Abstract
Impedance-type humidity sensors based on EuCl2, Eu2O3 and EuCl2/Eu2O3 blend films were fabricated. The electrical properties of the pure EuCl2 and Eu2O3 films and EuCl2/Eu2O3 blend film that was blended with different amounts of EuCl2 were investigated as functions of relative humidity. The influences of the EuCl2 to the humidity-sensing properties (sensitivity and linearity) of the EuCl2/Eu2O3 blend film were thus elucidated. The impedance-type humidity sensor that was made of a 7 wt% EuCl2/Eu2O3 blend film exhibited the highest sensitivity, best linearity, a small hysteresis, a fast response time, a small temperature coefficient and long-term stability. The complex impedance plots were used to elucidate the role of ions in the humidity-sensing behavior of the EuCl2/Eu2O3 blend film.
1. Introduction
Developing humidity sensors have attracted much interest because humidity is an important role in maintaining human health and an excellent quality of products [1,2,3]. Therefore, humidity sensors must have high sensitivity, a wide working humidity range, good linearity, fast response/recovery times, low hysteresis, good reversibility, stability and ease of fabrication for the mass production of humidity devices for using in food storage, industrial production and environmental monitoring [4,5]. Many materials, including ceramic, polyelectrolyte, organic polymer and composite materials, have been applied to humidity sensors [1,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14]. Ceramic materials, including metal oxides, perovskite- and spinel-type oxides and their hybrid systems, have some superiority in function because of their good chemical stability, high heat resistance, good water resistance under high humidity, cost-effectiveness and fast response to the changes of humidity [7,15], which means they can be applied to humidity detection. The humidity-sensing properties of ceramic humidity sensors is strongly influenced by the surface activity and the porous structure of the ceramic materials [15]. Therefore, many reports focused on researching the microstructure and morphology of ceramic materials and doping various dopants to tune the physico-chemical properties of ceramic materials [6,16].
The rare earth elements (i.e., lanthanides) could be considered as active cocatalysts and dopants for the improvement of new substances with appealing gas-sensing applications because of their 7f orbitals awarding special electronic properties [17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25]. Zhong et al. [17] fabricated Eu2O3-doped In2O3 using the sol-gel method for detecting H2S gas. Stănoiu et al. [18] fabricated ZnO–Eu2O3 binary oxide for sensing NO2 gas under humid condition. Wang et al. [19] fabricated Eu-doped SnO2 nanofibers for sensing acetone gas. Ortega et al. [20] fabricated Eu2O3-doped CeO2 for sensing CO gas. Er et al. [21] fabricated rare earth metals (Y, Ru and Cs)-doped ZnO thin films for sensing NH3 gas at room temperature. Jing et al. [22] fabricated a PANI/Eu3+ nanofiber for sensing NH3 gas. Costello et al. [23] fabricated Eu3+ ion-doped ZrO2 for sensing volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Mokoena et al. [24] fabricated Eu3+ ion-doped NiO for sensing toluene gas. Shen et al. [25] fabricated Ce-doped ZnO nanowires for sensing ethanol. Zhang et al. [26] fabricated a humidity sensor that was made of Eu-doped ZnO using the sol-gel method. Most literatures tend to explore the effects of rare earth ions and oxides doping on the enhancing gas-sensing properties. Recently, Wang et al. [27] fabricated a fast response humidity sensor that was made of CeO2 nanowires. However, no attempt has been used for fabricating an impedance-type humidity sensor that was made of pure EuCl2, Eu2O3 and EuCl2/Eu2O3 blend films. In this work, the impedance-type humidity sensors that were made of the EuCl2, Eu2O3 and EuCl2/Eu2O3 blend films were fabricated. The characterization of the EuCl2, Eu2O3 and EuCl2/Eu2O3 blend films were studied using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and X-ray diffraction (XRD). The humidity-sensing characteristics of the EuCl2, Eu2O3 and EuCl2/Eu2O3 blend films, including the response, linearity, hysteresis, response/recovery times, influence of ambient temperature, influence of applied frequency and stability, were studied. The complex impedance spectra were used to investigate the humidity-sensing mechanism of the EuCl2/Eu2O3 blend film.
2. Experimental Methods
2.1. Materials and Humidity Sensors Preparation
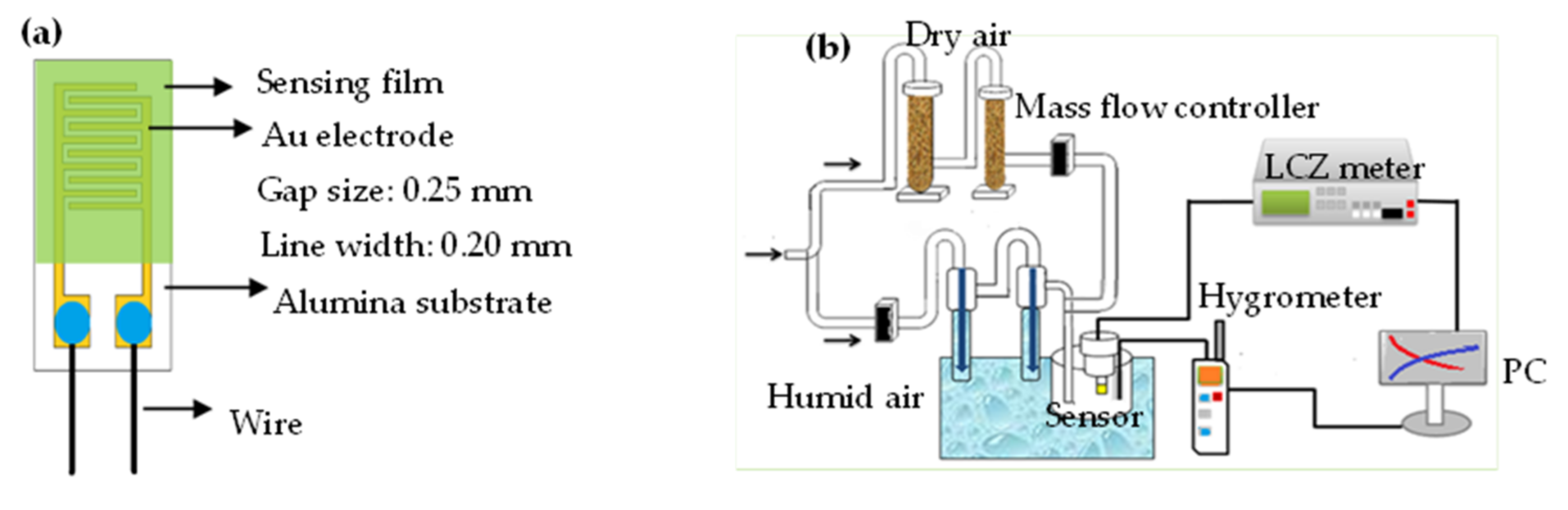
Europium dichloride (EuCl2, 99%, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) was used as received without further purification. The fabrication method of europium oxide (Eu2O3) was the thermal decomposition technique that was described in the literature [28]. The starting material was EuCl2 and the decomposition temperature was 600 °C for 5 h under the ambient atmosphere in furnace. The x wt% EuCl2 with 2, 5, 6, 7 and 8%wt/Eu2O3 blends were prepared using a wet-blending process. The Eu2O3 particles were impregnated with aqueous solutions of various x wt% EuCl2 solutions under ultrasonicating for 1 h to achieve a homogeneous dispersion of the Eu2O3 particles. Figure 1a shows the structure of an impedance-type humidity sensor. The interdigitated Au electrodes were made on an alumina substrate using a screen-printing method. The gap size and line width of the Au electrode were 0.25 and 0.2 mm, respectively. Then, 20 μL of the as-prepared uniformly EuCl2, Eu2O3 and EuCl2/Eu2O3 blend precursor solutions were drop-coated on an as-prepared alumina substrate using a micropipette, followed by drying at 110 °C.
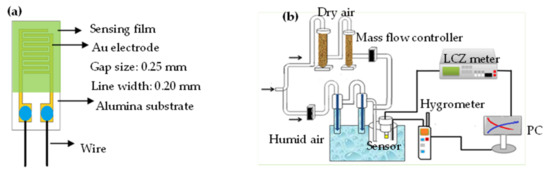
Figure 1.
(a) structure of humidity sensor and (b) the impedance measurement of humidity sensors and humidity atmosphere controller.
2.2. Characterization of EuCl2, Eu2O3 and EuCl2/Eu2O3 Bend Films
The composition and morphologies of the EuCl2, Eu2O3 and EuCl2/Eu2O3 blend film was investigated using an X-ray diffraction (XRD) using Cu Kα radiation (Shimadzu, Lab XRD-6000, Taipei, Taiwan) and a scanning electron microscope (SEM, Hitachi, TM400 Plus, Tokyo, Japan).
2.3. Measurement of Electrical and Humidity-Sensing Properties
Figure 1b shows the electrical and humidity-sensing measurement system. The generation of required humidity conditions for testing sensors was controlled using a divided humidity generator system in a temperature-controlled testing chamber. The principal apparatus for controlling the generation of humidity was a divided humidity generator, in which the proportion of dry and humid air under a total flow rate was 10 L/min to obtain the required humidity conditions for testing. The carrier gas was dry air. The relative humidity (RH) values were determined using the displayed readings of a standard humidity hygrometer (with an accuracy of ±0.1% RH). The electronic properties (impedance) of the as-prepared humidity sensors vs. RH were measured using an LCZ meter.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characteristics of EuCl2, Eu2O3 and EuCl2/Eu2O3 Blend Films
XRD Characterization and Morphology Observations
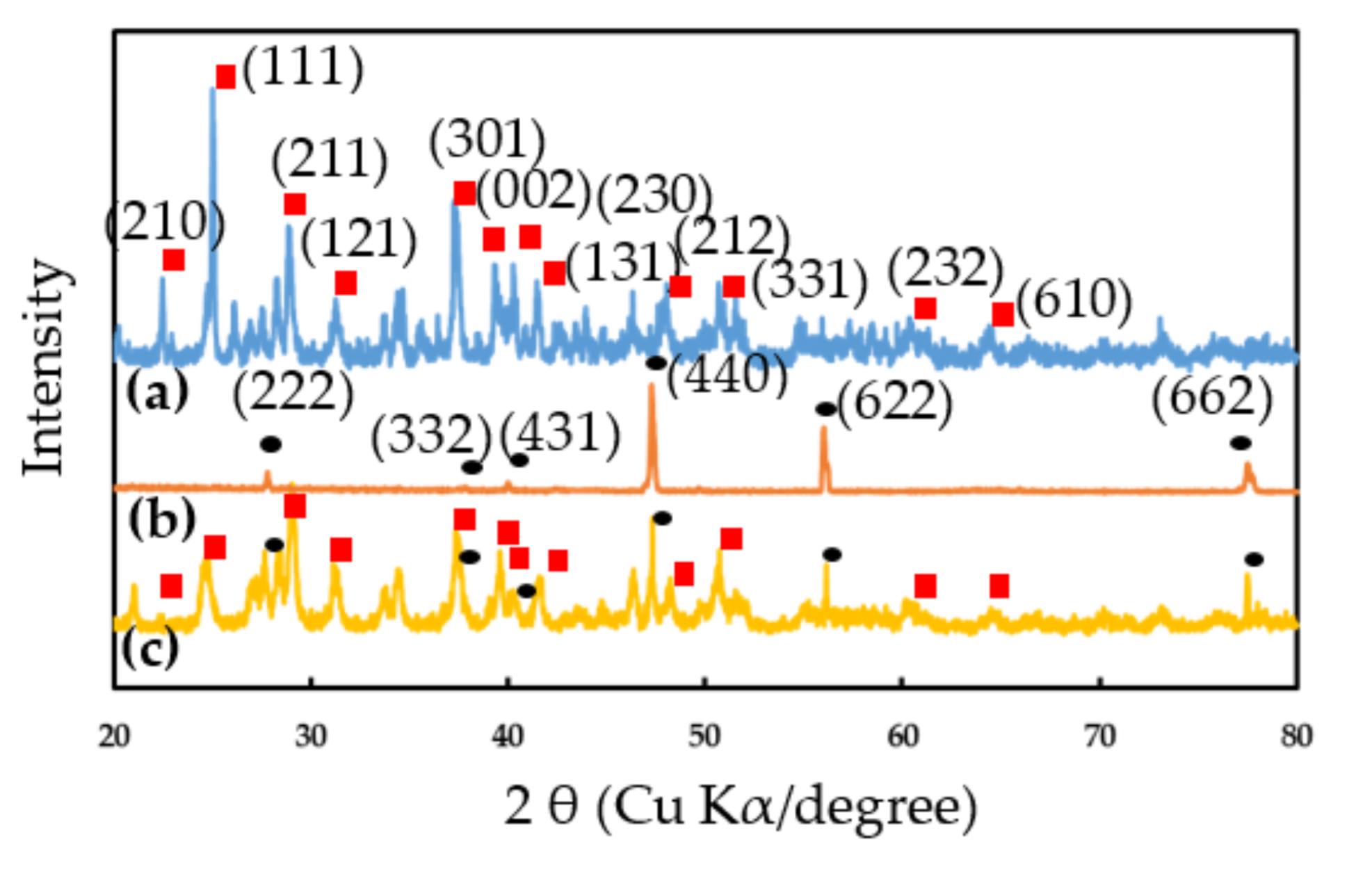
Figure 2a shows the XRD of EuCl2, the peaks appearing at 2θ = 23.1°, 26.1°, 29.4°, 32.1°, 35.6°, 38.1°, 39.6°, 41.2°, 47.8°, 50.9°, 60.9° and 64.9°corresponded to the (210), (111), (211), (121), (301), (002), (230), (131), (212), (331), (232) and (610) planes of the orthorhombic structure of EuCl2 [29]. Figure 2b shows the XRD spectrum of the Eu2O3 film that was made of the thermal decomposition of the EuCl2. The peaks appearing at 2θ = 28.5°, 38.0°, 42.4°, 47.3°, 56.0° and 77.0°corresponded to the (222), (332), (431), (440), (622) and (662) planes of the body-centered cubic (BCC) structure of Eu2O3, indicating the formation of Eu2O3 crystals [30,31]. Additionally, a very similar XRD spectrum has been reported for Eu2O3 prepared by using a solution method [31]. Figure 2c shows the XRD of the EuCl2/Eu2O3 blend; the peaks show it had mixed phases of EuCl2 and Eu2O3 and no noticeable peak shifts were observed.
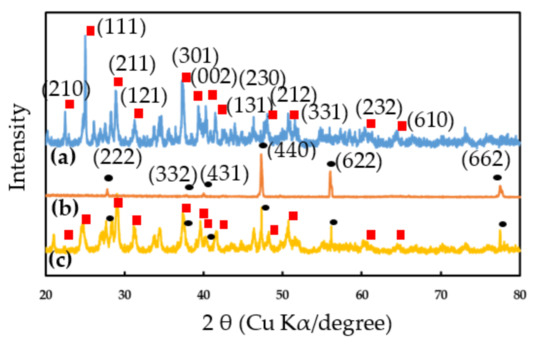
Figure 2.
XRD patterns of (a) EuCl2, (b) Eu2O3 and (c) EuCl2/Eu2O3 blend films.
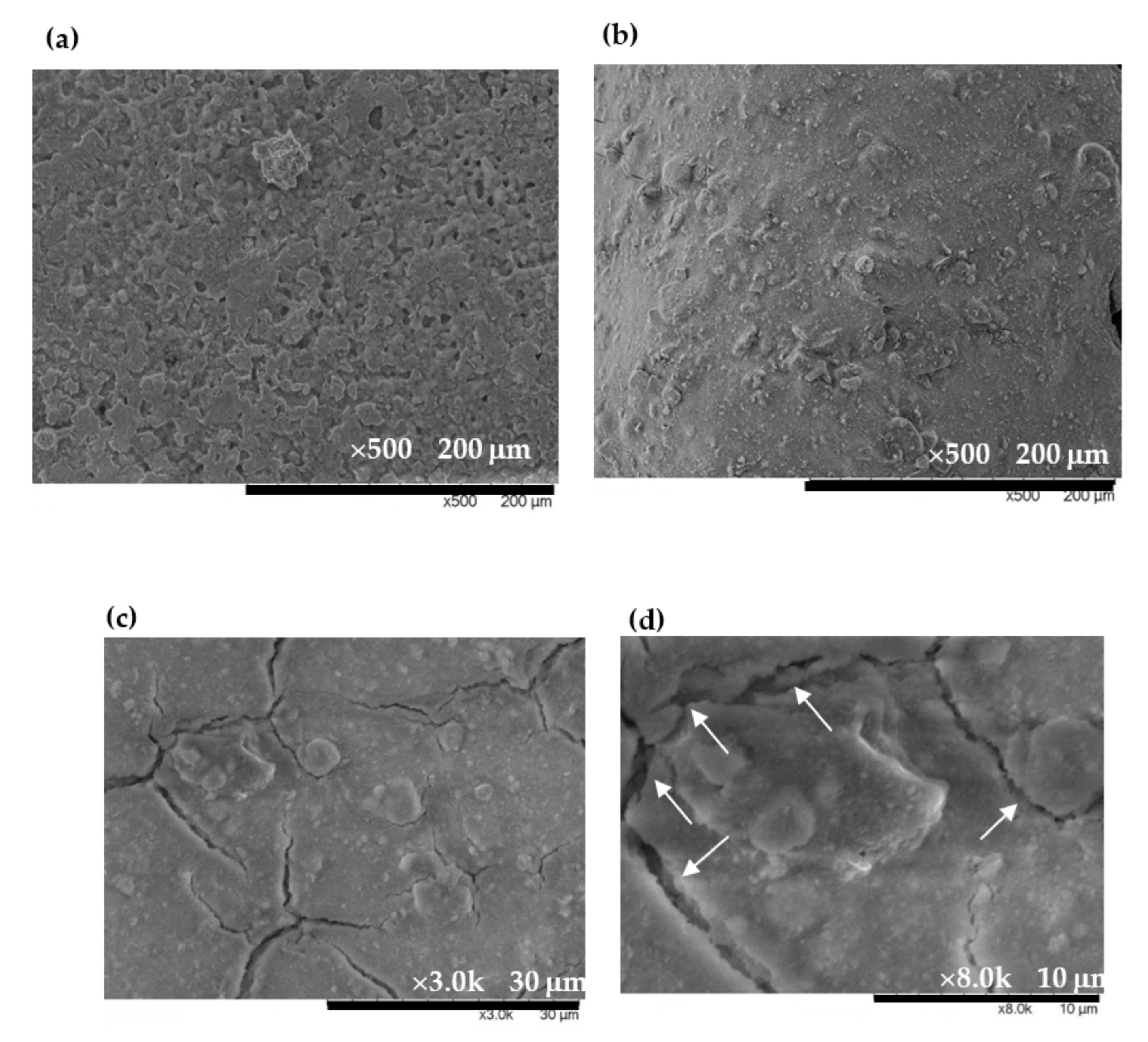
Figure 3 shows the morphology of the EuCl2, Eu2O3 and EuCl2/Eu2O3 blend films that were analyzed using scanning electron microscopy. Figure 3a shows the EuCl2 film that had various unfixed shapes of a massive lamination structure. Figure 3b shows the Eu2O3 film, the Eu2O3 particles obviously aggregated to form a tight surface morphology. Figure 3c shows the 7 wt% EuCl2/Eu2O3 blend film in a low-magnification image; this film had smoother surfaces than the Eu2O3 film did and many cracks in its surface. Figure 3d shows a high-magnification image of Figure 3c; the film exhibited porous structures marked by white arrows.
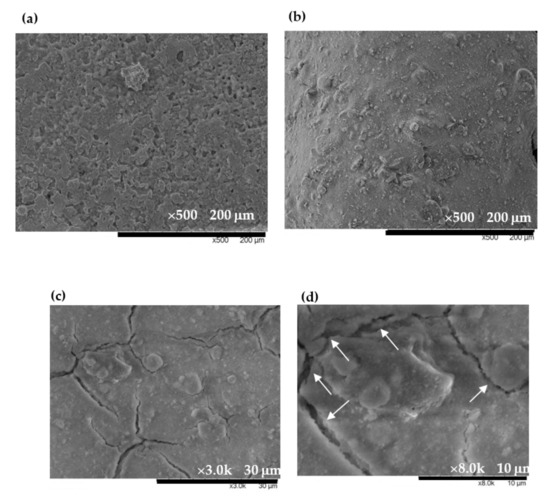
Figure 3.
SEM micrographs of (a) EuCl2 film, (b) Eu2O3 film, (c) 7 wt% EuCl2/Eu2O3 blend film and (d) high-magnification image of EuCl2/Eu2O3 blend film.
3.2. Electrical and Humidity-Sensing Properties of Humidity Sensors Based on EuCl2, Eu2O3 and EuCl2/Eu2O3 Blend Films
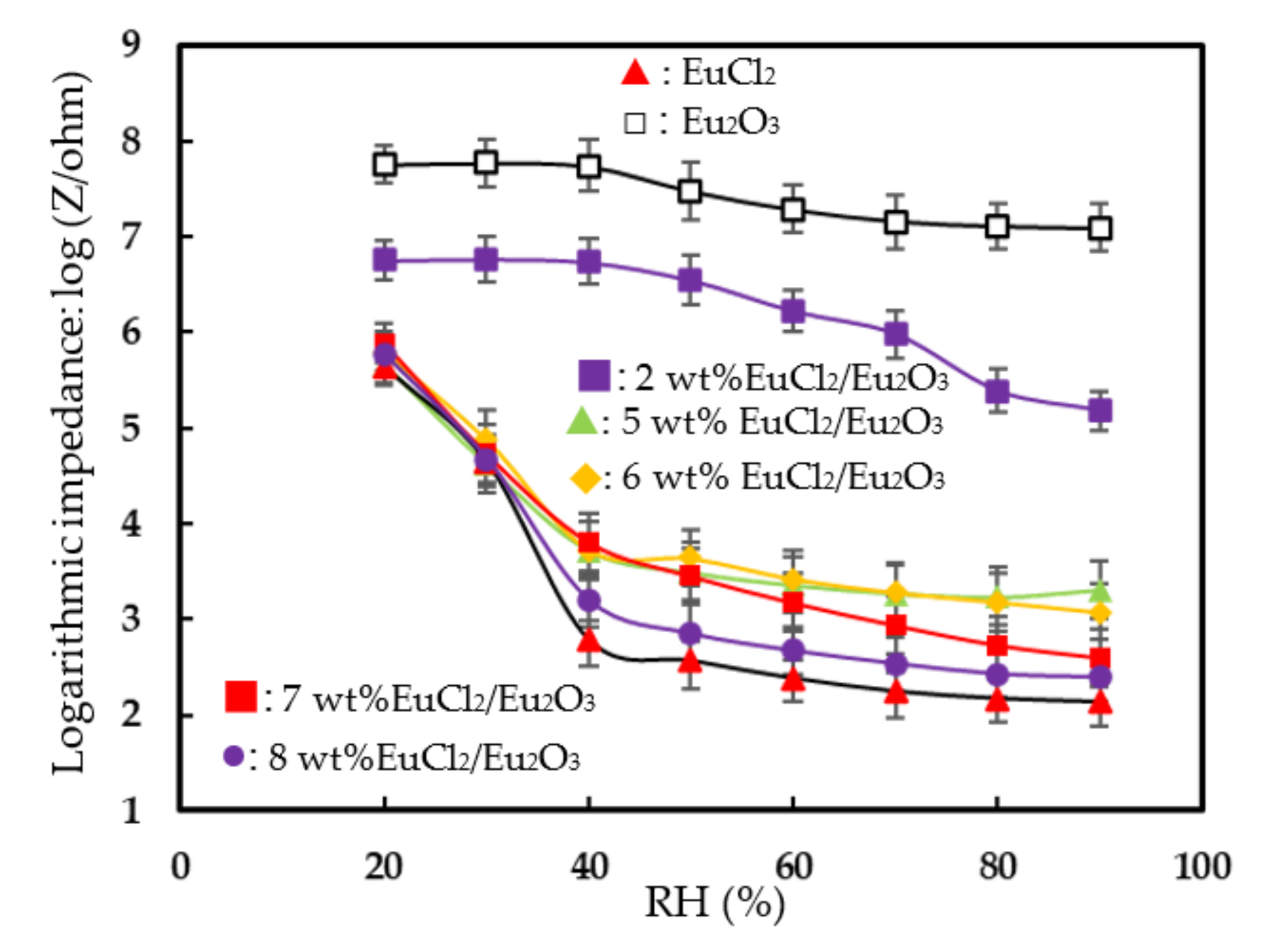
Figure 4 plots the log-impedance of the EuCl2, Eu2O3 and EuCl2/Eu2O3 blend films as a function of the relative humidity. Table 1 presents the results of the sensitivity and linearity of humidity sensing. The sensitivity and linearity were calculated as the slope and R-squared value (R2) of the linear fitting curve in the humidity range from 20 to 90% RH, respectively. The EuCl2 film exhibited a steep decrease in impedance as the RH changed from 20 to 40% RH, and very slowly decreased in the range of 40–90% RH. This result was related to the fact that EuCl2 is very moisture sensitive [28]. The Eu2O3 film had one less order changed in impedance, with the humidity ranging from 40 to 90% RH and almost no impedance changed in the range of 20–40% RH because of its weak water adsorption and low-conduction properties. For obtaining the higher sensitivity and better linearity of the Eu2O3 film in a wider humidity range, a EuCl2/Eu2O3 blend film was fabricated, and the optimum ratio of EuCl2 to Eu2O3 was studied. The impedance of all the EuCl2/Eu2O3 blend films continuously decreased along with the humidity increase in the range of 20–40% RH, suggesting that the strong water adsorption capacity of EuCl2 improved the sensitivity of the EuCl2/Eu2O3 blend film. The sensitivity (slope) of the 7 wt% EuCl2/Eu2O3 blend film was greater than those of the 2, 5, 6 and 8 wt% EuCl2/Eu2O3 blend films in the studied range (20 to 90% RH). This result was related to the fact that the blended amounts of EuCl2 increased, which increased the water adsorption capacity for physisorption and chemisorption layers on the EuCl2/Eu2O3 blend film with the humidity ranging from 40 to 90% RH. Additionally, the 7 wt% EuCl2/Eu2O3 blend film had better linearity than that of the 8 wt% EuCl2/Eu2O3 blend film because the impedance of the 8 wt% EuCl2/Eu2O3 blend film slightly changed in the range of 40–90% RH. The 7 wt% EuCl2/Eu2O3 blend film exhibited the highest response and best linearity; therefore, it was further tested to investigate its humidity-sensing properties and mechanism.
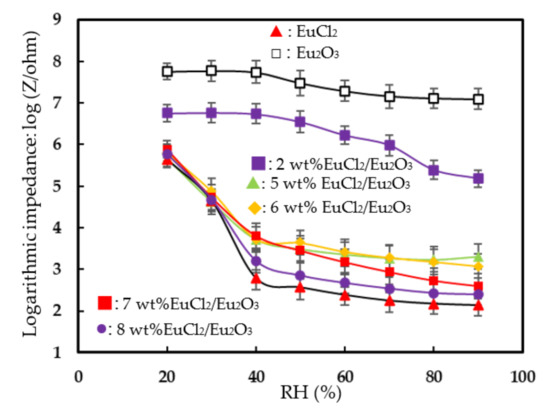
Figure 4.
Log-impedance vs. relative humidity for humidity sensors based on EuCl2, Eu2O3 and EuCl2/Eu2O3 blend films. Measurements were made at 25 °C, 1 V AC voltage and 1 kHz frequency.

Table 1.
Sensitivity and linearity of impedance-type humidity sensors based on EuCl2, Eu2O3 and EuCl2/Eu2O3 blend films.
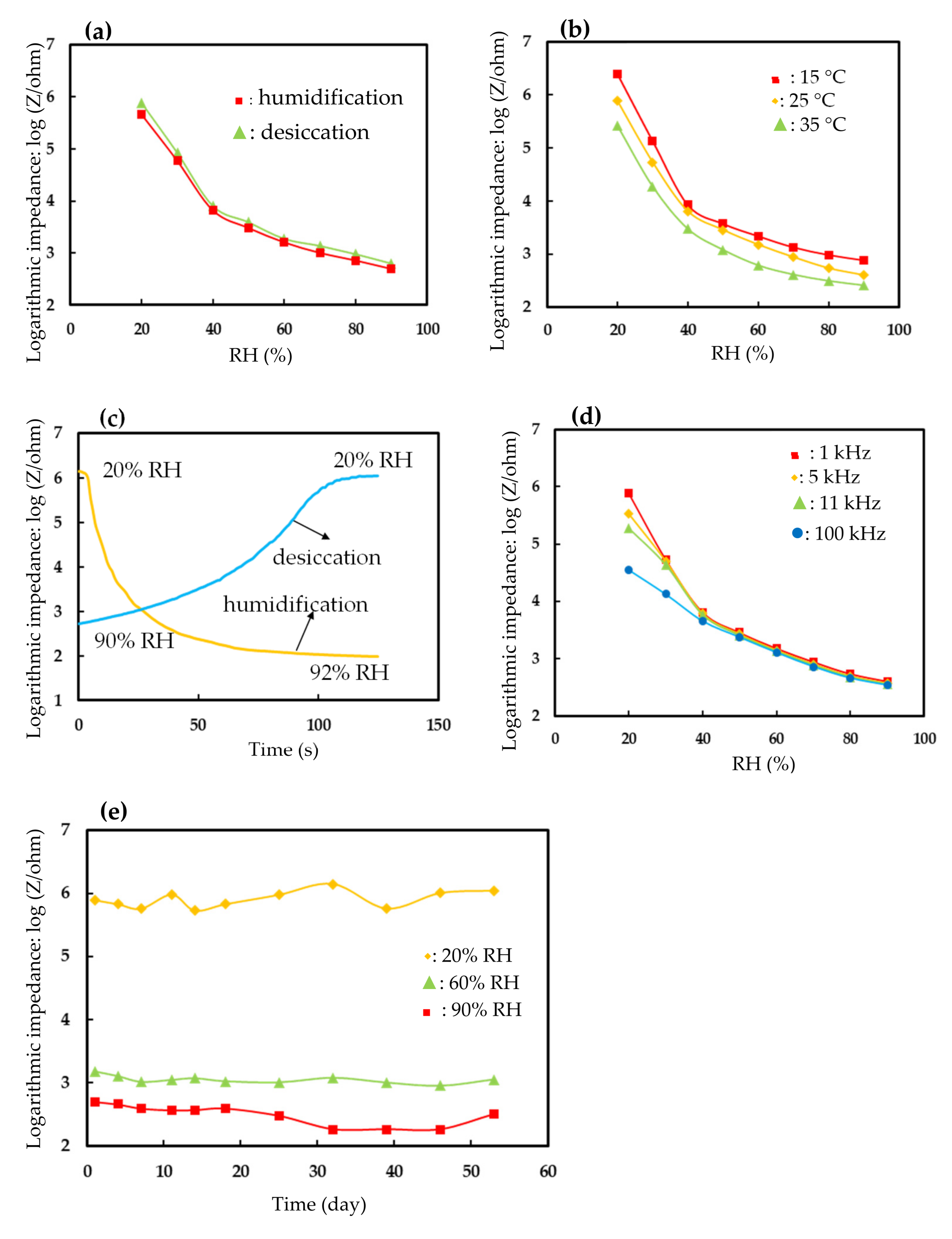
Figure 5a shows the hysteresis of the 7 wt% EuCl2/Eu2O3 blend film. The average hysteresis was below 1.1% RH as the humidity ranged from 20 to 90% RH in a desiccation-to-humidification cycle. The reversibility was investigated with the hysteresis of testing a desiccation-to-humidification cycle at 60% RH three times. The reversibility was 1.07% RH. Figure 5b shows the influence of ambient temperature on the impedance of the 7 wt% EuCl2/Eu2O3 blend film vs. RH. The average temperature coefficient was about −0.10% RH/°C. Figure 5c shows the response/recovery times of the 7 wt% EuCl2/Eu2O3 blend film. The response/recovery times were 40/80 s. The response/recovery times of the EuCl2 film were 30/140 s. The 7 wt% EuCl2/Eu2O3 blend film had faster response/recovery times than that of the EuCl2 film. This result was related to the strong water adsorption capacity of EuCl2. Figure 5d shows the influence of the applied frequency on the impedance of the 7 wt% EuCl2/Eu2O3 blend film vs. RH. The applied frequency affected the impedance at low humidity more significantly (<40% RH) than that at high humidity. Figure 5e plots the long-term stability of the 7 wt% EuCl2/Eu2O3 blend film. At testing points of 20, 60 and 90% RH, no obvious deviations in impedance were found within 53 days. The repeatability, on the same day, was performed by repeating testing at 60% RH three times and analyzed with relative standard deviation (RSD). The repeatability (RSD) was 6.3%. The humidity-sensing properties of this study were compared with those humidity sensors that were made of ceramic materials in the literature [31,32,33], as shown in Table 2. The present humidity sensor that was made of the 7 wt% EuCl2/Eu2O3 blend film using a simple thermal decomposition technique had a wide humidity-sensing range, a comparable sensitivity and low hysteresis compared to the humidity sensors that were made of Li+ and K+ ions-doped ZnO, SnO2 and TiO2.
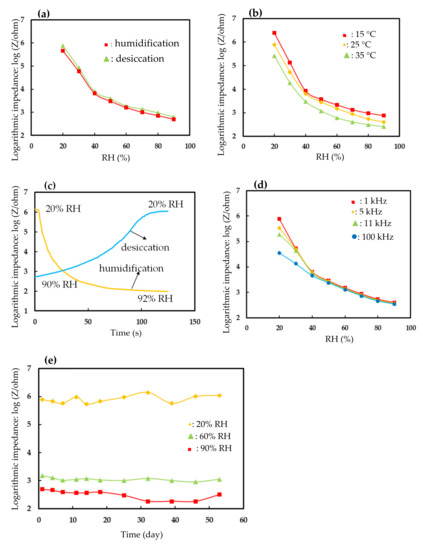
Figure 5.
Humidity-sensing properties of the humidity sensor based on 7 wt% EuCl2/Eu2O3 blend film. (a) Hysteresis, (b) effect of ambient temperature, (c) response/recovery times, (d) effect of applied frequency, (e) long-term stability.

Table 2.
Humidity sensor performance of this work compared with the humidity sensors based on ceramic materials in the literatures.
3.3. Humidity-Sensing Mechanism
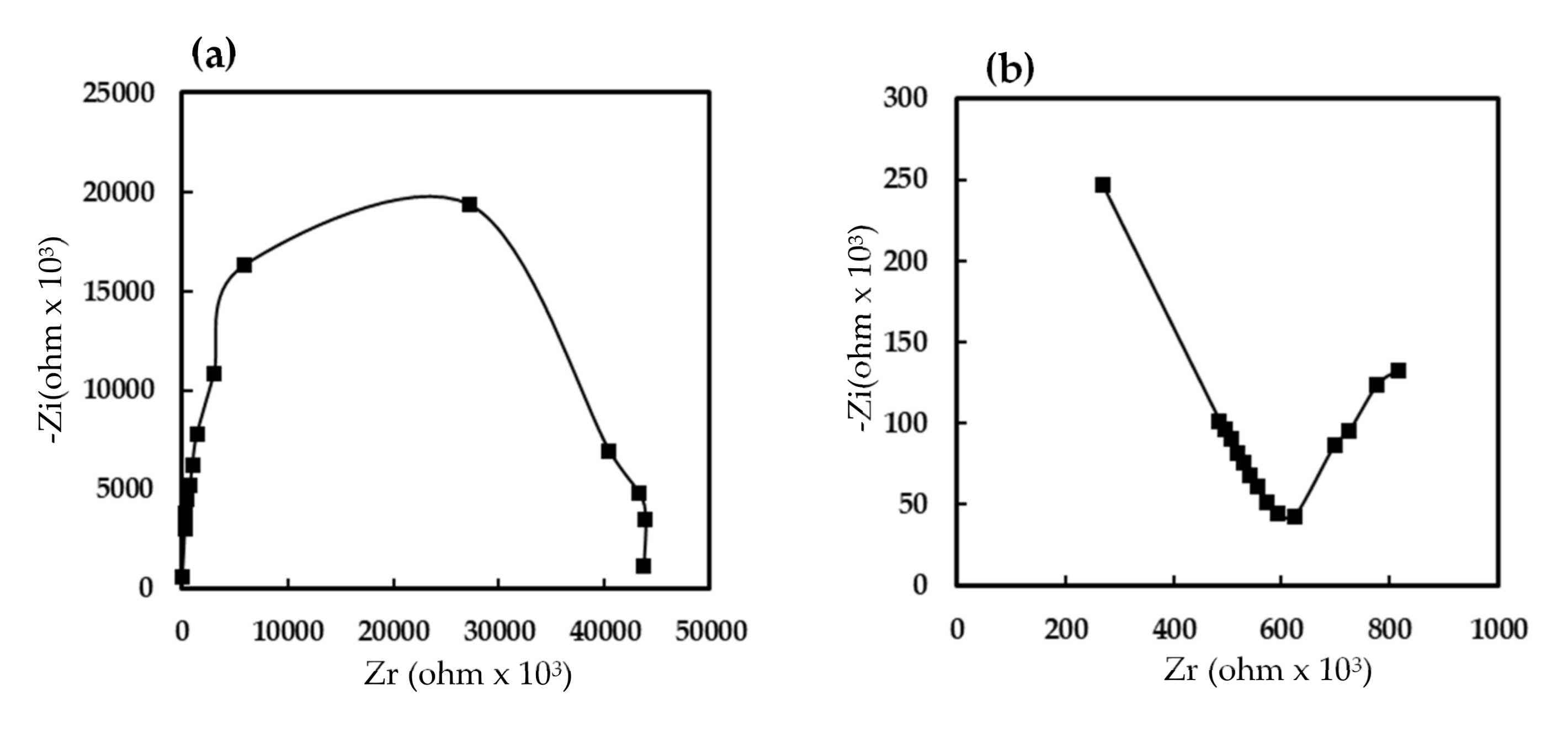
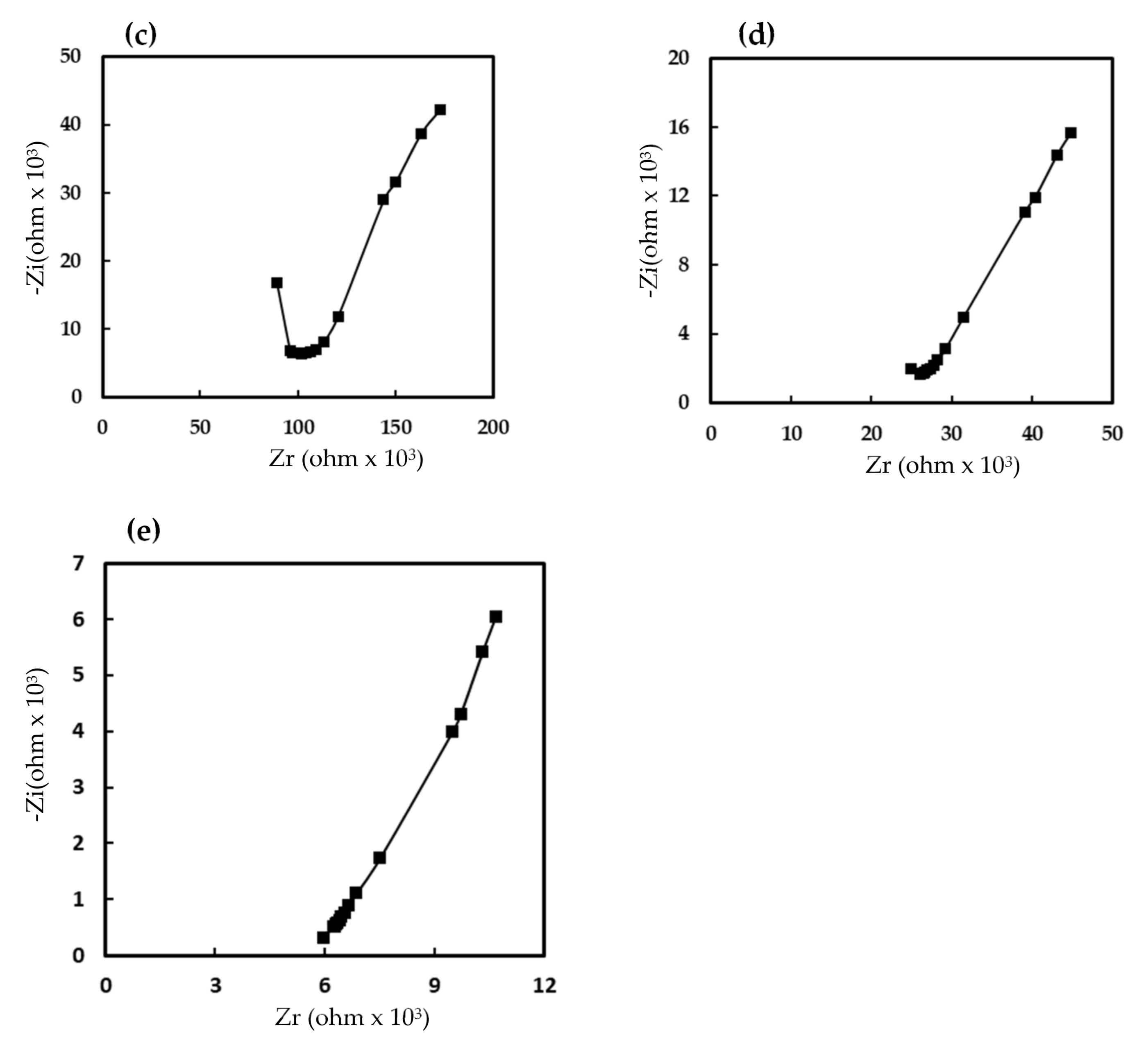
The complex impedance spectrum was useful for studying the conduction mechanisms of humidity sensors. Figure 6 shows the measured impedance spectra of the humidity sensor that was made of the 7 wt% EuCl2/Eu2O3 blend film. At low humidity (20% RH), a semicircular plot of the film impedance was obtained. The semicircle plot of the impedance has been explained by many authors [35,36,37], resulting mainly from the intrinsic impedance of the 7 wt% EuCl2/Eu2O3 blend film, and the film could be modeled as an equivalent parallel circuit that incorporates a resistor and a capacitor. When increasing the RH (40, 50 and 60%), the semicircle radius gradually reduced and a straight line appeared at low frequencies. The straight line represented Warburg impedance, which was caused by the diffusion of H3O+ ions across the interface between the electrode and the sensing film [35]. Finally, when increasing the RH to 80%, the semicircle disappeared and only a straight line was observed. These results were related to the fact that, upon the adsorption of water, the adsorbed water molecules on the 7 wt% EuCl2/Eu2O3 blend film formed a thin liquid layer, and resultingly, gradually dissociated to form H3O+ ions. At high RH, the sorbed water acted as a plasticizer, increasing the mobility of the solvated H3O+ ions diffusing across the interface between the electrode and the liquid-like 7 wt% EuCl2/Eu2O3 blend film. According to the obtained complex impedance plots, the humidity-sensing by the 7 wt% EuCl2/Eu2O3 blend film depended on the H3O+ ion transport mechanism [37,38].
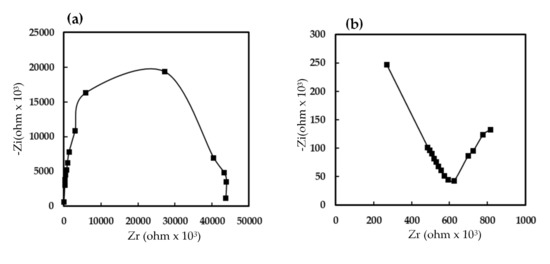
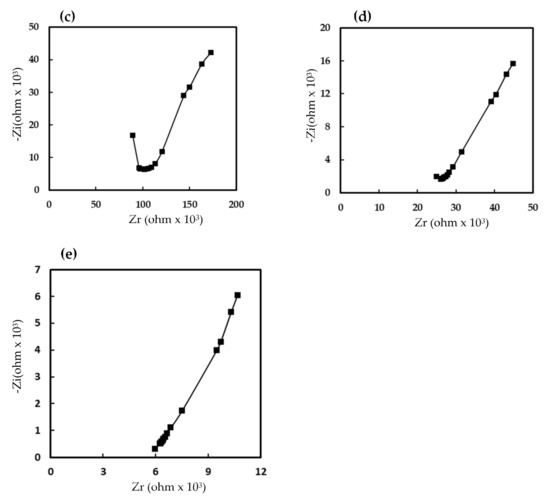
Figure 6.
Complex impedance plots of humidity sensor based on 7 wt% EuCl2/Eu2O3 blend film at (a) 20% RH, (b) 40% RH, (c) 50% RH, (d) 60% RH and (e) 80% RH. Measurements were made at frequency ranging from 50 to 100,000 Hz, RH ranging from 20 to 80% RH, at 1 V AC voltage and at 25 °C.
4. Conclusions
The humidity sensor based on the EuCl2 film was well suited to low humidity (20–40% RH) because of its strong water adsorption property. The humidity sensor based on the Eu2O3 film exhibited a small humidity-working range (40~90% RH) because of its weak water adsorption and low-conduction properties. The humidity sensor based on the EuCl2/Eu2O3 blend film exhibited high sensitivity and good linearity over the entire RH range (20 to 90% RH) because of the added EuCl2 to increase the water adsorption and conductance of the EuCl2/Eu2O3 blend film. The impedance-type humidity sensor that was made of the 7 wt% EuCl2/Eu2O3 blend film exhibited high sensitivity (slope = 0.0427) and the best linearity (R2 = 0.8601), small hysteresis (<1.1% RH), a small ambient temperature coefficient (−0.10% RH/ °C), fast response/recovery times (40/80 s) and good long-term stability (at least 53 days). The complex impedance plots of the EuCl2/Eu2O3 blend film changed from semicircular to linear as the RH increased. These results reflect the H3O+ ions that dominated the conductance of the EuCl2/Eu2O3 blend film.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.-G.S.; methodology, P.-G.S.; investigation, P.-G.S. and N.-H.C.; writing—original draft preparation, P.-G.S.; writing—review and editing, P.-G.S.; supervision, P.-G.S.; project administration, P.-G.S.; funding acquisition, P.-G.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was founded by Ministry of Science and Technology of Taiwan, grant no. MOST 110-2113-M-034-002.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sakai, Y.; Sadaoka, Y.; Matsuguchi, M. Humidity sensors based on polymer thin films. Sens. Actuators B 1996, 35–36, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Kun, Y.; Shi, Y.; Shang, C. Research of radiosonde humidity sensor with temperature compensation function and experimental verification. Sens. Actuators A 2014, 218, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.W.; Choi, B.I.; Kim, J.C.; Woo, S.B.; Kim, Y.G.; Yoo, J.; Seo, Y.S. Reduction and compensation of humidity measurement errors at cold temperatures using dual QCM humidity sensors based on graphene oxides. Sens. Actuators B 2019, 284, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahani, H.; Wagiran, R.; Hamidon, M.N. Humidity sensors principle, mechanism, and fabrication technologies: A comprehensive review. Sensors 2014, 14, 7881–7939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Najeeb, M.A.; Ahmad, Z.; Shakoor, R.A. Organic thin-film capacitive and resistive humidity sensors: A focus review. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 5, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blank, T.A.; Eksperiandova, L.P.; Belikov, K.N. Recent trends of ceramic humidity sensors development: A review. Sens. Actuators B 2016, 228, 416–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Tong, J.; Xia, B.; Xue, Q. Ultrahigh performance humidity sensor based on layer-by-layer self-assembly of graphene oxide/polyelectrolyte nanocomposite film. Sens. Actuators B 2014, 203, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, Y.; Matsuguchi, M.; Hurukawa, T. Humidity sensor using crosslinked poly(chloromethyl styrene). Sens. Actuators B 2000, 66, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Sun, Y.; Li, P.; Zhang, Y. Facile fabrication of MoS2-modified SnO2 hybrid nanocomposite for ultrasensitive humidity sensing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 14142–14149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taccola, S.; Greco, F.; Zucca, A.; Innocenti, C.; de Julián Fernández, C.; Campo, G.; Sangregorio, C.; Mazzolai, B.; Mattoli, V. Characterization of free-standing PEDOT: PSS/iron oxide nanoparticle composite thin films and application as conformable humidity sensors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 6324–6332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Tong, J.; Xia, B. Humidity-sensing properties of chemically reduced graphene oxide/polymer nanocomposite film sensor based on layer-by-layer nano self-assembly. Sens. Actuators B 2014, 197, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, D.; Boschetto, F.; Marin, E.; Palmero, P.; Pezzotti, G.; Tulliani, J.M. Rice husk ash as a new humidity sensing material and its aging behavior. Sens. Actuators B 2021, 328, 129049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Yao, Y.; Huang, X.H.; Liu, D.; Mao, K.l. Simulation analysis and experimental verification for sensitivity of IDE-QCM humidity sensors. Sens. Actuators B 2021, 341, 129992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Huang, X.H.; Yao, Y.; Luo, K.B.; Pan, H.Z.; Wang, Q. Ringed electrode configuration enhances the sensitivity of QCM humidity sensor based on lignin through fringing field effect. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 3109446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faia, P.M.; Furtado, C.S.; Ferreira, A.J. Humidity sensing properties of a thick-film titania prepared by a slow spinning process. Sens. Actuators B 2004, 101, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bârsan, N.; Simion, C.; Heine, T.; Pokhrel, S.; Weimar, U. Modeling of sensing and transduction for p-type semiconducting metal oxide based gas sensors. J. Electroceramics 2010, 25, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.; Zhong, H.; Wang, X.; Jiang, K. Sensing properties of rare earth oxide doped In2O3 by a sol–gel method. Sens. Actuators B 2006, 115, 434–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stănoiu, A.; Simiona, C.E.; Somăcescu, S. NO2 sensing mechanism of ZnO–Eu2O3 binary oxide under humid air conditions. Sens. Actuators B 2013, 186, 687–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Zhao, R.; Sun, B.; Nie, G.; Ji, H.; Lei, J.; Wang, C. Highly sensitive acetone sensor based on Eu-doped SnO2 electrospun nanofibers. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 15881–15888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, P.P.; Rocha, L.S.R.; Cortés, J.A.; Ramirez, M.A.; Buono, C.; Ponce, M.A.; Simões, A.Z. Towards carbon monoxide sensors based on europium doped cerium dioxide. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 464, 692–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarf, F.; Er, I.K.; Yakar, E.; Acar, S. The role of rare-earth metal (Y, Ru and Cs)-doped ZnO thin films in NH3 gas sensing performances at room temperature. J. Mater Sci. Mater Electron. 2020, 31, 10084–10095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, G.; She, C.; Liu, A.; Cheng, J.; Li, H.; Liu, S.; Jing, C.; Cheng, Y.; Chu, J. High performance tube sensor based on PANI/Eu3+ nanofiber for low-volume NH3 detection. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1093, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fois, M.; Cox, T.; Ratcliffe, N.; de Lacy Costello, B. Rare earth doped metal oxide sensor for the multimodal detection of volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Sens. Actuators B 2021, 330, 129264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokoena, T.P.; Swart, H.C.; Hillie, K.T.; Motaung, D.E. Engineering of rare-earth Eu3+ ions doping on p-type NiO for selective detection of toluene gas sensing and luminescence properties. Sens. Actuators B 2021, 347, 130530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Shen, Y.; Li, A.; Chen, Y.; Gao, S.; Liu, W.; Wei, D. Effects of rare earth elements doping on gas sensing properties of ZnO nanowires. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 24218–24226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Zhang, H.; Lin, C.; Bian, M. The enhancement of humidity sensing performance based on Eu-doped ZnO. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2019, 19, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.Q.; Wang, C.; Yu, H.C.; Wang, Y.G.; Wang, T.H. Fast humidity sensors based on CeO2 nanowires. Nanotechnology 2007, 18, 145503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyle, S.J.; Westall, W.A. A study of the thermal decomposition of hydrated europium (III) chloride and europium (III) bromide. Thermochim. Acta 1983, 68, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Bian, Z.; Hong, C.; Huang, C. A mild liquid reduction route toward uniform blue-emitting EuCl2 nanoprisms and nanorods. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 50, 6862–6864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Z.; Zhang, G.; Zhou, H.; Sun, P.; Li, B.; Ding, D.; Xhen, T. Macroporous lanthanide-organic coordination polymer foams and their corresponding lanthanide oxides. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 984–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, W.; Qian, Y. Preparation and characterization of Eu2O3 nanometer thin films by pulse ultrasonic spray pyrolysis method. Mater. Res. Bull. 2000, 35, 2057–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buvailo, A.I.; Xing, Y.; Hines, J.; Dollahon, N.; Borguet, E. TiO2/LiCl-based nanostructured thin film for humidity sensor applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 528–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Li, Z.; Liu, L.; Zhang, H.; Zheng, W.; Wang, Y.; Huang, H.; Wang, Z.; Wang, C. Humidity sensor based on LiCl-doped ZnO electrospun nanofibers. Sens. Actuators B 2009, 141, 404–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Qi, Q.; Zhang, T.; Wang, C. A humidity sensor based on KCl-doped SnO2 nanofibers. Sens. Actuators B 2009, 138, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.D.; Sun, S.L.; Wang, H.; Segre, C.U.; Stetter, J.R. Humidity sensing properties of Nafion and sol−gel derived SiO2/Nafion composite thin films, Sens. Actuators B 1997, 40, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lin, Q.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, R.; Xu, B. Humidity sensor based on composite material of nano-BaTiO3 and polymer RMX. Sens. Actuators B 2002, 81, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xu, B.K.; Ruan, S.P.; Wang, S.P. Preparation and electrical properties of humidity sensing films of BaTiO3/polystrene sulfonic sodium. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2003, 78, 746–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casalbore-Miceli, G.; Yang, M.J.; Camaioni, N.; Mari, C.M.; Li, Y.; Sun, H.; Ling, M. Investigations on the ion transport mechanism in conduction polymer films. Solid State Ionics 2000, 131, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).