Abstract
One of the main directions in the development of modern electroanalytical chemistry is the development of new effective methods for research and analysis of biological objects, particularly, human blood serum. The creation of new electrochemical sensors is a promising approach, which has determined several main directions in applied voltammetry in the field of chemical analytical control. In this work, the dynamics and parameters of total antioxidant activity of human serum blood of patients with chronic cerebral ischemia, during treatment with pharmaceutical drugs Mexidol, Cavinton Comfort, and Cytoflavin was tested by cathode voltammetry with a model process of oxygen electroreduction, using a new electrochemical sensor.
1. Introduction
The great potential and capabilities of modern electroanalytical methods are widely recognized and appreciated in science and industry due to their low investment and operating costs, as well as sufficient sensitivity, high selectivity, miniaturization, easy automation, and environmental friendliness [1,2,3,4]. One of the important areas of electroanalytical chemistry is the development of effective methods for research and analysis of biological objects for biology and medicine, in particular, human blood serum [5,6,7]. The creation of new electrochemical sensors has determined several applied directions in voltammetry, first of all, chemical-analytical control is actively developing [8].
The main element of any electrochemical sensor is a working electrode, which serves as a conversion element and on which an electrical signal is generated by an electrochemical process. The new generation of sensors, which is now actively developing, is based on the chemical modification of electrodes. In this case, chemical compounds are applied to the surface of the electrodes, which significantly change their ability to voltammetric response [9,10].
The easiest fixation of the modifier is carried out by physical adsorption. The advantage of this approach is that it does not require special reagents to attach active groups to the electrode; it is enough to activate and clean the electrode surface before modification. However, the lifetime of such an electrode is relatively short, since the modifier gradually goes into solution. The modifier is adhered to the electrode surface by adsorption. Its solution is applied by immersing the electrode in a modifier solution, followed by removal of the solvent. This method is quite simple and reproducible [11].
A feature of the modifier containing molecules with a branched system of π-electrons is the retention of porphyrin complexes of cobalt on the surface of carbon electrodes [12,13]. The adsorption was carried out by immersing the electrode in an aqueous solution of the adsorbed substance. Water-soluble complexes of cobalt phthalocyanine are adsorbed on pyrographite, which facilitates the reduction of the oxygen molecule.
Method for determining vitamin B6 can be used in dietary supplements at the carbon electrode modified with cobalt phthalocyanine [14].
The voltammetric method can be used for analytical control of antioxidant activity [15,16,17]. It should be noted that the assessment of activity of the free radicals is an important parameter for biological and medical research. Free radical activity and oxidative damage have been implicated in the pathogenesis of a number of diseases [18,19]. In particular, more and more attention is paid to their role in the development of vascular disorders and the progression of neurodegenerative syndromes. The depletion of the antioxidant potential in developing pathological processes can be corrected by pharmaceutical preparations that have an indirect antioxidant activity. Therefore, antioxidant drugs are widely used and new ones are being developed [20]. In addition to their main pharmacological actions, various drugs can reduce the oxidation of free radicals, restore the antioxidant defense system and relieve the severity of clinical symptoms.
There are several studies of efficacy and safety of Mexidol in patients with chronic brain ischemia (CHM) complicated with arterial hypertension and atherosclerosis [21,22,23]. The results show greater clinical efficacy and sufficient safety of such combination therapy. By the end of therapy, patients in the Mexidol group have a reliable improvement in motor activity, cognitive function, and psychoemotional sphere, as well as a decrease in fatigue and neurological manifestations compared with the comparison group.
Among Cytoflavin-treated patients, there was a twofold reduction in the proportion of patients in which the volume of cerebral ischemia increased during the period of 1–21 days [24]. In patients with initial assessments of at least 14 points on the NIH scale, Cytoflavin treatment for 20 days promoted more marked improvements in neurological, functional, and cognitive status than seen in patients given infusions for 10 days.
In this work, we have determined the total activity of antioxidants in the blood serum in patients with chronic cerebral ischemia. The method of voltammetry was applied using the process of oxygen electroreduction on a new electrochemical sensor.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Apparatus
A voltammetric analyzer TA–2 (“Tomanalyt,” Tomsk, Russia) connected with PC was used in this work. Voltammetric curves were recorded at room temperature in a three-electrode electrochemical cell connecting to the analyzer. A carbon electrode, a glassy carbon electrode (GCE), and platinum electrode were used as working electrodes. A silver–silver chloride electrode (1 M KCl) was used as the reference electrode. A silver–silver chloride electrode (1 M KCl) was used as the counter electrode. The diameter of the carbon electrode was 0.4 cm, resulting in geometrical surface of 0.126 cm2. The geometrical surface of glassy carbon electrode was 0.425 cm2. The geometrical surface of platinum electrode was 0.258 cm2.
An open type cell was used in this investigation. The working, reference, counter, and indicator electrodes were held in the electrochemical cell.
As a supporting electrolyte, 2.5 × 10−2 M (equimolar mixtures of Na2HPO4 and KH2PO4, pH 7.3) phosphate buffer was used. Nanopure water was used for making solutions.
The means and standard errors of the mean were calculated. Statistical analysis was performed using Statistica 6.0 software. Student’s t-test was used for statistical analysis of the data. The mean changes in coefficients of the total activity of antioxidants in the blood serum were calculated for patients with chronic cerebral ischemia before and after treatment. Data are presented as mean ± SD.
2.2. Voltametric Measurement
A volume of 10 cm3 of phosphate buffer was placed in the electrochemical cell. The measurement involved the recording of voltammograms of the cathodic reduction of oxygen by voltammetry without and with addition of 0.2 cm3 of serum blood under the following conditions: potential scan rate 30 mV s−1 and potential range E = 0 to −1.0 V. After substance addition, the solution was stirred about 20 s. After the stirring had stopped, the potential was scanned negatively, causing oxygen reduction, giving a current wave electroreduction of oxygen (ER O2). Its value was proportional to the amount of oxygen in the bulk of the solution. Inhibition of oxygen cathode waves and shear wave potential ER O2 in the positive region is due to a chemical reaction between antioxidant of serum with active oxygen radicals (in the first place, superoxide anion radicals). Thus, the components of blood serum, which are consisted is in solution, affect the ER O2, showing antioxidant activity.
Oxygen concentration was monitored by oxygen analyzer. Based on the ammetric measurements, the concentration of oxygen in phosphate buffer at 25.0 ± 0.5 °C was 2.56 ± 0.05 × 10−4 M.
2.3. Preparation of New Electrochemical Sensor
Cobalt phthalocyanine (dye content: ≈95%) was purchased from Alfa Aesar.
The methods of immobilization of the cobalt phthalocyanine modifier on the electrode are as follows:
- (1)
- The surface of the electrode is treated with nitric acid to remove organic and inorganic contaminants, washed with distilled water, and dried. Cobalt phthalocyanine is applied to the electrode by means of adsorption forces from a saturated solution of this metal complex in sulfuric acid (2 M). The acid is removed by short-term immersion of the working electrode surface in the distilled water. The electrode is dried in a thermostatically controlled cabinet at a temperature not exceeding 100 °C. After that, the modified electrodes were stored in air at room temperature in dark place prior to use.
- (2)
- For modification, a solution with a concentration of cobalt phthalocyanine of 1.0 × 10−1 M, dissolved in sulfuric acid, was used. The electrolysis was carried out at a potential of −0.1 V, and the electrolysis time was 30 min.
- (3)
- The modifier is added to the cell at a concentration of 1.0 × 10−4 M, where it is in free form.
2.4. Collection of Serum Samples and Patients Characteristic
The object of the study was the blood serum of people diagnosed with chronic cerebral ischemia. The patients were on outpatient treatment at the Department of Neurology and Neurosurgery of the Siberian State Medical University in Tomsk. The study involved 47 female patients with a diagnosis of chronic cerebral ischemia of the first stage, the average age is 61.5 years (from 52 to 67 years). The diagnosis was confirmed by the presence of a characteristic pathological change in the vessels of the brain by instrumental imaging methods (ultrasound examination of the vessels, computed tomography, or magnetic resonance imaging of the brain). All patients received basic therapy, including antihypertensive, antiplatelet, antidiabetic drugs.
In addition to basic therapy, patients took the following drugs according to the scheme:
- 13 patients received Cavinton Comfort 30 mg daily for 2 months.
- 13 patients received injections of Mexidol 500 mg intramuscularly for 10 days on an outpatient basis.
- 9 patients took Mexidol 375 mg orally per day for a month.
- 12 patients took Cytoflavin orally at 1520 mg per day for a month.
Venous blood, collected fasting, was placed in a glass centrifuge tube without anticoagulant and left at room temperature for 30 min to allow clot formation, which was immediately removed. The tubes were centrifuged in a tabletop centrifuge for 10 min at a rotation speed of 2000 rpm. The centrifugate was sampled in the volume of 1.0–1.5 cm3 for further study. Frozen samples were stored in a freezer at −20 °C [25].
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Influence of the Method of Immobilization of the Modifier on Signal Stability
Adsorption electrode modification is the fastest and easiest. After modification, the electrode surface was covered with a uniform layer of adsorbed modifier. Removal of the modifier to renew the surface of the working electrode was also carried out by simply dipping it into a sulfuric acid solution and dissolving the modifier from the electrode surface in it.
During the electrochemical modification, the modifier film was visually much thinner than in the modification by adsorption from a sulfate saturated solution of phthalocyanine cobalt. The electrolysis conditions were not optimized due to the long time of the electrode modification.
When the modifier was in the cell in a free form, the peak of oxygen electroreduction decreased in magnitude, changed its shape, and turned into a wave. The curves were poorly reproduced. Thus, it became impossible to process such a signal.
Therefore, the most preferred method for immobilizing cobalt phthalocyanine on the surface of the indicator electrode is modification from a saturated sulfuric acid solution of cobalt phthalocyanine by means of adsorption. This method was chosen to determine the total activity of antioxidants in blood serum using the process of electroreduction of oxygen.
Figure 1 shows the capacitive curve, which is characterized by two current minima. The capacitive current in these areas is significantly reduced, which corresponds to the adsorption of cobalt phthalocyanine by the indicator electrode.
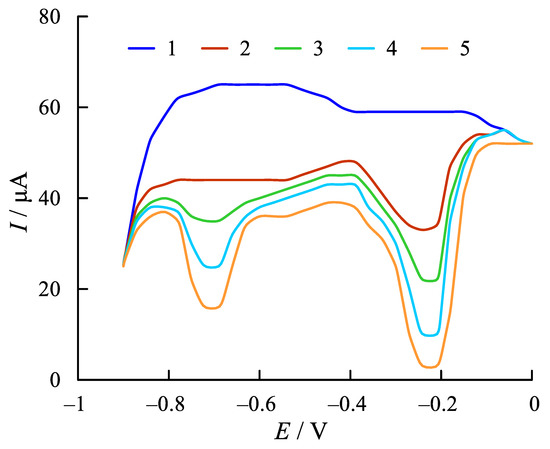
Figure 1.
Capacitive current curves in phosphate buffer (2.5 × 10−2 M, pH 7.3) on the glassy carbon electrode (GCE) without (1) and with cobalt phthalocyanine 2.5 × 10−5 M (2), 5.0 × 10−5 M (3), 7.5 × 10−5 M (4), and 1.0 × 10−4 M (5). Scan rate: 50 mV s−1.
To evaluate reproducibility of electrode preparation, three independent glassy carbon electrodes modified by cobalt phthalocyanine were prepared. Voltammograms of ER O2 current were recorded in supporting electrolyte. Relative standard deviations (RSDs) of the cathodic peak currents were 7.8%, indicating acceptable repeatability of the electrode preparation.
For long-term stability evaluation, three modified electrodes were stored in air at room temperature for 3 weeks. Here, 91% of the initial responses for ER O2 current were observed after 1 week, 86% after 2 weeks, and 78% after 3 weeks, indicating good stability of the modified electrode.
3.2. Effect of the Nature of the Electrode on Signal Stability
The platinum, graphite, and glassy carbon electrode surface was modified from cobalt phthalocyanine with a sulfuric acid solution.
Subsequent evaluation was carried out visually and by recording the capacitance curves. It was found that the modifier does not diffuse into the solution, but is stably fixed by means of adsorption forces on the branched surface of the graphite electrode, glassy carbon electrode, and, to a lesser extent, on the platinum electrode (Figure 2). The modified glassy carbon electrode showed stable performance with a reproducible oxygen electroreduction signal.
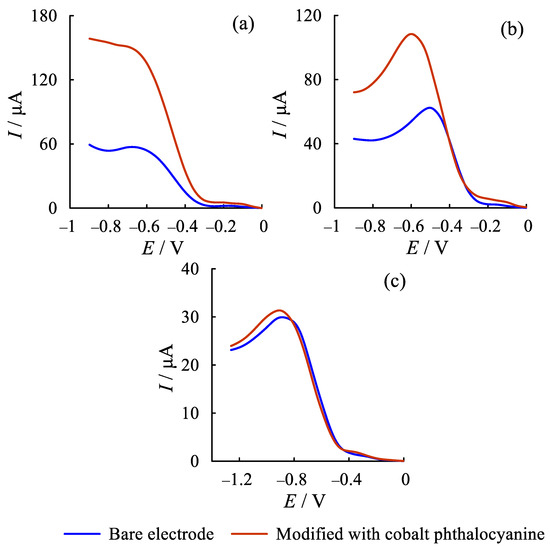
Figure 2.
Voltammograms of the electroreduction of oxygen (ER O2) current in phosphate buffer (2.5 × 10−2 M, pH 7.3) on the graphite electrode (a), glassy carbon electrode (b), and platinum electrode (c). Scan rate: 50 mV s−1.
The platinum electrode was poorly modified by the method proposed in the work. The modification of the working surface did not actually affect the quality of the received signals in comparison with the unmodified electrode. The limiting currents of oxygen electroreduction during modification on a platinum electrode were lower than on other electrodes.
The values of the oxygen electroreduction currents when using a modified glassy carbon electrode are lower than when using a modified graphite electrode. In this case, the curves are characterized by good reproducibility of the oxygen electroreduction signal and, with the interchangeability of electrodes, the repeatability of results is significantly higher compared to other electrodes used. When working with a graphite electrode, adsorption phenomena are strongly manifested, the signal of the oxygen electroreduction current changes with time towards a decrease in the peak.
Thus, it can be concluded that the optimal electrode for determining the total activity of antioxidants in blood serum is glassy carbon electrode modified with cobalt phthalocyanine.
3.3. Investigate the Total Antioxidant Activity of Human Serum Blood
In order to investigate the total activity of antioxidants in the blood serum, voltammograms of ER O2 current were recorded in supporting electrolyte containing the substances under investigation at the glassy carbon electrode modified by cobalt phthalocyanine (Figure 3).
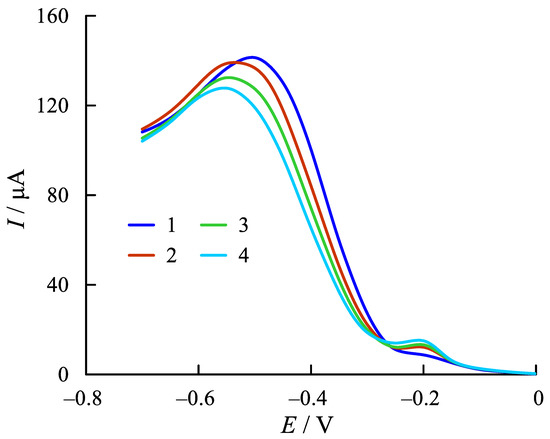
Figure 3.
Voltammograms of the ER O2 current in phosphate buffer (2.5 × 10−2 M, pH 7.3) on the GCE modified with cobalt phthalocyanine (1) and with 0.3 cm3 of human serum blood at t = 3 min (2), t = 6 min (3), and t = 9 min (4). Scan rate: 50 mV s−1.
The electroreduction of oxygen at the working electrode has been treated as a “model” reaction because of similar processes of ER O2 and the oxygen reduction in tissues. It proceeds at the cathode in several stages with formation of the reactive oxygen species (ROS), such as O2●− and HO2● according to stages (1)–(4):
O2●− + H+ ⇄ HO2●
HO2● + H+ + e− ⇄ H2O2
H2O2 + H+ + e− ⇄ H2O.
The concentration of oxygen and its radicals is decreased at the electrode and the current of ER O2 also decreases.
As a result, the curves of the relative change of the ER O2 current density (1 − I/I0) against time of the interaction between ROS and antioxidant at the glassy carbon electrode modified by cobalt phthalocyanine in supporting electrolyte were plotted (Figure 4).
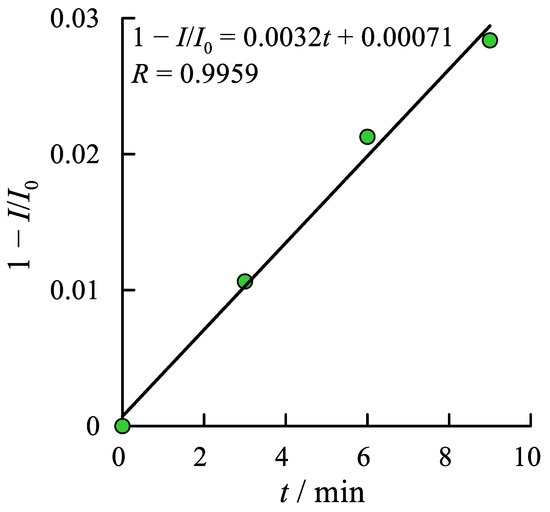
Figure 4.
Dependence of the relative change of the ER O2 current against time of the interaction between ROS and antioxidant at the glassy carbon electrode modified by cobalt phthalocyanine in phosphate buffer (2.5 × 10−2 M, pH = 7.3) for the blood serum of patient treated with Cytoflavin.
All the curves represent straight lines in the range of relatively low antioxidant concentrations. The slope angle tangent of these lines is suggested to be a coefficient of the antioxidant activity K given by Equation (5).
The hypothesis of linearity of the described curves by regression analysis was verified. The results were compared using the Fisher criterion, and they do not exceed the corresponding standard value. The estimated experimental errors (σ, %) do not exceed 10%.
In this work, the antioxidant activity (AOA) coefficient of substances was used in μM min−1 [26].
where C0 (μM) is the oxygen concentration at the electrode in absence of antioxidant, I (A) is the ER O2 current with the addition of the investigated substance in the solution, I0 (A) is the limiting ER O2 current without substance in the solution, and t (min) is time of the interaction between oxygen, its radicals and antioxidant at the working electrode.
3.3.1. Evaluation of the Effect of the Drug “Cavinton Comfort”
Cavinton Comfort was administered to 13 patients orally, 1 tablet three times a day, for 2 months (Table 1). After the first month of admission, seven people (54%) showed positive dynamics. The coefficient K of the total antioxidants activity (AOA) increased, on average, by 0.09 μM min−1 compared with the results obtained before the start of taking the drug and amounted to 0.63 μM min−1.

Table 1.
The value of the total activity of antioxidants in the blood serum of patients with chronic cerebral ischemia of the first degree (p = 0.95, n = 3) when taking the pharmacological drug Cavinton Comfort.
After the second month, the K coefficient practically did not change compared to the value before taking Cavinton Comfort (0.57 μM min−1).
After the first month, two people independently decided to stop taking the drug.
In six people, the indicator of total antioxidant activity did not change.
Figure 5 shows the results of the average values of the total activity of antioxidants in the blood serum of patients during the treatment course. Indicator of the total activity of antioxidants in the blood serum of patients at the beginning of treatment (K = 0.54 ± 0.04 μM min−1). After the first month of taking Cavinton Comfort, there was a significant increase in the total antioxidant activity (difference between the groups was significant, p < 0.013). During the second month, there was a decrease in this indicator in relation to the indicator after the first month of taking Cavinton Comfort. However, for most patients, the indicator of the total activity of antioxidants after the second month remained generally at the level of the first month.
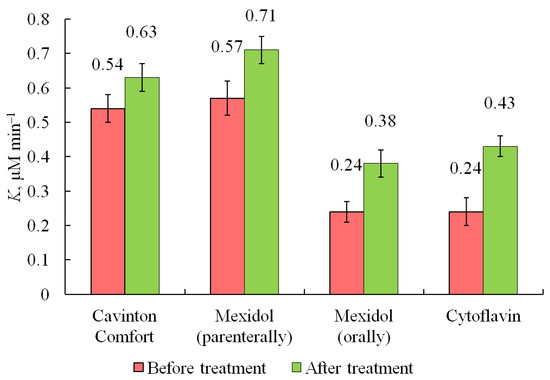
Figure 5.
Average values (means ± SD) of the total antioxidant activity in the blood serum of patients with chronic cerebral ischemia during therapy with Cavinton Comfort, Mexidol (parenterally), Mexidol (orally), and Cytoflavin.
3.3.2. Mexidol
Mexidol was prescribed to 13 patients parenterally at 500 mg per day for 10 days (Table 2). At the end of the therapeutic course, eight people (62%) showed positive dynamics. The index of total AOA increased by an average of 0.14 μM min−1 compared with the results obtained before the start of taking the drug, and it amounted to 0.71 μM min−1.

Table 2.
The values of the total activity of antioxidants in the blood serum of patients with chronic cerebral ischemia (p = 0.95, n = 3) when taking Mexidol (parenteral administration).
In five patients, the index of total antioxidant activity did not change.
Figure 5 shows the average values of the total activity of antioxidants in the blood serum of patients during the treatment course. There is a low level of the total activity of antioxidants in the blood serum of patients at the beginning of treatment (K = 0.57 ± 0.04 μM min−1). After the parenteral course of Mexidol, an increase in the total antioxidant activity is observed (difference between the groups was significant, p < 0.0001).
Another group of patients (9 people) received Mexidol orally, one tablet three times a day, for 1 month (Table 3). At the end of the therapeutic course, seven people (78%) showed positive dynamics, when the total AOA index increased by 0.14 μM min−1 compared to the results obtained before the start of treatment was 0.38 μM min−1. In five people, the total antioxidant activity indicator did not change.

Table 3.
The values of the total activity of antioxidants in the blood serum of patients with an established diagnosis of chronic cerebral ischemia (p = 0.95, n = 3) during treatment with Mexidol per os.
Figure 5 shows the results of the total activity of antioxidants in the blood serum of patients during the treatment course. There is a low level of total activity of antioxidants in the blood serum of patients upon admission to treatment (K = 0.24 ± 0.04 μM min−1). After the course of Mexidol per os, a significant increase in the total antioxidant activity indicator is observed (p < 0.0014).
3.3.3. Cytoflavin
Cytoflavin is a combined drug consisting of succinic acid (300 mg), inosine (50 mg), nicotinic acid (25 mg), and riboflavin (5 mg). Cytoflavin was administered orally to 12 patients, 2 tablets twice a day for 1 month (Table 4). At the end of the therapeutic course, eight people (67%) showed an increase in the total AOA, increased by 0.19 μM min−1 compared to the results obtained before the start of treatment and amounted to 0.43 μM min−1. In five people, the total antioxidant activity indicator did not change.

Table 4.
The values of the total activity of antioxidants in the blood serum of patients diagnosed with chronic cerebral ischemia (p = 0.95, n = 3) treated with Cytoflavin.
Figure 5 shows the results of the values of the indicator of the total activity of antioxidants in the blood serum of patients during the treatment course. There is a low level of the total activity of antioxidants in the blood serum of patients upon admission to outpatient treatment (K = 0.24 ± 0.04 μM min−1). However, after the course of Cytoflavin use, increase in the total antioxidant activity is detected (difference between the groups was significant, p < 0.0004).
Figure 6 shows the change in the indicator of the total activity of antioxidants in the groups of patients, where a positive trend was recorded.
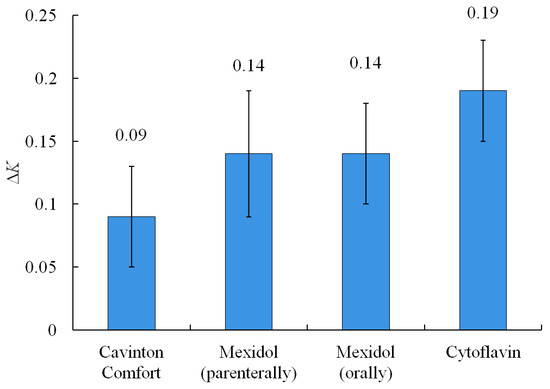
Figure 6.
General change of total activity of antioxidants in the blood serum before and after treatment.
4. Conclusions
As a result of the research, methods of electrode modification were selected for assessing antioxidant activity by voltammetry. A comparative analysis of the antioxidant activity of the blood serum of patients during therapy with the drugs Mexidol, Cavinton Comfort, and Cytoflavin was carried out.
All studied drugs showed the ability to change the antioxidant status of the body. For the most part, the effectiveness of antioxidant drugs depends on the individual characteristics of the organism (disease, nutrition, patient age, and influence of external factors).
It was found that the method of Mexidol administration, in general, does not affect the final efficacy of the drug. The change in the total activity of antioxidants while taking Cavinton Comfort is equivalent to Mexidol. Cytoflavin shows a greater increase in total antioxidant activity in patients.
Author Contributions
Data curation, O.I.L.; formal analysis, E.V.D.; investigation, I.S.G.; methodology, O.A.V.; project administration, E.I.K.; resources, N.G.K.; validation, K.V.D.; writing—original draft preparation, E.V.P. and A.V.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The reported study was funded by the RFBR and Czech Science Foundation according to the research project No. 19-53-26001 and the Russian State assignment “Science” FSWW-2020-0022.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethics Committee of Siberian State Medical University (protocol code 3604, 24/02/2014).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kirchner, E.M.; Hirsch, T. Recent developments in carbon-based two-dimensional materials: Synthesis and modification aspects for electrochemical sensors. Microchim. Acta 2020, 187, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghalkhani, M.; Ghorbani-Bidkorbeh, F. Development of Carbon Nanostructured Based Electrochemical Sensors for Pharmaceutical Analysis. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 2019, 18, 658. [Google Scholar]
- Coroş, M.; Pruneanu, S.; Stefan-van Staden, R.I. Recent Progress in the Graphene-Based Electrochemical Sensors and Biosensors. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2019, 167, 037528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveen, M.H.; Gurudatt, N.G.; Shim, Y.B. Applications of conducting polymer composites to electrochemical sensors: A review. Appl. Mater. Today 2017, 9, 419–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teselkin, J.O.; Babenkova, I.V.; Lyubitsky, O.B.; Klebanov, G.I.; Vladimirov, Y.A. Inhibition of luminol oxidation by serum antioxidants in presence of hydrogen peroxide and hemoglobin. Probl. Med. Chem. 1997, 43, 87–93. [Google Scholar]
- Gumus, S.; Yucel, O.; Gamsizkan, M.; Eken, A.; Deniz, O.; Tozkoparan, E.; Genc, O.; Bilgic, H. The role of oxidative stress and effect of alpha-lipoic acid in reexpansion pulmonary edema—An experimental study. Arch. Med. Sci. 2010, 6, 848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomic, S.; Brkic, S.; Maric, D.; Mikic, A.N. Lipid and protein oxidation in female patients with chronic fatigue syndrome. Arch. Med. Sci. 2012, 8, 886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutfi Yola, M.; Atar, N. A review: Molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensors for determination of biomolecules/drug. Curr. Anal. Chem. 2017, 13, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanssen, B.L.; Siraj, S.; Wong, D.K. Recent strategies to minimise fouling in electrochemical detection systems. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2016, 35, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipskikh, O.I.; Korotkova, E.I.; Khristunova, Y.P.; Barek, J.; Kratochvil, B. Sensors for voltammetric determination of food azodyes—A critical review. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 260, 974–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaegfeld, H.; Kuwana, T.; Jochansson, G. Electrochemical stability of catechols with a pyrene side chain strongly adsorbed on graphite electrodes for catalytic oxidation of dihydronicotinamide adenine dinucleotide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1983, 105, 1805–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collman, J.P.; Denisevich, P.; Konai, Y.; Marrocco, M.; Koval, C.; Anson, F.C. Electrode catalysis of the four-electron reduction of oxygen to water by dicobalt face-to-face porphyrins. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1980, 102, 6027–6036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagal, J.; Sen, R.K.; Yeager, E. The electrocatalysis of molecular oxygen reduction. J. Inorg. Chem. 1977, 16, 3379–3380. [Google Scholar]
- Korotkova, E.I.; Boev, A.S.; Bakibaev, A.A. New voltammetric sensor with phthalocyanine Co for the B6 vitamin determination in food additives. In Book of Abstracts, Proceedings of the International Symposium on Recent Advances in Food Analysis, Prague, Czech Republic, 2–4 November 2005, 2nd ed.; University of Chemistry and Technology: Prague, Czech Republic, 2005; p. 71. [Google Scholar]
- Korotkova, E.I.; Freinbichler, W.; Linert, W.; Dorozhko, E.V.; Bukkel, M.V.; Plotnikov, E.V.; Voronova, O.A. Study of total antioxidant activity of human serum blood in the pathology of alcoholism. Molecules 2013, 18, 1811–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korotkova, E.I.; Misini, B.; Dorozhko, E.V.; Bukkel, M.V.; Plotnikov, E.V.; Linert, W. Study of OH● radicals in human serum blood of healthy individuals and those with pathological schizophrenia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plotnikov, E.; Korotkova, E.; Voronova, O.; Sazhina, N.; Petrova, E.; Artamonov, A.; Chernyavskaya, L.; Dorozhko, E. Comparative investigation of antioxidant activity of human serum blood by amperometric, voltammetric and chemiluminescent methods. Arch. Med. Sci. 2016, 12, 1071–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartos, G. Total antioxidant capacity. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2003, 37, 219–292. [Google Scholar]
- Shalaby, E.A.; Shanab, S.M.M. Antioxidant compounds, assays of determination and mode of action. Afr. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2013, 7, 528–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plotnikov, E.; Voronova, O.; Linert, W.; Martemianov, D.; Korotkova, E.; Dorozhko, E.; Astashkina, A.; Martemianova, I.; Ivanova, S.; Bokhan, N. Antioxidant and Immunotropic Properties of some Lithium Salts. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 6, 86–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataeva, N.G.; Zamoshchina, T.A.; Svetlik, M.V. Effectiveness and safety of mexidol forte 250 in the sequential therapy in patients with chronic ischemia. Zhurnal Nevrol. Psikhiatrii Im. S.S. Korsakova 2020, 120, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chukanova, E.I.; Chukanova, A.S. Efficacy and safety of the drug mexidol FORTE 250 as part of sequential therapy in patients with chronic ischemia of the brain. Zhurnal Nevrol. Psikhiatrii Im. S.S. Korsakova 2019, 119, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antipenko, E.A.; Deruginf, A.V.; Gustov, A.V. The system stress-limiting action of mexidol in chronic cerebral ischemia. Zhurnal Nevrol. Psikhiatrii Im. S.S. Korsakova 2020, 116, 28–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumyantseva, S.A.; Kovalenko, A.L.; Silina, E.V.; Stupin, V.A.; Kabaeva, E.N.; Chichanovskaya, L.V.; Nazarov, M.V.; Tsukurova, L.A.; Burenichev, D.V.; Golikov, K.V.; et al. Efficacy of complex antioxidant energy correction of different durations in the treatment of cerebral infarction (results of a multicenter randomized study). Neurosci. Behav. Physiol. 2017, 47, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voronova, O.A.; Korotkova, E.I.; Plotnikov, E.V.; Gusakova, A.M.; Suslova, T.E.; Dorozhko, E.V.; Petrova, E.V.; Kustova, A.A. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and voltammetric methods for total antioxidant activity determination of human plasma blood of cardiovascular disease. Fundam. Res. 2013, 3, 570–574. [Google Scholar]
- Plotnikov, E.; Korotkova, E.; Voronova, O.; Dorozhko, E.; Bohan, N.; Plotnikov, S. Lithium-based antioxidants: Electrochemical properties and influence on immune cells. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2015, 19, 107–113. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).