Abstract
The increasing demand for rapid, sensitive, and eco-friendly methods for the detection of trace heavy metals in environmental samples, attributed to their serious threats to health and the environment, has spurred considerable interest in the development of sustainable sensor materials. Toxic metal ions, namely, lead (Pb2+), cadmium (Cd2+), mercury (Hg2+), arsenic (As3+), and chromium, are potential hazards due to their non-biodegradable nature with high toxicity, even at trace levels. Acute health complications, including neurological, renal, and developmental disorders, arise upon exposure to such metal ions. To monitor and mitigate these toxic exposures, sensitive detection techniques are essential. Pre-existing conventional detection methods, such as atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS) and inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (ICP-MS), involve expensive instrumentation, skilled operators, and complex sample preparation. Electrochemical sensing, which is simple, portable, and eco-friendly, is foreseen as a potential alternative to the above conventional methods. Carbon-based nanomaterials play a crucial role in electrochemical sensors due to their high conductivity, stability, and the presence of surface functional groups. Biochar (BC), a carbon-rich product, has emerged as a promising electrode material for electrochemical sensing due to its high surface area, sustainability, tunable porosity, surface rich in functional groups, eco-friendliness, and negligible environmental footprint. Nevertheless, broad-spectrum studies on the use of biochar in electrochemical sensors remain narrow. This review focuses on the recent advancements in the development of biochar-based electrochemical sensors for the detection of toxic heavy metals such as Pb2+, Cd2+, and Hg2+ and the simultaneous detection of multiple ions, with special emphasis on BC synthesis routes, surface modification methodologies, electrode fabrication techniques, and electroanalytical performance. Finally, current challenges and future perspectives for integrating BC into next-generation sensor platforms are outlined.
1. Introduction
Owing to rapid industrialization, huge amounts of toxic metal ions, including lead (Pb2+), cadmium (Cd2+), mercury (Hg2+), arsenic (As3+), and chromium, are being expelled into the water system globally, resulting in heavy metal ion pollution becoming a major concern of this 21st century [1]. These persistent contaminants accumulate, leading to severe health hazards to humans and wildlife even at trace concentrations. Once released, these heavy metal ions do not deteriorate; rather, they penetrate the soil, mix with the groundwater system, and percolate into biological systems, where they disrupt cellular function and accumulate over time [1,2].
Among analytical techniques, such as inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (ICP-MS), atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS) [3,4], and X-ray fluorescence (XRF) [5,6], which are considered prime methods for heavy metal detection, their expensive instrumentation, centralized laboratories, and intricate procedures limit their use in rapid field analysis and large-scale environmental inspection. Consequently, there is an urgent need for an alternative sensing platform that also fulfills the criteria for being sustainable, economical, and portable, along with being sensitive and selective. Recent advancements in electrochemical sensors have established sensor-based systems as potent alternatives to conventional analytical methods for heavy metal ion detection. They exhibit several advantages, including high sensitivity, selectivity, quick response, and the targeted detection of analytes even at trace levels [7,8]. To further enhance their performance, these sensors rely on diverse functional materials for electrode modification. An array of functional materials has been used for electrode modification [9] to improve the sensor performance, which includes metal nanoparticles, metal oxides, metal–organic frameworks (MOF) [10], quantum (carbon) dots, graphene [11], and several carbon-based materials [12] and their derivatives. These entities were found to help increase the surface area, electron-transfer kinetics, and specific binding affinity toward metal ions, collectively exhibiting more precise and facile detection in intricate environmental samples.
The fabrication of next-generation electrochemical sensors for heavy metal ion detection necessitates the assimilation of materials that manifest high sensitivity, selectivity, and operational stability. In this context, the synthesis of cost-effective, environmentally friendly, and electrochemically active carbon nanomaterials has come into the limelight. Specifically, biomass-derived carbons, commonly named biochar (BC), tend to be a potent alternative to traditional carbon-based nanomaterials due to their inherent abilities, such as renewability, surface functionality, and tunability. These BCs were found to possess enhanced adsorption capability and electron transfer kinetics, due to their high specific surface area, porosity, and copious amounts of oxygen-containing functional groups, which are the results of pyrolysis or hydrothermal carbonization [13,14]. In addition, the mechanical robustness, thermal stability, chemical stability, and compatibility of BC when combined with nanomaterials like metal nanoparticles, MOFs, etc., make it a prominent candidate for use in advanced electrochemical sensing platforms targeting trace-level heavy metal ions [15]. The incorporation of BC-derived nanocomposites represents a significant strategy to improve the electrochemical sensing performance for the precise detection of trace heavy metal ions in water, soil, and atmospheric gases.
BC, the product of biomass pyrolysis, is a carbonaceous substance with high surface area, porosity, tunability, and stability, assisting its application in environmental monitoring and pollutant remediation [13,14,15]. However, raw, unmodified BC undergoes structural disintegration and reduced electrochemical performance during extended operation [16,17]. To overcome these constraints, researchers have been focusing on the fabrication of modified BC-based nanocomposites using metal/metal oxide nanoparticles. These were found to exhibit enhanced electrocatalytic performance with high sensitivity and selectivity, making them robust materials for electrochemical sensing of trace heavy metal ions [18,19]. This review aims to provide consolidated information on the emerging role of BC-derived nanocomposites in the electrochemical sensing of trace heavy metal ions using electrochemical techniques, namely cyclic voltammetry (CV), differential pulse voltammetry (DPV), square wave anodic stripping voltammetry (SWASV), and adsorptive stripping differential pulse voltammetry (DPAdSV), thereby highlighting their potential to improve sustainable environmental monitoring and remediation. For the lowest possible detection limits, stripping voltammetry is the preferred method, especially for heavy metals like Pb2+, Cd2+, and Hg2+. SWASV usually offers better sensitivity and faster operation than DPASV. It is often preferred when ultra-trace detection and quick analysis are needed, such as in environmental field samples. DPASV delivers excellent peak resolution and consistent background suppression, making it a better choice for routine laboratory analysis, especially when dealing with complex matrices. Both methods take advantage of the high surface area and functional groups of biochar-based electrodes, but SWASV may better utilize the full sensitivity potential of biochar modifications. The choice between SWASV and DPASV should depend on the analytical challenge. Use SWASV when the lowest detection limits are needed for rapid or field testing. Use DPASV for robustness, reproducibility, and handling complex sample matrices. Both methods work well with green, biochar-based electrodes, taking advantage of their benefits while requiring careful optimization for the best results. Ultimately, the incorporation of BC-derived nanocomposites in the electrochemical sensing of heavy metal ions marks a significant advancement towards an eco-friendly pollutant detection technology with widespread implications for ecosystem protection and public health.
2. Biochar: A Green Electrode Material
Biochar, a carbon-rich material derived from naturally occurring, renewable, and cost-effective sources such as agricultural wastes and forest residues, adheres to the principles of green chemistry, sustainability, and the circular economy [20,21]. BC production from agricultural waste or forestry by-products usually requires relatively less energy, with material costs being low. It also needs an average amount of only 1–2 mg for one working electrode, rendering it pretty cheap [22]. The much lower environmental impacts of biochar-based materials as opposed to traditional carbonaceous materials motivate their use in developing sustainable sensors [23]. Li et al. assess the life cycle assessment (LCA) of BC used in agriculture. It focuses on how BC can reduce greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, its energy requirements for production, and its economic feasibility. The study shows that biochar can cut net GHG emissions by about 0.5 to 3.0 tons of CO2-equivalent per ton of biochar. This depends on the type of feedstock, production method, and application conditions. Gasification is identified as the most cost-effective approach (around $150 to $250 per ton). Hydrothermal carbonization (HTC) needs lower energy inputs (1.2 to 2.0 MJ/kg) but offers slightly lower carbon sequestration. BC has good carbon stability in soil, ranging from 60 to 90%. This translates to 2.2 to 3.3 tons of CO2-equivalent sequestered for each ton applied. However, the overall benefits depend on factors like feedstock drying, transport emissions, energy sources, and interactions between soil and BC. In conclusion, the paper emphasizes BC’s strong potential as a sustainable, carbon-negative approach. It also calls for more standard methods for LCA and validation on a larger scale [24]. Nevertheless, BC sustainability depends on feedstock choice and pyrolysis conditions. Sludge or any biomass with abnormally high metal content can be a precursor to the toxic emissions of PAHs and heavy metals [25,26,27]. Also, algae-derived biochar electrodes have an extremely low environmental impact (~0.02 kgs. CO2-eq per functional unit), contrary to the more polluting graphene-based electrodes (~0.21 kgs. CO2-eq) [28]. Together, these bring home the point that biochar can serve as a low-carbon, energy-saving, and renewable solution for electrochemical sensor platforms, especially when complemented with optimized fabrication processes and circular resource approaches. BC-based electrochemical sensors have the merits of portability, low cost, and real-time detection, but suffer from lower sensitivity and the need for matrix-matched calibration as compared to the conventional methods like AAS and ICP-MS [29]. In comparison to nanomaterials like graphene and CNTs, biochar is less conductive but environmentally friendlier and much easier to process. Hence, it finds its greatest applicability in point-of-care or field-level preliminary screening rather than ultra-trace detection in complex matrices [30]. BC consists of a hierarchical pore system, entailing micropores (pore diameters of less than 2 nm), mesopores (2–50 nm), and macropores (greater than 50 nm), which is crucial for effective adsorption and provides abundant active sites for electrochemical reactions [31]. Usually, pyrolysis temperatures in the range of 400 to 700 °C favor the development of its pore structure [32,33]. Depending on the biomass precursor and pyrolysis temperature, a genuine biochar exhibits higher-than-average BET surface areas ranging from 200 to more than 1500 m2/g [34]. BC’s skeletal density typically ranges from 1.34 to 1.96 g cm−3, increasing with pyrolysis temperature, while envelope density ranges from 0.25 to 0.60 g cm−3 [35]. In comparison with conventional carbon nanomaterials, such as graphene and its oxide, carbon nanotubes, and fullerenes, BC exhibits numerous advantages, encompassing high surface area, porosity, and copious amounts of surface functional groups (hydroxyl, carbonyl, and amino groups) supporting efficient electron transfer kinetics along with adsorption of metal ions. BC is generally produced via thermochemical conversion of biomass in an oxygen-deficient environment, where the synthesis route significantly influences its physicochemical properties and electrochemical performance [36]. To understand how BC’s properties contribute to sensor performance, it is first important to explore how it is synthesized and modified. The following are some of the reported synthesis routes for biochar manufacturing.
2.1. Synthesis of BC
2.1.1. Pyrolysis
Pyrolysis is one of the most predominantly used thermochemical techniques for BC manufacturing, involving the decomposition of organic biomass at higher temperatures (in the range of 300–800 °C), mostly in an inert or oxygen-deficient atmosphere, giving rise to solid BC, bio-oil, and syngas as products. When biomass is produced under a low heating rate, for instance, 5–10 °C per minute with sustained dwelling time (slow pyrolysis), solid BC with high carbon content and a thermally stable aromatic structure will be obtained at a higher yield, which is ideal for applications where carbon-rich nanomaterial is preferred. On the contrary, at a rapid heating rate of >100 °C per minute with minimal dwelling time, the obtained BC will be in a less solidified form with a distorted structure, whose electrochemical application can be improved through chemical activation [32,33]. The pyrolysis temperature plays an important role in the morphology and chemical characteristics of BC. Slow pyrolysis conserves functional groups, enabling higher adsorption of metal ions but with lower conductivity. On the other hand, fast pyrolysis enhances aromatization and deoxygenation, leading to improved electrical conductivity [32,33,37]. These surface functionalities also promote strong interactions with dopants or nanoparticles for further performance tuning. The inherent tunability of biochar’s porosity and chemical reactivity via controlled pyrolysis parameters makes it a versatile platform for heavy metal sensing.
2.1.2. Hydrothermal Carbonization (HTC)
Hydrothermal carbonization (HTC) is an emerging and versatile thermochemical method for BC manufacturing, particularly for high-moisture biomass under reasonably mild reaction conditions [38]. HTC operates at moderate temperatures (180–250 °C) and pressures (2–10 MPa) in aqueous conditions. The biomass is treated with water in a Teflon-lined, highly sealed, corrosion-resistant stainless-steel container under an inert atmosphere, which enables simultaneous reactions, namely hydrolysis, dehydration, decarboxylation, polymerization, and aromatization. The obtained BC will have high carbon content and enhanced surface oxygen functionality, while the aromatic structure depends on the reaction parameters (temperature, feedstock composition, and dwelling time) [39,40,41]. HTC-derived biochar has been explored in diverse applications, including soil quality monitoring [42], adsorption of environmental pollutants [43,44,45], catalyst support [46], and as an advanced functional material for electrochemical sensing [47] and energy storage [48], which has become a promising candidate for sustainable material development and green chemistry approaches by researchers. HTC produces hydrochar with different structural and chemical properties from pyrolyzed biochar. This process usually occurs at lower temperatures, between 180 and 250 °C, in water. HTC retains a higher amount of oxygen- and nitrogen-containing functional groups like hydroxyl, carboxyl, amine, and phenolic groups [49]. These groups increase surface polarity, help coordinate metal ions, and improve the redox activity of the carbon surface. Although hydrochar generally has lower surface areas (usually less than 50 m2/g) and less developed porosity than pyrochar, its surface chemistry makes it suitable for activation or doping after synthesis [49]. HTC retains more surface oxygen functionalities than pyrolysis, but results in a lower surface area. This lower surface area can be countered with post-treatment approaches. Moreover, HTC can customize carbon surface chemistry to enhance sensing performance. This ability makes HTC useful for creating adjustable biochar for specific electrochemical applications.
Overall, both pyrolysis and HTC present exciting and complementary options for biochar synthesis. Each method has distinct advantages based on different feedstocks and application requirements. While pyrolysis is known for making stable, carbon-rich biochar with high surface area, HTC offers a low-temperature, water-based route that improves the processing of wet biomass and produces hydrochar with unique properties. Although regular biochar shows potential, its characteristics can be significantly modified through techniques like chemical activation, heteroatom doping, and adding nanostructured materials such as metal oxides or MOFs. These changes can further enhance the selectivity, sensitivity, and stability of electrochemical sensors, which will be discussed in the next section.
2.2. Modification of the Synthesized BC
The modification of synthesized BC plays a crucial role in tailoring its physicochemical properties for improved performance in the fields of electrochemical sensing, adsorption, and catalysis. BC synthesized from pyrolysis or HTC usually requires modification to enhance its surface reactivity, porosity, and conductivity [50]. Common functionalization methods include chemical activation, heteroatom doping, and the incorporation of metal/metal oxide nanoparticles/MOFs. Modification using acids or bases may incorporate oxygen-containing functional groups like hydroxyl or carboxyl, which improves the adsorption capacity of BC for the targeted analytes [50]. These modifications also help with their enhanced interaction with other carbon nanomaterials and polymeric systems. Overall, the modification of BC demonstrates enhanced sensitivity, selectivity, and stability in the electrochemical sensing of heavy metal ions, supporting its role as a sustainable, high-performing nanomaterial in advanced sensing technologies. The different modification techniques are discussed as follows.
2.2.1. Chemical Activation
Chemical activation is a commonly used method to improve the surface and structural aspects of BC, making it highly efficient in the fields of electrochemical sensing, adsorption, and catalysis. The as-obtained or synthesized BC is treated with chemical activating agents, such as potassium hydroxide (KOH), phosphoric acid (H3PO4), or sulfuric acid (H2SO4), either before or during pyrolysis. This chemical activation process increases porosity by eliminating volatile components present in the material and introduces oxygen functional groups like hydroxyl, carbonyl, etc. Moreover, the surface area of BC also increases, which in turn improves analyte adsorption and electron transfer in electrochemical applications. The choice of activating chemicals also affects the surface chemistry of BC. For instance, KOH leads to the formation of oxygen functional groups (enhancing electrical conductivity), while H3PO4 increases phosphate concentration (enhancing metal ion binding) on the BC surface. Overall, chemical activation enhances the reactivity, porosity, and functional group influence in BC, converting it into a more efficient and tunable nanomaterial for environmental monitoring and sensing applications [51].
2.2.2. Heteroatom Doping
Apart from oxygen functional groups, heteroatoms like nitrogen (N), sulfur (S), phosphorus (P), or boron (B) are incorporated into the BC matrix to improve its electronic conductivity, chemical reactivity, and functional versatility in the fields of electrochemical sensing, energy storage, and catalysis. These heteroatoms are introduced either by using gas (e.g., N2 gas) or chemicals (e.g., H2SO4), which alters the surface chemistry by forming defects, enhancing porosity, and generating active sites for heavy metal ion sensing. Electron-donating N increases conductivity and facilitates redox reactions, whereas S and P improve metal ion affinity via coordination or complexation mechanisms. Thus, heteroatom doping makes BC a high-performing, multifunctional nanomaterial with enhanced sensitivity, selectivity, and stability for electrochemical sensing of heavy metal ions and environmental monitoring [52].
2.2.3. Incorporation of Metal/Metal Oxide Nanoparticles
Metal nanoparticles are introduced into the BC via wet impregnation, in situ synthesis, or sol–gel techniques using a precursor. These nanoparticles act as active sites that critically enhance catalytic activity, redox behavior, and electron transfer kinetics of the BC. For instance, magnetic iron oxide (Fe3O4) nanoparticles impart magnetic properties to the BC, in turn enhancing electron transfer in electrochemical sensing applications [53], while noble metal nanoparticles like gold (Au) [54] improve electrocatalytic sensitivity and stability. The strong interaction between the BC matrix and the incorporated nanoparticles ensures structural integrity and uniform distribution, which is vital for reproducible electrochemical sensor performance. This synergistic combination of BC and metal nanoparticles results in hybrid systems with enhanced sensitivity, selectivity, and robustness for detecting trace levels of heavy metal ions and other environmental contaminants. The above information is condensed in the form of a figure and represented in Scheme 1.
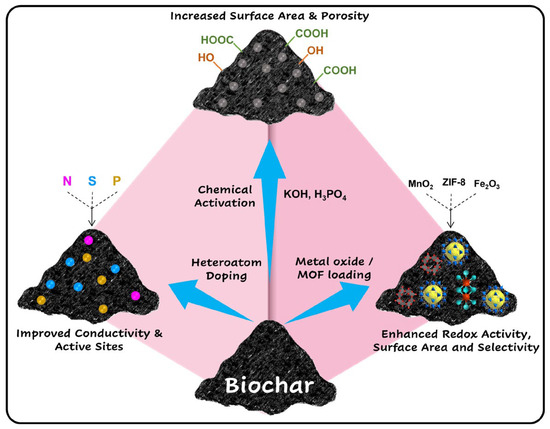
Scheme 1.
Methods for biochar modification: chemical activation, heteroatom doping, and metal oxide/MOF loading. Created using icons from www.flaticon.com (accessed on 22 July 2025).
Overall, modifying biochar with chemical activation, adding different atoms, and including metal oxides or MOFs significantly improves its structure and surface properties. This opens the door to new functions for specific applications. Chemical activation boosts porosity and surface area. Adding different atoms creates active sites, which improve reactivity. Loading with metal or metal oxide nanoparticles or MOFs gives it special catalytic, adsorptive, or electrochemical features. These modifications not only widen the use of biochar beyond its traditional roles but also make it a flexible and sustainable option for high-performance materials in environmental cleanup, energy storage, and sensor technologies.
3. Application of BC for Electrochemical Sensing of Heavy Metal Ions
3.1. Lead (Pb2+)
Lead (Pb2+) is a prevalent and extremely toxic heavy metal with no significant biological function and has a clear capacity to cause multisystem health damage [55]. Its toxicity is significantly pronounced in exposed populations, such as children and pregnant women, where chronic exposure, even at a trace level concentration of 10 µg dL−1, can impair neurological development, behavioral disorders, and reduce IQ levels [56]. In adults, continuous exposure gives rise to hypertension, anemia, nephrotoxicity, and, in extreme cases, reproductive dysfunction [57]. The subtle behavior of Pb2+, which has a biological half-life of up to a few years, lies in its ability to bioaccumulate in bones and soft tissues [57]. Environmental sources of Pb2+ contamination include industrial discharge, lead–acid batteries, plumbing materials, paints, ceramics, and electronic waste [58]. About 19 works have reported the electrochemical sensing and detection of Pb2+ ions using BC-derived electrodes as the substrate, with modification using various innovative electrode materials (Table 1).

Table 1.
Electrochemical sensors for the detection of Pb2+ ions.
Ouangpipat et al. prepared a BC material using Pennisetum setosum, a common grass species known for its rapid growth and bioaccumulative properties [59]. This was treated by the crosslink-xanthate method, focused on increasing its metal ion exchange capability by incorporating functional groups that support lead ion binding. Following the chemical treatment, the Pennisetum was mixed with graphite powder and mineral oil for the preparation of a carbon paste electrode (CPE), which was employed for the detection of Pb2+ ions. This report demonstrates the potential of biosorption-based materials in green chemistry, offering a low-cost, renewable, and potent alternative for heavy metal sensing in groundwater and canal water samples. Mojica et al. prepared a banana tissue-based BC by first removing the moisture from the tissue, followed by grinding it into a powder [60]. This powder was mixed with graphite powder and mineral oil to form a homogeneous CPE, which exhibits efficient sensing of Pb2+ ions owing to the intrinsic biosorptive properties of the banana tissue, which acts by providing active sites capable of complexing with Pb2+ ions. This work demonstrates eco-friendly and robust methods for Pb2+ ion sensing in water samples. Agustini et al. prepared a BC (derived from castor oil cake) and bismuth nanomaterial modified CPE for sensing Pb2+ ions in ceramic plates [61]. First, the castor oil cake was pyrolyzed at 300 °C, and the ground BC was mixed with graphite powder and mineral oil to form a CPE. To this electrode, bismuth nanoparticles were incorporated by electrochemical deposition at pH 1.5 for 30 s, forming an nBi-BchCPE modified electrode for Pb2+ sensing. This modified electrode was successfully utilized for the detection of Pb2+ ions released from overglaze-decorated ceramic dishes.
Tan et al. used cellulose extracted from Cladophora rupestris algae, followed by in situ polymerization of aniline monomer, forming a Clad-Polyaniline (PANI) composite, which was further acid-treated to ensure the PANI was present in its emeraldine form [62]. They prepared a stable, conductive paper-based electrode to electrochemically detect Pb2+ ions, which may be utilized as a potent water-quality sensor. Ajab et al. utilized oil palm empty fruit bunches (OPEFB) as a precursor for preparing BC [63]. Cellulose was extracted from the precursor, which was then combined with separately synthesized hydroxyapatite (Hap), forming a cellulose-Hap composite that was further made into a CPE with graphite powder and paraffin. This fabricated electrode was found to exhibit improved surface roughness, enhanced porosity, and crystalline structures, providing surplus active sites for highly sensitive and selective sensing of Pb2+ in blood serum samples.
Li et al. developed an N-doped wormlike mesoporous carbon material from bayberry kernels as a BC precursor and melamine as the N source [64]. The kernels were subjected to in situ pyrolysis at a range of temperatures from 500 to 900 °C using an ethanol–Nafion solution to obtain a homogeneous dispersion. This dispersion was coated onto a glassy carbon electrode (GCE), followed by curing with an infrared lamp. The composite pyrolyzed at 900 °C exhibited a unique interconnected mesoporous “blood vessel-like” structure with abundant graphitic carbon, quaternary, and pyridinic-N sites, which paved the way for enhanced electrochemical sensing of Pb2+ ions. The fabricated electrode was found to possess a high surface area, excellent conductivity, and fast charge-transfer kinetics, which enabled highly sensitive and selective detection of Pb2+ over a wide range of concentrations. Similar to the previous report, Baikeli et al. fabricated an N-doped activated nanoporous carbon obtained from almond shells [65]. The cleaned and ground almond shells were carbonized at 450 °C under N2 atmosphere, followed by KOH activation and subsequent pyrolysis at 600 °C to obtain the desired carbon. The “as-obtained” nanoporous carbon underwent HTC in the presence of urea at 180 °C to yield N-doped carbon having a high surface area with pores. This N-doped carbon was dispersed in a water–isopropanol–Nafion solution and made into a homogeneous suspension for drop-casting over a GCE. The modified electrode exhibited improved conductivity and a high electroactive surface area, which in turn displayed enhanced electron transfer kinetics, making it an efficient material for sensitive and selective detection of Pb2+ in real tap water samples.
Sivan et al. reported the green synthesis of titanium oxide (TiO2) nanoparticles using gum arabic as the biotemplate, followed by calcination at 500 °C [66]. The TiO2 nanoparticles were drop-casted over a previously fabricated CPE (using graphite powder and silicone oil) and were used for electrochemical sensing of Pb2+. The modified electrode displayed enhanced electrochemical sensing performance and was extended to real-sample analysis in plastic toys. Similar to [64], Xu et al. reported the fabrication of a wormlike N-doped carbon framework using Benincasa hispida (wax gourd) as the carbon source and Holstein Friesian (cattle milk) as the N source [67]. The wax gourd was first subjected to HTC at 180 °C, and subsequently pyrolyzed at 800 °C in the presence of milk and N2 atmosphere. The obtained BC was dispersed in a 1 wt% Nafion solution and drop-casted over a pretreated GCE, subjecting it to electrochemical measurements after drying under an infrared lamp. This fabricated electrode exhibited superior conductivity, abundant active sites, and excellent electrochemical sensing of Pb2+ ions, which was further extended to the detection of Pb2+ ions in tap and lake water samples.
Radotić et al. derived BC from maize stems, where the cell walls were extracted via sequential extraction using methanol [68], sodium chloride, Triton-X 100, water, acetone, and methanol, which gave rise to clean biomass rich in cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin. Unlike the previously reported literature, no pyrolysis was involved, yielding a low-energy, eco-friendly, non-pyrolyzed BC for the electrochemical sensing of heavy metal Pb2+ and non-heavy metal Cu2+ ions. Oliveira et al. utilized spent coffee grounds as the carbon source by pyrolyzing them at temperatures between 300 and 700 °C [69] and subsequently activating them with nitric acid under reflux at 60 °C for three hours to enrich the surface with oxygen functional groups. The CPE was fabricated by mixing the activated BC with graphite powder and mineral oil, further subjecting it to the electrochemical sensing of Pb2+ ions. The presence of oxygen functional groups in an abundant quantity aided in the facile, sensitive, and selective detection of Pb2+ ions when compared with a non-activated BC-based CPE and was used to detect Pb2+ ions in gun residues and hair dye.
Zou et al. reported the fabrication of a bismuth nanocluster-decorated porous activated BC, similar to the previous work [70]. The BC was prepared using Litsea cubeba shells via chemical activation with KOH and subsequent carbonization at 800 °C under N2 atmosphere. This process was found to give rise to an oxygen-functional-group-rich BC (activated), to which bismuth nitrate was added and reduced using sodium borohydride (Figure 1). The synthesized nanocomposite was drop-casted on a GCE, which exhibited enhanced electrochemical activity towards Pb2+ ion detection due to its high surface area with abundant oxygen-rich sites, and was further subjected to paddy water analysis. Similar to the previous work, a molybdenum oxide nanoparticle-based BC was prepared by Mamatha et al. for the electrochemical detection of Pb2+ ions. The Centella asiatica plant was used as the carbon source [71]. It was dried into a fine powder (using an autoclave) before the addition of molybdenum nitrate, followed by heating in a muffle furnace at 600 °C to form molybdenum oxide nanoparticles. These nanoparticles were mixed with graphite powder and silicone oil for CPE preparation and were found to exhibit enhanced redox behavior for the electrochemical detection of Pb2+ in alkaline media.
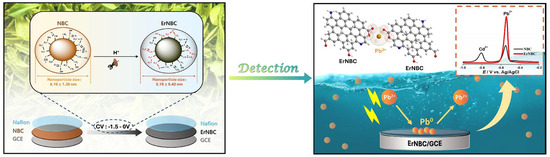
Figure 1.
Schematic illustration of the fabrication and application of electrochemically reduced nitrogen-doped biochar (ErNBC) for electrochemical detection of heavy metals. Reproduced with permission from [72]. © 2024 Elsevier B.V.
Su et al. reported a green and efficient electrochemical sensor for detecting Pb2+ in real water samples using in situ electrochemically reshaped nano-BC (ErNBC) made from tea residue [72]. The BC was created by heating it to 300 °C and reshaping it directly on the electrode surface through CV. This ErNBC showed a significant reduction in particle size, improved conductivity, better hydrophilicity, and increased oxygen content. The modified GCE/ErNBC demonstrated excellent electrochemical performance for lead detection, achieving a low detection limit of 0.49 µg/L, which is well below the standards set by the WHO and China. To improve predictive capabilities, the authors integrated machine learning models, including linear regression, K-nearest neighbor (KNN), and random forest, with electrochemical data. The random forest model performed the best, and the sensor was validated using river and farmland water. This work highlights the value of waste-derived nanomaterials for environmental sensing. It also shows the potential of combining green sensor development with machine learning for effective and sustainable heavy metal detection.
Similar to previous reports on N-doped BC-based nanocomposites, Sharma et al. fabricated N and S co-doped mesoporous carbon from coconut husk waste [73]. First, the coconut husk was chemically activated using H2SO4 and pyrolyzed at 1200 °C under an N2 atmosphere. Second, thiourea (S source) and melamine (N source) were added and subjected to HTC, which resulted in the formation of abundant functional groups. When drop-casted on a GCE, this displayed enhanced conductivity and electrocatalytic activity. This work presents a straightforward, scalable approach for electrode fabrication using biomass-derived doped carbon materials, resulting in eco-friendly and highly sensitive electrochemical sensors. Similar to previous reports, nanoscale zero-valent iron particles were synthesized using Yerba mate tea extract by Mampane et al. [74], where ferrous sulfate solution was mixed with the tea extract, followed by heating at a range of temperatures from 25 to 85 °C, which resulted in highly stable iron oxide nanoparticles with minimal agglomeration at 25 °C. The nanoparticles were drop-casted over Au screen-printed electrodes, which exhibited enhanced electrochemical activity with low charge transfer resistance and strong redox behavior, making them a suitable material for the electrochemical sensing of Pb2+ ions.
The works reviewed so far clearly show the potential of BC-derived materials as a sustainable and effective base for electrochemical sensors. Using various biomass sources and innovative modification methods, which include chemical functionalization, heteroatom doping, nanomaterial integration, and even in situ electrochemical reshaping, researchers have created strong, sensitive, and selective platforms for detecting key heavy metal ions, especially Pb2+. These studies promote green chemistry by using plentiful waste biomass. They also lead to practical, low-cost, and eco-friendly solutions for monitoring heavy metals in different complex mixtures, further improved by emerging methods like machine learning.
3.2. Cadmium (Cd2+)
Cadmium (Cd2+) is a highly toxic and non-essential heavy metal responsible for environmental and human health concerns. Human exposure causes renal dysfunction, skeletal demineralization, pulmonary damage, and carries high cancer risks for the prostate and lungs. It is considered a Group 1 carcinogen by the International Agency for Research on Cancer. It predominantly settles in the kidneys and liver, having a biological half-life of more than one to three decades [75]. Cd2+ accumulation in the environment comes from mining, electroplating, the usage of phosphate fertilizers, battery manufacturing, pigment (dye) production, and improper disposal of e-waste [76]. Several approaches have been carried out for its qualitative and quantitative detection, with electrochemical sensors playing a major role. Recently, BC-incorporated electrochemical sensors have gained researchers’ interest, and the reported works are discussed as follows (Table 2).

Table 2.
Electrochemical sensors for the detection of Cd2+ ions.
Incebay et al. prepared BC using dry green tea leaves as the source via Soxhlet extraction with ethanol at 30 °C for 2.5 h [77]. The obtained extract was washed repeatedly with ethanol to remove insoluble impurities, leaving behind a clean, bioactive material rich in polyphenols, alkaloids, proteins, and other biofunctional materials. This was then functionalized using multiwalled carbon nanotubes, and this nanocomposite was drop-casted over GCE and further utilized for the electrochemical sensing of Cd2+ in river water and drinking water samples. Similar to this work, Jangi and Khoobi used sour tea extract as a natural source for preparing sodium aluminate nanostructures by mixing aluminum nitrate nonahydrate, sodium sulfate, and sour tea extract at 50 °C [78]. To this, ethylenediamine was added to adjust the pH to 10–12, followed by heating at 100 °C to form a gel-like material, which was then calcined at 900 °C for three hours to produce the desired sodium aluminate nanostructures. The obtained gel was then incorporated into a carbon paste matrix and used for the electrochemical sensing of Cd2+ ions in milk and chocolate samples.
Rani et al. reported the fabrication of nanoceria (CeO2 nanoparticles)-based BC using orange peel extract [79], where the orange peels were washed, cut into small pieces, and extracted with deionized water at 90 °C for two hours. Similar to the previous work, the extract was added dropwise to cerium nitrate hexahydrate under continuous magnetic stirring for three hours at a pH between 6.3 and 7.2. The formed nanoceria was separated, washed, and dried at 80 °C for ten hours, followed by calcination at 600 °C for four hours. This process sustained only the natural antioxidants, namely ascorbic acid, flavonoids, polyphenols, and organic acids, which were responsible for reducing the cerium ions to highly crystalline, cubic nanoceria that exhibited highly sensitive and selective detection of Cd2+ ions.
Liang et al. reported the fabrication of two electrochemical sensors for Cd2+ detection using Plumeria alba flower extract (PAFE) [80,81]. In the first study [80], PAFE was mixed with iron (III) chloride hexahydrate and sodium acetate and subjected to one-pot HTC of iron (III) oxide nanoparticles (at 180 °C for 9 h). Using the same experimental conditions, the reduction of graphene oxide to reduced graphene oxide (rGO) was also performed, resulting in the formation of iron oxide-anchored rGO sheets. The product was separated magnetically, washed, and freeze-dried for 72 h to form a BC with high structural uniformity and electrochemical activity, targeting Cd2+ ions. On the contrary, the second report [81] aimed at the synthesis of rGO with iron oxide anchoring, where graphene oxide (synthesized by the modified Marcano method) was reduced using different weight ratios of PAFE under reflux at 110 °C for 8 h at pH 5 (Figure 2). The obtained product was found to be N-doped rGO, which exhibited higher electrochemical performance due to rich restored conjugation and N doping. The BC obtained from the first study was found to possess multifunctionality, namely magnetism and sensing, whereas the second BC was found to possess pure electrochemical activity with higher sensitivity.
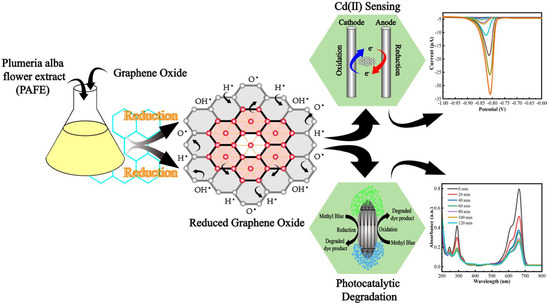
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of green synthesis of rGO using PAFE and its electrochemical sensing of Cd(II) ions. Reproduced with permission from [81]. © 2025 Elsevier B.V.
The works presented together show the flexible and significant use of plant-based bioresources in making effective electrochemical sensors for detecting Cd2+. These studies highlight new ways to turn natural extracts and biomass into useful materials, either directly as BC or as templates and reducing agents for creating nanostructures, such as carbon nanotubes, sodium aluminate, nanoceria, and iron oxide-anchored graphene. This green chemistry method produces sensors with improved electrochemical performance, displaying remarkable sensitivity and selectivity for Cd2+ in different complex samples, including environmental waters and food products. The findings highlight the strong potential of sustainable, biomass-focused methods for improving heavy metal detection technologies.
3.3. Mercury (Hg2+)
Mercury (Hg2+) is considered one of the most hazardous environmental pollutants, known for its neurotoxic, nephrotoxic, and immunotoxic effects. Among its several forms, divalent mercury, Hg (II), and methylmercury exhibit severe threats to human health owing to their high bioavailability and bioaccumulation potential. Hg2+ has the capability to penetrate the blood–brain barrier and placenta, which is responsible for causing irreversible neurological damage, developmental delays, and cognitive impairment in fetuses and children, whereas it causes tremors, memory loss, kidney dysfunction, and cardiovascular diseases in adults [82]. Coal combustion, artisanal gold mining, chloralkali industries, and improper disposal of Hg2+ from mercury-containing products, such as thermometers, fluorescent lamps, barometers, and dental fillings, are some of the key sources of environmental Hg2+ pollution [83]. The Hg2+, released into the environment, undergoes methylation in the aquatic systems, gets converted to the toxic methylmercury, and subsequently enters the food chain via aquatic species [84]. The determination of Hg2+ ions is quite challenging due to their low concentration, complex matrices, and co-existing interferents, which create difficulty in their selective and sensitive detection. Despite these challenges, electrochemical sensors have garnered significant attention for the detection of Hg2+ ions. The rich porosity, surface morphology, and tunability of BC help in the rapid adsorption of Hg2+ ions present in the samples, making them a green and efficient solution for environmental Hg2+ monitoring. The works reported so far in the literature are discussed as follows (Table 3).

Table 3.
Electrochemical sensors for the detection of Hg2+ ions.
Zou et al. reported two electrochemical sensors for the detection of Hg2+ using BC derived from Litsea cubeba wood, similar to that reported for Pb2+ ions [85,86]. In the first study [85], the BC was synthesized by activation pyrolysis at high temperatures (500–800 °C), yielding a highly porous, honeycomb-like structure. On this structure, bismuth molybdate nanosheets were grown in situ via the solvothermal reaction of bismuth nitrate and sodium molybdate. In the second study [86], the precursor was initially activated using KOH, followed by impregnation pyrolysis at high temperatures (600–800 °C), which led to the formation of surface oxygen groups, mesopores, and micropores (Figure 3). Subsequently, a copper precursor, such as copper nitrate or sulfate, was reduced to form copper oxide (Cu2O) nanoparticles. The former work enabled dual sensing and photocatalytic remediation, whereas the latter exhibited excellent electrochemical activity, making it ideal for ultra-trace Hg2+ ion sensing.
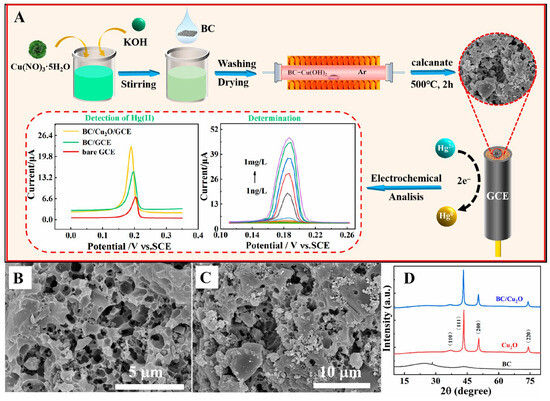
Figure 3.
(A) Schematic illustration of the fabrication of BC/Cu2O/GCE for electrochemical sensing of Hg(II) ions. (B,C) SEM images and (D) XRD analysis of the synthesized BC/Cu2O. Reproduced with permission from [86]. © 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland.
Hareesha et al. synthesized a highly porous BC from honeycomb polypore biomass waste using a thermal activation method [87]. The shade-dried biomass waste was crushed, washed with concentrated H2SO4 and water (to remove impurities), followed by pre-carbonization at 200 °C for three hours and subsequent chemical activation via soaking in sodium hydroxide (NaOH) for 12 h. The obtained mass was subjected to HTC at 300 °C for four hours, washed, filtered, and oven-dried to obtain NaOH-activated porous carbon nanosheets. These nanosheets were then mixed with graphite powder and Nafion to fabricate the electrodes. These electrodes were found to possess high porosity, conductivity, and an enhanced electroactive surface area, which exhibited improved electrocatalytic performance in both Hg2+ ion sensing and water splitting reactions. This fabricated electrode was found to be highly suited for eco-friendly multifunctional energy and sensing applications.
Zou et al. reported the development of a high-performance electrochemical sensor made from 3D hollow nickel–cobalt layered double hydroxide (NiCo-LDH) nanocages anchored on porous BC [88]. The BC was obtained from Magnolia soulangeana leaves and synthesized using a ZIF-67 MOF template-assisted method. The 3D NiCo-LDH/PBC hybrid had a large surface area, many electroactive sites, and excellent electrical conductivity. This allowed for highly sensitive and simultaneous detection of trace levels of Cu2+ and Hg2+. This work demonstrates the potential of using MOF-derived 3D hollow structures along with sustainable carbon materials in electrochemical sensing platforms.
The studies show how versatile and effective BC-derived materials are for high-performance electrochemical sensing of Hg2+ ions. By using different biomass sources and various preparation methods, such as templating with MOFs, high-temperature activation, and chemical functionalization, researchers have created BC-based composites. These include materials like bismuth molybdate, copper oxide, or NiCo-LDH nanocages, along with porous carbon nanosheets. These advancements produce materials with specific porosities, improved conductivity, and many active sites. This leads to highly sensitive and selective platforms that can also be multifunctional, enabling dual sensing, photocatalytic, or energy applications for detecting low levels of mercury in numerous environmental and biological samples. This research highlights the important role of sustainable biomass in improving electrochemical sensing technologies for environmental monitoring and public health.
3.4. Simultaneous Detection of Heavy Metal Ions
The simultaneous determination of heavy metal ions is significant for environmental monitoring, food safety, and public health, as these ions frequently co-exist and cause synergistic toxic effects. Conventional methods often require sequential analysis, which is time-consuming, requires trained personnel, and may fail to capture the dynamic interactions among the heavy metal ions. In contrast, simultaneous detection ensures rapid, economical, and thorough screening, which comprehensively analyzes heavy metal ions. This is highly valuable for detecting Pb2+, Cd2+, and Hg2+, as they have overlapping toxic thresholds and collectively cause neurotoxicity, nephrotoxicity, and carcinogenic effects even at trace levels [89].
Electrochemical sensors incorporating BC and advanced nanomaterials offer high sensitivity, selectivity, and portability for real-time field analysis. Thus, the development of robust BC-based electrochemical sensors capable of simultaneously detecting heavy metal ions is necessary for monitoring heavy metal contamination in health and the environment. The BC-based electrochemical sensors reported so far in the literature for the simultaneous detection of heavy metal ions are discussed in the following sections (Table 4).

Table 4.
Electrochemical sensors for the simultaneous detection of heavy metal ions.
3.4.1. Lead and Cadmium
Suguihiro et al. developed a castor oil cake-derived BC-modified carbon paste electrode (CPE) for the simultaneous detection of Pb2+ and Cd2+ ions [90]. The castor oil cake was pyrolyzed under different conditions, including heating rate (5–10 °C min−1), temperature range (300–350 °C), and duration (30–60 min). The BC prepared at 300 °C for 60 min with a 10 °C min−1 heating rate exhibited the most desired surface functional groups, such as hydroxyl, carboxyl, and nitrogen (N) groups, which in turn enhanced the adsorption of heavy metal ions upon combination with CPE. In a subsequent study [91], the same research group modified the experimental conditions for BC synthesis (pyrolysis temperature = 200–600 °C; heating rate = 5 °C per minute). This modification enhanced the electrocatalytic sensing performance of the BC-CPE and extended the electrochemical sensing capabilities to include Cu2+, in addition to Pb2+ and Cd2+ ions. The change in synthesis conditions resulted in the BC possessing greater aromaticity and higher carbon content. These two studies highlight the significance of optimizing pyrolysis conditions for altering the physical and chemical properties of the target BC.
Zeinu et al. reported the synthesis of bismuth oxide-doped BC for the simultaneous detection of Pb2+ and Cd2+ ions [92]. Corn flour was first activated with KOH, followed by drying and pre-carbonization at 500 °C under an N2 atmosphere. This material was then refluxed with H2O2 to incorporate oxygen functional groups and to adsorb bismuth from the subsequently added bismuth nitrate, along with carbonization from 500 to 900 °C. The BC carbonized at 900 °C with bismuth modification possessed enhanced graphitization and porosity. This modified BC was then combined with a glassy carbon electrode (GCE) for the electrochemical detection of Pb2+ and Cd2+ at picomolar levels. Qin et al. synthesized a bacterial cellulose-based BC using a one-step carbonization approach [93]. The freeze-dried bacterial cellulose was subjected to direct carbonization at a temperature of 800 °C for five hours under an N2 atmosphere. This technique produced a fluffy, lightweight, amorphous carbon nanofiber with a high level of interconnectivity. The obtained carbon was combined with Nafion and coated over a GCE for the electrochemical sensing of Pb2+ and Cd2+ ions. Similar to the previous work, a fungal biomass-derived BC was prepared by Dali et al. using Trichoderma asperellum strains extracted from metal-contaminated soils [94]. The dried fungal biomass, rich in functional groups like carboxyl, hydroxyl, amine, and imidazole, was made into a fine powder using a ball mill. This powder was then mixed with carboxyl-functionalized single-walled carbon nanotubes to improve the surface area and conductivity, and was drop-casted over a GCE to simultaneously detect Pb2+ and Cd2+ ions.
The same group of scientists from [63] utilized the same oil palm empty fruit bunch (OPEFB)-derived BC (under the same experimental conditions) for the simultaneous detection of Pb2+, Cd2+, Cu2+, and Zn2+ [95]. The former study focused more on clinical/biomedical applications by detecting Pb2+ in blood serum, whereas the latter focused more on environmental/industrial applications by simultaneously detecting the aforementioned ions in palm oil mill effluent. Zhang et al. used waste pomelo peels as the BC source, decorating them with palladium nanoparticles via a multi-step process [96]. First, the pomelo peels were dried at 80 °C and chemically activated using KOH for 24 h, followed by carbonization at 700 °C for 3 h under an argon atmosphere, which produced porous activated carbon. To this, palladium chloride was added, followed by a second thermal treatment at 900 °C for 3 h under an argon atmosphere, enabling uniform dispersion of palladium nanoparticles over the activated carbon. The obtained modified BC was found to possess a highly graphitic nature and porosity, which enhanced the simultaneous sensing of Pb2+, Cd2+, and Cu2+ ions with nanomolar-level detection limits. Following the bacterial cellulose [93] and fungal biomass [94]-derived BC reports, a study on an algal (kelp)-derived BC was carried out by the same group of scientists [97]. Dried kelp was immersed in KOH for chemical activation and freeze-dried for 48 h, followed by carbonization at 900 °C for three hours under an argon atmosphere. This resulted in improved graphitic nature, surface functionality, and enhanced electrochemical performance towards the simultaneous detection of Pb2+ and Cd2+ ions.
Aldrete et al. utilized spent coffee grounds as the biomass feedstock [98], which underwent extensive pretreatment via washing, drying, milling, and was finally enriched with carboxylic functional groups through the addition of citric acid. The obtained BC was mixed with graphite powder to form an electrode paste, which was then used for the simultaneous detection of Pb2+ and Cd2+ ions. Zhu et al. reported the incorporation of bismuth nanoparticles onto Platanus seeds-derived BC [99]. Initially, the Platanus seeds were ultrasonically washed, vacuum-dried, and pre-carbonized at 600 °C under an N2 atmosphere. This was followed by chemical activation with KOH and high-temperature pyrolysis at 900 °C, which resulted in a lotus-root-shaped porous BC. The BC was further subjected to microwave-assisted solvothermal deposition of bismuth nanoparticles from bismuth oxide, followed by carbothermal reduction at 500 °C, producing the desired bismuth-decorated BC for the simultaneous detection of Pb2+ and Cd2+ ions.
A nanoscale zero-valent iron nanoparticle-decorated BC was synthesized by Djebbi et al. using the marine biomass Posidonia oceanica [100]. The marine biomass was ultrasonically washed, dried, powdered, soaked in KOH solution, and carbonized at 700 °C under an N2 atmosphere, followed by acid-washing and drying (Figure 4). Simultaneously, the iron nanoparticles were synthesized and incorporated onto the BC through liquid-phase reduction with sodium borohydride. The obtained nanocomposite was found to possess a high surface area and conductivity, making it suitable for the simultaneous detection of Pb2+ and Cd2+ ions.
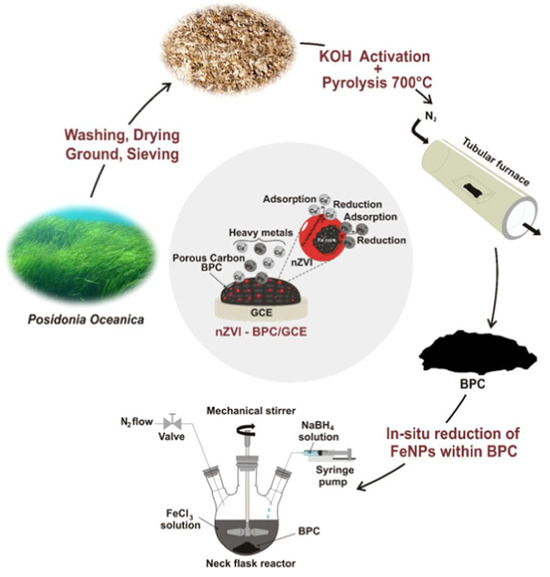
Figure 4.
Schematic representation of synthesis and application of nanoscale zero-valent iron-biochar composite obtained using Posidonia oceanica for simultaneous detection of Pb(II) and Cd(II) ions. Reproduced with permission from [100]. © 2022 American Chemical Society.
Xu et al. [101] reported a peanut shell-derived BC for a zeolitic imidazolate framework. In their method, the peanut shells were washed, dried, powdered, pre-carbonized at 300 °C, chemically activated using KOH, carbonized at 700 °C under a nitrogen atmosphere, and finally treated with H2SO4 to incorporate in situ self-assembly of the zeolitic imidazolate framework. This material exhibited high sensitivity and selectivity towards the simultaneous detection of Pb2+ and Cd2+ ions. In all the aforementioned reports, the significance of optimizing the pyrolysis temperature and chemical activation with KOH was evidenced by the high electrochemical performance obtained during the simultaneous detection of Pb2+ and Cd2+ ions.
Mosquera-Ortega et al. described an affordable, scalable way to create flexible plastic electrodes using BC from peanut shells, which is a plentiful agricultural byproduct [102]. They produced the BC in a custom kiln and modified it with chitosan and NaOH to improve its porosity, water affinity, and surface features. They then incorporated these chitosan-BC composites into plastic electrode films through a straightforward casting method using blends of polyvinyl chloride and graphite. This process allows for large-scale production under normal conditions. They further enhanced performance by depositing bismuth, achieving ultra-low LODs for lead and cadmium, well below the World Health Organization and Environmental Protection Agency regulatory limits. Additionally, the fabrication process followed the principles of green analytical chemistry, earning a higher AGREE score (0.75) than traditional pyrolysis methods. This study showed that peanut shell BC could be a sustainable and versatile base for eco-friendly heavy metal sensors of the future.
3.4.2. Lead and Mercury
A zirconium MOF-incorporated BC, designated as UiO-66-NH2/BC, was prepared by Zou et al. [103]. The BC precursor, Magnolia grandiflora fruit, was washed, dried, powdered, chemically activated using KOH, and pyrolyzed at 800 °C under an N2 atmosphere, yielding a BC with a high surface area and rough porous texture (Figure 5). The zirconium MOF was added to the BC via a layer-by-layer approach on a GCE, offering enhanced simultaneous electrochemical detection of Pb2+ and Hg2+ ions. Separately, Elamin et al. reported a BC using gum arabic (a natural biopolymer) as a green reducing and stabilizing agent for synthesizing platinum nanoparticles [104]. Chloroplatinic acid (a platinum precursor) and gum arabic were mixed and stirred at 60 °C for 24 h, which enabled the in situ reduction and encapsulation of platinum nanoparticles by the gum arabic biopolymer. Screen-printed electrodes modified with this nanocomposite were used for the simultaneous detection of Pb2+ and Hg2+ ions.
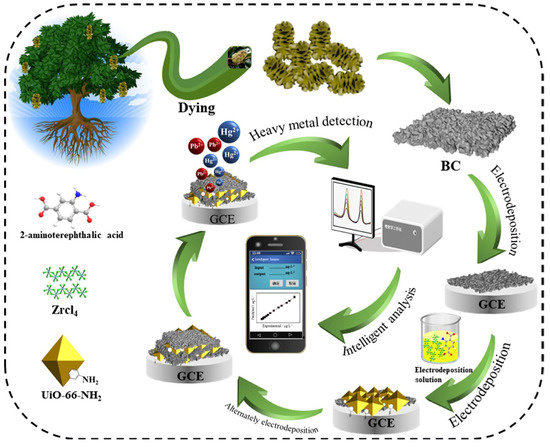
Figure 5.
Schematic illustration of the synthesis and application of UiO-66-NH2/BC-modified GCE for simultaneous detection of Pb(II) and Hg(II) ions. Reproduced with permission from [103]. © 2021 Elsevier B.V.
3.4.3. Cadmium and Mercury
Citrus fruit peel (lemon and orange) extracts were used by Okpara et al. for the formation of copper and zinc oxides from their respective precursors [105]. The salt solutions of copper and zinc precursors were heated from 60 to 100 °C with continuous magnetic stirring. To these, the citrus peel extracts were added, followed by NaOH to adjust the pH to a basic medium, enabling faster reduction and stabilization of the Cu2O and zinc oxide nanoparticles. The obtained material was washed, centrifuged, and oven-dried (>200 °C), after which polyaniline (PANI) was incorporated before its modification onto a screen-printed electrode. The fabricated modified electrode exhibited the simultaneous detection of Cd2+ and Hg2+ ions with high sensitivity and selectivity. Doloi et al. fabricated a silver oxide nanoparticle-decorated zirconium MOF nanocomposite using banana root bulb as a natural reducing agent for silver oxide [106]. First, a zirconium MOF was prepared using the solvothermal route with zirconium chloride and benzene dicarboxylic acid as precursors (Figure 6). Second, to this MOF, silver nitrate was added and boiled, followed by the addition of banana root bulb extract, which led to the in situ reduction and formation of silver oxide nanoparticles on the MOF. This was then annealed at 100 °C to obtain the desired nanocomposite. This nanocomposite-based electrochemical sensor exhibited the simultaneous detection of Cd2+ and Hg2+ ions.

Figure 6.
Schematic representation of a banana root bulb-derived MOF-based electrochemical sensing platform for the simultaneous detection of Cd(II) and Hg(II) ions. Reproduced with permission from [106]. © 2023 Elsevier Ltd., Amsterdam, The Netherlands.
3.4.4. Lead, Cadmium, and Mercury
Madhu et al. utilized dead mango leaves for the synthesis of spherical nanoparticle-decorated BC that simultaneously detected Pb2+, Cd2+, Cu2+, and Hg2+ [107]. The mango leaves were dried, pulverized, and chemically activated using KOH under an N2 atmosphere by pyrolyzing them at different temperatures (700, 800, and 900 °C) for two hours at a heating rate of 10 °C min−1. The resulting material was then washed with HCl and water, dried, and ground. Subsequent characterization revealed that the BC synthesized at 900 °C possessed a higher surface area and pore volume, which in turn enhanced the electrochemical sensing behavior upon coating over a GCE. A byproduct from the brewing industry, barley dust, was used for BC preparation by Djemmoe et al. [108]. The first step involved chemical activation with sodium carbonate upon continuous stirring for three hours, followed by washing to a neutral pH and drying at 105 °C. This material was further made into a carbon paste electrode (CPE) for the simultaneous detection of Pb2+, Cd2+, and Hg2+ ions. Walnut shells were used for BC synthesis by Hamdouni et al. [109] through cleaning, drying at 105 °C for 24 h, grinding, and pyrolyzing at 600 °C for 2 h under vacuum. The obtained BC was found to have a higher carbon content and was modified into a CPE by mixing with a poly-tyrosine film, which resulted in increased surface functionality and conductivity. This was extended to the simultaneous electrochemical detection of Pb2+, Cd2+, Hg2+, and Cu2+ ions.
Oak wood biomass was prepared by Pu et al. [110] by heating the BC, which was soaked in auric chloride solution, at 850 °C for two hours under an N2 atmosphere at a slow heating rate of 2 °C min−1, followed by treatment with HCl, water, ethanol, and drying at 60 °C. The obtained BC was found to be porous, thermally stable, and to exhibit a lotus-root-like microstructure. Lastly, this BC was modified into a CPE and used for the simultaneous detection of Pb2+, Cd2+, and Hg2+ ions. Li et al. used starch as the BC precursor, which was doped with N and S using thiourea as the source. These were subjected to HTC and fast pyrolysis [111]. Starch and thiourea were heated at 180 °C for 5 h, followed by carbonization at 800 °C in an N2 atmosphere and intermediate pre-carbonization at 300 °C (Figure 7). The obtained BC was used for the simultaneous detection of Pb2+, Cd2+, and Hg2+ ions and demonstrated the critical role of HTC doping and high-temperature carbonization in the synthesis of BC. Similar to the previous work, Huang et al. prepared a multi-doped porous BC from Cinnamomum camphora branches [112] by HTC using H3PO4 as a chemical activator and Pluronic F127 as a porogen. The chemical activator enabled P-doping, and the material was further doped with Fe3O4 nanoparticles (by chemical precipitation) and attapulgite clay, which increased its magnetic properties, ion exchange capacity, and surface area. Subsequently, the BC was doped with a bismuth film via electrodeposition, and the resulting sensor was integrated with a smartphone-operated wireless device, exhibiting simultaneous detection of Pb2+, Cd2+, and Hg2+ ions with ultra-low detection limits for field deployment.

Figure 7.
Schematic representation of the synthesis of N, S-co-doped BC derived from starch and its application for the simultaneous detection of Pb(II), Cd(II), and Hg(II) ions. Reproduced with permission from [111]. © 2023 Elsevier Inc.
Overall, this review highlights several research vignettes demonstrating how BC-derived electrochemical sensors detect trace amounts of heavy metals. For instance, the BCs created by Mojica et al. [60], Li et al. [64], and Agustini et al. [61] demonstrate that when BC’s surface chemistry and porosity are activated, they improve the sensitivity, selectivity, and strong detection of Pb2+. This often occurs in real, complex mixtures like groundwater, ceramics, and biological fluids. Radotić et al. [68] and Su et al. [72] support the benefits of green synthesis and processing through minimal energy use or direct modification of the electrode surface. This approach promotes sustainability while achieving effective sensing performance. Sharma et al. [73] and Mamatha et al. [71] focus on modification strategies, particularly doping and adding nanoparticles, as essential for adjusting sensor selectivity, sensitivity, and resilience against interference in complex environments. Suguihiro et al. [90], Zeinu et al. [92], and Qin et al. [93] show BC’s flexibility in multi-ion sensing platforms. Surface tuning, such as activation, doping, and integrating nanomaterials, enables cost-effective and portable solutions for environmental monitoring. Jangi and Khoobi [78], Rani et al. [79], and Zou et al. [85,86] utilize plant extracts and natural compounds in sensor construction. This method enables the green synthesis of nanomaterials and supports circular economy models, increasing the practical relevance and sustainability of sensor platforms. Su et al. and Huang et al. combine BC’s material benefits with improved signal processing and mobile technologies. These examples indicate a shift toward the next generation of intelligent, low-cost, and widely accessible environmental sensors. Through tailored production, functional improvement, and smart technology integration, research shows the significant potential for sensitive, selective, eco-friendly heavy metal detection, supported by practical studies from real-world environmental and biological settings.
A summary of all the works included in this review is given in Table 5. This extensive research highlights the impressive flexibility and importance of biochar (BC) in developing high-performance electrochemical sensors. These sensors can detect multiple heavy metal ions, including Pb2+, Cd2+, Cu2+, Zn2+, and Hg2+. The studies show that by carefully adjusting the synthesis conditions—such as pyrolysis parameters and chemical activation with substances like KOH or citric acid, and by strategically adding different nanomaterials like bismuth, palladium, iron, platinum, copper, silver, nickel-cobalt LDH, MOFs, and carbon nanotubes—biochar’s properties can be improved. This optimization enhances porosity, conductivity, surface functionality, and electrocatalytic activity. Using a variety of sustainable biomass sources not only helps create sensitive, selective, and often multi-functional sensors but also points to a clear path for eco-friendly and practical solutions for environmental monitoring and health diagnostics. This includes real-world applications and potential integration with smart technologies.

Table 5.
Summary of the works reported in this review.
3.5. Comparative Evaluation of Electrochemical Techniques in Biochar-Based Heavy Metal Detection
Various electrochemical techniques, including DPASV, SWASV, SWV, DPV, DPSV, and CV, have been extensively used in BC-modified sensor platforms to analyze trace metal ions. Each method offers specific advantages suited to different sensing conditions. Among these techniques, SWASV and DPASV are the most-used electroanalytical methods for detecting trace heavy metals with BC-based sensors. They are recognized for their high sensitivity, selectivity, and ease of operation. Both involve a pre-concentration step combined with sensitive voltammetric detection, enabling detection limits from sub-micromolar to nanomolar levels. This is shown in several studies summarized in Table 3. For example, BC made from OPEFB reached a limit of detection (LOD) of 0.001 µM for Cd2+ ions using SWASV [95]. Similarly, BC from castor oil cake demonstrated comparable sensitivity for Pb2+ with an LOD of 0.001 µM using DPASV [90]. These low detection limits, along with wide linear ranges (e.g., 0.088–0.44 µM and 0.05–10 µM), underscore the effectiveness of these voltammetric methods for analyzing environmental and biological samples, including blood serum, groundwater, and ceramic surfaces. SWASV offers several benefits, such as a fast scan rate, low capacitive background currents, and enhanced selectivity. These features make it particularly suitable for real-time and on-site measurements. It is especially effective for detecting multiple ions at once, as shown by BC platforms that identify Pb2+, Cd2+, and Cu2+ in complex samples like lake water and palm oil mill effluent [109]. Conversely, DPASV provides excellent resolution and peak separation for redox processes that are closely spaced. This allows for high precision even in samples containing interfering substances. DPASV is also more tolerant of small variations in experimental conditions and is often preferred for preparing modified electrodes through green and reproducible methods, such as using HTC-derived BC from almond shells [65] or Litsea cubeba [85,86].
However, both techniques have their limitations. The pre-concentration step relies on the surface, making the reproducibility of fabrication and electrode fouling major challenges—particularly when used repeatedly in complex samples like farm water and domestic sewage. Additionally, both SWASV and DPASV require careful adjustment of parameters such as pulse amplitude, frequency, and accumulation time, which can vary depending on different BC matrices and target ions. Another issue is the overlap of peak potentials among some metal ions, such as Pb2+ and Cd2+, which can compromise the accuracy of multi-ion detection unless advanced deconvolution or masking techniques are applied. Furthermore, while many studies utilize non-toxic carbon-based electrodes, some still employ mercury-based film electrodes, raising concerns about sustainability and safety. In contrast, SWV and DPV offer moderate to high sensitivity and are generally easier to implement. They are often used when the simultaneous detection of multiple ions is not necessary. Their shorter acquisition times and simple waveform generation make them suitable for low-resource sensing platforms. DPSV, though less frequently reported, has shown promising results with complex BC matrices in detecting heavy metals at ultra-trace levels. Studies using Plumeria alba [80,81] and walnut shell [109] biomass support this finding. CV is not ideal for detailed quantitative analysis but remains valuable for initial explorations of redox behavior and surface interactions between the BC electrode and metal ions. Researchers often use CV to characterize the electrochemical active surface area and to verify the presence of redox-active functional groups or pathways involved in metal ion interactions on BC-modified electrodes. Although CV helps study mechanisms, it lacks the sensitivity needed to detect ions at environmentally relevant levels. Peak overlap also presents a significant challenge during multi-metal analysis, often requiring complexing agents or advanced deconvolution algorithms. In conclusion, selecting and optimizing these voltammetric techniques, along with tailored biochar synthesis methods like pyrolysis or HTC, allows for the development of versatile and sustainable electrochemical sensors. Each technique contributes differently to sensitivity, selectivity, speed, and practicality, making their combined use crucial in metal ion sensor research.
4. Conclusions
Biochar-based electrochemical sensors have emerged as a promising and sustainable alternative for the determination of trace heavy metal ions owing to their low cost, high sensitivity, rapid response, and portable nature. Biochar has a high surface area and porosity, providing many active sites that are important for effectively adsorbing heavy metal ions and facilitating electrochemical reactions. Additionally, its properties can be modified through controlled pyrolysis, and it generally has good conductivity, especially after carbonization. This makes it a flexible platform. However, specific modifications come with their limitations. For instance, the surface functionalization methods like crosslink-xanthate or nitric acid activation improve the adsorption and binding of metal ions by adding specific functional groups such as hydroxyl, carboxyl, nitrogen, and oxygen but also include increased complexity in synthesis, the risk of leaching active components over time, and difficulties with large-scale production. Similarly, the integration of nanomaterials, like bismuth, palladium, iron oxides, or carbon nanotubes, has synergistic effects, merging biochar’s base properties with the unique catalytic activities and high surface areas of nanoparticles; however, these methods typically require complex, multi-step, and sometimes energy-consuming synthesis processes. Costs can rise, especially with noble metal nanoparticles, and there are concerns about the long-term stability and potential clumping of the added nanoparticles. Heteroatom doping, which involves adding elements like nitrogen or sulfur into the biochar matrix, improves the material’s electronic structure, enhances conductivity, improves wettability, and can even provide selectivity for specific ions. While some doping methods can be relatively simple, precisely controlling the type and level of doping remains challenging, and the stability of some heteroatom features at high temperatures must be considered. Optimizing pyrolysis conditions—such as temperature, heating rate, atmosphere, and pre-treatment—is crucial because it directly affects important biochar properties like surface area, porosity, and carbon content. This method is cost-effective and straightforward for creating the base material. However, pyrolysis alone may not provide the extreme sensitivity or selectivity that more complex modifications can achieve, and high-temperature processes consume a lot of energy. On the other hand, non-pyrolyzed or green extraction methods, such as using maize stems or tea leaves, are notable for their low energy usage and eco-friendliness. They also retain natural bioactive compounds with useful functional groups. The trade-offs include potentially lower carbon content and conductivity compared to carbonized biochar, reduced chemical and thermal stability, and generally higher detection limits. Finally, electrochemical reshaping, like in situ reshaped nano-biochar, offers an innovative approach. Its main benefits are on-site modifications on the electrode surface, which simplify fabrication, and major improvements in properties such as smaller particle size, better conductivity, and increased hydrophilicity. This method also shows potential for integration with machine learning. The key limitations are its potential specificity to certain biochar types and current challenges in scaling up direct electrode reshaping compared to bulk material synthesis. Ultimately, choosing how to modify biochar requires balancing cost with performance, balancing simplicity in synthesis against the achievable sensitivity and selectivity, and maintaining overall sustainability without sacrificing efficiency. The ultimate goal is to use biochar’s potential to create effective and eco-friendly solutions for heavy metal sensing.
Author Contributions
S.S.—conceptualization; methodology; writing—original draft, reviewing and editing; visualization. Y.-J.K.—conceptualization; methodology; writing—reviewing and editing; administration; supervision; funding acquisition. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF-2022R1F1A1074346, RS-2024-00433166), and the APC was borne by NRF-2022R1F1A1074346.
Data Availability Statement
No data were used for the research described in the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| AAS | Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy |
| DPAdSV | Adsorptive Stripping Differential Pulse Voltammetry |
| As3+ | Arsenic |
| BC | Biochar |
| B | Boron |
| Cd2+/Cd(II) | Cadmium |
| CPE | Carbon Paste Electrode |
| Cu2O | Copper Oxide |
| CV | Cyclic Voltammetry |
| DPSV | Differential Pulse Stripping Voltammetry |
| DPV | Differential Pulse Voltammetry |
| ErNBC | Electrochemically reshaped nano-BC |
| GCE | Glassy Carbon Electrode |
| GHG | Greenhouse Gas |
| Au | Gold |
| HCl | Hydrochloric Acid |
| HTC | Hydrothermal Carbonization |
| Hap | Hydroxyapatite |
| ICP-MS | Induction-Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry |
| Pb2+/Pb(II) | Lead |
| LCA | Life Cycle Assessment |
| LOD | Limit of Detection |
| Fe3O4 | Magnetic Iron Oxide |
| Hg2+/Hg(II) | Mercury |
| MOF | Metal Organic Framework |
| CeO2 nanoparticles | Nanoceria |
| N/N2 | Nitrogen |
| OPEFB | Oil Palm Empty Fruit Bunches |
| H3PO4 | Phosphoric Acid |
| P | Phosphorus |
| PAFE | Plumeria alba Flower Extract |
| PANI | Polyaniline |
| KOH | Potassium Hydroxide |
| rGO | Reduced Graphene Oxide |
| NaOH | Sodium Hydroxide |
| SWASV | Square Wave Anodic Stripping Voltammetry |
| SWV | Square Wave Voltammetry |
| S | Sulfur |
| H2SO4 | Sulfuric acid |
| TiO2 | Titanium Oxide |
| XRF | X-Ray Fluorescence |
| UiO-66-NH2/BC | Zirconium MOF Incorporated BC |
References
- Oladimeji, T.E.; Oyedemi, M.; Emetere, M.E.; Agboola, O.; Adeoye, J.B.; Odunlami, O.A. Review on the Impact of Heavy Metals from Industrial Wastewater Effluent and Removal Technologies. Heliyon 2024, 10, e40370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briffa, J.; Sinagra, E.; Blundell, R. Heavy Metal Pollution in the Environment and Their Toxicological Effects on Humans. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massas, I.; Kalivas, D.; Ehaliotis, C.; Gasparatos, D. Total and Available Heavy Metal Concentrations in Soils of the Thriassio Plain (Greece) and Assessment of Soil Pollution Indexes. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 6751–6766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gwimbi, P.; Kotelo, T.; Selimo, M.J. Heavy Metal Concentrations in Sediments and Cyprinus Carpio from Maqalika Reservoir–Maseru, Lesotho: An Analysis of Potential Health Risks to Fish Consumers. Toxicol. Rep. 2020, 7, 475–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dabek-Zlotorzynska, E.; Celo, V.; Ding, L.; Herod, D.; Jeong, C.-H.; Evans, G.; Hilker, N. Characteristics and Sources of PM2.5 and Reactive Gases near Roadways in Two Metropolitan Areas in Canada. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 218, 116980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, A.M.; Mawodza, T.; Sarkar, B.; Menon, M. Assessment of Potentially Toxic Trace Element Contamination in Urban Allotment Soils and Their Uptake by Onions: A Preliminary Case Study from Sheffield, England. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 170, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulthana, S.F.; Iqbal, U.M.; Suseela, S.B.; Anbazhagan, R.; Chinthaginjala, R.; Chitathuru, D.; Ahmad, I.; Kim, T. Electrochemical Sensors for Heavy Metal Ion Detection in Aqueous Medium: A Systematic Review. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 25493–25512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, K.A.; Kazemeini, S.; Weber, D.C.; Cordero, P.A.; Garcia, E.M.; Rusinek, C.A. Electrochemical Sensing of Heavy Metals in Biological Media: A Review. Electroanalysis 2023, 35, e202300098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L. Recent Advances in Functional Nanomaterials for Electrochemical Sensors and Biosensors. Molecules 2023, 28, 6798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Rajan, R.; Upadhyaya, K.; Behl, G.; Xiang, X.-X.; Huo, P.; Liu, B. Metal Oxide Nanomaterials Based Electrochemical and Optical Biosensors for Biomedical Applications: Recent Advances and Future Prospectives. Environ. Res. 2024, 247, 118002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Li, M.; Jiang, G.; Li, G.; Zhu, J.; Xiao, M.; Zhu, Y.; Gao, R.; Yu, A.; Feng, M.; et al. Graphene Quantum Dots-Based Advanced Electrode Materials: Design, Synthesis and Their Applications in Electrochemical Energy Storage and Electrocatalysis. Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 10, 2001275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kangmennaa, A.; Forkuo, R.B.; Agorku, E.S. Carbon-Based Electrode Materials for Sensor Application: A Review. Sens. Technol. 2024, 2, 2350174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onfray, C.; Thiam, A. Biomass-Derived Carbon-Based Electrodes for Electrochemical Sensing: A Review. Micromachines 2023, 14, 1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, V.S.; Supriya, S.; Hegde, G. Review—Biomass Derived Carbon Materials for Electrochemical Sensors. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 037526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmandoust, M.; Li, G.; Erk, N. Biomass-Derived Carbon Materials as an Emerging Platform for Advanced Electrochemical Sensors: Recent Advances and Future Perspectives. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2023, 62, 4628–4635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, G.; Wang, X.; Hu, X.; Gu, Y.; Yang, Z. Application of Biochar for the Removal of Pollutants from Aqueous Solutions. Chemosphere 2015, 125, 70–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Narvaez, O.M.; Peralta-Hernandez, J.M.; Goonetilleke, A.; Bandala, E.R. Biochar-Supported Nanomaterials for Environmental Applications. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 78, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghassemi-Golezani, K.; Farhangi-Abriz, S. Biochar-Based Metal Oxide Nanocomposites of Magnesium and Manganese Improved Root Development and Productivity of Safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.). under Salt Stress. Rhizosphere 2021, 19, 100416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaedi, S.; Rajabi, H.; Hadi Mosleh, M.; Sedighi, M. MOF Biochar Composites for Environmental Protection and Pollution Control. Biores. Technol. 2025, 418, 131982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoudho, K.N.; Khan, T.H.; Ara, U.R.; Khan, M.R.; Shawon, Z.B.Z.; Hoque, M.E. Biochar in Global Carbon Cycle: Towards Sustainable Development Goals. Curr. Res. Green Sustain. Chem. 2024, 8, 100409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel Olugbenga, O.; Goodness Adeleye, P.; Blessing Oladipupo, S.; Timothy Adeleye, A.; Igenepo John, K. Biomass-Derived Biochar in Wastewater Treatment- a Circular Economy Approach. Waste Manag. Bull. 2024, 1, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Ren, G.; Ran, L.; Liu, M.; Geng, P.; Yi, W. Green Synthesis of Biomass-Derived Porous Carbon for Electrochemical Detection of Heavy Metal Ions: Methods, Properties, and Applications. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 113903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.-H.; Hoang, A.T.; Nižetić, S.; Pandey, A.; Cheng, C.K.; Luque, R.; Ong, H.C.; Thomas, S.; Nguyen, X.P. Biomass-Derived Biochar: From Production to Application in Removing Heavy Metal-Contaminated Water. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 160, 704–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Sun, W.; Lichtfouse, E.; Maurer, C.; Liu, H. Life Cycle Assessment of Biochar for Sustainable Agricultural Application: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 951, 175448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, H.A.; Alotaibi, K.D.; EL-Saeid, M.H.; Giesy, J.P. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) and Metals in Diverse Biochar Products: Effect of Feedstock Type and Pyrolysis Temperature. Toxics 2023, 11, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.; Yadav, P.; Bojjagani, S.; Srivastava, J.K.; Raj, A. Investigation of the Speciation and Environmental Risk of Heavy Metals in Biochar Produced from Textile Sludge Waste by Pyrolysis at Different Temperatures. Chemosphere 2024, 360, 142454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wu, S.; Cao, Y.; Liang, P.; Zhang, J.; Wong, M.H.; Wang, M.; Shan, S.; et al. Influence of Pyrolysis Temperature on Properties and Environmental Safety of Heavy Metals in Biochars Derived from Municipal Sewage Sludge. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 320, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Zou, Y.; Li, Y.; Kong, F.; Yang, D. Environmental Life Cycle Assessment of Supercapacitor Electrode Production Using Algae Derived Biochar Aerogel. Biochar 2021, 3, 701–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilge, S.; Karadurmus, L.; Sınağ, A.; Ozkan, S.A. Green Synthesis and Characterization of Carbon-Based Materials for Sensitive Detection of Heavy Metal Ions. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 145, 116473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanda, A.; Raj, R.; Sathe, S.M.; Dubey, B.K.; Ghangrekar, M.M. Graphene and Biochar-Based Cathode Catalysts for Microbial Fuel Cell: Performance Evaluation, Economic Comparison, Environmental and Future Perspectives. Environ. Res. 2023, 231, 116143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Rajapaksha, A.U.; Lim, J.E.; Zhang, M.; Bolan, N.; Mohan, D.; Vithanage, M.; Lee, S.S.; Ok, Y.S. Biochar as a Sorbent for Contaminant Management in Soil and Water: A Review. Chemosphere 2014, 99, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Lee, C.T.; Ong, P.Y.; Wong, K.Y.; Bong, C.P.C.; Li, C.; Gao, Y. A Review on the Comparison Between Slow Pyrolysis and Fast Pyrolysis on the Quality of Lignocellulosic and Lignin-Based Biochar. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 1051, 012075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seow, Y.X.; Tan, Y.H.; Mubarak, N.M.; Kansedo, J.; Khalid, M.; Ibrahim, M.L.; Ghasemi, M. A Review on Biochar Production from Different Biomass Wastes by Recent Carbonization Technologies and Its Sustainable Applications. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, R.; Sajjadi, B.; Chen, W.-Y.; Mattern, D.L.; Hammer, N.; Raman, V.; Dorris, A. Effect of Pyrolysis Temperature on PhysicoChemical Properties and Acoustic-Based Amination of Biochar for Efficient CO2 Adsorption. Front. Energy Res. 2020, 8, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamini, G.P.; Tee, K.F.; Gimbun, J.; Chin, S.C. Biochar in Cementitious Material—A Review on Physical, Chemical, Mechanical, and Durability Properties. AIMS Mater. Sci. 2023, 10, 405–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhakta, A.K.; Fiorenza, R.; Jlassi, K.; Mekhalif, Z.; Ali, A.M.A.; Chehimi, M.M. The Emerging Role of Biochar in the Carbon Materials Family for Hydrogen Production. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2022, 188, 209–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bughani, A.; Mehtab, S.; Palariya, D.; Maheshwari, J.; Zaidi, M.G.H. Biochar-Derived Nanocomposites for Electrochemical Estimation of Heavy Metals and Organic Pollutants. In Biomass for Environmental Remediation; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2025; pp. 55–80. ISBN 9780443330148. [Google Scholar]
- Arellano, O.; Flores, M.; Guerra, J.; Hidalgo, A.; Rojas, D.; Strubinger, A. Hydrotermal Carbonization (HTC) of Corncob and Characterization of the Obtained Hydrochar. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2016, 50, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, S. Preparation, Modification and Environmental Application of Biochar: A Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 227, 1002–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, T.A.; Saud, A.S.; Jamari, S.S.; Rahim, M.H.A.; Park, J.-W.; Kim, H.-J. Hydrothermal Carbonization of Lignocellulosic Biomass for Carbon Rich Material Preparation: A Review. Biomass Bioenergy 2019, 130, 105384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniscalco, M.P.; Volpe, M.; Messineo, A. Hydrothermal Carbonization as a Valuable Tool for Energy and Environmental Applications: A Review. Energies 2020, 13, 4098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heikkinen, J.; Keskinen, R.; Soinne, H.; Hyväluoma, J.; Nikama, J.; Wikberg, H.; Källi, A.; Siipola, V.; Melkior, T.; Dupont, C.; et al. Possibilities to Improve Soil Aggregate Stability Using Biochars Derived from Various Biomasses through Slow Pyrolysis, Hydrothermal Carbonization, or Torrefaction. Geoderma 2019, 344, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.; Chowdhary, P.; Ahmad, A.; Shekher Giri, B.; Chaturvedi, P. Hydrothermal Liquefaction of Rice Husk and Cow Dung in Mixed-Bed-Rotating Pyrolyzer and Application of Biochar for Dye Removal. Biores. Technol. 2020, 309, 123294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, J.; Wang, S.; Jin, L.; Liu, Y.; Yin, R.; Jiang, Z.; Tao, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhang, Y. Magnetic Porous Biochar with High Specific Surface Area Derived from Microwave-Assisted Hydrothermal and Pyrolysis Treatments of Water Hyacinth for Cr(VI) and Tetracycline Adsorption from Water. Biores. Technol. 2021, 340, 125692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Li, M.; Li, P.; Yang, L.; Wu, L.; Gao, F.; Qi, X.; Zhang, Z. Hydrothermal Synthesis of Magnetic Sludge Biochar for Tetracycline and Ciprofloxacin Adsorptive Removal. Biores. Technol. 2021, 319, 124199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Huang, Z.; Zhu, S.; Luo, S.; Yan, L.; Dai, Y.; Guo, Y.; Yang, Y. Removal of Cr(VI) from Water by a Biochar-Coupled g-C3N4 Nanosheets Composite and Performance of a Recycled Photocatalyst in Single and Combined Pollution Systems. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2019, 243, 386–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, L.; Zhu, Y.; Duan, Z.; Xue, T.; Duan, X.; Wen, Y.; Kumar, A.S.; Zhang, W.; Xu, J.; Hojjati-Najafabadi, A. Lotus Seedpods Biochar Decorated Molybdenum Disulfide for Portable, Flexible, Outdoor and Inexpensive Sensing of Hyperin. Chemosphere 2022, 301, 134595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, W.; Yang, B.; Sun, Y.; Xiao, L.; Tang, D.; Chen, K.; Sun, J.; Ke, J.; Zhuang, Y. Self-Sacrificial Template Synthesis of Heteroatom Doped Porous Biochar for Enhanced Electrochemical Energy Storage. J. Power Sources 2021, 488, 229455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falco, C.; Perez Caballero, F.; Babonneau, F.; Gervais, C.; Laurent, G.; Titirici, M.-M.; Baccile, N. Hydrothermal Carbon from Biomass: Structural Differences between Hydrothermal and Pyrolyzed Carbons via13 C Solid State NMR. Langmuir 2011, 27, 14460–14471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, F.; Ali, M.; Khan, M.; Mbeugang, C.F.M.; Isa, Y.M.; Kozlov, A.; Penzik, M.; Xie, X.; Yang, H.; Zhang, S.; et al. A Review of Biochar Production and Its Employment in Synthesizing Carbon-Based Materials for Supercapacitors. Ind. Crops Prod. 2025, 227, 120830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, N.A.M.; Irfan, O.M.; Moustafa, H.M. H3PO4/KOH Activation Agent for High Performance Rice Husk Activated Carbon Electrode in Acidic Media Supercapacitors. Molecules 2022, 28, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Xiao, J.; Yılmaz, M.; Zhang, T.C.; Yuan, S. N, P Co-Doped Porous Biochar Derived from Cornstalk for High Performance CO2 Adsorption and Electrochemical Energy Storage. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 299, 121719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Qi, Z.; Wang, Z. Electrochemical-Enhanced Fe3O4/Biochar Activates Peroxymonosulfate (E/Nano-Fe3O4/BC/PMS) for Degradation of Oxytetracycline. Chemosphere 2022, 308, 136148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Liu, H.; Yang, J.; Shi, Z.; Tan, Y.; Jin, J.; Wang, R.; Zhang, S.; Wang, J. Biochar Decorated with Gold Nanoparticles for Electrochemical Sensing Application. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 261, 464–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahamed, M.; Singh, S.; Behari, J.R.; Kumar, A.; Siddiqui, M.K.J. Interaction of Lead with Some Essential Trace Metals in the Blood of Anemic Children from Lucknow, India. Clin. Chim. Acta 2007, 377, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balali-Mood, M.; Naseri, K.; Tahergorabi, Z.; Khazdair, M.R.; Sadeghi, M. Toxic Mechanisms of Five Heavy Metals: Mercury, Lead, Chromium, Cadmium, and Arsenic. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 643972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collin, M.S.; Venkatraman, S.K.; Vijayakumar, N.; Kanimozhi, V.; Arbaaz, S.M.; Stacey, R.G.S.; Anusha, J.; Choudhary, R.; Lvov, V.; Tovar, G.I.; et al. Bioaccumulation of Lead (Pb) and Its Effects on Human: A Review. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2022, 7, 100094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Guan, H.; Tian, Z.-Q.; Chen, M.-M.; Tian, K.-K.; Zhao, F.-J.; Wang, P. Exposure Sources, Intake Pathways and Accumulation of Lead in Human Blood. Soil. Secur. 2024, 15, 100150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouangpipat, W.; Lelasattarathkul, T.; Dongduen, C.; Liawruangrath, S. Bioaccumulation and Determination of Lead Using Treated-Pennisetum-Modified Carbon Paste Electrode. Talanta 2003, 61, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojica, E.-R.E.; Vidal, J.M.; Pelegrina, A.B.; Micor, J.R.L. Voltammetric Determination of Lead (II) Ions at Carbon Paste Electrode Modified with Banana Tissue. J. Appl. Sci. 2007, 7, 1286–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agustini, D.; Mangrich, A.S.; Bergamini, M.F.; Marcolino-Junior, L.H. Sensitive Voltammetric Determination of Lead Released from Ceramic Dishes by Using of Bismuth Nanostructures Anchored on Biochar. Talanta 2015, 142, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, D.S.Y.; Impas, M.G.W.; Camacho, D.H.; Palisoc, S.T. Paper-Based Electrode Using Cladophora Cellulosepolyaniline Composite for Electrochemical Quantification of Toxic Lead (II). Cellul. Chem. Technol. 2018, 52, 853–861. [Google Scholar]
- Ajab, H.; Dennis, J.O.; Abdullah, M.A. Synthesis and Characterization of Cellulose and Hydroxyapatite-Carbon Electrode Composite for Trace Plumbum Ions Detection and Its Validation in Blood Serum. Inter. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 113, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Wan, Z.; Liu, J.; Guliyeva, G. Bayberry-Kernel-Derived Wormlike Micro/Mesoporous Carbon Decorated with Human Blood Vessel-Like Structures and Active Nitrogen Sites as Highly Sensitive Electrochemical Sensors for Efficient Lead-Ion Detection. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 1191–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baikeli, Y.; Mamat, X.; Yalikun, N.; Wang, Y.; Qiao, M.; Li, Y.; Hu, G. Differential Pulse Voltammetry Detection of Pb(II) Using Nitrogen-Doped Activated Nanoporous Carbon from Almond Shells. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 23678–23685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivan, S.K.; Shankar, S.S.; Sajina, N.; Padinjareveetil, A.K.; Pilankatta, R.; Kumar, V.B.S.; Mathew, B.; George, B.; Makvandi, P.; Černík, M.; et al. Fabrication of a Greener TiO2 @Gum Arabic-Carbon Paste Electrode for the Electrochemical Detection of Pb2+ Ions in Plastic Toys. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 25390–25399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Liu, J.; Bi, Y.; Ma, C.; Bai, J.; Hu, Z.; Zhou, M. Biomass Derived Worm-like Nitrogen-Doped-Carbon Framework for Trace Determination of Toxic Heavy Metal Lead (II). Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1116, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radotić, K.; Djikanović, D.; Simonović Radosavljević, J.; Jović-Jovičić, N.; Mojović, Z. Comparative Study of Lignocellulosic Biomass and Its Components as Electrode Modifiers for Detection of Lead and Copper Ions. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2020, 862, 114010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, G.A.; Gevaerd, A.; Mangrich, A.S.; Marcolino-Junior, L.H.; Bergamini, M.F. Biochar Obtained from Spent Coffee Grounds: Evaluation of Adsorption Properties and Its Application in a Voltammetric Sensor for Lead (II) Ions. Microchem. J. 2021, 165, 106114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Yu, Q.; Gao, Y.; Chen, S.; Huang, X.; Hu, D.; Liu, S.; Lu, L.-M. Bismuth Nanoclusters/Porous Carbon Composite: A Facile Ratiometric Electrochemical Sensing Platform for Pb2+ Detection with High Sensitivity and Selectivity. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 1132–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamatha, K.M.; Srinivasa Murthy, V.; Ravikumar, C.R.; Murthy, H.C.A.; Kumar, V.G.D.; Kumar, A.N.; Jahagirdar, A.A. Facile Green Synthesis of Molybdenum Oxide Nanoparticles Using Centella Asiatica Plant: Its Photocatalytic and Electrochemical Lead Sensor Applications. Sens. Int. 2022, 3, 100153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Wang, J.; Hu, S.; Cheng, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, S.; Chen, M.; Cao, Q.; Zhang, S.; Yang, L.; et al. In-Situ Reshaping Nano-Biochar on Electrode Surface for Machine Learning Assisted Selective Sensing of Pb2+ in Real Water Samples. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2024, 665, 160294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Rana, D.S.; Awasthi, A.; Singh, D.; Ibrahim, A.A.; Umar, A.; Baskoutas, S. Nitrogen Functionalized Biomass Derived Mesoporous Carbon Nanomaterials for Electrochemical Detection of Lead (II) Ions. Heliyon 2024, 10, e39090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mampane, L.; Moothi, K.; Ntwampe, O.; Moloto, N.; Ndlovu, G.; Jijana, A.; Tetyana, P.; Mphuthi, N.; Ngqalakwezi, A.; Shumbula, P.; et al. Yerba Mate Tea Mediated Synthesis of Nanoscale Zero Valent Iron Particles and Their Application in Detection of Pb Ions in Water. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2025, 47, 100728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanfani, A.; Papini, S.; Bortolotti, E.; Vagnoni, G.; Saieva, C.; Bonaccorsi, G.; Caini, S. Cadmium in Biological Samples and Site-Specific Cancer Risk and Mortality: A Systematic Review of Original Articles and Meta-Analyses. Cancer Epidemiol. 2024, 92, 102550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasin, P.; Ashwathi, A.V.; Basheer, S.M.; Haribabu, J.; Santibanez, J.F.; Garrote, C.A.; Arulraj, A.; Mangalaraja, R.V. Exposure to Cadmium and Its Impacts on Human Health: A Short Review. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2025, 17, 100608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Incebay, H.; Aktepe, L.; Leblebici, Z. An Electrochemical Sensor Based on Green Tea Extract for Detection of Cd(II) Ions by Differential Pulse Anodic Stripping Voltammetry. Surf. Interf. 2020, 21, 100726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jangi, S.H.; Khoobi, A. Detection of Cadmium Heavy Metal Ions Using a Nanostructured Green Sensor in Food, Biological and Environmental Samples. Food Chem. 2024, 458, 140307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, R.H.; Rahale, C.S.; Prasanthrajan, M.; Girija, S.; Wilson, J.; Sharmila, D.J.; Saranya, N.; Maragatham, S. Eco-Friendly Synthesis of Nanoceria Using Orange Peel Extract for Electrochemical Detection of Selective Cadmium Ions. Microchem. J. 2024, 202, 110794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Lin, X.; Liao, H.; Gong, S.; Hasan, M.; Zhou, X.; Gunasekaran, S. Bioengineering of Green rGO/Fe3O4 Nanocomposites for Rapid Cadmium Sensing and Dye Decomposition. Ceram. Inter. 2025, 51, 5273–5286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Liao, H.; Gong, S.; Lan, L.; Hasan, M.; Zhou, X.; Gunasekaran, S. Green Synthesis of Reduced Graphene Oxide Nanosheets: An Efficient Material for Electrochemical Sensor and Photocatalytic Agent. Microchem. J. 2025, 209, 112799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.-S.; Osman, A.I.; Hosny, M.; Elgarahy, A.M.; Eltaweil, A.S.; Rooney, D.W.; Chen, Z.; Rahim, N.S.; Sekar, M.; Gopinath, S.C.B.; et al. The Toxicity of Mercury and Its Chemical Compounds: Molecular Mechanisms and Environmental and Human Health Implications: A Comprehensive Review. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 5100–5126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavithra, K.G.; SundarRajan, P.; Kumar, P.S.; Rangasamy, G. Mercury Sources, Contaminations, Mercury Cycle, Detection and Treatment Techniques: A Review. Chemosphere 2023, 312, 137314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Yang, Y.; Yang, S.; Li, L.; Song, L. Recent Advance of Microbial Mercury Methylation in the Environment. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 108, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, J.; Liu, J.; Xie, Y.; Peng, G.; Duan, L.; Hu, D.; Chen, S.; Qu, F.; Lu, L. Bifunctional Bismuth Molybdate/Biochar Composite with an Enhanced Photo-Assisted Electrochemical Activity: Memory Effect-Free Hg(II) Detection and Efficient Photocatalytic Reduction of Cr(VI). Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 468, 143849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Liu, J.; Peng, G.; Huang, H.; Wang, L.; Lu, L.; Gao, Y.; Hu, D.; Chen, S. An Electrochemical Sensor Based on a Porous Biochar/Cuprous Oxide (BC/Cu2O) Composite for the Determination of Hg(II). Molecules 2023, 28, 5352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hareesha, N.; Soumya, D.M.; Mounesh; Manjunatha, J.G.; Rohit, R.N.; Manikanta, P.; Varun, D.N.; Ataollahi, N.; Thippeswamy, B.A.; Pramoda, K.; et al. Honeycomb Polypore Biomass-Derived Activated Porous Carbon Nanosheets/Graphite/Nafion Composite: Green and Sensitive Electrocatalyst for Nanomolar Detection of Hg2+ Ions and Water-Splitting Reactions. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 113584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Zou, J.; Li, L.; Chen, H.; Liu, S.; Gao, Y.; Huang, X.; Wang, L.; Lu, L. Enhanced Electrocatalytic Activity in MOFs-Derived 3D Hollow NiCo-LDH Nanocages Decorated Porous Biochar for Simultaneously Ultra-Sensitive Electrochemical Sensing of Cu2+ and Hg2+. Talanta 2024, 279, 126624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karazan, Z.M.; Roushani, M.; Hoseini, S.J. Simultaneous Electrochemical Sensing of Heavy Metal Ions (Zn2+, Cd2+, Pb2+, and Hg2+) in Food Samples Using a Covalent Organic Framework/Carbon Black Modified Glassy Carbon Electrode. Food Chem. 2024, 442, 138500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suguihiro, T.M.; De Oliveira, P.R.; De Rezende, E.I.P.; Mangrich, A.S.; Marcolino Junior, L.H.; Bergamini, M.F. An Electroanalytical Approach for Evaluation of Biochar Adsorption Characteristics and Its Application for Lead and Cadmium Determination. Biores. Technol. 2013, 143, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinke, C.; Mangrich, A.S.; Marcolino-Junior, L.H.; Bergamini, M.F. Biochar Prepared from Castor Oil Cake at Different Temperatures: A Voltammetric Study Applied for Pb2+, Cd2+ and Cu2+ Ions Preconcentration. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 318, 526–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeinu, K.M.; Hou, H.; Liu, B.; Yuan, X.; Huang, L.; Zhu, X.; Hu, J.; Yang, J.; Liang, S.; Wu, X. A Novel Hollow Sphere Bismuth Oxide Doped Mesoporous Carbon Nanocomposite Material Derived from Sustainable Biomass for Picomolar Electrochemical Detection of Lead and Cadmium. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 13967–13979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, D.; Gao, S.; Wang, L.; Shen, H.; Yalikun, N.; Sukhrobov, P.; Wagberg, T.; Zhao, Y.; Mamat, X.; Hu, G. Three-Dimensional Carbon Nanofiber Derived from Bacterial Cellulose for Use in a Nafion Matrix on a Glassy Carbon Electrode for Simultaneous Voltammetric Determination of Trace Levels of Cd(II) and Pb(II). Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 2759–2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dali, M.; Zinoubi, K.; Chrouda, A.; Abderrahmane, S.; Cherrad, S.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N. A Biosensor Based on Fungal Soil Biomass for Electrochemical Detection of Lead (II) and Cadmium (II) by Differential Pulse Anodic Stripping Voltammetry. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2018, 813, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajab, H.; Ali Khan, A.A.; Nazir, M.S.; Yaqub, A.; Abdullah, M.A. Cellulose-Hydroxyapatite Carbon Electrode Composite for Trace Plumbum Ions Detection in Aqueous and Palm Oil Mill Effluent: Interference, Optimization and Validation Studies. Environ. Res. 2019, 176, 108563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Jin, H.; Fang, Y.; Guan, J.; Ma, S.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhu, H.; Liu, X.; Du, M. Detection of Trace Cd2+, Pb2+ and Cu2+ Ions via Porous Activated Carbon Supported Palladium Nanoparticles Modified Electrodes Using SWASV. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2019, 225, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, J.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Wang, L.; Zhu, H.; Du, M.; Zhang, M. Kelp-Derived Activated Porous Carbon for the Detection of Heavy Metal Ions via Square Wave Anodic Stripping Voltammetry. Electrocatalysis 2020, 11, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrada-Aldrete, J.; Hernández-López, J.M.; García-León, A.M.; Peralta-Hernández, J.M.; Cerino-Córdova, F.J. Electroanalytical Determination of Heavy Metals in Aqueous Solutions by Using a Carbon Paste Electrode Modified with Spent Coffee Grounds. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2020, 857, 113663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Liu, B.; Chen, S.; Wu, L.; Yang, J.; Liang, S.; Xiao, K.; Hu, J.; Hou, H. Ultrasensitive and Simultaneous Electrochemical Determination of Pb2+ and Cd2+ Based on Biomass Derived Lotus Root-Like Hierarchical Porous Carbon/Bismuth Composite. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 087505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djebbi, M.A.; Allagui, L.; El Ayachi, M.S.; Boubakri, S.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N.; Namour, P.; Ben Haj Amara, A. Zero-Valent Iron Nanoparticles Supported on Biomass-Derived Porous Carbon for Simultaneous Detection of Cd2+ and Pb2+. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2022, 5, 546–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Sun, L.; Guo, H.; Wei, Y.; Feng, H.; Liu, B.; Yu, J.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, X. Controllable Synthesis of Zeolitic Imidazolate Frameworks and the Peanut Shell Carbon Composite for Sensitive and Selective Detection of Pb2+ and Cd2+ Ions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 658, 130657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosquera-Ortega, M.; Figueredo, F.; Fernandez, F.; Arnal, P.; Cortón, E.; Susmel, S. Peanut Shell Biochar for Plastic Electrodes: Green E-Sensors for Sensitive Heavy Metal Detection. Carbon Trends 2025, 20, 100520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Qian, W.; Li, Y.; Yu, Q.; Yu, Y.; Chen, S.; Qu, F.; Gao, Y.; Lu, L. Multilayer Activated Biochar/UiO-66-NH2 Film as Intelligent Sensing Platform for Ultra-Sensitive Electrochemical Detection of Pb2+ and Hg2+. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 569, 151006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elamin, M.B.; Chrouda, A.; Ali, S.M.A.; Alhaidari, L.M.; Jabli, M.; Alrouqi, R.M.; Renault, N.J. Electrochemical Sensor Based on Gum Arabic Nanoparticles for Rapid and In-situ Detection of Different Heavy Metals in Real Samples. Heliyon 2024, 10, e26364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okpara, E.C.; Fayemi, O.E.; Sherif, E.-S.M.; Ganesh, P.S.; Swamy, B.E.K.; Ebenso, E.E. Electrochemical Evaluation of Cd2+ and Hg2+ Ions in Water Using ZnO/Cu2ONPs/PANI Modified SPCE Electrode. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2022, 35, 100476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doloi, K.; Badhai, N.; Mohanta, D. Nanoscale Ag2O Decorated UiO-66 Metal Organic Framework for Simultaneous Electrochemical Sensing of Heavy Metals, Cd2+ and Hg2+. Mater. Res. Bull. 2024, 170, 112558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhu, R.; Sankar, K.V.; Chen, S.-M.; Selvan, R.K. Eco-Friendly Synthesis of Activated Carbon from Dead Mango Leaves for the Ultrahigh Sensitive Detection of Toxic Heavy Metal Ions and Energy Storage Applications. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 1225–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djemmoe, L.G.; Njanja, E.; Tchieno, F.M.M.; Ndinteh, D.T.; Ndungu, P.G.; Tonle, I.K. Activated Hordeum vulgare, L. Dust as Carbon Paste Electrode Modifier for the Sensitive Electrochemical Detection of Cd2+, Pb2+ and Hg2+ Ions. Inter. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2020, 100, 1429–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hamdouni, Y.; El Hajjaji, S.; Szabó, T.; Trif, L.; Felhősi, I.; Abbi, K.; Labjar, N.; Harmouche, L.; Shaban, A. Biomass Valorization of Walnut Shell into Biochar as a Resource for Electrochemical Simultaneous Detection of Heavy Metal Ions in Water and Soil Samples: Preparation, Characterization, and Applications. Arab. J. Chem. 2022, 15, 104252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, H.; Ruan, S.; Yin, M.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, P.; Liang, X.; Yin, W.; Fa, H. Performance Comparison of Simultaneous Detection Heavy-Metal Ions Based on Carbon Materials Electrochemical Sensor. Microchem. J. 2022, 181, 107711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, N.; Zuo, P.; Qu, S.; Qin, F.; Shen, W. Utilization of Nitrogen, Sulfur Co-Doped Porous Carbon Micron Spheres as Bifunctional Electrocatalysts for Electrochemical Detection of Cadmium, Lead and Mercury Ions and Oxygen Evolution Reaction. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2023, 640, 391–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Xiong, Y.; Ge, Y.; Wen, Y.; Zeng, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, P.; Wang, Z.; Chen, S. Magnetic Fe3O4 Nanoparticles Decorated Phosphorus-Doped Biochar-Attapulgite/Bismuth Film Electrode for Smartphone-Operated Wireless Portable Sensing of Ultra-Trace Multiple Heavy Metal Ions. Microchim. Acta 2023, 190, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).