Abstract
Waste from zinc−carbon batteries poses a serious environmental protection problem. One of the main problems is also the reliable and rapid determination of some compounds that may be present in food and beverages consumed worldwide. This study addresses these problems and presents a possible solution for the electrochemical detection of xanthine using carbon from spent batteries. Cyclic voltammetry and differential pulse voltammetry are electrochemical methods used for the detection of xanthine. The techniques used demonstrate the mechanism of xanthine oxidation in the tested environment. A linear correlation was found between the oxidation current peaks and the xanthine concentration in the range of 5·10−7 to 1·10−4 M, as well as the values for the limit of detection and the limit of quantification, 7.86·10−8 M and 2.62·10−7 M, respectively. The interference test shows that the electrode obtained from waste Zn-C batteries has good selectivity, which means that the electrode can be used for xanthine determination in the presence of various ions. The data obtained show that carbon sensors from used zinc−carbon batteries can be used to detect xanthine in real samples.
1. Introduction
Carbon-based sensor electrodes have been widely researched and proven to be efficient for the determination of numerous elements and compounds, such as antibiotics [1], vitamins [2], organic and inorganic environmental pollutants such as dyes and pesticide compounds, 4-nitrophenol, tetracycline, diazinon, and heavy metals [3,4]. They include a wide range of materials with the same chemical composition but very different structures and properties. For example, carbon comes in the form of diamond, graphite, graphene, and carbon nanotubes, and there are sensor electrodes based on all these carbon structures [1,3], and even graphene-based nanomaterials derived from banana pulp biomass [5] or activated carbon from Theobroma cocoa pods [6]. The most commonly used electrodes are modified glassy carbon electrodes [5,6,7,8,9,10,11], carbon paste electrodes [2,4], carbon nanotube-modified electrodes [12,13], graphene and graphene oxide electrodes [14,15,16], amorphous carbon-diamond-like carbon (DLC) and carbon nitride (CNx) electrodes [17], and ordered mesoporous and macroporous carbon materials [18]. An increasing number of studies have focused on the reuse and upcycling of waste materials, and one promising strategy for waste batteries is the use of recovered graphite as a sensor electrode. A graphite rod from zinc−carbon batteries has been tested for the detection of L-tryptophan [19] and tannic acid [20]. A graphite rod modified with Au (CG/Au electrode) was designed for the parallel electrochemical monitoring of dopamine and uric acid [21]. A graphite electrode modified with gold nanoparticles/polynicotinic acid (AuNPs/poly(NA)-BGE) was used as a bifenazate (BF) sensor [22]. A sensor based on a graphite electrode from recycled batteries with a surface modified by multi-walled carbon nanotubes and electropolymerized hippuric acid (Poly(HA)/MWCNTs/BGE) was used to detect serotonin [23]. Two possible electrodes obtained from waste batteries, graphite rods, and carbon paste electrodes, were developed as nitrate-ion selective electrodes [24], and graphite rods from spent zinc−carbon batteries modified with bismuth nanoparticles (BiNP), multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNT), and Nafion were used for the determination of Cd2+ and Pb2+ in herbal supplements [25]. A graphite and carbon nanotube composite electrode modified with tartrazine (TZ/GP-CNTCPE), for which graphite powder was obtained from used batteries, was tested for dopamine analysis [26]. Graphene oxide and zinc oxide obtained from waste batteries are used to modify a glassy carbon electrode (GCE) as a sensor for the detection of bisphenol A [27]. Electrochemically reduced graphene oxide (ERGO) films deposited on GCE, where graphene oxide is prepared from graphite obtained from discharged Zn-C batteries, can enable the efficient determination of paracetamol and hydroquinone [28]. In this paper, the results for the detection of xanthine using a graphite rod obtained from a zinc−carbon battery are presented.
Kapri et al. [29] consider xanthine (3,7-dihydropurine-2,6-dione) to be the most widely distributed heterocyclic aromatic compound. The xanthine ring is present in numerous natural and synthetic compounds and forms the backbone of many alkaloids. In nature, it is found in plants such as tea, coffee, and cocoa. Natural xanthine derivatives (caffeine, theobromine, and theophylline) are frequently used in traditional medicine. The xanthine ring serves as the basic scaffold for the synthesis of numerous nitrogen-containing drugs that exhibit various pharmacological effects in the respiratory tract, heart, smooth muscle cells, central nervous system (CNS), kidney, and stomach.
Xanthine can be formed during the breakdown of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) via two pathways: from guanine by guanine deaminase and from hypoxanthine by xanthine oxidoreductase or xanthine oxidase. The end product of the purine degradation cycle, in which xanthine is formed and degraded, is uric acid, which is excreted in urine [30,31].
The importance of monitoring xanthine concentrations in clinical conditions and food is summarized in a review published by Dervisevic et al. [30]. Monitoring xanthine concentration in meat can be an indicator of meat freshness, which is important for maintaining product quality and consumer health. Lin et al. [32] present an interesting solution for real-time monitoring of xanthine content in fish, which can provide information on whether the fish is safe to use, which in turn can contribute to the safety of human health and reduce food waste. Alterations in purine metabolism can be associated with various diseases, such as xanthinuria, hyperuricemia, gout, Parkinson’s disease, inflammatory arthritis, perinatal asphyxia, and obstructive sleep apnea syndrome, and in these cases, xanthine concentrations are clinically relevant [30].
In addition, xanthines are used in the treatment of various diseases due to their antihistaminic, antimicrobial, antituberculous, neurological, cytotoxic effects on cancer cells, cholinergic, anticancer, antiasthmatic, antidiabetic, antiepileptic, and analgesic effects. They have numerous applications as bronchodilators, mild stimulants, phosphodiesterase inhibitors, adenosine receptor antagonists, (CFTR) chloride channel activators, and in the treatment of depression, anxiety, cognitive impairment, ischemic disorders, and schizophrenia. In addition, some xanthine derivatives are considered potential agents against Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinsonism, and they also exhibit anti-obesity activity [29,31].
The importance of the detection and determination of xanthine has led to several reviews on sensors for xanthine detection. For example, Dervisevic et al. [30] discussed sensors based on nanomaterials, while Pundir and Devi [33] focused on biosensors. Recently, Ahlawat et al. [34] discussed advances in both sensors and biosensors for xanthine detection, while Moutcine et al. [35] presented results on chemically modified electrodes with different compositions as sensors for xanthine and uric acid detection. The results of numerous studies on xanthine detection using modified carbon-based electrodes are listed in Table 1. There is a wide range of options for both the base electrode materials and modifiers. However, to the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to use a graphite rod from a waste Zn-C battery for this purpose.
2. Experimental
Xanthine (XA) (Sigma Aldrich, Hamburg, Germany), acetic acid (Zorka Šabac, Jelenča, Serbia), orthoboric acid (Zorka Šabac, Serbia), and phosphoric acid (Merck, Skopje, North Macedonia) were used for the preparation of the Britton−Robinson buffer solution (BR). Sodium hydroxide (NRK Inženjering, Belgrade, Serbia) was used to adjust the pH of the working solution. Glutamic acid (Sigma Aldrich, Germany), caffeine (Merck, Darmstadt, Germany), cysteine (Sigma Aldrich, Germany), histidine (Sigma Aldrich, Germany), potassium chloride (Merck, Skopje, North Macedonia), and sodium chloride (VWR Prolabo, Leuven, Belgium) were used to prepare the solution for the interference study. All chemicals used were of p.a. purity.
All tests were performed at least three times at room temperature. The results shown are the average values of the measurements. Electrochemical measurements were performed using a potentiostat (IVIUM XRE, IVIUM Technologies, Eindhoven, The Netherlands) with appropriate software in a three-electrode system. The working electrode was fabricated from a recycled graphite rod originating from a zinc–carbon battery, while a platinum rod and a saturated calomel electrode functioned as the auxiliary and reference electrodes, respectively.
The graphite electrode was prepared using a graphite rod obtained from a spent zinc−carbon battery. The graphite rod was removed, cleaned, and dried to remove moisture. After drying, the graphite rod was polished with silicon carbide paper (200, 400, 1000, and 2000) and rinsed with water and alcohol. The graphite rod was then glued to the copper wire with silver glue and sealed with a methyl methacrylate-based material. The prepared graphite working electrode was polished with aluminum oxide paste (0.3 μm Al2O3, Buehler, Lake Bluff, IL, USA), rinsed with distilled water, and air-dried after each measurement.
Cyclic voltammetry (CV) and differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) were used as electrochemical methods to investigate the sensor properties of the graphite electrode for xanthine detection. Cyclic voltammetry measurements were carried out in the potential range from 0.2 V vs. SCE to 1.5 V vs. SCE at different scan rates (5–200 mV/s) in the BR solution at pH = 3 with the addition of 1·10−3 M XA. Differential pulse voltammetry measurements were conducted within the potential range from 0.2 V vs. SCE to 1.5 V vs. SCE, at a pulse amplitude of 50 mV, a pulse time of 20 ms, a potential step of 5 mV, and a scan rate of 50 mV/s in a wide range of XA concentrations (5·10−7–1·10−4 M). The structure and crystallinity of the graphite rod obtained from waste Zn−C batteries were analyzed using X-ray diffraction (XRD). XRD analysis was performed using a Rigaku MiniFlex 600 instrument with Cu-Kα radiation (λ = 0. l5406 nm) for 2θ = 3–90°, and D/teXUltra 250 high-speed detector and X-ray tube with a copper anode. The scanning speed was 10°/min. The voltage of the X-ray tube was set to 40 kV.
Real samples of beer, cola, green tea, and cocoa were prepared using supplies purchased from the local market. Real samples were filtered before further examination using differential pulse voltammetry. Prior to analysis, each sample was diluted 10-fold with Britton−Robinson buffer, and varying amounts of xanthine were introduced to obtain different concentration levels (2·10−5 M, 5·10−5 M, and 8·10−5 M). Differential pulse voltammetry measurements were performed on the previously prepared real samples.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. XRD Characterization
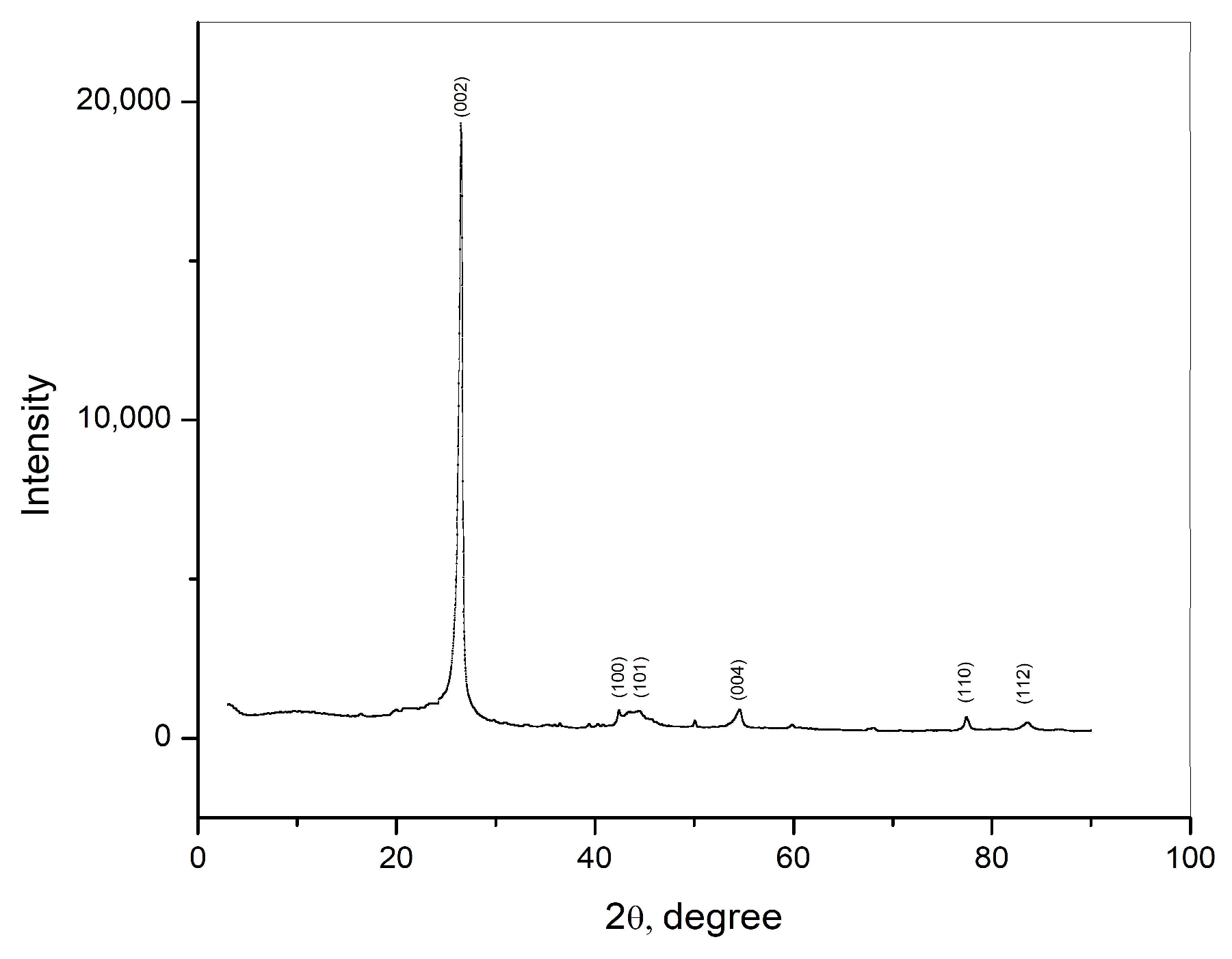
The crystal structure of the carbon rod was examined using XRD, and the obtained results are shown in Figure 1. The detected diffraction peaks correspond to the (002), (100), (101), (004), (110), and (112) diffraction planes of the graphite structure of the sample. The diffraction peak corresponding to the (002) diffraction planes is a characteristic peak for graphite. This peak is narrow and sharp, indicating high crystallinity of the sample.
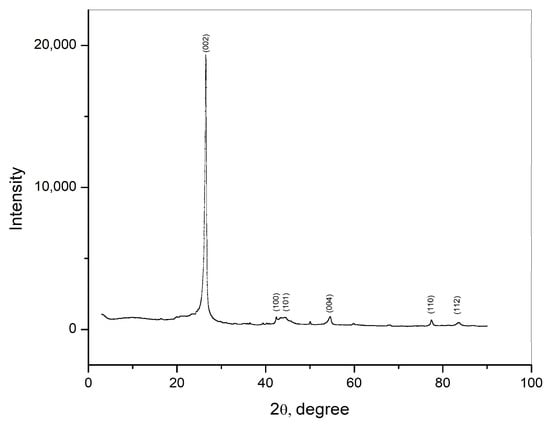
Figure 1.
XRD pattern of graphite obtained from waste Zn—C battery.
3.2. Electrochemical Behavior of the Xanthine
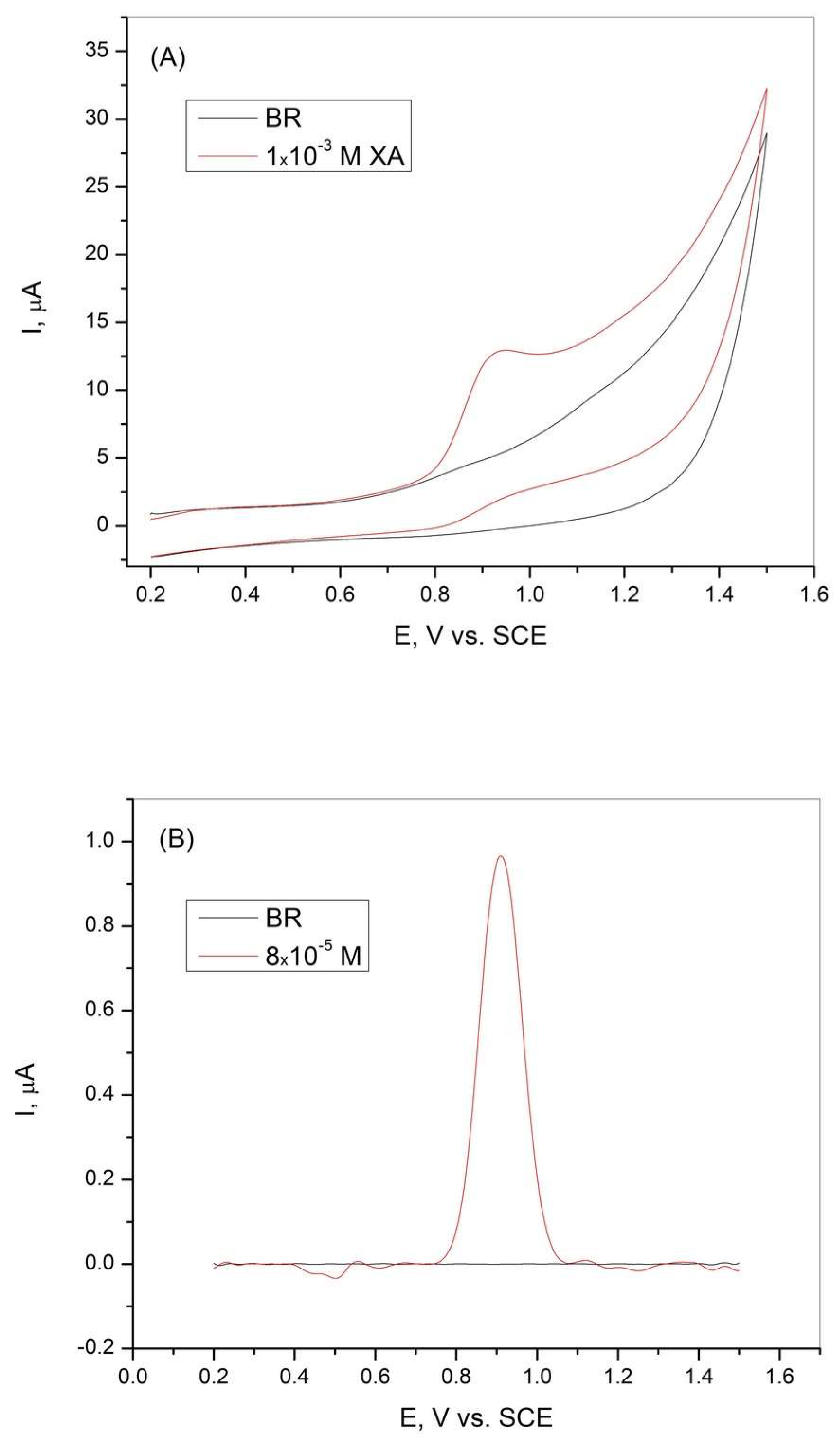
To determine the electrochemical behavior of xanthine at the graphite electrode, cyclic voltammetry and differential pulse voltammetry were performed in BR buffer solution at pH = 3, with and without the addition of XA. The results are shown in Figure 2. The CV curves shown in Figure 2A indicate an oxidation current peak in the presence of XA, suggesting the oxidation of XA. The absence of a reduction peak in the cyclic voltammogram indicates that the oxidation of XA is an irreversible process. The curves obtained during the DPV measurements (Figure 2B) showed a sharp current peak in the presence of XA, which can be attributed to the high sensitivity of the graphite electrode tested, which was made from graphite rods from a spent battery.
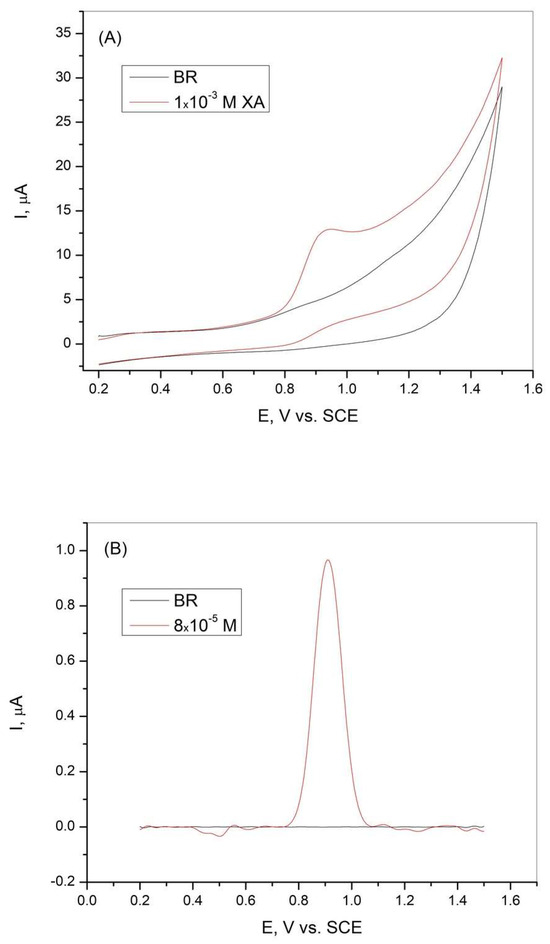
Figure 2.
(A) Cyclic voltammetry curves and (B) differential pulse voltammetry curves of the graphite electrode obtained in Britton−Robinson buffer solution in the absence and presence of xanthine. pH = 3, scan rate = 50 mV/s.
3.3. Effect of pH
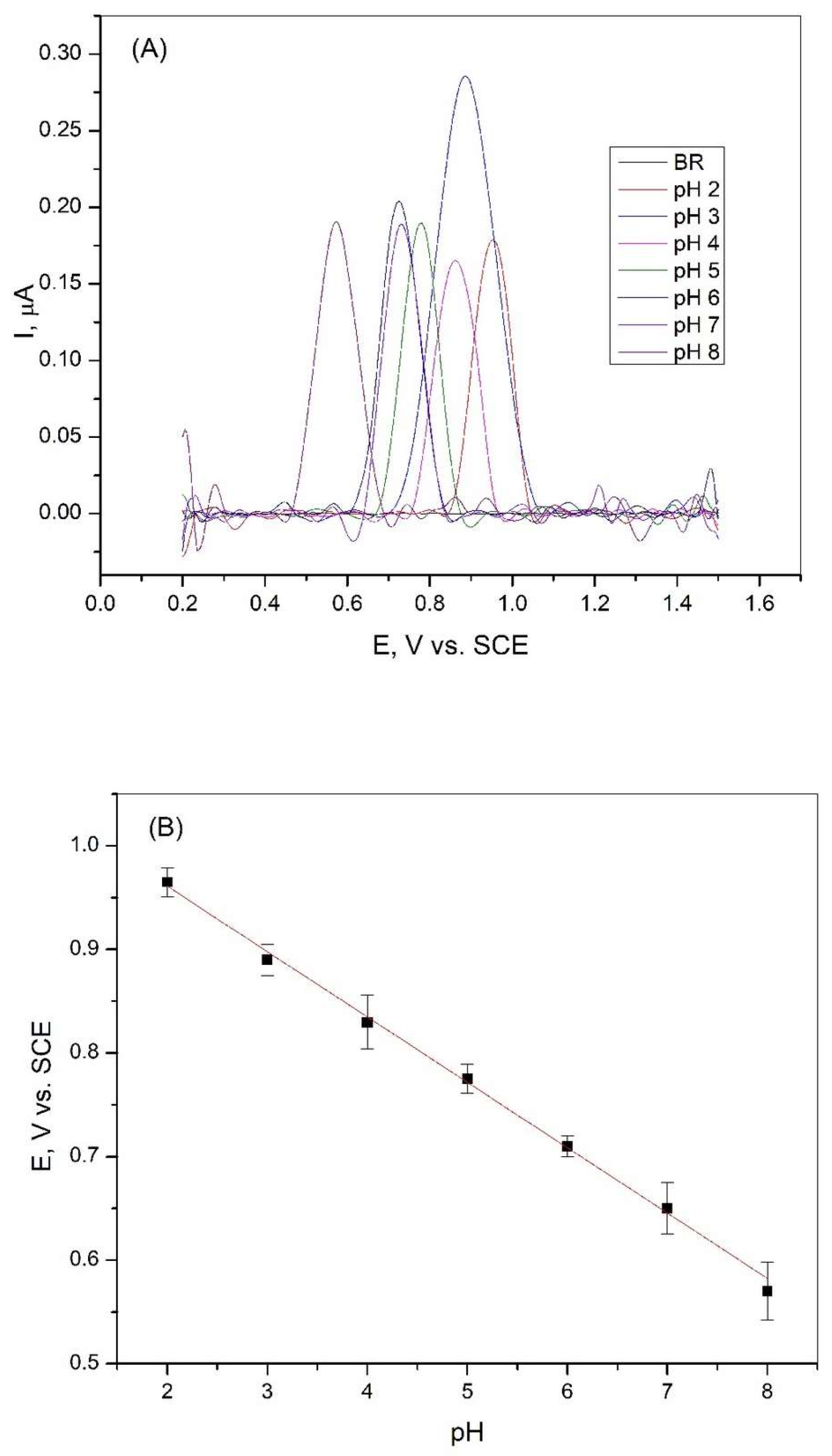
The effect of the pH value of the Britton−Robinson solution on the peak intensity, which correlates with the oxidation of xanthine, was carried out in a wide range from pH = 2.0 to pH = 8.0. Differential pulse voltammetry measurements were performed in the BR solution with and without the addition of xanthine. The results of these experiments are shown in Figure 3A. It can be seen from the figure that the intensity of the xanthine oxidation peak in BR solution varies at different pH values. The electrochemical oxidation response in BR buffer exhibits pH-dependent peak potential shifts. The highest oxidation peak was reached in the Britton−Robinson solution at pH = 3, and this solution was used for further studies. Figure 3B shows that the potential of the peak decreases with increasing pH in the observed range. This shift in the peak potential values indicates that protons were involved in the reactions that occurred during the oxidation of xanthine [36].
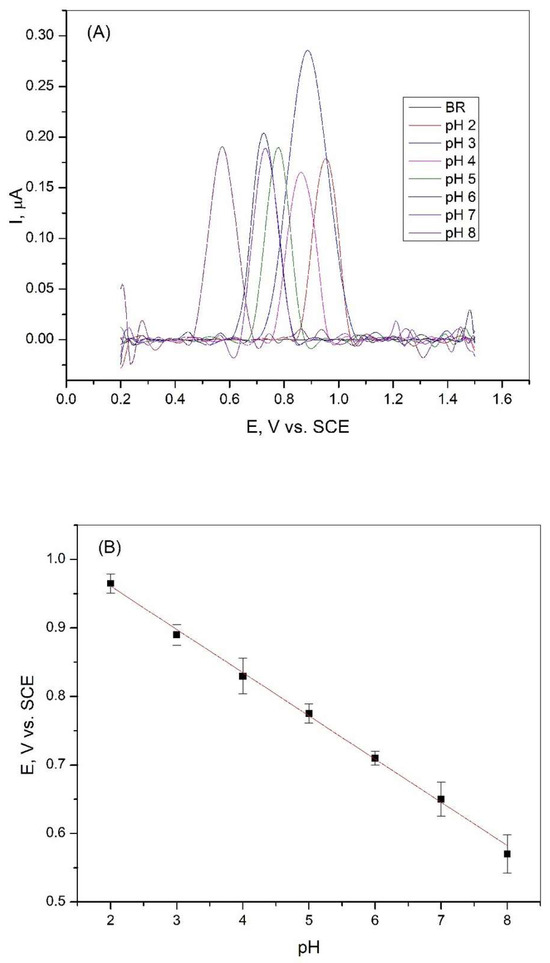
Figure 3.
(A) Differential pulse voltammetry curves of 2∙10−6 M XA on a graphite electrode in Britton−Robinson buffer solution at different pH values, scan rate 50 mV/s; (B) Dependence of the peak potential of 2∙10−6 M XA on the pH value of the Britton−Robinson buffer solution (R2 = 0.9977).
The linear relationship between the peak potential and pH is expressed by the following equation:
According to Equation (1), the calculated ratio of the number of protons to electrons is 1.07, indicating that the same number of protons and electrons were involved in the electrochemical reaction of xanthine oxidation at the graphite electrode.
3.4. Effect of Scan Rate
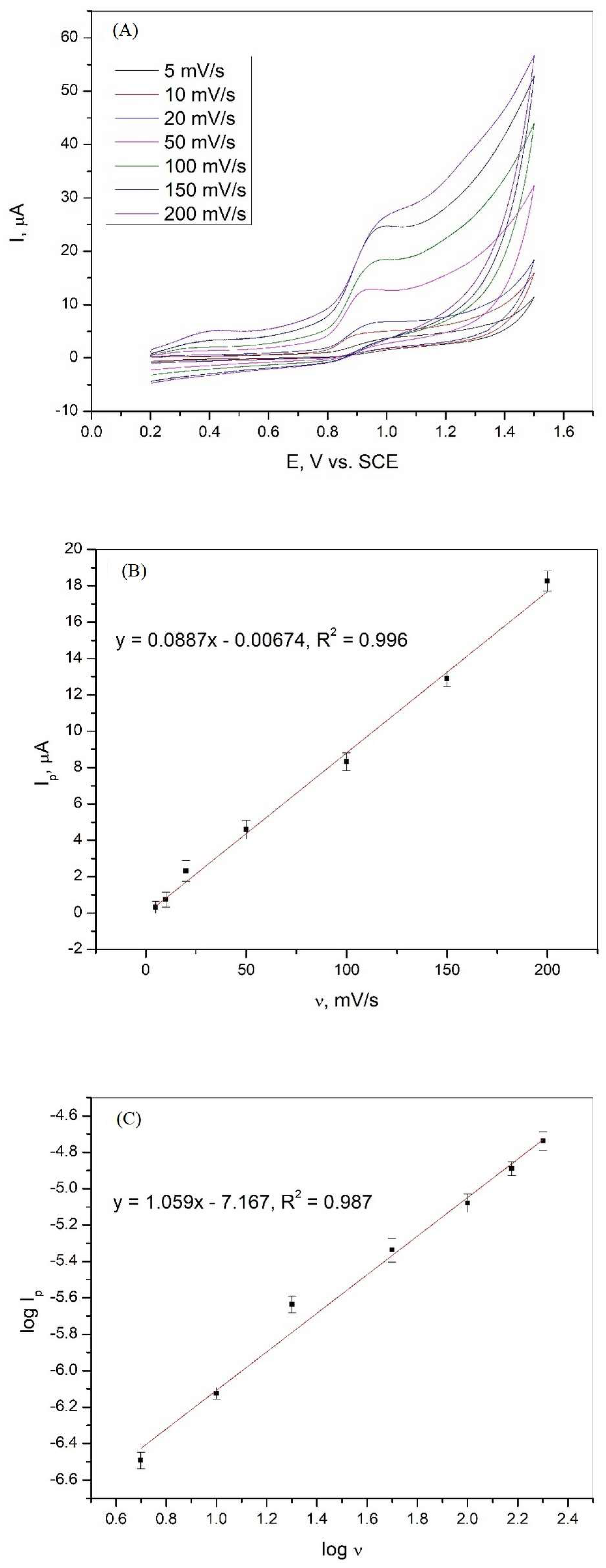
The changes in the oxidation peak current of XA as a function of the scan rate were evaluated using cyclic voltammetry, and the obtained curves are shown in Figure 4A. It can be seen that the current peak is affected by the scan rate in the range of 5 to 200 mV/s. To show that the oxidation of xanthine is controlled by diffusion or adsorption, the relationships between Ip and v and log Ip and log v were analyzed. The dependencies and linear relationships obtained are shown in Figure 4B,C. Equations (2) and (3) show the linear relationships between Ip and v and log Ip and log v with the regression coefficient.
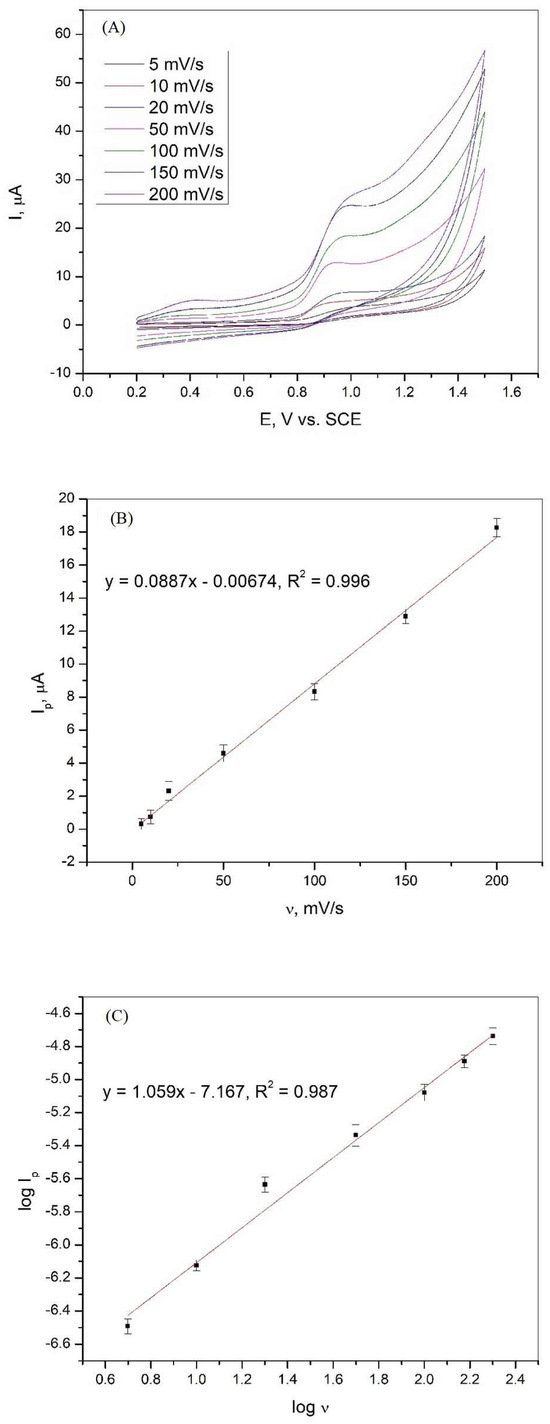
Figure 4.
(A) Cyclic voltammetry curves of 1·10−3 M xanthine on a graphite electrode in Britton−Robinson buffer solution (pH 3) at various scan rates; (B) dependence of the peak current of xanthine on the various scan rates; (C) dependence of the logarithm of the peak current of xanthine on the logarithm of the various scan rates.
The strong linear relationship between Ip and v indicates that adsorbed species are involved in the electrochemical oxidation of xanthine at the graphite electrode. The linear relationship between log Ip and log v and the slope of the curve, which has a value close to unity, confirms that the oxidation of XA is an adsorption-controlled process [37,38,39].
3.5. Oxidation of Xanthine
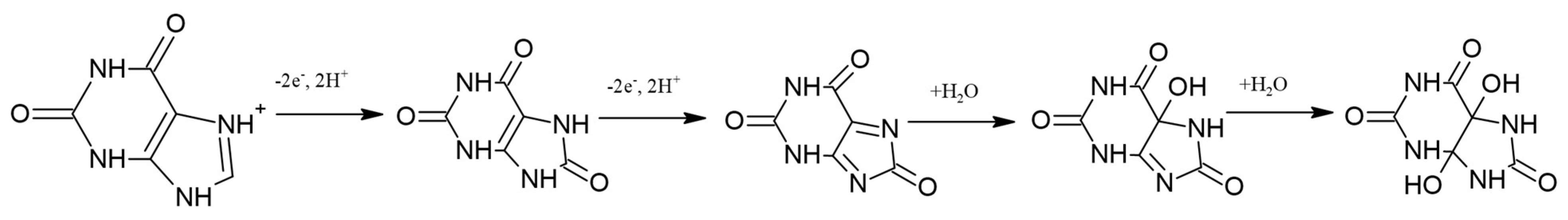
As illustrated in Figure 4A, the cyclic voltammograms recorded in Britton−Robinson buffer solution containing 1·10−3 M XA show that the oxidation process of xanthine is irreversible, since only the oxidation peak is present without the corresponding reduction peak. In the BR buffer solution at pH = 3, xanthine is present as positively charged ions (pKa = 7.45). The process of xanthine oxidation can be explained by the occurrence of electrochemical and chemical reactions in the solution [40]. The electrochemical process involves the transfer of two electrons and two protons to form uric acid. Uric acid immediately oxidizes to the intermediate diimine via a two-electron/two-proton reaction mechanism. The overall reaction of xanthine oxidation involves the participation of 4e− and 4H+ [41]. The intermediate diimine is a highly reactive compound that reacts with an H2O molecule to form an imine alcohol intermediate, which in turn reacts with another H2O molecule to form uric acid-4,5-diol [42]. These reactions are chemical and occur in solution. The entire reaction mechanism of xanthine oxidation, proposed by combining electrochemical and literature [40,41,42] data, can be described using the reactions shown in Figure 5.
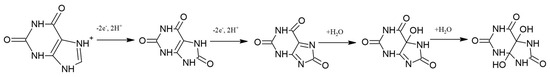
Figure 5.
Oxidation mechanism of xanthine.
3.6. Differential Pulse Voltammetry Determination of Xanthine on Graphite Electrode
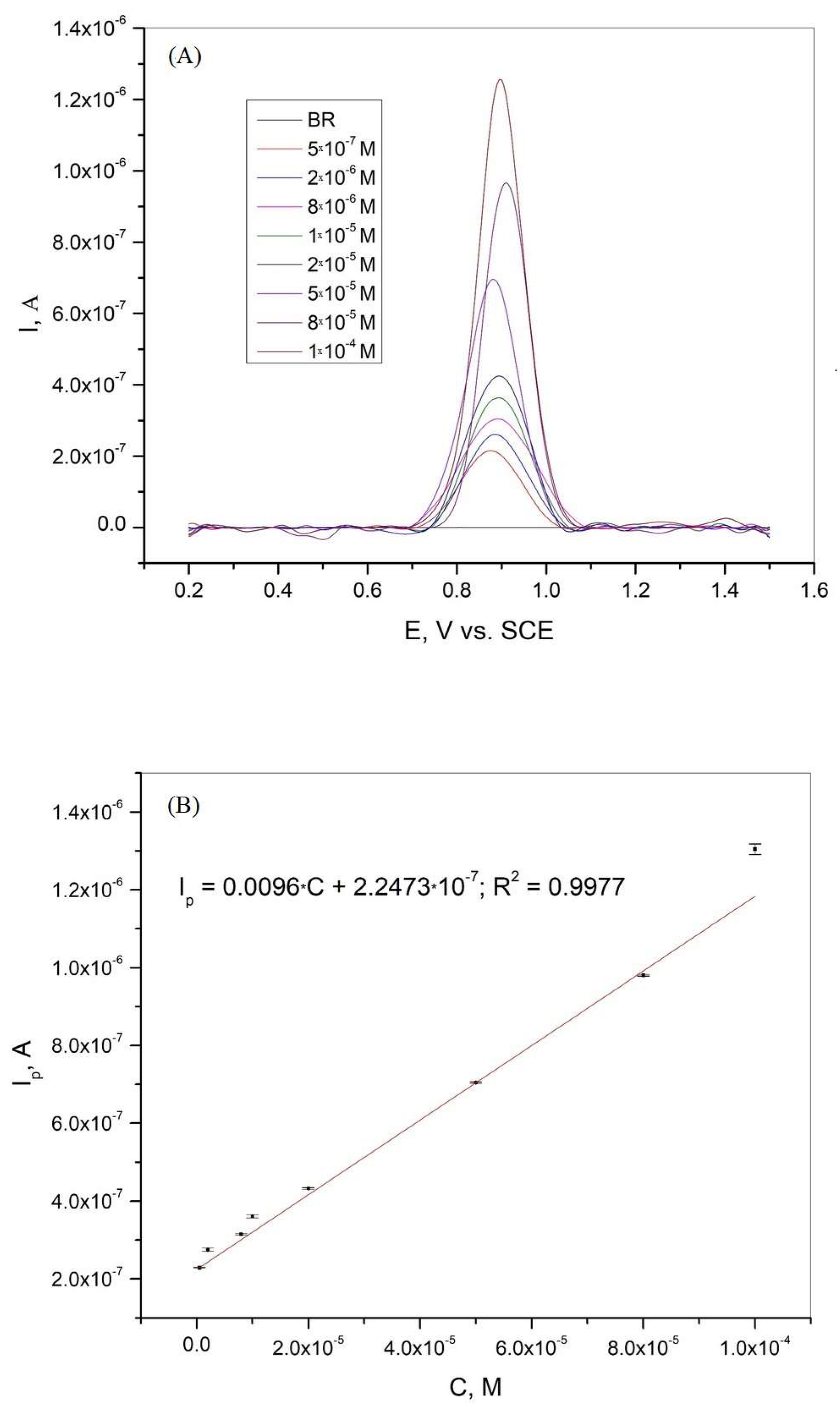
Differential pulse voltammetry was used as one of the most suitable analytical methods to determine the calibration curve, limit of detection (LOD), and limit of quantification (LOQ) for xanthine in the BR buffer solution. Figure 6A shows the differential pulse voltammogram of xanthine at different concentrations in BR buffer solution at pH = 3. The calibration curve obtained from the DPV results is presented in Figure 6B. A linear correlation between the current peaks and concentration was obtained in the range of 5·10−7 to 1·10−4 M. The regression equation with a linear relative coefficient is as follows:
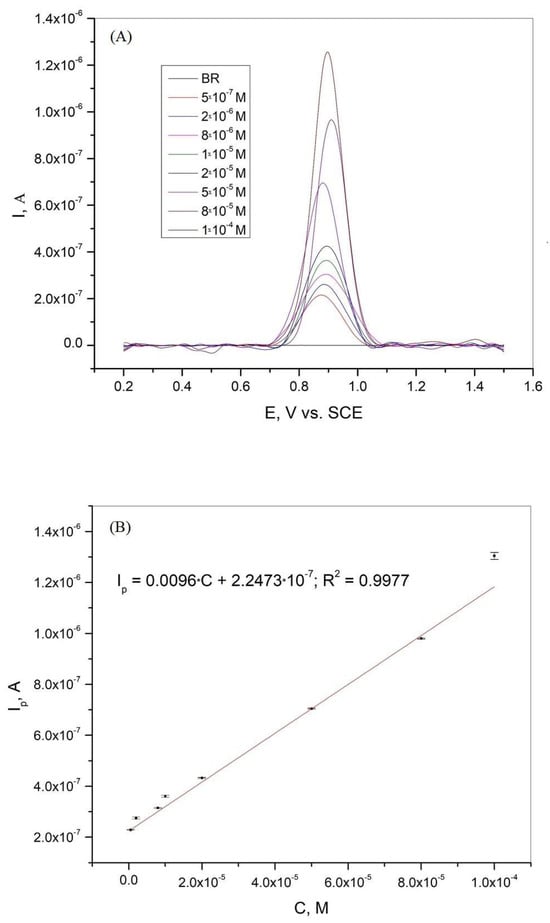
Figure 6.
(A) Differential pulse voltammogram of xanthine on graphite electrode in BR solution at pH 3.0, scan rate 50 mV/s; (B) Calibration curve for xanthine in the concentration range 5·10−7–1·10−4 M. The mean values of the three measurements are presented with the corresponding error bars.
The limit of detection (LOD) and limit of quantification (LOQ) were determined according to the following equations [19,43]:
where S is the standard deviation of the peak currents and m is the slope of the calibration curve. The LOD and LOQ values were 7.86·10−8 M and 2.62·10−7 M, respectively. As shown in Figure 6A, the peak potential changed slightly in the presence of different xanthine concentrations. This variation in the peak potential values can be attributed to the complex oxidation mechanism [19,44]. The combination of the complex electrochemical and chemical oxidation processes and the formation of adsorbed products leads to the variation of the peak potential values in the presence of different xanthine concentrations in BR solution at pH = 3.

Table 1.
Results achieved during differential pulse voltammetry determination of xanthine and xanthine derivatives in different solutions according to literature data.
Table 1.
Results achieved during differential pulse voltammetry determination of xanthine and xanthine derivatives in different solutions according to literature data.
| Electrode | Method | Analyte | Media | LOD | Linear Range | Real Sample | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pt@MIL-101(Cr)/GCE | DPV | XA + UA, HX, DA | 0.1 M PBS, pH 7 | 0.42 μM | 0.5–162 μM | human serum | [45] |
| Poly(l-methionine) modified GCE | DPV | XA + UA, HX | 0.1 M PBS, pH 7.2 | 0.004 μM | 0.02–0.1 μM | blood serum sample | [46] |
| NiO/MWCNT/NNaM/PGE | DPV | XA + TP, TB | BR, pH 2.0 | 0.077 μM | 0.5–150 μM | chocola-te black tea human urine | [47] |
| MWCNT-AuNP-CCE | DPV | XA + UA, CF | 0.1 M PBS, pH 6.0 | 63 nM | 2.5–300 μM | human serum urine | [48] |
| KH/GTD/XOD/CHT modified GCE | DPV | XA | 0.1 M PBS, pH 7 | 0.0215 μmol/L | 0.5–18 μmol/L | [49] | |
| CNF-CPE | DPV | XA + HX, UA | 0.1 M PBS, pH 6.0 | 0.5 μM | 1.5 μM to 218 μM | urine samples | [50] |
| DPV | XA + UA, HX | 0.1 M PBS, pH 7.0 | 0.083 μmol/L | 0.5–140 μmol/L | human serum | ||
| P(L-Arg)/GPE | DPV | XA + UA | 0.1 M PBS pH 6.0 | 10.36 × 10−7 M | 10 to 138 μmol/L 139 to 330 μmol/L | fish meat | [51] |
| PTA/CeO2@Pt/GCE | DPV | XA + CF | 0.2 M PBS pH 5.0 | 10 nM | 0.1–100 μM | urine blood | [7] |
| P-g-C3N4@ GCE | DPV | XA + HX, UA | PBS pH 7.2 | 0.93 μM | 15–40 μM | Sea food | [8] |
| CuO nanostructures prepared with 1 mL sugar molasses/GCE | DPV | XA | 0.1 M BR, pH 5 | 0.264 μM | 1.0–12.0 μM | fish | [9] |
| GCE/ACCP | DPV | XA + UA | 0.1 M BR, pH 4 | 0.547 μM | 5–10 μM, 10–49.5 μM, and 49.5–327.1 μM | urine | [6] |
| 0.08 Co/UiO-66/GCE | DPV | XA + HA | 0.1 M PBS, pH 8.0 | 0.24 μM | 1–900 μM | meat | [10] |
| p(g42T-TT)-based enzymatic biosensors | DPV | XA | PBS | 27.4 nM | 0.5–1 μM | Rohu Fish Extract | [32] |
| Graphite electrode | DPV | XA | BR, pH 3 | 7.86·10−8 M | 5·10−7–1·10−4 M | Beer, Cola drink | This research |
XA—xanthine; HX—hypoxanthine; UA—uric acid; DA—dopamine; TB—theobromine; TP—theophylline; CF—caffeine; PBS—phosphate buffer solution; BR—Britton−Robinson buffer solution; DPV—differential pulse voltammetry; Pt@MIL-101(Cr)/GCE—GCE modified with a Cr-based metal-organic framework MIL-101(Cr) loaded with platinum nanoparticles (PtNPs); NiO/MWCNT/NNaM/PGE—pencil graphite electrode (PGE) modified with a composite solution including NiO nanoparticles, multi-walled carbon nanotube (MWCNT), and natural nano-Na-montmorillonite clay (NNaM); MWCNT-AuNP-CCE—thiol-functionalized sol-gel-based carbon ceramic electrode (CCE) modified by immobilizing gold nanoparticles (AuNP) in the thiol-functionalized ceramic matrix and incorporating multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNT) within the pores of this ceramic sol-gel; KH/GTD/XOD/CHT modified GCE—xanthine oxidase (XOD) immobilized onto the chitosan (CHT) modified electrode by cross-linking with glutaraldehyde (GTD) and 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane (KH); CNF-CPE—carbon paste electrode modified by carbon nanofibers; P(L-Arg)/GPE—poly L-Arginine flexible graphene platform electrode; PTA/CeO2@Pt / GCE—cerium dioxide (CeO2) composite platinum (Pt) and polymer 3-amino-5-mercapto-1,2,4-triazole (PTA) deposited on GCE; P-g-C3N4@ GCE—phosphorous doped g-C3N4 (P-g-C3N4) modified GCE; GCE/ACCP—GCE modified by activated carbon from cocoa pods (Theobroma cacao); p(g42T-TT)-based enzymatic biosensors, organic electrochemical transistor (OECT)-based biosensor integrates a thin film of the p-type conjugated polymer p(g42T-TT) as the channel material and XOD as the biorecognition element, p-type conjugated polymer, p(g42T-TT).
The results presented in Table 1 show that, according to the literature data, predominantly modified glassy carbon electrodes and some carbon paste and pencil graphite electrodes have been investigated as electrochemical sensors for the determination of xanthine and xanthine derivatives. The graphite electrodes obtained from used batteries have not yet been tested as electrochemical sensors for xanthine determination. According to the results shown in Table 1, the graphite electrode produced from a waste Zn-C battery shows satisfactory results in the determination of xanthine compared to the results obtained in the reviewed literature, with a low LOD and wide linear range.
3.7. Interference Studies
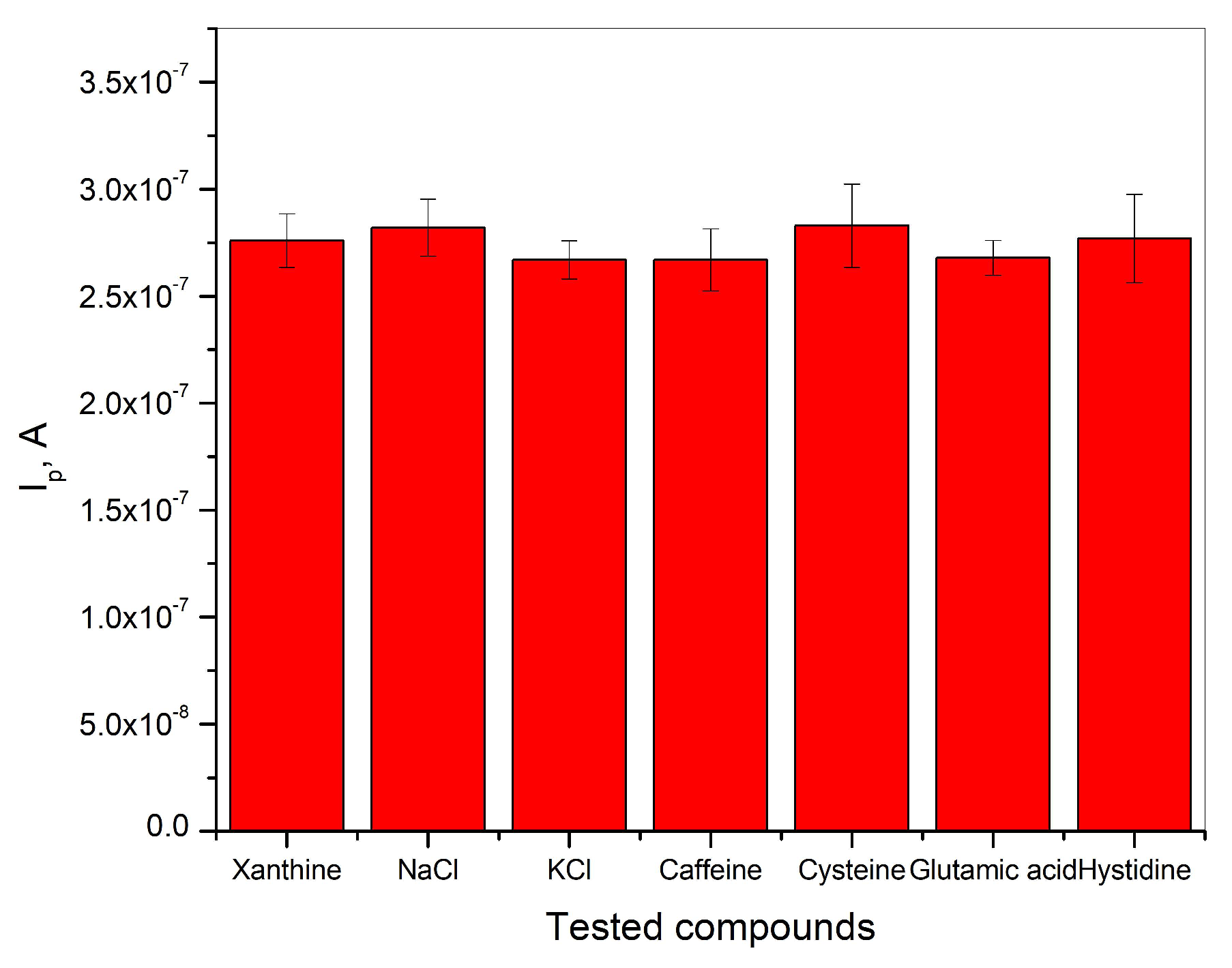
The determination of xanthine in BR buffer solution was carried out in the presence of a 100-fold excess concentration of NaCl, KCl, caffeine, cysteine, glutamic acid, and histidine in the presence of 2∙10−6 M xanthine. The results shown in Figure 7 indicate that the analytical signal for the detection of xanthine remains unchanged in the presence of the tested compounds, and the relative error is below ±5%. This indicates that the tested compounds have no negative influence on the detection of xanthine in BR buffer solution at pH = 3. The investigated electrode shows good selectivity, which leads to the graphite electrode obtained from waste batteries being considered as a good electrochemical sensor for the determination of xanthine in real samples.
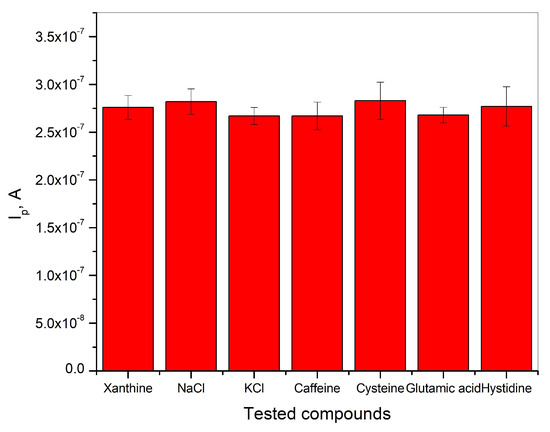
Figure 7.
Selectivity of graphite electrode for the detection of xanthine in Britton−Robinson buffer solution at pH = 3.
3.8. Real Sample Analysis
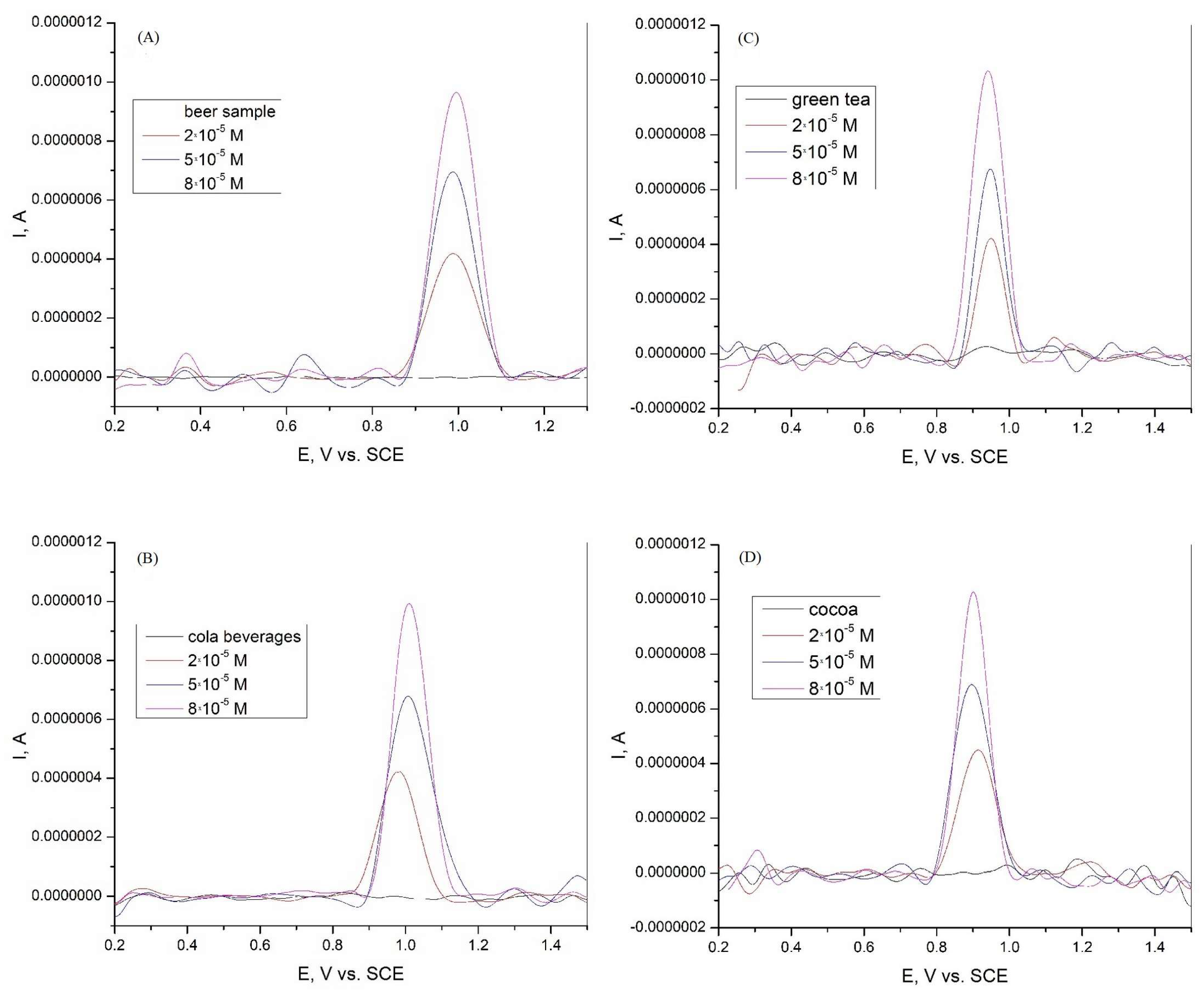
The graphite electrode obtained from spent batteries was tested for the determination of xanthine in real samples. Because xanthine could not be detected in the beer and cola samples, a certain amount of XA was added. Xanthine was added in concentrations of 2·10−5, 5·10−5, and 8·10−5 M in beer, cola beverage, green tea, and cocoa samples. Differential pulse voltammetry tests were then performed to determine the xanthine content. The results are presented in Figure 8 and Table 2. The graphite electrode used, which was obtained from used batteries, shows a good recovery in the range of 99.1 to 101.0% and a relative standard deviation (RSD) in the range of 0.82 to 2.55 for the beer sample. The electrode also shows a good recovery in the range of 98.5 to 101.8% with an RSD in the range of 3.04 to 5.05. For the green tea sample, the electrode showed a recovery in the range of 97.1 to 98.5% and an RSD in the range of 7.02 to 9.87. For the cocoa sample, the recovery of the electrode was in the range of 97.6 to 101.3%, with an RSD between 3.34 and 4.08. According to the results obtained, the graphite electrode can be used for the detection and determination of xanthine in various real-world samples.
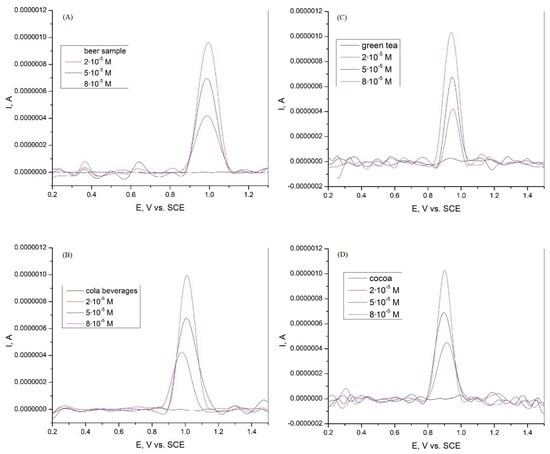
Figure 8.
Differential pulse voltammogram of xanthine in (A) beer sample in Britton−Robinson buffer solution at graphite electrode; (B) Cola beverages sample in Britton−Robinson buffer solution at graphite electrode; (C) green tea sample in Britton−Robinson buffer solution at graphite electrode; and (D) cocoa sample in Britton−Robinson buffer solution at graphite electrode.

Table 2.
Determination of xanthine in beer, cola beverages, green tea, and cocoa samples in Britton−Robinson buffer solutions at a graphite electrode (N = 3).
3.9. Stability and Repeatability of the Graphite Electrode
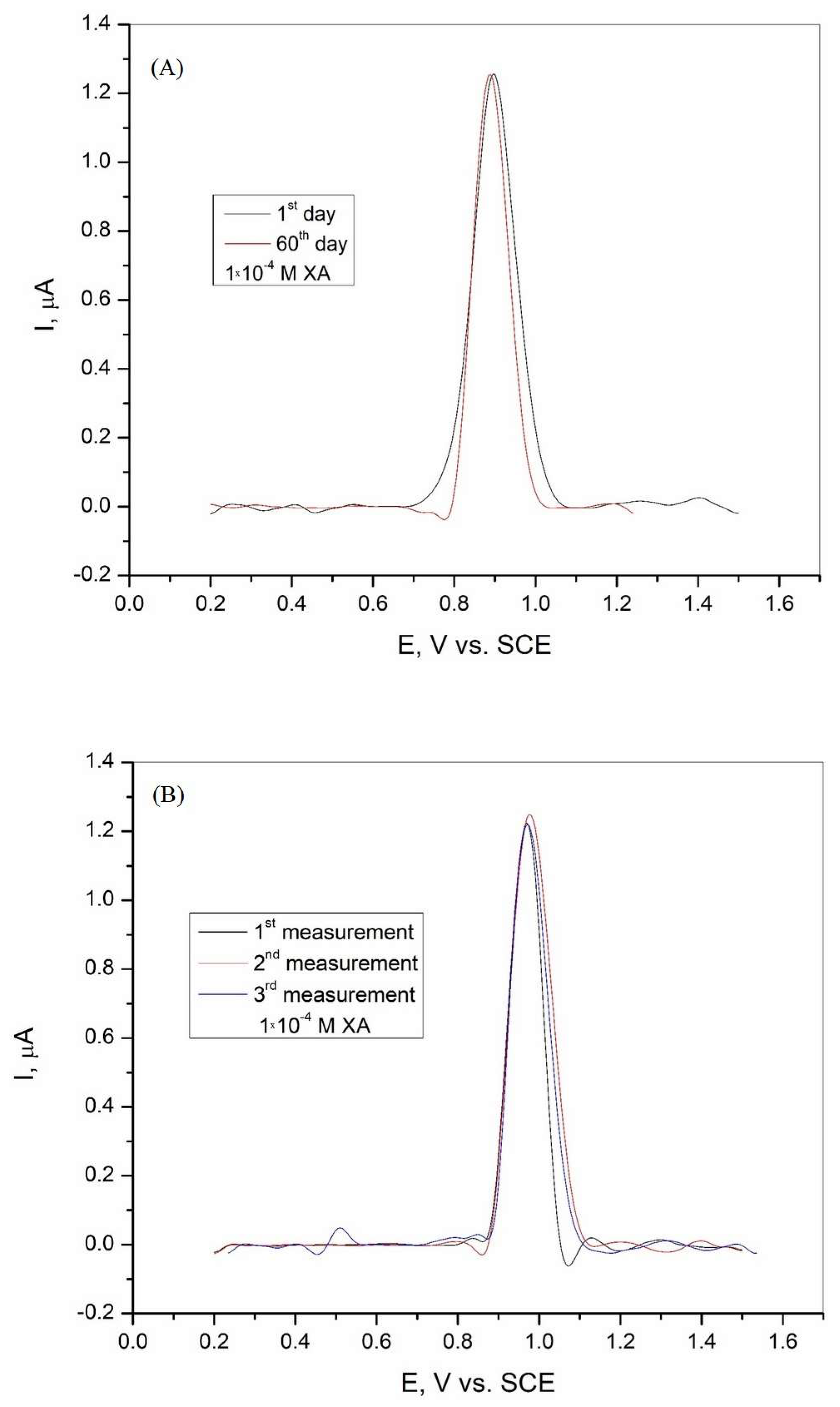
The electrode can be reused because it is suitable for multiple consecutive measurements with polishing and rinsing to obtain a clean and fresh surface. The stability of the graphite electrode was investigated in Britton−Robinson buffer solution with the addition of 1·10−4 M xanthine after 60 days, and the results are shown in Figure 9A. The tested electrode shows good stability with a current peak of 103.82% and an RSD of 1.87% after 60 days. The repeatability of the sensor was analyzed by three repeated measurements in BR buffer solution in the presence of 1·10−4 M xanthine. The DPV curves obtained are shown in Figure 9B, and the results show that the graphite electrode has good repeatability, with a calculated RSD of 0.63%.
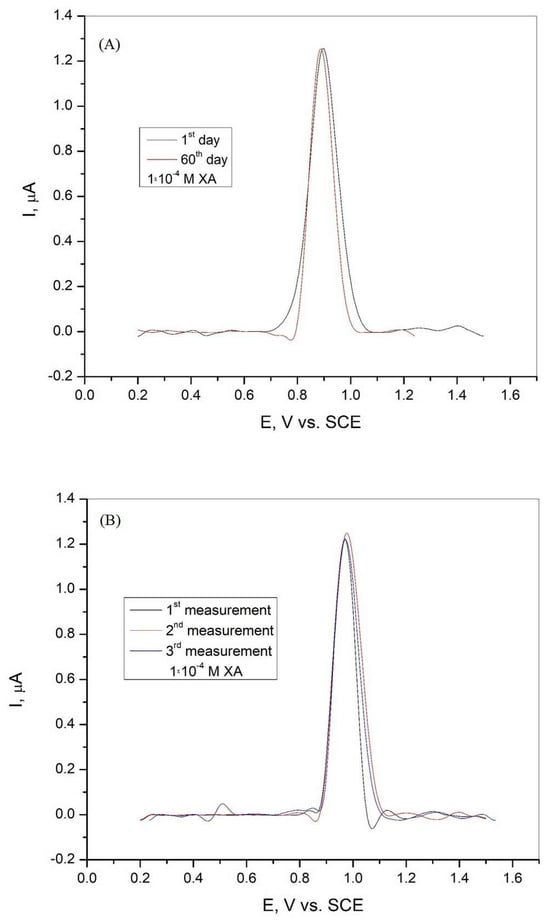
Figure 9.
(A) Differential pulse voltammogram of the graphite electrode after 60 days in Britton−Robinson buffer solution (pH = 3) with the addition of 1·10−4 M xanthine and (B) differential pulse voltammogram of the graphite electrode recorded during three consecutive measurements in Britton−Robinson buffer solution (pH = 3) with the addition of 1·10−4 M xanthine.
4. Conclusions
This work deals with the possibility of using a graphite electrode obtained from used batteries as an electrochemical sensor for the detection and determination of xanthine in Britton−Robinson buffer solution. According to the experimental results obtained by cyclic voltammetry and differential pulse voltammetry, the tested graphite electrode shows good sensor properties for the determination of xanthine in BR solution as well as in various real samples. Cyclic voltammetry shows that the oxidation of xanthine in the tested solution at pH = 3 is an irreversible process. The oxidation of xanthine is a complex process consisting of electrochemical and chemical mechanisms, with an equal number of protons and electrons involved in the electrochemical reaction. The differential pulse voltammetry measurements show that the graphite electrode produced has good sensitivity suitable for the determination of xanthine in Britton−Robinson buffer solution. The results show that the graphite electrode tested has good selectivity for the determination of xanthine in samples with a 100-fold higher concentration of NaCl, KCl, caffeine, cysteine, glutamic acid, and histidine. The tests carried out in beer, cola, green tea, and cocoa samples show good sensitivity, which indicates the possibility of using the tested electrode as a sensor for the determination of xanthine in various real samples.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.B.R.; methodology, M.B.R., M.B.P.M., A.T.S. and Ž.Z.T.; investigation, M.B.R. and A.T.S.; writing—original draft preparation, M.B.R.; writing—review and editing, M.B.P.M., A.T.S. and Ž.Z.T.; supervision, M.M.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The research presented in this paper was performed with the financial support of the Ministry of Science, Technological Development, and Innovation of the Republic of Serbia, within the funding of the scientific research work at the University of Belgrade, Technical Faculty in Bor, according to the contract with registration number 451-03-137/2025-03/200131.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available upon request from the corresponding author. The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Jiwanti, P.K.; Wardhana, B.Y.; Sutanto, L.G.; Chanif, F.A. Review on Carbon-based Electrodes for Electrochemical Sensor of Quinolone Antibiotics. ChemistrySelect 2022, 7, e202103997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.; Jayaprakash, G.K. Fabrications of electrochemical sensors based on carbon paste electrode for vitamin detection in real samples: Review Paper. J. Electrochem. Sci. Eng. 2022, 12, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratiwi, N.H.; Azis, M.Y.; Satiyanto, H. Review of Developments of Modified Carbon-Based Electrodes on ElectrochemicalSensors for Water Environment Monitoring. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. Res. 2024, 11, 91–109. [Google Scholar]
- Mostafiz, B.; Bigdeli, S.A.; Banan, K.; Afsharara, H.; Hatamabadi, D.; Mousavi, P.; Hussain, C.M.; Keçili, R.; Ghorbani-Bidkorbeh, F. Molecularly imprinted polymer-carbon paste electrode (MIP-CPE)-based sensors for the sensitive detection of organic and inorganic environmental pollutants: A review. Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 2021, 32, e00144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monisha, S.; Subhashri, M.; Devi, S.K.S.; Manju, V.; Kumar, A.S. Defective graphene-nanomaterials derived from banana-biomass for simultaneous electrochemical detection of xanthine, hypoxanthine, and uric acid: Insights from scanning electrochemical microscopy on edge and basal planes. Electrochim. Acta 2024, 497, 144515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somba, A.V.; Kamgaing, T.; Fotsop, C.G.; Deffo, G.; Nkuigoua, B.W.; Tagne, R.F.T.; Tajeu, K.Y.; Temgoua, R.C.T.; Njanja, E.; Tonlé, I.K. Preparation and Characterization of Alkali Activated Carbon Based Theobroma Cocoa Pods: Application for Electrochemical Determination of Xanthine in Fresh Fish Sample. ChemistrySelect 2024, 9, e202303250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Yue, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, L.; Ma, Y. PTA/CeO2@Pt-based electrochemical sensors to detect xanthine and uric acid, and evaluate fish freshness. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 490, 151646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakthivel, A.; Alwarappan, S. Phosphorous Doped Graphitic Carbon Nitride (P-g-C3N4) as an Electrochemical Platform for the Simultaneous Detection of Xanthine and Caffeine. ChemNanoMat 2024, 10, e202400327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waryani, B.; Tahira, A.; Saeed, S.; Bibi, A.; Bhatti, M.A.; Siddiqui, A.; Mahar, I.A.; Parveen, M.; Dawi, E.; Shah, A.A.; et al. Utilizing CuO nanostructures derived from sugar molasses for the detection of xanthine. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2024, 35, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.T.; Manh, T.D.; Man, N.Q.; Thoa, P.T.H.; Khieu, D.Q. Electrochemical detection of uric acid and xanthine in human urine using the Co/UiO-66 modified glassy carbon electrode. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2024, 54, 2361–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Niu, Y.; Wang, S.; Shi, Y.; Wang, Y. Flower-like nickel-doped tin disulfide multi-walled carbon nanotube-based electrochemical sensor for the detection of xanthine and hypoxanthine. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2024, 135, 106586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsan, M.M.; Ghica, M.E.; Brett, C.M.A. Electrochemical sensors and biosensors based on redox polymer/carbon nanotube modified electrodes: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 881, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. Carbon-Nanotube Based Electrochemical Biosensors: A Review. Electroanalysis 2005, 17, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, R.; Mani, V.; Chen, S.M.; Saraswathi, R.; Lou, B.S. Recent Trends in Graphene based Electrode Materials for Energy Storage Devices and Sensors Applications. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2013, 8, 11680–11694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pumera, M.; Ambrosi, A.; Bonanni, A.; Chng, E.L.K.; Poh, H.L. Graphene for electrochemical sensing and biosensing. Trends Anal. Chem. 2010, 29, 954–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zeng, Z.; Zhanxi Fan, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhang, H. Graphene-Based Electrodes. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 5979–6004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zouaoui, F.; Menassol, G.; Ducros, C.; Mailley, P.; Thomas, Y. Electrochemical sensors based on amorphous carbon electrode: A review. Microchem. J. 2025, 209, 112650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walcarius, A. Electrocatalysis, sensors and biosensors in analytical chemistry based on ordered mesoporous and macroporous carbon-modified electrodes. Trends Anal. Chem. 2012, 38, 79–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasić, Ž.Z.; Petrović Mihajlović, M.B.; Radovanović, M.B.; Simonović, A.T.; Dragana, V.; Medić, D.V.; Antonijević, M.M. Electrochemical determination of L-tryptophan in food samples on graphite electrode prepared from waste batteries. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 5469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palisoc, S.T.; Cansino, F.E.J.; Dy, I.M.O.; Razal, C.F.A.; Reyes, K.C.N.; Racines, L.R.; Natividad, M.T. Electrochemical determination of tannic acid using graphite electrodes sourced from waste zinc-carbon batteries. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2020, 28, 100326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, C.S.; Pawlak, V.G.; Oliveira, R.D.; Fujiwara, S.T.; Pessôa, C.A. Carbon Graphite Obtained of Zinc-Carbon Exhausted Batteries Applied as Electrode in Electrochemical Sensors. Rev. Virtual Quim. 2018, 11, 275–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Naggar, M.R.; Fahmy, H.M.; El Nashar, R.M. Decoration of recycled battery graphite functionalized with gold nanoparticles/poly(nicotinic acid) for detection of bifenazate pesticide in tea and food samples. Microchem. J. 2024, 206, 111519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Nasser, A.G.; Metwally, M.G.; Shoukry, A.A.; El Nashar, R.M. Application of recycled battery graphite decorated with poly hippuric acid/ multiwalled carbon nanotubes as an ecofriendly sensor for serotonin. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 29304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alva, S.; Septyanda, P.; Burhanudin, A.; Khaerudini, D.S.; Nurul, S.; Jenie, A.; Sundari, R.; Suhud, K. Development of Nitrate-Ion Selective Electrode (NO3-ISE) Based on Carbon from Disposal Battery. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 2023, 12, 057010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palisoc, S.; Vitto, R.I.M.; Natividad, M. Determination of Heavy Metals in Herbal Food Supplements using Bismuth/Multi-walled Carbon Nanotubes/Nafion modified Graphite Electrodes sourced from Waste Batteries. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulya, K.P.; Manjunatha, J.G.; Aldossari, S.A.; Mohammad, S.; Ataollahi, N. Recycled Battery Carbon Composite Sensor for the Electrochemical Analysis of the Neurotransmitter Dopamine. Top. Catal. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, M.H.; Pabel, M.Y.; Bristy, N.T.; Salam, M.A.; Bashar, M.S. Sabina Yasmin from e-waste to eco-sensors: Synthesis of reduced graphene oxide/ZnO from discarded batteries for a rapid electrochemical bisphenol A sensor. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 36073–36083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.M.; Sperandio, G.H.; da Silva, A.D.; Okumura, L.L.; da Silva, R.C.; Moreira, R.P.L.; Silva, T.A. Electrochemically reduced graphene oxide films from Zn C battery waste for the electrochemical determination of paracetamol and hydroquinone. Mikrochim. Acta 2023, 190, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapri, A.; Pant, S.; Gupta, N.; Nain, S. Recent Advances in the Biological Significance of Xanthine and its Derivatives: A Review. Pharm. Chem. J. 2022, 56, 461–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dervisevic, M.; Dervisevic, E.; Şenel, M. Recent progress in nanomaterial-based electrochemical and optical sensors for hypoxanthine and xanthine. A review. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Hashem, A.A.; Hakami, O.; El-Shazly, M.; El-Nashar, H.A.S.; Yousif, M.N.M. Caffeine and Purine Derivatives: A Comprehensive Review on the Chemistry, Biosynthetic Pathways, Synthesis-Related Reactions, Biomedical Prospectives and Clinical Applications. Chem. Biodivers. 2024, 21, e202400050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Kroon, R.; Zeglio, E.; Herland, A. P-type accumulation mode organic electrochemical transistor biosensor for xanthine detection in fish. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2025, 269, 116928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pundir, C.S.; Devi, R. Biosensing methods for xanthine determination: A review. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2014, 57, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlawat, J.; Sharma, M.; Pundir, C.S. Advances in xanthine biosensors and sensors: A review. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2024, 174, 110377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moutcine, A.; Laghlimi, C.; Ziat, Y.; El Bahraoui, S.; Belkhanchi, H.; Jouaiti, A. Advanced design of chemically modified electrodes for the electrochemical analysis of uric acid and xanthine. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2025, 253, 116536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, D.; Zhang, L. Electrochemical synthesis of a novel purine-based polymer and its use for the simultaneous determination of dopamine, uric acid, xanthine and hypoxanthine. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2015, 757, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masood, Z.; Muhammad, H.; Tahiri, I.A. Comparison of Different Electrochemical Methodologies for Electrode Reactions: A Case Study of Paracetamol. Electrochem 2024, 5, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishwanathan, M.S.; Swamy, B.E.K.; Vishnumurthy, K.A. Iron Oxide Modified Carbon Paste Electrode Sensor for Guanine and Dopamine: A Voltammetric Technique. Anal. Bioanal. Electrochem. 2023, 15, 444–457. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Tang, W.; Wang, J.; Zhang, G.; Chai, S.; Liang Zhang, L.; Liu, T. Selective determination of dopamine and uric acid using electrochemical sensor based on poly(alizarin yellow R) film-modified electrode. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 3474–3481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jesny, S.; Kumar, K.G. Non-enzymatic Electrochemical Sensor for the Simultaneous Determination of Xanthine, its Methyl Derivatives Theophylline and Caffeine as well as its Metabolite Uric Acid. Electroanalysis 2017, 29, 1828–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.S.; Temerk, Y.M.; Kamal, M.M.; Ahmed, G.A.-W.; Ibrahim, H.S.M. Ultra-Sensitive Anodic Striping Voltammetry for the Determination of Xanthine at a Glassy Carbon Electrode. Microchim. Acta 2004, 144, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelmea, L.; Badea, M.; Ioan Scarneciu, I.; Moga, M.A.; Dima, L.; Restani, P.; Murdaca, C.; Ciurescu, D.; Gaman, L.E. New Trends in Uric Acid Electroanalysis. Chemosensors 2023, 11, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radovanović, M.B.; Petrović Mihajlović, M.B.; Simonović, A.T.; Tasić, Ž.; Antonijević, M.M. Electrochemical Detection of Cadmium Using a Bismuth Film Deposited on a Brass Electrode. Sensors 2025, 25, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaczmarska, K.; Brycht, M.; Leniart, A.; Skrzypek, S. Differential pulse voltammetric determination of an immunosuppressive drug teriflunomide on an edge plane pyrolytic graphite electrode. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 26028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, S.; Xin, J.; Ma, H.; Pang, H.; Tan, L.; Wang, X. A non-enzymatic voltammetric xanthine sensor based on the use of platinum nanoparticles loaded with a metal-organic framework of type MIL-101(Cr). Application to simultaneous detection of dopamine, uric acid, xanthine and hypoxanthine. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojani, R.; Alinezhad, A.; Abedi, Z. A highly sensitive electrochemical sensor for simultaneous detectionof uric acid, xanthine and hypoxanthine based on poly(l-methionine) modified glassy carbon electrode. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 188, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitoz, A.; Yazan, Z.; Önal, M. Simultaneous Trace Electrochemical Determination of Xanthine Theophylline and Theobromine with a Novel Sensor Based on a Composite Including Metal Oxide Nanoparticle Multi-walled Carbon Nanotube and Nano- Na-montmorillonite Clay. Electroanalysis 2021, 33, 2226–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrag, C.; Noroozifar, M.; Kerman, K. Thiol functionalized carbon ceramic electrode modified with multi-walled carbon nanotubes and gold nanoparticles for simultaneous determination of purine derivatives. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 110, 110568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, W.; Wei, C.; Lü, L. Preparation of a Xanthine Sensor Based on the Immobilization of Xanthine Oxidase on a Chitosan Modified Electrode by Cross-linking. Chin. J. Chem. 2012, 30, 1601–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Liu, Y.; Hou, H.; You, T. A nonenzymatic sensor for xanthine based on electrospun carbon nanofibers modified electrode. Talanta 2011, 83, 1410–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.K.; Zhang, Y.T.; Li, S.H.; Luo, H.X.A. Flexible Electrochemical Sensor Based on L-Arginine Modified Chemical Vapor Deposition Graphene Platform Electrode for Selective Determination of Xanthine. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2020, 48, 1149–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).