Abstract
Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) is an important molecule within the human body, but many of its roles in physiology and pathophysiology are not well understood. To better understand the importance of H2O2 in biological systems, it is essential that researchers are able to quantify this reactive species in various settings, including in vitro, ex vivo and in vivo systems. This review covers a broad range of H2O2 sensors that have been used in biological systems, highlighting advancements that have taken place since 2015.
1. Introduction
Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) is a reactive oxygen species (ROS) that is present throughout the body, playing various roles in physiological processes, including cellular signaling, where it regulates cell growth, immune activation, and apoptosis [1,2,3,4]. However, at high levels, H2O2 can be detrimental to the body, causing cell damage [5], inflammatory disease [6], and cancer [7]. H2O2′s reactivity and low physiological concentration makes accurate detection difficult, leading to confusion over the roles of H2O2 within the body. To improve our understanding of H2O2‘s role in biological systems, researchers are developing sensors to detect and quantify H2O2 under various conditions. This paper reviews some of the H2O2 sensors that have advanced the field, with a focus on advancements made since 2015.
There are a variety of methods to detect and quantify H2O2 that have been in use for many years, including titration, chromotography, light detection, and electrochemical sensors [8,9,10,11,12,13]. While titration and chromotography can be used to quantify H2O2 levels, they are not ideal for in vitro and in vivo testing [14,15]. The two classes of sensors that are typically used for H2O2 detection in biological systems are light detecting sensors and electrochemical sensors [16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24]. Light detection sensors function through the detection and analysis of light emitted from a sample; besides that, they can greatly vary in their method of excitation, method in which light is changed, and emission wavelengths [16,17]. Chemiluminescence sensors use a chemical compound to excite or alter the H2O2, while fluorescence sensors use an external energy source, typically light [16,17]. Sensors frequently exhibit changes in emission intensity, but they can also function through shifts in their emission profiles, such as a red or blue shift of peaks [10,25,26,27].
Electrochemical sensors function through the quantification of changes in chemical energy through an electrical transducer [18,20,23]. Potentiometric sensors measure the potential (voltage) between probes for which there is no current [18,20,23], and amperometric sensors measure the current while the potential (voltage) is maintained [18,20,24]. Both potentiometric and amperometric sensors have been used to quantify H2O2 levels and are discussed in greater detail in this paper [12,13].
2. Light Detecting Sensors
2.1. Chemiluminescence
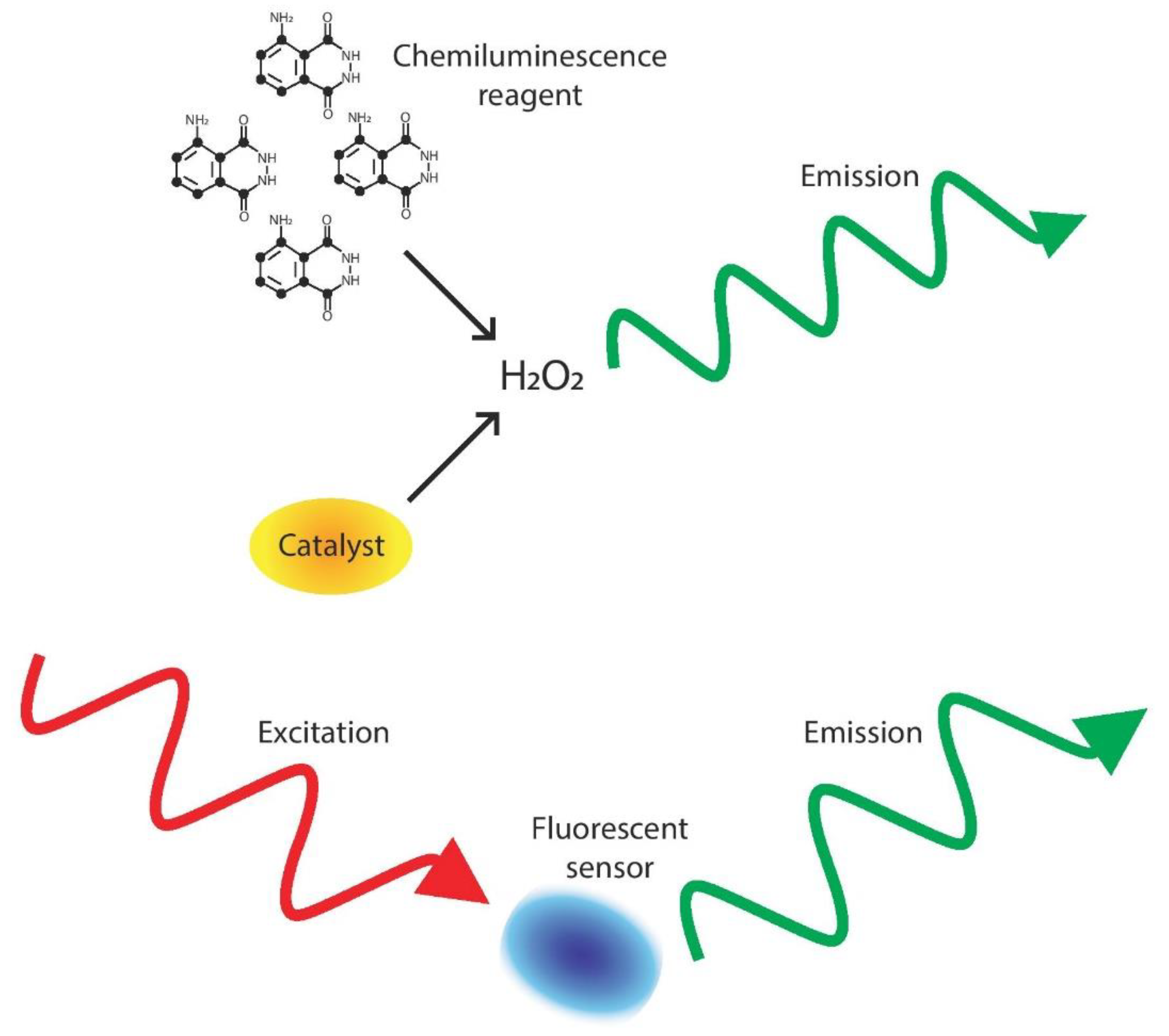
Chemiluminescence (Figure 1) is a versatile detection method in which an H2O2 sensitive reagent promotes a chemical reaction for which the emission’s signal intensity or wavelength change can be measured to determine the concentration of H2O2 [16]. There are many different chemiluminescence H2O2 sensors that could be used by researchers, including those outlined below [10,25,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38].
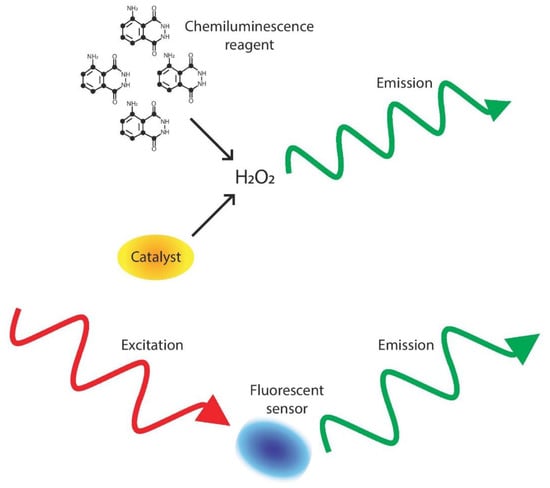
Figure 1.
Process of light-based detection. In chemiluminescence detection, a substance (such as luminol) and catalyst (except in the enzyme free reactions) react with H2O2, causing an emission of light that can then be read to determine H2O2 concentration [16]. In fluorescent detection, an outside photon source excites a sample, causing an emission that corresponds to H2O2 concentration [17].
2.1.1. Developments Prior to 2015
Chemiluminescence methods include using luminol [10], eosin [28,29], peroxalate nanoparticles [25], and D-aminoluciferin [30] for H2O2 detection and have been used to detect H2O2 in the peritoneal cavity of a mouse [25], in mouse tumor xenografts [30], as an intermediate step to determine glucose levels in human serum [10], and to determine the peroxidase activity of human red blood cell membranes [29].
Of note is Lee et al.’s in vivo chemiluminescent H2O2 sensor created with peroxalate esters and fluorescent dyes [25]. Lee et al.’s H2O2 sensor can detect intramuscular exogenous H2O2 at a depth of 3 mm, as well as H2O2 production in the peritoneal cavity during lipopolysaccharide-induced stress [25].
Reverse micelles were used to develop a luminol-based H2O2 sensor that allows reactions to be conducted in a low pH setting [10]. Igarashi et al. used their hexadecyltrimethylammonium bromide reverse micellar system to determine the substrate concentrations of L-phenylalanine and glucose, as well as to find the concentration of glucose in human serum [10].
2.1.2. Developments from 2015 to 2019
In 2015, Yu et al. discovered that the luminol reaction could be catalyzed by iodophenol blue, providing a less expensive method for H2O2 detection than the commonly used horseradish peroxidase (HRP) assays; the method also increased reproducibility compared to peroxidase-mimicking nanoparticle assays, whose detection properties depend on particle size [31].
He et al. used the luminol–H2O2 reaction to spatially position an electrochemical probe in order to record intracellular H2O2 levels [32]. Previously, a nanometer-sized electrode had been inserted into a cell for the electrochemical measurement of H2O2, but this method suffered from a lack of awareness of where the probe was located within the cell [39,40]. He et al. designed a chitosan-luminol probe attached to the electrochemical probe in order to provide spatial information about the probe’s location within the cell, allowing for more precise data collection [32].
In 2016, Koren et al. used Prussian white’s ability to convert to Prussian blue when oxidized to form a rechargeable optical sensor for H2O2 [33]. Prussian blue’s ability to be recharged in a 0.05 M ascorbic acid doped agarose gel allows the components to be reused multiple times [33]. Koren et al. demonstrated the ability of the Prussian white/Prussian blue assay to detect biologically-relevant samples by quantifying H2O2 levels in activated neutrophils [33].
In the following year, Sheng et al. used silver nanocluster-capped bovine serum albumin (BSA) as a catalyst for the luminol–H2O2 reaction [34]. The silver nanocluster capped BSA is a small alteration that allows for variable emission wavelengths, creating a tunable sensor [34].
Moẞhammer et al. combined a previous luminescence flow injection assay technique by King et al. [38] with microdialysis probes to decrease the impact of pH on readings as well as to allow for the continuous monitoring of a system [35]. Moẞhammer et al. demonstrated the probe’s ability to detect H2O2 concentration in biological solutions by detecting the H2O2 created due to the reaction of glucose oxidase and a catalyst in a phosphate buffered saline (PBS) glucose solution. This method was used to determine the change in H2O2 levels in a Pseudomonas aeruginosa solution, which is known to cause acute and chronic infections in many systems throughout the body, including the urinary tract, the dermal system, and the respiratory system [35,41,42].
In 2019, Wang et al. decreased the H2O2 detection limit of the luminol reaction via the synthesis and use of a hemin and poly(ethylene glycol) methyl ether catalyst [36]. The new catalyst resulted in a detection limit of 1.8 nM [36], lower than other luminol–H2O2 detection levels [31,36,43,44,45].
Additionally in 2019, Jiao et al. detected intracellular H2O2 in cervical cancer cells (HeLa) by using iron–nitrogen–carbon single-atom nanozymes, which exhibit peroxidase-like activity, allowing for the catalyzation of H2O2 [37].
2.2. Fluorescence
Fluorescent signal detection (Figure 1), another widely used method for H2O2 detection, involves the quantification of a signal that is emitted from the excitation of electrons by light [17]. For fluorescence sensors, the excitation is caused by an external photon source, rather than a chemical reaction, as is the case in chemiluminescence [17].
2.2.1. Developments Prior to 2015
There have been several fluorescent probes using different materials made over the years, including naphthofluorescein disulfonate [46], homovanillic acid [47,48], peroxyfluor-1 [49,50], Escherichia coli OxyR [51], peroxyresorufin-1 [49], single-walled carbon nanotubes [11,52], peroxyxanthone-1 [49], and phosphine-based fluorescent reagents [53]. Fluorescent sensors have been used to detect intracellular H2O2 in mice peritoneal macrophages [46], to detect intracellular H2O2 levels when human embryotic kidney cells are bathed in H2O2 [49], and to measure single molecule efflux from human umbilical vein endothelial cells [11].
An important advancement in H2O2 detection occurred in 2005 with the development of three fluorescent probes from the peroxysensor family [49]. The probes are detectable via confocal and two-photon spectroscopy, and each emits at a different wavelength, allowing for different uses depending on the desired emission wavelength [49]. Miller et al. demonstrated that the probes were taken up by live human embryotic kidney (HEK) cells, where they responded to the introduction of extracellular H2O2; they also demonstrated that the probes can detect simulated conditions of oxidative stress in embryonic rat hippocampal neurons [49].
In 2006, Belousov et al. developed an H2O2 sensor named HyPer that can detect intracellular H2O2 levels [51]. HyPer was created from the insertion of a yellow fluorescent protein into Escherichia coli [51]. HyPer was able to detect an increase in H2O2 levels in HeLa cells during Apo2L/TRAIL protein-induced apoptosis and in rat adrenal medulla (PC-12) cells exposed to nerve growth factor [51].
2.2.2. Developments from 2015 to 2019
In 2015, Xu et al. developed Mito-H2O2, a probe specifically designed for the detection of mitochondrial-associated hydrogen peroxide [27]. After confirming the location of Mito-H2O2 within the mitochondria with MitoTracker Deep Red and the selectivity of the probe against several different reactive oxygen and nitrogen species, Xu et al. delivered Mito-H2O2 to HeLa cells and recorded its response to the addition of H2O2, confirming the creation of a mitochondrial-targeted sensor with a high selectivity and rapid response time [27].
In the following year, Xiao et al. developed two florescent probes (MI-H2O2 and ER-H2O2) that were capable of targeting the mitochondria and the endoplasmic reticulum, respectively, have high specificity for H2O2, and have a fast response time [26]. MI-H2O2 and ER-H2O2 have different emission wavelengths and can therefore be used together to simultaneously measure H2O2 associated with the two organelles [26]. Xiao et al. was able to detect H2O2 associated with each organelle during L-buthionine sulfoximine-induced apoptosis [26].
Qian et al. developed a ratiometric H2O2 sensor in 2019 in an attempt to decrease the false positive and false negative readings that frequently occur with non-ratio sensors [52,54]. Using a cobalt/carbon nanotube hybrid nanocomplex as a catalyst for Amplex Red and fluorescent scopoletin, Qian et al. created a cost-effective and sensitive ratiometric H2O2 sensor capable of detecting hydrogen peroxide concentrations as low as 100 nM [52].
3. Electrochemical Probes
Two types of electrochemical probes are frequently used for H2O2 detection, specifically potentiometric and amperometric [12,55]. The way in which the two classes of probes function is different. Potentiometric probes measure the potential (voltage) between a working and reference electrode in a system that has no significant current flow [18,19,20,21,22,23]. The working electrode needs to be modified so that changes in potential correlate to changes in H2O2 concentration, and the reference electrode must remain constant so that it can serve as a reference, or comparison, to the working electrode [18,19,20,21,22,23]. Amperometric sensors rely on the principle that changes in current are correlated to change in concentration [18,19,20,22,24]. Therefore, amperometric sensors use two or three electrodes to measure the change in the current of a sample while the potential (voltage) is held constant [18,19,20,22,24].
3.1. Potentiometric
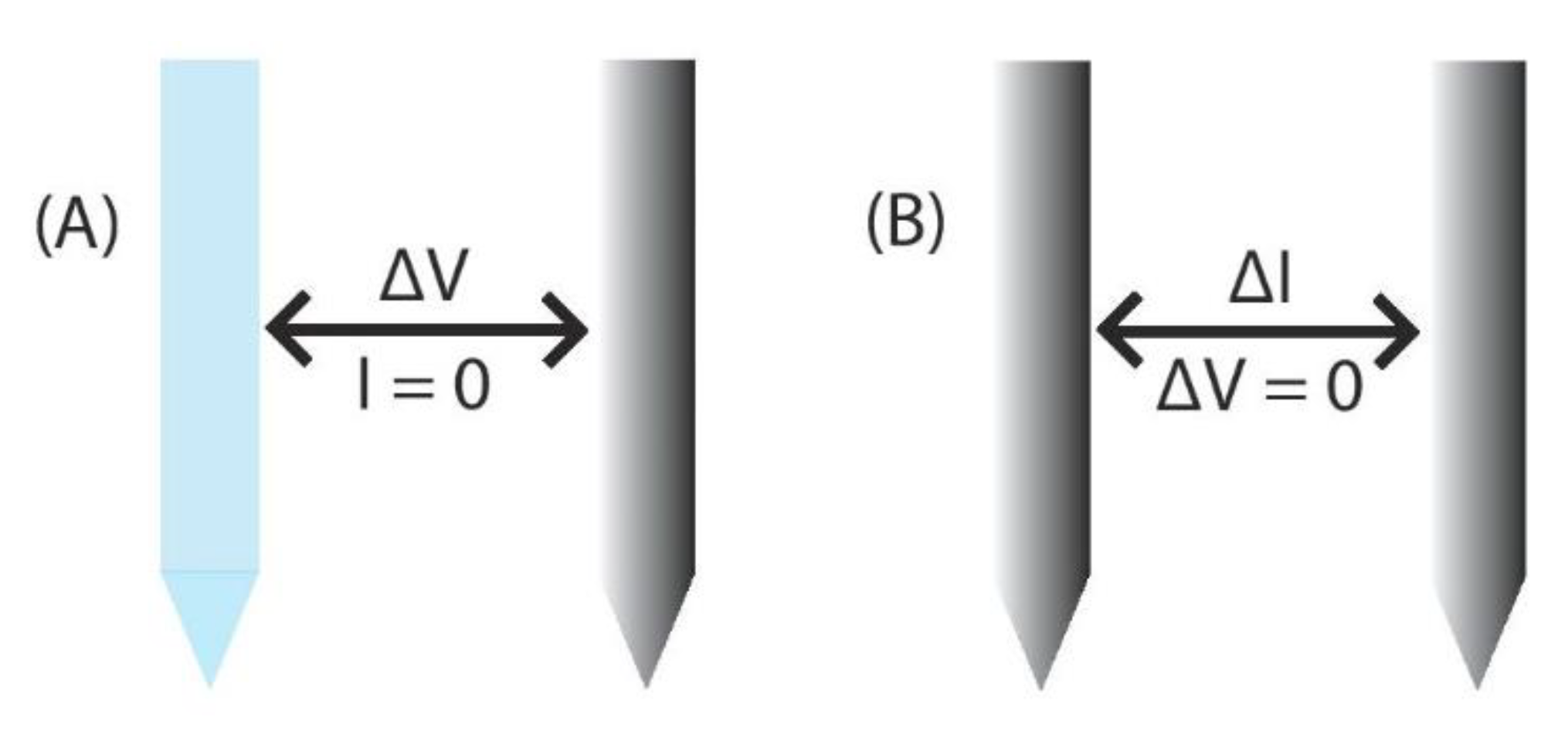
Potentiometric sensors (Figure 2) measure the electrical potential of an electrode when there is no significant current in the system by using a reference electrode and a functional electrode [18,19,20,21,22,23]. Electrodes are tuned to detect specific analytes with membranes that surround their surface [20,23]. When the target analyte reacts with the membrane, the corresponding change in electrical potential can be read by the electrode [20,23].
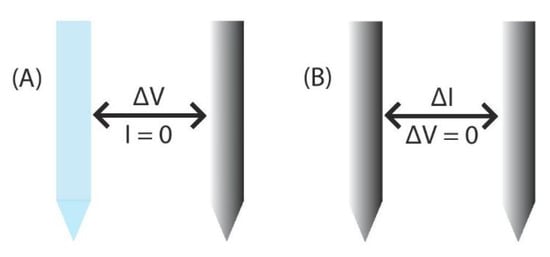
Figure 2.
Two different methods of electrochemical detection. (A) Potentiometric probes measure the potential between a working and reference electrode in a system with no significant current flow [18,19,20,21,22,23]. (B) Amperometric sensors use two or three electrodes and measure the change in current while the voltage is held constant [18,19,20,22,24].
3.1.1. Developments Prior to 2015
There have been several potentiometric sensors for H2O2 developed over the years; unfortunately, very few have been used in biomedical systems [56]. One of the potentiometric H2O2 sensors to be used in biomedical research is the N,N’,N,N’-Tetramethylbenzidine with horseradish peroxidase system that has been used to detect H2O2 as an indicator of glucose levels in human blood samples [12].
3.1.2. Developments from 2015 to 2019
Parrilla et al. created a potentiometric H2O2 sensor in 2017 by coating platinum electrodes with Nafion, a sulfonated tetrafluoroethylene-based fluoropolymer-copolymer [57]. Parrilla et al. showed that the Nafion coating decreased signal interference from ascorbate, which commonly interferes with signal detection in biological systems, and acted as a permselective barrier, increasing the sensor’s sensitivity in comparison to a bare electrode [57].
Cánovas et al. created a different Nafion-based H2O2 sensor in which paper coated with a Nafion membrane containing glucose oxidase was used to detect blood glucose levels [58]. The sensor is a low-cost alternative that can detect glucose levels in both human serum and whole blood samples [58].
In 2018, Iwata et al. used a previously-reported glutamate sensor, which was based on the redox reaction of a gold electrode [59], as an H2O2 sensor that functioned independently of the pH of the solution [60]. Iwata et al. showed that both a ferrocenyl methanol solution and a 11-ferrocenyl-1-undecanethiol-coated electrode were capable of H2O2 detection but that the ferrocenyl methanol solution had a lower detection limit [60].
3.2. Amperometric
Amperometric sensors (Figure 2) are similar to potentiometric sensors in that they use electrodes, but amperometric sensors use two or three [24] electrodes to measure the current at a fixed potential and therefore rely on analyte diffusion to perform their measurements [18,19,20,22,24].
3.2.1. Developments Prior to 2015
Amperometric sensors are common for H2O2 detection systems, and many different methods, including hemoglobin adhered to gold nanoparticle hybrid microspheres [55], graphene/platinum nanoparticles on glassy carbon electrodes [61], nanoceria capped with hexamethylene-tetra-amine or fructose [13], and (3-aminopropyl) triethoxysilane functionalized reduced graphene oxide [62] have been used in biological systems. Some of the biomedical applications for the use of amperometric sensors include quantifying H2O2 in disinfectants [63], determining the antioxidant activity of cerium oxide nanoparticles with rat cardiomyoblast cells (H9c2) [13], and the release of H2O2 from rat adrenal medulla pheochromocytoma cells (PC12) [61].
3.2.2. Developments from 2015 to 2019
Amperometric sensors have experienced a lot of improvement over the past five years, including improvements to stability [64,65], detection limit [65], and cost [66]. Since H2O2 can decay in rapid and unpredictable ways, Draminska et al. developed a bienzymatic system to detect the catalase reaction as well as the decay of the H2O2 [67]; their bienzymatic sensor is created by coating a glassy carbon electrode in multi-walled carbon nanotubes with absorbed catalase and either laccase or bilirubin oxidase [67]. Draminska et al. demonstrated the use of their sensor by measuring H2O2 concentration in pharmaceutical formulations [67].
Since amperometric sensors frequently rely on enzymes and mediators to facilitate electron transfer, they often suffer from instability, which can lead to inconsistent results [64,68]. A common cause of instability is enzyme dependence on pH [64]. Thenmozhi et al. created a more stable H2O2 sensor by covalently linking enzymes and mediators, specifically 3-aminopropyl trimethoxy silane with HRP and toluidine blue, which was deposited onto a graphite powder electrode [65]. Thenmozhi et al. determined that the sensor retained 86.7% of its initial response after being stored at 4 °C for three months, and they were able to use their stable sensor to quantify H2O2 concentrations in pharmaceutical preparations [65].
Enzyme-Free Sensors
Many amperometric sensors use enzymes, but this unfortunately leads to increased costs due to the extraction and purification techniques that are necessary to acquire the enzymes [69,70]. In 2015, Sekar et al. circumvented this extraction and purification issue by immobilizing raw turnip peroxidase and potassium hexacyanoferrate into a cellulose paper that is both disposable and biodegradable [66]. Sekar et al.’s sensor, which can be used to detect H2O2 in a commercial wound disinfectant, does use an enzyme, but is able to do so in a more cost-effective manner [66].
In 2016, Bai et al. created an enzyme-free H2O2 sensor with platinum nanoparticles and reduced graphene oxide–chitosan–ferrocene carboxylic acid nanohybrids [71]. Bai et al.’s sensors showed a negligible response to ascorbic and uric acid (two electroactive species that can interfere with H2O2 sensing), retained 80% of their initial value after 22 days, and successfully detected H2O2 released from adenocarcinomic human epithelial (A549) and stimulated human liver cancer cells (HepG2 and LO2) [71].
In 2017, Liu et al. used a porphyrinic iron metal–organic framework decorated with ordered mesoporous carbon to create an enzyme-free H2O2 sensor [72]. Liu et al.’s sensor was successfully used to observe the H2O2 levels in HeLa cells after exposure to CdTe quantum dots, which cause cells to produce increased levels of ROS [72,73,74,75].
Recently, in 2019, Liu et al. developed an immobilization-free H2O2 sensor, which can be created much faster than an immobilized sensor, by using the difference in diffusivity between single-stranded DNA and CeO2 nanoparticles [76]. Liu et al.’s sensor was used to detect both intercellular and extracellular H2O2 levels in stimulated human breast cancer cells (MCF-7) [76].
4. Sensor Specifics
Sensors and Biosensors Discussed in this Review as follows(Table 1):

Table 1.
Sensors and Biosensors Discussed in this Review.
5. Conclusions
Hydrogen peroxide is an important molecule within the human body, but its roles and interactions are not well understood. Before we are able to understand H2O2’s role in the body, there must be reliable, fast, and versatile methods of detection with appropriate range and detection limits to function within biological systems and to detect biologically-relevant concentrations. In the past five years, researchers have continued to improve existing H2O2 sensors [26,27,33,34,36,52,57,65,66,71,76] and developed novel methods of H2O2 detection [26,27,32,66,67]. Sensor developments have occurred in the improvement of H2O2 detection limits, with researchers able to detect much smaller concentrations than in the past; longevity, with researchers developing sensors that function over multiple weeks/months; and cost, with prices dropping in sensor development, this making sensors easier to manufacture at desired price points [65,66,71]. These improvements, and many more, have been accomplished by researchers who have expanded their materials and techniques in sensor design and manufacturing. Despite the advances that have been made in H2O2 detection over the past five years, there is still room for growth in the field. Between fluorescent, chemiluminescent, amperometric, and potentiometric systems, researchers have been able to detect H2O2 in within single cells (in vitro), solutions (ex vivo), and animal models (in vivo) [26,27,32,46,51,58,61,71]. With the continued development and refinement of H2O2 sensors, we predict that even more knowledge about H2O2′s impact on cellular signaling and biological processes will soon be discovered.
Author Contributions
Data curation, J.M.; E.M.H.; J.A.S. and N.M.I.; writing—original draft preparation, J.M. and N.M.I.; writing—review and editing, J.M.; E.M.H.; J.A.S. and N.M.I.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Wang, X.; Martindale, J.L.; Liu, Y.; Holbrook, N.J. The cellular response to oxidative stress: Influences of mitogen-activated protein kinase signalling pathways on cell survival. Biochem. J. 1998, 333, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreck, R.; Rieber, P.; Baeuerle, P.A. Reactive oxygen intermediates as apparently widely used messengers in the activation of the NF-kappa B transcription factor and HIV-1. EMBO J. 1991, 10, 2247–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, J.; Berk, B. Fyn and JAK2 mediate ras activation by reactive oxygen species. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 21003–21010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elias, H.; Vayssié, S. Reactive peroxo compounds generated in situ from hydrogen peroxide: Kinetics and catalytic application in oxidation processes. Peroxide Chem. 2000, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imlay, J.A.; Linn, S. Mutagenesis and stress responses induced in Escherichia coli by hydrogen peroxide. J. Bacteriol. 1987, 169, 2967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, M.; Siddiqui, M.R.; Tran, K.; Reddy, S.P.; Malik, A.B. Reactive oxygen species in inflammation and tissue injury. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2013, 20, 1126–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, S.; Chakraborty, R.; Sridhar, C.; Reddy, Y.S.R.; De, B. Free radicals, antioxidants, Diseases and phytomedicines: Current status and Future prospect. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Rev. Res. 2010, 3, 91–100. [Google Scholar]
- Klassen, N.V.; Marchington, D.; McGowan, H.C.E. H2O2 Determination by the I3-Method and by KMnO4 Titration. Anal. Chem. 1994, 66, 2921–2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimeno, P.; Bousquet, C.; Lassu, N.; Maggio, A.-F.; Civade, C.; Brenier, C.; Lempereur, L. High-performance liquid chromatography method for the determination of hydrogen peroxide present or released in teeth bleaching kits and hair cosmetic products. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2015, 107, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igarashi, S.; Hinze, W.L. Enzymatic assay with detection by enhanced luminol chemiluminescence in a reversed micellar system: Determination of l-amino acids and glucose. Anal. Chim. Acta 1989, 225, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H.; Patra, C.R.; Arkalgud, J.R.; Boghossian, A.A.; Zhang, J.; Han, J.-H.; Reuel, N.F.; Ahn, J.-H.; Mukhopadhyay, D.; Strano, M.S. Single-molecule detection of H2O2 mediating angiogenic redox signaling on fluorescent single-walled carbon nanotube array. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 7848–7857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Qin, W. Reactive intermediates-induced potential responses of a polymeric membrane electrode for ultrasensitive potentiometric biosensing. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 4073–4075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ujjain, S.K.; Das, A.; Srivastava, G.; Ahuja, P.; Roy, M.; Arya, A.; Bhargava, K.; Sethy, N.; Singh, S.K.; Sharma, R.K.; et al. Nanoceria based electrochemical sensor for hydrogen peroxide detection. Biointerphases 2014, 9, 031011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ettre, L.S.; Zlatkis, A. 75 Years of Chromatography: A Historical Dialogue; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Vogel, A.I.; Mendham, J. Vogel’s Textbook of Quantitative Chemical Analysis; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Andreotti, P.E. Chemiluminescence: Principles and Applications in Biology and Medicine. J. Pharm. Sci. 1989, 78, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilbault, G.G. Practical Fluorescence: Theory, Methods and Techniques; M. Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Galus, Z. Fundamentals of Electrochemical Analysis; Ellis Horwood: Chichester, UK; Halsted Press, a division of Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Lingane, J.J. Electroanalytical Chemistry; Interscience Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 1958. [Google Scholar]
- Pundir, C.S.; Deswal, R.; Narwal, V. Quantitative analysis of hydrogen peroxide with special emphasis on biosensors. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2018, 41, 313–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yunus, S.; Attout, A.; Vanlancker, G.; Bertrand, P.; Ruth, N.; Galleni, M. A method to probe electrochemically active material state in portable sensor applications. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 156, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, J.; Fidanovski, K.; Lauto, A.; Mawad, D. All-organic semiconductors for electrochemical biosensors: An overview of recent progress in material design. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2019, 7, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunus, S.; Jonas, A.M.; Lakard, B. Potentiometric biosensors. In Encyclopedia of Biophysics; Roberts, G.C.K., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2013; pp. 1941–1946. [Google Scholar]
- Villagrasa, J.P.; Colomer-Farrarons, J.; Miribel, P.L. Bioelectronics for amperometric biosensors. In State of the Art in Biosensors-General Aspects; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, D.; Khaja, S.; Velasquez-Castano, J.C.; Dasari, M.; Sun, C.; Petros, J.; Taylor, W.R.; Murthy, N. In vivo imaging of hydrogen peroxide with chemiluminescent nanoparticles. Nat. Mater. 2007, 6, 765–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Li, P.; Hu, X.; Shi, X.; Zhang, W.; Tang, B. Simultaneous fluorescence imaging of hydrogen peroxide in mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum during apoptosis. Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 6153–6159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, H.; Gao, X.; Shao, S. Mitochondria-targeted fluorescent probe for imaging hydrogen peroxide in living cells. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 1455–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- J.O’Brien, P.; Bechara, E.J.H.; R.O’Brien, C.; Duran, N.; Cilento, G. Generation of bio-electronic energy by electron transfer: Reduction of peroxidase compound I and compound II by eosine. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1978, 81, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Toledo, S.M.; Haun, M.; Bechara, E.J.H.; Durán, N. Peroxidase and hydrogen peroxide detection by a bioenergized method. Anal. Biochem. 1980, 105, 36–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Li, J.; Chen, L.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Du, L.; Li, M. Bioluminescent probe for hydrogen peroxide imaging in vitro and in vivo. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 9800–9806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, D.; Wang, P.; Zhao, Y.; Fan, A. Iodophenol blue-enhanced luminol chemiluminescence and its application to hydrogen peroxide and glucose detection. Talanta 2016, 146, 655–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.; Tang, H.; Jiang, D.; Chen, H.-Y. electrochemical visualization of intracellular hydrogen peroxide at single cells. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 2006–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koren, K.; Jensen, P.Ø.; Kühl, M. Development of a rechargeable optical hydrogen peroxide sensor–sensor design and biological application. Analyst 2016, 141, 4332–4339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Y.; Yang, H.; Wang, Y.; Han, L.; Zhao, Y.; Fan, A. Silver nanoclusters-catalyzed luminol chemiluminescence for hydrogen peroxide and uric acid detection. Talanta 2017, 166, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moßhammer, M.; Schrameyer, V.; Jensen, P.Ø.; Koren, K.; Kühl, M. Extracellular hydrogen peroxide measurements using a flow injection system in combination with microdialysis probes–Potential and challenges. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 128, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Dong, B.; Feng, G.; Shan, H.; Huan, Y.; Fei, Q. Water soluble Hemin-mPEG-enhanced luminol chemiluminescence for sensitive detection of hydrogen peroxide and glucose. Anal. Sci. 2019, 19P150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, L.; Xu, W.; Yan, H.; Wu, Y.; Liu, C.; Du, D.; Lin, Y.; Zhu, C. Fe–N–C single-atom nanozymes for the intracellular hydrogen peroxide detection. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 11994–11999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, D.W.; Cooper, W.J.; Rusak, S.A.; Peake, B.M.; Kiddle, J.J.; O’Sullivan, D.W.; Melamed, M.L.; Morgan, C.R.; Theberge, S.M. Flow injection analysis of H2O2 in natural waters using acridinium ester chemiluminescence: Method development and optimization using a kinetic model. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 4169–4176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, P.; Laforge, F.O.; Abeyweera, T.P.; Rotenberg, S.A.; Carpino, J.; Mirkin, M.V. Nanoelectrochemistry of mammalian cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Noël, J.-M.; Velmurugan, J.; Nogala, W.; Mirkin, M.V.; Lu, C.; Guille Collignon, M.; Lemaître, F.; Amatore, C. Nanoelectrodes for determination of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species inside murine macrophages. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 11534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, S.; Nursal, T.Z.; Tarim, A.; Torer, N.; Noyan, T.; Demiroglu, Y.Z.; Moray, G.; Haberal, M. Bacteriological profile and antibiotic resistance: Comparison of findings in a burn intensive care unit, other intensive care units, and the hospital services unit of a single center. J. Burn Care Res. 2005, 26, 488–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauser, A.R.; Rello, J. Severe Infections Caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2012; Volume 7. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, M.; Xu, S.; Chen, F. Enhanced chemiluminescence of the luminol-hydrogen peroxide system by BSA-stabilized Au nanoclusters as a peroxidase mimic and its application. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 3117–3123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.X.; Chen, W.J.; Wu, X.X.; Wu, Y.Y.; Lin, H. Enhanced luminol chemiluminescence by Co–Fe LDH nanoplates and its application in H2O2 and glucose detection. Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 974–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaichi, M.J.; Ehsani, M. Determination of glucose and cholesterol using a novel optimized luminol-CuO nanoparticles-H2O2 chemiluminescence method by box–behnken design. J. Fluoresc. 2015, 25, 861–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Tang, B.; Huang, H.; Yang, G.; Chen, Z.; Li, P.; An, L. Strong red fluorescent probes suitable for detecting hydrogen peroxide generated by mice peritoneal macrophages. Chem. Commun. 2005, 5974–5976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paździoch-Czochra, M.; Wideńska, A. Spectrofluorimetric determination of hydrogen peroxide scavenging activity. Anal. Chim. Acta 2002, 452, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paital, B. A modified fluorimetric method for determination of hydrogen peroxide using homovanillic acid oxidation principle. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, E.W.; Albers, A.E.; Pralle, A.; Isacoff, E.Y.; Chang, C.J. Boronate-based fluorescent probes for imaging cellular hydrogen peroxide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 16652–16659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, M.C.Y.; Pralle, A.; Isacoff, E.Y.; Chang, C.J. A selective, cell-permeable optical probe for hydrogen peroxide in living cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 15392–15393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belousov, V.V.; Fradkov, A.F.; Lukyanov, K.A.; Staroverov, D.B.; Shakhbazov, K.S.; Terskikh, A.V.; Lukyanov, S. Genetically encoded fluorescent indicator for intracellular hydrogen peroxide. Nat. Methods 2006, 3, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, P.; Qin, Y.; Lyu, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y. A hierarchical cobalt/carbon nanotube hybrid nanocomplex-based ratiometric fluorescent nanosensor for ultrasensitive detection of hydrogen peroxide and glucose in human serum. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 1517–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onoda, M.; Uchiyama, T.; Mawatari, K.-I.; Kaneko, K.; Nakagomi, K. Simple and rapid determination of hydrogen peroxide using phosphine-based fluorescent reagents with sodium tungstate dihydrate. Anal. Sci. 2006, 22, 815–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.; Xu, S. Visualizing BPA by molecularly imprinted ratiometric fluorescence sensor based on dual emission nanoparticles. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 92, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Y.; Chen, X.; Lu, Y.; Yang, W. Self-assembled dipeptide–gold nanoparticle hybrid spheres for highly sensitive amperometric hydrogen peroxide biosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 66, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponmozhi, J.; Frias, C.; Marques, T.; Frazão, O. Smart sensors/actuators for biomedical applications: Review. Measurement 2012, 45, 1675–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrilla, M.; Cánovas, R.; Andrade, F.J. Enhanced potentiometric detection of hydrogen peroxide using a platinum electrode coated with nafion. Electroanalysis 2017, 29, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cánovas, R.; Parrilla, M.; Blondeau, P.; Andrade, F.J. A novel wireless paper-based potentiometric platform for monitoring glucose in blood. Lab Chip 2017, 17, 2500–2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizutani, S.; Okumura, Y.; Horio, T.; Iwata, T.; Okumura, K.; Takahashi, K.; Murakami, Y.; Dasai, F.; Ishida, M.; Sawada, K. Development of glutamate sensor for neurotransmitter imaging. Sens. Mater. 2017, 29, 253–260. [Google Scholar]
- Iwata, T.; Mizutani, S.; Okumura, K.; Okumura, Y.; Takahashi, K.; Sawada, K. H2O2 Detection by redox-based potentiometric sensors under biological environments. Sens. Mater. 2018, 30, 2359–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Bai, X.; Wang, X.; Shiu, K.-K.; Zhu, Y.; Jiang, H. Highly sensitive graphene–pt nanocomposites amperometric biosensor and its application in living cell H2O2 detection. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 9459–9465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guler, M.; Turkoglu, V.; Kivanc, M.R. A novel enzymatic glucose biosensor and nonenzymatic hydrogen peroxide sensor based on (3-Aminopropyl) triethoxysilane functionalized reduced graphene oxide. Electroanalysis 2017, 29, 2507–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.X.; Zhang, J.X.; Guo, F.; Zheng, W.; Zhou, H.M.; Wang, B.L.; Zheng, Y.F.; Wang, Y.B.; Cheng, Y.; Lou, X.; et al. A novel amperometric hydrogen peroxide biosensor based on immobilized Hb in Pluronic P123-nanographene platelets composite. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2011, 84, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, Y.; Jia, D.; He, Y.; Miao, Y.; Wu, H.-L. Nano nickel oxide modified non-enzymatic glucose sensors with enhanced sensitivity through an electrochemical process strategy at high potential. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 2948–2952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thenmozhi, K.; Narayanan, S.S. Horseradish peroxidase and toluidine blue covalently immobilized leak-free sol-gel composite biosensor for hydrogen peroxide. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 70, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekar, N.C.; Ge, L.; Mousavi Shaegh, S.A.; Ng, S.H.; Tan, S.N. A mediated turnip tissue paper-based amperometric hydrogen peroxide biosensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 210, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dramińska, S.; Bilewicz, R. Bienzymatic mediatorless sensing of total hydrogen peroxide with catalase and multi-copper enzyme co-adsorbed at carbon nanotube-modified electrodes. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 248, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, T.D. Biosensors: The stabilité problem. Analusis 1999, 27, 630–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oungpipat, W.; Alexander, P.W.; Southwell-Keely, P. A reagentless amperometric biosensor for hydrogen peroxide determination based on asparagus tissue and ferrocene mediation. Anal. Chim. Acta 1995, 309, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campàs, M.; Carpentier, R.; Rouillon, R. Plant tissue-and photosynthesis-based biosensors. Biotechnol. Adv. 2008, 26, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Z.; Li, G.; Liang, J.; Su, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, H.; Huang, Y.; Sui, W.; Zhao, Y. Non-enzymatic electrochemical biosensor based on Pt NPs/RGO-CS-Fc nano-hybrids for the detection of hydrogen peroxide in living cells. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 82, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Bo, X.; Yang, J.; Yin, D.; Guo, L. One-step synthesis of porphyrinic iron-based metal-organic framework/ordered mesoporous carbon for electrochemical detection of hydrogen peroxide in living cells. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 248, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Tang, M.; Zhang, T.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Kong, L.; Xue, Y. Determination of a threshold dose to reduce or eliminate CdTe-induced toxicity in L929 cells by controlling the exposure dose. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovrić, J.; Cho, S.J.; Winnik, F.M.; Maysinger, D. Unmodified cadmium telluride quantum dots induce reactive oxygen species formation leading to multiple organelle damage and cell death. Chem. Biol. 2005, 12, 1227–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.J.; Jana, N.R.; Gao, S.; Patra, P.K.; Ying, J.Y. Surface-ligand-dependent cellular interaction, subcellular localization, and cytotoxicity of polymer-coated quantum dots. Chem. Mater. 2010, 22, 2239–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Yang, L.; Yin, X.; Liu, X.; Ge, L.; Li, F. A facile homogeneous electrochemical biosensing strategy based on displacement reaction for intracellular and extracellular hydrogen peroxide detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 141, 111446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).