Colorimetric Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Sensors for Rapid Detection of Organic Compounds: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
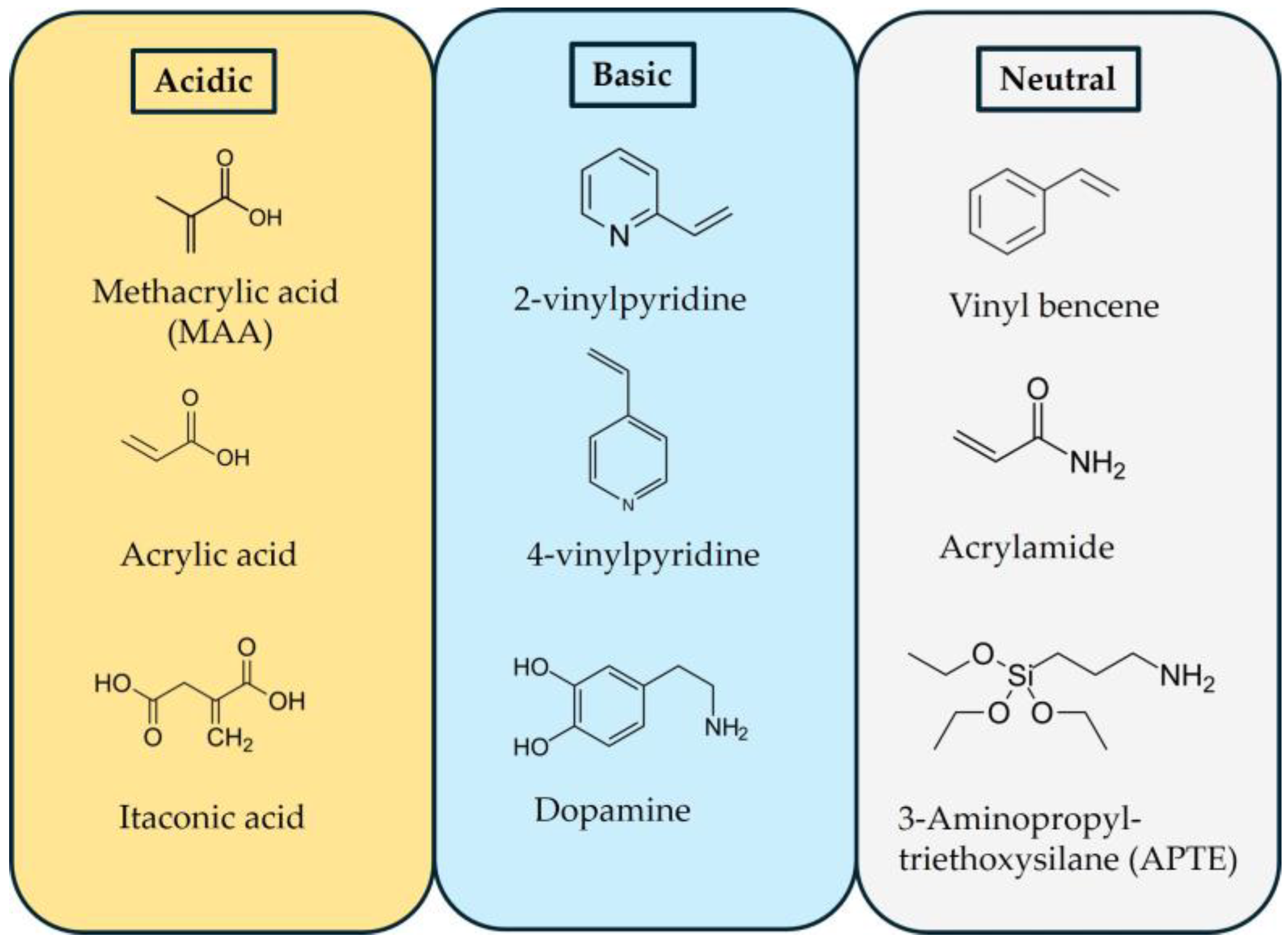
2. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers (MIPs)
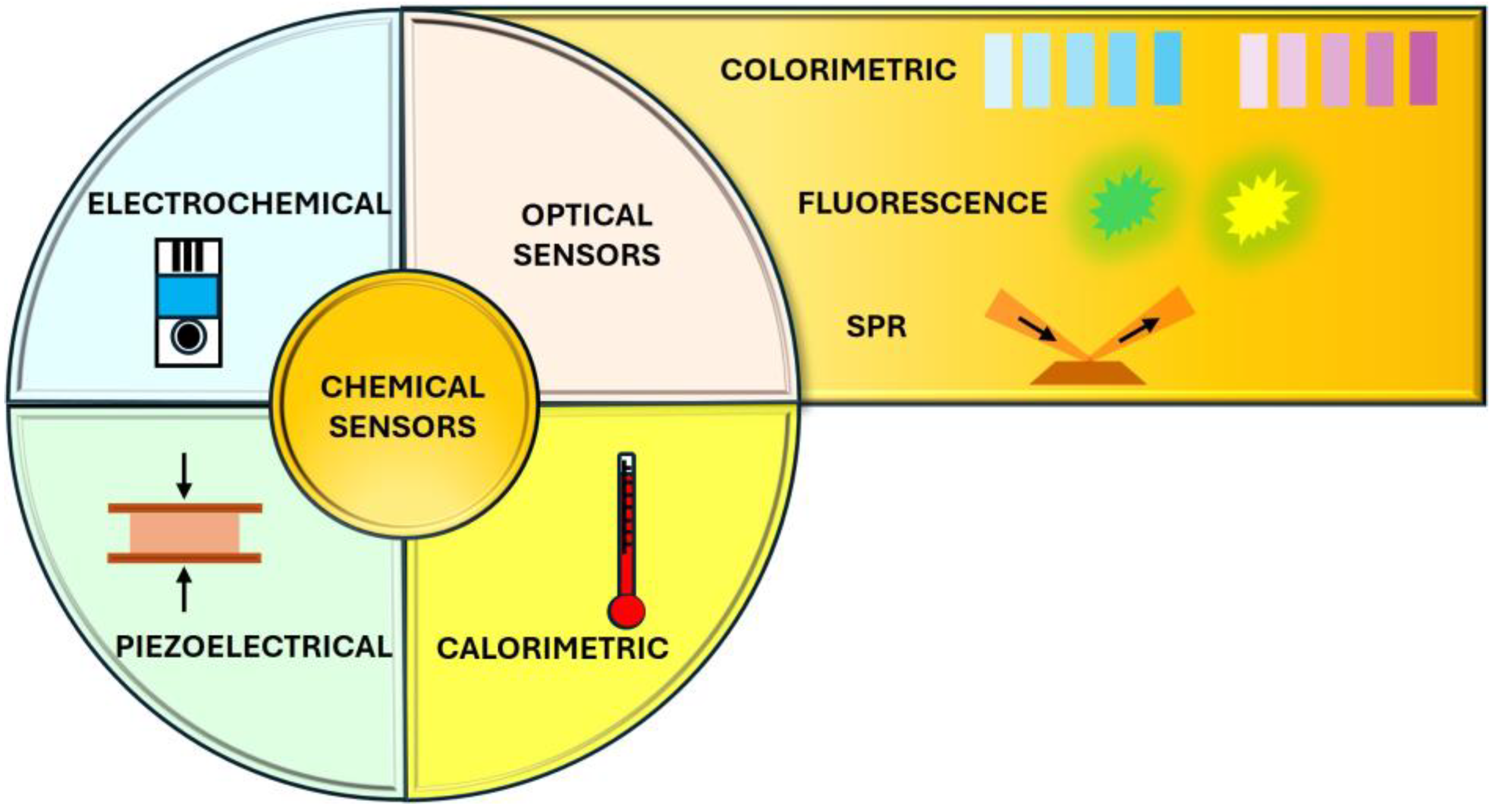
3. Colorimetric Sensors
3.1. Smartphone-Based Colorimetry
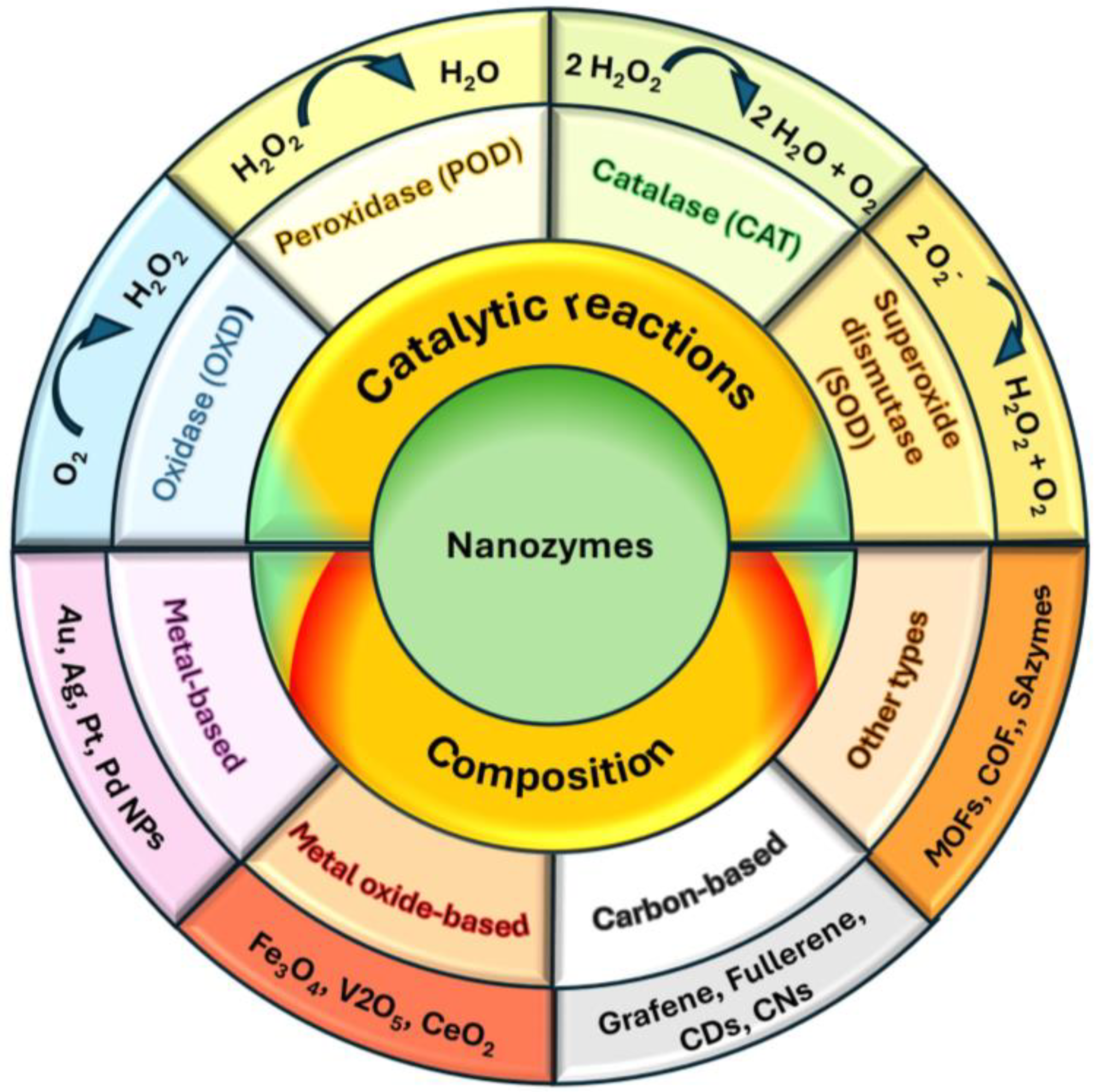
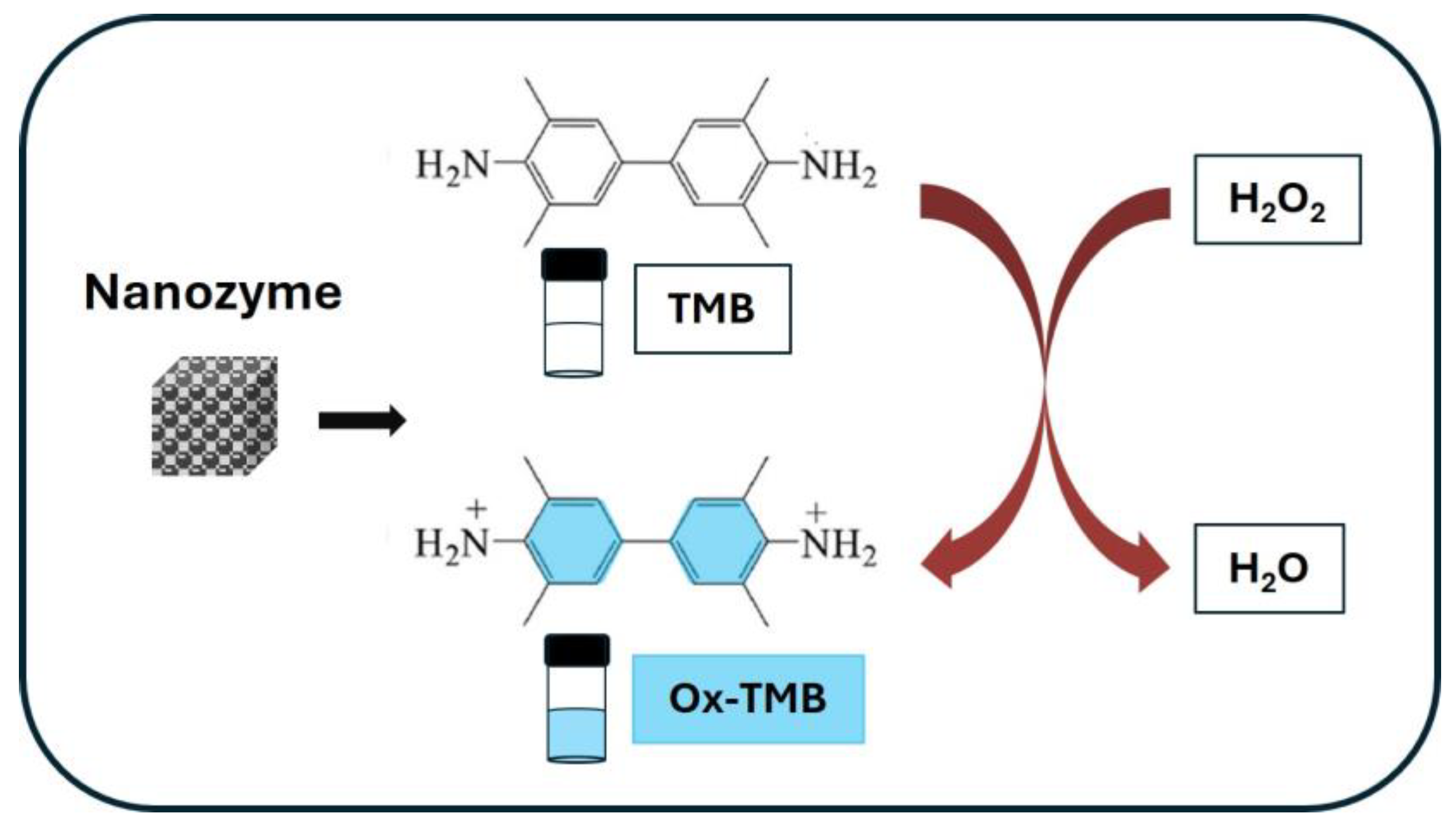
3.2. Nanozymes
- Main nanozyme catalytic mechanisms
- Main nanozymes according to the composition material
4. MIP-Based Colorimetric Sensors
4.1. MIP-Based Colorimetric Sensors Mechanisms
4.2. MIP-Based Colorimetric Sensors by Target
4.2.1. Pharmaceuticals
- Antibiotics
- Psychoactive Compounds and Stimulants
- Analgesics and anti-inflammatory drugs
- Others
4.2.2. Pesticides
4.2.3. Toxins
4.2.4. Amino Acids and Proteins
4.2.5. Colorants
4.2.6. Other Compounds
5. Conclusions and Future Challenges
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ni, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Cui, G.; Meng, X.; Chen, W.; Jin, M.; Shao, H.; Zhang, F.; Wang, C. Rapid and On-Site Approaches for Determination of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Water and Air by Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. ACS Omega 2025, 10, 6258–6266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Ye, H.; Yan, S.; Chu, C.; Yang, T. Rapid On-Site and Sensitive Detection of Microplastics Using Zirconium(IV)-Assisted SERS Label. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2025, 73, 5757–5766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, L.; Tian, Y.; Chen, M.; Phillip Shelor, C. On-site determination of aquatic arsenic using hydride generation combined with portable absorbance detector. Microchem. J. 2025, 209, 112878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, M.; Han, Z.; Li, M.; Shen, Y.; Liu, Z.; Geng, X.; Li, X.; Cao, Y.; Shi, H.; Li, X.; et al. Smartphone-based colorimetric sensor for on-site and tri-mode detection of ascorbic acid using Zn/Co bimetallic organic framework-derived nanozymes. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2025, 141, 107334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakoti, A.; Das, A.K.; Saikia, P.K.; Khakhlary, P. A starch–polyvinyl alcohol polymer film-based on-site sensor for ammonia: A cost effective day-to-day technique for monitoring fish and meat spoilage. Anal. Methods 2025, 17, 1648–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Q.; Deng, J.; Zhou, T. A facile rapid-response and on-site sensor for tetracycline detection in environmental water based on europium-doped carbonized polymer dots. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altahan, M.F.; Esposito, M.; Achterberg, E.P. Improvement of On-Site Sensor for Simultaneous Determination of Phosphate, Silicic Acid, Nitrate plus Nitrite in Seawater. Sensors 2022, 22, 3479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piriya, V.S.A.; Joseph, P.; Daniel S.C.G., K.; Lakshmanan, S.; Kinoshita, T.; Muthusamy, S. Colorimetric sensors for rapid detection of various analytes. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 78, 1231–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nghia, N.N.; Hieu, N.H.; Khanh, D.N.N.; Vy, N.T.T.; Phuong, N.T.K. Development of a portable colorimetric sensor using Prussian blue nanoparticles for the detection of hydrazine. Microchem. J. 2025, 208, 112510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Wen, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, W.; Long, D. Antioxidants Recognition Colorimetric Sensor Array Based on Multicolor System. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2025, 39, e7886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Li, S.; Yang, F.; Yue, W. Construction of a colorimetric sensor array for the identification of phenolic compounds by the laccase-like activity of N-doped manganese oxide. Talanta 2024, 268, 125324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alizadeh, S.; Pirsa, S.; Amiri, S. Development of a colorimetric sensor based on nanofiber cellulose film modified with ninhydrin to measure the formalin index of fruit juice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 127035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Lin, X.; Zheng, X.; Lai, W.; Lin, Y.; Zou, Z.; Wang, Q.; Zheng, X. Fluorine-fluorine interaction-driven colorimetric sensor for PFOA-sensitive detection using F-functionalized Ce-UiO-66-NH2 MOF with oxidase-like activity. Microchim. Acta 2025, 192, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, P.; Chen, J.; Li, Q.; Luo, M.; Chang, W.; Xue, Z. Self-signaling colorimetric sensor for selective detection of dopamine based on CoFe2O4 nanozyme accelerated dopamine polymerization. Anal. Chim. Acta 2025, 1338, 343596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, W.; Kuang, G.; Gu, C.; Wang, J.; Jiang, X.; Zhu, R.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Z. Enzyme cascade nanozyme based colorimetric sensor for detection of uric acid as a biomarker of hyperuricemia. Microchim. Acta 2025, 192, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Wei, J.; Xiang, C.; Yang, D.; Yang, Y. A colorimetric sensor for the sensitive and rapid detection of ampicillin based on CS-Cu,Fe/HS nanozyme. Microchim. Acta 2025, 192, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, J.; Kim, Y. Overcoming interferences in the colorimetric and fluorimetric detection of γ-hydroxybutyrate in spiked beverages. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 364, 131861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, S.; Syed, Z.U.Q. Colorimetric Visual Sensors for Point-of-needs Testing. Sens. Actuators Rep. 2022, 4, 100078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wackerlig, J.; Schirhagl, R. Applications of Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Nanoparticles and Their Advances toward Industrial Use: A Review. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 250–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wang, X.; Lu, W.; Wu, X.; Li, J. Molecular imprinting: Perspectives and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 2137–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haupt, K.; Mosbach, K. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers and Their Use in Biomimetic Sensors. Chem. Rev. 2000, 100, 2495–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cieplak, M.; Kutner, W. Artificial Biosensors: How Can Molecular Imprinting Mimic Biorecognition? Trends Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 922–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Liu, Y.; Du, X.; Gui, Y.; He, J.; Xie, F.; Cai, J. Recent Advances in Design and Application of Nanomaterials-Based Colorimetric Biosensors for Agri-food Safety Analysis. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 46346–46361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wu, Q.; Wu, Z.; Zhuang, Y.; Sun, L.; Fan, X.; Zhao, T.; Yi, L.; Gu, Y. Biomimetic functional material-based sensors for food safety analysis: A review. Food Chem. 2023, 405, 134974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, V.X.T.; Wong, T.I.; Zheng, X.T.; Tan, Y.N.; Zhou, X. Colorimetric biosensors for point-of-care virus detections. Mater. Sci. Energy Technol. 2020, 3, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbanizamani, F.; Moulahoum, H.; Zihnioglu, F.; Timur, S. Molecularly imprinted polymers-based biosensors for gynecological diagnostics and monitoring. Talanta Open 2024, 10, 100364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Pagett, M.; Zhang, W. Molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP) based electrochemical sensors and their recent advances in health applications. Sens. Actuators Rep. 2023, 5, 100153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akgönüllü, S.; Kılıç, S.; Esen, C.; Denizli, A. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Sensors for Protein Detection. Polymers 2023, 15, 629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Peng, H.; Xiong, H.; Chen, L. Strategies of molecular imprinting-based fluorescence sensors for chemical and biological analysis. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 112, 54–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Meng, C.; Liu, H.; Sun, B. Progress in research on smartphone-assisted MIP optosensors for the on-site detection of food hazard factors. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2024, 170, 117459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, X.; Yang, J.; Yu, X.; Peng, Z.; Zhang, G.; Li, Y. Wearable molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor with integrated nanofiber-based microfluidic chip for in situ monitoring of cortisol in sweat. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2023, 381, 133451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazim, T.; Lusina, A.; Cegłowski, M. Recent Developments in the Detection of Organic Contaminants Using Molecularly Imprinted Polymers Combined with Various Analytical Techniques. Polymers 2023, 15, 3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leibl, N.; Haupt, K.; Gonzato, C.; Duma, L. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Chemical Sensing: A Tutorial Review. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayerdurai, V.; Cieplak, M.; Kutner, W. Molecularly imprinted polymer-based electrochemical sensors for food contaminants determination. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 158, 116830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamel, A.H.; Abd-Rabboh, H.S.M.; Hefnawy, A. Molecularly imprinted polymer-based electrochemical sensors for monitoring the persistent organic pollutants chlorophenols. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 20163–20181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Ko, C.-C. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Luminescent Chemosensors. Biosensors 2023, 13, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Xu, S.; Zhou, Q.; Liu, Z.; Xu, Z. State-of-the-art molecular imprinted colorimetric sensors and their on-site inspecting applications. J. Sep. Sci. 2023, 46, 2201059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karadurmus, L.; Bilge, S.; Sınağ, A.; Ozkan, S.A. Molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP)-Based sensing for detection of explosives: Current perspectives and future applications. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2022, 155, 116694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrovidov, S.; Ramalingam, M.; Bae, H.; Orive, G.; Fujie, T.; Hori, T.; Nashimoto, Y.; Shi, X.; Kaji, H. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Sensors for the Detection of Skeletal- and Cardiac-Muscle-Related Analytes. Sensors 2023, 23, 5625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarejousheghani, M.; Rahimi, P.; Borsdorf, H.; Zimmermann, S.; Joseph, Y. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Sensors for Priority Pollutants. Sensors 2021, 21, 2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, F.; Meng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Huang, S.; Wang, Q.; Lu, W.; Xue, M. A molecularly imprinted colloidal array as a colorimetric sensor for label-free detection of p-nitrophenol. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 831–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Dong, X.; Qiu, L.; Yan, Z.; Meng, Z.; Xue, M.; He, X.; Liu, X. Colorimetric sensor arrays based on pattern recognition for the detection of nitroaromatic molecules. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 326, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Cao, X.; Zhang, Z.; Yin, J.; Wang, D.; Xu, Y.; Zheng, W.; Li, X.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, L. Synthesis of dummy-template molecularly imprinted polymer adsorbents for solid phase extraction of aminoglycosides antibiotics from environmental water samples. Talanta 2020, 208, 120385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arshady, R.; Mosbach, K. Synthesis of substrate-selective polymers by host-guest polymerization. Die Makromol. Chem. 1981, 182, 687–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Tian, W. Selective extraction and determination of chlorpyrifos residues from aqueous samples using biochar-functionalized molecularly imprinted polymer combined with high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2025, 1741, 465611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, S.; Sun, X.; Wang, J.; Chen, H.; Xu, Q.; Ye, H.; Li, S.; Shi, S.; Zhang, X. Preparation of novel magnetic ethylene glycol dimethacrylate-based molecularly imprinted polymer for rapid adsorption of phthalate esters from ethanol aqueous solution. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 361, 124891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeleke, V.T.; Ebenezer, O.; Lasich, M.; Tuszynski, J.; Robertson, S.; Mugo, S.M. Design and Optimization of Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Targeting Epinephrine Molecule: A Theoretical Approach. Polymers 2024, 16, 2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Guan, Y.; Zhang, Y. Molecularly imprinted polymer for selective insulin capture and separation. Polymer 2024, 307, 127290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisi, O.I.; Francomano, F.; Dattilo, M.; Patitucci, F.; Prete, S.; Amone, F.; Puoci, F. The Evolution of Molecular Recognition: From Antibodies to Molecularly Imprinted Polymers (MIPs) as Artificial Counterpart. J. Funct. Biomater. 2022, 13, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Lin, X.; Ee, L.Y.; Li, S.F.Y. Research Progress on Molecularly Imprinted Materials for the Screening and Identification of Organic Pollutants. Chemosensors 2024, 12, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaerani, W.; Ibrahim, A.U.; Pratomo, U.; Rahimah, S.; Irkham; Hartati, Y.W. Advancements in synthesis of Molecularly Imprinted Polymer (MIPs) for highly selective alcohol sensors. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2025, 47, 100729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapacz, D.; Smolińska-Kempisty, K.; Wolska, J. A novel green molecularly imprinted polymers synthesized in an aqueous medium as S-metolachlor sensitive materials. Talanta 2024, 280, 126674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yao, X. Preparation of molecularly imprinted polymer for vanillin via seed swelling and suspension polymerization. Polym. Sci. Ser. B 2014, 56, 538–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, H.; Park, J.K. The preparation of D-phenylalanine imprinted microbeads by a novel method of modified suspension polymerization. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2006, 11, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, K. Synthesizing Vitamin E Molecularly Imprinted Polymers via Precipitation Polymerization. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2019, 64, 1045–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renkecz, T.; Horvath, V. Preparation of Molecularly Imprinted Microspheres by Precipitation Polymerization. In Synthetic Antibodies; Tiller, E.T., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2017; Volume 1575, pp. 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalogiouri, N.P.; Tsalbouris, A.; Kabir, A.; Furton, K.G.; Samanidou, V.F. Synthesis and application of molecularly imprinted polymers using sol–gel matrix imprinting technology for the efficient solid-phase extraction of BPA from water. Microchem. J. 2020, 157, 104965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kia, S.; Fazilati, M.; Salavati, H.; Bohlooli, S. Preparation of a novel molecularly imprinted polymer by the sol–gel process for solid phase extraction of vitamin D3. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 31906–31914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zidarič, T.; Majer, D.; Maver, T.; Finšgar, M.; Maver, U. The development of an electropolymerized, molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP) sensor for insulin determination using single-drop analysis. Analyst 2023, 148, 1102–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwanza, C.; Zhang, W.-Z.; Mulenga, K.; Ding, S.-N. Advancing green chemistry in environmental monitoring: The role of electropolymerized molecularly imprinted polymer-based electrochemical sensors. Green Chem. 2024, 26, 11490–11517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilvenyte, G.; Ratautaite, V.; Boguzaite, R.; Ramanavicius, S.; Chen, C.-F.; Viter, R.; Ramanavicius, A. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Electrochemical Sensors for the Diagnosis of Infectious Diseases. Biosensors 2023, 13, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Xia, L.; Li, G. Recent Progress of Molecularly Imprinted Optical Sensors. Chemosensors 2023, 11, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Jia, M.; Zhao, H.; Kang, L.; Shi, L.; Zhou, L.; Kong, W. Molecularly imprinted polymer-based optical sensors for pesticides in foods: Recent advances and future trends. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 116, 387–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Poma, A. Advances in Molecularly Imprinted Polymers as Drug Delivery Systems. Molecules 2021, 26, 3589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djunaidi, M.C.; Putri, V.R.; Maharani, N.D.; Lusiana, R.A.; Siahaan, P.; Sunarno, S. Precipitation Polymerization-Based Molecularly Imprinted Polymers: A Novel Approach for Transdermal Curcumin Delivery. Polymers 2024, 16, 3456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonatti, A.F.; De Maria, C.; Vozzi, G. Molecular Imprinting Strategies for Tissue Engineering Applications: A Review. Polymers 2021, 13, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, Y.L.; Keirouz, A.; Leese, H.S. Molecularly imprinted polymers in diagnostics: Accessing analytes in biofluids. J. Mater. Chem. B 2022, 10, 7418–7449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köse, K.; Kehribar, D.Y.; Uzun, L. Molecularly imprinted polymers in toxicology: A literature survey for the last 5 years. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 35437–35471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razavipanah, I.; Alipour, E.; Deiminiat, B.; Rounaghi, G.H. A novel electrochemical imprinted sensor for ultrasensitive detection of the new psychoactive substance “Mephedrone”. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 119, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, G.J.; Singh, R.K.; Foroutan, F.; Alqaysi, M.; Han, C.-M.; Mahapatra, C.; Kim, H.-W.; Knowles, J.C. Sol–gel based materials for biomedical applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2016, 77, 1–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Jiang, D.; Xu, C.; Ge, Y.; Liu, X.; Wei, Q.; Huang, L.; Ren, X.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y. Wearable electrochemical biosensor based on molecularly imprinted Ag nanowires for noninvasive monitoring lactate in human sweat. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 320, 128325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugo, S.M.; Lu, W.; Robertson, S. A Wearable, Textile-Based Polyacrylate Imprinted Electrochemical Sensor for Cortisol Detection in Sweat. Biosensors 2022, 12, 854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira Gonçalves, L. Electropolymerized molecularly imprinted polymers: Perceptions based on recent literature for soon-to-be world-class scientists. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2021, 25, 100640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldara, M.; Van Wissen, G.; Cleij, T.J.; Diliën, H.; Van Grinsven, B.; Eersels, K.; Lowdon, J.W. Deposition Methods for the Integration of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers (MIPs) in Sensor Applications. Adv. Sens. Res. 2023, 2, 2200059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayankojo, A.G.; Reut, J.; Syritski, V. Electrochemically Synthesized MIP Sensors: Applications in Healthcare Diagnostics. Biosensors 2024, 14, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulanicki, A.; Glab, S.; Ingman, F. Chemical sensors: Definitions and classification. Pure Appl. Chem. 1991, 63, 1247–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willner, M.R.; Vikesland, P.J. Nanomaterial enabled sensors for environmental contaminants. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, C.; Li, H.; Zhou, S.; Li, G.; Wang, C.; Snyders, R.; Bittencourt, C.; Li, W. Bi2S3/rGO Composite Based Electrochemical Sensor for Ascorbic Acid Detection. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanniarachchi, P.C.; Upul Kumarasinghe, K.G.; Jayathilake, C. Recent advancements in chemosensors for the detection of food spoilage. Food Chem. 2024, 436, 137733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustafa, F.; Andreescu, S. Chemical and Biological Sensors for Food-Quality Monitoring and Smart Packaging. Foods 2018, 7, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, A.; Salunke-Gawali, S. Overview of the chemosensor ligands used for selective detection of anions and metal ions (Zn2+, Cu2+, Ni2+, Co2+, Fe2+, Hg2+). Inorganica Chim. Acta 2018, 482, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrucci, R.; Pasquali, M.; Scaramuzzo, F.A.; Curulli, A. Recent Advances in Electrochemical Chitosan-Based Chemosensors and Biosensors: Applications in Food Safety. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabri, N.; Aljunid, S.A.; Salim, M.S.; Ahmad, R.B.; Kamaruddin, R. Toward Optical Sensors: Review and Applications. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2013, 423, 012064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anas, N.A.A.; Fen, Y.W.; Omar, N.A.S.; Daniyal, W.M.E.M.M.; Ramdzan, N.S.M.; Saleviter, S. Development of Graphene Quantum Dots-Based Optical Sensor for Toxic Metal Ion Detection. Sensors 2019, 19, 3850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.-Q.; Ge, L. Colorimetric Sensors: Methods and Applications. Sensors 2023, 23, 9887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, G.; Zanoni, C.; Magnaghi, L.R.; Biesuz, R. Disposable and Low-Cost Colorimetric Sensors for Environmental Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 8331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umapathi, R.; Sonwal, S.; Lee, M.J.; Mohana Rani, G.; Lee, E.-S.; Jeon, T.-J.; Kang, S.-M.; Oh, M.-H.; Huh, Y.S. Colorimetric based on-site sensing strategies for the rapid detection of pesticides in agricultural foods: New horizons, perspectives, and challenges. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 446, 214061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alawsi, T.; Mattia, G.P.; Al-Bawi, Z.; Beraldi, R. Smartphone-based colorimetric sensor application for measuring biochemical material concentration. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2021, 32, 100404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciaccheri, L.; Adinolfi, B.; Mencaglia, A.A.; Mignani, A.G. Smartphone-Enabled Colorimetry. Sensors 2023, 23, 5559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Li, J.; Guo, Y.; Xie, L.; Zhang, G. Digital image colorimetry on smartphone for chemical analysis: A review. Measurement 2021, 171, 108829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masawat, P.; Harfield, A.; Namwong, A. An iPhone-based digital image colorimeter for detecting tetracycline in milk. Food Chem. 2015, 184, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horta-Velázquez, A.; Ramos-Ortiz, G.; Morales-Narváez, E. The optimal color space enables advantageous smartphone-based colorimetric sensing. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2025, 273, 117089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantrell, K.; Erenas, M.M.; de Orbe-Payá, I.; Capitán-Vallvey, L.F. Use of the hue parameter of the hue, saturation, value color space as a quantitative analytical parameter for bitonal optical sensors. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 531–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Aviño, A.; de Diego-Llorente-Luque, M.; Molins-Legua, C.; Campíns-Falcó, P. Advances in the Measurement of Polymeric Colorimetric Sensors Using Portable Instrumentation: Testing the Light Influence. Polymers 2022, 14, 4285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elagamy, S.H.; Adly, L.; Abdel Hamid, M.A. Smartphone based colorimetric approach for quantitative determination of uric acid using Image J. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 21888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhou, R.; Zhang, H.; Cai, D.; Lin, X.; Lang, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Shentu, X.; Ye, Z.; Yu, X. A Smartphone Colorimetric Sensor Based on Pt@Au Nanozyme for Visual and Quantitative Detection of Omethoate. Foods 2022, 11, 2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Mao, K.; Cao, H.; Feng, R.; Chen, Z.; Du, W.; Zhang, H. Portable sensors equipped with smartphones for organophosphorus pesticides detection. Food Chem. 2024, 434, 137456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Xue, B.; Lin, Y.; Wu, X.; Fang, F.; Qi, P.; Guo, J.; Zhou, X. A cellphone-based colorimetric multi-channel sensor for water environmental monitoring. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2022, 16, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Guo, Y.; Yue, Y.; Zhang, J.; Fan, L.; Li, F.; Zhao, Y.; Dong, C.; Shuang, S. Smartphone-assisted colorimetric sensing platform based on molybdenum-doped carbon dots nanozyme for visual monitoring of ampicillin. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 468, 143615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Zhan, X.; Zheng, J.; Xie, Z.; Zhu, S.; Wu, Y. Facile colorimetric smartphone-based biosensor for rapid detection of organophosphorus pesticides residues in environment using the aptamer-enhanced oxidase activity of octahedral Ag2O particles. Anal. Chim. Acta 2023, 1264, 341325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, M.-Y.; Wu, Q.-S.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Guan, Y.-F.; Feng, L. The calibration of cellphone camera-based colorimetric sensor array and its application in the determination of glucose in urine. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 74, 1029–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, C.-K.; Shaban, S.M.; Moon, B.-S.; Pyun, D.-G.; Kim, D.-H. Smartphone-assisted point-of-care colorimetric biosensor for the detection of urea via pH-mediated AgNPs growth. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1170, 338630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Lu, Y.; Yang, J.; Chen, Y.; Jing, W.; He, L.; Liu, Y. A smartphone readable colorimetric sensing platform for rapid multiple protein detection. Analyst 2017, 142, 3177–3182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Ruiz, N.; Curto, V.F.; Erenas, M.M.; Benito-Lopez, F.; Diamond, D.; Palma, A.J.; Capitan-Vallvey, L.F. Smartphone-Based Simultaneous pH and Nitrite Colorimetric Determination for Paper Microfluidic Devices. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 9554–9562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solmaz, M.E.; Mutlu, A.Y.; Alankus, G.; Kılıç, V.; Bayram, A.; Horzum, N. Quantifying colorimetric tests using a smartphone app based on machine learning classifiers. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 255, 1967–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ren, X.; Li, X. Smartphone-assisted colorimetry and array test strip integrated platform for urine multi-index simultaneous precise quantification and personalized healthcare monitoring. Microchem. J. 2025, 208, 112329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yetisen, A.K.; Martinez-Hurtado, J.L.; Garcia-Melendrez, A.; Da Cruz Vasconcellos, F.; Lowe, C.R. A smartphone algorithm with inter-phone repeatability for the analysis of colorimetric tests. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 196, 156–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, R.O.; Othman, H.O.; Ali, D.S. New spectrophotometric and smartphone-based colorimetric methods for determination of atenolol in pharmaceutical formulations. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2023, 302, 123009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helfer, G.A.; Magnus, V.S.; Böck, F.C.; Teichmann, A.; Ferrão, M.F.; Costa, A.B.D. PhotoMetrix: An Application for Univariate Calibration and Principal Components Analysis Using Colorimetry on Mobile Devices. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2016, 28, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Li, M.; Wang, L.; Wang, M. A Colorimetric Sensor Enabled with Heterogeneous Nanozymes with Phosphatase-like Activity for the Residue Analysis of Methyl Parathion. Foods 2023, 12, 2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Y.; O’Hagan, M.P.; Willner, I. Functional catalytic nanoparticles (nanozymes) for sensing. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 218, 114768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Shao, N.; Zhang, A.-C.; Chen, C.-F.; Wang, D.; Luo, L.-P.; Xiao, Z.-Y. Smart Biomimetic Nanozymes for Precise Molecular Imaging: Application and Challenges. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, X.; Liu, B.; Hu, P.; Zhu, H.; Wang, M. Nanozymes with Multiple Activities: Prospects in Analytical Sensing. Biosensors 2022, 12, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Zhu, P.; Liu, S.; Chen, Y.; Liang, D.; Liu, Y.; Chen, W.; Du, L.; Wu, C. Application of Nanozymes in Environmental Monitoring, Management, and Protection. Biosensors 2023, 13, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attar, F.; Shahpar, M.G.; Rasti, B.; Sharifi, M.; Saboury, A.A.; Rezayat, S.M.; Falahati, M. Nanozymes with intrinsic peroxidase-like activities. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 278, 130–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demkiv, O.; Stasyuk, N.; Serkiz, R.; Gayda, G.; Nisnevitch, M.; Gonchar, M. Peroxidase-Like Metal-Based Nanozymes: Synthesis, Catalytic Properties, and Analytical Application. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Yao, T.; Ma, Z. Recent advances of peroxidase-active nanozymes in electrochemical immunoassays. Sens. Diagn. 2023, 2, 781–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Shao, Z.; Yan, S.; Lin, Y.; Liu, Y.; Feng, X.; Sha, J.; Ding, L.; Wang, K. Coencapsulating TMB Probes and Bimetallic MOF Nanozymes in a Hydrogel Patch for Fabricating Reusable Visual VC Sensors. Anal. Chem. 2024, 96, 17310–17318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishan, U.; Jabeen, N.; Badshah, A.; Muhammad, N.; Shah, M.; Ullah, I.; Afridi, S.; Iqbal, J.; Asad, M.; Ullah, R.; et al. Nanozyme-based sensing of dopamine using cobalt-doped hydroxyapatite nanocomposite from waste bones. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2024, 12, 1364700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Xue, Y.; Gao, Z.; Tang, K.; Wang, G.; Chen, Z.; Zuo, X. Antioxidant identification using a colorimetric sensor array based on Co-N-C nanozyme. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2021, 208, 112060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Tang, P.; Xing, X.; Cheng, W.; Liu, S.; Lu, X.; Zhong, L. Colorimetry/SERS dual-sensor of H2O2 constructed via TMB–Fe3O4@ AuNPs. Talanta 2022, 240, 123118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, Y.; Liu, Q.; Ge, C. Advances in oxidase-mimicking nanozymes: Classification, activity regulation and biomedical applications. Nano Today 2021, 37, 101076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S. Nanomaterials Exhibiting Enzyme-Like Properties (Nanozymes): Current Advances and Future Perspectives. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Chen, S.; Ye, F.; Su, L.; Zhang, C.; Shen, S.; Zhao, S. Synthesis of a mixed valence state Ce-MOF as an oxidase mimetic for the colorimetric detection of biothiols. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 4635–4638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.K.; Bijalwan, K.; Kaushal, N.; Kumari, A.; Saha, A.; Indra, A. Oxidase-like Nanozyme Activity of Manganese Metal–Organic Framework Nanosheets for Colorimetric and Fluorescence Sensing of L -Cysteine. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2023, 6, 8036–8045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Wu, L.; Yao, H.; Zhao, L. Catalase-Like Nanozymes: Classification, Catalytic Mechanisms, and Their Applications. Small 2022, 18, 2203400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, B.; Li, K.; Lin, Y. Superoxide dismutase nanozymes: Current status and future perspectives on brain disease treatment and diagnosis. Chem. Commun. 2024, 60, 4140–4147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhang, A.; Wang, R.; Zhang, Q.; Cui, D. A Review on Metal- and Metal Oxide-Based Nanozymes: Properties, Mechanisms, and Applications. Nano-Micro Lett. 2021, 13, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, L.; Cai, R.; Liu, J.; Wu, X. A Novel Nanoprobe Based on Core–Shell Au@Pt@Mesoporous SiO2 Nanozyme With Enhanced Activity and Stability for Mumps Virus Diagnosis. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Duan, D.; Gao, L.; Zhou, M.; Fan, K.; Tang, Y.; Xi, J.; Bi, Y.; Tong, Z.; Gao, G.F.; et al. Standardized assays for determining the catalytic activity and kinetics of peroxidase-like nanozymes. Nat. Protoc. 2018, 13, 1506–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Chen, Q.; Ren, Q.; Zhong, W.; Zhang, H.; Wang, G.; Zhang, Y. Transition metal-based nanozymes: Classification, catalytic mechanisms and emerging biomedical applications. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2024, 508, 215771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmir, M.; Shemirani, F. Gold nanoparticles coated with PVP as a novel colorimetric sensor for sensitive and selective determination of Atenolol. Heliyon 2023, 9, e22675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, Y. A simple and rapid chemosensor for colorimetric detection of dimethoate pesticide based on the peroxidase-mimicking catalytic activity of gold nanoparticles. Anal. Methods 2019, 11, 5337–5347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girgin, A.; Akbıyık, H.; Zaman, B.T.; Çetin, G.; Bakırdere, S. Colorimetric Sensor Based AgNPs for the Detection of Cyanide using UV-Vis Spectrophotometry. ChemistrySelect 2023, 8, e202301663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Huang, Z.; Sun, Y.; Xu, Z.; Liu, J. The Most Active Oxidase-Mimicking Mn2O3 Nanozyme for Biosensor Signal Generation. Chem.–A Eur. J. 2021, 27, 9597–9604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.; Duan, D.; Sun, L.; Li, J.; Wang, M.; Chang, Z.; Thorne, R.F.; Chen, C.; Duan, D. High-sensitivity colorimetric sensor based on oxidase-like Mn3O4 nanozyme for Cys detection. Sens. Actuators Rep. 2025, 9, 100296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Xu, B.; Pan, X.; Wang, H.; Wu, Q.; Li, S.; Jiang, B.; Liu, H. Carbon-based nanozymes: Design, catalytic mechanism, and bioapplication. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2023, 475, 214896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, L.; Li, S.; Jiang, L.; Bu, L.; Dong, G.; Song, D.; Liao, J.; Tang, G.; Zhou, Q. A colorimetric sensor based on multiple elements doped carbon dot nanozyme for rapid detection of 1-naphthol in human urine samples. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2025, 678, 266–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Wang, C.; You, L.; Fu, F.; Liu, Q. Nanozyme colorimetric sensing of L-cysteine and copper ions based on PtCo nanoparticles@multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Anal. Sci. 2023, 39, 1669–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Kaur, N.; Singh, N. Colorimetric Nanozyme Sensor Array Based on Metal Nanoparticle-Decorated CNTs for Quantification of Pesticides in Real Water and Soil Samples. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 728–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Liu, S.; Hu, Y. Recent Advances in Nanozyme Sensors Based on Metal–Organic Frameworks and Covalent–Organic Frameworks. Biosensors 2024, 14, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Li, Y.; Qi, S.; Chen, Y.; Yin, M.; Zhang, L.; Tian, X.; Gong, S.; Wang, F.; Zhu, Y.; et al. Ce-MOF Nanosphere as Colorimetric Sensor with High Oxidase Mimicking Activity for Sensitive Detection of H2O2. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2022, 32, 3595–3600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wu, H.; Chen, J.; Su, Y.; Lin, P.; Xiao, W.; Cao, D. Highly Sensitive Colorimetric Detection of Glutathione in Human Serum Based on Iron–Copper Metal–Organic Frameworks. Langmuir 2022, 38, 15559–15569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Hu, Z.; Wu, S.; Pan, J.; Xu, X.; Niu, X. A peroxidase-mimicking Zr-based MOF colorimetric sensing array to quantify and discriminate phosphorylated proteins. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1121, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Y.; Cao, Z.; Zhao, M.; Xu, Y.; Lu, N. Single-Atom Fe Nanozyme with Enhanced Oxidase-like Activity for the Colorimetric Detection of Ascorbic Acid and Glutathione. Biosensors 2023, 13, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Z. Advancements and Applications of Single-Atom Nanozymes in Sensing Analysis. Chemosensors 2024, 12, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Sharma, D.; Singh, D.K.; Sarraf, S.; Basu, A.K.; Ganesan, V.; Saha, A.; Indra, A. Oxidase-Like Nanozyme Activity of Ultrathin Copper Metal–Organic Framework Nanosheets With High Specificity for Catechol Oxidation. ChemCatChem 2025, 17, e202401029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, A.R.; Frasco, M.F.; Serrano, V.; Fortunato, E.; Sales, M.G.F. Molecular Imprinting on Nanozymes for Sensing Applications. Biosensors 2021, 11, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, J. Nanozyme’s catching up: Activity, specificity, reaction conditions and reaction types. Mater. Horiz. 2021, 8, 336–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Önal Acet, B.; İnanan, T.; Salieva, K.; Borkoev, B.; Odabaşı, M.; Acet, Ö. Molecular imprinted polymers: Important advances in biochemistry, biomedical and biotechnology. Polym. Bull. 2024, 81, 10439–10459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karrat, A.; Amine, A. Bioinspired synergy strategy based on the integration of nanozyme into a molecularly imprinted polymer for improved enzyme catalytic mimicry and selective biosensing. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2024, 266, 116723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, C.; Qu, L.; Yu, L. A novel molecularly imprinted sensor based on PtCu bimetallic nanoparticle deposited on PSS functionalized graphene with peroxidase-like activity for selective determination of puerarin. Talanta 2020, 210, 120621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Liu, B.; Liu, J. Molecular Imprinting on Inorganic Nanozymes for Hundred-fold Enzyme Specificity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 5412–5419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, J.; Du, M.; Wu, W.; Yang, J.; Chen, Q. Advances in the selection of functional monomers for molecularly imprinted polymers: A review. J. Sep. Sci. 2024, 47, 2400353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Aurelio, R.; Chianella, I.; Goode, J.A.; Tothill, I.E. Molecularly Imprinted Nanoparticles Based Sensor for Cocaine Detection. Biosensors 2020, 10, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Feng, W.; Liang, K.; Chen, C.; Cai, C. A novel fluorescence molecularly imprinted sensor for Japanese encephalitis virus detection based on metal organic frameworks and passivation-enhanced selectivity. Talanta 2020, 212, 120744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Akaad, S.; Mohamed, M.A.; Abdelwahab, N.S.; Abdelaleem, E.A.; De Saeger, S.; Beloglazova, N. Capacitive sensor based on molecularly imprinted polymers for detection of the insecticide imidacloprid in water. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Liu, S.; Sun, D.; Peng, S.; Ming, Y.; Ostovan, A.; Song, Z.; You, J.; Li, J.; Fan, H. Molecularly Imprinted Ratiometric Fluorescent Sensors for Analysis of Pharmaceuticals and Biomarkers. Sensors 2024, 24, 7068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.; Durairaj, S.; Prins, S.; Chen, A. Nanomaterial-based electrochemical sensors and biosensors for the detection of pharmaceutical compounds. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 175, 112836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Mao, S.; Chen, F.; Zhao, S.; Su, W.; Lai, G.; Yu, A.; Lin, C.-T. Graphene-based electrochemical sensors for antibiotic detection in water, food and soil: A scientometric analysis in CiteSpace (2011–2021). Chemosphere 2022, 297, 134127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frigoli, M.; Krupa, M.P.; Hooyberghs, G.; Lowdon, J.W.; Cleij, T.J.; Diliën, H.; Eersels, K.; Van Grinsven, B. Electrochemical Sensors for Antibiotic Detection: A Focused Review with a Brief Overview of Commercial Technologies. Sensors 2024, 24, 5576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, N.; Chen, J.; Rao, Z.; Guo, B.; Xu, Y. Recent Advances of Biosensors for Detection of Multiple Antibiotics. Biosensors 2023, 13, 850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamaoui, A.; Lahcen, A.A.; García-Guzmán, J.J.; Palacios-Santander, J.M.; Cubillana-Aguilera, L.; Amine, A. Study of solvent effect on the synthesis of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers based on ultrasound probe: Application for sulfonamide detection. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2019, 58, 104670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamaoui, A.; Karrat, A.; Amine, A. Molecularly imprinted polymer integrated into paper-based analytical device for smartphone-based detection: Application for sulfamethoxazole. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 368, 132122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowdon, J.W.; Diliën, H.; Van Grinsven, B.; Eersels, K.; Cleij, T.J. Colorimetric Sensing of Amoxicillin Facilitated by Molecularly Imprinted Polymers. Polymers 2021, 13, 2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Zhu, H.; Feng, R.; Wang, M.; Hu, P.; Pan, J.; Niu, X. Facile molecular imprinting on magnetic nanozyme surface for highly selective colorimetric detection of tetracycline. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 370, 132451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Zhu, H.; Liu, J.; Wang, M.; Pan, J.; Feng, R.; Hu, P.; Niu, X. Alkali-Etched Imprinted Mn-Based Prussian Blue Analogues with Superior Oxidase-Mimetic Activity and Precise Recognition for Tetracycline Colorimetric Sensing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 24736–24746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Xiao, L.; Ling, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhong, S. Mobile phone-assisted imprinted nanozyme for bicolor colorimetric visual detection of erythromycin in river water and milk samples. Food Chem. 2024, 449, 139291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugan, K.; Natarajan, A. A novel N -CNDs/PAni modified molecular imprinted polymer for ultraselective and sensitive detection of ciprofloxacin in lentic ecosystems: A dual responsive optical sensor. Anal. Methods 2024, 16, 3413–3429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, G.; Zhang, S.; Han, Z.; Yi, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, L. Construction of a sensor array using TiO2 NRs/CuO/rMIP with imprinted sites regulation as light-activated nanozyme to colorimetric detect fluoroquinolones. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2024, 419, 136373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Han, D.; Liang, Z.; Han, F.; Fu, W.; Wang, W.; Han, D.; Wang, Y.; Niu, L. Novel electrochemical-surface plasmon resonance (EC-SPR) sensor for amphetamine-type stimulants detection based on molecularly imprinted strategy. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 369, 132258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowdon, J.W.; Eersels, K.; Arreguin-Campos, R.; Caldara, M.; Heidt, B.; Rogosic, R.; Jimenez-Monroy, K.L.; Cleij, T.J.; Diliën, H.; Van Grinsven, B. A Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-based Dye Displacement Assay for the Rapid Visual Detection of Amphetamine in Urine. Molecules 2020, 25, 5222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhoundian, M.; Alizadeh, T. Enzyme-free colorimetric sensor based on molecularly imprinted polymer and ninhydrin for methamphetamine detection. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2023, 285, 121866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhoundian, M.; Alizadeh, T. An ultra-selective and non-enzymatic colorimetric sensor based on imprinted polymer for ephedrine assay in urine samples. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 39, 109193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowdon, J.W.; Eersels, K.; Rogosic, R.; Heidt, B.; Diliën, H.; Redeker, E.S.; Peeters, M.; Van Grinsven, B.; Cleij, T.J. Substrate displacement colorimetry for the detection of diarylethylamines. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 282, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Wang, B.; Wu, M.; Deng, B.; Xie, L.; Guo, Y. Rapidly colorimetric detection of caffeine in beverages by silver nanoparticle sensors coupled with magnetic molecularly imprinted polymeric microspheres. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Majumder, A.; Mandal, P.; Yadav, M.K. Analgesics in wastewater matrix: A comprehensive review on occurrence, toxicity, and sustainability assessment of biological, tertiary, and hybrid treatment processes. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2025, 23, 101039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.K. Advances in detecting non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) using molecular receptors and nanostructured assemblies. RSC Med. Chem. 2025, 16, 511–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, A.M.; Kelani, K.M.; Hegazy, M.A.; Nadim, A.H. Colorimetric approach based on iron oxide magnetic molecularly imprinted nanozyme for sensitive determination of antipyrine and benzocaine: Application to environmental water samples and pharmaceutical dosage form. Microchem. J. 2024, 207, 111790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Yin, X.; Wei, X.; Xu, R.; Wei, L.; Chen, Y.; Ding, L.; Song, D. A facile colorimetric sensor for ketoprofen detection in milk: Integrating molecularly imprinted polymers with Cu-doped Fe3O4 nanozymes. Food Chem. 2025, 463, 141207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasilewski, T.; Kamysz, W.; Gębicki, J. AI-Assisted Detection of Biomarkers by Sensors and Biosensors for Early Diagnosis and Monitoring. Biosensors 2024, 14, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attallah, O.A.; Al-Ghobashy, M.A.; Ayoub, A.T.; Tuszynski, J.A.; Nebsen, M. Computer-aided design of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles for solid-phase extraction and determination of levetiracetam in human plasma. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 14280–14292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, M.; Wang, Y.; Kan, X. Dual-recognition colorimetric sensing of thrombin based on surface-imprinted aptamer–Fe3O4. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 4249–4256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Peng, J.; Xi, L.; Lu, Z.; Yu, L.; Liu, M.; Huo, D.; He, H. Molecularly imprinted polymers enhanced peroxidase-like activity of AuNPs for determination of glutathione. Microchim. Acta 2022, 189, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Yan, L.; Zhou, X.; Qu, T. Highly selective colorimetric determination of glutathione based on sandwich-structured nanoenzymes composed of gold nanoparticle–coated molecular imprinted metal–organic frameworks. Microchim. Acta 2024, 191, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
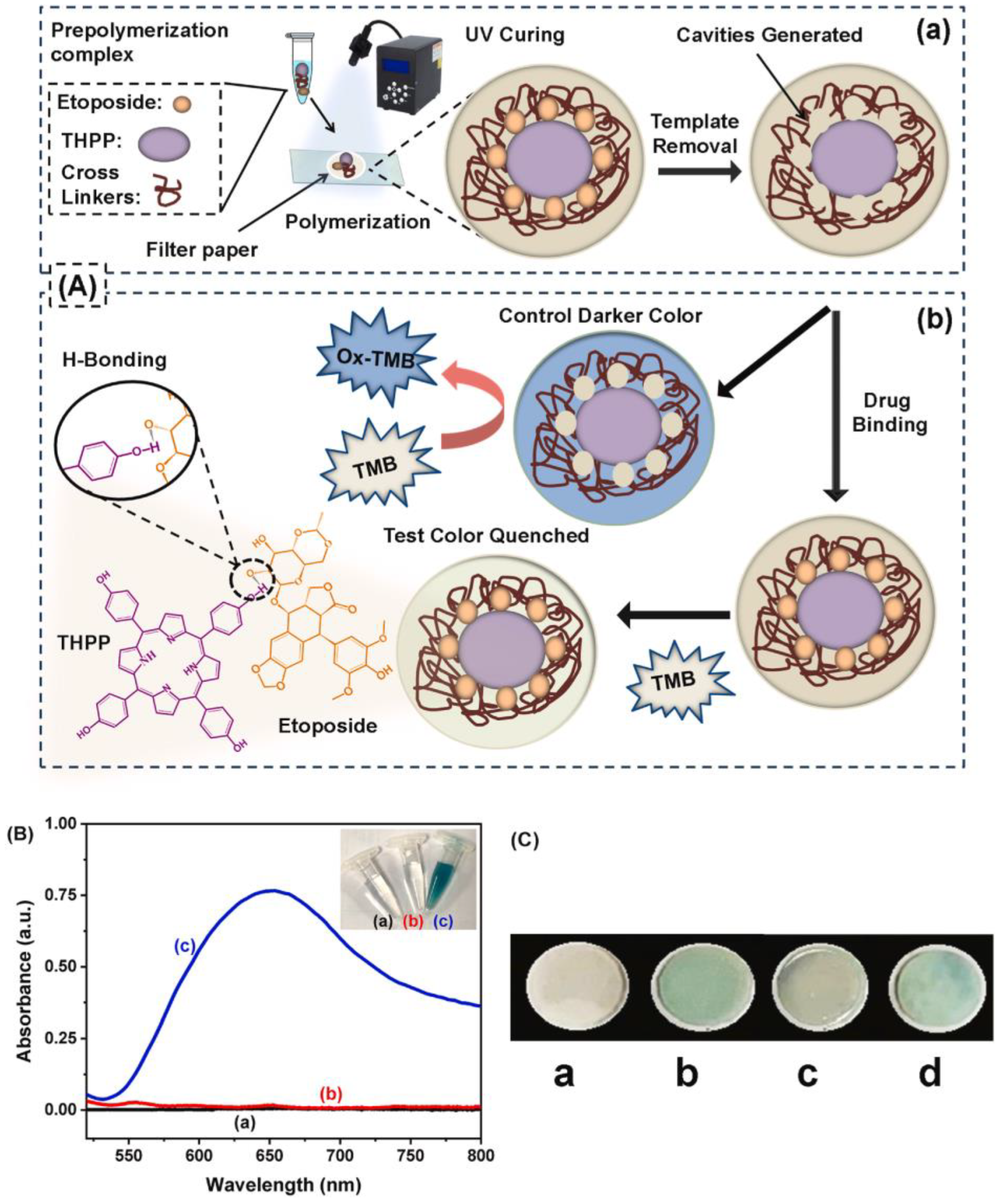
- Tariq, A.; Arif, A.; Akram, M.; Latif, U.; Nawaz, M.H.; Andreescu, S.; Zhang, H.; Hayat, A. Tailoring molecular recognition in predesigned multifunctional enzyme mimicking porphyrin imprinted interface for high affinity and differential selectivity; sensing etoposide in lung cancer patients. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2024, 245, 115833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehru, R.; Chen, C.-W.; Dong, C.-D. A review of smart electrochemical devices for pesticide detection in agricultural food and runoff contaminants. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 935, 173360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Abd El-Aty, A.M.; Eun, J.-B.; Shim, J.-H.; Zhao, J.; Lei, X.; Gao, S.; She, Y.; Jin, F.; Wang, J.; et al. Recent Advances in Rapid Detection Techniques for Pesticide Residue: A Review. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 13093–13117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Hu, Y.; Ma, L.; Lu, X. Development of molecularly imprinted polymers-surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy/colorimetric dual sensor for determination of chlorpyrifos in apple juice. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 241, 750–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, T.; Yin, W.; Zhu, N.; Yuan, M.; Cao, H.; Yu, J.; Gou, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhu, H.; Reyihanguli, A.; et al. Colorimetric detection of pyrethroid metabolite by using surface molecularly imprinted polymer. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 254, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Feng, S.; Hu, Y.; Wang, S.; Lu, X. Rapid determination of atrazine in apple juice using molecularly imprinted polymers coupled with gold nanoparticles-colorimetric/SERS dual chemosensor. Food Chem. 2019, 276, 366–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirzehni, M.; Hassanzadeh, J.; Vahid, B. Surface imprinted CoZn-bimetalic MOFs as selective colorimetric probe: Application for detection of dimethoate. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 325, 128768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
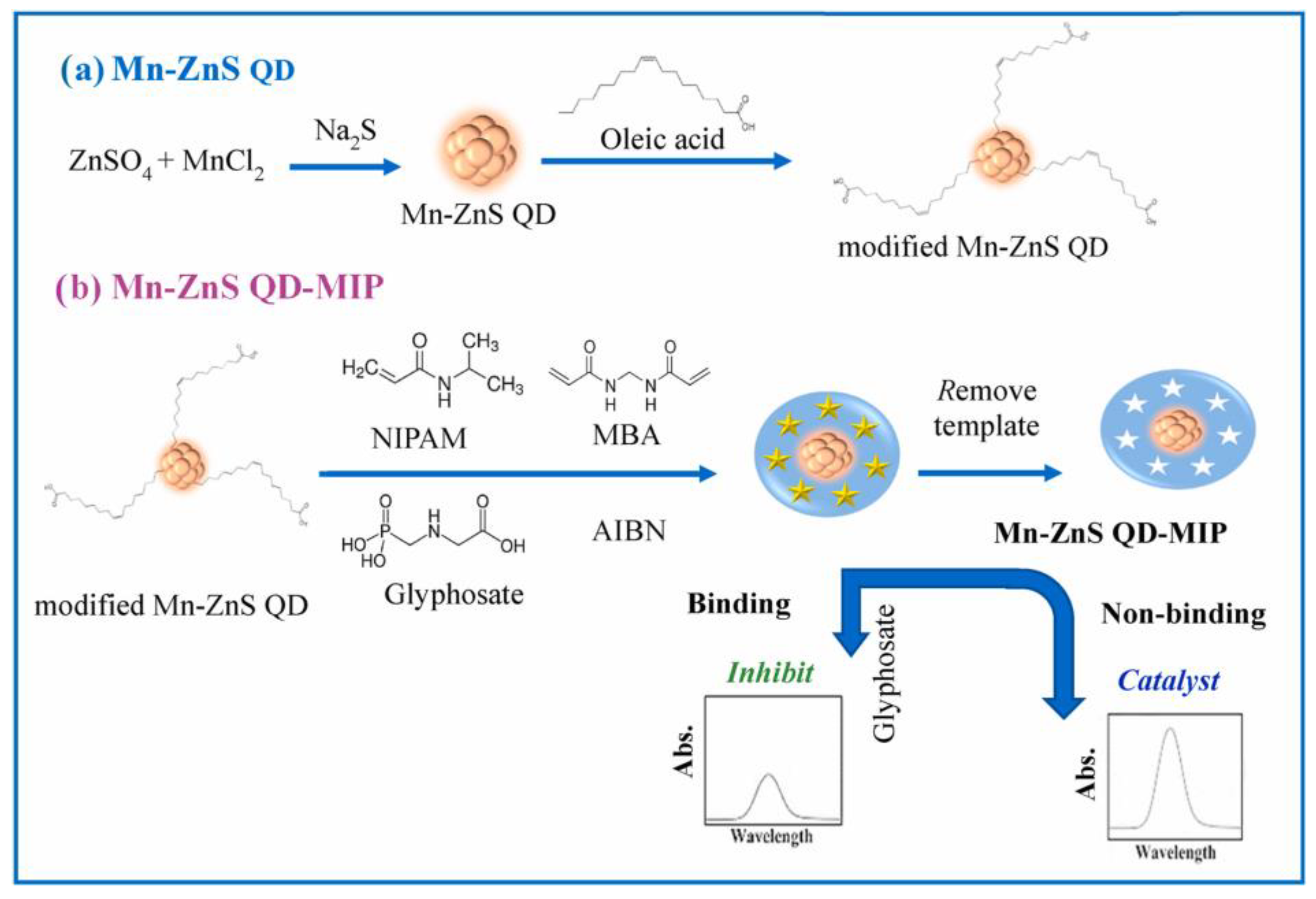
- Sawetwong, P.; Chairam, S.; Jarujamrus, P.; Amatatongchai, M. Enhanced selectivity and sensitivity for colorimetric determination of glyphosate using Mn–ZnS quantum dot embedded molecularly imprinted polymers combined with a 3D-microfluidic paper-based analytical device. Talanta 2021, 225, 122077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahdost-fard, F.; Fahimi-Kashani, N.; Hormozi-nezhad, M.R. A ratiometric fluorescence nanoprobe using CdTe QDs for fast detection of carbaryl insecticide in apple. Talanta 2021, 221, 121467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amatatongchai, M.; Thimoonnee, S.; Somnet, K.; Chairam, S.; Jarujamrus, P.; Nacapricha, D.; Lieberzeit, P.A. Origami 3D-microfluidic paper-based analytical device for detecting carbaryl using mesoporous silica-platinum nanoparticles with a molecularly imprinted polymer shell. Talanta 2023, 254, 124202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfadil, D.; Saidi, K.; Amine, A. Selective extraction of maleic hydrazide in foods using magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers and colorimetric detection via smartphone. Talanta 2024, 269, 125488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, D.; Zhao, N.; Wang, S.; Cui, Y.; Yan, H. Bimetallic metal-organic framework-based molecularly imprinted sensors for selective on-site detection of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid. Microchem. J. 2024, 205, 111318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zang, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, W.; Fang, Y.; Cui, B. Molecularly imprinted electrochemiluminescence-colorimetric dual-mode sensor based on Mn@NC nanozyme amplification for the detection of phoxim. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 500, 156817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alahi, M.; Mukhopadhyay, S. Detection Methodologies for Pathogen and Toxins: A Review. Sensors 2017, 17, 1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, J.; Qi, J.; Hu, D.; Wang, C.; Wang, L.; Wu, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Li, B.; et al. Molecularly imprinted metal-organic frameworks assisted cloth and paper hybrid microfluidic devices for visual detection of gonyautoxin. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 469, 133969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Xu, Y.; Cao, J.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, X.; Hu, X.; Song, X. A smartphone-enabled visual platform for detecting aflatoxins in peanut oil using colorimetric analysis coupled with magnetic imprinted solid-phase extraction. Food Chem. 2024, 456, 139294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damphathik, C.; Prakobkij, A.; Jarujamrus, P.; Boonmak, J.; Suebphanpho, J.; Bunkoed, O.; Samphao, A. Colorimetric sensor comprising metal-organic frameworks and molecularly imprinted polymers for aflatoxin B1 detection in agricultural commodities. Food Chem. 2025, 474, 143105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Li, Y.; Han, Y.; Liu, X.; Han, B.; Mao, H.; Chen, Q. A dual-mode optical sensor for sensitive detection of saxitoxin in shellfish based on three-in-one functional nanozymes. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2024, 130, 106190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, R.; Pyreddy, S.; Redmond, C.E.; Qazi, F.; Khalid, A.; O’Brien-Simpson, N.M.; Shukla, R.; Tomljenovic-Hanic, S. Detection and identification of amino acids and proteins using their intrinsic fluorescence in the visible light spectrum. Anal. Chim. Acta 2023, 1282, 341925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, N.P.; Kumar, M.S.; Vishnu, S.; Mukherjee, B.; Karthik, N.; Dutta, G.; Das, A.K. A fast survey on recent developments in designing colorimetric and fluorescent sensors for the selective detection of essential amino acids. Anal. Methods 2023, 15, 2546–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Huang, K.; Zhang, H.; Zeng, L.; Zhou, Y.; Jing, T. Preparation of molecularly imprinted polymers on hemin-graphene surface for recognition of high molecular weight protein. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 105, 110141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
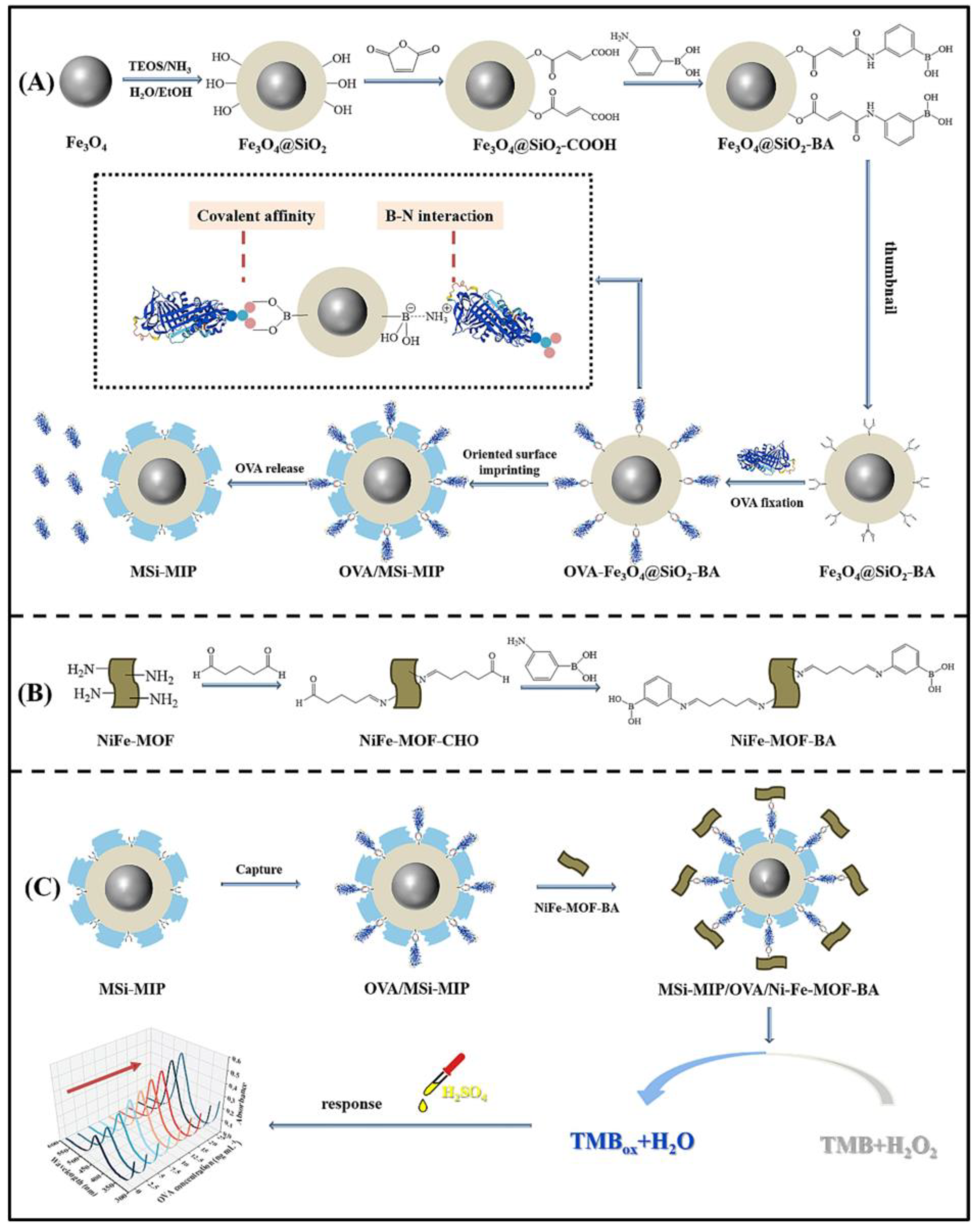
- Xu, Z.; Jin, D.; Lu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, W. Sandwich-type colorimetric assay based on molecularly imprinted polymers and boronic acid functionalized Ni-Fe-MOF nanozyme for sensitive detection of allergen ovalbumin. Microchem. J. 2023, 194, 109349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhoundian, M.; Khaki, M.; Alizadeh, T. Ultra-selective colorimetric sensor based on molecularly imprinted polymer for proline detection in food samples. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2025, 332, 125860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Liu, Y.; Gai, Z.; Yang, F.; Yang, Y. Highly specific colorimetric detection of sarcosine using surface molecular imprinted Zn/Ce-ZIF. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2025, 681, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessegato, G.G.; Brugnera, M.F.; Zanoni, M.V.B. Electroanalytical sensing of dyes and colorants. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2019, 16, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuşçuoğlu, C.K.; Güner, H.; Söylemez, M.A.; Güven, O.; Barsbay, M. A smartphone-based colorimetric PET sensor platform with molecular recognition via thermally initiated RAFT-mediated graft copolymerization. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 296, 126653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfadil, D.; Della Pelle, F.; Compagnone, D.; Amine, A. Green Synthesis of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Dispersive Magnetic Solid-Phase Extraction of Erythrosine B Associated with Smartphone Detection in Food Samples. Materials 2022, 15, 7653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imtiaz, T.; Shah, A.; Ullah, N.; Iftikhar, F.J.; Shah, I.; Shah, S.M.; Shah, S.S. Electrochemical nanosensor for ultrasensitive detection of malachite green and monitoring of its photocatalytic degradation. Npj Clean Water 2022, 5, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Aidy, H.; Amdeha, E. Green adsorbents based on polyacrylic acid-acrylamide grafted starch hydrogels: The new approach for enhanced adsorption of malachite green dye from aqueous solution. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2021, 101, 2796–2816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yang, Y.; Shen, Q.; Shen, D.; Kang, Q. A smartphone-based long optical path colorimetric turntable for selective determination of malachite green and investigation the specific adsorption behavior of the imprinted cavities within molecularly imprinted polymers. Microchem. J. 2023, 190, 108629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- State, R.G.; Van Staden, J.K.F.; State, R.N.; Papa, F. Rapid and sensitive electrochemical determination of tartrazine in commercial food samples using IL/AuTiO2/GO composite modified carbon paste electrode. Food Chem. 2022, 385, 132616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacinto, C.; Maza Mejía, I.; Khan, S.; López, R.; Sotomayor, M.D.P.T.; Picasso, G. Using a Smartphone-Based Colorimetric Device with Molecularly Imprinted Polymer for the Quantification of Tartrazine in Soda Drinks. Biosensors 2023, 13, 639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Wu, M.; Shi, M.; Shi, P.; Zhao, N.; Zhu, Y.; Karimi-Maleh, H.; Ye, C.; Lin, C.-T.; Fu, L. An Overview to Molecularly Imprinted Electrochemical Sensors for the Detection of Bisphenol A. Sensors 2023, 23, 8656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Chamoli, S.; Khondakar, K.R. Advances in optical and electrochemical sensing of bisphenol a (BPA) utilizing microfluidic Technology: A mini perspective. Methods 2023, 220, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
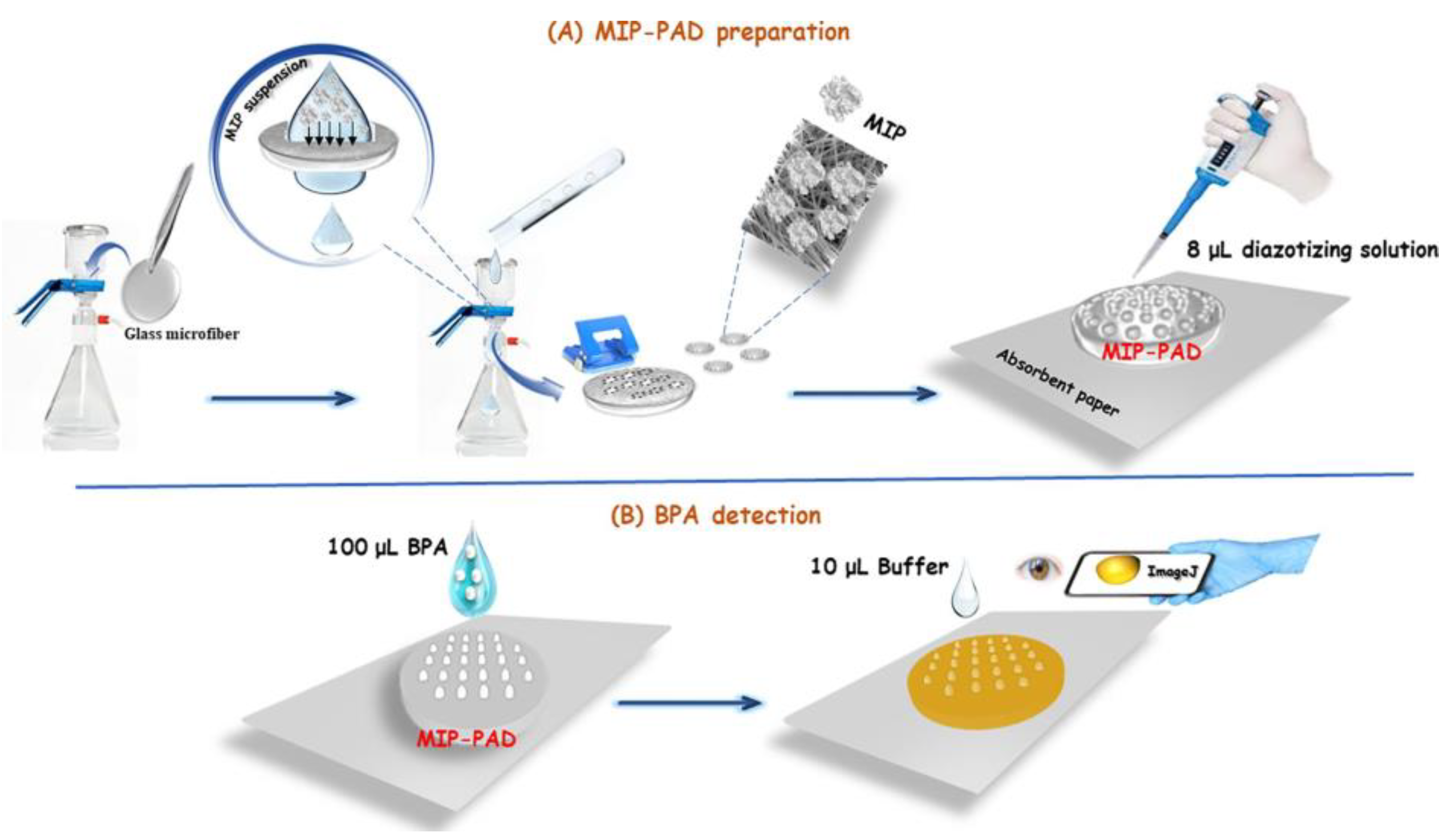
- Kong, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Ge, S.; Yu, J. A novel microfluidic paper-based colorimetric sensor based on molecularly imprinted polymer membranes for highly selective and sensitive detection of bisphenol A. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 243, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hani, O.; Karrat, A.; Digua, K.; Amine, A. Advanced molecularly imprinted polymer-based paper analytical device for selective and sensitive detection of Bisphenol-A in water samples. Microchem. J. 2023, 184, 108157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarynka, D.; Honcharenko, A.; Gorbach, L.; Piletska, E.; Piletsky, S.; Brovko, O.; Sergeyeva, T. Validation of a smartphone-compatible MIP-based sensor for bisphenol A determination in wastewater samples. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2024, 416, 7121–7129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elfadil, D.; Amine, A. Molecularly imprinted photopolymers combined with smartphone-based optical sensing for selective detection of bisphenol A in foods. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2024, 416, 2479–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, S.; Cui, F.; Zhuo, B.; Wang, S.; Zhao, C.; Liu, W. Sensitive and selective detection of puerarin based on the hybrid of reduced graphene oxide and molecularly imprinted polymer. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 185, 113221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Zhang, L.; Yu, Y.; Lin, B.; Wang, Y.; Guo, M.; Cao, Y. Dual-mode of electrochemical-colorimetric imprinted sensing strategy based on self-sacrifice beacon for diversified determination of cardiac troponin I in serum. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 167, 112502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, B.; Yakubu, S.; Zhu, Q.; Issaka, E.; Zhang, Y.; Adams, M. A Review on Tetrabromobisphenol A: Human Biomonitoring, Toxicity, Detection and Treatment in the Environment. Molecules 2023, 28, 2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Cui, H.; Chao, J.; Huang, K.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Jing, T. Colorimetric determination of tetrabromobisphenol A based on enzyme-mimicking activity and molecular recognition of metal-organic framework-based molecularly imprinted polymers. Microchim. Acta 2020, 187, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, L.; Beier, R.C.; Jin, Y.; Wang, W.; Li, H.; Hou, X. Antibacterial Activity and Membrane-Targeting Mechanism of Aloe-Emodin Against Staphylococcus epidermidis. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 621866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Kan, X. Imprinted polymer/Fe3O4 micro-particles decorated multi-layer graphite paper: Electrochemical and colorimetric dual-modal sensing interface for aloe-emodin assay. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 323, 128672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarannum, N.; Kumar, D.; Agrawal, R.; Verma, Y. Selectively Imprinted β-cyclodextrin Polymer for Colorimetric Assay of Lysophosphatidic Acid for Point of Care Detection of Ovarian Cancer. ChemistrySelect 2022, 7, e202202027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.Y. Enterovirus 71 infection and neurological complications. Korean J. Pediatr. 2016, 59, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Liang, K.; Wang, L.; Chen, C.; Cai, C.; Gong, H. Construction of an Ultrasensitive Molecularly Imprinted Virus Sensor Based on an “Explosive” Secondary Amplification Strategy for the Visual Detection of Viruses. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 13879–13888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaji, A.; Bathinapatla, A.; Manuel, M.; Mulpuri, R.K.; Kanchi, S. Recent developments in melamine detection: Applications of gold and silver nanostructures in colorimetric and fluorometric assays. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2025, 17, 100553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dikici, E.; Önal Acet, B.; Acet, Ö.; Odabaşı, M. “Lab-on-pol” colormatic sensor platforms: Melamine detection with color change on melamine imprinted membranes. Microchem. J. 2023, 188, 108468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.; Huang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Cui, L.; Li, A.; Xu, J.; Liu, J. Molecularly imprinted sensor based on cascade enzyme system supported by metal-organic framework (UiO-66-NH2) for sensitive colorimetric detection of cholesterol. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2024, 404, 135235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, X.; Liu, L.; Li, Z.; Yang, Q.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, W.; Wang, J. Highly specific and sensitive determination of propyl gallate in food by a novel fluorescence sensor. Food Chem. 2018, 256, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pashayi Sarnaghi, S.; Ayazi, Z. Synthesis of a molecularly imprinted polymer-based thin film as a smart sorbent for microextraction by packed syringe of n-propyl gallate in vegetable edible oils followed by its colorimetric detection applying a smartphone. Microchem. J. 2024, 203, 110772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nhiem, L.T.; Quy, C.H.Q.; Tuan, H.N.A.; Do, M.H.; Noh, J.-S.; Ta, Q.T.H. Micromolar-level glucose detection using a colorimetric sensor based on imprinted polymer-coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Microchem. J. 2025, 208, 112347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidya, A.; Sahoo, J.; Shende, P. Molecularly imprinted polymer-based biosensor for detection of salivary glucose in diabetes. Int. J. Pharm. 2025, 671, 125219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



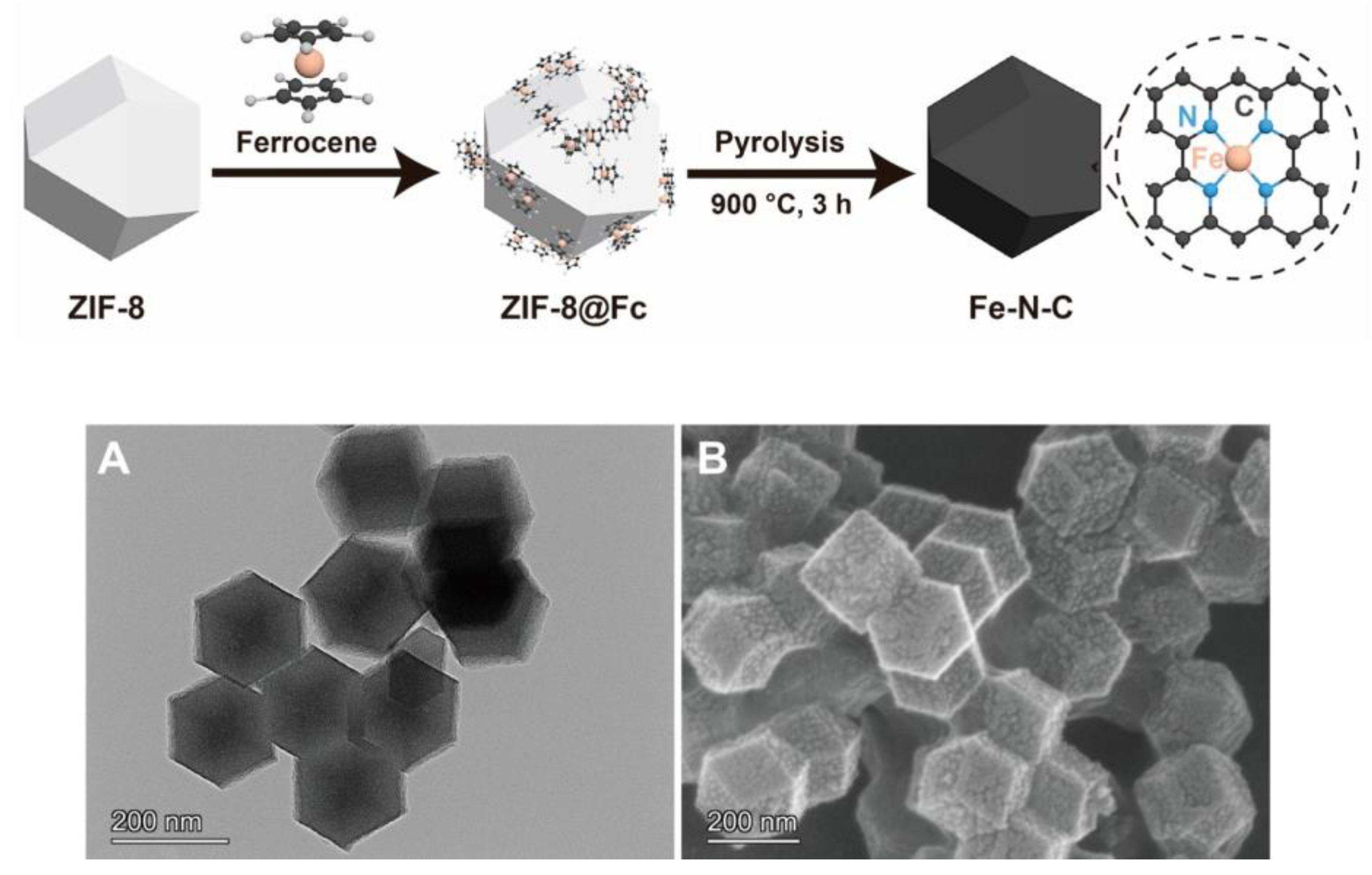

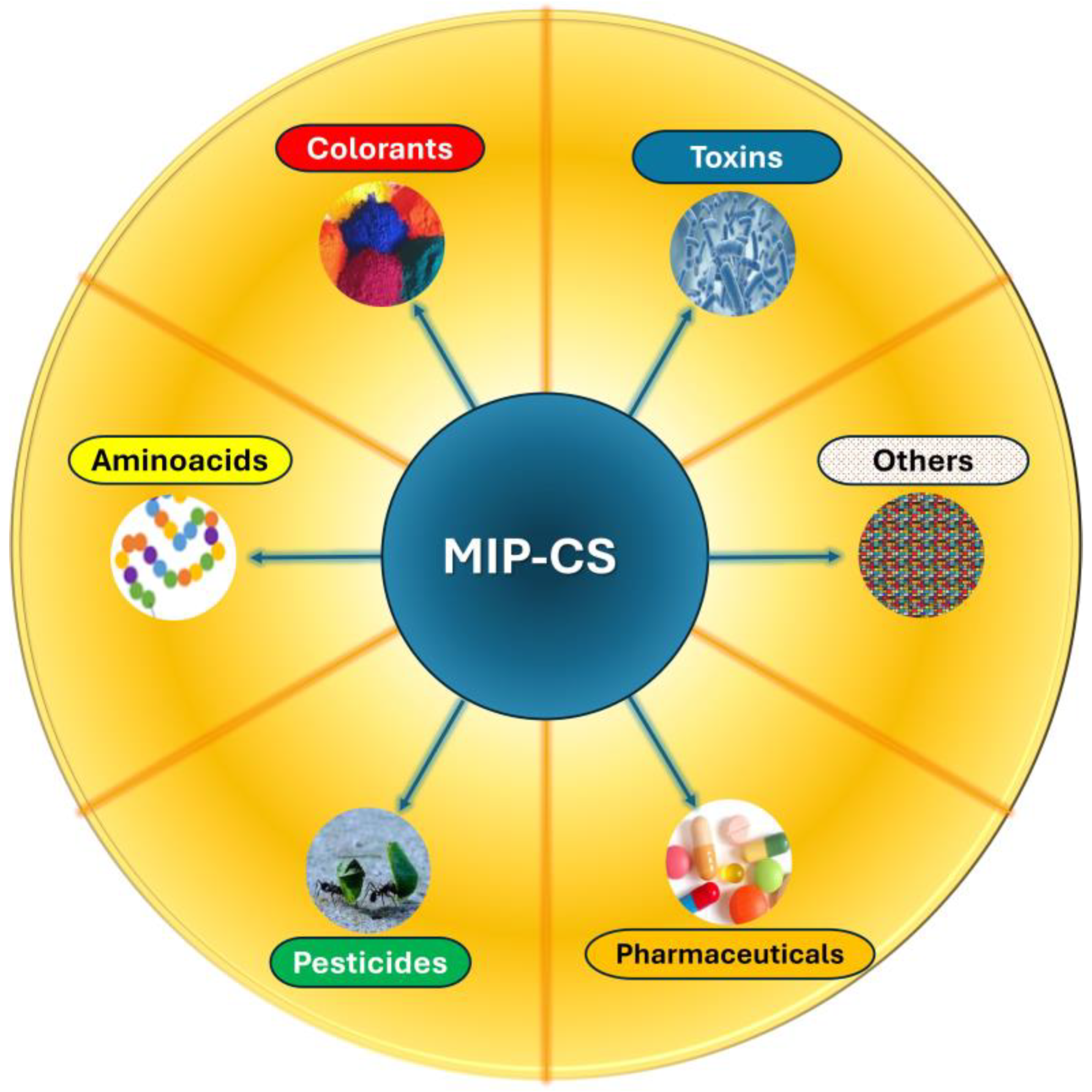
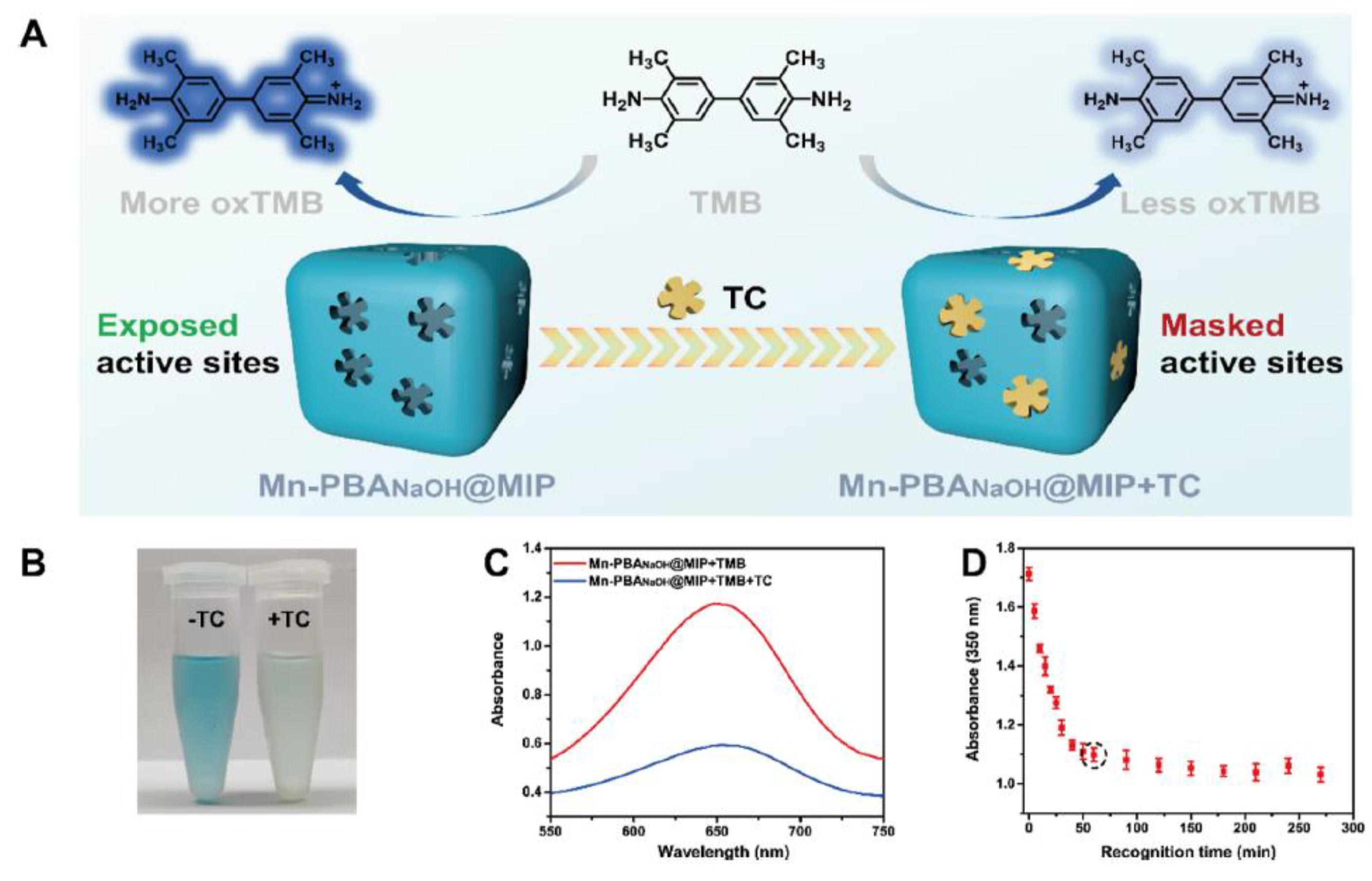
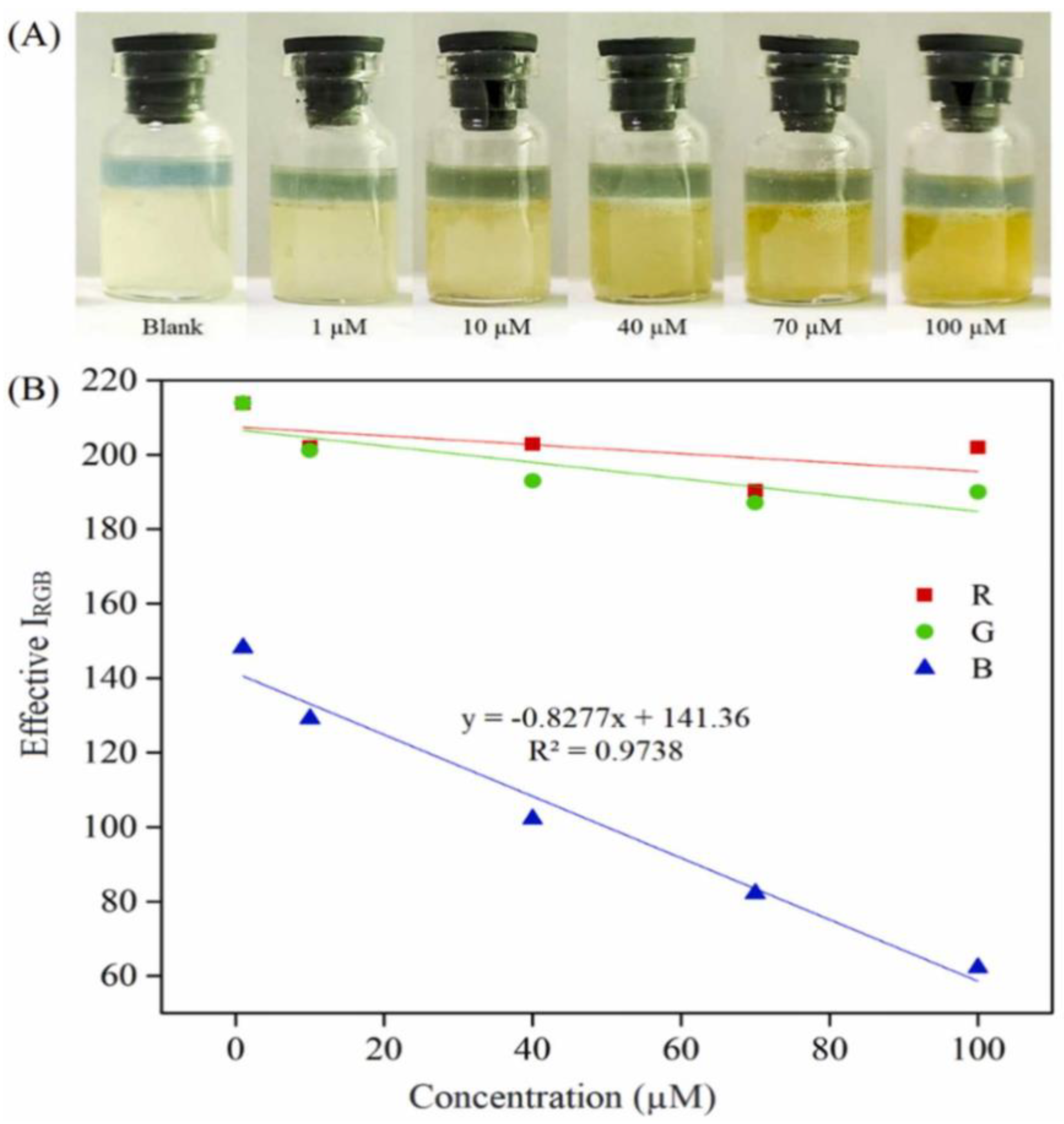

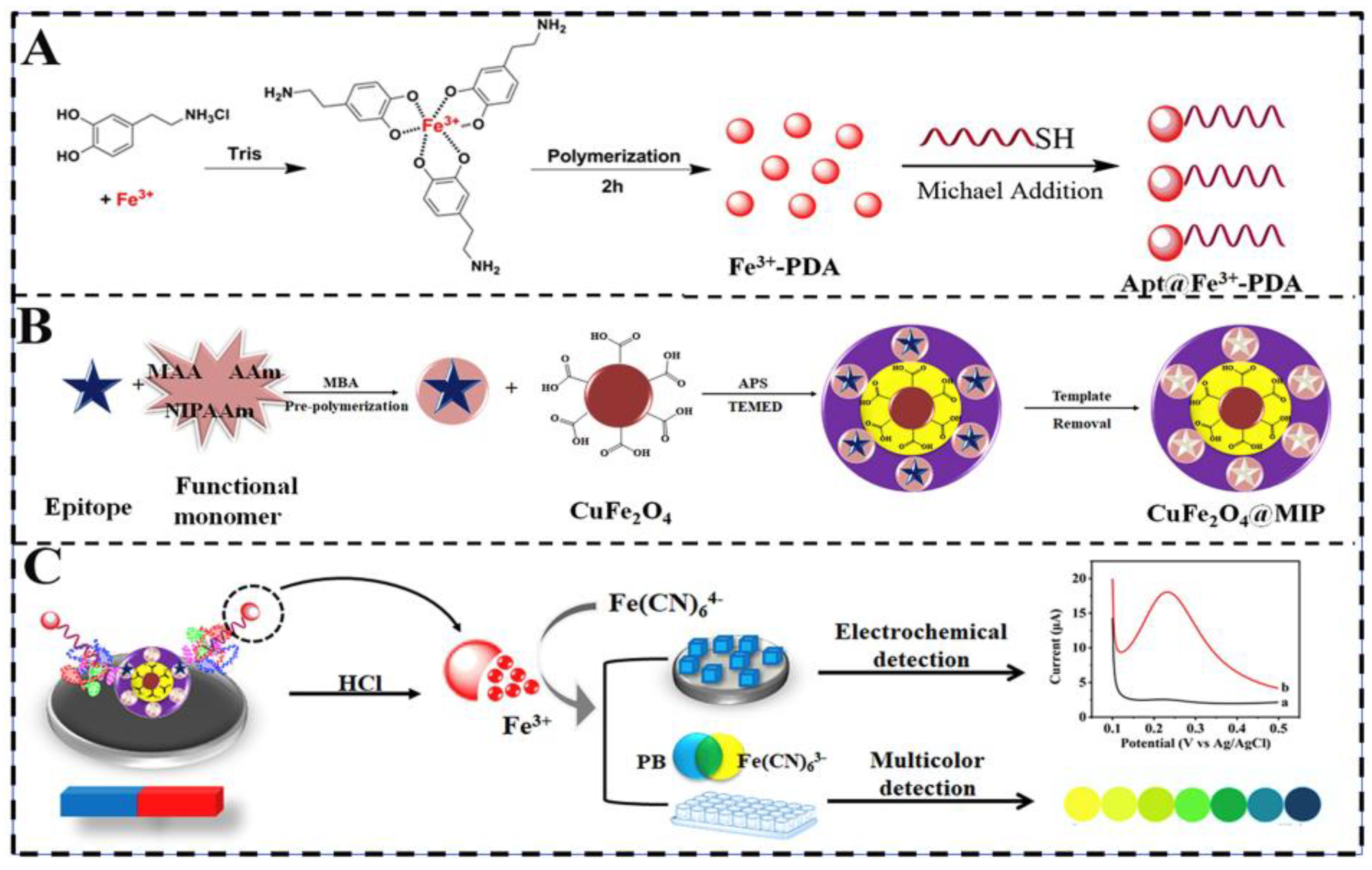
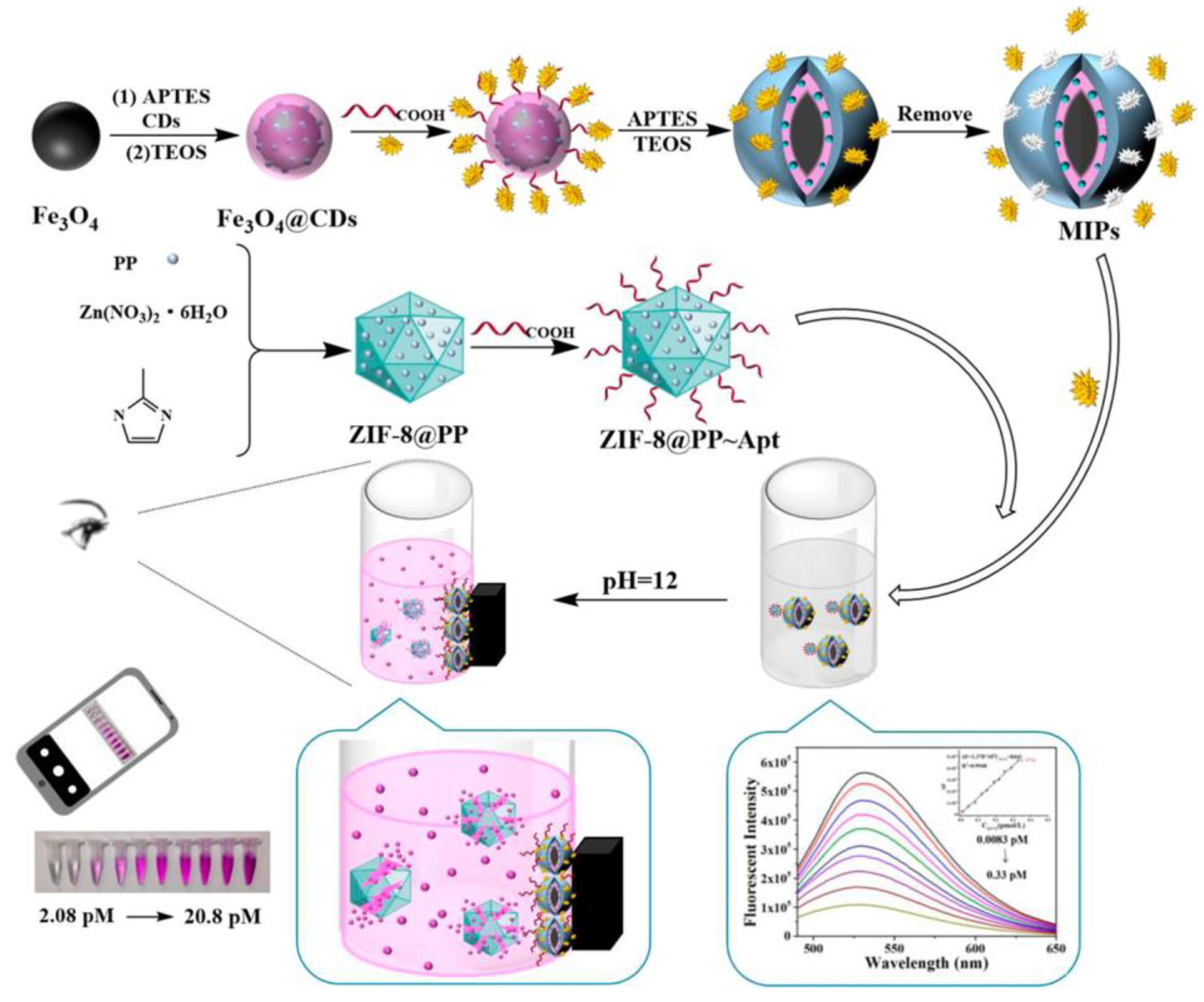
| Application | Analyte | Sample | LOD | Linear Range | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Environmental | Sulfamethoxazole | Water | 0.06 μg mL−1 | 0.2–5 μg mL−1 | [163] |
| Sulfamethoxazole | River and tap water | 0.17 μg mL−1 | 0.5–10 μg mL−1 | [164] | |
| Amoxicillin | Aqueous media | Qualitative | - | [165] | |
| Tetracycline | Water | 0.4 μM | 2–225 μM | [166] | |
| Tetracycline | Water | 0.07 μM | 0.2–200 μM | [167] | |
| Ciprofloxacin | Lentic and tap water | 3.5 nM | 0.038–200 nM | [169] | |
| Fluoroquinolones | Water | - | 0.1–3000 μM | [170] | |
| Healthcare | Amphetamine | Urine | 0.009 mg mL−1 | 0.01–0.20 mg mL−1 | [172] |
| Methamphetamine | Urine | 1.44 μM | 5–100 μM | [173] | |
| Ephedrine | Urine | 0.6 μM | 1–100 μM | [174] | |
| 2-methoxyphenidine | Powder mixtures | 0.015 mg mL−1 | - | [175] | |
| Antipyrine and Benzocaine | Ear drops | 1.405 ng mL−1 0.658 ng mL−1 | 5.0–60.0 ng mL−1 5.0–65.0 ng mL−1 | [179] | |
| Levetiracetam | Human plasma | 2.32 mg mL−1 | - | [182] | |
| Thrombin | Blood | 27.8 pmol L−1 | 108.1 pmol L−1–2.7 × 10−5 mol L−1 | [183] | |
| Glutathione | Serum | 1.16 μM | 5–40 μM | [184] | |
| Glutathione | Bovine serum | 0.231 μM | 1–50 μM | [185] | |
| Etoposide | Serum | 0.002 μg mL−1 | 0.005–10 μg mL−1 | [186] | |
| Foods | Erythromycin | Milk and river water | 4.27 μM | 15–135 μM | [168] |
| Caffeine | Beverages | - | 0.1–5 mg L−1 | [176] | |
| Ketoprofen | Milk | 0.073 μM | 0.25–100 μM | [180] |
| Application | Analyte | Sample | LOD | Linear Range | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Environmental | 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid | Water | 2.26 μM | 6–45 μM | [197] |
| Foods | Chlorpyrifos | Apple juice | 5 mg L−1 | - | [189] |
| 3-Phenoxybenzaldehyde | Fruit juice, beverages and river water | 0.052 μg mL−1 | 0.1 μg mL−1–1 μg mL−1 | [190] | |
| Atrazine | Apple juice | 0.01 mg L−1 | - | [191] | |
| Dimethoate | Fruit | 5.6 nM | 0.02–1.2 μM | [192] | |
| Glyphosate | Whole grain | 0.002 μg mL−1 | 0.005–50 μg mL−1 | [193] | |
| Carbaryl | Fruit | 1.5 ng g−1 | 0.002–20.00 mg kg−1 | [195] | |
| Maleic hydrazide | Potatoes and carrots | 0.6 ppm | - | [196] | |
| Phoxim | Fruit and vegetable | 1.27 ng mL−1 | 5–1000 ng mL−1 | [198] |
| Application | Analyte | Sample | LOD | Linear Range | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Environmental | Gonyautoxin | Shellfish and seawater | 0.65 μg L−1 | 1–200 μg L−1 | [200] |
| Foods | Aflatoxins | Peanut oil | 0.21 μg kg−1 | 0.5–57 μg kg−1 | [201] |
| Aflatoxin B1 | Peanut, chicken feed, and corn | 0.25 ng mL−1 | 0.5–5 ng mL−1 and 5–50 ng mL−1 | [202] | |
| Saxitoxin | Seafood | 3.1 nM | 0.01 μM–100 μM | [203] |
| Application | Analyte | Sample | LOD | Linear Range | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Healthcare | Thyroglobulin | Serum | 1 ng mL−1 | 5–100 ng mL−1 | [206] |
| Ovalbumin | Vaccine | 1.02 ng mL−1 | 2.5–25 ng mL−1 | [207] | |
| Sarcosine | Urine | 1.32 μM | 2 μM–500 μM | [208] | |
| Foods | Proline | Vegetable | 0.07 μM | 0.5–700 μM | [209] |
| Application | Analyte | Sample | LOD | Linear Range | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Environmental | Basic red 9 | Tap and industrial wastewater | 1.9 μM | 1.9–173 μM | [211] |
| Malachite green | Water | 1.1 μg L−1 | 0–60 μg L−1 | [215] | |
| Foods | Erythrosine B | Juice and candy | 0.04 mg L−1 | 0.5–10 mg L−1 | [212] |
| Tartrazine | Soda | 1.2 mg L−1 | 0–20 mg L−1 | [217] |
| Application | Analyte | Sample | LOD | Linear Range | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Environmental | Bisphenol A | - | 6.18 nM | 10 nM–1000 nM | [220] |
| Bisphenol A | Water | 0.03 μg mL−1 | 0.1 μg mL−1–5 μg mL−1 | [221] | |
| Bisphenol A | Wastewater | 5 μM | 5–250 μM | [222] | |
| Tetrabromobisphenol A | Dust | 3 pg g−1 | 0.01–10 ng g−1 | [227] | |
| Aloe-emodin | Cassia seed and aloe | 5.0 × 10−8 mol L−1–1.0 × 10−4 mol L−1 | 3.8 × 10−8 mol L−1 | [229] | |
| Healthcare | Puerarin | Plasma | 1 × 10−5 mol L−1 | 2 × 10−5–6 × 10−4 | [152] |
| Troponin I | Serum | 7.4 pg mL−1 | 1.0 × 10−2–1.0 × 103 ng mL−1 | [225] | |
| Lysophosphatidic acid | Serum | 0.078 μmol L−1 | - | [230] | |
| Enterovirus 71 | Serum | 2.08 pM | - | [232] | |
| Cholesterol | Blood | 5.18 mM | 2.9 mM–6.7 mM | [235] | |
| Glucose | Blood | 10 μM | 10 μM–0.01 M | [238] | |
| Glucose | Saliva | 0.9–3.9 mg dL−1 | 0.5–22 mg dL−1 | [239] | |
| Foods | Bisphenol A | Juice | 0.144 mg L−1 | 0.25–8 mg L−1 | [223] |
| Melamine | Milk | 9.9 μM | 10 μM–50 μM | [234] | |
| Propyl gallate | Sesame oil | 0.03 μg mL−1 | 0.1–1 μg mL−1 | [237] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bravo-Yagüe, J.C.; Paniagua-González, G.; Garcinuño, R.M.; García-Mayor, A.; Fernández-Hernando, P. Colorimetric Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Sensors for Rapid Detection of Organic Compounds: A Review. Chemosensors 2025, 13, 163. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13050163
Bravo-Yagüe JC, Paniagua-González G, Garcinuño RM, García-Mayor A, Fernández-Hernando P. Colorimetric Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Sensors for Rapid Detection of Organic Compounds: A Review. Chemosensors. 2025; 13(5):163. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13050163
Chicago/Turabian StyleBravo-Yagüe, Juan Carlos, Gema Paniagua-González, Rosa María Garcinuño, Asunción García-Mayor, and Pilar Fernández-Hernando. 2025. "Colorimetric Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Sensors for Rapid Detection of Organic Compounds: A Review" Chemosensors 13, no. 5: 163. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13050163
APA StyleBravo-Yagüe, J. C., Paniagua-González, G., Garcinuño, R. M., García-Mayor, A., & Fernández-Hernando, P. (2025). Colorimetric Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Sensors for Rapid Detection of Organic Compounds: A Review. Chemosensors, 13(5), 163. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13050163





