XPS Study of Nanostructured Pt Catalytic Layer Surface of Gas Sensor Dubbed GMOS
Abstract
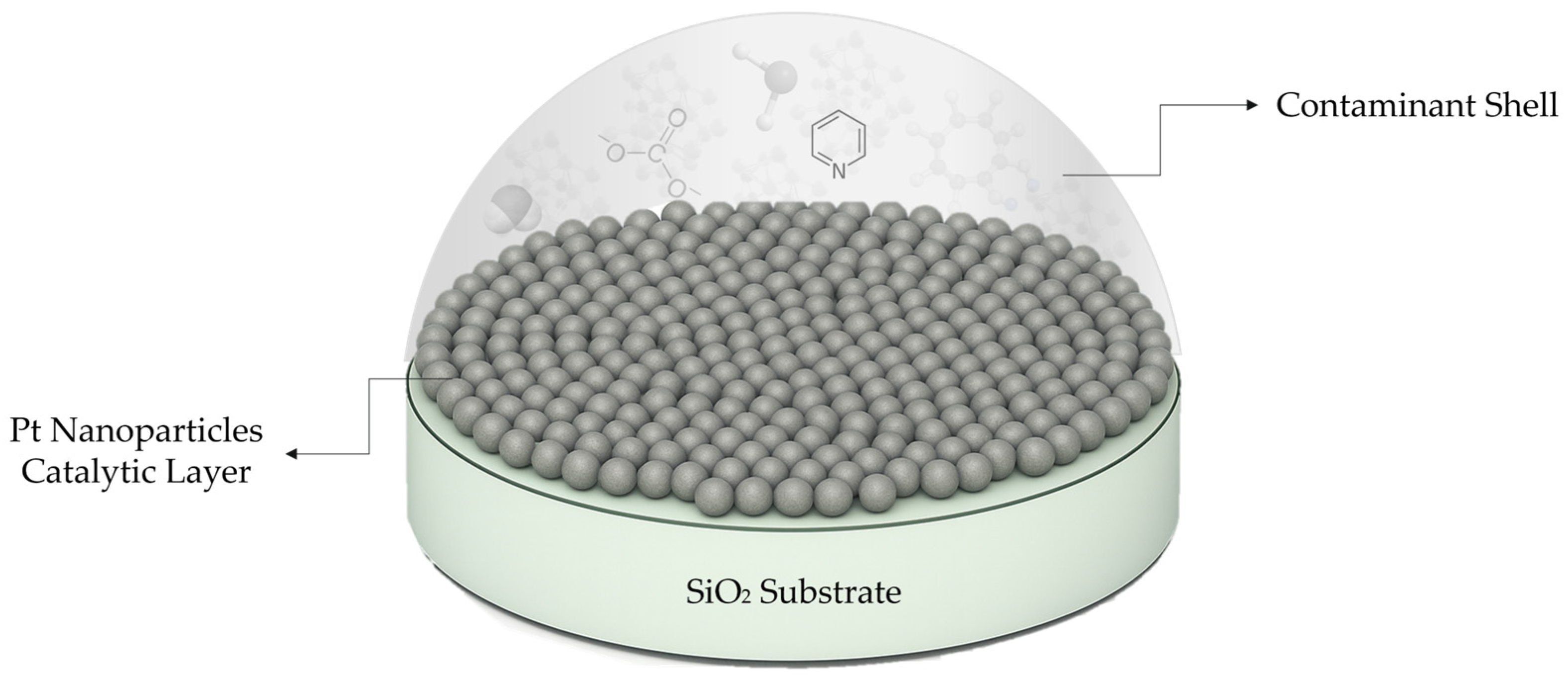
1. Introduction
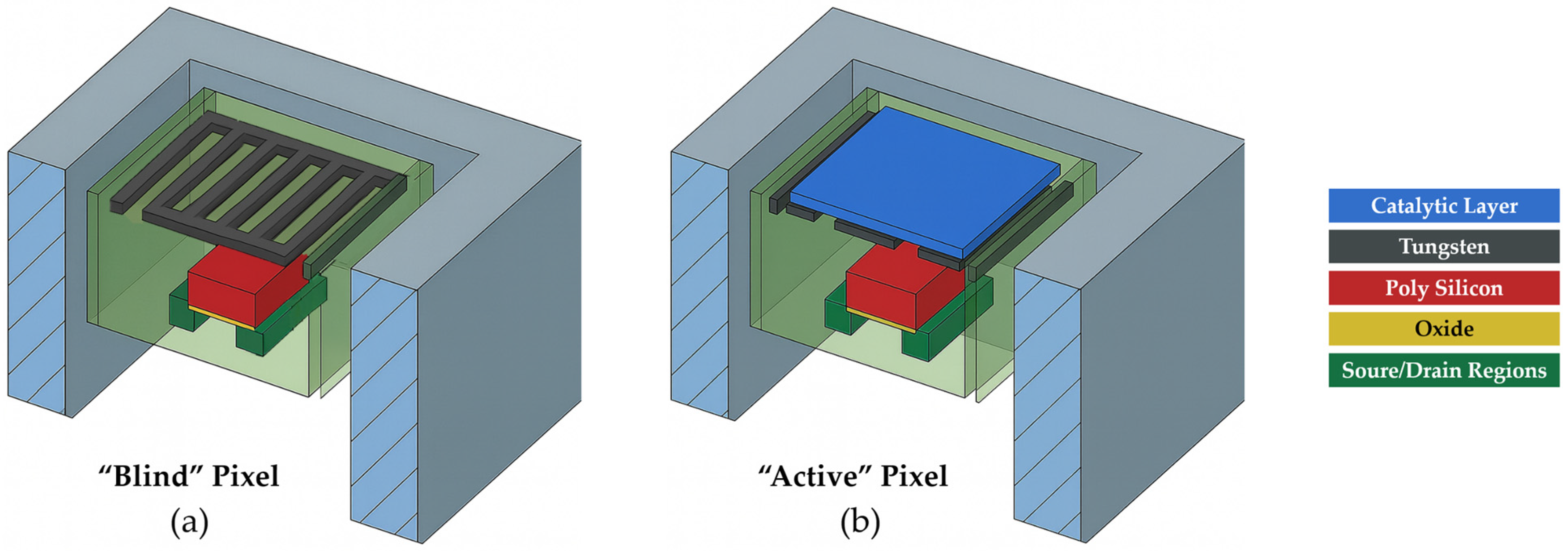
2. Experiment Setup
2.1. Catalytic Layer Preparation
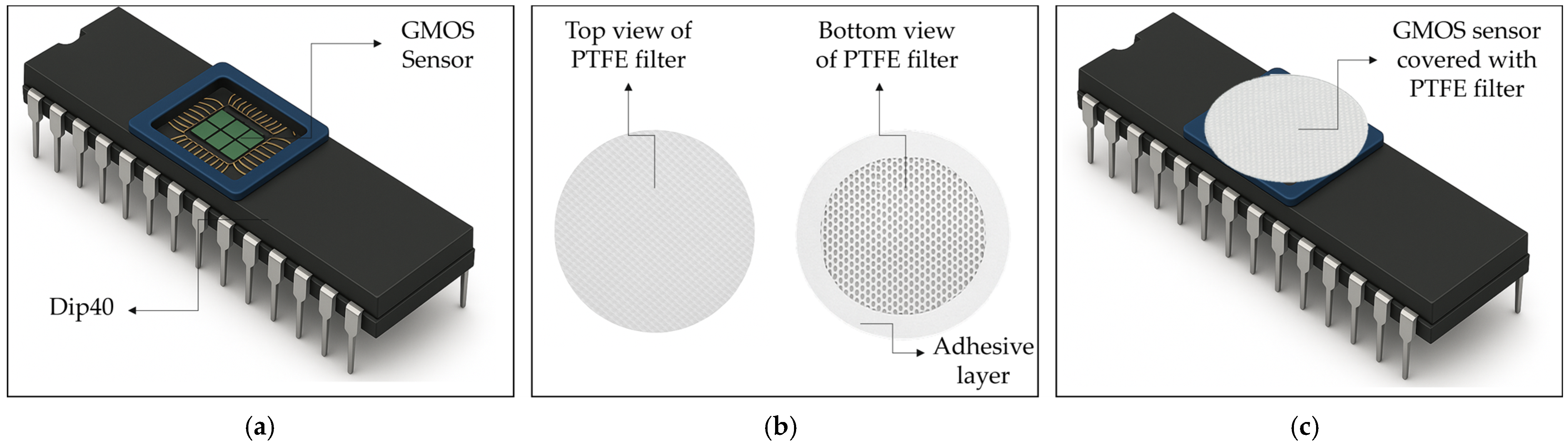
2.2. Sample Conditioning
2.3. Analytical Techniques
3. Results and Discussion
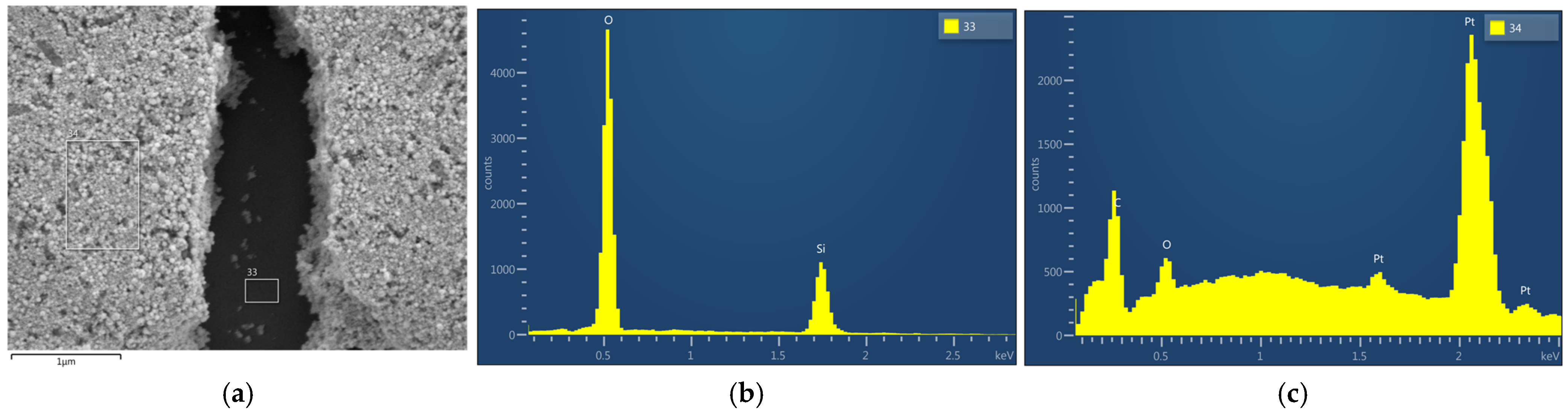
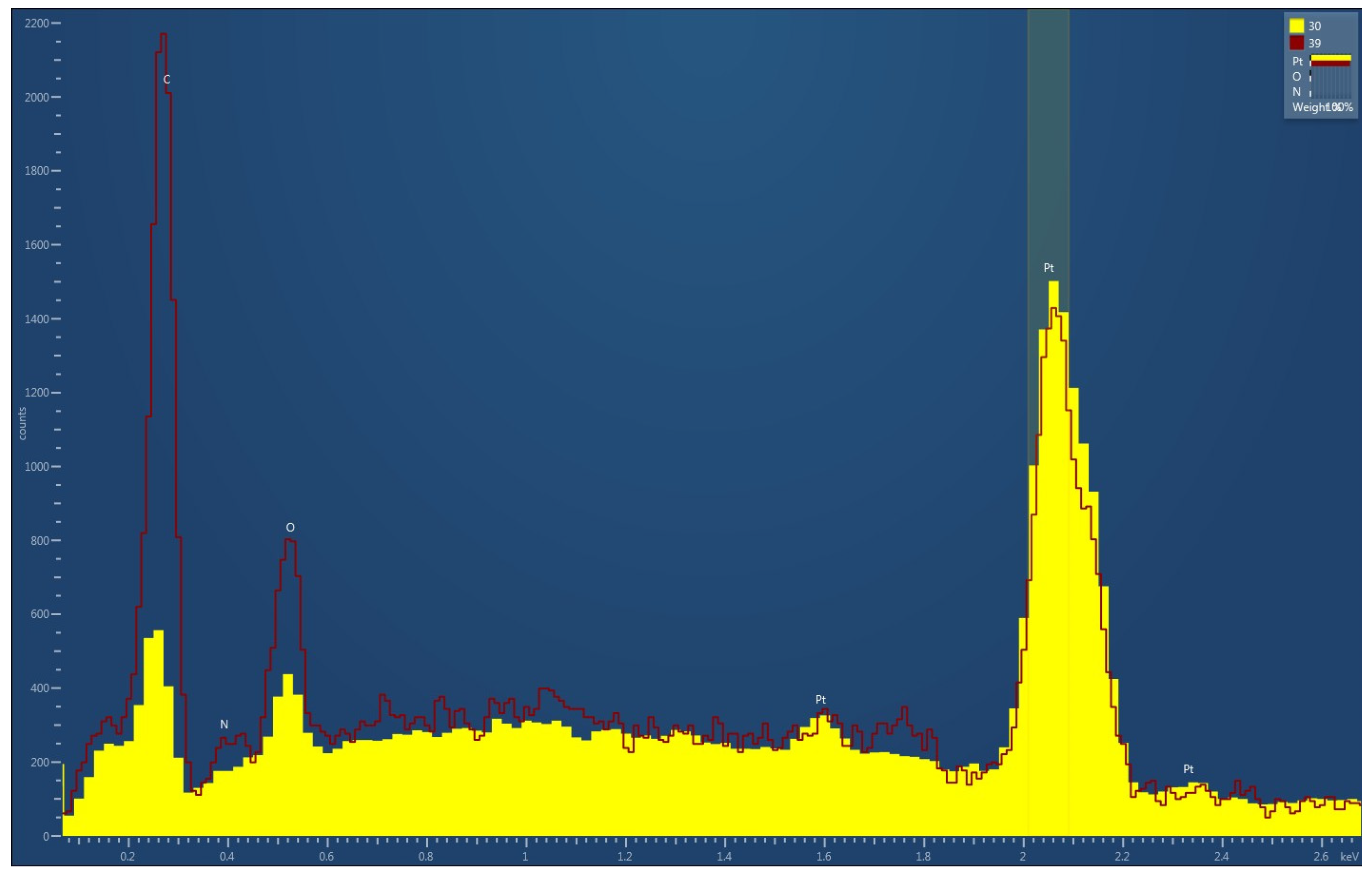
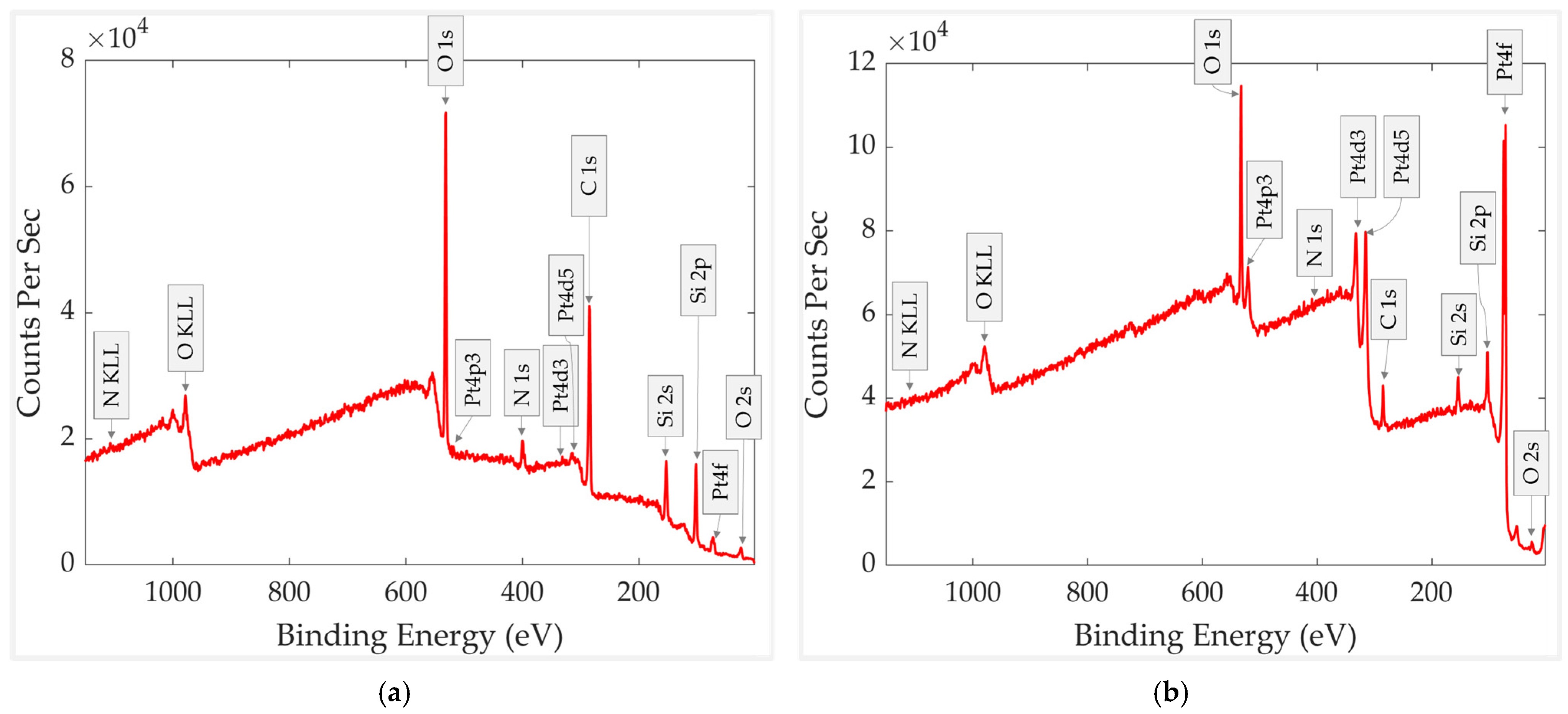
3.1. Analysis of the Freshly Prepared Sample
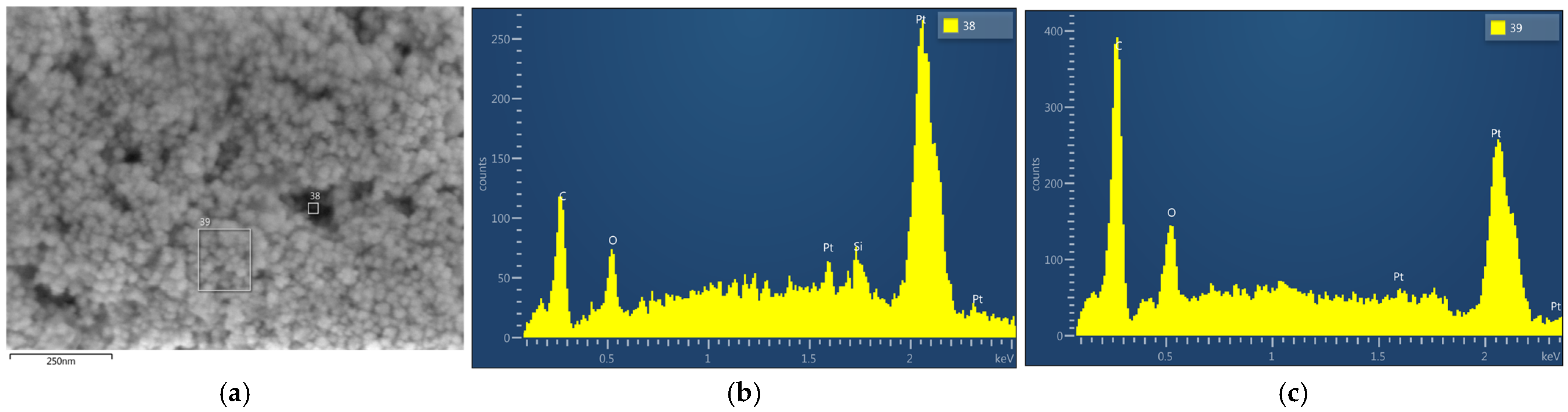
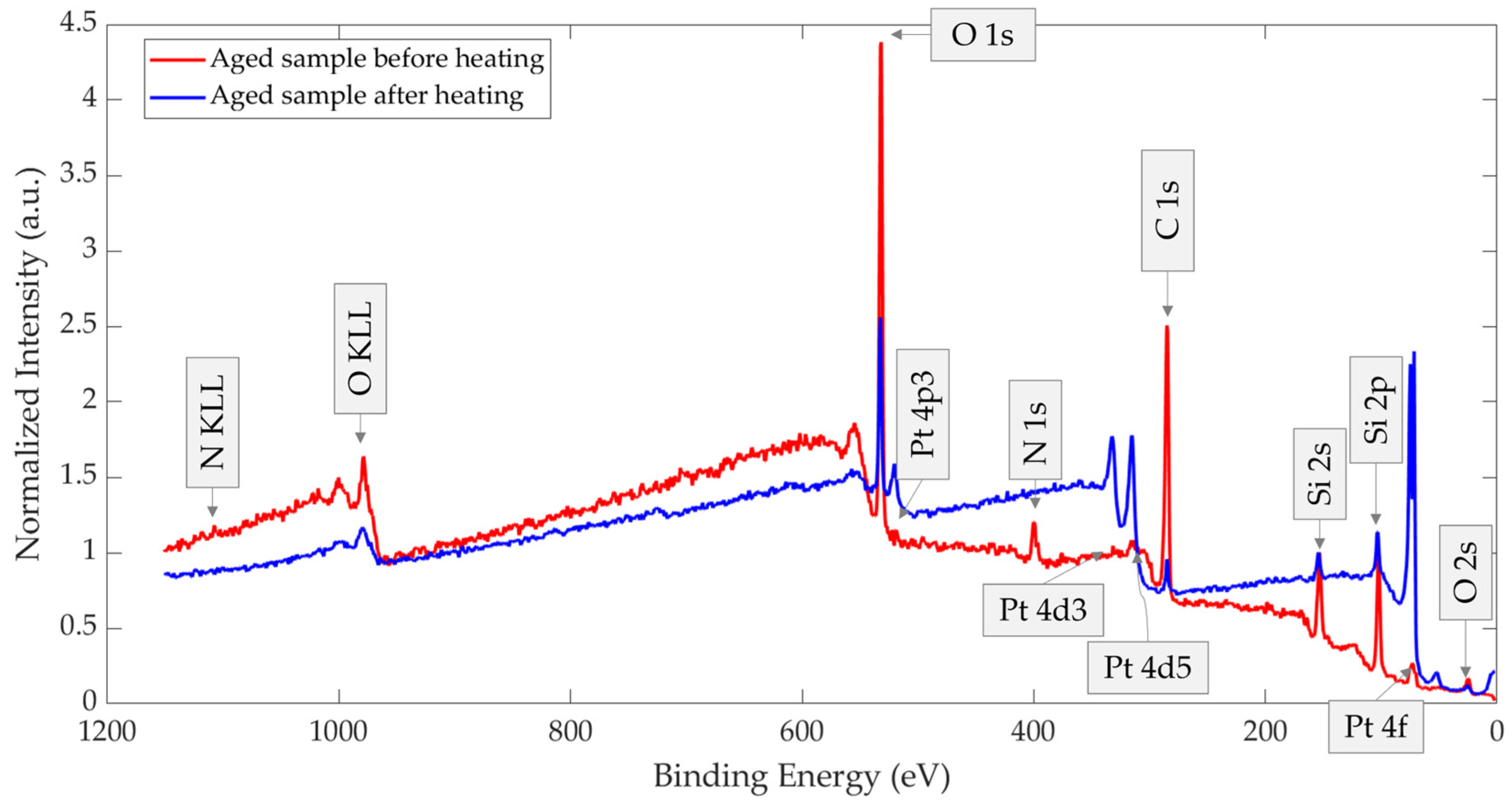
3.2. Aged Sample Without vs. with Thermal Treatment
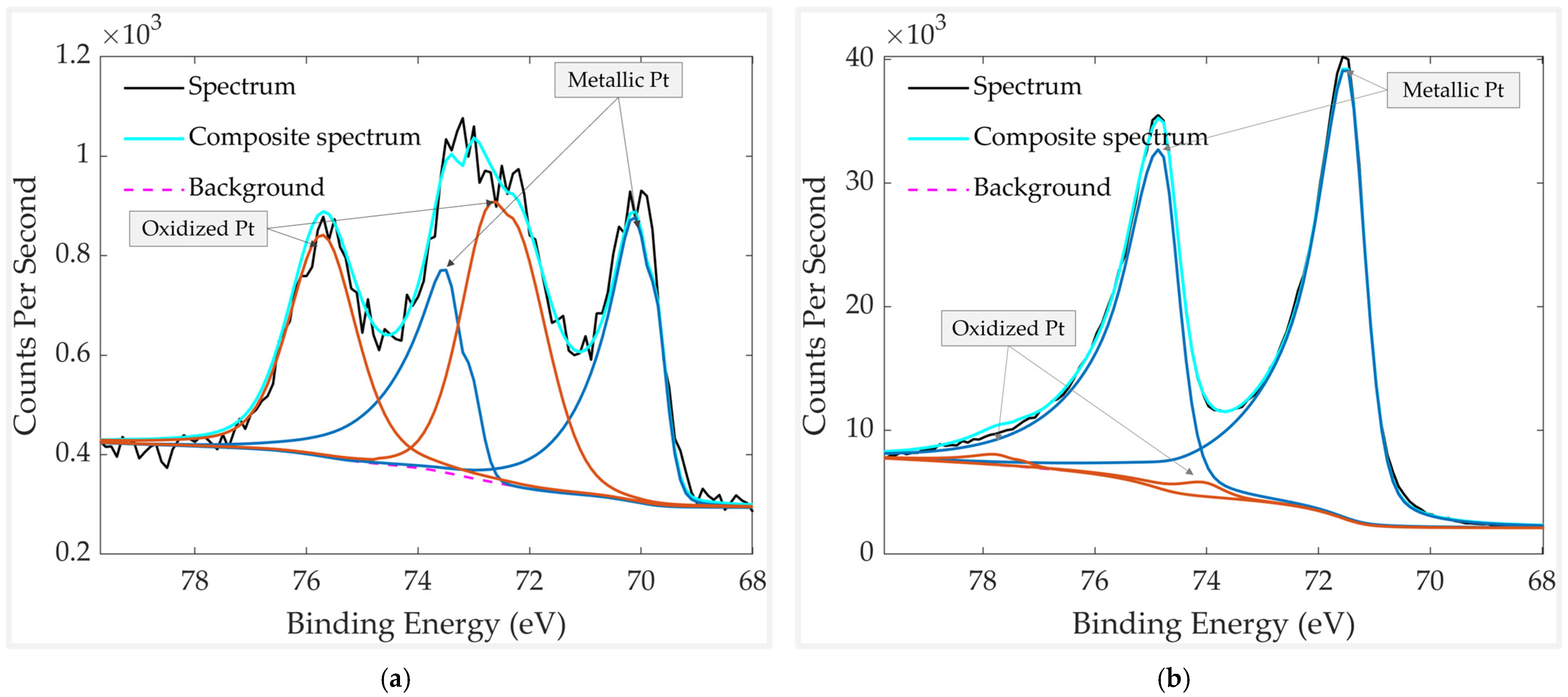
3.3. Thermally Treated Samples: With vs. Without a Mechanical Filter
3.4. Results Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cincinelli, A.; Martellini, T. Indoor air quality and health. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.S.; Chiang, S.; Athni, T.S.; Shah, J.; McCurdy, K.; Yu, S.E.; Kariveda, R.; Mitchell, M.; Ruan, M.; Zou, J.; et al. Characterizing everyday exposure to volatile organic compounds and upper respiratory health effects. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 23555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumchev, K.; Brown, H.; Spickett, J. Volatile organic compounds: Do they present a risk to our health? Rev. Environ. Health 2007, 22, 39–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashkar, H.; Stolyarova, S.; Blank, T.; Nemirovsky, Y. The role of Pd–Pt bimetallic catalysts in ethylene detection by CMOS-MEMS gas sensor dubbed GMOS. Micromachines 2025, 16, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krayden, A.; Avraham, M.; Ashkar, H.; Blank, T.; Stolyarova, S.; Nemirovsky, Y. TinyML-based real-time drift compensation for gas sensors using spectral-temporal neural networks. Chemosensors 2025, 13, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemirovsky, Y.; Stolyarova, S.; Blank, T.; Bar-Lev, S.; Zviagintsev, A.; Svetlitza, A.; Brouk, I. A new pellistor-like gas sensor based on micro machined CMOS transistor. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2018, 99, 5494–5498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shlenkevich, D.; Stolyarova, S.; Blank, T.; Brouk, I.; Nemirovsky, Y. A novel miniature and selective combustion on type CMOS gas sensor for gas mixture analysis—Part 1: Emphasis on chemical aspects. Micromachines 2020, 11, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, M.; Stolyarova, S.; Blank, T.; Bar-Lev, S.; Golan, G.; Nemirovsky, Y. A novel miniature and selective CMOS gas sensor for gas mixture analysis—Part 2: Emphasis on physical aspects. Micromachines 2020, 11, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avraham, M.; Krayden, A.; Ashkar, H.; Aronin, D.; Stolyarova, S.; Blank, T.; Shlenkevitch, D.; Nemirovsky, Y. A novel miniature and selective CMOS gas sensor for gas mixture analysis—Part 4: The effect of humidity. Micromachines 2024, 15, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brauns, E.; Morsbach, E.; Kunz, S.; Bäumer, M.; Lang, W. A fast and sensitive catalytic gas sensor for hydrogen detection based on stabilized nanoparticles as catalytic layer. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 193, 895–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturm, H.; Brauns, E.; Seemann, T.; Zoellmer, V.; Lang, W. A highly sensitive catalytic gas sensor for hydrogen detection based on sputtered nanoporous platinum. Procedia Eng. 2010, 5, 123–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, W.; Nishibori, M.; Houlet, L.F.; Itoh, T.; Izu, N.; Matsubara, I. Fabrication of thermoelectric gas sensors on micro-hotplates. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2009, 139, 340–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishibori, M.; Shin, W.; Tajima, K.; Houlet, L.F.; Izu, N.; Itoh, T.; Matsubara, I. Long-term stability of Pt/alumina catalyst combustors for micro-gas sensor application. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2008, 28, 2183–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavelko, R.G.; Vasiliev, A.A.; Llobet, E.; Vilanova, X.; Barrabés, N.; Medina, F.; Sevastyanov, V.G. Comparative study of nanocrystalline SnO2 materials for gas sensor application: Thermal stability and catalytic activity. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2009, 137, 637–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Jang, I.; Lee, S. Advanced strategies for mitigating catalyst poisoning in low and high temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cells: Recent progress and perspectives. Crystals 2025, 15, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, A.; Scibioh, M.A.; Prabhuram, J.; An, M.-G.; Ha, H.Y. A review on durability issues and restoration techniques in long-term operations of direct methanol fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2015, 297, 224–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpova, E.; Mironov, S.; Suchkov, A.; Karelin, A.; Karpov, E.E.; Karpov, E.F. Increase of catalytic sensors stability. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 197, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraunhofer Institute. Available online: https://www.dresden.fraunhofer.de/en.html (accessed on 14 August 2025).
- Cobetter. Membrane Filters. Cobetter Official Shop. Available online: https://shop.cobetter.com/collections/membrane-filters (accessed on 15 September 2025).
- Biesinger, M.C. Accessing the Robustness of Adventitious Carbon for Charge Referencing (Correction) Purposes in XPS Analysis: Insights From a Multi-User Facility Data Review. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 597, 153681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosvenor, A.P.; Kobe, B.A.; McIntyre, N.S. Studies of the oxidation of iron by water vapour using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and QUASES. Surf. Sci. 2004, 572, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://xpsdatabase.com/oxygen-o-z8/?v=4605f628f91d (accessed on 20 November 2025).
- Miller, D.J.; Öberg, H.; Kaya, S.; Sanchez Casalongue, H.; Friebel, D.; Anniyev, T.; Ogasawara, H.; Bluhm, H.; Pettersson, L.G.M.; Nilsson, A. Oxidation of Pt(111) under near-ambient conditions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 107, 195502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, F.; King, R.C., Jr. Handbook of X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy; Perkin-Elmer Corporation: Waltham, MA, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- NIST X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) Database; National Institute of Standards and Technology: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 1990. Available online: https://srdata.nist.gov/xps/ (accessed on 16 August 2025).
- Thermo Scientific. XPS Simplified. Available online: http://www.xpssimplified.com/ (accessed on 16 August 2025).
- XPSFitting.com. XPS Peak Fitting Tutorial and Tools. Available online: https://www.xpsfitting.com/ (accessed on 20 September 2025).
- Thermo Fisher Scientific. Oxygen | XPS Periodic Table: Non-Metal Elements—Oxygen. Materials Science Learning Center. Available online: https://www.thermofisher.com/il/en/home/materials-science/learning-center/periodic-table/non-metal/oxygen.html (accessed on 20 September 2025).
- Bayindir, Z.; Duchesne, P.N.; Cook, S.C.; MacDonald, M.A.; Zhang, P. X-ray spectroscopy studies on the surface structural characteristics and electronic properties of platinum nanoparticles. J. Chem. Phys. 2009, 131, 244716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, M.-J.; Park, H.; Engelhard, M.H.; Li, D.; Sushko, P.V.; Du, Y. Reevaluation of XPS Pt 4f Peak Fitting: Ti 3s Plasmon Peak Interference and Pt Metallic Peak Asymmetry in Pt@TiO2 System. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 2024, 42, 063209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, D.J. XPS Insights: Asymmetric Peak Shapes in XPS. Surf. Interface Anal. 2023, 55, 7215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelhard, M.H.; Baer, D.R.; Herrera-Gomez, A.; Sherwood, P.M.A. Introductory Guide to Backgrounds in XPS Spectra and Their Impact on Determining Peak Intensities. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 2020, 38, 063203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- XPSFitting.com. What Is Adventitious Carbon? January 2011. Available online: https://www.xpsfitting.com/2011/01/what-is-adventitious-carbon.html (accessed on 20 September 2025).
- Frankcombe, T.J.; Liu, Y. Interpretation of Oxygen 1s X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy of ZnO. Chem. Mater. 2023, 35, 5468–5474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalyst Poisoning. ChemEurope Encyclopedia. Available online: https://www.chemeurope.com/en/encyclopedia/Catalyst_poisoning.html (accessed on 31 August 2025).
- Maxted, E.V. The Poisoning of Metallic Catalysts. Adv. Catal. 1951, 3, 129–178. [Google Scholar]
- Schmeltz, I.; Hoffmann, D. Nitrogen-Containing Compounds in Tobacco and Tobacco Smoke. Chem. Rev. 1977, 77, 295–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutlu, E.; Kismali, G.; Emen, F.; Demindogen, R.E. Pyridine Derivative Platinum Complexes: Synthesis, Molecular Structure, DFT and Initial Anticancer Activity Studies. J. Mol. Struct. 2021, 1234, 130191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juhász, M.; Takahashi, S.; Arulmozhiraja, S.; Fujii, T. Bond Energies (Pt–NH3, Pt–Cl) and Proton Affinity of Cisplatin: A Density Functional Theory Approach. J. Struct. Chem. 2012, 53, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

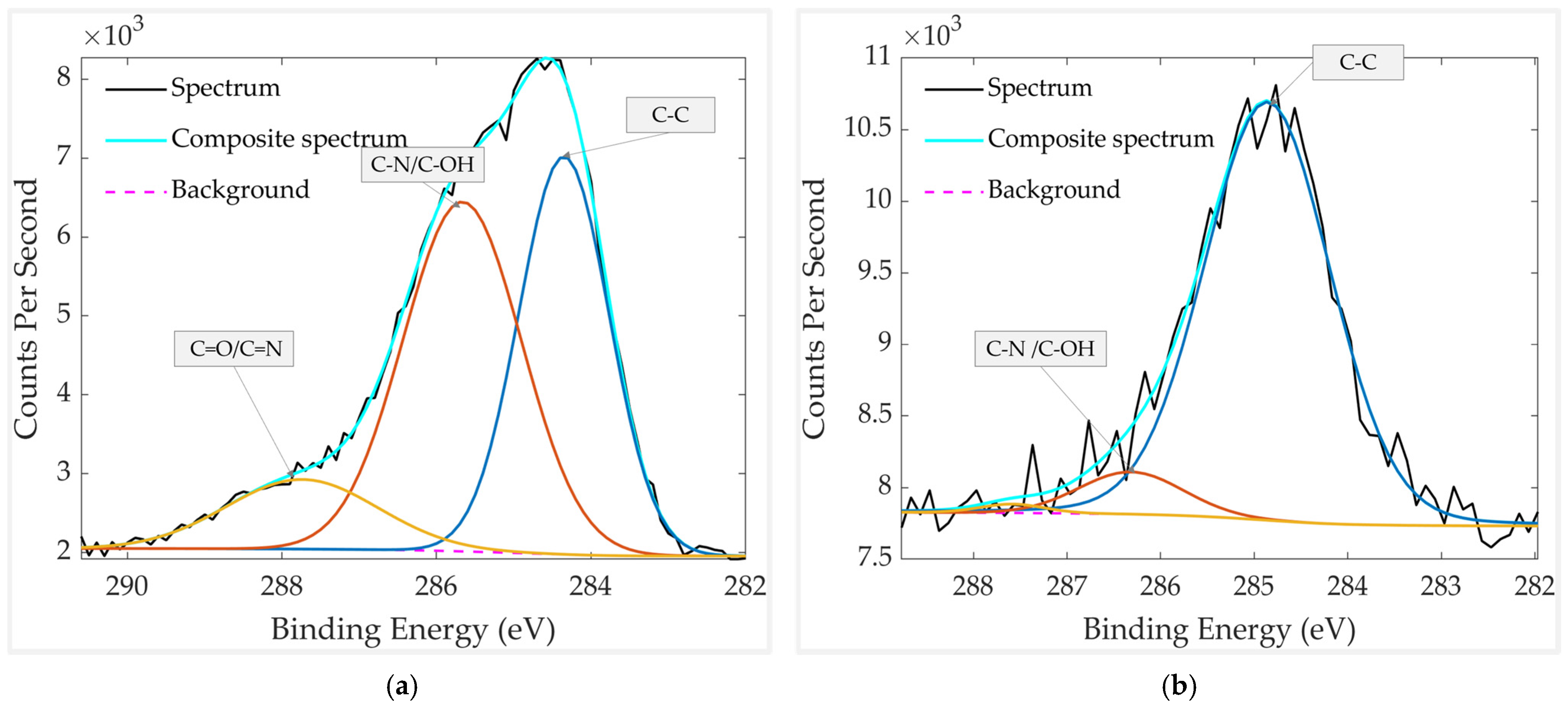
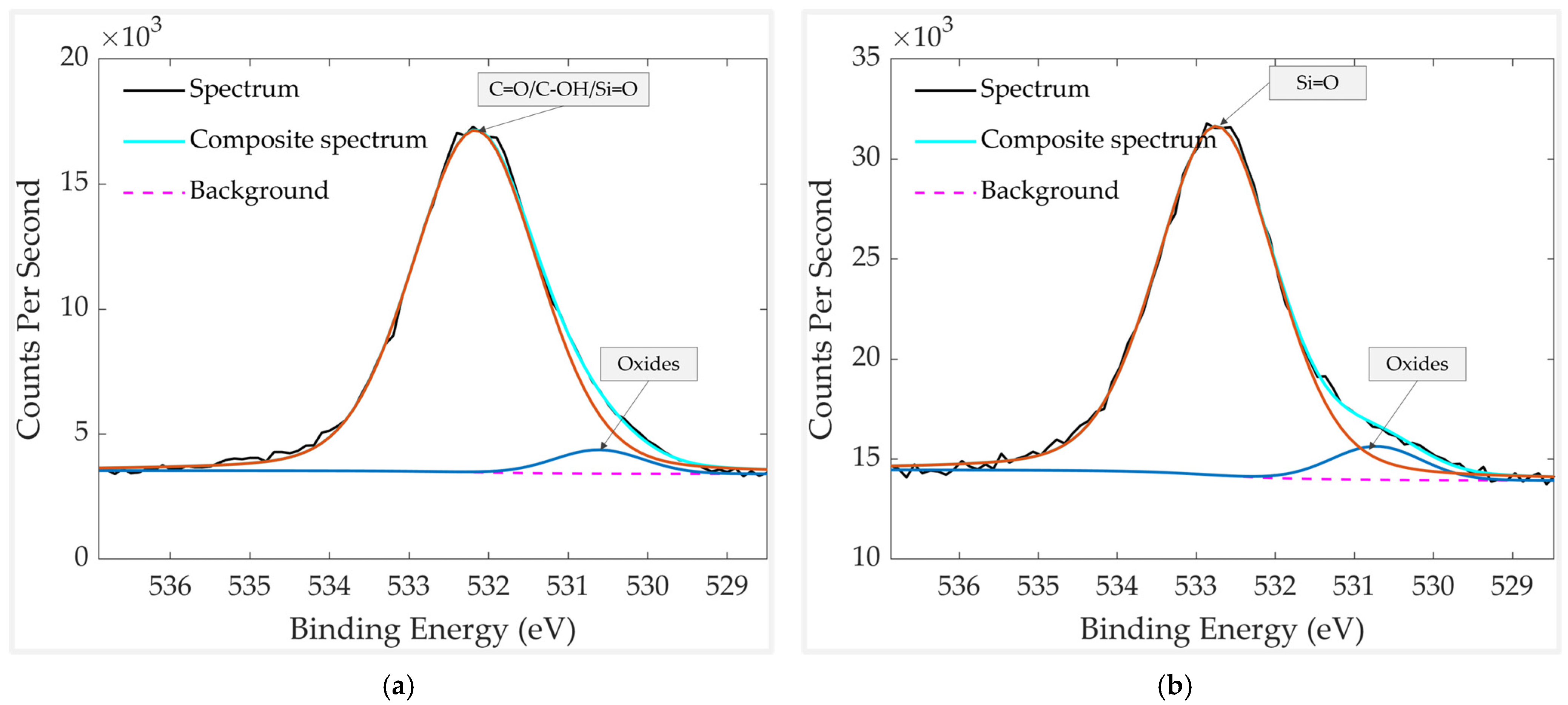

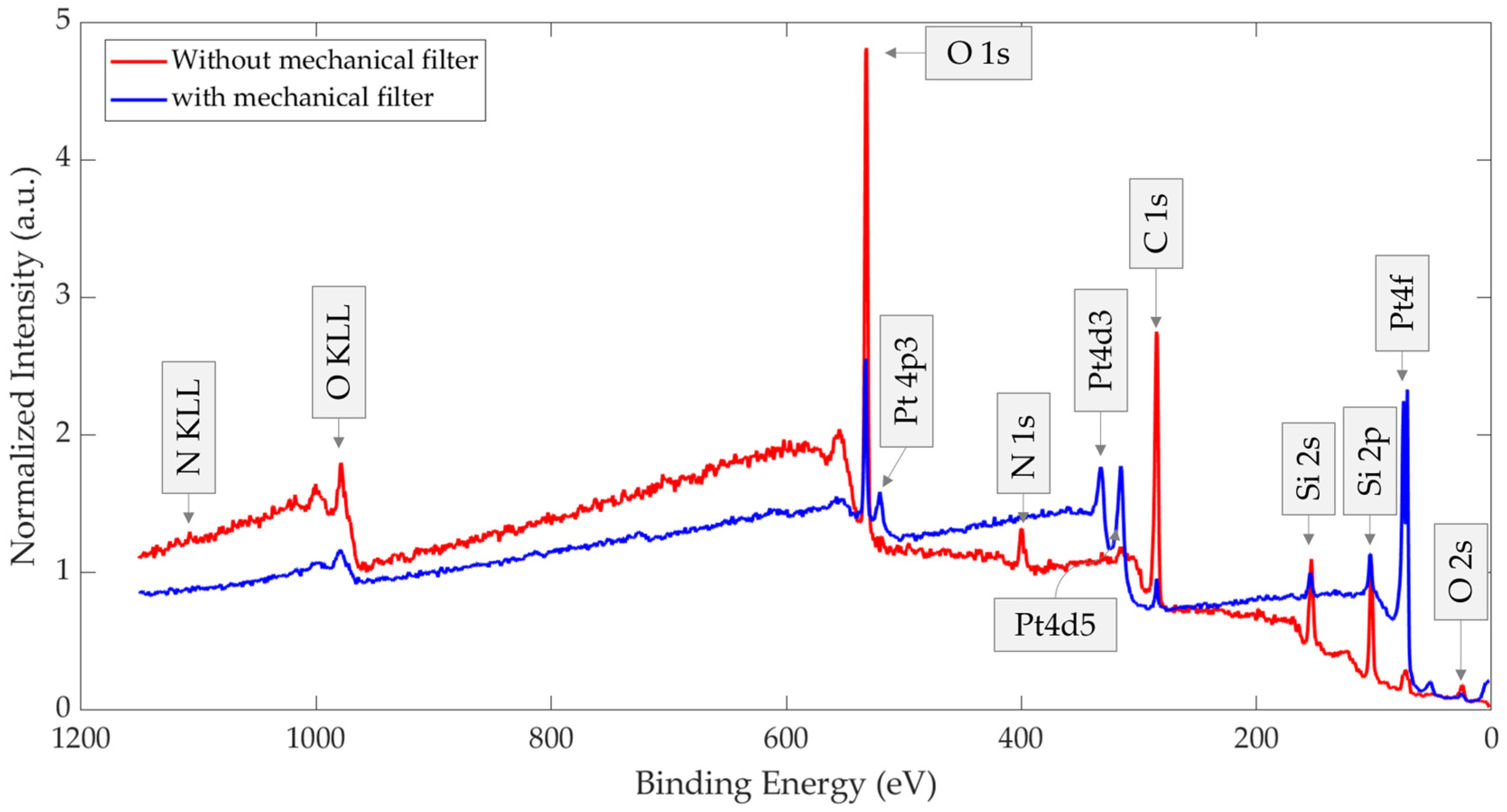
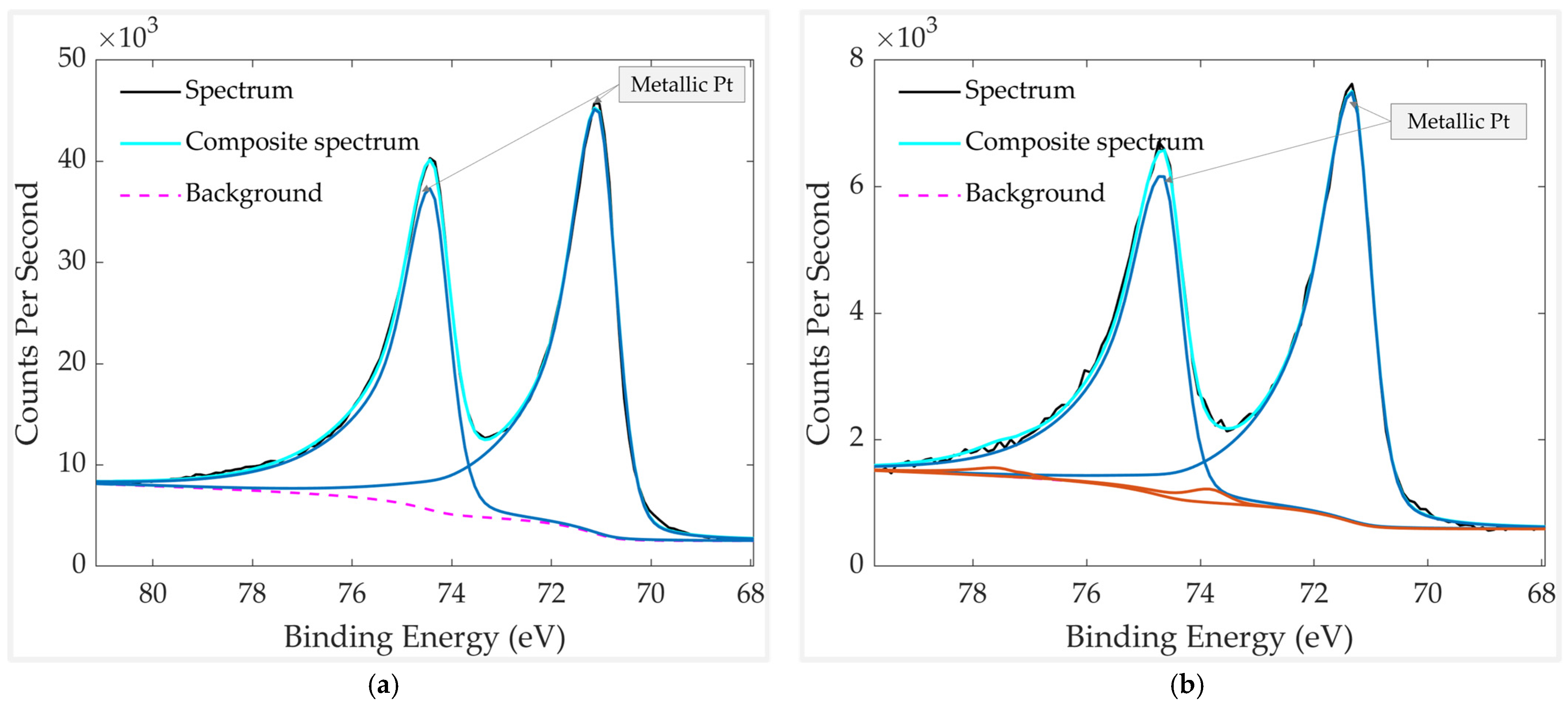

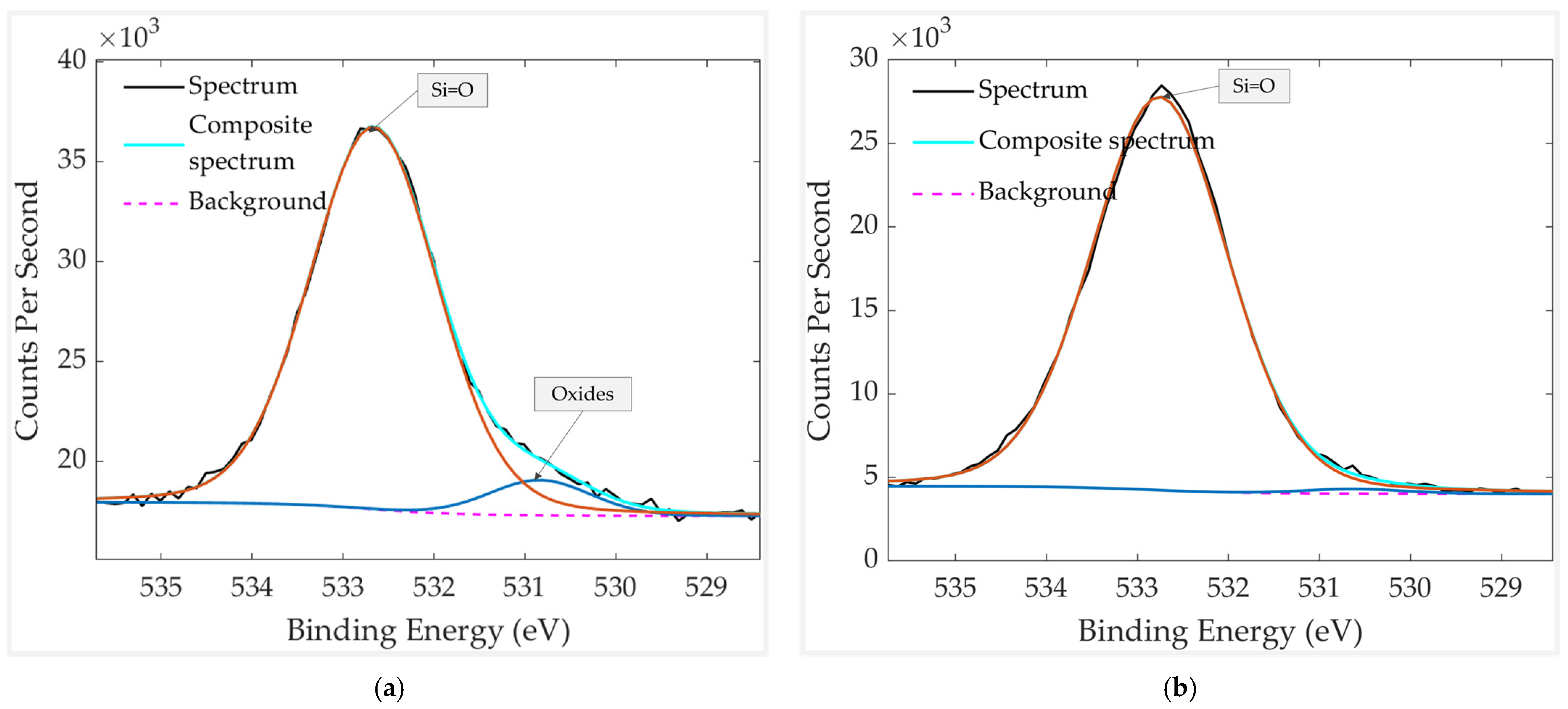

| Element | Chemical Bond/Compound | Binding Energy [eV] |
|---|---|---|
| Pt | Pt0 4f7/2/Pt0 4f5/2 | 71.0/74.3 |
| Pt(OH)2 (Pt+2) | 72.6 | |
| PtO (Pt+2) | 72.4 | |
| PtO2 (Pt+4) | 74.9 | |
| C | C-C, C-H | 284.8–285.2 |
| C-OH | 286.0 | |
| C-N | 285.7 | |
| O-C=O | 288.5 | |
| C=N | 287.3 | |
| C=O | 287.7 | |
| O | Me-O | 529–530 |
| C=O | 531.6–532.0 | |
| C-OH | 532.0–532.8 | |
| Si=O | 532.9 |
| Sample | C 1s | O 1s | N 1s | Si 2p | Pt 4f | C l2p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aged sample without heating treatment before XPS. | 49.4 | 31.7 | 4.7 | 13.7 | 0.3 | 0.2 |
| An aged sample that was heated before XPS | 18.0 | 44.4 | 0.5 | 23.1 | 14.8 | - |
| Sample | C–C | C=O; C=N | C–OH | O | Pt–Metal | Pt–Compound | Si | N | Cl |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| An aged sample without heating treatment before XPS | 19.8 | 6.4 | 23 | 31.7 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 13.7 | 4.7 | 0.2 |
| An aged sample that was heated before XPS | 16.6 | 0.05 | 1.4 | 44.4 | 13.9 | 0.9 | 23.1 | 0.5 | - |
| Sample | C 1s | O 1s | N 1s | Si 2p | Pt 4f |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| An aged sample that was heated and then stored for 10 days without a mechanical filter before XPS | 22.4 | 42.1 | 3.4 | 18.3 | 13.8 |
| An aged sample that was heated and then stored for 10 days with a mechanical filter before XPS | 15.2 | 45.6 | 0.2 | 22.9 | 16.1 |
| Sample | C–C | C=O; C=N | C–OH | O | Pt–Metal | Pt–Compound | Si | N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| An aged sample that was heated and then stored for 10 days without a mechanical filter before XPS | 20 | - | 2 | 42 | 13.8 | - | 18.3 | 3.4 |
| An aged sample that was heated and then stored for 10 days with a mechanical filter before XPS | 14 | - | 1.2 | 45.6 | 15.8 | 0.3 | 22.9 | 0.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ashkar, H.; Stolyarova, S.; Blank, T.; Nemirovsky, Y. XPS Study of Nanostructured Pt Catalytic Layer Surface of Gas Sensor Dubbed GMOS. Chemosensors 2025, 13, 407. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13120407
Ashkar H, Stolyarova S, Blank T, Nemirovsky Y. XPS Study of Nanostructured Pt Catalytic Layer Surface of Gas Sensor Dubbed GMOS. Chemosensors. 2025; 13(12):407. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13120407
Chicago/Turabian StyleAshkar, Hanin, Sara Stolyarova, Tanya Blank, and Yael Nemirovsky. 2025. "XPS Study of Nanostructured Pt Catalytic Layer Surface of Gas Sensor Dubbed GMOS" Chemosensors 13, no. 12: 407. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13120407
APA StyleAshkar, H., Stolyarova, S., Blank, T., & Nemirovsky, Y. (2025). XPS Study of Nanostructured Pt Catalytic Layer Surface of Gas Sensor Dubbed GMOS. Chemosensors, 13(12), 407. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13120407





