Enhancement of Ion-Sensitive Field-Effect Transistors through Sol-Gel Processed Lead Zirconate Titanate Ferroelectric Film Integration and Coplanar Gate Sensing Paradigm
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material Specifications
2.2. Formation of PZT Thin Film and Fabrication Process of FeFET
2.3. Fabrication of pH Selective EG Sensing Unit
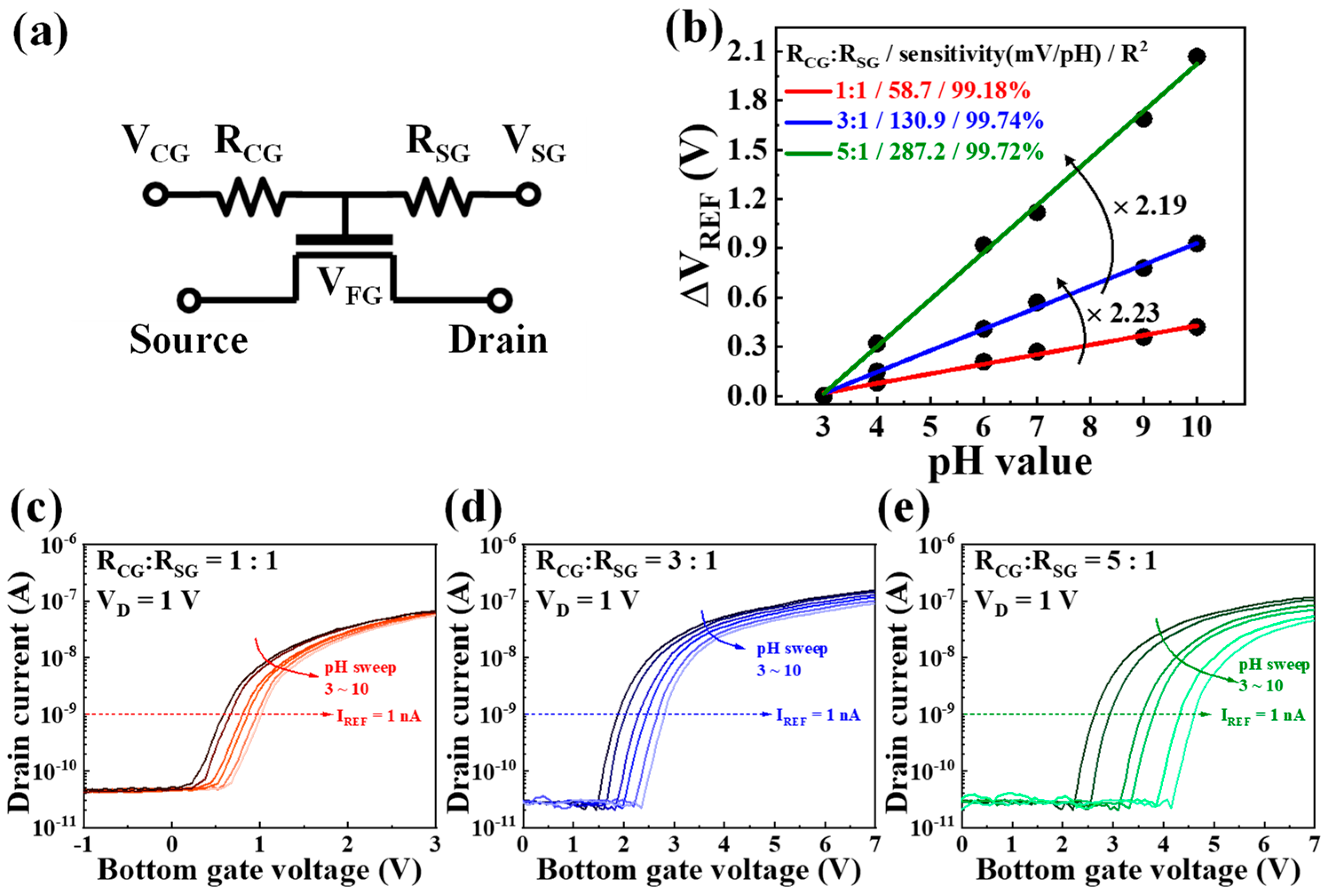
2.4. Design of a Self-Resistive Coupling Circuit for Sensitivity Amplification
2.5. Device Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Electrical Characteristics and Mechanism of PZT-FeFET
3.2. DC Bias Test for the Application of PZT-FeFET as Transducer
3.3. SG-Based EG-ISFET for pH Sensing
3.4. Sensitivity Amplification by Self-Resistive Coupling
3.5. Non-Ideal Effects of the Proposed Sensor Platform
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Capua, L.; Sprunger, Y.; Elettro, H.; Risch, F.; Grammoustianou, A.; Midahuen, R.; Ernst, T.; Barraud, S.; Gill, R.; Ionescu, A.M. Label-Free C-Reactive Protein Si Nanowire FET Sensor Arrays with Super-Nernstian Back-Gate Operation. IEEE Trans. Electron. Devices 2022, 69, 2159–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolai, S.; Tabib-Azar, M. Zika virus field effect transistor. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 4122–4128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Pandey, A.; Chakrabarti, P. Fabrication, characterization, and application of CuO nano wires as electrode for ammonia sensing in aqueous environment using extended gate-FET. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 5779–5786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bausells, J.; Carrabina, J.; Errachid, A.; Merlos, A. Ion-sensitive field-effect transistors fabricated in a commercial CMOS technology. Sens. Actuators B 1999, 57, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olthuis, W.; Robben, M.A.M.; Bergveld, P.; Bos, M.; van der Linden, W.E. pH sensor properties of electrochemically grown iridium oxide. Sens. Actuators B 1990, 2, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moser, N.; Lande, T.S.; Toumazou, C.; Georgiou, P. ISFETs in CMOS and emergent trends in instrumentation: A review. IEEE Sens. J. 2016, 16, 6496–6514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Yu, H.; Liu, X.; Jiang, Y.; Yan, M.; Wu, D.; Dual-Mode, A. A Dual-Mode Large-arrayed CMOS ISFET sensor for accurate and high-throughput PH sensing in biomedical diagnosis. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2015, 62, 2224–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pijanowska, D.G.; Torbicz, W. PH-ISFET based urea biosensor. Sens. Actuators B 1997, 44, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chodavarapu, V.P.; Titus, A.H.; Cartwright, A.N. CMOS ISFET microsystem for biomedical applications. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE International Reliability Physics Symposium, Irvine, CA, USA, 30 October 2005; IEEE Publications: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2005; Volume 2005, p. 4. [Google Scholar]
- Rezaee, A.; Carrabina, J. Dual-gate organic thin-film transistor and multiplexer chips for the next generation of flexible EG-ISFET sensor chips. Sensors 2023, 23, 6577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, T.M.; Lin, L.A.; Ding, H.Y.; Her, J.L.; Pang, S.T. A simple and highly sensitive flexible sensor with extended-gate field-effect transistor for epinephrine detection utilizing InZnSnO sensing films. Talanta 2024, 275, 126178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.H.; Liu, S.B.; Chang, S.P. Performance Improvement of a ZnGa2O4 Extended-Gate Field-Effect Transistor pH Sensor. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 15304–15310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gubanova, O.; Poletaev, A.; Komarova, N.; Grudtsov, V.; Ryazantsev, D.; Shustinskiy, M.; Shibalov, M.; Kuznetsov, A. A novel extended gate ISFET design for biosensing application compatible with standard CMOS. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process 2024, 177, 108387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harb, A.; Istanbullu, M. High sensitive PH sensor with graphene based dual-gate ISFET. J. Nano. Sci. Adv. Mater. 2023, 2, 19–24. [Google Scholar]
- Zain, A.S.M.; Dinar, A.M.; Salehuddin, F.; Hazura, H.; Hanim, A.R.; Idris, S.K.; Hamid, A.M.A. Beyond Nernst sensitivity of ion sensitive field effect transistor based on ultra-thin body box FDSOI. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1502, 012048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-U.; Cho, W.-J. Self-sensitivity amplifiable dual-gate ion-sensitive field-effect transistor based on a high-k engineered dielectric layer. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2023, 62, SC1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun, T.H.; Cho, W.J. High-performance FET-based dopamine-sensitive biosensor platform based on SOI substrate. Biosensors 2023, 13, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, G.; Kweon, S.H.; Kanno, I. Piezoelectric properties of epitaxial Pb(Zr Ti)O3 thin films grown on Si substrates by the sol–gel method. Thin Solid. Film. 2023, 764, 139612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Whatmore, R.W. Sol-gel PZT and Mn-doped PZT thin films for pyroelectric applications. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2001, 34, 2296–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kweon, S.H.; Kanayama, Y.; Tan, G.; Koganezawa, T.; Kanno, I. In-situ study on piezoelectric responses of sol-gel derived epitaxial Pb[Zr,Ti]O3 thin films on Si substrate. J. Eur. Ceram. 2024, 44, 3887–3894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, L.; Bao, X.; Sagoe-Crentsil, K. Effect of acetylacetone on the preparation of PZT materials in sol-gel processing. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2002, 96, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Jie, W.; Yang, Z.; Hao, J. Hybrid heterostructures and devices based on two-dimensional layers and wide bandgap materials. Mater. Today Nano 2020, 12, 100092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, R.M.R.; Gund, V.; Dias, R.A.; Nagaraja, K.K.; Vinayakumar, K.B. CMOS-integrated aluminum nitride MEMS: A review. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2022, 31, 500–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pintilie, I.; Pasuk, I.; Ibanescu, G.A.; Negrea, R.; Chirila, C.; Vasile, E.; Pintilie, L. The impact of the Pb(Zr,Ti)O3-ZnO interface quality on the hysteretic properties of a metal-ferroelectric-semiconductor structure. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 112, 104103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damjanovic, D. Contributions to the piezoelectric effect in ferroelectric single crystals and ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2005, 88, 2663–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.M.; Lee, J.Y.M. Electron trapping process in ferroelectric lead–zirconate–titanate thin-film capacitors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1998, 73, 309–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afanasjev, V.P.; Petrov, A.A.; Pronin, I.P.; Tarakanov, E.A.; Kaptelov, E.J.; Graul, J. Polarization and self-polarization in thin PbZr1−xTixO3 (PZT) films. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 2001, 13, 8755–8763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Dun, G.; Hu, J.; Lin, Z.; Wang, Y.; Lu, T.; Li, P.; Wei, T.; Zhu, J.; Wang, J.; et al. Polarized tunneling transistor for ultrafast memory. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 12374–12382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Wang, X.; Raju, S.; Lin, Z.; Villaroman, D.; Huang, B.; Chan, H.L.W.; Chan, M.; Chai, Y. Low voltage and high ON/OFF ratio field-effect transistors based on CVD MoS2 and ultra high-k gate dielectric PZT. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 8695–8700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, S.K.; Cho, W.J. Ultra-high sensitivity pH-sensors using silicon nanowire channel dual-gate field-effect transistors fabricated by electrospun polyvinylpyrrolidone nanofibers pattern template transfer. Sens. Actuators B 2021, 326, 128835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parizi, K.B.; Xu, X.; Pal, A.; Hu, X.; Wong, H.S.P. ISFET pH sensitivity: Counter-ions play a key role. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido, J.A.; Härtl, A.; Kuch, S.; Stutzmann, M.; Williams, O.A.; Jackmann, R.B. pH sensors based on hydrogenated diamond surfaces. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 86, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.K.; Cho, W.J. High-sensitivity pH sensor based on coplanar gate AlGaN/GaN metal-oxide-semiconductor high electron mobility transistor. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, J.C.; Wang, Y.F. Preparation and study on the drift and hysteresis properties of the tin oxide gate ISFET by the sol-gel method. Sens. Actuators B 2002, 86, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, S.; Rahman, M.T. Micro-heater embedded ISFET pH sensor with high-k gate dielectrics for enhanced sensitivity. Eng. Res. Express 2023, 5, 035068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Jiang, S.Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhu, H.; Chen, L.; Sun, Q.Q.; Zhang, D.W. Ferroelectric HfZrOx-based MoS2 negative capacitance transistor with ITO capping layers for steep-slope device application. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2018, 112, 103104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam Sakib, F.; Hasan, M.A.; Mohona, M.D.; Hossain, M. Negative capacitance dual-gated ISFETs as ultra-sensitive pH sensors. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 48756–48763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, H.; Peng, Y.; Jing, Q.; Zhou, J.; Han, G.; Fu, W. Sensing with extended gate negative capacitance ferroelectric field-effect transistors. Chip 2024, 3, 100074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, L.L.; Chou, J.C.; Chung, W.Y.; Sun, T.P.; Hsiung, S.K. Study on extended gate field effect transistor with tin oxide sensing membrane. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2000, 63, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besleaga, C.; Radu, R.; Balescu, L.M.; Stancu, V.; Costas, A.; Dumitru, V.; Stan, G.; Pintilie, L. Ferroelectric field effect transistors based on PZT and IGZO. IEEE J. Electron. Devices Soc. 2019, 7, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, Y.; Lee, J.Y.; Park, E.; Kim, H.S.; Choi, H.J.; Mun, S.; Kim, Y.; Hur, S.; Yoon, J.H.; Jang, J.S.; et al. Epitaxial PZT film-based ferroelectric field-effect transistors for artificial synapse. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2023, 5, 4549–4555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tue, P.T.; Miyasako, T.; Trinh, B.N.Q.; Li, J.; Tokumitsu, E.; Shimoda, T. Optimization of Pt and PZT films for ferroelectric-gate thin film transistors. Ferroelectrics 2010, 405, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, W.; Bao, S.Y.; Hu, Y.Q.; Deng, X.; Guan, Z.; Chen, B.B.; Zhong, N.; Xiang, P.H. Ferroelectric controlled interfacial effect on the electronic properties of PZT gated IGZO channel thin-film transistors. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2024, 6, 1063–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, E.; Pretsch, E.; Bühlmann, P. Selectivity of potentiometric ion sensors. Anal. Chem. 2000, 72, 1127–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.N.T.; Qiu, S.; Chung, H.-J. Potassium ion selective electrode using polyaniline and matrix-supported ion-selective PVC membrane. IEEE Sens. J. 2018, 18, 9081–9087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.-W.; Huang, S.-R.; Huang, N.-T. Dual Ion-Selective Membrane Deposited Ion-Sensitive Field-Effect Transistor Integrating a Whole Blood Processing Microchamber for In Situ Blood Ion Testing. ACS Sens. 2023, 8, 904–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van den Berg, A.; Grisel, A.; Verney-Norberg, E. An ISFET-based calcium sensor using a photopolymerized polysiloxane membrane. Sens. Actuators B 1991, 4, 235–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, J.C.; Weng, C.Y. Sensitivity and hysteresis effect in Al2O3 gate pH-ISFET. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2001, 71, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamasb, S.; Collins, S.; Smith, R.L. A physical model for drift in pH ISFETs. Sens. Actuators B 1998, 49, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, J.L.; Jan, S.S.; Chou, J.C.; Chen, Y.C. Study on the temperature effect, hysteresis and drift of PH-ISFET devices based on amorphous tungsten oxide. Sens. Actuators B 2001, 76, 624–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousse, L.; Bergveld, P. The role of buried OH sites in the response mechanism of inorganic-gate pH-sensitive ISFETs. Sens. Actuators 1984, 6, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
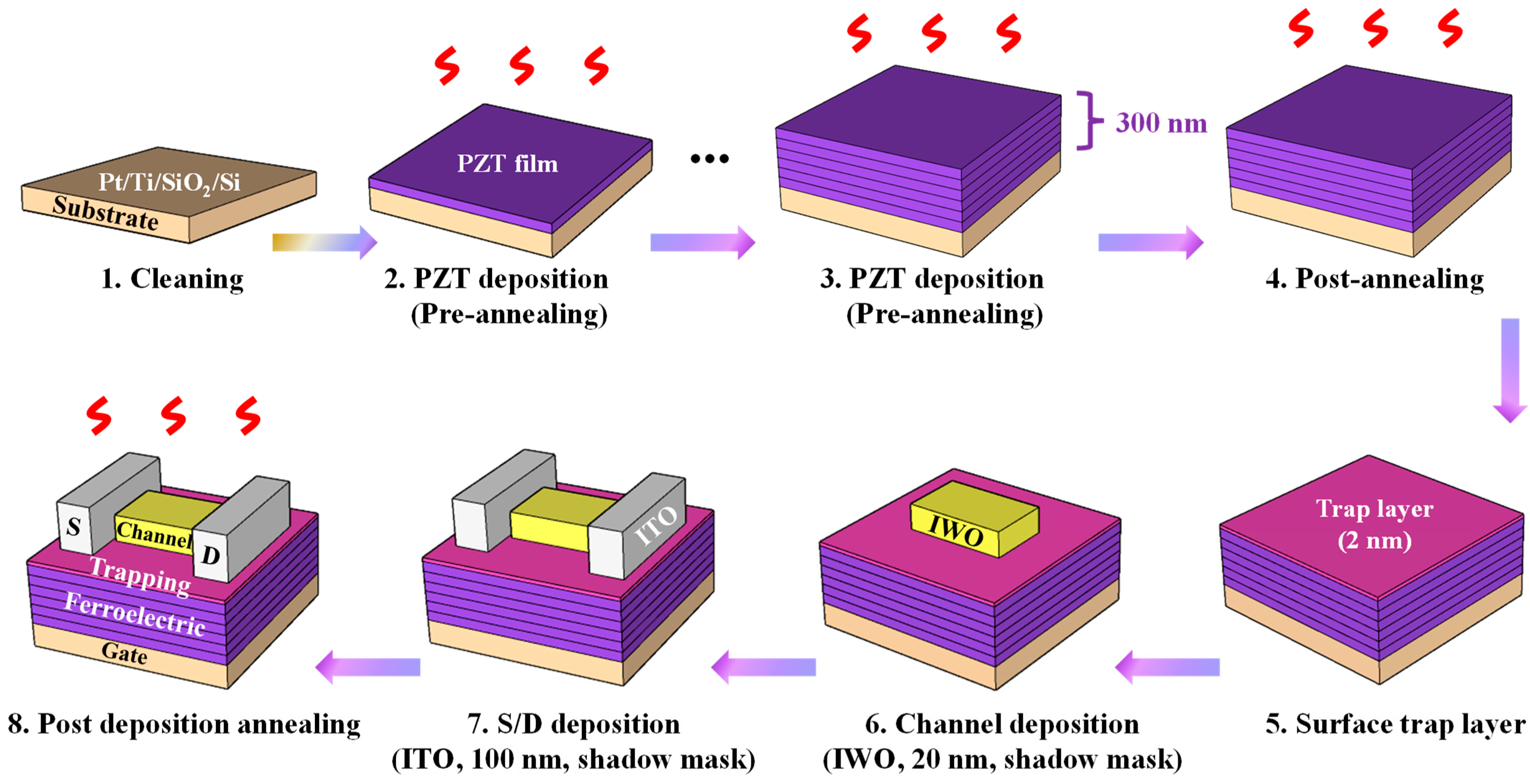

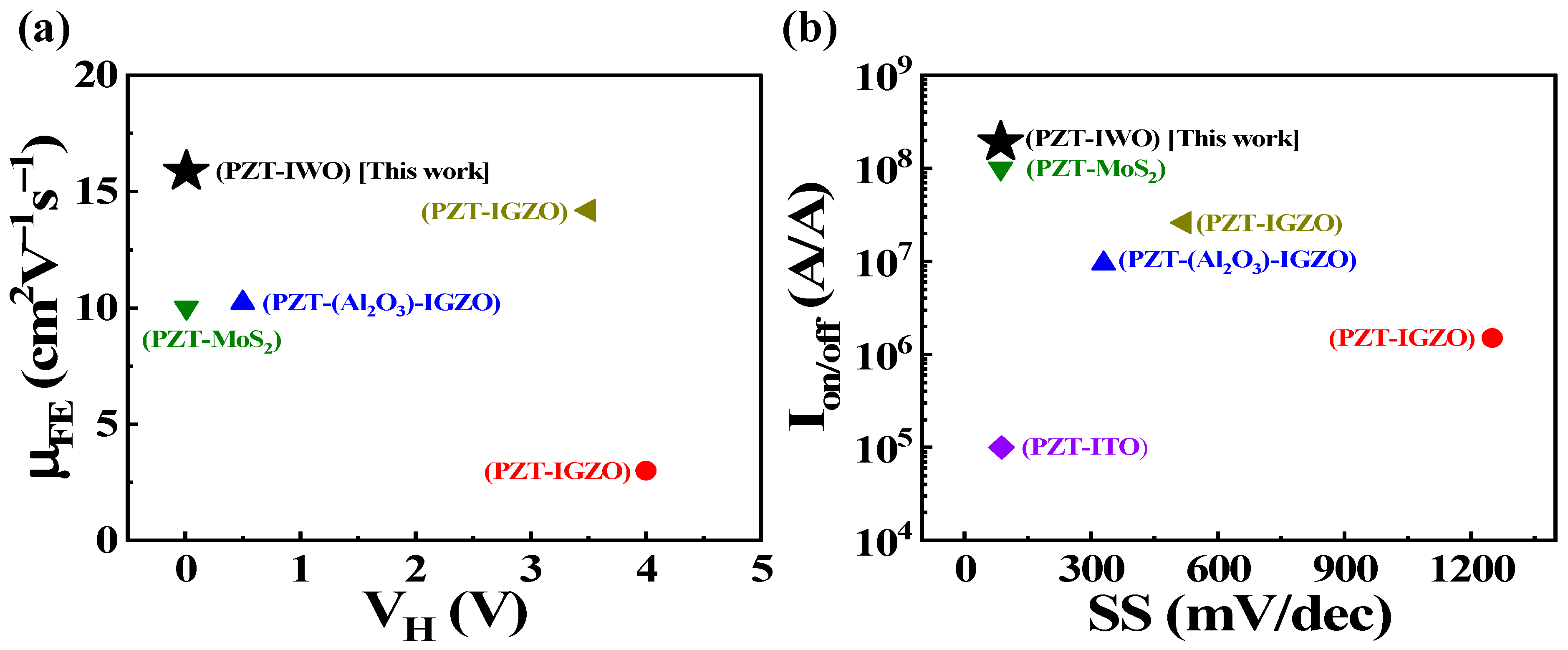



| Channel | VH (V) | Vth (V) | SS (mV/dec) | µFE (cm2V−1s−1) | Ion/off (A/A) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IGZO | 4 | 1.2, 2.6 | 1250 | 1.5, 3 | 1.5 × 106 | [40] |
| IGZO | 0.5 | - | 330 | 10.23 | 9.5 × 106 | [41] |
| MoS2 | 0.01 | 0.2~0.4 | 85.9 | 10.01 | ~108 | [29] |
| ITO | 1.2 | - | 88 | - | 105 | [42] |
| IGZO | 3.5 | - | 520 | 14.2 | 5.6 × 107 | [43] |
| IWO | 0.01 | 0.8 | 85.75 | 15.87 | 1.91 × 108 | This work |
| Amplification Ratio (RCG/RSG) | Hysteresis Voltage (mV) | Drift Rate (mV/h) | Sensitivity (mV/pH) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ×1 (SG mode) | 5.8 | 4.24 | 57.2 |
| ×1 (RC mode) | 6.1 | 4.48 | 58.7 |
| ×3 (RC mode) | 10.1 | 6.82 | 130.9 |
| ×5 (RC mode) | 15.8 | 9.18 | 287.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mah, D.-G.; Oh, S.-M.; Jung, J.; Cho, W.-J. Enhancement of Ion-Sensitive Field-Effect Transistors through Sol-Gel Processed Lead Zirconate Titanate Ferroelectric Film Integration and Coplanar Gate Sensing Paradigm. Chemosensors 2024, 12, 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors12070134
Mah D-G, Oh S-M, Jung J, Cho W-J. Enhancement of Ion-Sensitive Field-Effect Transistors through Sol-Gel Processed Lead Zirconate Titanate Ferroelectric Film Integration and Coplanar Gate Sensing Paradigm. Chemosensors. 2024; 12(7):134. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors12070134
Chicago/Turabian StyleMah, Dong-Gyun, Seong-Moo Oh, Jongwan Jung, and Won-Ju Cho. 2024. "Enhancement of Ion-Sensitive Field-Effect Transistors through Sol-Gel Processed Lead Zirconate Titanate Ferroelectric Film Integration and Coplanar Gate Sensing Paradigm" Chemosensors 12, no. 7: 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors12070134
APA StyleMah, D.-G., Oh, S.-M., Jung, J., & Cho, W.-J. (2024). Enhancement of Ion-Sensitive Field-Effect Transistors through Sol-Gel Processed Lead Zirconate Titanate Ferroelectric Film Integration and Coplanar Gate Sensing Paradigm. Chemosensors, 12(7), 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors12070134





