Abstract
Sotol is a traditional distilled alcoholic beverage produced in Mexico and the United States. Unfortunately, local authorities have detected that these beverages are sometimes adulterated with toxic substances such as ethylene glycol. This illegal practice of adulteration is dangerous and can cause serious health problems for the end consumers. In this work, an alternative, reliable, and rapid method is presented for identifying the presence of ethylene glycol in sotol samples using UV-Vis spectroscopy and neural networks with an accuracy of up to 100%.
1. Introduction
Beyond Tequila and Mezcal, it is often forgotten that Mexico is a true gastronomic universe. Mixology is also gastronomy, “liquid gastronomy” as experts in the field call it, and from the north to the south of the country, recipes and drinks that most people do not know about can be found. In fact, many foreigners are unaware of the existence of sotol, an emblematic distillate of ancestral origin from northern Mexico, mainly from the States of Chihuahua, Durango and Coahuila. The drink is extracted from a plant that is only found in these lands. Since 2002, the drink has had a Designation of Origin (DO). This allowed, two years later, the receipt of a regulation that authorized sotol production in Mexican territory. Although this recognition is relatively young, the history of this liquor goes back hundreds of years. It is known that 800 years ago, sotol was used as a medicinal remedy or as a drink in religious ceremonies by the indigenous people of the north of the country, such as the Rarámuri and Anazasis ethnicities. Thus, its natural production area is located in the physiographic province of the Central Plateau, which is located at an average of 1000 to 2000 m above sea level, between the Sierra Madre Oriental and the Sierra Madre Occidental [1].
Sotol is a drink with a strong character. Its content ranges from 38% to 55% alcohol, and it has a smoky flavor reminiscent of firewood and land. According to the estimates of the Mexican Council of Sotol A.C. and the Sotol Certification Council, 500,000 L of sotol ready for sale are produced annually. It is considered that this industry presents a growth of 5% annually [1]. In recent years, the production of distilled beverages has grown with the tastes of local, national and foreign consumers and has moved from being a regional drink to a traditional Mexican drink with recognition inside and outside of the national territory, bringing with it demand in national and international markets. Given the growing demand for the consumption of spirit drinks, there is a great opportunity with sotol. Different producers in the state of Chihuahua have the DO declaration and therefore can market their product with added value [1].
Sotol is obtained according to the fermentation of rectified musts from the heads of Dasylirion cedrosanum and/or D. duranguensis. This colorless or yellowish alcoholic drink is manufactured in the north of Mexico in the states of Chihuahua, Durango, and Coahuila and in the southern United States in the states of New Mexico and West Texas [2]. According to the Official Mexican Standard NOM-159-SCFI-2004, the sotol beverage is classified into four categories: silver, gold, aged, and extra aged. Their main components are alcohols, aldehydes, esters, and furfural (Table 1) [3,4]. Unfortunately, the Mexican authorities have found substances of different concentrations than those allowed in the regulations in alcoholic beverages [5]. One of these substances is ethylene glycol (C2H6O2), which is a polyhydric alcohol solvent that is illegally added to alcoholic beverages with the purpose of increasing the state of intoxication. Based on the published data, the minimum human lethal dose of ethylene glycol has been estimated at approximately 100 mL for a 70 kg adult or 1.6 g/kg body weight (calculation of dose in mL/kg to mg/kg based on EG density = 1.11 g/L) [6]. The most common symptoms of ethylene glycol poisoning are nervous system depression, coma, renal failure, and cardiovascular collapse [7,8,9]. Therefore, the early identification of beverages adulterated with ethylene glycol is an essential process to protect public health. In order to reduce the number of cases of people poisoned by the ingestion of sotol adulterated with ethylene glycol, adulteration tests should be carried out more frequently by the Mexican authorities, manufacturers, and suppliers. To achieve this goal, it is desirable that the adulteration test be simple, low-cost, and able to be carried out in a short time.

Table 1.
Physicochemical specifications of sotol.
Before now, the most widely used technique for the identification of alcoholic beverage adulterants such as ethylene glycol has been gas chromatography [10]. The main advantage of this analytic technique is its high sensitivity and resolution, which depend on the type of detector incorporated into the gas chromatograph equipment, allowing in some cases the identification of substances with concentrations as low as 1 × 10−12 g. However, there are also other non-destructive techniques that could be considered for the same purpose [11]. These techniques include (a) infrared spectroscopy (analysis of the interaction of infrared light with molecules) [12], (b) Raman spectroscopy (analysis of the inelastic scattering of photons by matter after laser excitation) [13], (c) fluorescence spectroscopy (analysis of the light emissions which take place after the excitation of the electrons in a material) [14], (d) an electronic tongue (this is a multisensor system based on various sensor arrays with limited selectivity and allowing for advanced mathematical data analysis) [15], (e) nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (analysis of the molecular structure of a material by observing and measuring the interaction of nuclear spins when placed in a powerful magnetic field) [16], (f) an electronic nose (captures the fingerprints of volatile organic compounds present in an alcoholic beverage sample using an array of semi-selective sensors) [17], (g) a colorimetric sensor array (produces a chemical interaction between the active center and analyte, which results in chemo-responsive changes in color) [18], (h) a combination of sensors (involves a data fusion approach with various sensors to acquire an optimal response) [19] and UV-Vis spectroscopy [20], which is the selected analytical technique carried out in the present work.
UV-Vis spectroscopy measures the amount of ultraviolet or visible electromagnetic radiation that is absorbed by a sample. This absorbance is influenced by the sample composition and, according to Beer’s law, is proportional to the concentration of the absorbing species. Unlike gas chromatography equipment, the spectrophotometers used for this technique do not require the use of an inert carrier gas, and in some cases, the sample does not require initial preparation [21]. However, sometimes, it is difficult to relate the absorbance bands to the concentration of a specific analyte, especially in cases in which the concentration of the analyte is very low or is found within another substance that has similar absorption bands. In this complicated scenario, the use of computational algorithms has proven to be an alternative solution [22,23].
Regarding tequila beverages, the application of chemometric algorithms is a crucial step for identifying specific compounds that distinguish between various types of tequila, including authentic and counterfeit versions, as well as for distinguishing tequila from other similar products. In the work [24], nonlinear models were employed to analyze the UV-Vis spectra of certified tequilas. The most effective approaches utilized Classification and Regression Trees, Random Forest, and Support Vector Machines, achieving accuracies exceeding 0.98 for calibration and 0.94 for validation.
In [25], the identification and authentication of whiskies using a dynamic evaporative headspace analysis were applied. The compounds of the whisky are obtained using a NIST library search. Based on these compounds, the brand of the whisky can be determined using headspace analysis. In this research, principal component analysis and a two-layer artificial neural network were implemented, where it was found that the artificial neural network had a better accuracy (over 95%).
In this work, an alternative, reliable, and rapid method is presented to identify the presence of ethylene glycol in sotol samples using UV-Vis spectroscopy and neural networks. For this purpose, a database was first created with the absorbance spectra of sotol samples with different concentrations of ethylene glycol. After that, each absorbance spectrum was analyzed and classified correctly using artificial neural networks. It is expected that this method could be used by Mexican authorities, manufacturers, or suppliers interested in identifying sotol adulteration. In addition, an alternative method for the determination of the presence of ethylene glycol in sotol using gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC-MS) was introduced.
Multilayer Artificial Neural Networks
Automatic Learning (AL) and Deep Learning (DL) are machine learning techniques that are based on the human brain. AL and DL algorithms analyze data using a logical structure similar to that used by human beings. AL and DL use smart systems called Multilayer Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs) to process data according to layers. Data flow from the input layer through one or more hidden neural network layers before arriving at the output layer. The layers are ANN nodes which work like the neurons of the human brain. Each node or artificial neuron is connected to another node, and it has an associated value number and value threshold. When there is an activation, the node sends its value number as input to the next layer. It is activated only if its output is above the specified value threshold. Otherwise, no data are transmitted [26,27]. An artificial neuron with n inputs, consisting of:
- A set of inputs xi = x1, x2, x3, …, xn.
- The synaptic weights wi = w1, w2, w3, …, wn corresponding to each input.
- An aggregation function, ∑.
- An activation function .
- An output.
The artificial neuron can adapt to the surrounding environment and learn from it by modifying the value of its synaptic weights, and for this reason, they are known as the free parameters of the model since they can be modified and adapted to perform a specific task. In this model, the neural output Y is given by (1).
The activation function is chosen according to the task performed by the artificial neuron. Among the most common within the field of artificial neural networks, we can highlight the sigmoidal function, linear function, hyperbolic tangent sigmoid function, and rectified linear unit function. For training the artificial neural network, the back-propagation method is often used to update the weights of the artificial neurons in each epoch. The algorithm for learning can be the descendent gradient, with the variants of learning rate, momentum, and optimizer, among others.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. UV-Vis Spectroscopy and the Artificial Neural Network: The Proposed Method
For this study, a bottle of Sotol ONÓ (produced by “Destilados y Productos Noa Norte” from Mexico) was purchased at a conventional store located in the city of Chihuahua, and a bottle of ethylene glycol (HOCH2CH2OH, GC purity greater than 99% and water content less than 0.20%) from J.T. Baker (Phillipsburg, NJ, USA). In order to evaluate the presence of ethylene glycol (EG) in the sotol, 13 different mixtures were prepared by changing the volume percentage of ethylene glycol, defined as the amount of ethylene glycol (in mL) present in 100 mL of sotol (v/v%). Each mixture represents a group of samples with similar characteristics, labeled as class 1–13; see Table 2. For instance, class 1 represents a group of samples of pure sotol, and class 2 a mixture of 95 mL of sotol and 5 mL of ethylene glycol. The absorbance spectra of each class were acquired 50 times using UV-Vis equipment (Hach UV-Vis model DR 5000 spectrophotometer, Hach Company, Loveland, CO, USA) in the interval from 200 nm to 1100 nm with a step of 1 nm. In all the experiments, a quartz rectangular cell with a 10 mm pathlength was filled with the sample. Prior to measurement, the surfaces of the cell were cleaned with lens paper wetted with spectro-grade ethanol. Special care was taken to avoid scratching and leaving fingerprints on the surface of the cell. The total number of samples generated from the mixture of sotol and ethylene glycol was 650, 50 of each one of the 13 classes.

Table 2.
Volume percentage of ethylene glycol in each class.
For the classification experimentation, the entire absorption spectrum of the samples was used in the training and testing, like the input for the artificial neural network, with its output allowing the classification of the corresponding class. In order to evaluate the effect of the number of training/testing samples on the accuracy of the classification, the dataset was partitioned into three training and test databases as follows: 80% training and 20% testing (520 training and 130 testing), 50% and 50% (325 training and 325 testing) and 20% and 80% (130 training and 520 testing).
A multilayer artificial neural network (ANN) was implemented for classification. Three different architectures were developed for the three databases created. The architectures were created with 2 hidden layers: for 80% training/20% testing samples, the first layer with 325 neurons and the second layer with 163 neurons; for 50%/50%, the first layer with 130 neurons and the second layer with 65 neurons and for 20%/80%, the first layer with 65 neurons and the second layer with 33 neurons.
In the three architectures, the activation functions used in the first, second, and output layers were sigmoidal tangent, sigmoidal tangent, and sigmoidal logarithm, respectively; the goal error and epochs number were 0.000001 and 8000, respectively. Gradient descent with momentum and an adaptive learning rate (GDX), gradient descent with an adaptive learning rate (GDA), and scaled conjugate gradient (SCG) were the learning algorithms for backpropagation used for the training of the artificial neural network. An architecture of the artificial neural network for the classification of sotol adulteration is presented in Figure 1.
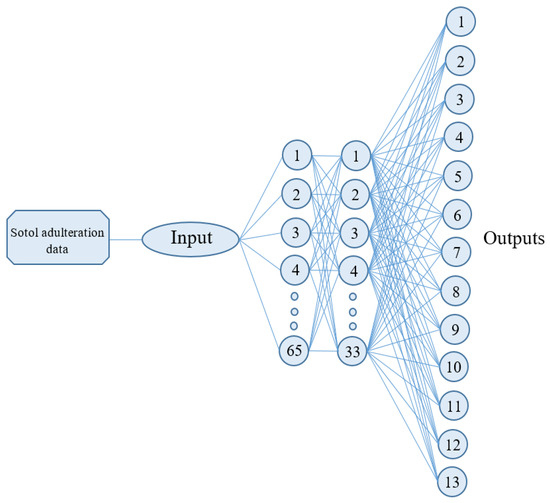
Figure 1.
Architecture example of artificial neural network used in the classification of sotol adulteration which was created with two hidden layers of 65 and 33 neurons and 13 outputs.
To measure the efficiency of the classification models, the accuracy, precision, and recall metrics are implemented. Accuracy is the percentage of predictions that the model performs correctly. Accuracy is defined in Equation (2):
Precision represents the percentage of positive classifications of each class that are identified correctly. Precision is defined in Equation (3):
Recall represents the percentage of positive classifications of each class that are identified correctly. Recall is defined in Equation (4):
where:
- TP = True Positive, indicates correct identification of the class.
- FP = False Positive, indicates incorrect identification of the class.
- FN = False Negative, indicates incorrect identification of another class.
Also, to test the robustness of the architectures of the artificial neural networks (ANN) implemented in this work, a 10-fold cross-validation test was performed. The cross-validation consisted of generating 10 variations of the database with the same proportions and evaluating and calculating the average of the 10 variations with the proposed architectures for an ANN.
2.2. Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry: An Alternative Method
Ethylene glycol (EG) was used to prepare solutions of EG in sotol at the same concentrations employed for the UV-Vis test (from 0 to 60%). Due to the high concentrations of the EG solutions, ethanol (Sigma-Aldrich, Saint Louis, MI, USA) was used to prepare the working samples, diluting 100-fold the solutions of EG in sotol. Therefore, 50 µL of the solutions of EG in sotol was added to 4.9 mL of ethanol. An EG standard (0.1% of EG in ethanol) was run to identify its retention time. Butyl acetate (Honeywell, Seelze, Germany) was employed as an internal standard. A stock solution of butyl acetate was prepared at 5000 ppm in ethanol, and 50 µL was added to each solution to obtain a concentration of 500 ppm.
For the determination of the presence of ethylene glycol in the sotol at several concentrations, the Agilent 5975C chromatography–mass spectrophotometer equipment (Agilent Technologies Manufacturer, Santa Clara, CA, USA) was employed. The GC-MS was provided for using an Agilent HP-INNOWax column 30 m × 0.25 mm, 0.25 μm. The injector and the detector were set at 250 °C and 230 °C, respectively. The method used was set according to [28] with modifications. The oven temperature was initially set at 100 °C (1 min), raised to 170 °C at a rate of 10 °C/min, then raised to 230 °C at a rate of 30 °C/min and held for 4 min. One µL of the sample was manually injected at a split ratio of 10:1. Helium was used as the carrier gas with a flow rate of 2.0 mL/min. Ethylene glycol was detected in split mode without solvent delay. Selected Ion Monitoring mode (SIM) was set in the MS detector to obtain the data for the chromatogram. The monitored fragments were at m/z 31 and 43 for EG and 45 and 58 for butyl acetate.
3. Results
3.1. Absorbance Spectra
Figure 2 shows the absorption spectra of the pure substances of sotol and ethylene glycol. The spectrum of sotol presents a strong absorption band centered at 278 nm and two small shoulders at 908 nm and 987 nm. On the other hand, the absorbance results for ethylene glycol show three small shoulders of absorption around 268 nm, 925 nm, and 1011 nm. In order to compare the absorbance results, the area under the curve of each absorption band was calculated, and the results are presented in Table 3. In the near-ultraviolet region, the area under the absorbance curve of sotol is 23 times higher than that of ethylene glycol, but in the near-infrared region, they are very similar, at a ratio of 1.6.
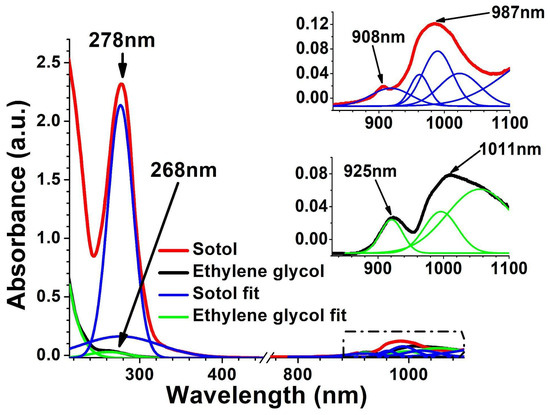
Figure 2.
Absorbance spectra of sotol (class 1) and ethylene glycol (class 13). The inset figure shows the small bands of sotol and ethylene glycol in the infrared region from 880 nm to 1100 nm.

Table 3.
Area under the absorbance curve for sotol and ethylene glycol in the near-ultraviolet (230–425 nm) and near infrared region (850–1100 nm).
Figure 3 shows the evolution of the absorption spectra depending on the concentration of ethylene glycol. It is observed that the intensity of the main absorption band at 278 nm decreases with an increasing ethylene glycol concentration. As mentioned before, the absorbance of ethylene glycol in this region is very weak, and therefore the intensity of this band decreases proportionally to the sotol concentration. In addition, small changes in both the position and peak intensity of the absorbance bands at 908 nm and 987 nm are observed.
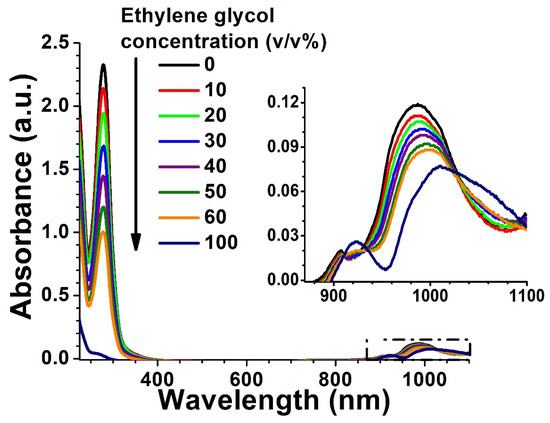
Figure 3.
Sotol absorption spectra as a function of ethylene glycol concentration. The inset figure shows the small bands of sotol and ethylene glycol in the infrared region from 880 nm to 1100 nm. For the purpose of improving the analysis of the figure, curves with concentrations of (v/v%) 5, 15, 25, 35 and 45 were intentionally removed.
3.2. The Artificial Neural Network
The accuracy results obtained from the artificial neural network for the datasets 80% training and 20% testing, 50% training and 50% testing, and 20% training and 80% testing are presented in Table S1, Table S2 and Table S3, respectively. It is worth mentioning that 50 experiments were performed for each dataset but only 10 experiments were presented in these tables.
The accuracy results for the dataset with 80% training and 20% testing show that a 100% average classification accuracy can be achieved using any of the three algorithms. This means that all the testing samples (130) in this dataset were classified correctly.
The same average classification accuracy (100%) was achieved in the second 50% training and 50% testing dataset (Table S2) using the scaled conjugate gradient algorithm, but a small decrease, less than 2%, in the average classification was observed when using gradient descent momentum and an adaptive learning rate and gradient descent with adaptive learning rate algorithms, which indicates that the optimal learning algorithm for this classification model is the scaled conjugate gradient algorithm. This algorithm uses second-order derivatives, which usually improve the speed of convergence in backpropagation. This could have accelerated the learning of the experimental data and therefore the accuracy of the classification model.
On the other hand, it is observed that the average classification accuracy decreases when the number of total training samples is less than 325, that is, 25 training samples for each class. The best accuracy and the average classification accuracy obtained for the 20% training/80% testing dataset were 99.81% and 96.38%, respectively (Table S3). These results indicate that some of the predicted values were falsely predicted; these errors are best known as false positives (the actual value was negative, but the model predicted a positive value) or false negatives (the actual value was positive, but the model predicted a negative value).
In order to show an example of the origin of this error, a confusion matrix for experiment #1 is presented in Figure 4. This is a square NxN matrix, where N = 13 corresponds to the number of different classes, the columns represent the original or expected class distribution, the rows represent the predicted or output distribution by the classifier and each of their elements contain the predicted value.
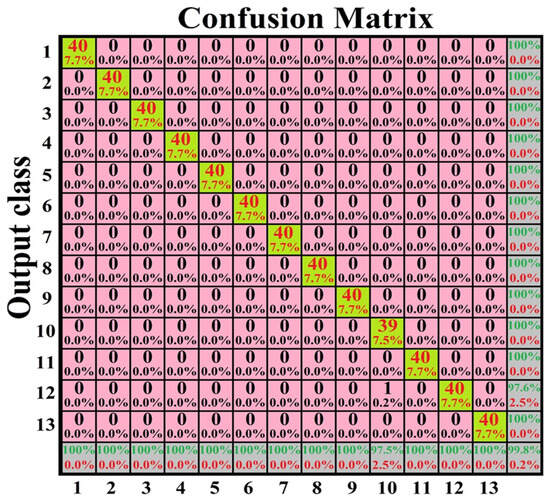
Figure 4.
Confusion matrix of artificial neural network with the scaled conjugate gradient learning algorithm’s best result for the dataset with 20% training and 80% testing samples.
The confusion matrix shows that of a total of 520 testing samples, only 1 from class 10 was classified incorrectly as class 12. It is worth mentioning that no type of data preprocessing was necessary to achieve 100% accuracy. However, this technique could be used or recommended if the number of adulterant substances increases or the training data decreases.
The precision in the experiments undertaken for each class in the three datasets is presented in Table S4. Precision represents the percentage of correct classification when a sample is classified as one class; for example, for the 20/80 dataset with the SCG algorithm, this indicates that when a class was identified, it was correct on average 99.81% of the time at the moment when an attempt was made to identify it.
The recall in the experiments obtained for each class in the three datasets is presented in Table S5. Recall represents the percentage of correctly identified classes; for example, for the 20/80 dataset with an SCG algorithm, the model presents on average a recall of 99.81%, namely correctly identifying 99.81% of the samples of the classes.
In machine learning, the cross-validation technique to evaluate the performance of a model on the database of a certain problem is commonly used. This technique consists of dividing the database utilized into k-folds or subsets, using part of the folds for the testing set and the remaining part for training the model. The process of dividing k-folds is repeated k times, each time generating a different subset for the testing and training set. Finally, the average of the results for each testing set is calculated to obtain robustness in the model performance. In this work, we used the k-fold cross-validation technique [29]. The results of the 10-fold cross-validation are presented in Table S6. Cross-validation is performed for the model with the best results in terms of accuracy in each database implemented, which is the architecture of an artificial neural network with a scaled conjugated gradient (ANN-SCG) using a different number of neurons in the two hidden layers. A total of 50 experiments were performed for the three datasets, but only 3 experiments were presented. The average for the datasets 80/20 and 50/50 decreases in comparison with that obtained in Tables S1 and S2, but the results maintain a good performance of above 99% for classification; the results for the dataset 20/80 decreased by 4 points in comparison with those obtained in Table S3.
3.3. Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry
Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry was employed to determine the EG intentionally added in several concentrations to sotol. Figure 5 shows the chromatograms obtained for several concentrations of EG in sotol displayed one after another. Retention times of 1.88 and 6.11 correspond to butyl acetate and EG, respectively. The chromatogram showed an appropriate distance between both peaks. An acceptable peak shape was achieved by modulating the gas flow rate in the split mode, and it follows a regular relation: the higher the concentration of ethylene glycol in the working sample, the larger the areas of the peak in the chromatogram.
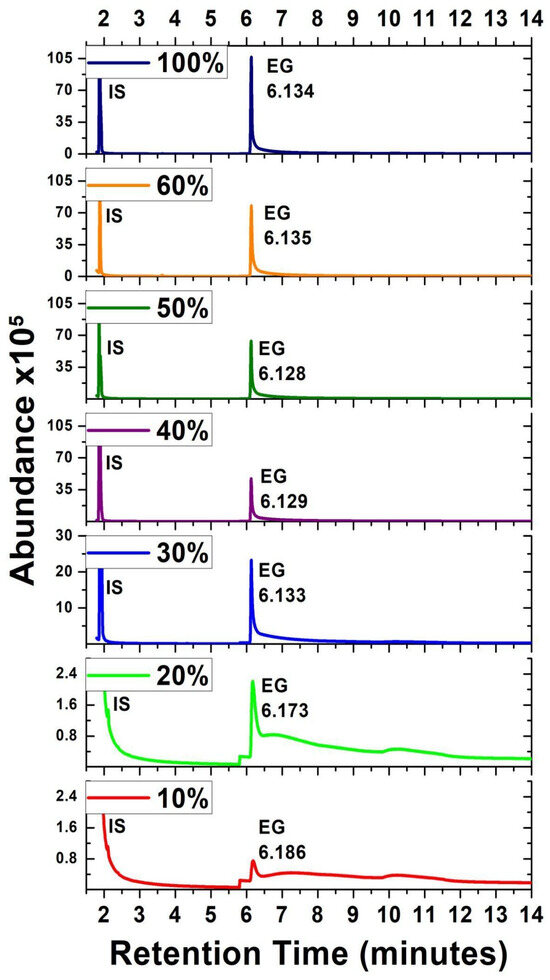
Figure 5.
Chromatograms of sotol with different ethylene glycol concentrations. For the purpose of improving the analysis of the figure, chromatograms with concentrations of (v/v%) 5, 15, 25, 35, and 45 were intentionally removed.
4. Conclusions
A reliable and rapid method is presented to identify the concentration of ethylene glycol in sotol samples using UV-Vis spectroscopy and artificial neural networks. For this purpose, three different learning algorithms and partitions of the dataset were evaluated. The best accuracy results were obtained using the scaled conjugate gradient learning algorithm and a dataset partition of 50% for training and 50% for testing, which means that at least 25 samples of each class are required for training the machine. The results indicate that it is possible to classify samples of sotol with concentrations of ethylene glycol as low as 5 v/v% with an accuracy of 100%. This high performance could be explained by the process of weight updates generated using the SCG allowing for a better convergence of the gradient and therefore resulting in better weights, which allows for better classification learning. It is worth mentioning that these results apply exclusively to the sotol ONÓ adulterated with ethylene glycol, and new datasets would be needed to identify ethylene glycol in other sotol varieties, but good results could be expected considering the current performance of the neural network.
In addition, the presence of EG in the sotol samples was determined using GC-MS, which is a method with a high selectivity, amply recommended for application to adulterant control in spirit beverages. Nevertheless, further work is required to develop a method involving GC-MS and artificial neural networks.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/chemosensors12030046/s1. Table S1. Results on accuracy, precision, and recall obtained from the artificial neural network using scaled conjugate gradient (SCG), gradient descent momentum, and an adaptive learning rate (GDX) and gradient descent with adaptive learning rate (GDA) learning algorithms for the dataset with 80% training and 20% testing samples. Table S2. Results on accuracy obtained from the ANN using SCG, GDX, and GDA algorithms for the dataset with 50% training and 50% testing samples. Table S3. Results on accuracy obtained from the ANN using SCG, GDX, and GDA algorithms for the dataset with 20% training and 80% testing samples. Table S4. Results on precision for the best accuracy obtained for each class from the ANN in Tables S1–S3, using SCG, GDX, and GDA learning algorithms for the datasets with 80% training and 20% testing (80/20), 50% training and 50% testing (50/50) and 20% training and 80% testing (20/80) samples. Table S5. Results on recall for the best accuracy obtained for each sample class from the ANN in Tables S1–S3, using SCG, GDX, and GDA learning algorithms for the datasets with 80% training and 20% testing (80/20), 50% training and 50% testing (50/50) and 20% training and 80% testing (20/80) samples. Table S6. Results on accuracy for the 10-fold cross-validation obtained using the ANN using a SCG for the three datasets.
Author Contributions
Investigation, R.N.-G., J.J.L., A.M.-M., I.S., J.R.L.-M. and F.G.; writing—original draft preparation, R.N.-G., A.M.-M. and F.G.; software, A.M.-M. and F.G.; writing—review and editing, R.N.-G., J.J.L., A.M.-M., I.S., J.R.L.-M. and F.G.; super-vision, R.N.-G.; project administration, R.N.-G.; validation, I.S. and J.R.L.-M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data can be made available by contacting the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
Authors would like to thank CONAHCYT for the postdoctoral scholarship granted to J. J. Leal-Ramos and to J.R. Linares-Morales.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Madrid-Solórzano, J.M.; García-Alcaraz, J.L.; Macías, E.J.; Cámara, E.M.; Fernández, J.B. Life Cycle Analysis of Sotol Production in Mexico. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2021, 5, 769478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Gallegos, A.C.; Cruz-Requena, M.; Castillo-Reyes, F.; Rutiaga-Quiñones, O.M.; Sepulveda Torre, L.; Paredes-Ortíz, A.; Soto, O.N.; Rodriguez-Herrera, R. 5—Sotol, an Alcoholic Beverage with Rising Importance in the Worldwide Commerce. In Alcoholic Beverages, 1st ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2019; Volume 7, pp. 141–160. [Google Scholar]
- NOM-159-SCFI-2004 Norma Oficial Mexicana NOM-159-SCFI-2004, Bebidas Alcohólicas-Sotol-Especificaciones y Métodos de Prueba. Planta 2004. Available online: http://www.ordenjuridico.gob.mx/Documentos/Federal/wo45110.pdf (accessed on 7 March 2024).
- De la Garza, T.H.; Martínez, M.; Lara, L.; Rodríguez-Herrera, R.; Rodríguez-Martínez, J.; Aguilar, C.N. Production of a Mexican Alcoholic Beverage: Sotol. Res. J. Biol. Sci. 2008, 3, 566–571. [Google Scholar]
- Secretaría de Salud; Comisión Nacional Contra las Adicciones; Dirección de la Oficina Nacional para el Control del Tabaco y Alcohol Intoxicación Por Bebidas Alcohólicas Adulteradas En México. 2020. Available online: https://www.gob.mx/salud/conadic/documentos/intoxicacion-por-bebidas-alcoholicas-adulteradas-en-mexico (accessed on 7 March 2024).
- Hess, R.; Bartels, M.J.; Pottenger, L.H. Ethylene glycol: An estimate of tolerable levels of exposure based on a review of animal and human data. Arch. Toxicol. 2004, 78, 671–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, L.B.; Schreiner, G.E.; Feys, J. The Nephrotoxic Lesion of Ethylene Glycol. Ann. Intern. Med. 1957, 46, 611–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barceloux, D.G.; Krenzelok, E.P.; Olson, K.; Watson, W. American Academy of Clinical Toxicology Practice Guidelines on the Treatment of Ethylene Glycol Poisoning. Ad Hoc Committee. J. Toxicol. Clin. Toxicol. 1999, 37, 537–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriarty, R.W.; McDonald, R.H. The Spectrum of Ethylene Glycol Poisoning. Clin. Toxicol. 1974, 7, 583–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNair, H.M.; Miller, J.M. Introduction. In Basic Gas Chromatography, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008; Volume 1, pp. 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Arslan, M.; Tahir, H.E.; Zareef, M.; Shi, J.; Rakha, A.; Bilal, M.; Huang, X.; Li, Z.; Zou, X. Recent Trends in Quality Control, Discrimination and Authentication of Alcoholic Beverages Using Nondestructive Instrumental Techniques. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 107, 80–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, A.; Montero-Fernández, I.; Monago-Maraña, O.; Martín-Tornero, E.; Martín-Vertedor, D. Acrylamide–Fat Correlation in Californian-Style Black Olives Using Near-Infrared Spectroscopy. Chemosensors 2023, 11, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller Molnár, C.; Berghian-Groșan, C.; Măgdaș, D.A.; Cîntă Pînzaru, S. Surface-Enhance Raman Spectroscopy Detection of Thiabendazole in Frozen Food Products: The Case of Blueberries and Their Extracts. Chemosensors 2023, 11, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, J.; Nørgaard, L.; Bro, R.; Engelsen, S.B. Multivariate Autofluorescence of Intact Food Systems. Chem. Rev. 2006, 106, 1979–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlasov, Y.; Legin, A.; Rudnitskaya, A.; Di Natale, C.; D’Amico, A. Nonspecific sensor arrays (“electronic tongue”) for chemical analysis of liquids (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2005, 77, 1965–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proietti, N.; Capitani, D.; Aru, V.; Bellomaria, A.; Bertocchi, F.; Botta, B.; Cagliani, L.R.; Caligiani, A.; Capozzi, F.; Çela, D. NMR Applications in Food Analysis-Part B. In Analytical Chemistry: Developments, Applications and Challenges in Food Analysis; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 255–296. [Google Scholar]
- Röck, F.; Barsan, N.; Weimar, U. Electronic Nose: Current Status and Future Trends. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 705–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Askim, J.R.; Suslick, K.S. The Optoelectronic Nose: Colorimetric and Fluorometric Sensor Arrays. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 231–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borràs, E.; Ferré, J.; Boqué, R.; Mestres, M.; Aceña, L.; Busto, O. Data Fusion Methodologies for Food and Beverage Authentication and Quality Assessment—A Review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 891, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philippidis, A.; Poulakis, E.; Kontzedaki, R.; Orfanakis, E.; Symianaki, A.; Zoumi, A.; Velegrakis, M. Application of Ultraviolet-Visible Absorption Spectroscopy with Machine Learning Techniques for the Classification of Cretan Wines. Foods 2020, 10, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sellitto, P.; Di Noia, A.; Del Frate, F.; Burini, A.; Casadio, S.; Solimini, D. On the Role of Visible Radiation in Ozone Profile Retrieval from Nadir UV/VIS Satellite Measurements: An Experiment with Neural Network Algorithms Inverting SCIAMACHY Data. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2012, 113, 1429–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Zhang, J.; Lu, W. Characterizing Variances of Adulterated Extra Virgin Olive Oils by UV-Vis Spectroscopy Combined with Analysis of Variance-Projected Difference Resolution (ANOVA-PDR) and Multivariate Classification. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 4360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerslake, F.; Longo, R.; Dambergs, R. Discrimination of Juice Press Fractions for Sparkling Base Wines by a UV-Vis Spectral Phenolic Fingerprint and Chemometrics. Beverages 2018, 4, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Caballero, G.; Andrade, J.M.; Olmos, P.; Molina, Y.; Jiménez, I.; Durán, J.J.; Fernandez-Lozano, C.; Miguel-Cruz, F. Authentication of Tequilas Using Pattern Recognition and Supervised Classification. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 94, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swift, J.R.; Turner, M.A.; Reynolds, J.C. A Rapid Dynamic Headspace Method for Authentication of Whiskies Using Artificial Neural Networks. Food Chem. Adv. 2023, 3, 100417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, B.; Titterington, D.M. Neural Networks: A Review from a Statistical Perspective. Stat. Sci. 1994, 9, 2–30. Available online: http://www.jstor.org/stable/2246275 (accessed on 7 March 2024).
- McCulloch, W.S.; Pitts, W. A Logical Calculus of the Ideas Immanent in Nervous Activity. Bull. Math. Biophys. 1943, 5, 115–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldeira, L.; Madureira, F.; Maia, T.; Muller, C.; Fernandes, C. Simultaneous quantification of ethylene glycol and diethylene glycol in beer by gas chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2020, 346, 128871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruni, M.E.; Lazzaroli, V.; Perboli, G.; Vandoni, C. Machine Learning to Forecast Rainfall Intensity. In Proceedings of the IEEE 47th Annual Computers, Software, and Applications Conference (COMPSAC 2023), Torino, Italy, 26–30 June 2023; pp. 1762–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).