Abstract
Hydroxychloroquine (HCQ), a cornerstone therapeutic agent for autoimmune diseases, requires precise serum concentration monitoring due to its narrow therapeutic window. Current HCQ monitoring methods such as HPLC and LC-MS/MS are sensitive but costly and complex. While electrochemical sensors offer rapid, cost-effective detection, their large chambers and high sample consumption hinder point-of-care use. To address these challenges, we developed a microfluidic electrochemical sensing platform based on a screen-printed carbon electrode (SPCE) modified with a hierarchical nanocomposite of gold nanoparticles (AuNPs), copper-based metal–organic frameworks (Cu-MOFs), and multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs). The Cu-MOF provided high porosity and analyte enrichment, MWCNTs established a 3D conductive network to enhance electron transfer, and AuNPs further optimized catalytic activity through localized plasmonic effects. Structural characterization (SEM, XRD, FT-IR) confirmed the successful integration of these components via π-π stacking and metal–carboxylate coordination. Electrochemical analyses (CV, EIS, DPV) revealed exceptional performance, with a wide linear range (0.05–50 μM), a low detection limit (19 nM, S/N = 3), and a rapid response time (<5 min). The sensor exhibited outstanding selectivity against common interferents, high reproducibility (RSD = 3.15%), and long-term stability (98% signal retention after 15 days). By integrating the nanocomposite-modified SPCE into a microfluidic chip, we achieved accurate HCQ detection in 50 μL of serum, with recovery rates of 95.0–103.0%, meeting FDA validation criteria. This portable platform combines the synergistic advantages of nanomaterials with microfluidic miniaturization, offering a robust and practical tool for real-time therapeutic drug monitoring in clinical settings.
1. Introduction
Hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) remains a cornerstone therapeutic agent for malaria, rheumatoid arthritis, and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), with irreplaceable clinical value in SLE management due to its potent anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory properties, which effectively suppress disease progression. However, the therapeutic efficacy of HCQ critically depends on maintaining serum concentrations within a narrow therapeutic window (0.5–1.0 μg/mL) [1,2]. Subtherapeutic levels not only compromise clinical outcomes but also elevate risks of disease flare-ups, whereas supratherapeutic concentrations (≥1.0 μg/mL) may trigger irreversible retinopathy, life-threatening cardiotoxicity, and severe gastrointestinal complications. This delicate balance between therapeutic benefits and dose-dependent toxicity underscores the imperative for real-time therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) to optimize treatment safety and efficacy. Therefore, it is critically important to develop a detection method for HCQ that combines high selectivity, low detection limits (nM to μM), minimal sample consumption (μL), and rapid analysis within clinically actionable timeframes.
Up to now, multiple approaches have been investigated to monitoring the concentration of HCQ in serum such as high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) [3], liquid chromatograph mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) [4], and spectrophotometry [5,6]. While their results are extremely sensitive and have high reliability, these techniques typically necessitate costly equipment and intricate operational procedures. Conversely, electrochemical sensors, with advantages in terms of detection efficiency and usage convenience, have attracted growing attention in pharmaceutical analysis [7,8]. These methods offer a rapid and cost-effective analytical platform for TDM, facilitating the assessment of drugs in real biological samples [9,10]. Nevertheless, existing electrochemical methods suffer from the issues of large detection chambers and high sample consumption, meaning they are still insufficient for achieving point-of-care monitoring of HCQ [9].
Microfluidic chips, characterized by their integration, miniaturization, and portability [11,12,13,14,15], synergize perfectly with electrochemical sensors’ inherent advantages of rapid detection and low cost. These integrated systems offer unique benefits for blood drug concentration detection including minimal sample/reagent consumption (μL-level), automated fluid control and convenient use [16,17,18,19,20]. However, despite these systemic improvements, unmodified electrodes inherently suffer from sluggish redox kinetics and susceptibility to biofouling in complex biological matrices, which limit sensitivity and reliability. To fully harness the potential of microfluidic–electrochemical integration, targeted electrode modification becomes imperative [21,22]. Metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) have emerged as promising candidates for electrochemical sensing due to their ultrahigh porosity, tunable pore structures, and abundant catalytically active metal sites [23,24,25]. However, their practical application is hindered by limited electrical conductivity caused by insulating organic ligands. To address this, MOF-based composites have been strategically engineered to synergize the advantages of MOFs with conductive materials [10,26]. For example, Hamide et al. demonstrated that a ternary nanocomposite of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs), Cu-MOF, and polypyrrole-reduced graphene oxide (PPy-rGO) significantly enhanced electron transfer kinetics and interfacial stability, achieving superior sensitivity and selectivity in metronidazole detection [24]. This underscores the critical role of rational electrode modification with MOF composites in overcoming inherent material limitations.
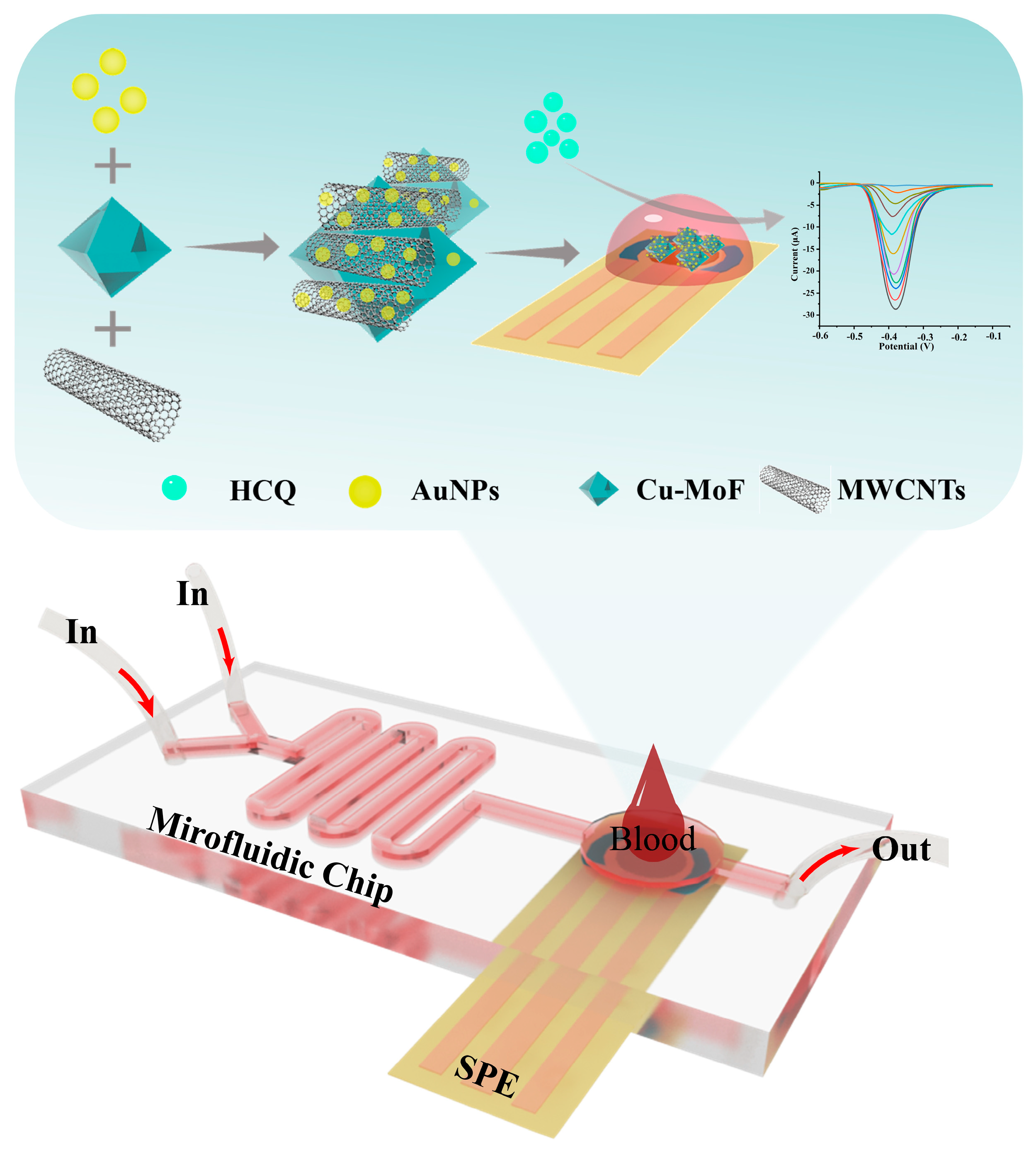
In this study, we engineered a microfluidic electrochemical platform that synergistically integrates material innovation and device miniaturization for high-performance hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) detection in serum (Figure 1). The sensing architecture was constructed by hierarchically assembling Cu-MOF, multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs), and gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) on a screen-printed carbon electrode (SPCE). The MWCNTs significantly enhanced the electrical conductivity of Cu-MOF via their three-dimensional conductive network, while their high mechanical strength effectively improved the interfacial stability of the composite. AuNPs decorated on the material surface optimized electron transfer pathways via localized plasmonic effects while acting as rigid supports to suppress Cu-MOF structural distortion, thereby preserving catalytic active site stability. Benefiting from the inherent high specific surface area and ordered pore channels of Cu-MOF, the composite electrode enabled efficient adsorption and directional enrichment of analyte molecules, significantly amplifying the detection signal intensity. By integrating the optimized Au@Cu-MOF/MWCNT sensor into a multifunctional microfluidic chip, we successfully established an interference-resistant and precise detection system. This platform demonstrated excellent HCQ analysis performance in complex serum matrices, highlighting its potential for practical clinical applications in real-time monitoring.
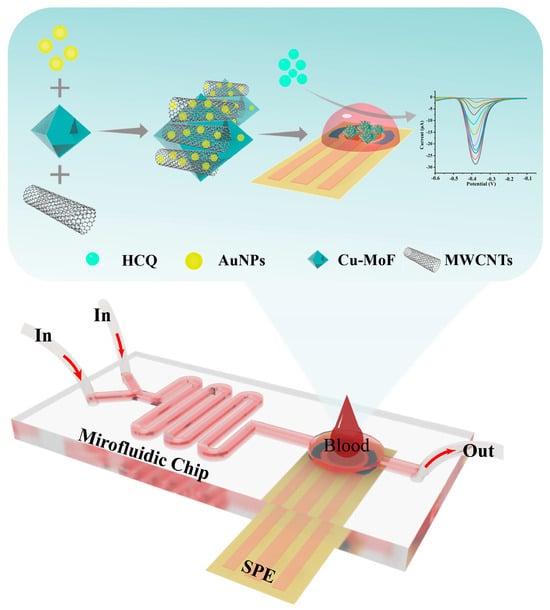
Figure 1.
The schematic diagram illustrates the architecture of a microfluidic-integrated AuNPs@Cu-MOF/MWCNT-modified electrochemical sensor for rapid HCQ detection in blood samples.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Trimesic acid (H3BTC) was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich Co. (St. Louis, MO, USA). Copper nitrate hydrate (Cu (NO3)2·3H2O), N, N-Dimethylformamide (DMF), potassium hexacyanoferrate (K4[Fe(CN)6]), sodium phosphate dibasic (Na2HPO4), and monosodium phosphate (NaH2PO4) were purchased from Shanghai Macklin Biochemical Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). Multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs), potassium chloride (KCl), potassium ferricyanide (K3[Fe(CN)6]), and potassium bromide(KBr) were purchased from Aladdin Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) and a curing agent were purchased from Dow Corning Corp. (St. Salsburg, MI, USA).
2.2. Synthesis of Cu-MOF
The Cu-MOF was synthesized following a previously reported method [27,28]. Briefly, copper (II) nitrate trihydrate (Cu(NO3)2·3H2O, 0.204 g) was dissolved in 7.1 mL of deionized water, while trimesic acid (0.25 g) was dissolved in 7.1 mL of ethanol. The two solutions were thoroughly mixed under vigorous stirring for 30 min. Subsequently, the homogeneous mixture was transferred into a 100 mL Teflon-lined autoclave and heated at 150 °C for 24 h. After cooling to room temperature, the resulting blue precipitate was collected by centrifugation, washed repeatedly with a 1:1 (v/v) ethanol/water solution, and finally vacuum-dried at 60 °C for 6 h.
2.3. Preparation of CuMOF/MWCNTs
The Cu-MOF/MWCNT composite was synthesized through a solvent-based hybridization strategy. Briefly, 0.03 g of Cu-MOF and 0.03 g of MWCNTs were dispersed in 30 mL of DMF under ultrasonication for 30 min to achieve a homogeneous suspension. The mixture was then magnetically stirred at 25 °C for 12 h to facilitate interfacial interactions. Afterward, the composite product was collected via centrifugation, followed by three cycles of washing with deionized water to eliminate residual reactants. Finally, the purified Cu-MOF/MWCNT nanocomposite was vacuum-dried at 60 °C for 6 h prior to further characterization.
2.4. Preparation of AuNPs@Cu-MOF/MWCNT-Modified Electrode
The AuNPs@Cu-MOF/MWCNT-modified electrode was fabricated through a sequential modification process. First, 1 mg of Cu-MOF/MWCNT composite was dispersed in 1 mL of deionized water under ultrasonication for 10 min. Subsequently, 1 mL of pre-synthesized AuNP colloid was dropwise added to the suspension under gentle stirring, forming AuNPs@Cu-MOF/MWCNT hybrids. The resulting composite dispersion (15 μL) was uniformly drop-casted onto the working electrode area of the electrode and air-dried at 25 °C for 30 min to form the AuNPs@Cu-MOF/MWCNT sensor.
2.5. Preparation of Microfluidic Chips
The microfluidic chip was fabricated using a two-layer polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) structure, comprising a fluidic channel layer and a sensor insertion layer. The process involved the following steps including mold preparation via photolithography, hydrophobic treatment, PDMS layer casting and curing, and chip assembly and sensor integration. Firstly, the chip mold was designed using AutoCAD 2019 software, and the layout was exported as a high-resolution film mask via Adobe Illustrator 2024. A silicon wafer was spin-coated with SU-8 2050 photoresist at 1000 rpm for 30 s, followed by pre-baking at 95 °C to achieve a 250 μm thick layer. A second spin-coating and pre-baking cycle was performed to attain a final thickness of 500 μm. Then the photoresist-coated wafer was exposed to UV light through the film mask for 8 s, developed to remove uncured regions, and dried to finalize the mold structure. Next, the mold surface was treated with 1H, 1H, 2H, and 2H-perfluorooctylmethyldichlorosilane (100 μL) under a vacuum for 12 h to enhance hydrophobicity. After that, a PDMS precursor and curing agent (10:1 w/w ratio) were mixed, degassed, and poured into the molds at 70 °C for 2 h. Fluidic access ports (0.5 mm diameter) were punched into the upper PDMS layer using a Harris micro-punch. Finally, the two PDMS layers were plasma-treated (high mode, 1 min) for irreversible bonding, aligned under a microscope, and baked at 80 °C for 2 h to ensure robust adhesion. The AuNPs@Cu-MOF/MWCNT-modified electrochemical sensor was inserted into the designated cavity on the chip’s backside and secured using hot-melt adhesive to prevent leakage.
2.6. Preparation of Real Sample Analysis
To evaluate the clinical applicability of the microfluidic sensor, real-sample analysis was conducted using human serum obtained from healthy donors (ethically sourced from China-Japan Friendship Hospital, Beijing). For spike-and-recovery experiments, HCQ stock solutions were prepared in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS, pH 7.4) and serially diluted to target concentrations. Aliquots of these solutions were spiked into human blood samples to simulate clinically relevant HCQ levels.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of the Composite Materials
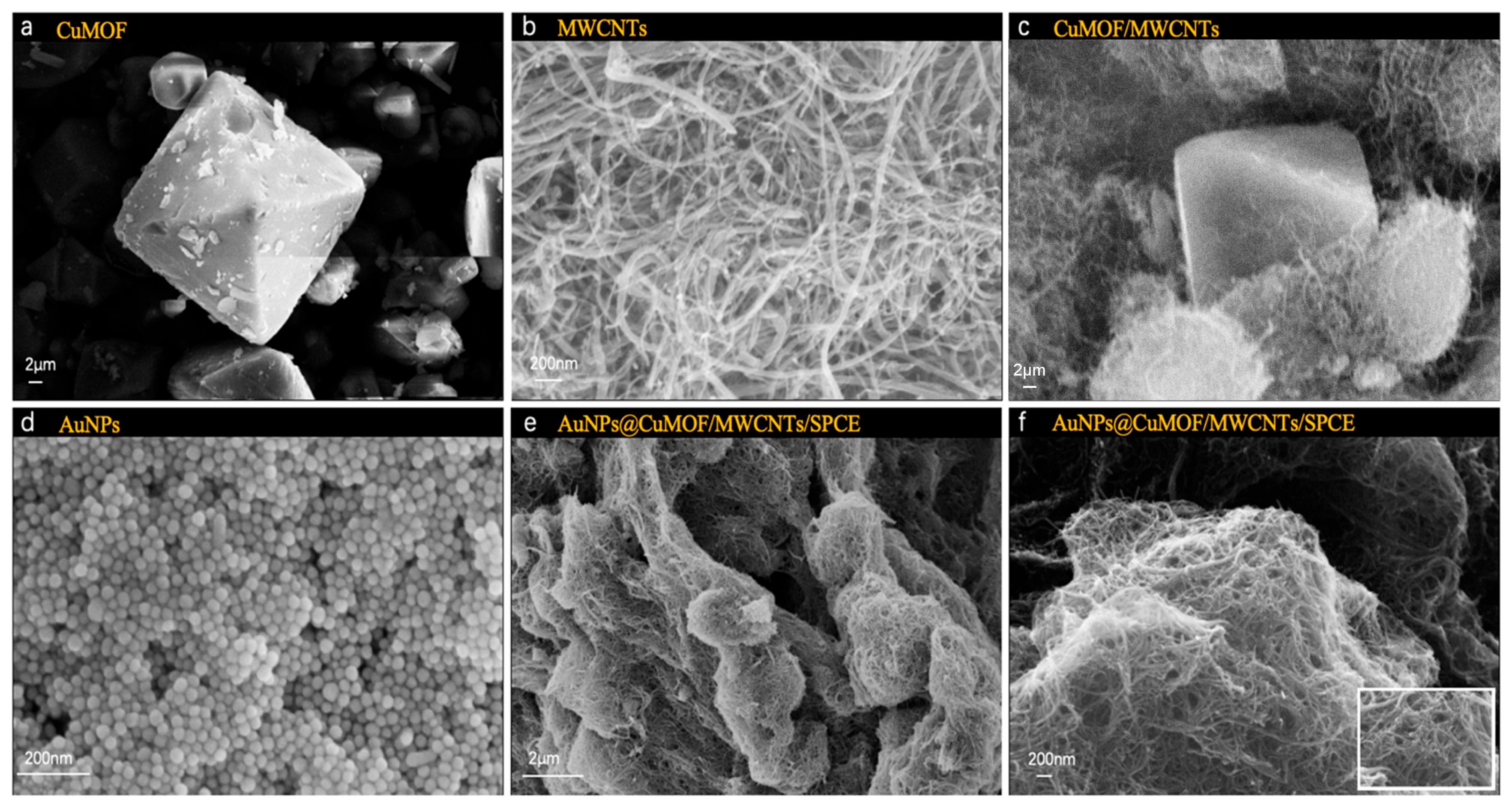
The morphological evolution of the hierarchical composite materials was systematically performed via scanning electron microscopy (SEM, EVO 18, Carl Zeiss, Oberkochen, Germany). As shown in Figure 2a, pristine Cu-MOF crystals exhibited well-defined octahedral morphologies. MWCNTs displayed characteristic tubular structures with smooth surfaces and closed termini, featuring diameters of 20–40 nm and lengths exceeding 10 μm (Figure 2b). The Cu-MOF/MWCNT hybrid demonstrated intimate interfacial integration, where MWCNTs interpenetrated the octahedral Cu-MOF frameworks, forming three-dimensional conductive networks critical for electron transport enhancement (Figure 2c). Notably, colloidal AuNPs synthesized via citrate reduction exhibited uniform spherical morphologies with a narrow size distribution (Figure 2d). Upon functionalization, dense AuNP anchored on both Cu-MOF facets and MWCNT surfaces, confirming the successful assembly of AuNPs@Cu-MOF/MWCNTs, where the nanocomposites formed a porous yet continuous catalytic layer, optimally balancing surface area and charge transfer efficiency, facilitated by π-π stacking and metal–carboxylate coordination (Figure 2e,f).
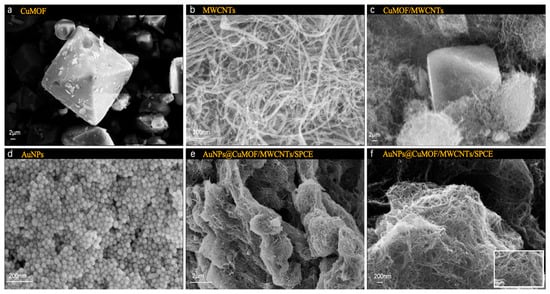
Figure 2.
SEM images of (a) Cu-MOF, (b) MWCNTs, (c) Cu-MOF/MWCNTs, (d) AuNPs, (e) AuNPs@Cu-MOF/MWCNTs, (f) enlarged AuNPs@Cu-MOF/MWCNTs.
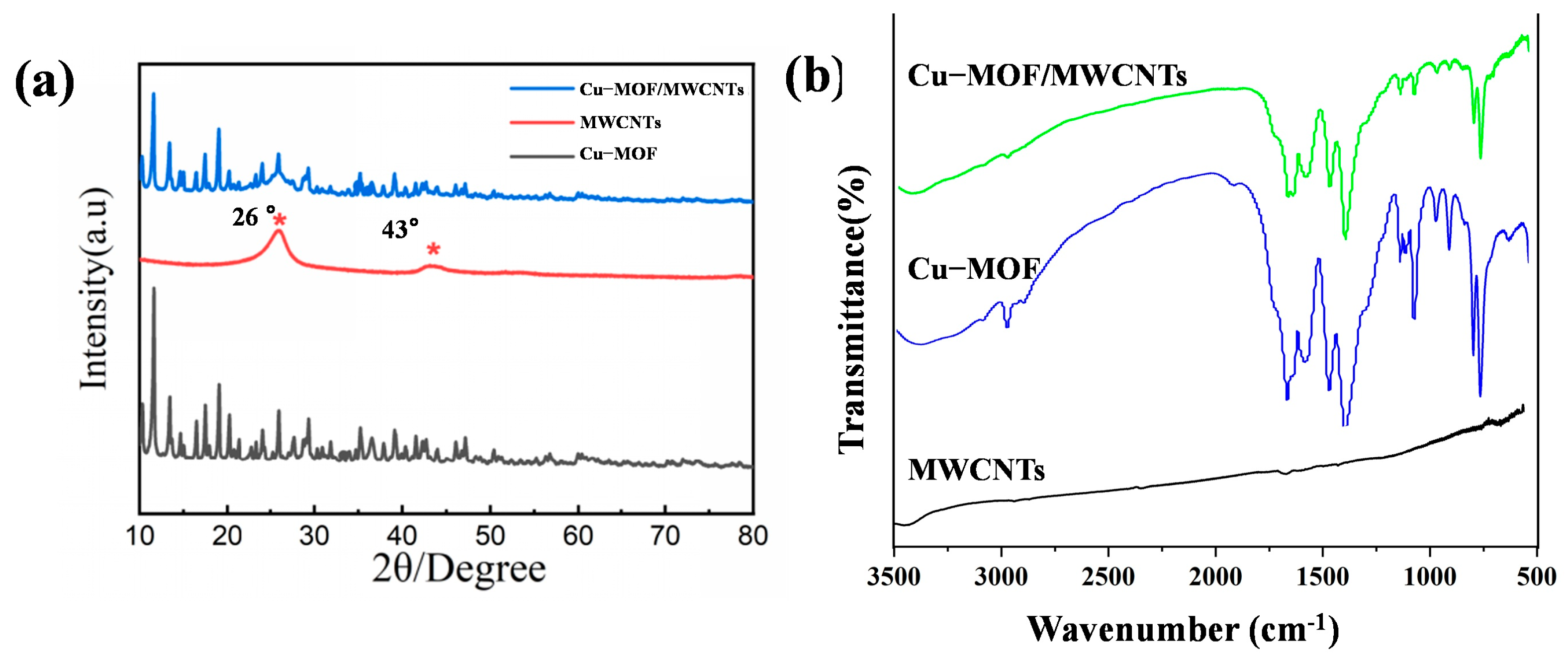
The crystalline structures of Cu-MOF, MWCNTs, and Cu-MOF/MWCNT composites were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD, Empyrean, Malvern Panalytical), as shown in Figure 3a. The XRD pattern of Cu-MOF exhibited distinct diffraction peaks at 2θ = 11.6°, 13.4°, 14.6°, 16.5°, 17.5°, and 19°, corresponding to the (444), (800), (662), (844), (666), and (880) crystal planes, respectively. These diffraction features were consistent with the characteristic crystalline framework of HKUST-1, confirming the successful synthesis of the Cu-MOF structure. For MWCNTs, two prominent diffraction peaks were observed at 2θ = 26° and 43°, indexed to the (002) and (100) crystallographic planes, respectively, which were typical of graphitic carbon structures. Notably, the XRD pattern of the Cu-MOF/MWCNT composite demonstrated a superposition of the characteristic peaks from both pristine Cu-MOF and MWCNTs. This observation provided definitive evidence for the effective integration of MWCNTs into the Cu-MOF matrix without compromising the structural integrity of either component, thereby verifying the successful formation of the Cu-MOF/MWCNT composite material.
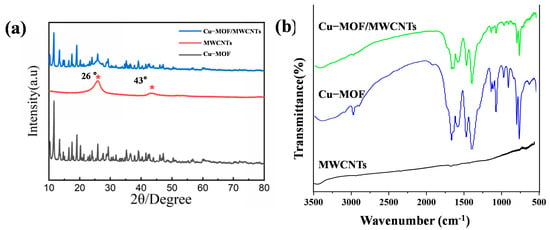
Figure 3.
Structural characterization of prepared materials. (a) XRD patterns of Cu-MOF, MWCNTs, and Cu-MOF/MWCNTs. (b) FT-IR patterns of Cu-MOF and Cu-MOF/MWCNTs.
The characteristic absorption bands of Cu-MOF and Cu-MOF/MWCNTs were characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR spectra, Nicole iS50, Thermo Fisher Scientific), as shown in Figure 3b. The FT-IR spectra of pristine Cu-MOF and Cu-MOF/MWCNTs exhibit nearly identical absorption bands in the range of 500–3500 cm−1. The peak at 3091 cm−1 was attributed to aromatic C-H stretching vibrations, while the band at 2975 cm−1 arose from alkyl C-H stretching modes. Notably, the disappearance of the absorption peak at 1700 cm−1 (originally associated with protonated carboxyl groups in trimesic acid) confirmed the complete deprotonation of carboxylic acid ligands into carboxylate species. Characteristic vibrational modes of the carboxylate groups were observed at 1563 cm−1 (asymmetric stretching, νₐₛ(COO−)) and 1372 cm−1 (symmetric stretching, νₛ(COO−)). Peaks at 1614 cm−1 and 1444 cm−1 corresponded to aromatic ring skeletal vibrations, whereas in-plane and out-of-plane bending vibrations of aromatic C–H bonds were identified at 1102 cm−1 and 1043 cm−1 and within the 900–680 cm−1 range, respectively. Crucially, the absorption band at 728 cm−1 was assigned to Cu-O stretching vibrations, unequivocally verifying the coordination bonding between Cu2⁺ ions and carboxylate groups within the MOF framework. The absence of new absorption bands further suggests no covalent interactions between Cu-MOF and MWCNTs, implying a physical integration mechanism. These observations collectively validate the successful formation of the Cu-MOF/MWCNT composite with preserved structural integrity of both components.
3.2. Electrochemical Analysis of AuNPs@Cu-MOF/MWCNT Sensor
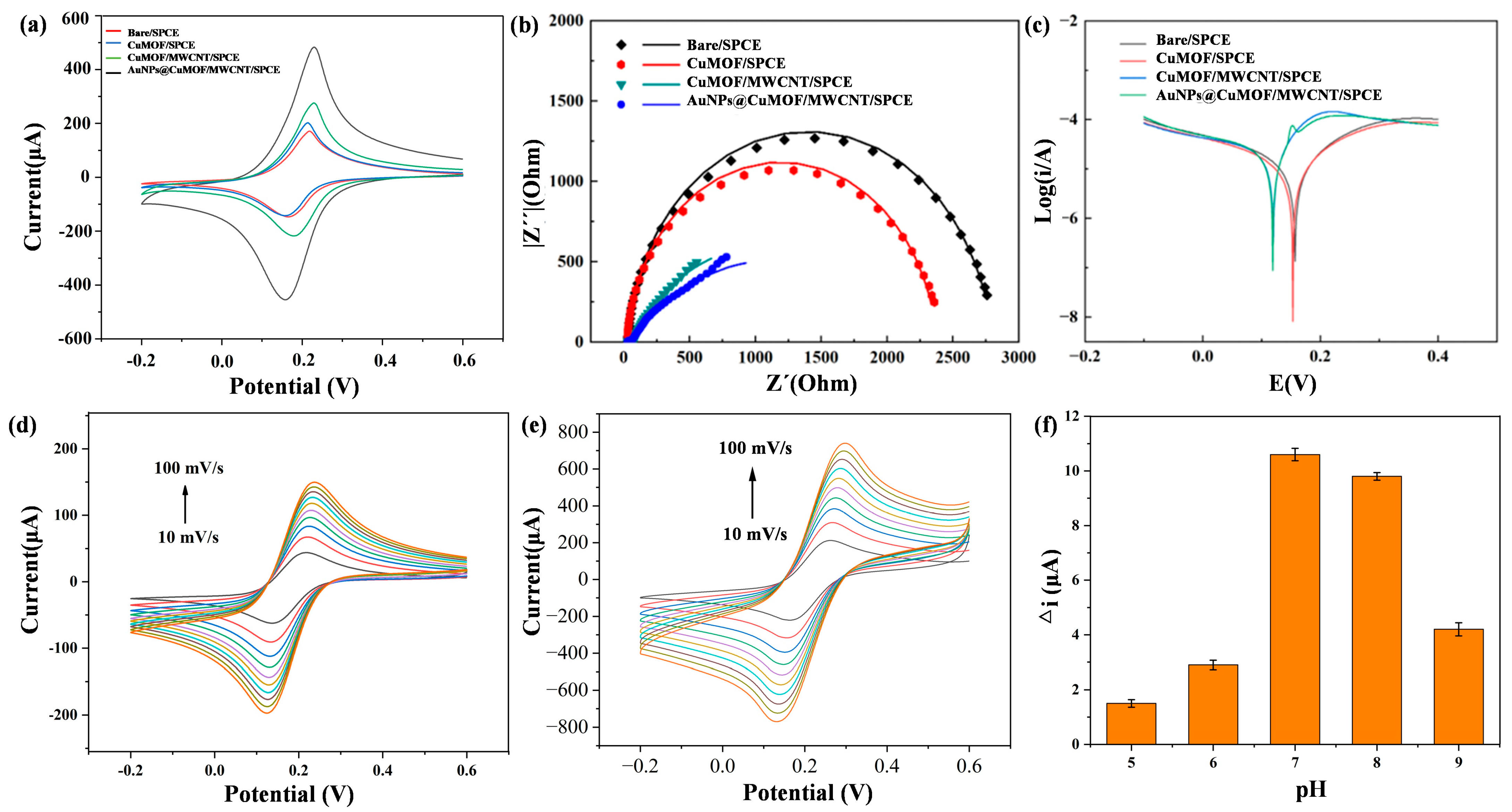
The electrochemical activities of Cu-MOF, Cu-MOF/MWCNTs, and AuNPs@Cu-MOF/MWCNT-modified SPCEs were systematically evaluated using cyclic voltammetry (CV) in 0.1 M KCl containing 5 mM [Fe(CN)₆]3⁻/4⁻ (1:1). As depicted in Figure 4a, Cu-MOF/SPCE exhibited a slight increase in redox peak currents compared to bare SPCE. In contrast, Cu-MOF/MWCNTs/SPCE exhibited an excellent electrochemical performance, characterized by a significant increase in redox peak height. A further enhancement of electrochemical activity was observed in AuNPs@Cu-MOF/MWCNTs/SPCE after AuNP loading, confirming the synergistic interplay between AuNPs’ localized plasmonic effects and MWCNTs’ electrical conductivity. To further investigate the electrochemical performance differences among various modified electrodes, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) was employed to analyze the charge transfer kinetics of these four electrodes, as shown in Figure 4b. Charge transfer resistance (Rct) had a positive correlation with the semicircle diameter in the high-frequency region. The Rct values exhibited a sequential reduction across the modified electrodes: 2810 Ω (bare SPCE) → 2410 Ω (Cu-MOF/SPCE) → 943 Ω (Cu-MOF/MWCNTs/SPCE) → 745 Ω (AuNPs@Cu-MOF/MWCNTs/SPCE), culminating in a 73.5% decrease compared to the unmodified electrode. This confirmed the effectiveness of the composite material strategy in enhancing electrode performance. Additionally, the Tafel plot analysis revealed that AuNPs@Cu-MOF/MWCNTs/SPCE had the smallest cathodic Tafel slope, indicating the fastest reaction rate constant (Figure 4c). In addition, the electrochemical responses of the bare SPCE and AuNPs@Cu-MOF/MWCNTs/SPCE were evaluated by CV at scan rates ranging from 10 to 100 mV/s. As shown in Figure 4d,e, the modified electrode exhibited a progressive increase in redox peak currents with escalating scan rates, consistently outperforming the bare electrode in current magnitude. This scan rate-dependent behavior further confirmed an enlarged electroactive surface area of the AuNPs@Cu-MOF/MWCNTs/SPCE.
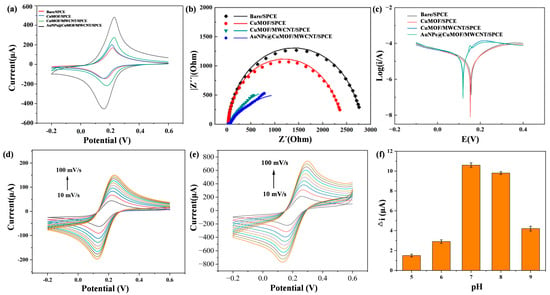
Figure 4.
Electrochemical analysis of bare SPCE, Cu-MOF/SPCE, Cu-MOF/MWCNTs/SPCE, and AuNPs@Cu-MOF/MWCNTs/SPCE. (a) CV of different modified electrodes. (b) EIS of different modified electrodes. (c) Tafel plot analysis of different modified electrodes. (d,e) Electrochemical responses of the bare SPCE (d) and AuNPs@Cu-MOF/MWCNTs/SPCE (e) evaluated by CV at scan rates ranging from 10 to 100 mV/s. (f) The current variation under varying pH conditions for the investigation of the pH effect on electrochemical performance.
3.3. Effect of pH on Electrochemical Performance
To elucidate the kinetic behavior and optimize detection conditions, the electrochemical response of the AuNPs@Cu-MOF/MWCNTs/SPCE was systematically investigated across a pH range of 5.0–9.0. The results revealed distinct behaviors under varying conditions (Figure 4f). Under acidic conditions, protonation of the amino group in HCQ occupied its lone electron pairs, significantly weakening its coordination ability with Cu2⁺. Consequently, Cu2⁺ retained unhindered redox activity, leading to minimal current variation (Δi). At a neutral pH, deprotonated HCQ formed stable [HCQ-Cu2⁺] coordination complexes, effectively blocking redox-active sites, which maximized Δi while maintaining optimal MOF structural stability. Under strongly alkaline conditions, however, competitive hydroxide coordination (Cu(OH)2 precipitation) reduced the available Cu2⁺ concentration, while electrostatic repulsion between negatively charged HCQ− species and carboxylate-functionalized MOF surfaces further diminished coordination efficiency. These combined effects resulted in reduced Δi. These findings collectively demonstrate that neutral pH conditions achieved an optimal detection performance by balancing coordination efficiency and structural stability.
3.4. Analysis of the Performance of the Microfluidic Biosensor
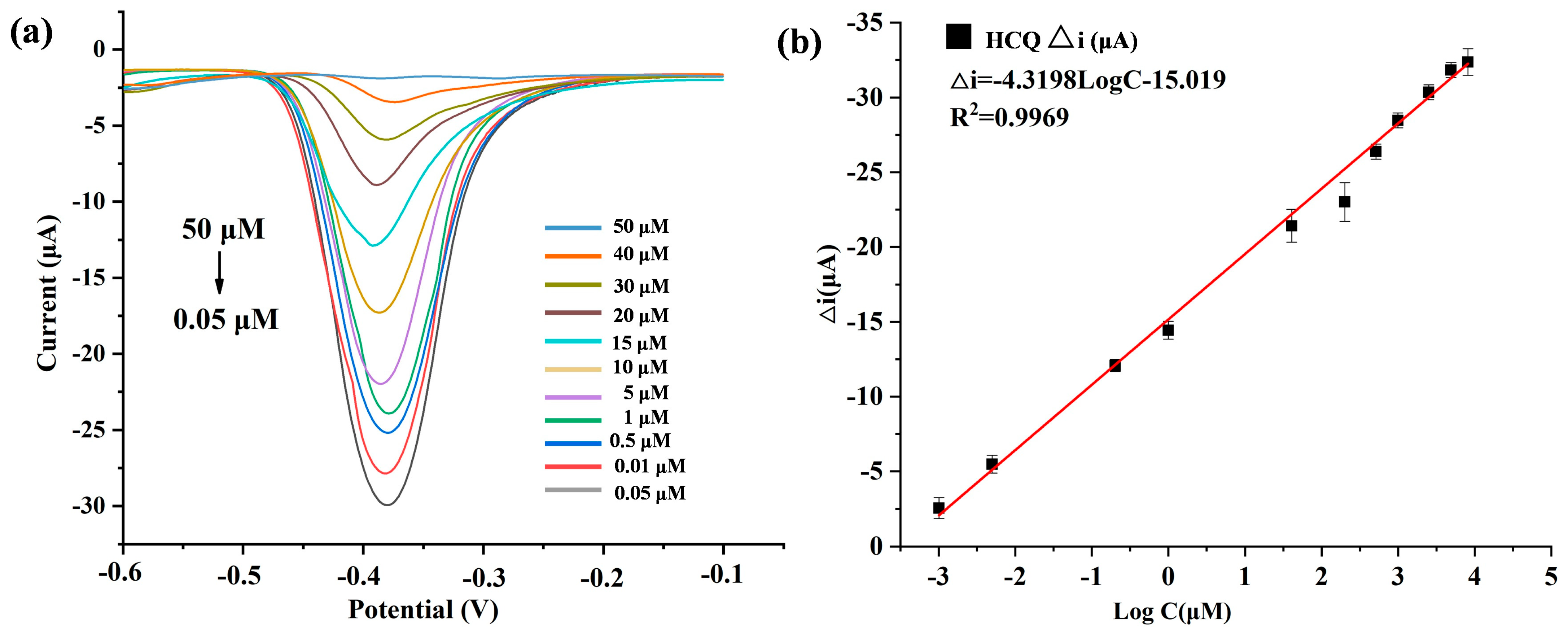
To validate the quantitative detection capability of the developed Au@Cu-MOF/MWCNT-based microfluidic electrochemical sensor, differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) was used to detect HCQ at gradient concentrations under optimized conditions. As shown in Figure 5a, the redox peak current decreased proportionally with increasing HCQ concentration, a phenomenon attributed to coordination-induced electron transfer suppression: the lone electron pairs of HCQ occupied the vacant d orbitals of Cu(II) in Cu-MOF, forming stable metal–ligand complexes that hinder redox-active site accessibility. A robust linear correlation was observed between the peak current variation and the logarithmic HCQ concentration, which could be described by the equation Δi (μA) = −4.3195logC−15.091 (R2 = 0.9969) (Figure 5b). The sensor was demonstrated to have a wide dynamic range from 0.05 to 50 μM, and an ultra-low detection limit (LOD) of 19 nM, calculated via the 3σ method using baseline noise and the calibration slope.
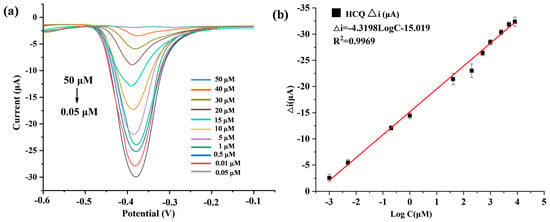
Figure 5.
(a) DPV plots of HCQ (different concentrations) detected by AuNPs@Cu-MOF/MWCNTs based microfluidic electrochemical sensor. (b) Linear relationships of peak current variation (△i) and logarithmic HCQ concentration in this microfluidic electrochemical sensor. △i: The peak current obtained in the absence of HCQ minus the peak current recorded in the presence of HCQ.
3.5. Evaluation of the Interference Resistance, Reproducibility, and Stability
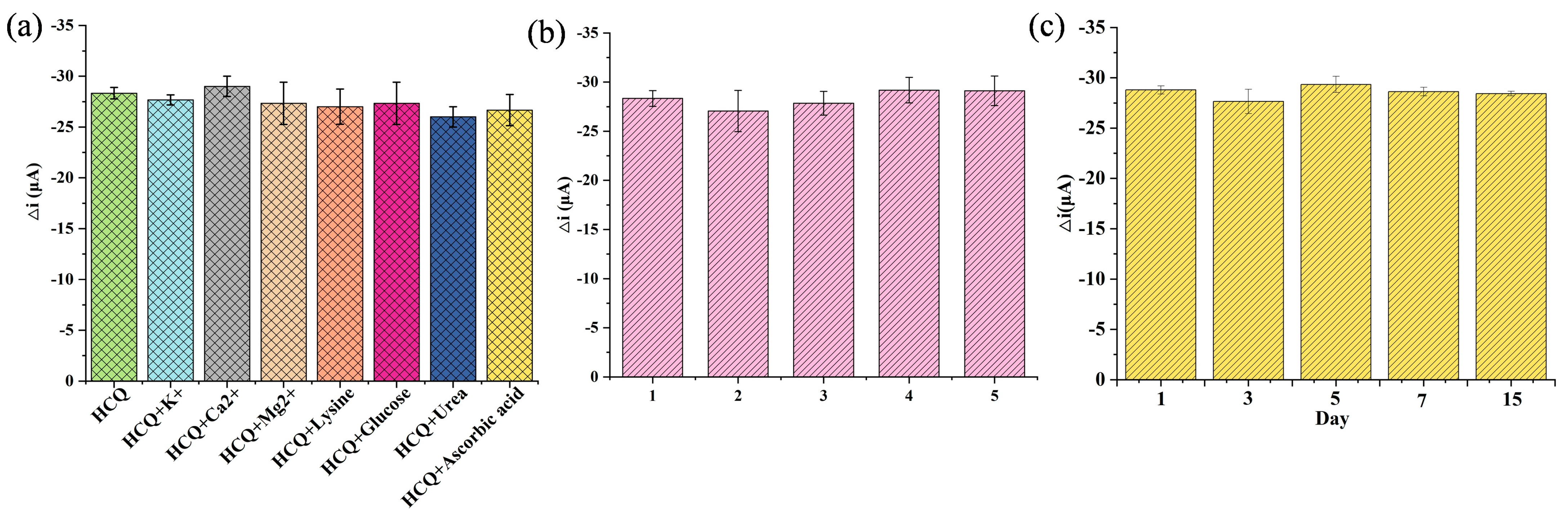
The selectivity was assessed under physiologically relevant conditions. The sensor’s anti-interference capability was tested against common endogenous substances with similar concentrations to HCQ. As illustrated in Figure 6a, no significant current variation (<5% signal change) was observed in the presence of organic interferents (e.g., glucose, lysine, urea, ascorbic acid) and inorganic ions (K⁺, Ca2⁺, Mg2⁺), confirming the coordination-driven specificity between Cu (II) sites and HCQ’s lone electron pairs. This selectivity stemmed from the preferential formation of stable Cu-HCQ complexes over non-specific interactions. To evaluate the reproducibility, five independently fabricated electrodes exhibited consistent responses to 10 μM HCQ with a low relative standard deviation (RSD = 3.15%, Figure 6b), demonstrating excellent inter-batch reproducibility, a critical metric for scalable sensor production. Furthermore, the sensor retained 98% of its initial response after a 15-day storage at 25 °C, attributable to the structural robustness of the Au@Cu-MOF/MWCNT composite, which prevented nanoparticle aggregation and MOF framework collapse, confirming the stability (Figure 6c).
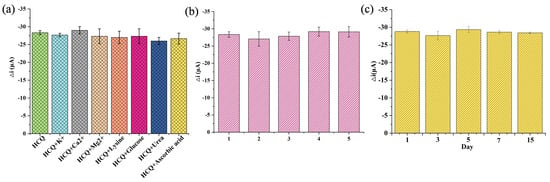
Figure 6.
Evaluation of the interference resistance, reproducibility, and stability of this AuNPs@Cu-MOF/MWCNT-based microfluidic sensor using DPV. (a) Selectivity evaluation under physiologically relevant conditions. (b) Reproducibility evaluation in five independently fabricated electrodes. (c) Stability evaluation during 15-day storage.
3.6. Serum Sample Spiked Recovery Experiment
To assess the clinical applicability of the microfluidic electrochemical sensor, HCQ detection was performed in spiked human serum samples under physiologically relevant conditions (pH 7.4, 37 °C). Using a standard addition method, three concentrations of HCQ (10, 5, and 1 μM) were spiked into serum, with triplicate measurements at each level. As summarized in Table 1, the sensor achieved recovery rates of 95.0–103.0% and RSD values of 2.39–6.18%, demonstrating high accuracy and precision across clinically relevant concentrations. Notably, the recovery performance aligned with FDA guidelines for bioanalytical method validation (acceptance criteria: 85–115% recovery, RSD ≤ 15%), confirming its reliability for complex biological matrices.

Table 1.
AuNPs@Cu-MOF/MWCNT-based microfluidic electrochemical sensor for the detection of HCQ in spiked serum samples.
4. Conclusions
In this work, we developed a hierarchical nanocomposite-based microfluidic electro-chemical sensing platform for rapid and precise monitoring of HCQ in serum. The AuNPs@Cu-MOF/MWCNT composite was rationally designed and integrated into a SPCE platform, leveraging synergistic interactions among its components. Further, by coupling this nanocomposite electrode with a PDMS-based microfluidic chip, we engineered a detection system capable of quantifying HCQ at clinically relevant concentrations without requiring complex sample pretreatment. This electrochemical sensor has been demonstrated to have a comparable analytical performance to conventional methods such as HPLC and LC-MS/MS (Table 2), while offering significantly simpler operation and eliminating the need for costly instrumentation. However, it should be noted that the current fabrication strategy, relying on nanomaterial synthesis (e.g., Cu-MOF, AuNPs), presents challenges for scalable manufacturing and cost reduction at this stage. In our future work, to advance this technology toward real-world applications, we plan to integrate peristaltic pumps and fluidic circuits into iterations of the microfluidic sensor, enabling controlled sample recirculation within the chip. By systematically optimizing flow parameters and engineering the device into a user-friendly format, we aim to achieve rapid and accurate detection with portability and affordability.

Table 2.
Performances of the proposed method and other reported methods to monitor HCQ.
In conclusion, this study not only advances nanomaterial-engineered sensing strategies but also offers a diagnostic platform targeting critical pharmacological analytes, bridging the gap between laboratory innovation and clinical deployment.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, W.Z. and H.L.; methodology, W.Z.; validation, X.F., J.Z., and S.W.; formal analysis and investigation, X.F. and J.Z.; resources, W.Z.; data curation, W.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, X.F. and J.Z.; writing—review and editing, W.Z. and Y.K.; visualization, J.Z.; supervision, W.Z. and H.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Key R&D Program of China, grant number 2021YFF0600705, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number 22204155, and the National Institute of Metrology Fundamental Research Project, grant number AKYJJ2302.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Schrezenmeier, E.; Dörner, T. Mechanisms of action of hydroxychloroquine and chloroquine: Implications for rheumatology. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2020, 16, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorge, A.; Ung, C.; Young, L.H.; Melles, R.B.; Choi, H.K. Hydroxychloroquine retinopathy—Implications of research advances for rheumatology care. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2018, 14, 693–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noé, G.; Amoura, Z.; Combarel, D.; Lori, L.; Tissot, N.; Seycha, A.; Funck-Brentano, C.; Zahr, N. Development and validation of a fast ultra-high performance liquid chromatography–fluorescent method for the quantification of hydroxychloroquine and its metabolites in patients with lupus. Ther. Drug Monit. 2019, 41, 476–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Austin, D.; John, C.; Hunt, B.J.; Carling, R.S. Validation of a liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry method for the simultaneous determination of hydroxychloroquine and metabolites in human whole blood. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2020, 58, 2047–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, M.S.; Rocha, R.G.; de Faria, L.V.; Richter, E.M.; Dantas, L.M.F.; da Silva, I.S.; Muñoz, R.A.A. Additively manufactured electrodes for the electrochemical detection of hydroxychloroquine. Talanta 2022, 250, 123727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastava, A. Analytical methods for the determination of hydroxychloroquine in various matrices. Int. J. Appl. Pharm. 2020, 12, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvau, M.D.; Tartaggia, S.; Meneghello, A.; Casetta, B.; Calia, G.; Serra, P.A.; Polo, F.; Toffoli, G. Enzyme-based electrochemical biosensor for therapeutic drug monitoring of anticancer drug irinotecan. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 6012–6019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.; Durairaj, S.; Prins, S.; Chen, A. Nanomaterial-based electrochemical sensors and biosensors for the detection of pharmaceutical compounds. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 175, 112836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Chen, Y.; Mo, X.; Sun, K.; Du, Y.; Hu, F. Construction of a microfluidic electrochemical sensor based on screen printing electrode for the detection of fluoxetine. Microchem. J. 2024, 204, 111103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Li, W.; Xin, H.; Tang, L.; Zhou, X.; Zhou, T.; Xuan, C.; Tian, Q.; Pan, D. Engineering of CuMOF-SWCNTs@AuNPs-based electrochemical sensors for ultrasensitive and selective monitoring of imatinib in human serum. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 4744–4753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Zhang, W.; Lin, H.; Lin, J.-M. Di-4-ANEPPDHQ probes the response of lipid packing to the membrane tension change in living cells. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2022, 33, 1377–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Zhang, W.; Li, Y.; Lin, J.-M. Analysis of cellular biomolecules and behaviors using microfluidic chip and fluorescence method. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 117, 200–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, N.; Lin, L.; Li, H.; Lin, J.-M. Metabolism-based capture and analysis of circulating tumor cells in an open space. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 6955–6960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.; Zhang, W.; Li, H.; Li, N.; Lin, J.-M. Advances in droplet digital polymerase chain reaction on microfluidic chips. Lab Chip 2023, 23, 1258–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, N.; Lin, L.; Huang, Q.; Uchiyama, K.; Lin, J.-M. Concentrating single cells in picoliter droplets for phospholipid profiling on a microfluidic system. Small 2020, 16, 1903402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Liu, X.; Yang, J.; He, Y.; Li, Y. Application of multiplex microfluidic electrochemical sensors in monitoring hematological tumor biomarkers. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 11981–11986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Han, L.; Li, D.; Pu, Z. High-frequency ultrasound based microfluidic chip for high-sensitive and quick-response electrochemical biosensing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2025, 427, 137204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Kan, Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, H.; Zhang, W. MOFs-modified electrochemical sensors and the application in the detection of opioids. Biosensors 2023, 13, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, M.A.U.; Kim, K.H.; Salih, A.R.C.; Hyun, K.; Park, S.H.; Kang, B.; Soomro, A.M.; Ali, M.; Jun, Y.; Huh, D.; et al. High performance inkjet printed embedded electrochemical sensors for monitoring hypoxia in a gut bilayer microfluidic chip. Lab Chip 2022, 22, 1764–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.; Lee, J.; Kim, J.; Choi, H.S.; Kim, J.; Lee, S.; Lee, H. Single microfluidic electrochemical sensor system for simultaneous multi-pulmonary hypertension biomarker analyses. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosy; Yadav, S.K.; Agrawal, B.; Oyama, M.; Goyal, R.N. Graphene modified Palladium sensor for electrochemical analysis of norepinephrine in pharmaceuticals and biological fluids. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 125, 622–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajid, M.; Nazal, M.K.; Mansha, M.; Alsharaa, A.; Jillani, S.M.S.; Basheer, C. Chemically modified electrodes for electrochemical detection of dopamine in presence of uric acid and ascorbic acid: A review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 76, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.-L.; Gao, E.-Q. Metal–organic frameworks for electrochemical sensors of neurotransmitters. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 434, 213784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saedi, H.; Fat’hi, M.R.; Zargar, B. Synthesis of AgNPs functionalized CuMOF/PPy–rGO nanocomposite and its use as an electrochemical sensor for metronidazole determination. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2021, 68, 1954–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatamluyi, B.; Rezayi, M.; Beheshti, H.R.; Boroushaki, M.T. Ultra-sensitive molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor for patulin detection based on a novel assembling strategy using Au@Cu-MOF/N-GQDs. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 318, 128219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, S.; Yang, J.; Dong, J.; Lu, X. MXene/CNTs/Cu-MOF electrochemical probe for detecting tyrosine. Carbon 2022, 199, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlichte, K.; Kratzke, T.; Kaskel, S. Improved synthesis, thermal stability and catalytic properties of the metal-organic framework compound Cu3(BTC)2. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2004, 73, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Mu, X.; Lester, E.; Wu, T. High efficiency synthesis of HKUST-1 under mild conditions with high BET surface area and CO2 uptake capacity. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 2018, 25, 584–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Wang, Z.; Qiu, S.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Y.; Xu, F.; Song, X.; Gao, S.; Chen, W. LC-MS/MS Method for Determination of Hydroxychloroquine and Metabolites: Application in a Pharmacokinetic Study. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2022, 6058445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soichot, M.; Mégarbane, B.; Houzé, P.; Chevillard, L.; Fonsart, J.; Baud, F.J.; Laprévote, O.; Bourgogne, E. Development, Validation and Clinical Application of a LC-MS/MS Method for the Simultaneous Quantification of Hydroxychloroquine and Its Active Metabolites in Human Whole Blood. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2014, 100, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhonker, Y.S.; Sleightholm, R.L.; Li, J.; Oupický, D.; Murry, D.J. Simultaneous Quantitation of Hydroxychloroquine and Its Metabolites in Mouse Blood and Tissues Using LC-ESI-MS/MS: An Application for Pharmacokinetic Studies. J. Chromatogr. B 2018, 1072, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, N.; Richez, M.; Raoult, D.; Chabriere, E. Simultaneous UHPLC-UV analysis of hydroxychloroquine, minocycline and doxycycline from serum samples for the therapeutic drug monitoring of Q fever and Whipple’s disease. J. Chromatogr. B. 2017, 1060, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).