The Use of Low-Cost Gas Sensors for Air Quality Monitoring with Smartphone Technology: A Preliminary Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
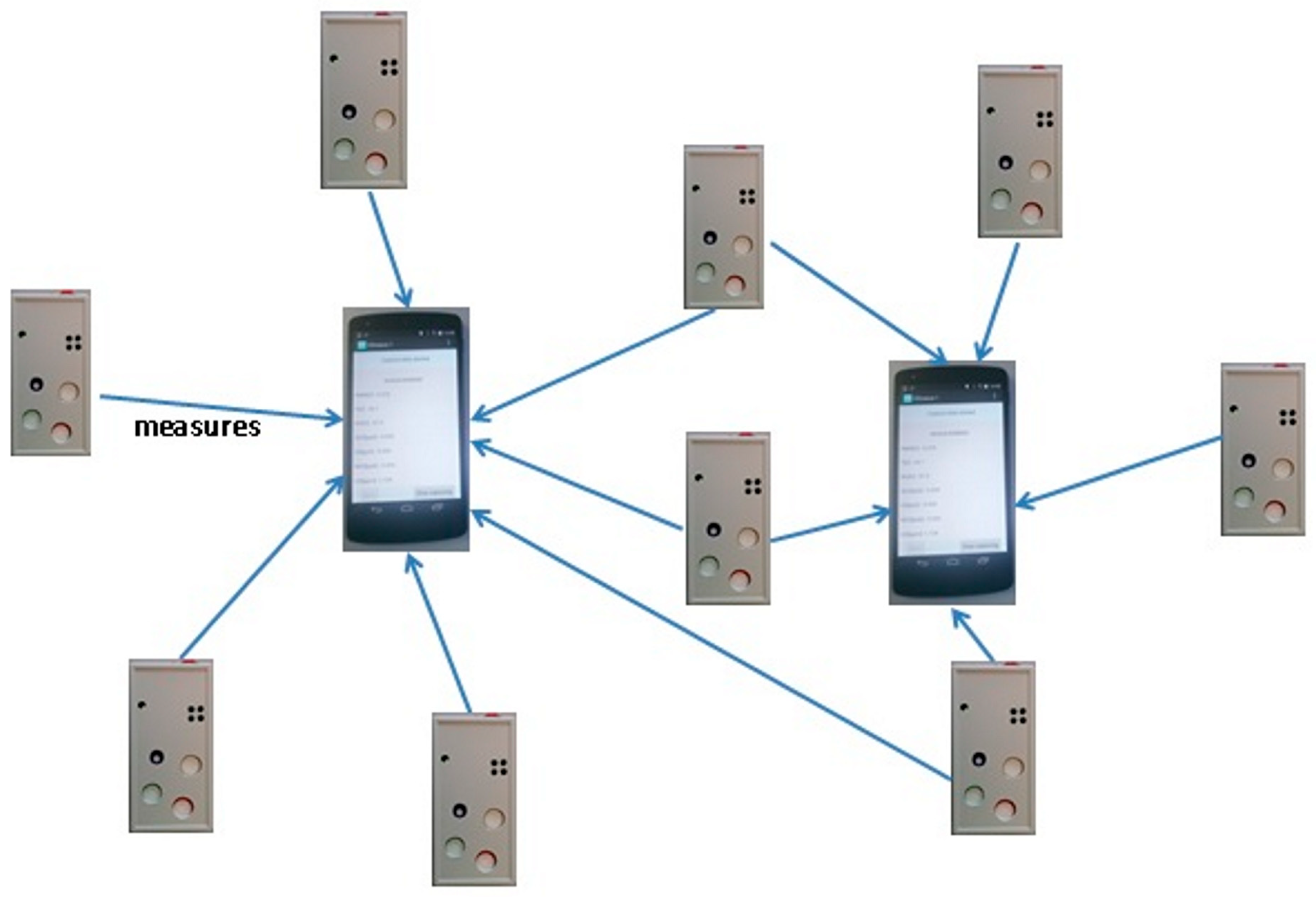
2.1. The Devices and the Sensors Used for the Experiments
2.2. The Calibration of the Sensors
2.3. The Indoor Monitoring
2.4. The Mobile Monitoring
3. Results
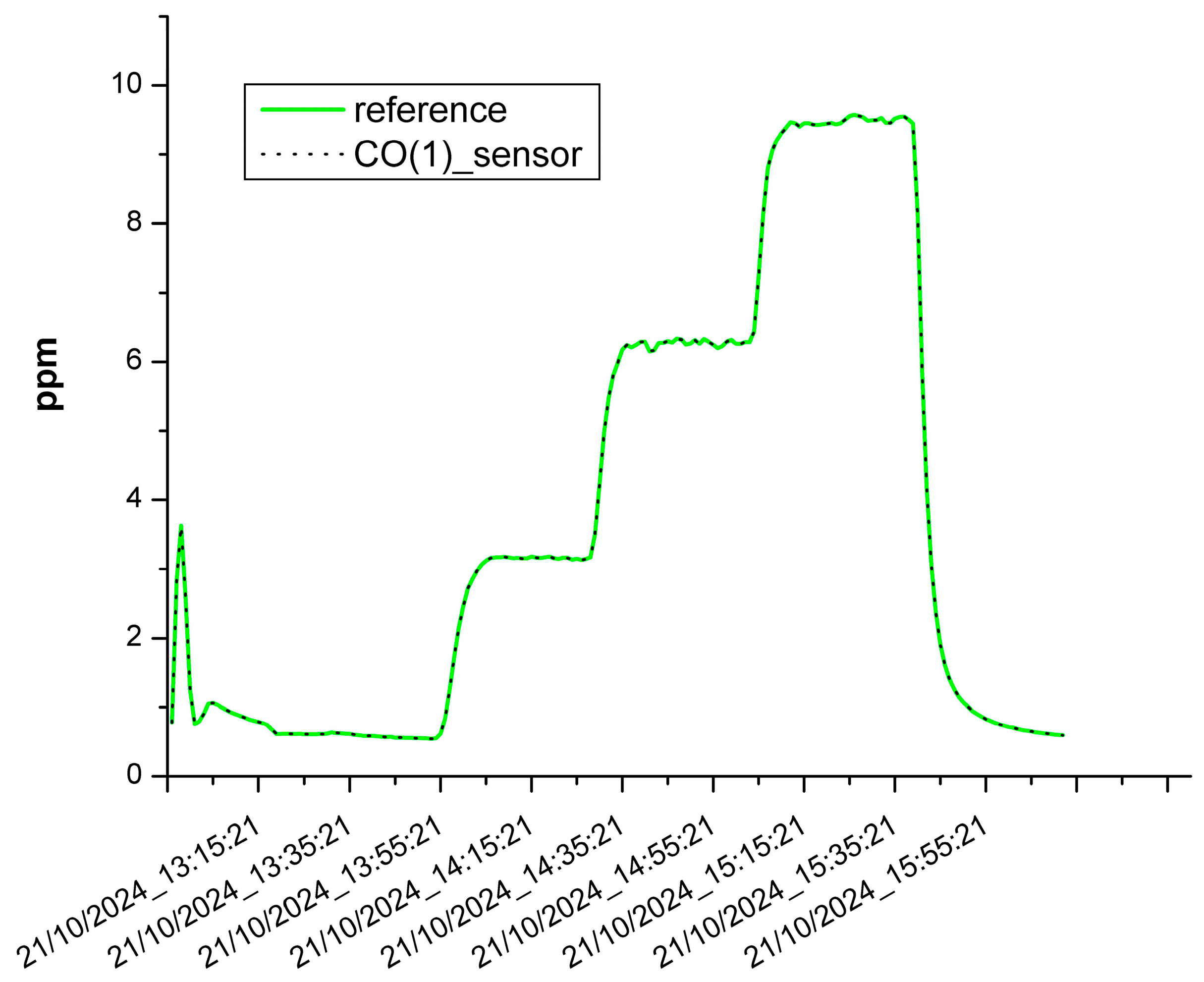
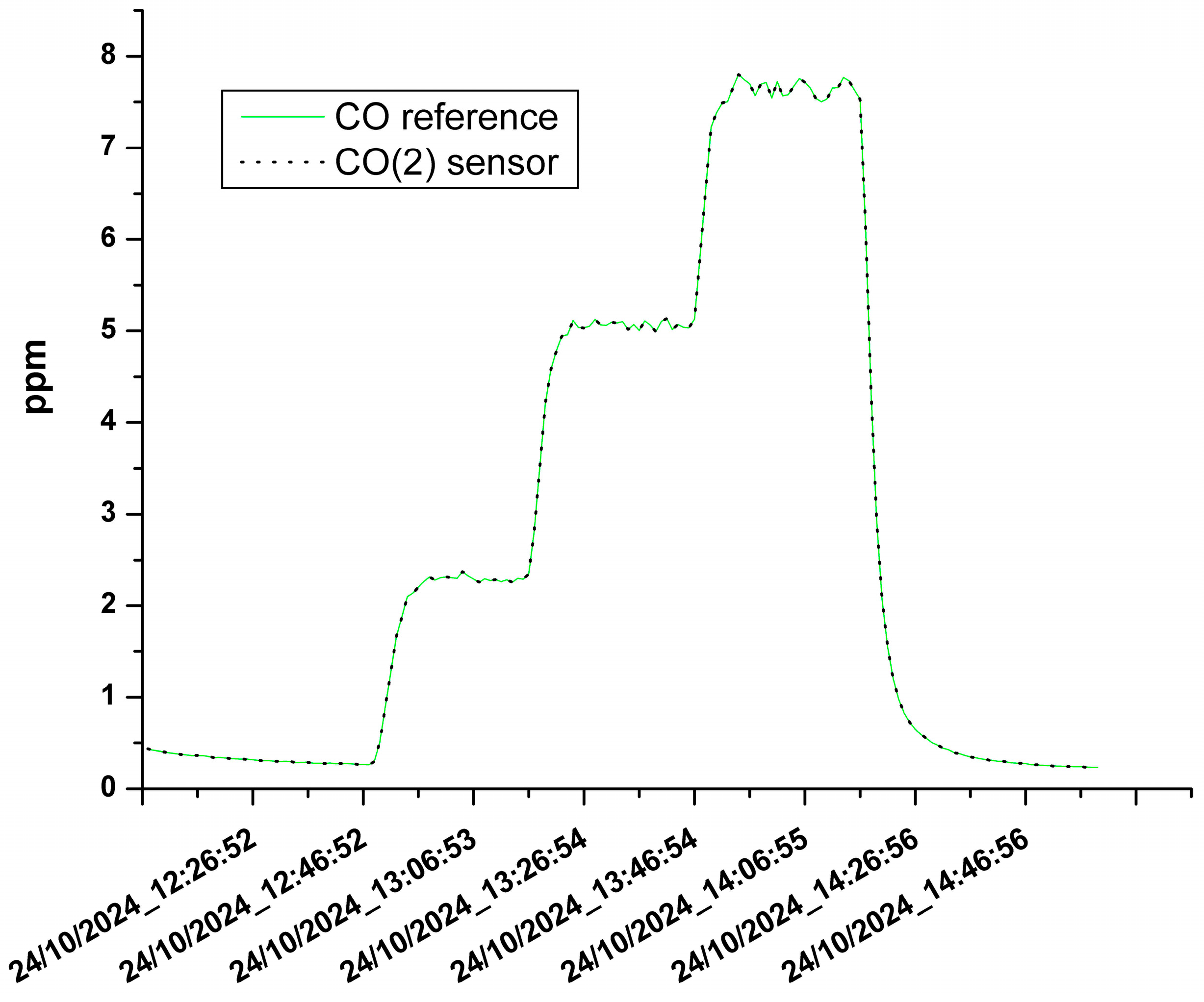
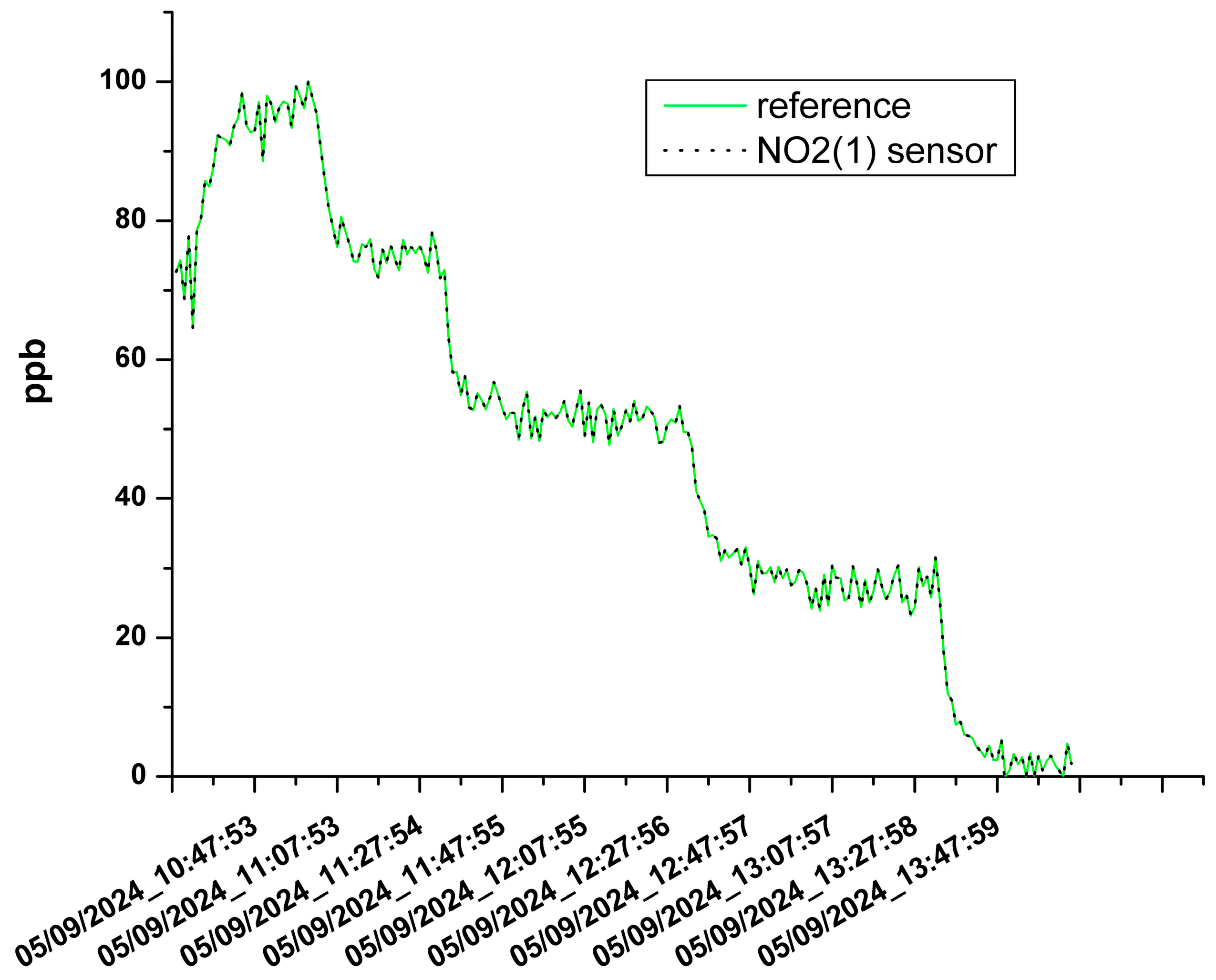
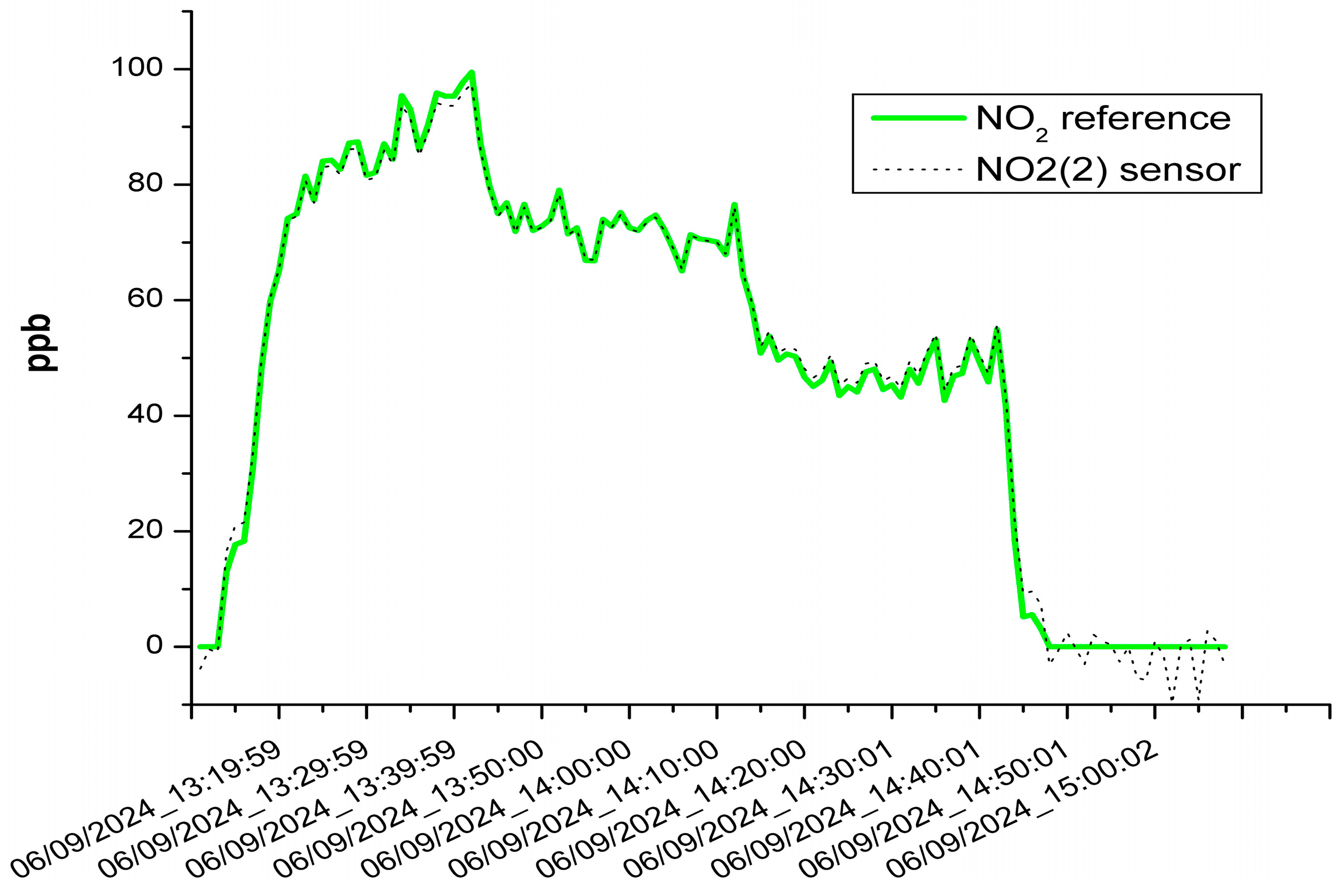
3.1. The Results of the Sensor Calibration
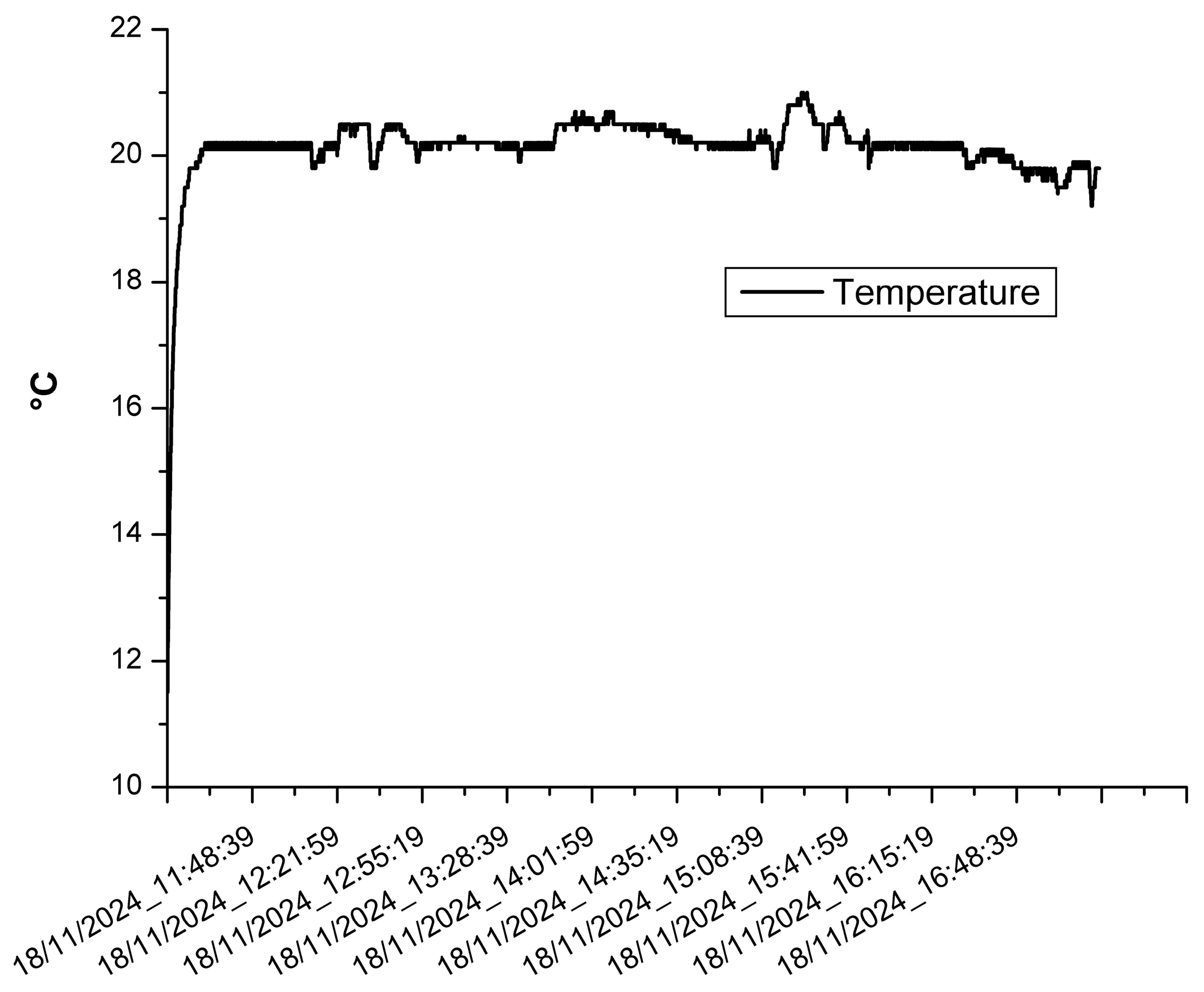
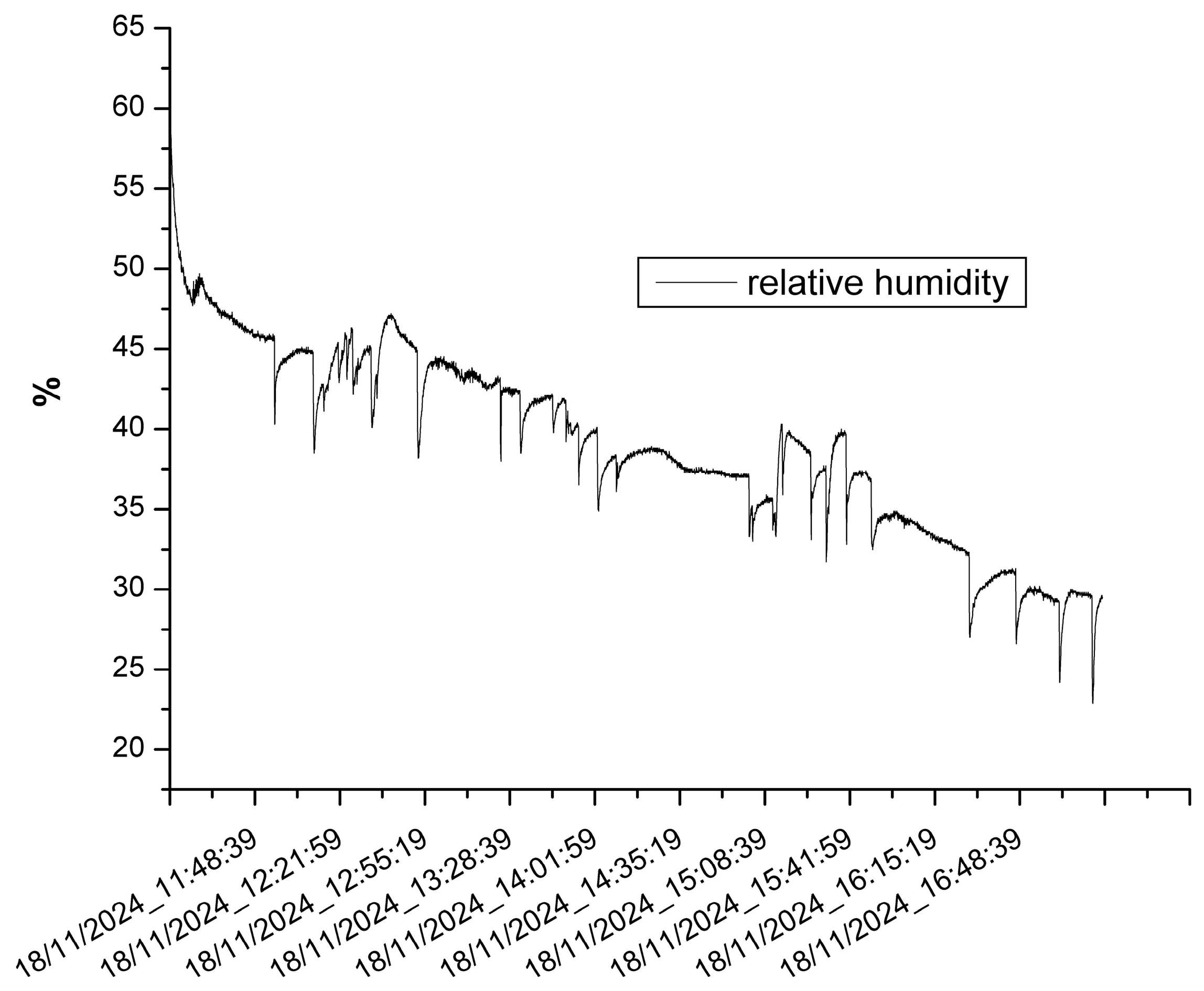
3.2. The Results of the Indoor Monitoring
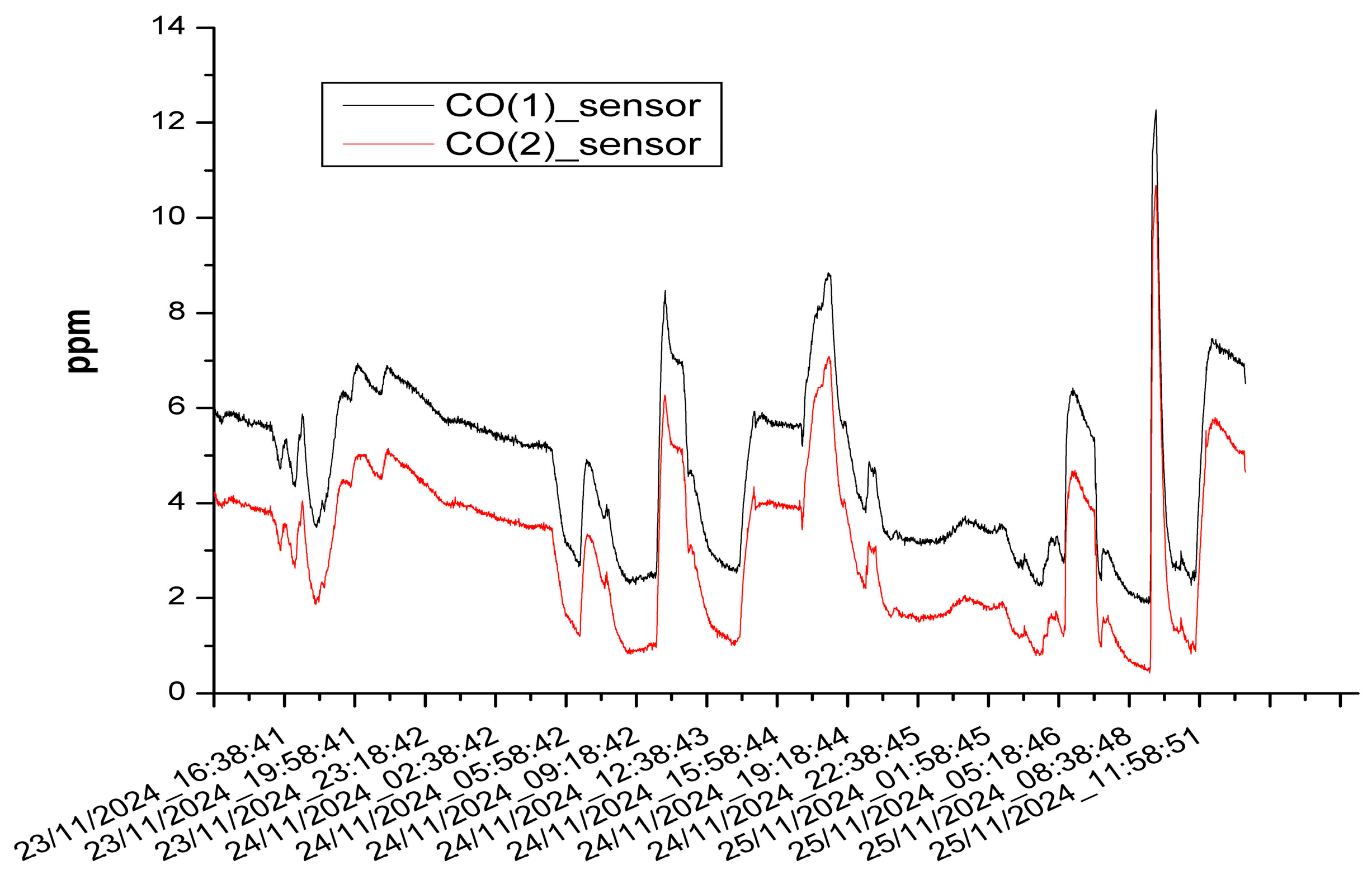
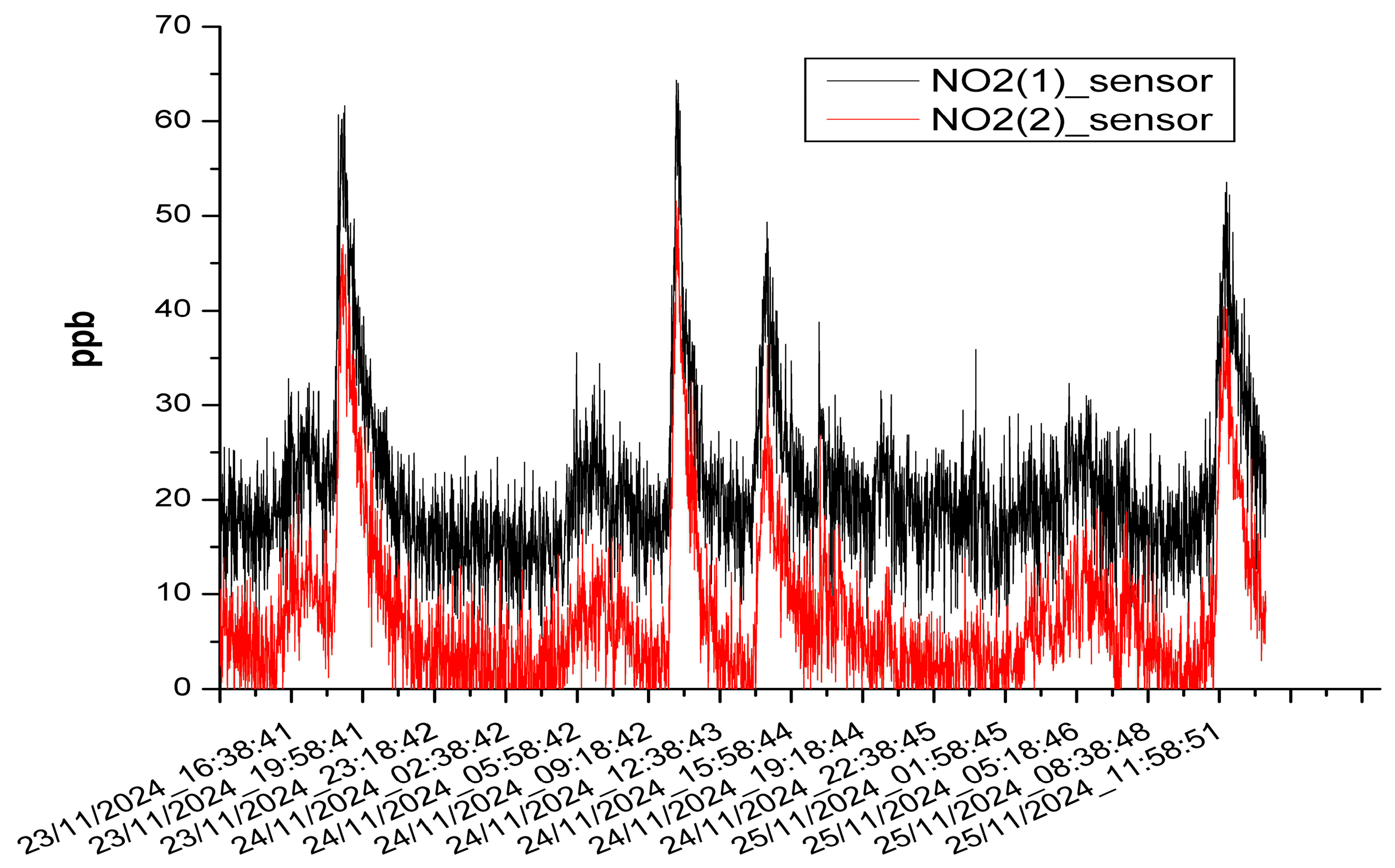
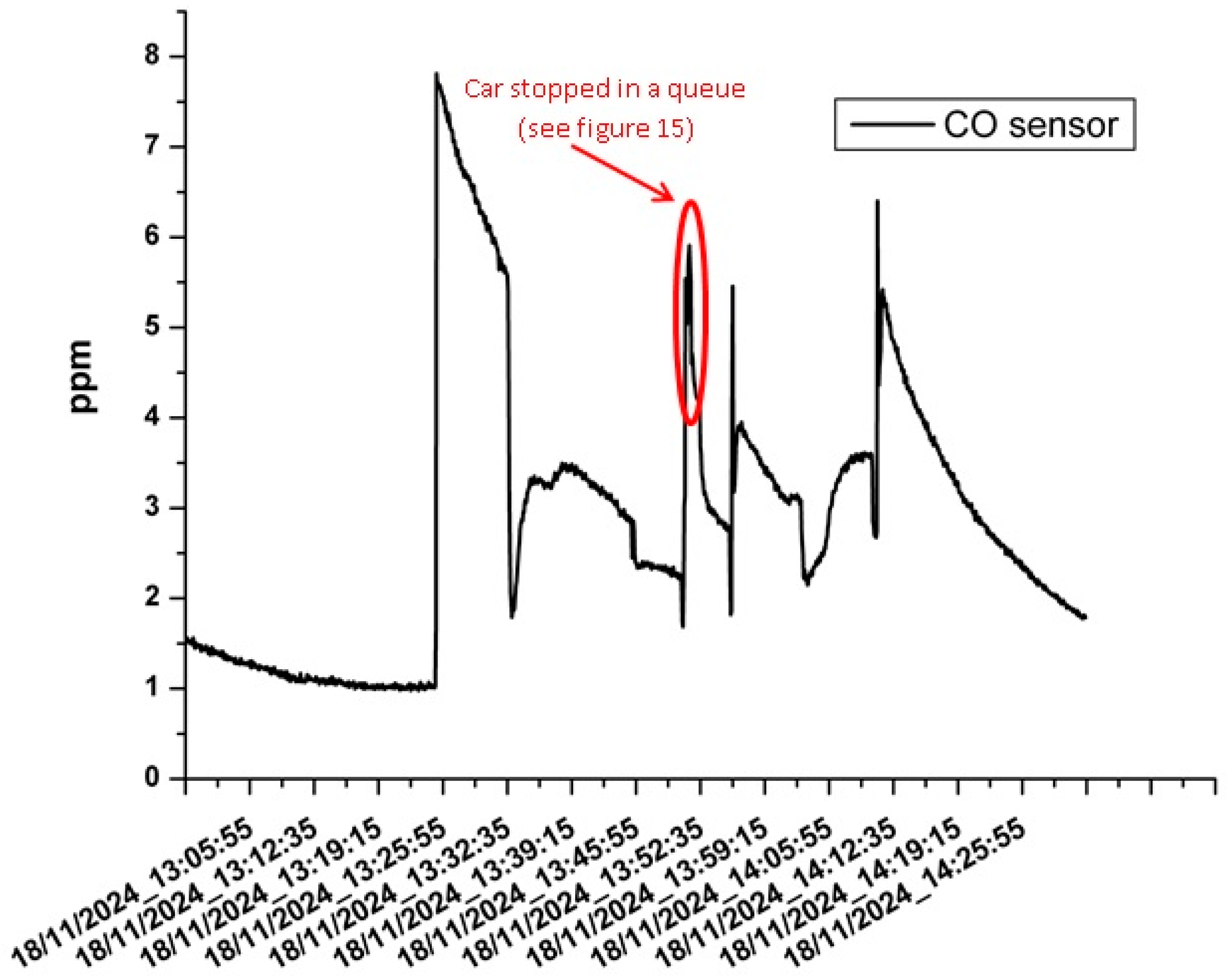
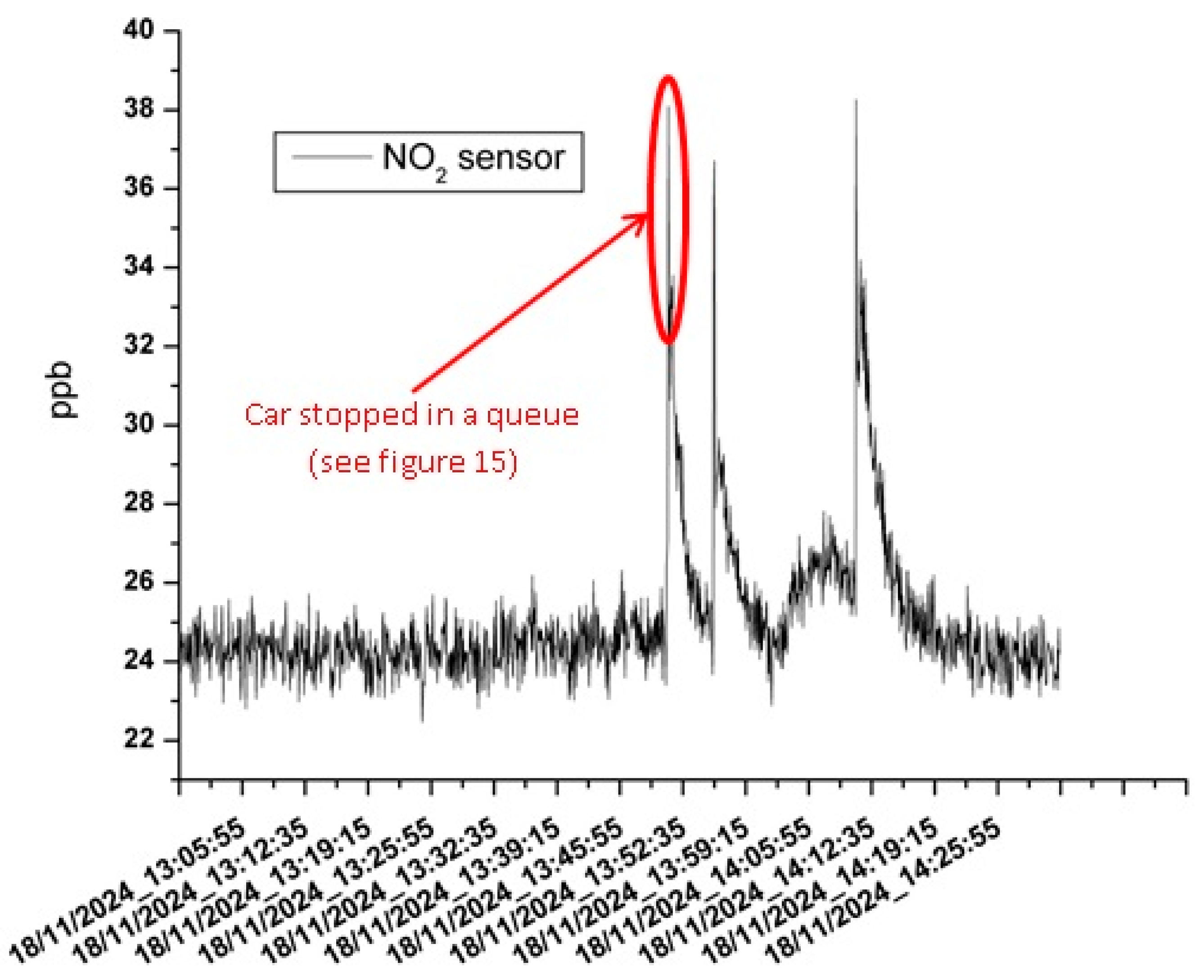
3.3. The Results of the Mobile Measurements
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gumy, S.; Prüss-Üstün, A. Ambient Air Pollution: A Global Assessment of Exposure and Burden of Disease; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016.
- European Commission. Indoor Air Pollution: New EU Research Reveals Higher Risks than Previously Thought. 2017. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/commission/presscorner/detail/en/IP_03_1278 (accessed on 10 December 2024).
- WHO. How Air Pollution Is Destroying Our Health. 2018. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/spotlight/how-air-pollution-is-destroying-our-health (accessed on 10 December 2024).
- EPA. The Inside Story: A Guide to Indoor Air Quality. 2017. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/indoor-air-quality-iaq/inside-story-guide-indoor-air-quality (accessed on 10 December 2024).
- Karagulian, F.; Barbiere, M.; Kotsev, A.; Spinelle, L.; Gerboles, M.; Lagler, F.; Redon, N.; Crunaire, S.; Borowiak, A. Review of the Performance of Low-Cost Sensors for Air Quality Monitoring. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinelle, L.; Gerboles, M.; Villani, M.G.; Aleixandre, M.; Bonavitacola, F. Field calibration of a cluster of low-cost commercially available sensors for air quality monitoring. Part B: NO, CO and CO2. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 238, 706–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mead, M.I.; Popoola, O.A.M.; Stewart, G.B.; Landshoff, P.; Calleja, M.; Hayes, M.; Baldovi, J.J.; McLeod, M.W.; Hodgson, T.F.; Dicks, J.; et al. The use of electrochemical sensors for monitoring urban air quality in low-cost, high-density networks. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 70, 186–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castell, N.; Dauge, F.R.; Schneider, P.; Vogt, M.; Lerner, U.; Fishbain, B.; Broday, D.; Bartonova, A. Can commercial low-cost sensor platforms contribute to air quality monitoring and exposure estimates? Environ. Int. 2017, 99, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKercher, G.R.; Salmond, J.A.; Vanos, J.K. Characteristics and applications of small, portable gaseous air pollution monitors. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 223, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.; Morawska, L.; Martani, C.; Biskos, G.; Neophytou, M.; Di Sabatino, S.; Bell, M.; Norford, L.; Britter, R. The rise of low-cost sensing for managing air pollution in cities. Environ. Int. 2015, 75, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, E.G.; Watkins, T.H.; Solomon, P.A.; Thoma, E.D.; Williams, R.W.; Hagler, G.S.; Shelow, D.; Hindin, D.A.; Kilaru, V.J.; Preuss, P.W. The Changing Paradigm of Air Pollution Monitoring. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 11369–11377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Aye, L.; Ngo, T.D.; Zhou, J. Performance evaluation of low-cost air quality sensors: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 818, 151769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suriano, D. SentinAir system software: A flexible tool for data acquisition from heterogeneous sensors and devices. SoftwareX 2020, 12, 100589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tryner, J.; Phillips, M.; Quinn, C.; Neymark, G.; Wilson, A.; Jathar, S.H.; Carter, E.; Volckens, J. Design and testing of a low-cost sensor and sampling platform for indoor air quality. Build. Environ. 2021, 206, 108398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, J.; Jo, B.; Kim, J.; Kim, S.; Han, W. Development of an IoT-Based Indoor Air Quality Monitoring Platform. J. Sens. 2020, 2020, 8749764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, D.; Banerjee, S. Surface Acoustic Wave (SAW) Sensors: Physics, Materials, and Applications. Sensors 2022, 22, 820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.; Nag, A.; Mukhopadhyay, S.C.; Xu, Y. Carbon nanotubes and its gas-sensing applications: A review. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2019, 291, 107–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayahi, T.; Garff, A.; Quah, T.; Lê, K.; Becnel, T.; Powell, K.M.; Gaillardon, P.E.; Butterfield, A.E.; Kelly, K.E. Long term calibration models to estimate ozone concentrations with a metal oxide sensor. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 267, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velasco, A.; Ferrero, R.; Gandino, F.; Montrucchio, B.; Rebaudengo, M. A mobile and low-cost system for environmental monitoring: A case study. Sensors 2016, 16, 710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinelle, L.; Gerboles, M.; Villani, M.G.; Aleixandre, M.; Bonavitacola, F. Field calibration of a cluster of low-cost available sensors for air quality monitoring. Part A: Ozone and nitrogen dioxide. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 215, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mijling, B.; Jiang, Q.; De Jonge, D.; Bocconi, S. Field calibration of electrochemical NO2 sensors in a citizen science context. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 1297–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagan, D.H.; Isaacman-VanWertz, G.; Franklin, J.P.; Wallace, L.M.; Kocar, B.D.; Heald, C.L.; Kroll, J.H. Calibration and assessment of electrochemical air quality sensors by co-location with regulatory-grade instruments. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demanega, I.; Mujan, I.; Singer, B.C.; Anđelković, A.S.; Babich, F.; Licina, D. Performance assessment of low-cost environmental monitors and single sensors under variable indoor air quality and thermal conditions. Build. Environ. 2021, 187, 107415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, P.; Sun, L.; Anand, A.; Zhang, Q.; Huixin, Z.; Deng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Ning, Z. Development and evaluation of a robust temperature sensitive algorithm for long term NO2 gas sensor network data correction. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 230, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, P.; Ning, Z.; Ye, S.; Sun, L.; Yang, F.; Wong, K.C.; Westerdahl, D.; Louie, P.K.K. Impact Analysis of Temperature and Humidity Conditions on Electrochemical Sensor Response in Ambient Air Quality Monitoring. Sensors 2018, 18, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, K.R.; Edwards, P.M.; Ivatt, P.D.; Lee, J.D.; Squires, F.; Dai, C.; Peltier, R.E.; Evans, M.J.; Sun, Y.; Lewis, A.C. An improved low–power measurement of ambient NO2 and O3 combining electrochemical sensor clusters and machine learning. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2019, 12, 1325–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, N.; Presto, A.A.; Kumar, S.P.N.; Gu, J.; Hauryliuk, A.; Robinson, E.S.; Robinson, A.L.; Subramanian, R. A machine learning calibration model using random forests to improve sensor performance for lower-cost air quality monitoring. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 291–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.; Saffell, J.; Baron, R. Differentiating NO2 and O3 at low cost air quality amperometric gas sensors. ACS Sens. 2016, 1, 1291–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigi, A.; Mueller, M.; Grange, S.K.; Ghermandi, G.; Hueglin, C. Performance of NO, NO2 low cost sensors and three calibration approaches within a real world application. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 3717–3735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suriano, D.; Penza, M. Assessment of the Performance of a Low-Cost Air Quality Monitor in an Indoor Environment through Different Calibration Models. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordero, J.M.; Borge, R.; Narros, A. Using statistical methods to carry out in field calibrations of low cost air quality sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 267, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trizio, L.; Brattoli, M.; De Gennaro, G.; Suriano, D.; Rossi, R.; Alvisi, M.; Cassano, G.; Pfister, V.; Penza, M. Application of artificial neural networks to a gas sensor-array database for environmental monitoring. In Sensors and Microsystems; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2012; pp. 139–144. [Google Scholar]
- Cross, E.S.; Williams, L.R.; Lewis, D.K.; Magoon, G.R.; Onasch, T.B.; Kaminsky, M.L.; Worsnop, D.R.; Jayne, J.T. Use of electrochemical sensors for measurement of air pollution: Correcting interference response and validating measurements. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2017, 10, 3575–3588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Wu, C.; Jiang, S.; Li, Y.J.; Wu, D.; Li, M.; Cheng, P.; Yang, W.; Cheng, C.; Li, L.; et al. Field comparison of electrochemical gas sensor data correction algorithms for ambient air measurements. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 327, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, P.; Mei, H.; Liu, D.; Zeng, N.; Tang, X.; Wang, Y.; Pan, Y. Calibrations of Low-Cost Air Pollution Monitoring Sensors for CO, NO2, O3, and SO2. Sensors 2021, 21, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Mazzeo, A.; Zhong, J.; Cai, X.; Mele, B.; Toscano, D.; Murena, F.; MacKenzie, A.R. Modelling of Deep Street Canyon Air Pollution Chemistry and Transport: A Wintertime Naples Case Study. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, D.L.; Benney, T.M.; Boll, S. Long-term analysis of the relationships between indoor and outdoor fine particulate pollution: A case study using research grade sensors. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 776, 145778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baron, R.; Saffell, J. Amperometric gas sensors as a low cost emerging technology platform for air quality monitoring applications: A review. ACS Sens. 2017, 2, 1553–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najafi, P.; Ghaemi, A. Chemiresistor gas sensors: Design, Challenges, and Strategies: A comprehensive review. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 498, 154999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NO2-B43F Datasheet. Available online: https://ametekcdn.azureedge.net/mediafiles/project/oneweb/oneweb/alphasense/products/datasheets/alphasense_no2-b43f_datasheet_en_4.pdf (accessed on 27 March 2025).
- CO2-B4 Datasheet. Available online: https://ametekcdn.azureedge.net/mediafiles/project/oneweb/oneweb/alphasense/products/datasheets/alphasense_co-b4_datasheet_en_2.pdf (accessed on 27 March 2025).
- Suriano, D. Design and Development of an Electronic Board for Supporting the Operation of Electrochemical Gas Sensors. Hardware 2024, 2, 173–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alphasense Ozone Sensors. Available online: https://www.alphasense.com/products/view-by-target-gas/ozone-sensors-o3 (accessed on 27 March 2025).
- WHO. World Health Organization (WHO) Air Quality Guidelines (AQGs) and Estimated Reference Levels (RLs). Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/publications/status-of-air-quality-in-Europe-2022/europes-air-quality-status-2022/world-health-organization-who-air (accessed on 27 March 2025).






| Sensor | Sensitivity | Response Time | Zero Current | Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CO-B4 | +420/+650 nA/ppm | <30 s | +30/−250 nA | 1000 ppm |
| NO2-B43F | −200/−650 nA/ppm | <80 s | −80/+80 nA | 20 ppm |
| Sensor | R2 | MAE |
|---|---|---|
| CO(1) | 0.999 | 0.001 ppm |
| CO(2) | 0.999 | 0.0009 ppm |
| NO2(1) | 0.999 | 0.053 ppb |
| NO2(2) | 0.995 | 1.415 ppb |
| Sensor | a | b | c |
|---|---|---|---|
| CO(1) | −3150 ppm/V | 3.127 ppm/V | 6.243 ppm |
| CO(2) | −2.762 ppm/V | 2.705 ppm/V | 5.239 ppm |
| NO2(1) | 104.933 ppb/V | −103.909 ppb/V | 93.010 ppb |
| NO2(2) | 98.294 ppb/V | −97.607 ppb/V | 91.989 ppb |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Suriano, D.; Abulude, F.O.; Penza, M. The Use of Low-Cost Gas Sensors for Air Quality Monitoring with Smartphone Technology: A Preliminary Study. Chemosensors 2025, 13, 189. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13050189
Suriano D, Abulude FO, Penza M. The Use of Low-Cost Gas Sensors for Air Quality Monitoring with Smartphone Technology: A Preliminary Study. Chemosensors. 2025; 13(5):189. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13050189
Chicago/Turabian StyleSuriano, Domenico, Francis Olawale Abulude, and Michele Penza. 2025. "The Use of Low-Cost Gas Sensors for Air Quality Monitoring with Smartphone Technology: A Preliminary Study" Chemosensors 13, no. 5: 189. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13050189
APA StyleSuriano, D., Abulude, F. O., & Penza, M. (2025). The Use of Low-Cost Gas Sensors for Air Quality Monitoring with Smartphone Technology: A Preliminary Study. Chemosensors, 13(5), 189. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13050189








