Deposition Time and Annealing Effects of ZnO Seed Layer on Enhancing Vertical Alignment of Piezoelectric ZnO Nanowires
Abstract
1. Introduction
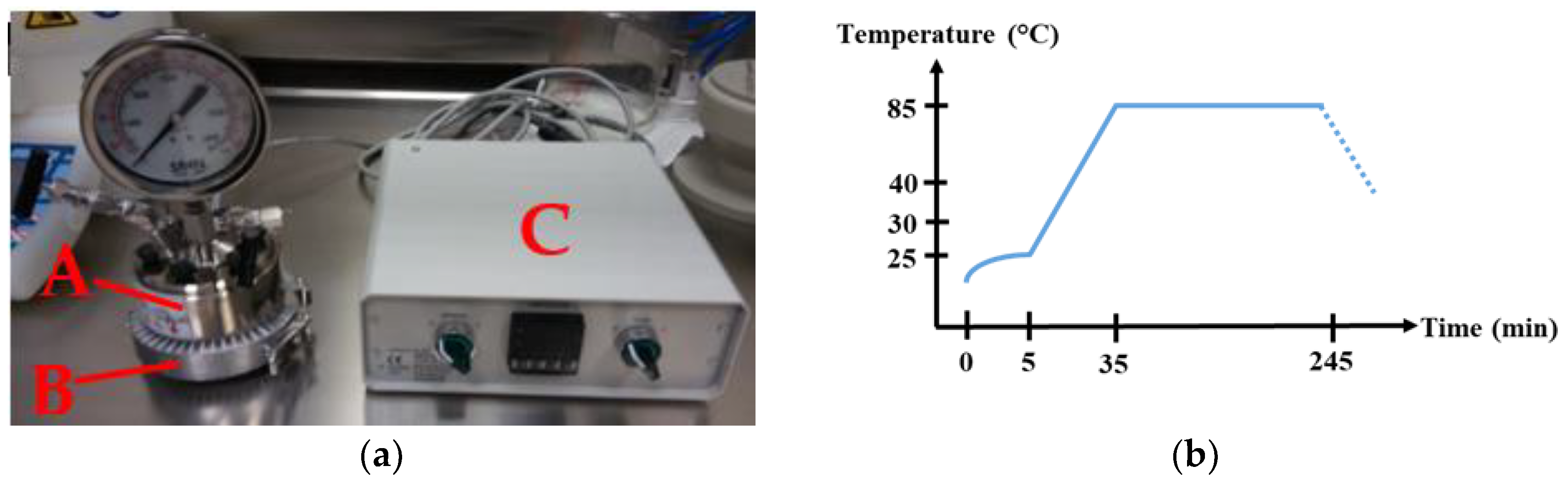
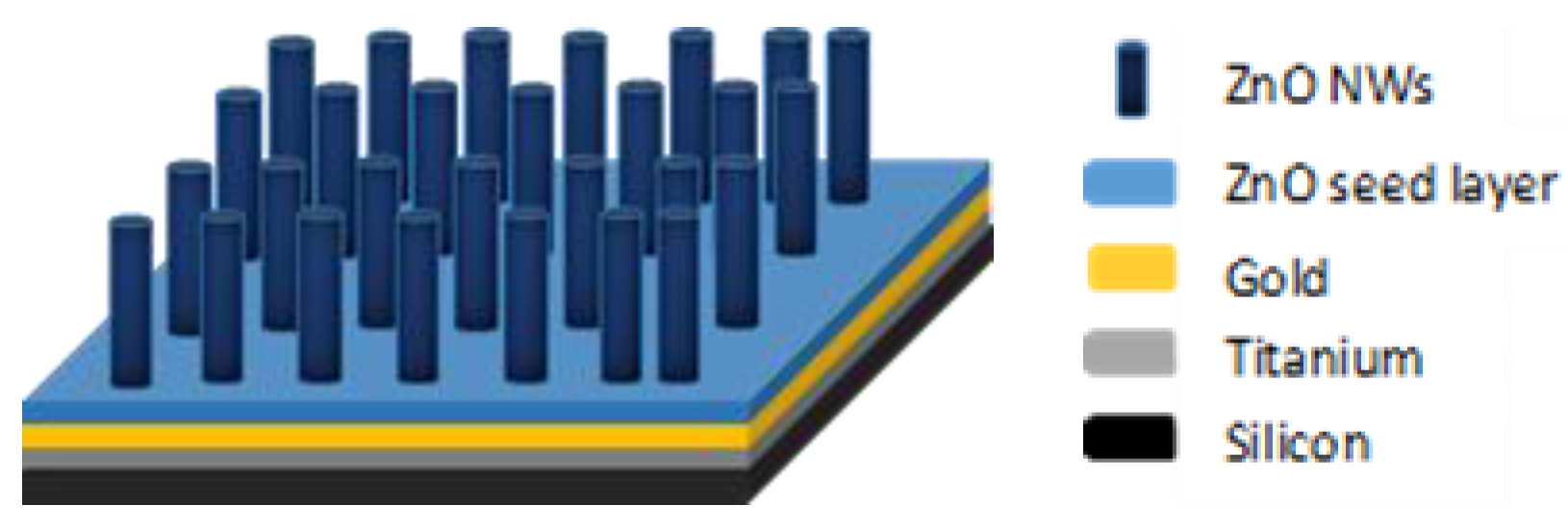
2. Experimental Details
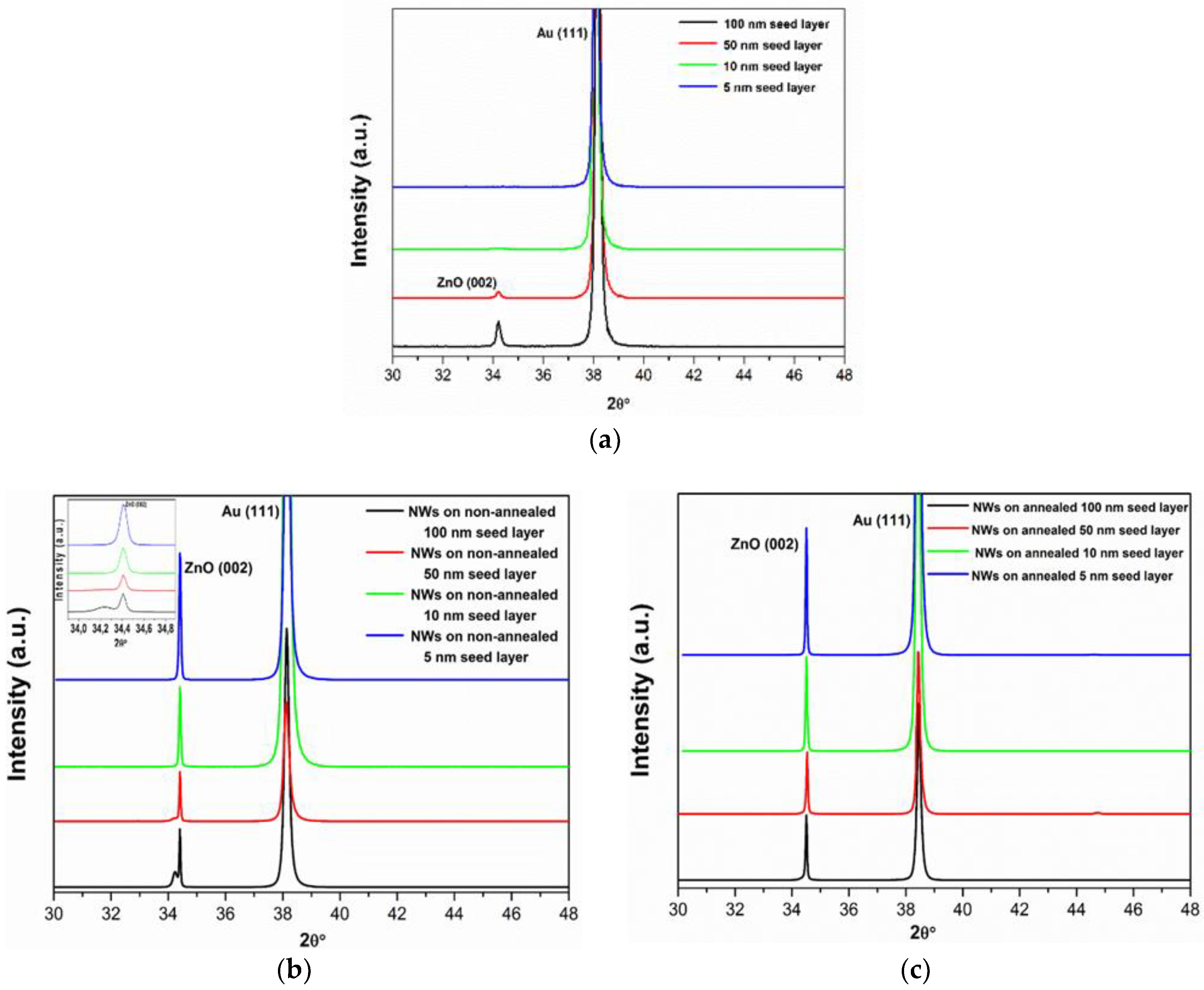
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Z.L.; Song, J. Piezoelectric Nanogenerators Based on Zinc Oxide Nanowire Arrays. Science 2006, 312, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallampati, B.; Nair, S.V.; Ruda, H.E.; Philipose, U. ZnO Nanowire Based Photoconductor with High Photoconductive Gain. Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 2015, 1805, 720–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Z.; She, J.; Deng, S.; Xu, N.; Chen, J. Investigation of the temperature dependent field emission from individual ZnO nanowires for evidence of field-induced hot electrons emission. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2018, 30, 315002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.T.; Raza, S.R.; Jeon, P.J.; Ha, R.; Choi, H.J.; Im, S. Long single ZnO nanowire for logic and memory circuits: NOT, NAND, NOR gate, and SRAM. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 4181–4185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamson, T.L.; Khan, S.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.K.; Yu, Y.; Chen, Z.S.; Xu, H. Patterned synthesis of ZnO nanorod arrays for nanoplasmonic waveguide applications. Opt. Commun. 2018, 411, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiliç, B.; Wang, L.; Ozdemir, O.; Lu, M.; Tüzemen, S. One-Dimensional (1D) ZnO Nanowires Dye Sensitized Solar Cell. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2013, 13, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galstyan, V.; Comini, E.; Ponzoni, A.; Sberveglieri, V.; Sberveglieri, G. ZnO Quasi-1D Nanostructures: Synthesis, Modeling, and Properties for Applications in Conductometric. Chem. Sens. 2016, 4, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Song, J.; Zhou, J.; Wang, Z.L. Piezoelectric and Semiconducting Coupled Power Generating Process of a Single ZnO Belt/Wire. A Technology for Harvesting Electricity from the Environment. Nano Lett. 2006, 6, 1656–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malakooti, M.H.; Patterson, B.A.; Hwang, H.S.; Sodano, H.A. ZnO nanowire interfaces for high strength multifunctional composites with embedded energy harvesting. Energy Environ. Sci. 2016, 9, 634–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, S.; Yang, R.; Ding, Y.; Wang, X.; Bando, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Synthesis of vertically aligned ultra-long ZnO nanowires on heterogeneous substrates with catalyst at the root. Nanotechnology 2012, 23, 055604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falyouni, F.; Benmamas, L.; Thiandoume, C.; Barjon, J.; Lusson, A.; Galtier, P.; Sallet, V. Metal organic chemical vapor deposition growth and luminescence of ZnO micro- and nanowires. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 2009, 27, 1662–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Li, Y.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, Z. Growth of catalyst-free high-quality ZnO nanowires by thermal evaporation under air ambient. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2012, 7, 220–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Ehlert, G.; Sodano, H.A. Increased Interface Strength in Carbon Fiber Composites through a ZnO Nanowire Interphase. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2009, 19, 2654–2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumdar, A.; Singh Butola, B.; Awasthi, N.; Chauhan, I.; Hatua, P. Improving the Mechanical Properties of p-Aramid Fabrics and Composites by Developing ZnO Nanostructures. Polym. Compos. 2017, 39, 3300–3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Z.H.; Chia, Z.X.; Kevin, M.; Wong, A.S.W.; Ho, G.W. A facile approach towards ZnO nanorods conductive textile for room temperature multifunctional sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2010, 151, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opoku, C.; Dahiya, A.S.; Oshman, C.; Daumont, C.; Cayrel1, F.; Poulin-Vittrant, G.; Alquier, D.; Camara, N. Fabrication of high performance field-effect transistors and practical Schottky contacts using hydrothermal ZnO nanowires. Nanotechnology 2015, 26, 355704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Opoku, C.; Dahiya, A.S.; Cayrel, F.; Poulin-Vittrant, G.; Alquier, D.; Camara, N. Fabrication of field-effect transistors and functional nanogenerators using hydrothermally grown ZnO nanowires. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 69925–69931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boubenia, S.; Dahiya, A.S.; Poulin-Vittrant, G.; Morini, F.; Nadaud, K.; Alquier, D. A facile hydrothermal approach for the density tunable growth of ZnO nanowires and their electrical characterizations. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, U.; Santiago, P. Controlling the Morphology of ZnO Nanostructures in a Low-Temperature Hydrothermal Process. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 15317–15321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Huang, X.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Ji, X.; Li, G. Growth and comparison of different morphologic ZnO nanorod arrays by a simple aqueous solution route. Matter. Lett. 2007, 61, 4362–4365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, R.B.M.; De Souza, M.M.; Sankara Narayanan, E.M. A low temperature combination method for for the production of ZnO nanowires. Nanotechnology 2005, 16, 2188–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, C.H.; Whang, W.T. A novel low-temperature growth and characterization of single crystal ZnO nanorods. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2003, 82, 705–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Lim, S. Effect of Seed Layer on the Growth of ZnO Nanorods. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 596–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.W.; Peng, S.M.; Wu, J.S.; Shih, W.S.; Wu, C.S.; Tang, I.T. Effect of seed layer on the growth of well-aligned ZnO nanowires. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2009, 70, 1359–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghayour, H.; Rezaie, H.R.; Mirdamadi, S.; Nourbakhsh, A.A. The effect of seed layer thickness on alignment and morphology of ZnO nanorods. Vacuum 2011, 86, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.Y.; Yeh, C.C.; Ting, J.M. Effects of Seed Layer Characteristics on the Synthesis of ZnO Nanowires. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2009, 92, 2718–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malakooti, M.H.; Zhou, Z.; Sodano, H.A. Enhanced energy harvesting through nanowire based functionally graded interfaces. Nano Energy 2018, 52, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malakooti, M.H.; Zhou, Z.; Spears, J.H.; Shankwitz, T.J.; Sodano, H.A. Biomimetic nanostructured interfaces for hierarchical composites. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 2, 1500404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamieniecki, E.; Foggiato, G. Analysis and contol of electrically active contaminants by surface charge analysis. In Handbook of Semiconductor Wafer Cleaning Technology: Science, Technology and Applications; Werner Kern Associates: Westwood, NJ, USA, 1993; pp. 497–535. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.; Qin, Y.; Xu, C.; Wei, Y.; Yang, R.; Wang, Z.L. Self-powered nanowire devices. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2010, 5, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenanakis, G.; Vernardou, D.; Koudoumas, E.; Katsarakis, N. Growth of c-axis oriented ZnO nanowires from aqueous solution: The decisive role of a seed layer for controlling the wires’ diameter. J. Cryst. Growth 2009, 311, 4799–4804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ram, M.K.; Stefanakos, E.K.; Yogi Goswami, D. Synthesis, Characterization, and Applications of ZnO Nanowires. J. Nanomater. 2012, 624520, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Lao, C.; Weintraub, B.; Wang, Z.L. Density-controlled growth of aligned ZnO nanowire arrays by seedless chemical approach on smooth surfaces. J. Mater. Res. 2008, 23, 2072–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.-H.; Hu, J.; Li, S.-S.; Zhang, F.; Liu, J.; Shi, J.; Li, X.; Tian, Z.-Q.; Chen, Y. Improved seedless hydrothermal synthesis of dense and ultralong ZnO nanowires. Nanotechnology 2011, 22, 245601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugunan, A.; Warad, H.C.; Boman, M.; Dutta, J. Zinc oxide nanowires in chemical bath on seeded substrates: Role of hexamine. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2006, 39, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Narasimulu, A.A.; Garcia-Gancedo, L.; Fu, Y.Q.; Soin, N.; Shao, G.; Luo, J.K. Novel ZnO Nanorod Films by Chemical Solution Deposition for Planar Device Applications. Nanotechnology 2013, 24, 275601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strano, V.; Urso, R.G.; Scuderi, M.; Iwu, K.O.; Simone, F.; Ciliberto, E.; Spinella, C.; Mirabella, S. Double Role of HMTA in ZnO Nanorods Grown by Chemical Bath Deposition. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 28189–28195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govender, K.; Boyle, D.S. Understanding the factors that govern the deposition and morphology of thin film of ZnO from aqueous solution. J. Mater. Chem. 2004, 14, 2575–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skompska, M.; Zarębska, K. Electrodeposition of ZnO Nanorod Arrays on Transparent Conducting Substrates. Electron. Acta 2014, 127, 467–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupan, O.; Pauporté, T.; Chow, L.; Viana, B.; Pellé, F.; Ono, L.K.; Roldan Cuenya, B.; Heinrich, H. Effects of annealing on properties of ZnO thin films prepared by electrochemical deposition in chloride medium. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 256, 1895–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-W.; Wu, J.-M. Nucleation mechanisms and their influences on characteristics of ZnO nanorod arrays prepared by a hydrothermal method. Acta Mater. 2011, 59, 841–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.; Lee, J.; Lim, S. Annealing effects of ZnO nanorods on dye-sensitized solar cell efficiency. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2010, 405, 2593–2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.Y.; Kim, S.W.; Yoo, D.H.; Kim, E.J.; Hahn, S.H. Annealing Effect of ZnO Seed Layer on Enhancing Photocatalytic Activity of ZnO/TiO2 Nanostructure. Int. J. Photoenergy 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillemin, S.; Consonni, V.; Appert, E.; Puyoo, E.; Rapenne, L.; Roussel, H. Critical nucleation effects on the structural relationship between ZnO seed layer and nanowires. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 25106–25111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahiya, A.S.; Morini, F.; Boubenia, S.; Nadaud, K.; Alquier, D.; Poulin-Vittrant, G. Organic/Inorganic hybrid stretchable piezoelectric nanogenerators for self-powered wearable electronics. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2017, 3, 1700249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinchet, R.; Lee, S.; Ardila, G.; Montès, L.; Mouis, M.; Wang, Z.L. Performance Optimization of Vertical Nanowire-based Piezoelectric Nanogenerators. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 971–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Qiu, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Guo, Z.; Song, W.; Xu, J.; Zong, Y.; Feng, Q.; Sun, X. Patterned growth of ZnO nanowires on flexible substrates for enhanced performance of flexible piezoelectric nanogenerators. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2017, 110, 063901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
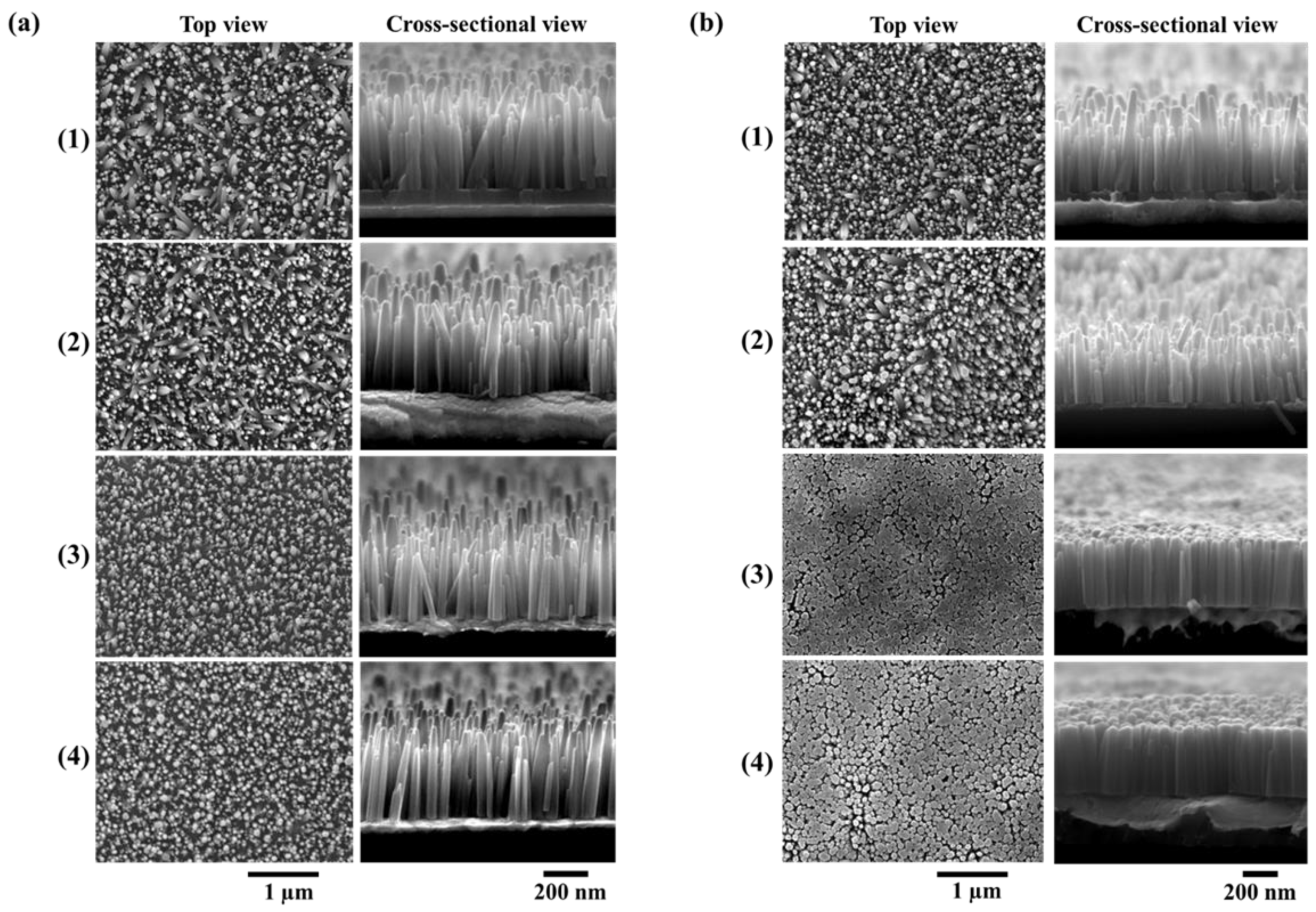
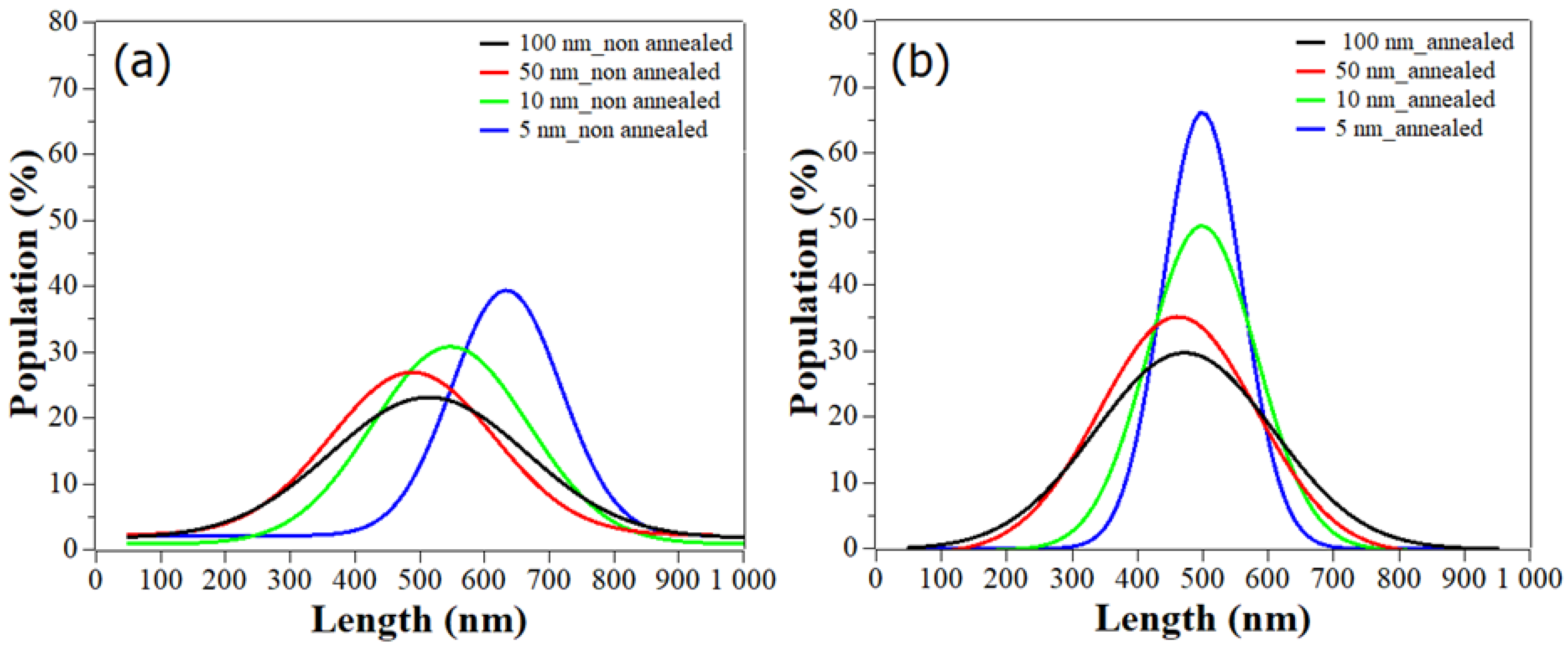
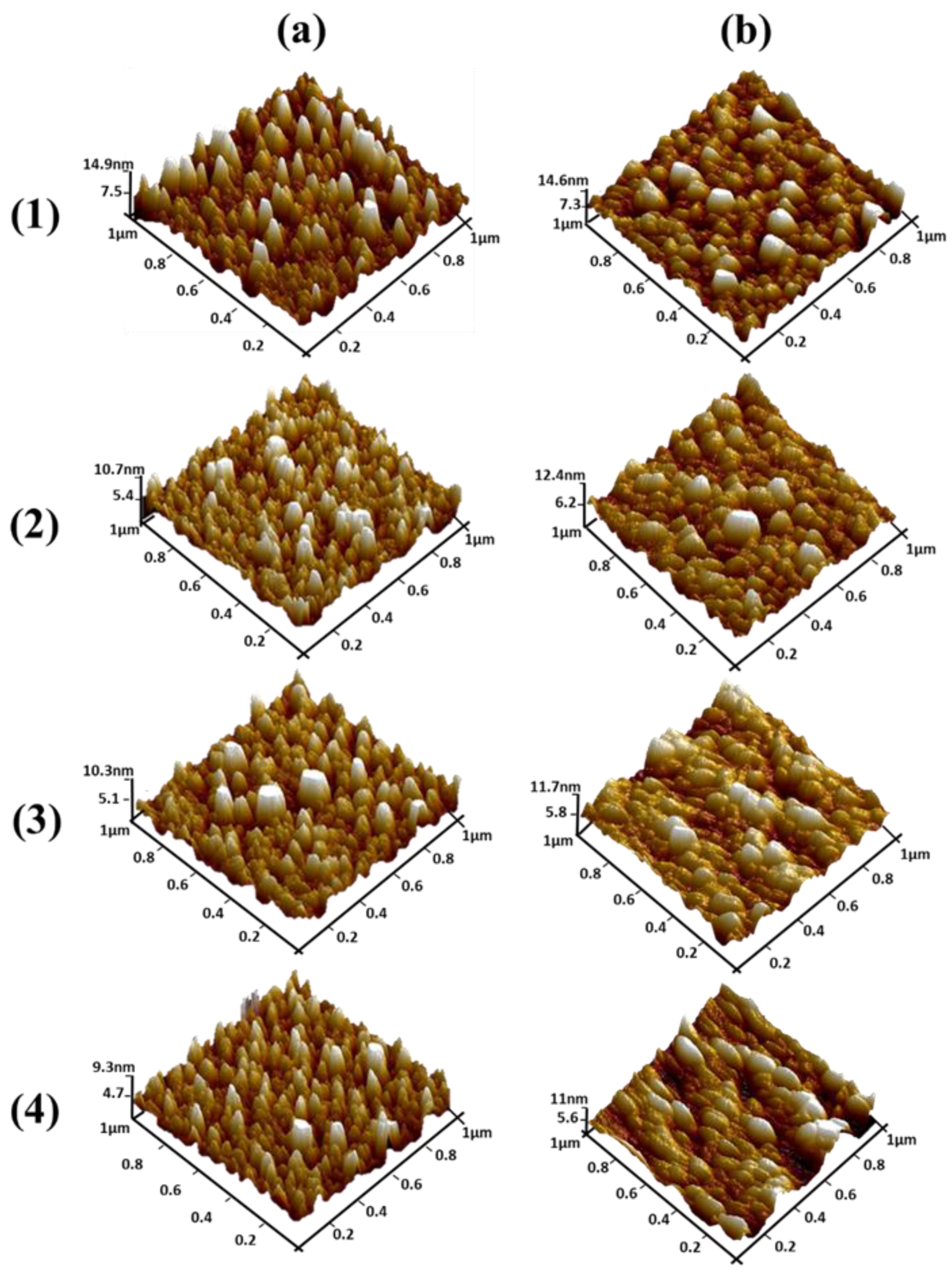
| Deposition time | 1 min 36 s | 3 min 12 s | 16 min | 32 min |
| Thickness obtained | 5 nm | 10 nm | 50 nm | 100 nm |
| Seed layer state | Non annealed | Non annealed | Non annealed | Non annealed |
| Annealed | Annealed | Annealed | Annealed |
| Thickness of Seed Layer (nm) | NWs Density (NWs/cm²) | NWs Mean Diameter (nm) | NWs Mean Length (nm) | NWs Aspect Ratio L/d | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-annealed seed layer | 100 | 35 ± 1.8 | 70 ± 30 | 570 ± 180 | 8 |
| 50 | 45 ± 2.3 | 60 ± 30 | 530 ± 160 | 8 | |
| 10 | 52 ± 2.6 | 60 ± 20 | 570 ± 130 | 10 | |
| 5 | 54 ± 2.7 | 70 ± 30 | 620 ± 130 | 9 | |
| Annealed seed layer | 100 | 50 ± 2.5 | 70 ± 30 | 490 ± 130 | 8 |
| 50 | 52 ± 2.6 | 60 ± 30 | 460 ± 100 | 7 | |
| 10 | 73 ± 3.7 | 80 ± 20 | 440 ± 60 | 6 | |
| 5 | 71 ± 3.5 | 90 ± 20 | 480 ± 40 | 6 |
| Thickness of Seed Layer (nm) | FWHM for Non-Annealed NWs (nm) | FWHM for Annealed NWs (nm) |
|---|---|---|
| 100 nm | 400 | 325 |
| 50 nm | 333 | 291 |
| 10 nm | 308 | 208 |
| 5 nm | 216 | 150 |
| Thickness of Seed Layer (nm) | Roughness for Non-Annealed Seed Layer (nm) | Roughness for Annealed Seed Layer (nm) |
|---|---|---|
| 100 nm | 2.50 | 2.86 |
| 50 nm | 1.73 | 2.07 |
| 10 nm | 1.62 | 1.66 |
| 5 nm | 1.48 | 1.58 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Slimani Tlemcani, T.; Justeau, C.; Nadaud, K.; Poulin-Vittrant, G.; Alquier, D. Deposition Time and Annealing Effects of ZnO Seed Layer on Enhancing Vertical Alignment of Piezoelectric ZnO Nanowires. Chemosensors 2019, 7, 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors7010007
Slimani Tlemcani T, Justeau C, Nadaud K, Poulin-Vittrant G, Alquier D. Deposition Time and Annealing Effects of ZnO Seed Layer on Enhancing Vertical Alignment of Piezoelectric ZnO Nanowires. Chemosensors. 2019; 7(1):7. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors7010007
Chicago/Turabian StyleSlimani Tlemcani, Taoufik, Camille Justeau, Kevin Nadaud, Guylaine Poulin-Vittrant, and Daniel Alquier. 2019. "Deposition Time and Annealing Effects of ZnO Seed Layer on Enhancing Vertical Alignment of Piezoelectric ZnO Nanowires" Chemosensors 7, no. 1: 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors7010007
APA StyleSlimani Tlemcani, T., Justeau, C., Nadaud, K., Poulin-Vittrant, G., & Alquier, D. (2019). Deposition Time and Annealing Effects of ZnO Seed Layer on Enhancing Vertical Alignment of Piezoelectric ZnO Nanowires. Chemosensors, 7(1), 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors7010007







