Optical Fiber Refractometer Based Metal Ion Sensors
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. The Optical Fiber Sensor
1.2. Environmental Monitoring for Heavy Metal Ion Contamination
1.3. Choosing Optical Fiber Sensors for Metal Ion Detection
1.4. Scope of Paper
2. Principles of Surface Coated Optical Fiber Refractometers
3. Common Optical Fiber Refractometers
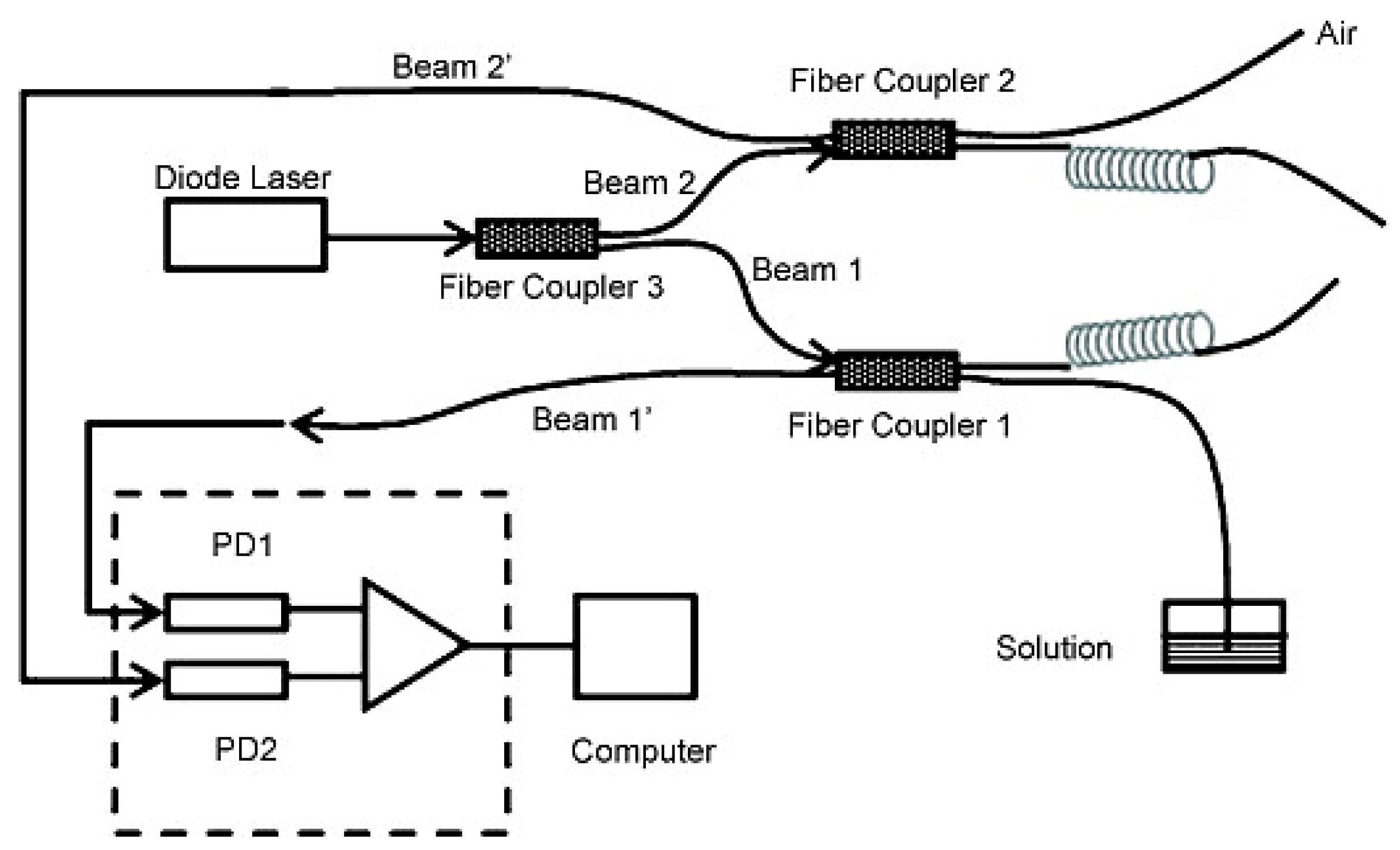
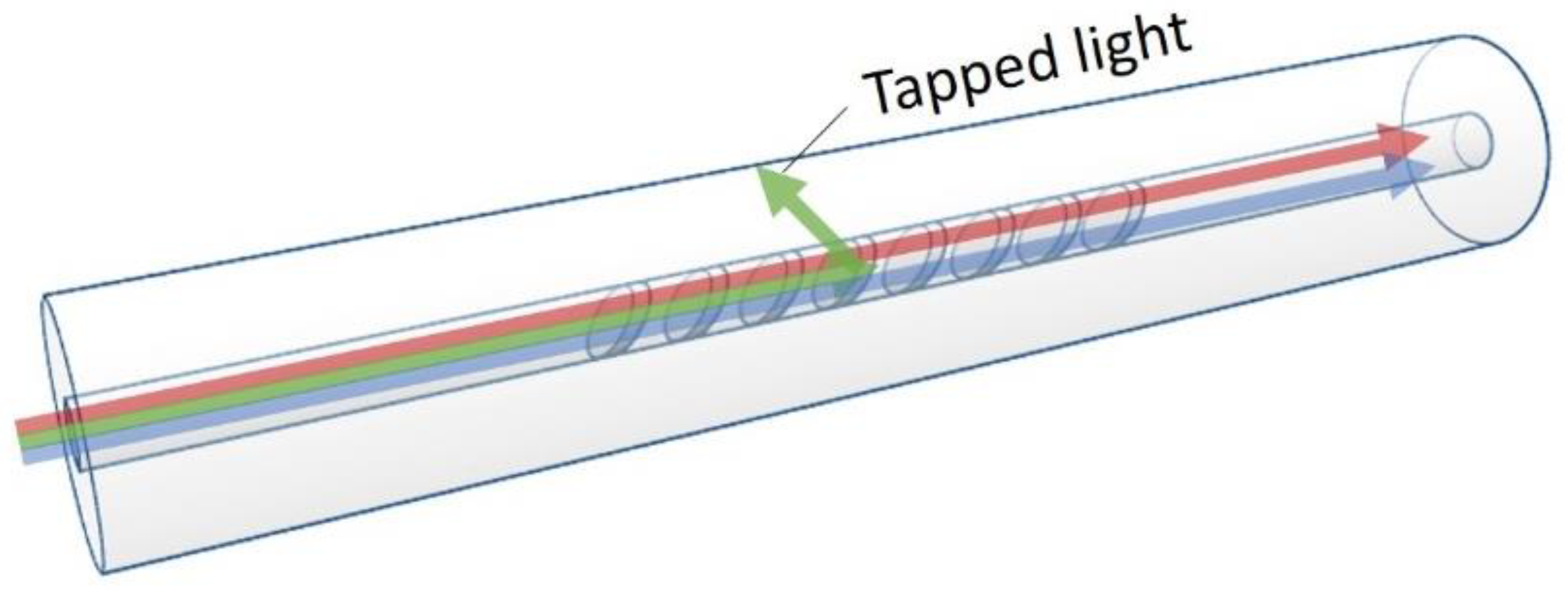
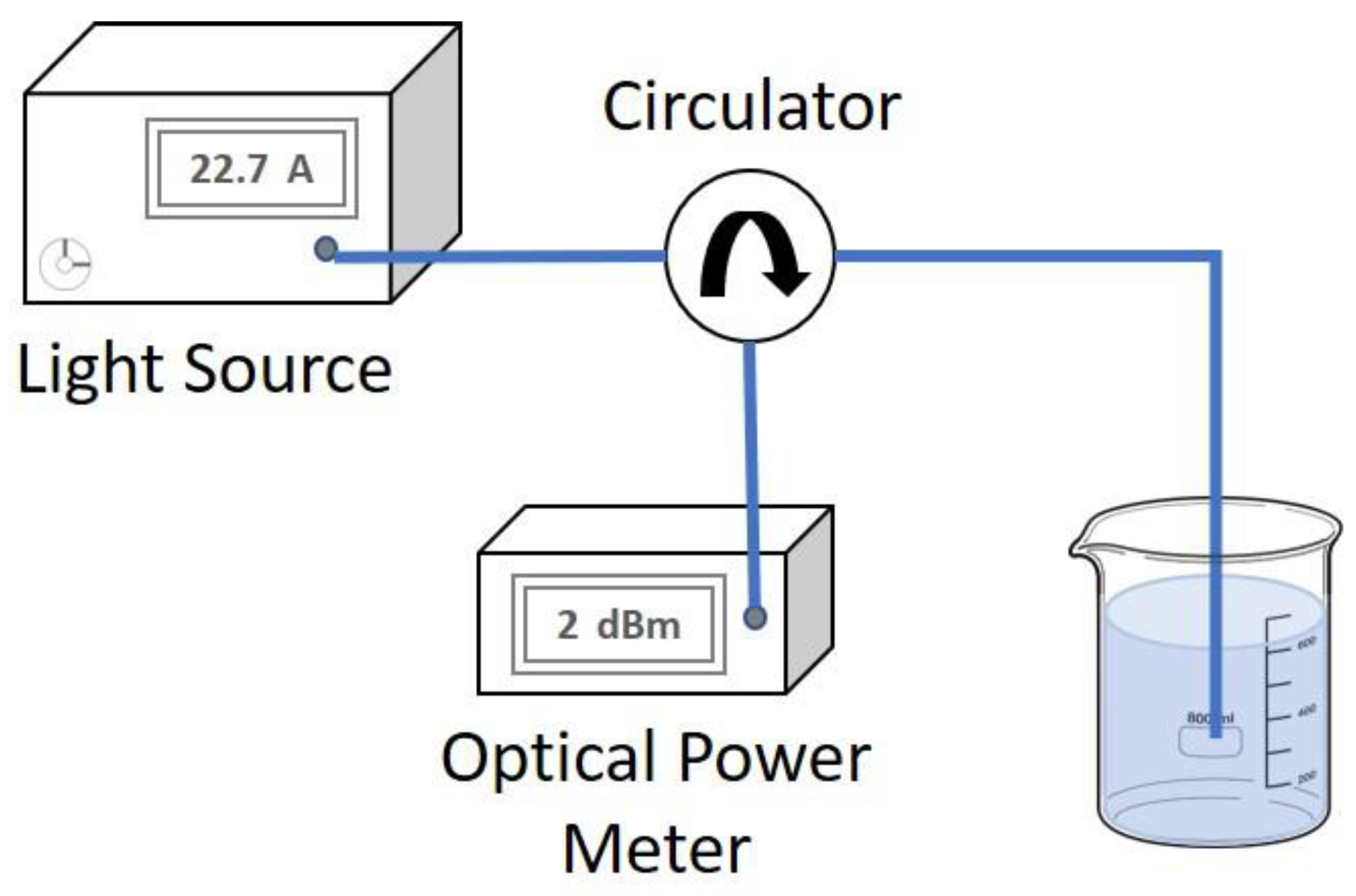
3.1. Fiber End Ratiometer
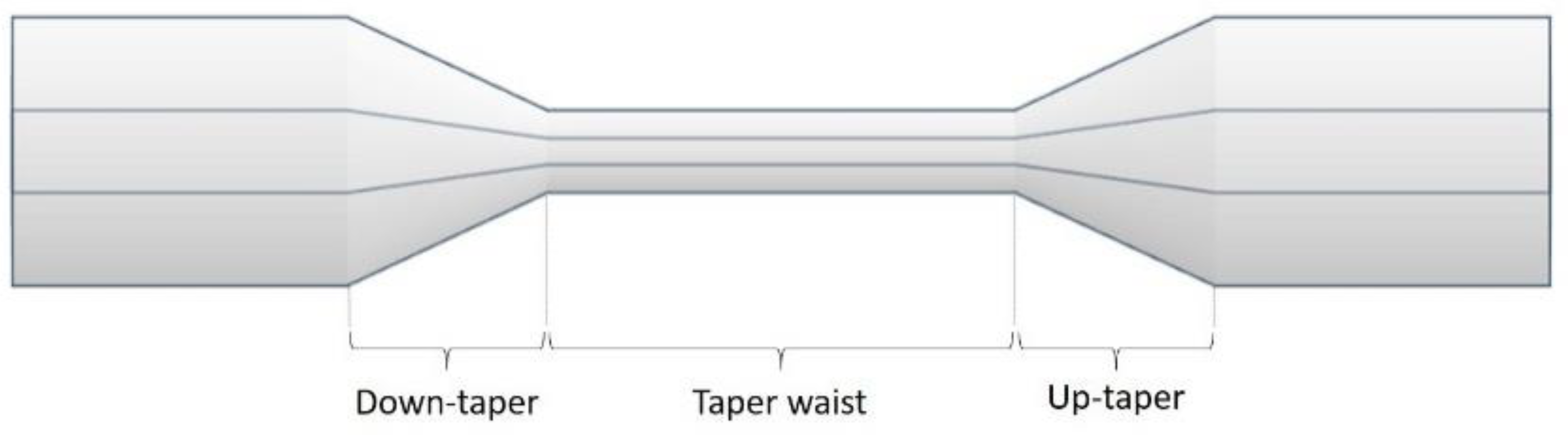
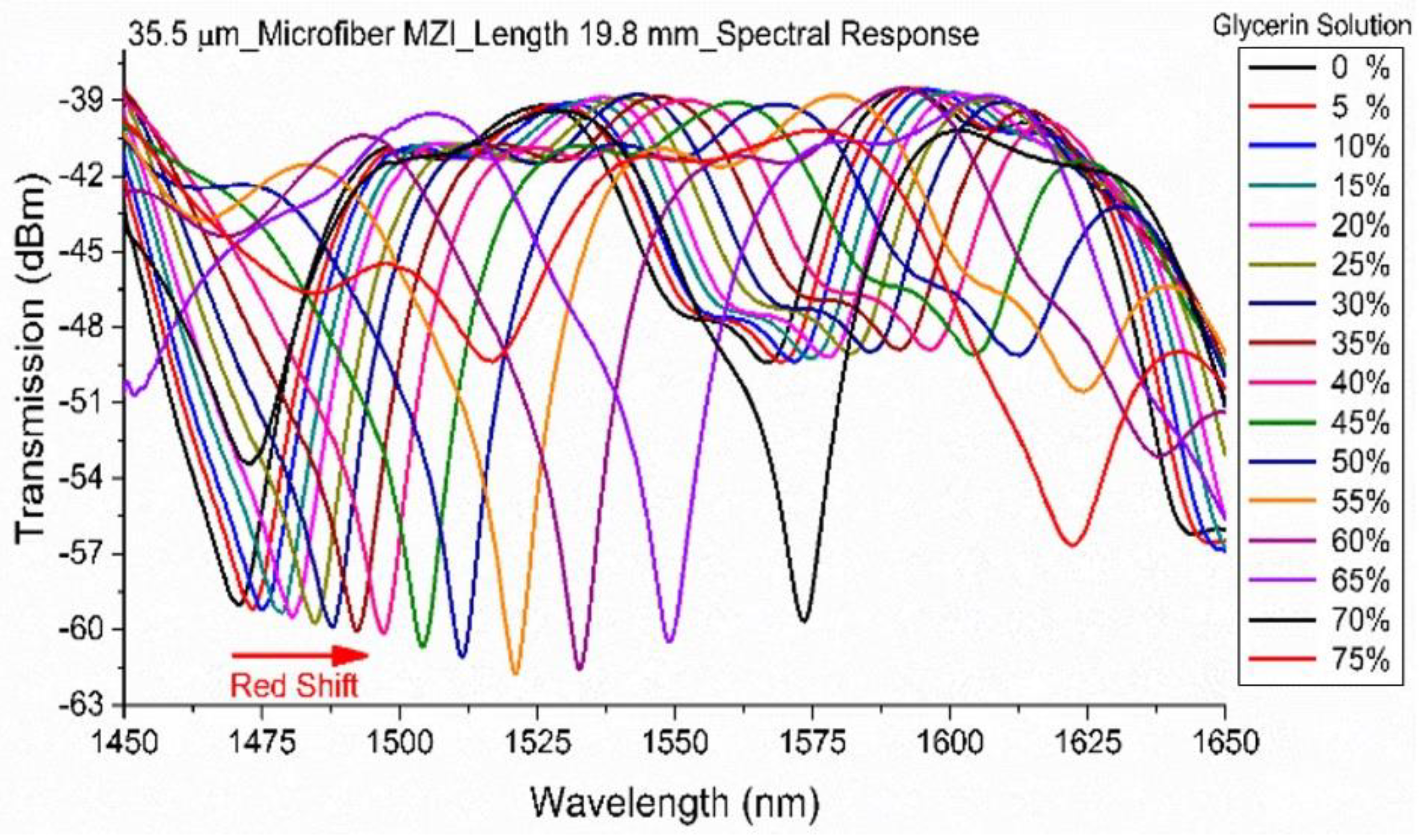
3.2. Tapered Microfiber
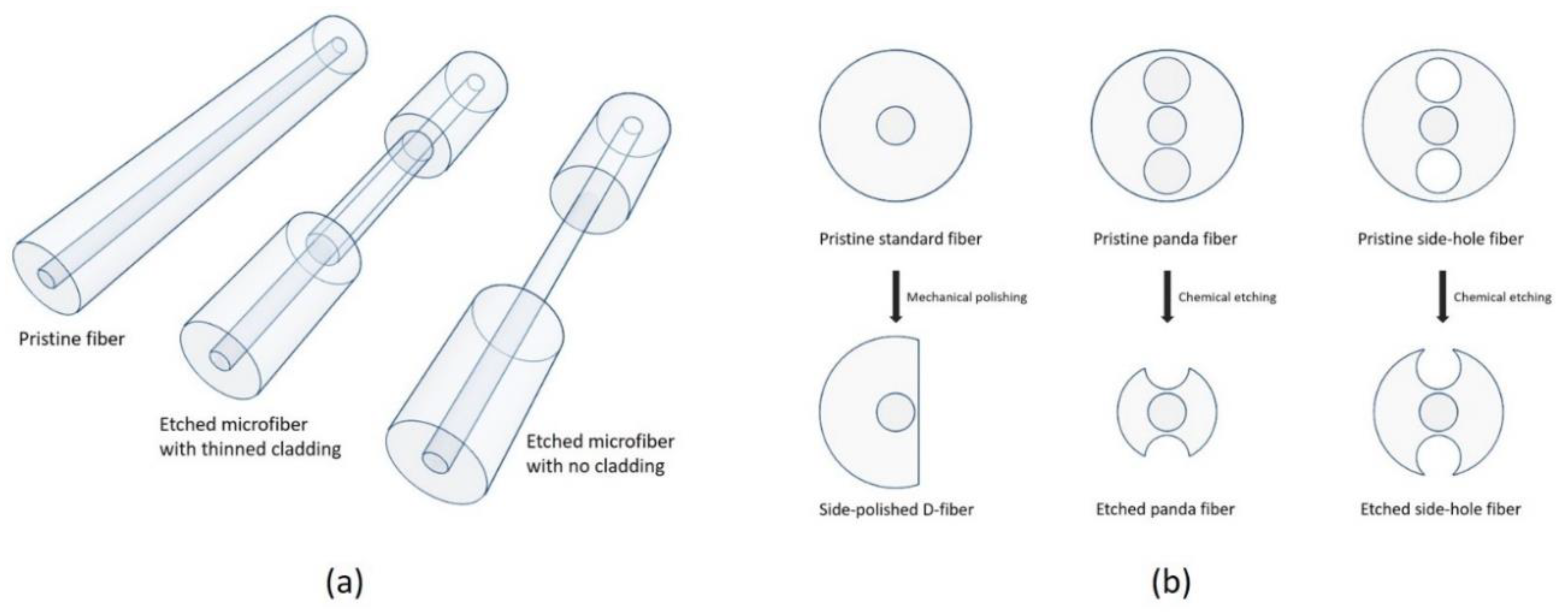
3.3. Cladding Modified Fiber
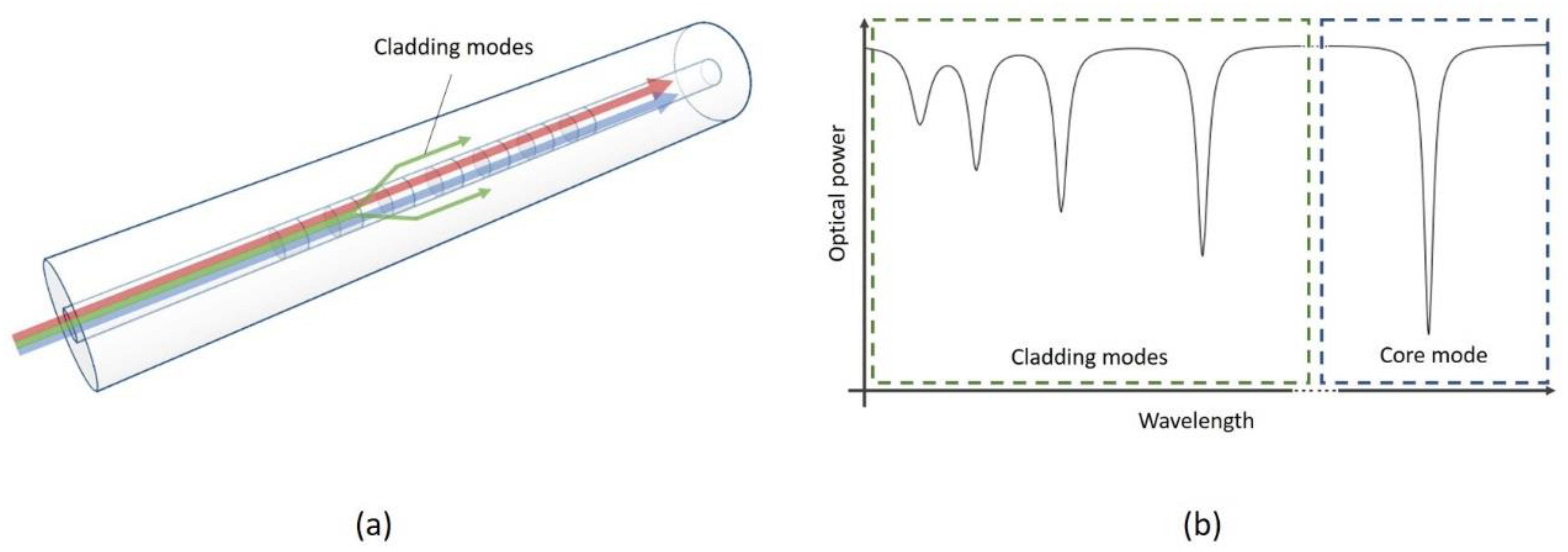
3.4. Fiber Grating Sensors
3.4.1. Long Period Fiber Grating
3.4.2. Fiber Bragg Grating
4. Common Surface Coating Techniques
4.1. Drop Casting
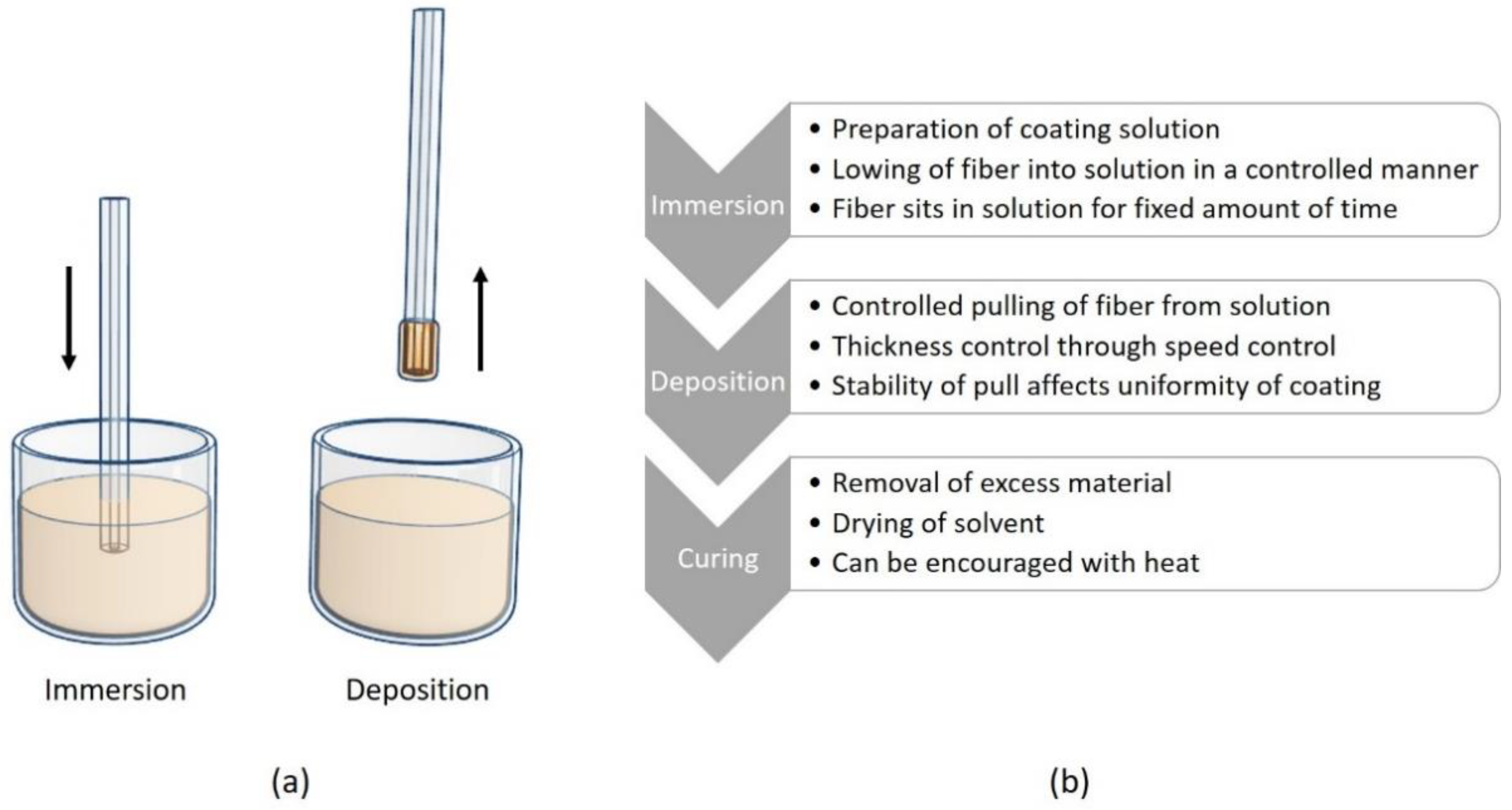
4.2. Dip Coating
4.3. Optical Deposition
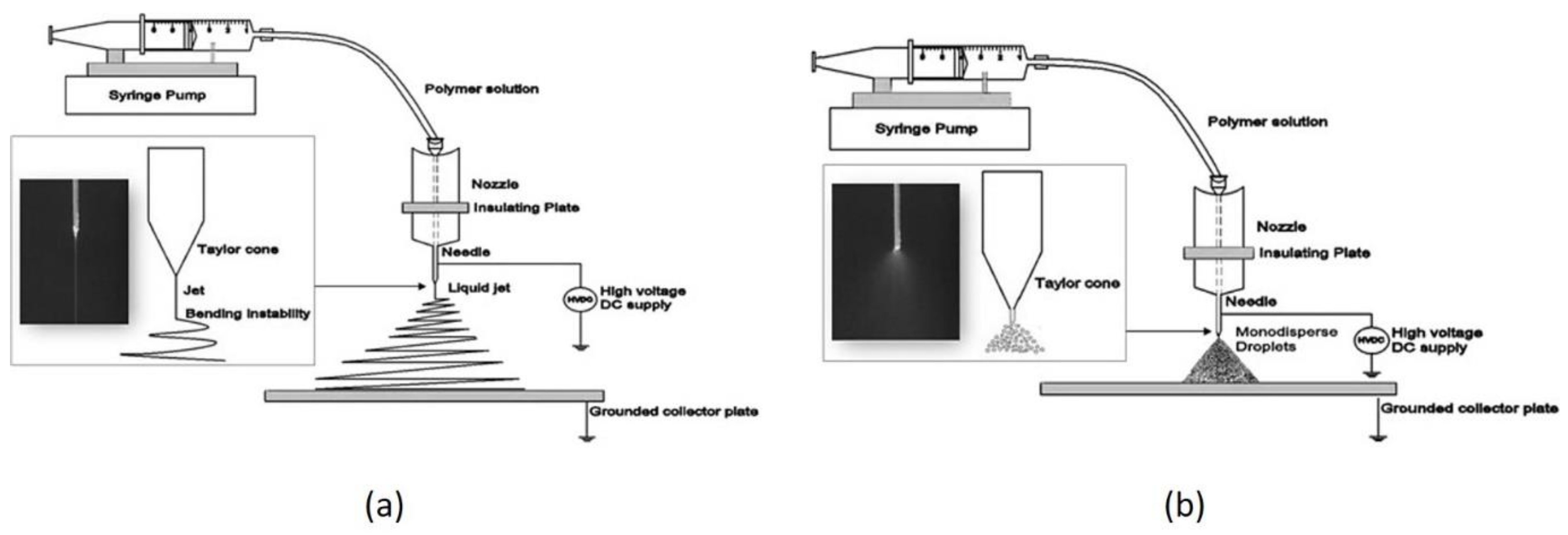
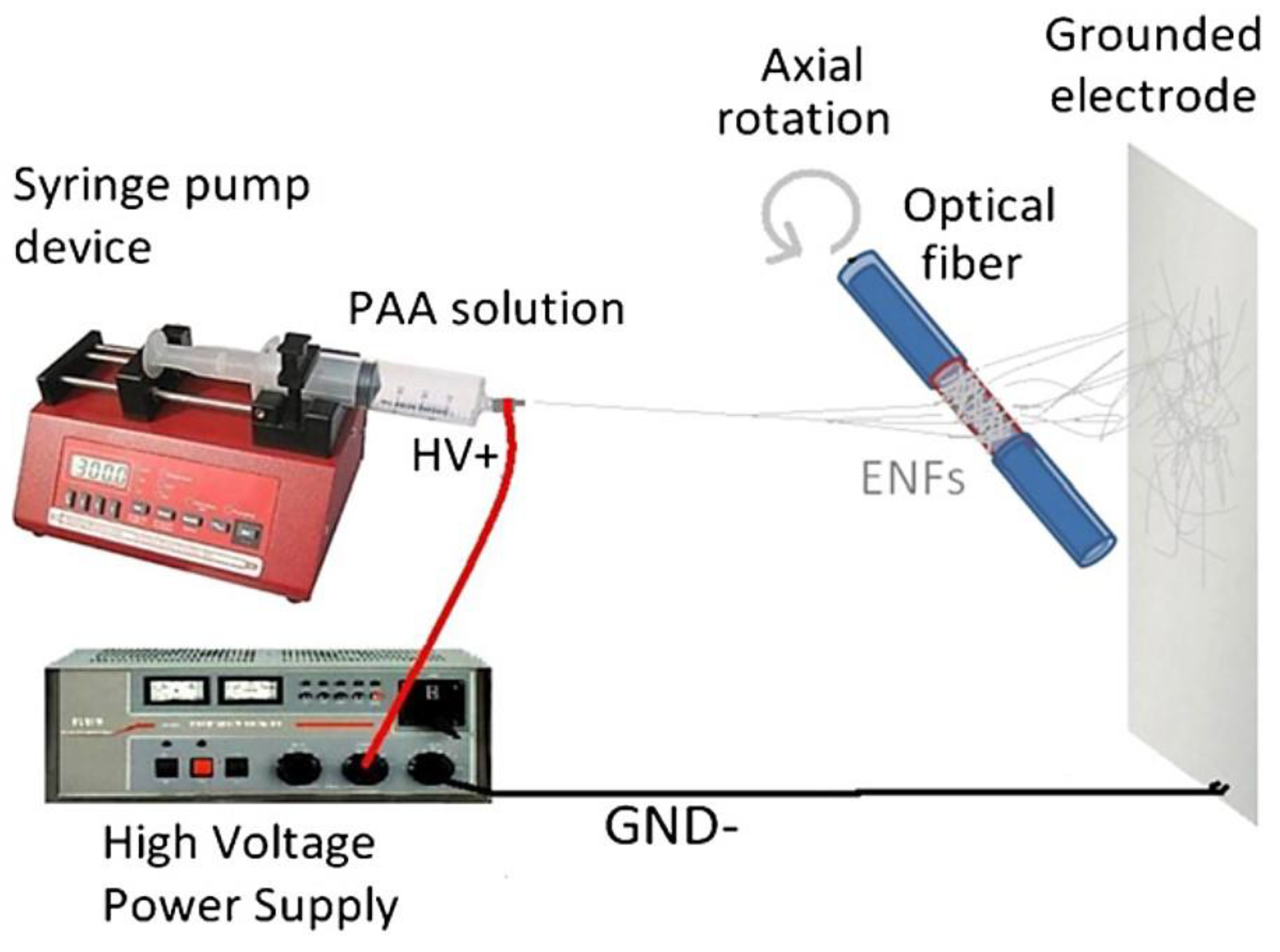
4.4. Electrospining and Electrospraying
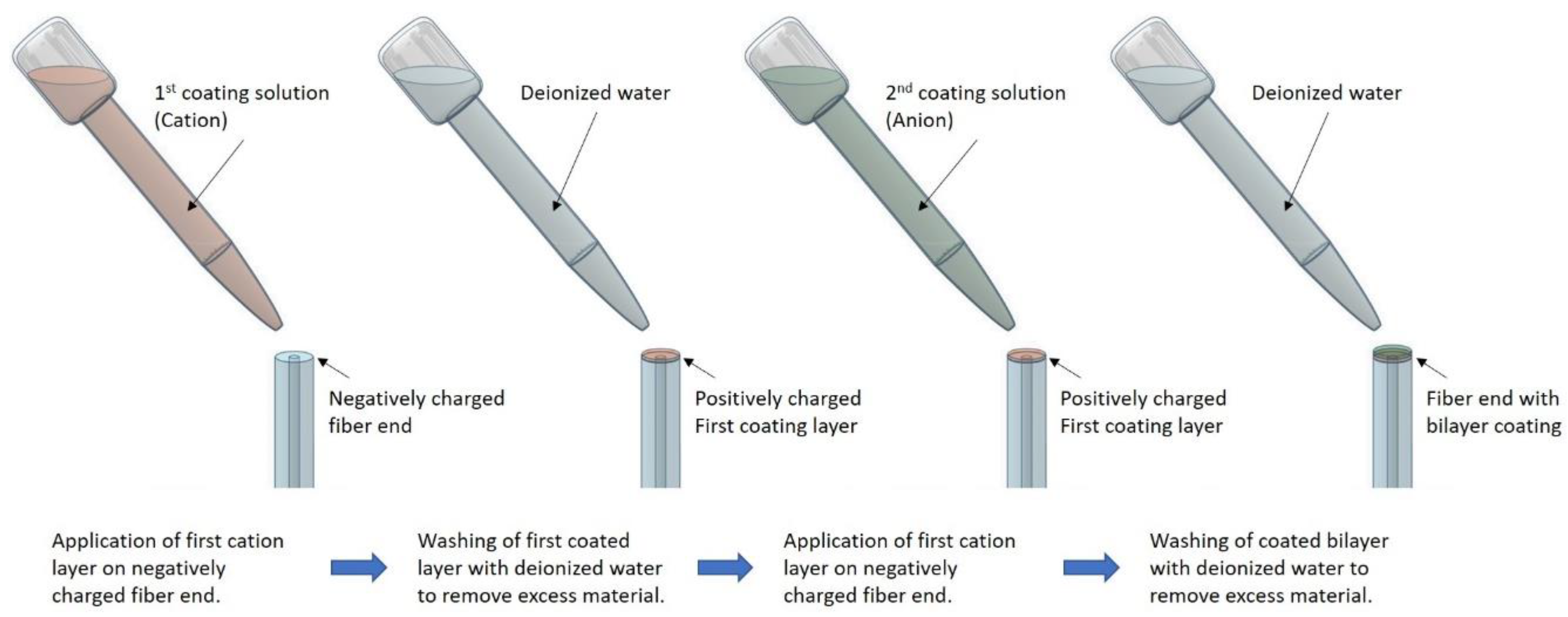
4.5. Layer by Layer Deposition
5. Recent Demonstration of Surface Functionalized Refractometer for Metal Ion Detection
5.1. Detection of Cadmium Ion
5.2. Detection of Cobalt Ion
5.3. Detection of Copper Ion
5.4. Detection of Iron Ion
5.5. Detection of Lead Ion
5.6. Detection of Mercury Ion
5.7. Detection of Nickel Ion
6. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van Heel, A. Newton’s Work on Geometrical Optical Aberrations. Nature 1953, 171, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Heel, A.C. A new method of transporting optical images without aberrations. Nature 1954, 173, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, P.C. Making the first low loss optical fibers for communications. In Proceedings of the 36th European Conference and Exhibition on Optical Communication, Torino, Italy, 19–23 September 2010; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Artiola, J.; Brusseau, M. The Role of Environmental Monitoring in Pollution Science. In Environmental and Pollution Science; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 149–162. [Google Scholar]
- Luan, I.O.B. Singapore water management policies and practices. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2010, 26, 65–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekonnen, M.M.; Hoekstra, A.Y. Four billion people facing severe water scarcity. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1500323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duruibe, J.O.; Ogwuegbu, M.; Egwurugwu, J. Heavy metal pollution and human biotoxic effects. Int. J. Phys. Sci. 2007, 2, 112–118. [Google Scholar]
- Bürck, J.; Conzen, J.-P.; Ache, H.-J. A fiber optic evanescent field absorption sensor for monitoring organic contaminants in water. Fresenius J. Anal. Chem. 1992, 342, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dybko, A.; Wroblewski, W.; Maciejewski, J.; Romaniuk, R.S.; Brzozka, Z. Fiber optic probe for monitoring of drinking water. In Proceedings of the Chemical, Biochemical and Environmental Fiber Sensors IX, Munich, Germany, 30 May 1997; pp. 361–366. [Google Scholar]
- Oehme, I.; Wolfbeis, O.S. Optical sensors for determination of heavy metal ions. Microchim. Acta 1997, 126, 177–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wo, J.; Wang, G.; Cui, Y.; Sun, Q.; Liang, R.; Shum, P.P.; Liu, D. Refractive index sensor using microfiber-based Mach–Zehnder interferometer. Opt. Lett. 2012, 37, 67–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, W.B.; Liu, H.H.; Tjin, S.C.; Chow, K.K.; Lim, A. Ultrahigh sensitivity refractive index sensor based on optical microfiber. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2012, 24, 1872–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, W.B.; Tan, Y.C.; Lin, B.; Tjin, S.C.; Chow, K.K. Nonadiabatically tapered microfiber sensor with ultrashort waist. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2014, 26, 2303–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, N.; Zheng, J.; Zhao, X.; Teng, C. Refractive index sensing based on a side-polished macrobending plastic optical fiber. IEEE Sens. J. 2014, 15, 2898–2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iadicicco, A.; Cusano, A.; Cutolo, A.; Bernini, R.; Giordano, M. Thinned fiber Bragg gratings as high sensitivity refractive index sensor. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2004, 16, 1149–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, H.; Sun, L.-P.; Huang, Y.; Jin, L.; Guan, B.-O. Etching Bragg gratings in Panda fibers for the temperature-independent refractive index sensing. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 31917–31923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, J.H.; Shum, P.; Haryono, H.; Yohana, A.; Rao, M.; Lu, C.; Zhu, Y. Measurements of refractive index sensitivity using long-period grating refractometer. Opt. Commun. 2004, 229, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, F.; Wang, C.; Sun, Z.; Zhou, K.; Zhang, L.; Shu, X. Small-period long-period fiber grating with improved refractive index sensitivity and dual-parameter sensing ability. Opt. Lett. 2017, 42, 199–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, R.X.; Ho, D.; Tse, C.H.; Tan, Y.C.; Yoo, S.W.; Tjin, S.C.; Ibsen, M. Birefringent Bragg Grating in C-Shaped Optical Fiber as a Temperature-Insensitive Refractometer. Sensors 2018, 18, 3285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, R.; Yap, S.; Tan, Y.; Tjin, S.; Ibsen, M.; Yong, K.; Lai, W. Functionalized fiber end superstructure fiber bragg grating refractive index sensor for heavy metal ion detection. Sensors 2018, 18, 1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Huang, X.G.; Pan, J.S. Simple fiber-optic refractive index sensor based on fresnel reflection and optical switch. IEEE Sens. J. 2012, 13, 1571–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.-R. The Principles of Nonlinear Optics; Wiley-Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 1984; p. 575. [Google Scholar]
- Agrawal, G.P. Nonlinear fiber optics. In Nonlinear Science at the Dawn of the 21st Century; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2000; pp. 195–211. [Google Scholar]
- Su, H.; Huang, X.G. Fresnel-reflection-based fiber sensor for on-line measurement of solute concentration in solutions. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2007, 126, 579–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.-B.; Su, C.B. Measurement of the refractive index of liquids at 1.3 and 1.5 micron using a fibre optic Fresnel ratio meter. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2004, 15, 1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villatoro, J.; Monzón-Hernández, D.; Mejía, E. Fabrication and modeling of uniform-waist single-mode tapered optical fiber sensors. Appl. Opt. 2003, 42, 2278–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brambilla, G. Optical fibre nanowires and microwires: A review. J. Opt. 2010, 12, 043001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Brambilla, G.; Ding, M.; Semenova, Y.; Wu, Q.; Farrell, G. High-sensitivity, evanescent field refractometric sensor based on a tapered, multimode fiber interference. Opt. Lett. 2011, 36, 2233–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, H.A.; Harun, S.W.; Yasin, M.; Phang, S.W.; Damanhuri, S.S.A.; Arof, H.; Ahmad, H. Tapered plastic multimode fiber sensor for salinity detection. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2011, 171, 219–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biazoli, C.R.; Silva, S.; Franco, M.A.; Frazão, O.; Cordeiro, C.M. Multimode interference tapered fiber refractive index sensors. Appl. Opt. 2012, 51, 5941–5945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latifi, H.; Zibaii, M.I.; Hosseini, S.M.; Jorge, P. Nonadiabatic tapered optical fiber for biosensor applications. Photonic Sens. 2012, 2, 340–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, R.X.; Yap, S.H.K.; Tjin, S.C. Fiber gratings enabled interrogation of Mach-Zehnder interferometer tapered fiber sensor. In Proceedings of the 2017 Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics Pacific Rim (CLEO-PR), Singapore, 31 July–4 August 2017; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.Y.; Ding, M.; Newson, T.; Brambilla, G. A review of microfiber and nanofiber based optical sensors. Open Opt. J. 2013, 7, 32–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, L.; Zi, F.; Guo, X.; Lou, J. Optical microfibers and nanofibers: A tutorial. Opt. Commun. 2012, 285, 4641–4647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieu, K.Q.; Mansuripur, M. Biconical fiber taper sensors. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2006, 18, 2239–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsani, V.; Ahmed, F.; Jun, M.B.; Bradley, C. Tapered Fiber-Optic Mach-Zehnder Interferometer for Ultra-High Sensitivity Measurement of Refractive Index. Sensors 2019, 19, 1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Yam, S.S.-H.; Barnes, J.; Bock, W.; Greig, P.; Fraser, J.M.; Loock, H.-P.; Oleschuk, R.D. Refractive index sensing with Mach–Zehnder interferometer based on concatenating two single-mode fiber tapers. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2008, 20, 626–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namiq, M.F.; Ibsen, M. Simple technique of determining the fibre diameter during etching. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 32908–32917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, H.; Zhu, J.; Yin, H.; Wang, R.; Wang, H.; Yu, B. Optical fiber refractometer based on etched-stress applying parts PANDA fiber. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2014, 26, 1356–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De-Jun, F.; Mao-Sen, Z.; Liu, G.; Xi-Lu, L.; Dong-Fang, J. D-shaped plastic optical fiber sensor for testing refractive index. IEEE Sens. J. 2014, 14, 1673–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.-W.; Yamashita, S.; Goh, C.S.; Set, S.Y. Carbon nanotube mode lockers with enhanced nonlinearity via evanescent field interaction in D-shaped fibers. Opt. Lett. 2007, 32, 148–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qazi, H.H.; Memon, S.F.; Ali, M.M.; Irshad, M.S.; Ehsan, S.A.; Salim, M.R.B.; Mohammad, A.B.B.; Zulkifli, M.Z.; Idrees, M. Surface roughness and the sensitivity of D-shaped optical fibre sensors. J. Mod. Opt. 2019, 66, 1244–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Sun, L.-P.; Gao, S.; Quan, Z.; Chang, Y.-L.; Ran, Y.; Jin, L.; Guan, B.-O. Ultrasensitive refractive-index sensors based on rectangular silica microfibers. Opt. Lett. 2011, 36, 3593–3595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, K.O.; Meltz, G. Fiber Bragg grating technology fundamentals and overview. J. Lightwave Technol. 1997, 15, 1263–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasil’ev, S.A.; Dianov, E.M.; Medvedkov, O.I.; Protopopov, V.N.; Costantini, D.; Iocco, A.; Limberger, H.; Salathe, R. Properties of the cladding modes of an optical fibre excited by refractive-index gratings. Quantum Electron. 1999, 29, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, V.; Vengsarkar, A.M. Optical fiber long-period grating sensors. Opt. Lett. 1996, 21, 692–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duhem, O.; Henninot, J.-F.; Warenghem, M.; Douay, M. Demonstration of long-period-grating efficient couplings with an external medium of a refractive index higher than that of silica. Appl. Opt. 1998, 37, 7223–7228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.H.; Liu, Y.; Lee, S.B.; Choi, S.S.; Jang, J.N. Displacements of the resonant peaks of a long-period fiber grating induced by a change of ambient refractive index. Opt. Lett. 1997, 22, 1769–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, X.; Zhang, L.; Bennion, I. Sensitivity characteristics near the dispersion turning points of long-period fiber gratings in B/Ge codoped fiber. Opt. Lett. 2001, 26, 1755–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.-L.; Wang, J.-N. Chemical sensing sensitivity of long-period grating sensor enhanced by colloidal gold nanoparticles. Sensors 2008, 8, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Villar, I.; Matias, I.R.; Arregui, F.J. Enhancement of sensitivity in long-period fiber gratings with deposition of low-refractive-index materials. Opt. Lett. 2005, 30, 2363–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meltz, G.; Morey, W.W.; Glenn, W. Formation of Bragg gratings in optical fibers by a transverse holographic method. Opt. Lett. 1989, 14, 823–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, A.D.; Silveira, B.; Warren-Smith, S.C.; Becker, M.; Rothhardt, M.; Frazão, O. Temperature independent refractive index measurement using a fiber Bragg grating on abrupt tapered tip. Opt. Laser Technol. 2018, 101, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, M.; Zang, Y.; Qiao, X.; Fu, H.; Jia, Z.-A. Humidity sensor based on hybrid fiber Bragg grating/abrupt fiber taper. IEEE Sens. J. 2017, 17, 1302–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namiq, M.F.; Ibsen, M. Simple Salinity Sensor Based on Cladding-Etched Fibre Bragg Gratings. In Proceedings of the Bragg Gratings, Photosensitivity, and Poling in Glass Waveguides, Sydney, Australia, 5–8 September 2016; p. BM4B.3. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, C.; Wang, Q.; Xu, L.; Liu, S.; He, J.; Zhao, J.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y. D-shaped fiber grating refractive index sensor induced by an ultrashort pulse laser. Appl. Opt. 2016, 55, 1525–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.; Liu, F.; Guan, B.-O.; Albert, J. Tilted fiber grating mechanical and biochemical sensors. Opt. Laser Technol. 2016, 78, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laffont, G.; Ferdinand, P. Tilted short-period fibre-Bragg-grating-induced coupling to cladding modes for accurate refractometry. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2001, 12, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherino, L.; Giaquinto, M.; Micco, A.; Aliberti, A.; Bobeico, E.; La Ferrara, V.; Ruvo, M.; Ricciardi, A.; Cusano, A. A Time-Efficient Dip Coating Technique for the Deposition of Microgels onto the Optical Fiber Tip. Fibers 2018, 6, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNab, G.; Meisen, A. Thermophoresis in liquids. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1973, 44, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, J.; Windeler, R.; DiGiovanni, D. Optically driven deposition of single-walled carbon-nanotube saturable absorbers on optical fiber end-faces. Opt. Express 2007, 15, 9176–9183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashiwagi, K.; Yamashita, S. Optical deposition of carbon nanotubes for fiber-based device fabrication. Front. Guided Wave Opt. Optoelectron. 2010, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Kim, H.I.; Oh, C.H.; Sun, X.; Lee, H. Multidimensional manipulation of carbon nanotube bundles with optical tweezers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 88, 053123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmukh, M.A.; Shirsat, M.D.; Ramanaviciene, A.; Ramanavicius, A. Composites based on conducting polymers and carbon nanomaterials for heavy metal ion sensing. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2018, 48, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Shi, Z.; Wan, X.; Fang, H.; Yu, D.-G.; Chen, X.; Liu, P. The Relationships between Process Parameters and Polymeric Nanofibers Fabricated Using a Modified Coaxial Electrospinning. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Hai, T.; Feng, Z.; Yu, D.-G.; Yang, Y.; Annie Bligh, S. The relationships between the working fluids, process characteristics and products from the modified coaxial electrospinning of zein. Polymers 2019, 11, 1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.-P.; Zhang, L.-L.; Yang, Y.-Y.; Wu, D.; Jiang, G.; Yu, D.-G. Preparing composite nanoparticles for immediate drug release by modifying electrohydrodynamic interfaces during electrospraying. Powder Technol. 2018, 327, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wen, H.-F.; Yu, D.-G.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, D.-F. Electrosprayed hydrophilic nanocomposites coated with shellac for colon-specific delayed drug delivery. Mater. Des. 2018, 143, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhushani, J.A.; Anandharamakrishnan, C. Electrospinning and electrospraying techniques: Potential food based applications. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 38, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urrutia, A.; Goicoechea, J.; Rivero, P.J.; Matías, I.R.; Arregui, F.J. Electrospun nanofiber mats for evanescent optical fiber sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 176, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reneker, D.H.; Chun, I. Nanometre diameter fibres of polymer, produced by electrospinning. Nanotechnology 1996, 7, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.-M.; Zhang, Y.-Z.; Kotaki, M.; Ramakrishna, S. A review on polymer nanofibers by electrospinning and their applications in nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2003, 63, 2223–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decher, G. Fuzzy nanoassemblies: Toward layered polymeric multicomposites. Science 1997, 277, 1232–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benounis, M.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N.; Halouani, H.; Lamartine, R.; Dumazet-Bonnamour, I. Detection of heavy metals by an optical fiber sensor with a sensitive cladding including a new chromogenic calix [4] arene molecule. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2006, 26, 364–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Dong, X.; Yang, J.; Maa, H.; Zu, P.; So, P.L.; Chan, C.C. Detection of Ni2+ with optical fiber Mach-Zehnder interferometer coated with chitosan/MWCNT/PAA. In Proceedings of the 2017 16th International Conference on Optical Communications and Networks (ICOCN), Wuzhen, China, 7–10 August 2017; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, L.; Lv, J.; Yu, X.; Chen, X. Black phosphorus integrated tilted fiber grating for ultrasensitive heavy metal sensing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 257, 1093–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahendra, N.; Gangaiya, P.; Sotheeswaran, S.; Narayanaswamy, R. Investigation of a fibre optic copper sensor based on immobilised α-benzoinoxime (cupron). Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2003, 90, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghunandhan, R.; Chen, L.; Long, H.; Leam, L.; So, P.; Ning, X.; Chan, C. Chitosan/PAA based fiber-optic interferometric sensor for heavy metal ions detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 233, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghunandhan, R.; Chen, L.; Chan, C. Fiber optic nickel ion sensor based on direct ligand immobilization. In Proceedings of the 2017 25th Optical Fiber Sensors Conference (OFS), Jeju, Korea, 24–28 April 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Ravikumar, R.; Chen, L.H.; Hui, M.M.X.; Chan, C.C. Ion-Imprinted Chitosan-Based Interferometric Sensor for Selective Detection of Heavy Metal Ions. J. Lightwave Technol. 2019, 37, 2778–2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.-Y.; Lee, S.-C.; Okazaki, T.; Kuramitz, H.; Abd-Rahman, F. Detection of mercury (II) ions in water by polyelectrolyte–gold nanoparticles coated long period fiber grating sensor. Opt. Commun. 2018, 419, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, V.; Tran, N.; Nguyen, T.; Yoon, W.; Ju, H. Liquid Cladding Mediated Optical Fiber Sensors for Copper Ion Detection. Micromachines 2018, 9, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Chen, L.H.; Zheng, Y.; Dong, X.; Raghunandhan, R.; So, P.L.; Chan, C.C. Heavy metal ions probe with relative measurement of fiber Bragg grating. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 230, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, S.H.K.; Chien, Y.-H.; Tan, R.; bin Shaik Alauddin, A.R.; Ji, W.B.; Tjin, S.C.; Yong, K.-T. An Advanced Hand-Held Microfiber-Based Sensor for Ultrasensitive Lead Ion Detection. ACS Sens. 2018, 3, 2506–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, S.H.K.; Chan, K.K.; Zhang, G.; Tjin, S.C.; Yong, K.-T. Carbon Dot-functionalized Interferometric Optical Fiber Sensor for Detection of Ferric Ions in Biological Samples. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 28546–28553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yulianti, I.; Putra, N.; Akmalia, N.; Pratiwi, D.; Albadiah, I. Study of chitosan layer-based Fabry Perot Interferometer optical fiber sensor properties for detection of Pb2+, Hg2+ and Ni2+. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1170, 012079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Han, B.; Gao, P.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, A. Reflective mercury ion and temperature sensor based on a functionalized no-core fiber combined with a fiber Bragg grating. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 272, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, N.; Wang, Z.; Chen, M.; Xin, X.; Wu, R.; Cen, Y.; Li, Y. Three-layer-structure polymer optical fiber with a rough inter-layer surface as a highly sensitive evanescent wave sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 254, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Publication | Ion | Refractometer Scheme | Coating Material | Sensitivity and Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Benounis et al., 2006 [74] | Cu2+ | Plastic cladding silica fiber | Calixarene | Range(Cu2+): >1 μM |
| Co2+ | Range(Co2+): >10−3 μM | |||
| Cd2 | Range(Cd2+): >10−4 μM | |||
| Lin et al., 2017 [75] | Ni2+ | Cascade tapered fiber interferometer | multi-layer film of chitosan, multi-walled carbon nanotubes and poly acrylic acid | Sensitivity: 56.5 dB/mM |
| Range: 0.3–0.7 mM. | ||||
| Liu et al., 2018 [76] | Pb2+ | Tilted fiber Bragg grating | Black phosphorus | Sensitivity: 0.5 × 10−3 dB/ppb |
| Range: >0.25 ppb | ||||
| Mahendra et al., 2003 [77] | Cu2+ | Fiber end reflectance | Immobilized α-benzoinoxime | Range: >5 ppm |
| Raghunandhan et al., 2016 [78] | Ni2+ | Interferometer formed from no-core fiber between single mode fiber | Bilayer of chitosan and poly acrylic acid | Sensitivity: 0.05537 nm/μM |
| Range: >0.1671 μM. | ||||
| Raghunandhan et al., 2017 [79] | Ni2+ | Interferometer formed between no-core fiber spliced to fiber end | Meso-Tetra(4-carboxyphenyl)porphine | Sensitivity: 121.03 nm/mM |
| Raghunandhan et al., 2019 [80] | Ni2+ | Interferometer formed from photonic crystal fiber between single mode fiber | Nickel-adsorbed chitosan crosslinked with epichlorohydrin | Sensitivity: 0.0632 nm/μM |
| Range: 0.57 μM. | ||||
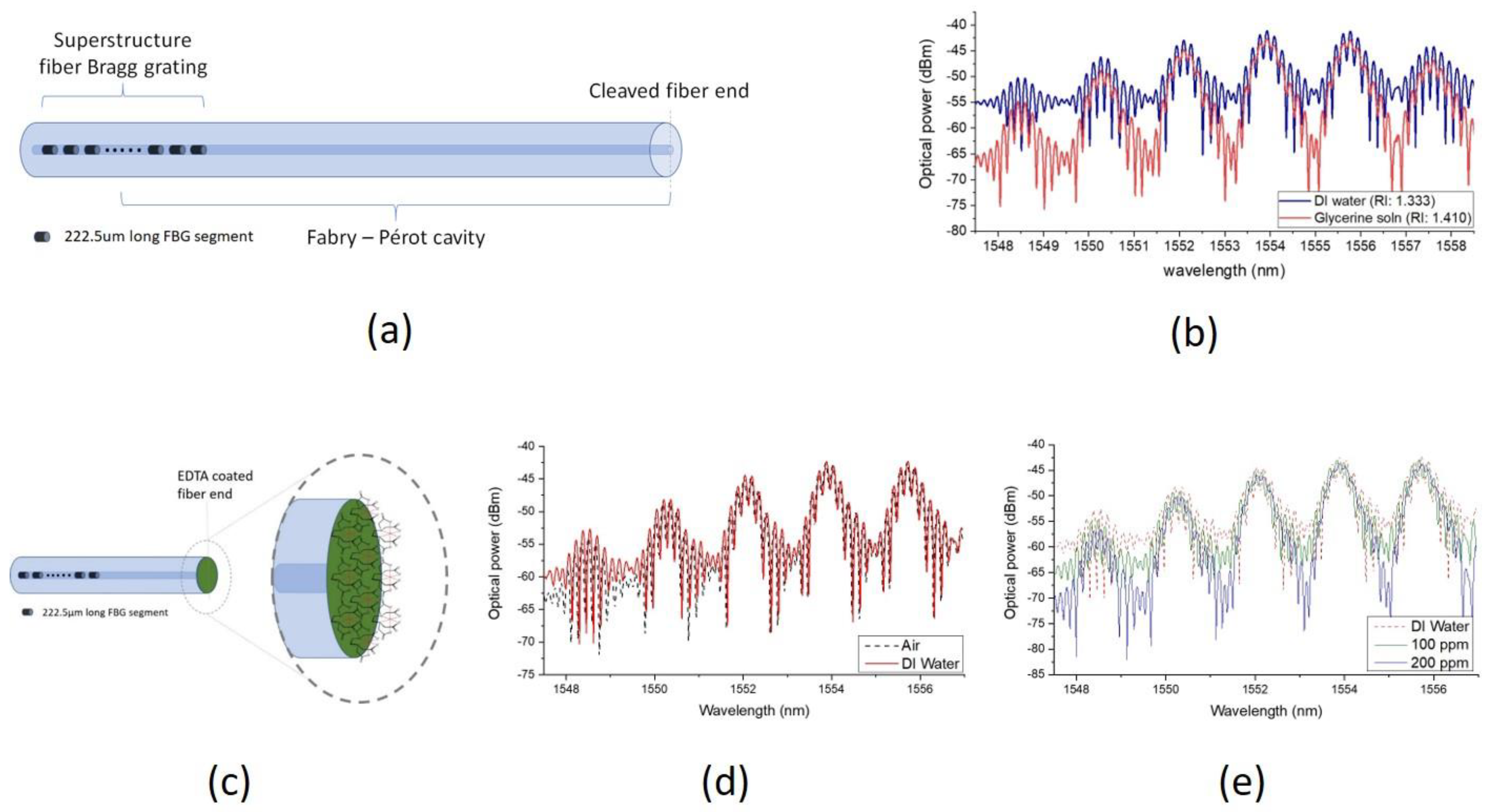
| Tan et al., 2018 [20] | Cd2+ | Interferometer formed between superstructure fiber Bragg grating and fiber end | Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid | Range: >10 ppm |
| Tan et al., 2018 [81] | Hg2+ | Single longer period grating | Polyelectrolyte and gold nanoparticles | No information |
| Tran el al., 2018 [82] | Cu2+ | Special fiber with liquid cladding | Chitosan conjugated Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid | Range: >1.62 nM |
| Yang et al., 2016 [83] | Ni2+ | Ratiometer formed by comparing Bragg grating and fiber end reflection | Bilayers of chitosan and poly acrylic acid | Sensitivity: 40.52 dB/mM |
| Yap et al., 2018 [84] | Pb2+ | Single fiber taper | l-glutathione | Range: >5 μg/L |
| Yap et al., 2019 [85] | Fe3+ | Single fiber taper | Nitrogen- and sulfur-codoped carbon dots | Sensitivity: 0.0061 nm/(μg/L) Range: 0–300 μg/L |
| Yulianti et al., 2019 [86] | Pb2+ | Fiber end FPI | Chitosan | Sensitivity(Pb2+): 0.177 dBm/ppm |
| Hg2+ | Sensitivity(Hg2+): 0.215 dBm/ppm | |||
| Ni2+ | Sensitivity(Ni2+): 0.1445 dBm/ppm | |||
| Zhang et al., 2018 [87] | Hg2+ | Bragg grating cascade with no core fiber | Bilayers of chitosan and poly acrylic acid | Sensitivity: 0.0178 nm/μM |
| Range: 100–500 μM | ||||
| Zhong N. et al., 2018 [88] | Hg2+ | Side polished D-shaped polymer fiber | Three-layer structure polymer | Range: >0.1 mg/L |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tan, R.X.; Ibsen, M.; Tjin, S.C. Optical Fiber Refractometer Based Metal Ion Sensors. Chemosensors 2019, 7, 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors7040063
Tan RX, Ibsen M, Tjin SC. Optical Fiber Refractometer Based Metal Ion Sensors. Chemosensors. 2019; 7(4):63. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors7040063
Chicago/Turabian StyleTan, Rex Xiao, Morten Ibsen, and Swee Chuan Tjin. 2019. "Optical Fiber Refractometer Based Metal Ion Sensors" Chemosensors 7, no. 4: 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors7040063
APA StyleTan, R. X., Ibsen, M., & Tjin, S. C. (2019). Optical Fiber Refractometer Based Metal Ion Sensors. Chemosensors, 7(4), 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors7040063






