Highly Selective and Stable Electrochemical Sensor for Hydrogen Peroxide—Application in Cosmetics Quality Control
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Apparatus and Measurements
2.3. Electrochemical Deposition of Rhodium onto GCE
2.4. Reference Method for Determination of H2O2 in Hair-Care Products
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy Studies
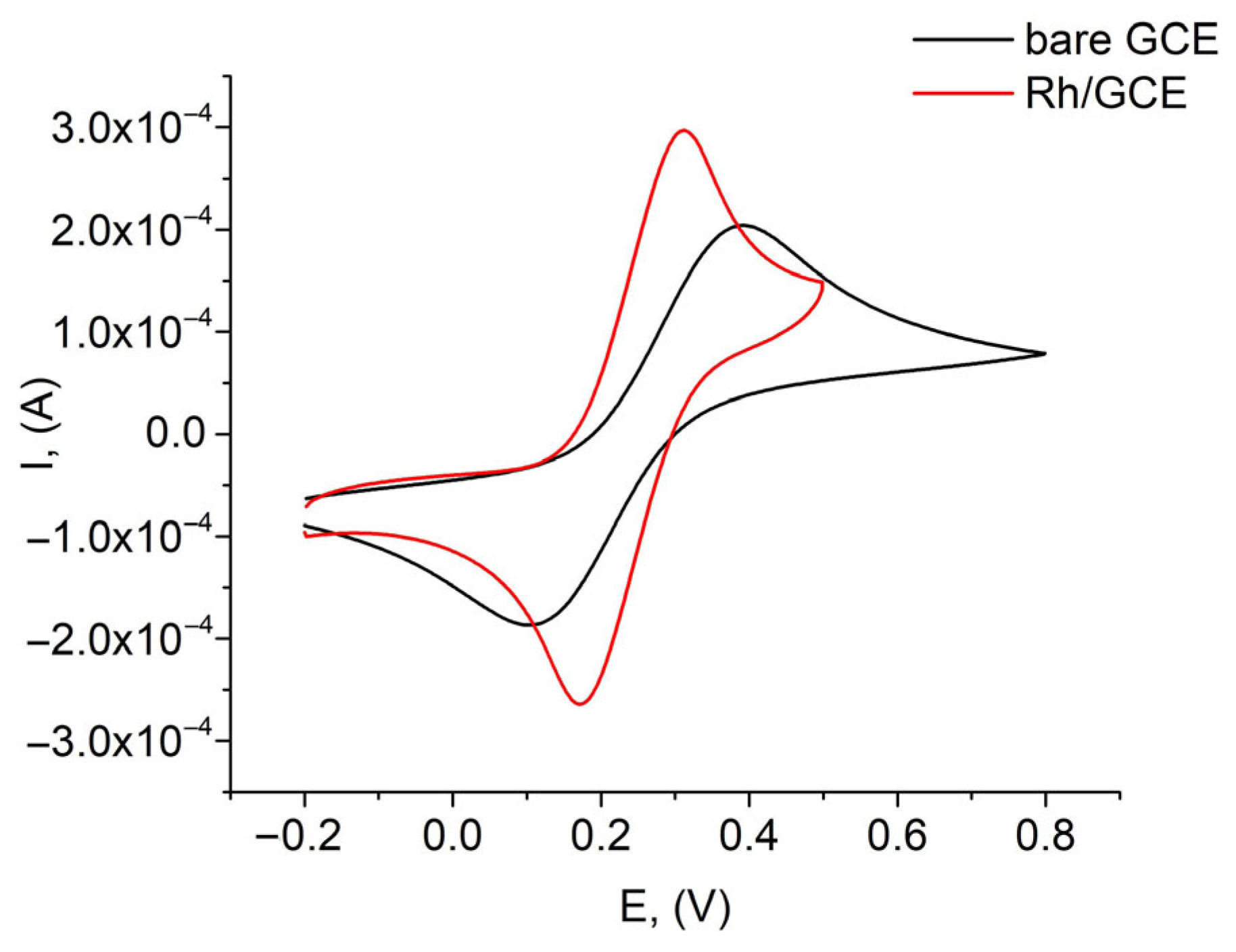
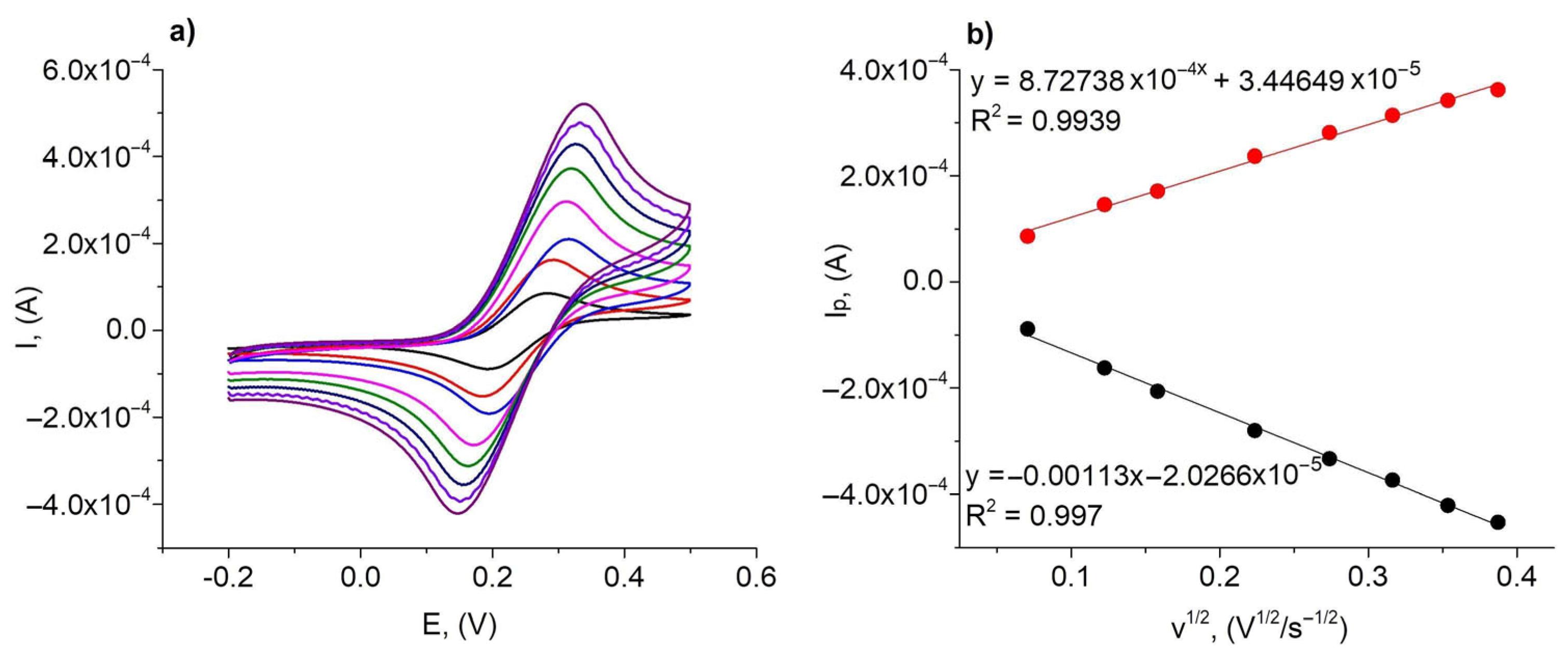
3.2. Electrochemical Characterization
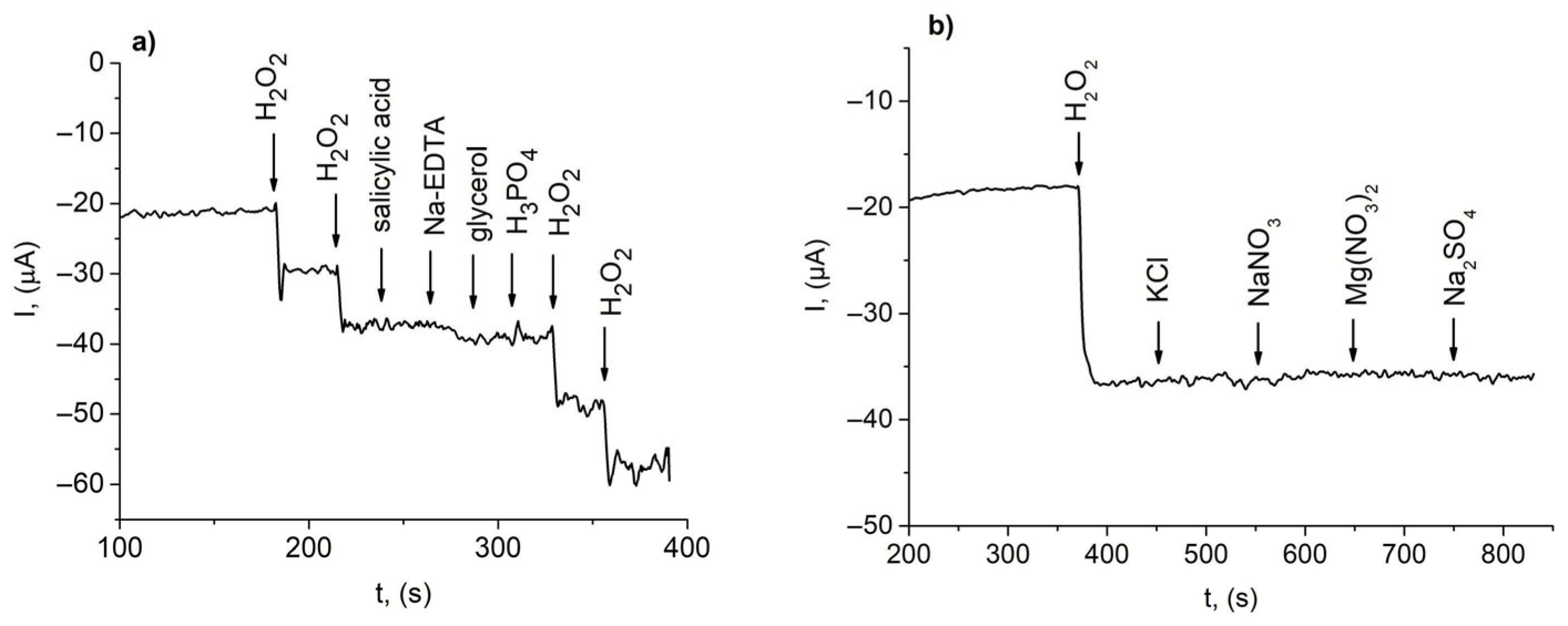
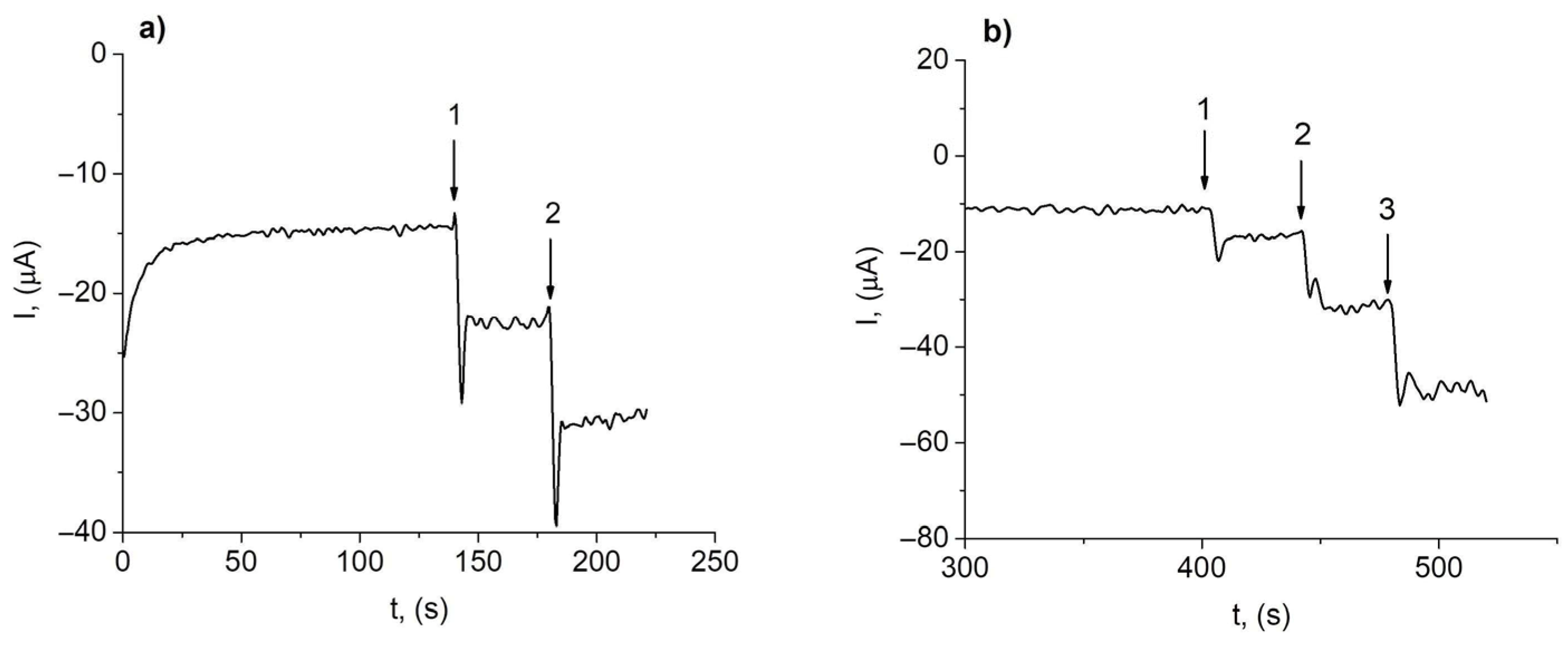
3.3. Interference Study
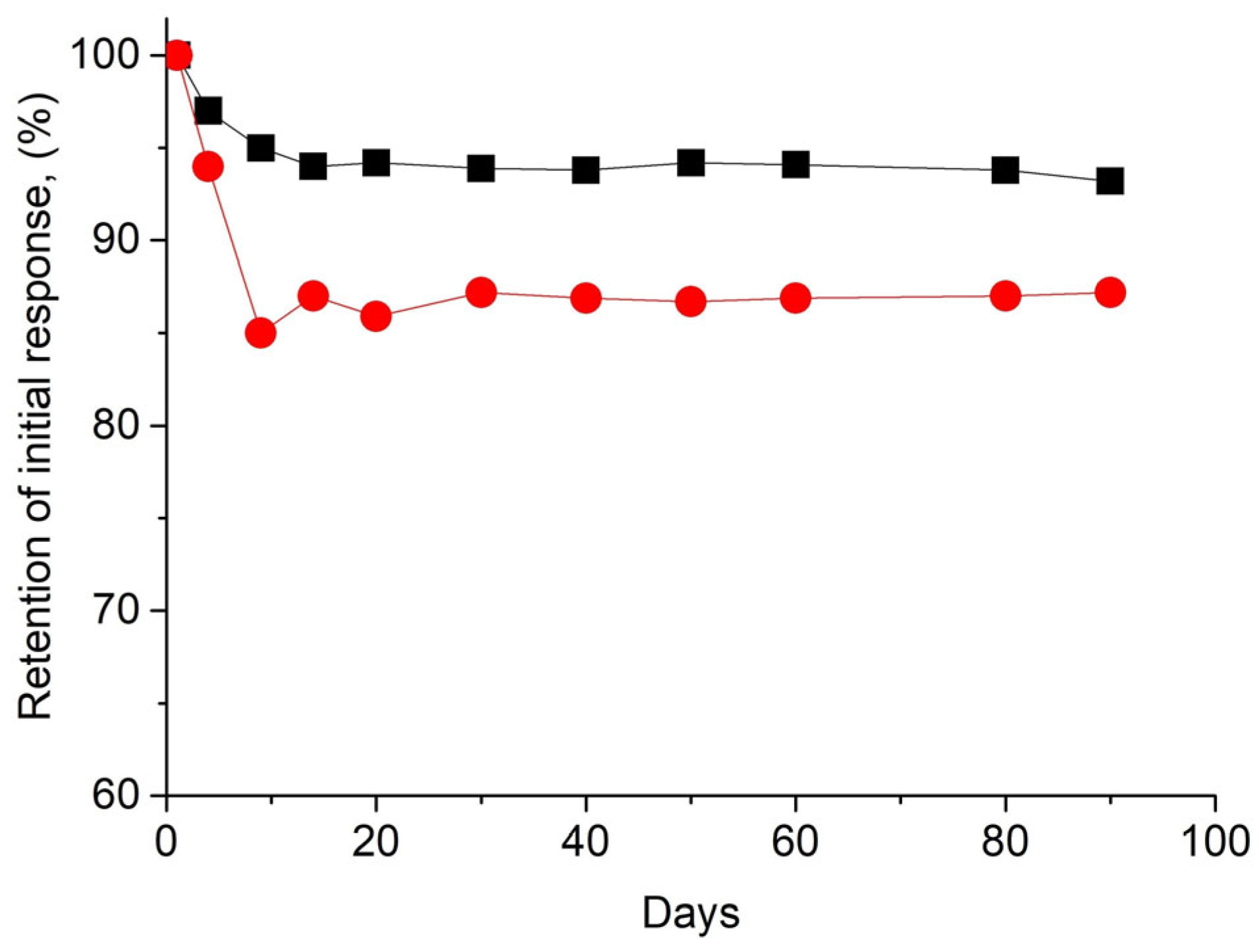
3.4. Reproducibility, Repeatability, and Stability
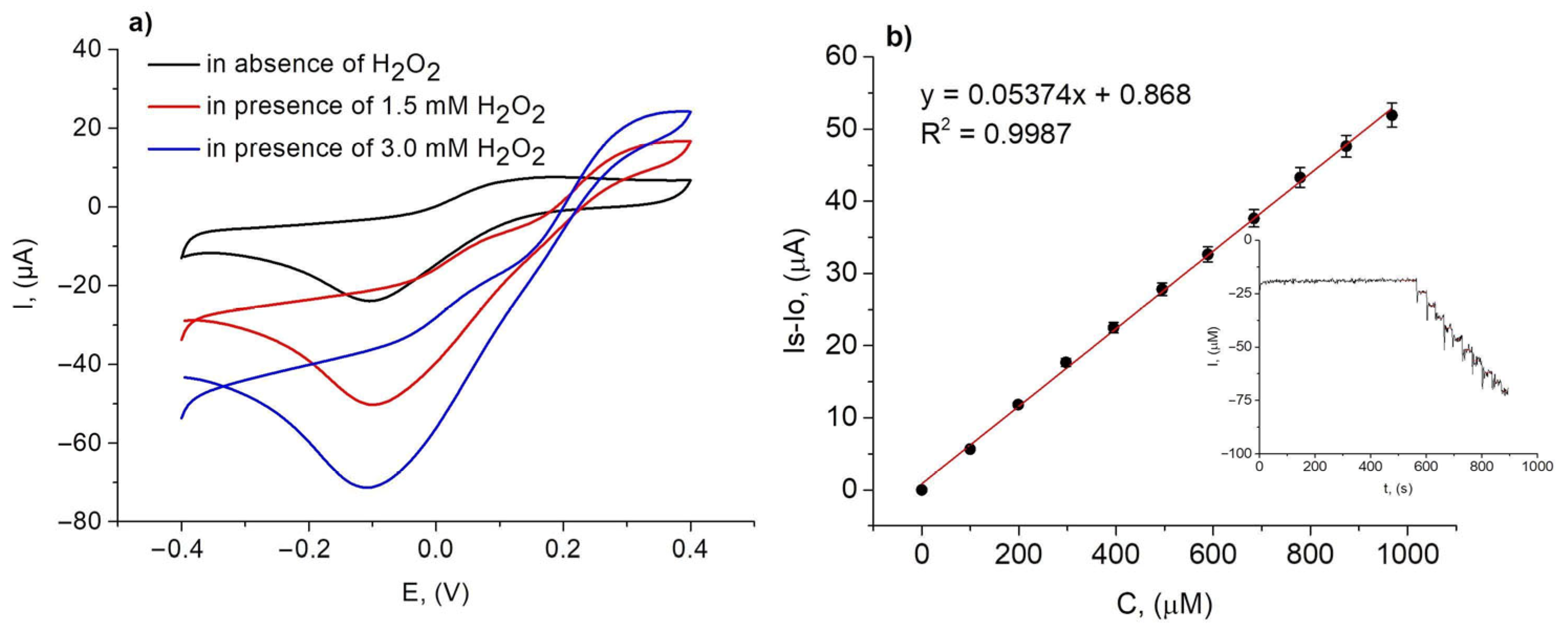
3.5. Application of Rh/GCE for Determination of H2O2 Content in Cosmetic and Medical Products
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Becker, L.C.; Cherian, P.A.; Bergfeld, W.F.; Belsito, D.V.; Hill, R.A.; Klaassen, C.D.; Liebler, D.C.; Marks, J.G., Jr.; Shank, R.C.; Slaga, T.J.; et al. Safety Assessment of Hydrogen Peroxide as Used in Cosmetics. Int. J. Toxicol. 2024, 43, 5S–63S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yıldırım, A.; Demir, N.B.; İzgi, B.A.; Erkol, B.N.; Özsu, Ç.; Aydemir, G.E.; Mustafaoğlu, M.; Kızıl, M.; Ayhan, N.; Emen, S. The chemistry mechanism of hair dyes. Middle East J. Appl. Sci. 2022, 8, 173–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.-A.; Bae, I.-H.; Jang, W.-H.; Kim, J.-H.; Bak, S.-Y.; Han, S.-H.; Park, Y.-H.; Lim, K.-M. Hydrogen peroxide and monoethanolamine are the key causative ingredients for hair dye-induced dermatitis and hair loss. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2012, 66, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Huang, X.; Zhu, W.; Ding, C.; Huang, P.; Li, R. H2O2 gel bleaching induces cytotoxicity and pain conduction in dental pulp stem cells via intracellular reactive oxygen species on enamel/dentin disc. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0257221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin Hassan, S.A. Tooth Sensitivity Following Hydrogen Peroxide Bleaching With and Without Ozone: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Pain Res. Manag. 2024, 2024, 2695533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scientific Committee on Safety (SCCS). Opinion on Oxidative Hair Dye Substances and Hydrogen Peroxide Used in Products to Colour Eyelashes; Report No. SCCS/1475/12; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2012; pp. 1–21. Available online: http://ec.europa.eu/health/scientific_committees/consumer_safety/docs/sccs_o_111.pdf (accessed on 20 August 2025).
- Klassen, N.V.; Marchington, D.; McGowan, H.C.E. H2O2 Determination by the I3− Method and by KMnO4 Titration. Anal. Chem. 1994, 66, 2921–2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimeno, P.; Bousquet, C.; Lassu, N.; Maggio, A.-F.; Civade, C.; Brenier, C.; Lempereur, L. High-performance liquid chromatography method for the determination of hydrogen peroxide present or released in teeth bleaching kits and hair cosmetic products. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2015, 107, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunil, K.; Narayana, B. Spectrophotometric Determination of Hydrogen Peroxide in Water and Cream Samples. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2008, 81, 422–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsaplev, Y.B. Chemiluminescence determination of hydrogen peroxide. J. Anal. Chem. 2012, 67, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodevska, T.; Hadzhiev, D.; Shterev, I. Electrochemical sensors for the safety and quality control of cosmetics: An overview of achievements and challenges. J. Electrochem. Sci. Eng. 2024, 14, 3–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydar Barutçu, S.; Eskiköy Bayraktepe, D.; Yazan, Z.; Polat, K.; Filik, H. Investigation of electrochemical oxidation mechanism, rapid and low-level determination for whitening cosmetic: Arbutin in aqueous solution by nano sepiolite clay. Chem. Pap. 2021, 75, 3483–3491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, Q.; Feng, Y.; Ye, B.-C. A robust electrochemical sensor based on N,S-FeNi3/C for simultaneous detection of hydroquinone and arbutin in cosmetics. Microchim. Acta 2023, 190, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohari, N.A.; Siddiquee, S.; Saallah, S.; Misson, M.; Arshad, S.E. Electrochemical Behaviour of Real-Time Sensor for Determination Mercury in Cosmetic Products Based on PANI/MWCNTs/AuNPs/ITO. Cosmetics 2021, 8, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chairunisa, A.; Wahyuni, W.T.; BatuBara, I.; Putra, B.R. A composite of platinum nanoparticles and multiwalled carbon nanotubes modified electrode for sensitive and simultaneous detection of hydroquinone and methylparaben in cosmetic products. Sens. Int. 2025, 6, 100335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi-Maleh, H.; Darabi, R.; Shabani-Nooshabadi, M.; Baghayeri, M.; Karimi, F.; Rouhi, J.; Alizadeh, M.; Karaman, O.; Vasseghian, Y.; Karaman, C. Determination of D&C Red 33 and Patent Blue V Azo dyes using an impressive electrochemical sensor based on carbon paste electrode modified with ZIF-8/g-C3N4/Co and ionic liquid in mouthwash and toothpaste as real samples. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2022, 162, 112907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charoenkitamorn, K.; Siangproh, W.; Chailapakul, O.; Oyama, M.; Chaneam, S. Simple Portable Voltammetric Sensor Using Anodized Screen-Printed Graphene Electrode for the Quantitative Analysis of p-Hydroxybenzoic Acid in Cosmetics. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 16116–16126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bounegru, A.V.; Apetrei, C. Development of a Novel Electrochemical Biosensor Based on Carbon Nanofibers–Gold Nanoparticles–Tyrosinase for the Detection of Ferulic Acid in Cosmetics. Sensors 2020, 20, 6724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riaz, M.A.; Chen, Y. Electrodes and electrocatalysts for electrochemical hydrogen peroxide sensors: A review of design strategies. Nanoscale Horiz. 2022, 7, 463–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trujillo, R.M.; Barraza, D.E.; Zamora, M.L.; Cattani-Scholz, A.; Madrid, R.E. Nanostructures in Hydrogen Peroxide Sensing. Sensors 2021, 21, 2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Li, M.; Liu, W.; Hao, Z.; Zhang, F.; Pang, H.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, L. Advances in Non-Enzymatic electrochemical materials for H2O2 sensing. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2024, 954, 118060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Sun, H.; Chen, S.; Yang, M.; Dong, R.; Yang, X.; Zang, L. Chemosensors for H2O2 Detection: Principles, Active Materials, and Applications. Chemosensors 2025, 13, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, M.-H.; Kumar, A.S.; Sornambikai, S.; Chen, P.-Y.; Shih, Y.; Zen, J.-M. Cosmetic Hydrogen Peroxide Detection Using Nano Bismuth Species Deposited Built-in Three-in-One Screen-Printed Silver Electrode. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2011, 6, 2352–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangamuthu, R.; Pan, Y.-C.; Chen, S.-M. Electrocatalytic reduction of hydrogen peroxide and its determination in antiseptic and soft-glass cleaning solutions at phosphotungstate-doped-glutaraldehyde-cross-linked poly-l-lysine film electrodes. Sens. Actuat. B 2011, 151, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Li, L.; Ding, Y.; Cui, S. Electrochemical hydrogen peroxide sensors based on electrospun La0.7Sr0.3Mn0.75Co0.25O3 nanofiber modified electrodes. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 6083–6088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benvidi, A.; Nafar, M.T.; Jahanbani, S.; Tezerjani, M.D.; Rezaeinasab, M.; Dalirnasab, S. Developing an electrochemical sensor based on a carbon paste electrode modified with nano-composite of reduced graphene oxide and CuFe2O4 nanoparticles for determination of hydrogen peroxide. Mat. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 75, 1435–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katic, V.; dos Santos, P.L.; dos Santos, M.F.; Pires, B.M.; Loureiro, H.C.; Lima, A.P.; Queiroz, J.C.M.; Landers, R.; Muñoz, R.A.A.; Bonacin, J.A. 3D Printed Graphene Electrodes Modified with Prussian Blue: Emerging Electrochemical Sensing Platform for Peroxide Detection. ACS App. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 35068–35078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atacan, K.; Özacar, M. Construction of a non-enzymatic electrochemical sensor based on CuO/g-C3N4 composite for selective detection of hydrogen peroxide. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2021, 266, 124527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihailova, I.; Gerbreders, V.; Krasovska, M.; Sledevskis, E.; Mizers, V.; Bulanovs, A.; Ogurcovs, A. A non-enzymatic electrochemical hydrogen peroxide sensor based on copper oxide nanostructures. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2022, 13, 424–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, E.; Rahman, G.; Wu, Y.; Bokhari, T.H.; Rahman, A.; Zafar, A.; Rana, Z.; Shah, A.; Hussain, S.; Maaz, K.; et al. Amphiphilic Polyoxometalate-CNTs Nanohybrid as Highly Efficient Enzyme-free Electrocatalyst for H2O2 Sensing. New J. Chem. 2022, 46, 16280–16288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarova, Y.; Dodevska, T. Amperometric sensing of hydrogen peroxide using glassy carbon electrode modified with rhodium. Food Sci. Appl. Biotechnol. 2018, 1, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission: Directorate-General for Enterprise and Industry. The Rules Governing Cosmetic Products in the European Union. Volume 2, Cosmetics Legislation—Cosmetic Products—Methods of Analysis—2000 Edition; Catalogue number NB-26-99-966-EN-C; Office for Official Publications of the European Communities: Luxembourg, 2000; ISBN 92-828-8546-1. Available online: https://op.europa.eu/en/publication-detail/-/publication/17655e26-e423-4179-adcc-0bac7d666ebb (accessed on 12 February 2025).
- Dodevska, T. Electrochemical Sensors for Bisphenol A Analysis in Foods and Beverages—A New Approach in Food Quality Control. Acta Chim. Slov. 2025, 72, 217–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Electrode Material | Method (Potential) | Electrolyte | Linear Range (µM) | LOD (µM) | Stability | Real Sample | Ref. (Year) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPAgE-Binano | CV | PBS pH 7.0 | 100–5000 | 56.59 | – | Hair dyes | [23] (2011) |
| PLL-GA/PW/GCE | Amp. (−0.3 V *) | 0.1 M H2SO4 | 2.5–6850 | – | – (2 weeks) | Antiseptic solution, soft-contact lens cleaning solution | [24] (2011) |
| La0.7Sr0.3Mn0.75Co0.25O3/CPE | Amp. (0.6 V *) | 0.1 M NaOH | 0.5–1000 | 0.17 | 91.8% (1 month) | Toothpaste, medical solution | [25] (2015) |
| RGO/CuFe2O4/CPE | Amp. (−0.15 V *) | PBS pH 5.0 | 2–200 | 0.52 | 95.8% (2 weeks) | Hair dye, mouthwash solution | [26] (2017) |
| DPV | 2–10 10–1000 | 0.064 | |||||
| 3DGrE/PB | Amp. (0.0 V *) | PBS pH 7.4 | 1–700 | 0.11 | – | Mouthwash solution | [27] (2019) |
| CuO/g-C3N4/GCE | DPV | PBS pH 7.0 | 0.5–50 | 0.31 | 92% (2 months) | Makeup remover | [28] (2021) |
| CuO/Cu wire | Amp. (−0.7 V *) | 0.1 M NaOH | 10–1800 | 1.34 | 95% (1 month) | Listerine mouthwash | [29] (2022) |
| POM–CNT/Au | Amp. (−0.7 V *) | 0.1 M PBS pH 5.0 | 300–1350 | 0.5 | 90% (9 weeks) | Hand sanitizer, surface cleaner, contact lens preservation solution | [30] (2022) |
| Rh/GCE | Amp. (−0.1 V *) | PBS pH 7.0 | 5–1000 | 1.2 | 93% (3 months) | Hair dye, medical solution | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dodevska, T.; Hadzhiev, D.; Dimcheva, N. Highly Selective and Stable Electrochemical Sensor for Hydrogen Peroxide—Application in Cosmetics Quality Control. Chemosensors 2025, 13, 376. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13110376
Dodevska T, Hadzhiev D, Dimcheva N. Highly Selective and Stable Electrochemical Sensor for Hydrogen Peroxide—Application in Cosmetics Quality Control. Chemosensors. 2025; 13(11):376. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13110376
Chicago/Turabian StyleDodevska, Totka, Dobrin Hadzhiev, and Nina Dimcheva. 2025. "Highly Selective and Stable Electrochemical Sensor for Hydrogen Peroxide—Application in Cosmetics Quality Control" Chemosensors 13, no. 11: 376. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13110376
APA StyleDodevska, T., Hadzhiev, D., & Dimcheva, N. (2025). Highly Selective and Stable Electrochemical Sensor for Hydrogen Peroxide—Application in Cosmetics Quality Control. Chemosensors, 13(11), 376. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13110376







