lin, Y.-J.; Chou, Y.C. Novel ascorbic acid sensor prepared from gold/aniline-pentamer-based electroactive polyamide composites. Express Pol. Lett. 2018, 12, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broncová, G.; Řezanka, P.; Vosmanská, M.; Shishkanova, T.V. List of Laboratory Task, UCT Prague Coulometry. 2019. Available online: https://uanlch.vscht.cz/studies/bachelor_en/laboratories_en/lachi_en/list_en (accessed on 1 January 2020).
- Pisoschi, A.M.; Pop, A.; Serban, A.I.; Fafaneata, C. Electrochemical methods for ascorbic acid determination. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 121, 443–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullin, I.F.; Turova, E.N.; Ziyatdinova, G.K.; Budnikov, G.K. Potentiometric determination of ascorbic acid: Estimation of its contribution to the total antioxidant capacity of plant materials. J. Anal. Chem. 2002, 57, 353–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, J.C.B.; Kubota, L.T.; de Oliveira Neto, G. Potentiometric biosensor for l-ascorbic acid based on ascorbate oxidase of natural source immobilized on ethylene–vinylacetate membrane. Anal. Chim. Acta 1999, 385, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.-L.; Xu, J.-J.; Zhao, W.; Chen, H.-Y. Ascorbic acid sensor based on ionsensitive field-effect transistor modified with MnO2 nanoparticles. Anal. Chim. Acta 2004, 512, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalimuthu, P.; John, A.S. Electropolymerized film of functionalized thiadiazole on glassy carbon electrode for the simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid. Bioelectrochemistry 2009, 77, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, P.R.; Okajima, T.; Ohsaka, T. Simultaneous electroanalysis of dopamine and ascorbic acid using poly(N-N′-dimethylaniline)-modified electrodes. Bioelectrochemistry 2003, 59, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Sun, Y.; Lin, X.; Tang, Y.; Huang, L. Electrochemical characterization of poly(eriochrome black T) modified glassy carbon electrode and its application to simultaneous determination of dopamine, ascorbic acid and uric acid. Electrochim. Acta 2007, 52, 6165–6171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasantha, V.S.; Chen, S.-M. Electrocatalysis and simultaneous detection of dopamine and ascorbic acid using poly(3,4-ethylenedioxy)thiophene film modified electrodes. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2006, 592, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riul, A.; Gallardo Soto, A.M.; Mello, S.V.; Bone, S.; Taylor, D.M.; Mattoso, L.H.C. An electronic tongue using polypyrrole and polyaniline. Synth. Met. 2003, 132, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paolesse, R.; Lvova, L.; Nardis, S.; Di Natale, C.; D’Amico, A.; Castro, F.L. Chemical imagines by porphyrin arrays of sensors. Microchim. Acta 2008, 163, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riul, A.; Malmegrim, R.R.; Fonseca, F.J.; Mattoso, L.H.C. An artificial taste sensor based on conducting polymers. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2003, 18, 1365–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishkanova, T.V.; Broncová, G.; Krondak, M.; Sýkora, D.; Král, V. Important aspects influencing stability of the electrochemical potential of conductive polymer-based electrodes. J. Mater. Sci. 2011, 46, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maksymiuk, K.; Nybäck, A.-S.; Bobacka, J.; Ivaska, A.; Lewenstam, A. Metallic and non-metallic redox response of conducting polymers. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1997, 430, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobacka, J.; Ivaska, A.; Lewenstam, A. Potentiometric Ion Sensors Based on Conducting Polymers. Electroanalysis 2003, 15, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broncová, G.; Shishkanova, T.V.; Dendisova, M.; Clupek, M.; Kubac, D.; Matejka, P. Poly(4-amino-2,1,3-benzothiadiazole) films: Preparation, characterization and applications. Chem. Pap. 2017, 71, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broncová, G.; Matějka, P.; Němečková, Z.; Vrkoslav, V.; Shishkanova, T.V. Electrochemical detection of sialic acid using phenylboronic acid-modified poly(diaminobenzoic) acid. Electroanalysis 2018, 30, 672–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broncová, G.; Shishkanova, T.V.; Matějka, P.; Volf, R.; Král, V. Citrate selectivity of poly(neutral red) electropolymerized films. Anal. Chim. Acta 2004, 511, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Březnová, H.; Volf, R.; Král, V.; Sessler, J.L.; Try, A.C.; Shishkanova, T.V. Monomer and polymer quinoxaline derivatives for cationic recognition. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2003, 375, 1193–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broncová, G.; Shishkanova, T.V.; Krondak, M.; Volf, R.; Král, V. Potentiometric Sensors Based on Conducting Polymers: Preparation, Response Mechanisms and Applications. Chem. Listy 2009, 103, 795–799. [Google Scholar]
- Karyakin, A.A.; Ivanova, Y.N.; Karyakina, E.E. Equilibrium (NADţ/NADH) potential on poly(Neutral Red) modified electrode. Electrochem. Commun. 2003, 5, 677–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaidarova, L.G.; Gedmina, A.V.; Artamonova, M.L.; Chelnokova, I.A.; Budnikov, H.C. Voltammetry determination of dopamine by the electrocatalytic response of an electrode modified by a polyaniline film with an inclusion of copper(II) tetrasulfophthalocyanine. J. Anal. Chem. 2013, 68, 516–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broncová, G.; Shishkanova, T.V.; Krondak, M.; Volf, R.; Král, V. Optimalization of Poly(neutral red) Coated-wire Electrode for Determination of Citrate in Soft Drinks. Sensors 2008, 8, 594–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, X.; Bae, I.T.; Shao, M.; Liu, C.C. Electra-oxidation of L-ascorbic acid on platinum in acid solutions: An in-situ FTIRRAS study. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1993, 346, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brezina, M.; Koryta, J.; Loucka, T.; Marsikova, D.; Pradac, J. Adsorption and kinetics of oxidation of ascorbic acid at platinum electrodes. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1972, 40, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thacker, R.; Hoare, J.P. Sorption of oxygen from solution by noble metals: I. Bright platinum. J. Electroanal. Chem. Interf. Electrochem. 1971, 30, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, J.; O’Riordan, D.; Jacquier, J.-C.; O’Sullivan, M. Masking of bitterness in dairy protein hydrolysates: Comparison of an electronic tongue and a trained sensory panel as means of directing the masking strategy. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 63, 751–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesoły, M.; Cetó, X.; del Valle, M.; Ciosek, P.; Wróblewski, W. Quantitative Analysis of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) Using a Potentiometric Electronic Tongue in a SIA Flow System. Electroanalysis 2016, 28, 626–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutés, A.; Calvo, D.; Cespedes, F.; del Valle, M. Automatic sequential injection analysis electronic tongue with integrated reference electrode for the determination of ascorbic acid, uric acid and paracetamol. Microchim. Acta 2007, 157, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casilli, S.; De Luca, M.; Apetrei, C.; Parra, V.; Arrieta, Á.A.; Valli, L.; Jiang, J.; Rodríguez-Méndez, M.L.; De Saja, J.A. Langmuir–Blodgett and Langmuir–Schaefer films of homoleptic and heteroleptic phthalocyanine complexes as voltammetric sensors: Applications to the study of antioxidants. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2005, 246, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarma, M.; Romero, N.; Cetó, X.; del Valle, M. Optimization of Sensors to be Used in a Voltammetric Electronic Tongue Based on Clustering Metrics. Sensors 2020, 20, 4798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Composition of the Polymerization Bath | Polymerization Parameters | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monomer (Electrode with Polymer) | Concentration of Monomer [mol L−1] | Supporting Electrolyte | Potential Range vs. Ag/AgCl [V] | Number of Cycles | Scan Rate [mV s−1] |
| ABTD (PABTD_1, _2, _3) | 0.005 | 3 M H2SO4 | 0.00 ÷ 1.25 | 25 | 50 |
| DABA (PDABA_1, _2, _3) | 0.005 | 0.5 M H2SO4 | 0.00 ÷ 1.20 | 20 | 50 |
| NR (PNR_1, _2, _3) | 0.005 | acetonitrile, 0.05 M Bu4NClO4 | −0.20 ÷ 1.80 | 20 | 50 |
| Tablets | Weight [g] | Acetate Buffer pH | Redistill Water pH | Appearance of the Solution 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S_A | 4.0147 ± 0.0124 | 4.98 | 4.06 | Clear yellow |
| S_B | 3.9736 ± 0.0112 | 4.97 | 4.05 | Clear orange |
| S_C | 3.9501 ± 0.0099 | 4.97 | 3.9 | Cloudy pink, traces of filler |
| S_D | 3.1566 ± 0.0119 | 4.98 | 3.77 | Cloudy yellow |
| S_E | 3.0553 ± 0.0095 | 5.01 | 4.32 | Clear yellow |
| Position order | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 |
| Sample | 0 1 | AcB 2 | AcB | S_A | 0 | AcB | AcB | S_B | 0 | AcB | AcB | S_C | 0 |
| Position order | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 14 | 15 |
| Sample | AcB | AcB | S_D | 0 | AcB | AcB | S_E | AcB | AcB | 0 | 0 | AcB | AcB |
| Effervescent Tablets | Producer | Concentration of AA in Tablet [mM] Dissolved in 100 mL Volume Flask | Amount of AA Declared by Manufacturer in Tablet [mg] | Amount of AA Obtained by Coulometric Titration in Tablet [mg] 1 | Difference in Declared Experimental Amount of AA [mg] | Deviation [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S_A | Haas | 4.5 | 80 | 85.8 ± 0.9 | 5.8 | 7.3 |
| S_B | Haas | 4.5 | 80 | 87.1 ± 0.7 | 7.1 | 8.9 |
| S_C | Haas | 2.3 | 40 | 39.7 ± 0.8 | 0.3 | 0.8 |
| S_D | MaxiVita | 4.5 | 80 | 97.2 ± 1.7 | 17.2 | 21.5 |
| S_E | MaxiVita | 13.6 | 240 | 263.0 ± 1.7 | 23.0 | 9.6 |
| Electronic Tongue | Electrode | Layer/ Receptor | Statistical Method | Analyte | Concentration (mol L−1) | Real Sample | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Potentiometric ET | 8: miniaturized PVC membrane electrodes | an ion-exchanger | PLS | AA, acetylsalicylic acid, acetaminophen | 10−5.5–10−1.5 | quantitative analysis of mixtures, no real samples | [37] |
| Voltammetric ET | 3: Pt, Au, epoxy-graphite | – | ANN | AA, uric acid, acetaminophen (paracetamol) | 10−4–10−3 | 50 standard solutions, mixture, no real sample | [38] |
| Voltammetric ET | 4: ITO | phthalocyanine films (LB or LS technique) | PCA | AA, vannilic acid, pyrogallol, catechin | 10−3 | mixture solutions, no real sample | [39] |
| Voltammetric ET | 7: graphite epoxy composite electrodes or 8: Pt disc | cobalt (II) phthalocyanine, polypyrrole, Prussian blue, 4 different oxide nanoparticles | PCA CVA ANN | AA, paracetamol uric acid | 10−4 | mixture solutions | [40] |
| Our potentiometric ET | 12: Pt | Electro-polymerized films | PCA | AA | 10−6.1–10−4.3 | evanescent tablets | – |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Broncová, G.; Prokopec, V.; Shishkanova, T.V. Potentiometric Electronic Tongue for Pharmaceutical Analytics: Determination of Ascorbic Acid Based on Electropolymerized Films. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 110. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9050110
Broncová G, Prokopec V, Shishkanova TV. Potentiometric Electronic Tongue for Pharmaceutical Analytics: Determination of Ascorbic Acid Based on Electropolymerized Films. Chemosensors. 2021; 9(5):110. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9050110
Chicago/Turabian StyleBroncová, Gabriela, Vadim Prokopec, and Tatiana V. Shishkanova. 2021. "Potentiometric Electronic Tongue for Pharmaceutical Analytics: Determination of Ascorbic Acid Based on Electropolymerized Films" Chemosensors 9, no. 5: 110. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9050110
APA StyleBroncová, G., Prokopec, V., & Shishkanova, T. V. (2021). Potentiometric Electronic Tongue for Pharmaceutical Analytics: Determination of Ascorbic Acid Based on Electropolymerized Films. Chemosensors, 9(5), 110. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9050110







