Abstract
Accurate and effective diagnosis and individualized management of gout can be potentially achieved by detecting uric acid (UA) and xanthine (XT) simultaneously using an easy-to-use method. Herein, we report simultaneous detection of UA and XT using a 3-dimensional (3D) macroporous gold nanoparticle-incorporated reduced graphene oxide–carbon nanotube nanocomposite (GNP/rGO-CNT). The GNP/rGO-CNT was simply prepared on a glassy carbon electrode (GCE) by one-step electrochemical deposition/co-reduction. It displayed highly sensitive and selective responses to UA and XT, showing excellent stability and good reproducibility in neutral pH. It was demonstrated that 3D GNP/rGO-CNT on GCE could detect UA and XT in human saliva and blood serum simultaneously. This GNP/rGO-CNT for simultaneous detection of UA and XT in human body fluids can be utilized for monitoring drug adherence for gout treatment, together with gout diagnosis.
Keywords:
uric acid; xanthine; simultaneous detection; saliva; serum; 3D reduced graphene oxide; nanocomposite 1. Introduction
Gout, the most common form of inflammatory arthritis, is characterized by deposition of monosodium urate (MSU) monohydrate in synovial fluid and other tissues [1]. Its prevalence, incidence, and years lived with have been increasing globally [2]. Hyperuricemia is defined as a serum uric acid (UA) level of more than 7.0 mg/dL [416 μmol/L] in men or more than 6.0 mg/dL [357 μmol/L] in women. It is the most important risk factor for gout. Although a definite diagnosis of gout is made by demonstration of MSU crystals in synovial fluid or tophus aspirate, sampling sometimes fails. In addition, MSU crystal identification is considerably dependent on an observer [3]. Therefore, clinical diagnosis of gout is mainly based on the presence of hyperuricemia and symptoms suggestive of acute or chronic gout. However, it is well recognized that normouricemia is common in acute gout attacks [1,4], which might cause misdiagnosis and lead to unnecessary cost and time losses.
Recent gout treatment guidelines [5] recommend a treat-to-target approach by achieving and maintaining a serum urate level <6 mg/dL. Drug compliance, under-dosing, and impaired response to urate-lowering agents can influence the achievement of treatment target [6]. In a real-world setting, less than 50% of gout patients are adhered to urate-lowering agents [7]. Pill counts and patient self-reports frequently used to monitor adherence are of low reliability [8], and measurements of drugs and their metabolites by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) are often limited due to accessibility. Thus, for more accurate and effective diagnosis and treatment of gout, additional biochemical indicators and an easy-to-use method are needed.
As UA is produced from xanthine (XT) and hypoxanthine by xanthine oxidase, XT is the precursor metabolite of UA in the purine metabolic pathway [9]. Zhao et al. [10] have shown that XT and hypoxanthine concentrations are increased in gout patients whose UA levels are abnormally high. XT levels are reportedly higher in gout patients than those in healthy controls regardless of serum urate levels [11]. Moreover, xanthine oxidase inhibitors such as allopurinol and febuxostat significantly increase XT levels whereas they significantly decrease UA [12,13]. Based on these findings, simultaneous detection of UA and XT might be helpful in the diagnosis and individualized management approach for gout.
Until now, high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) [11,14,15] and electrochemical methods [16,17,18,19] have been utilized to simultaneously determine UA and XT in human samples such as serum and urine. Although HPLC is a highly sensitive and precise method, it has some limitations, such as complex sample preparation and time-consuming procedure, as well as expensive instruments and experts. On the contrary, electrochemical sensors can be used as alternatives due to their high sensitivity, rapid response, and simplicity [20,21,22,23]. In particular, non-enzymatic electrochemical sensors [24,25,26] have been employed for multiple analysis because they are more stable and cost-effective than enzymatic sensors, which require specific enzymes such as uricase or xanthine oxidase. A variety of modified electrodes have been proposed for simultaneous detection of UA and XT, including carbon or graphene derivatives [18,20] and their composites with metal nanoparticles or polymer [19,21,22,23,24,25,26]. In particular, reduced graphene oxide (rGO) has received great attention in electrode material due to the good electrical conductivity, excellent physical and chemical properties, and high electrochemical activity [20,24,26]. However, the strong π–π stacking interaction of each rGO sheet causes restacking or aggregation of rGO sheets, consequently reducing the surface area. Recently, Ghanbari et al. [27] have reported a simultaneous determination of UA and XT using a nanocomposite synthesized from electropolymerized L-cysteine, gold nanoparticle (GNP), boron atom (B), and nitrogen atom (N) co-doped rGO. Doping of rGO with B and N increases the surface area because they increase the interlayer spacing of rGO sheets [27]. Although this nanocomposite showed a high sensitivity and selectivity, it required a complicated and time-consuming process with high temperature for synthesis of B and N co-doped rGO, as well as additional two steps for electrodeposition. In a previous study, we have reported three-dimensional (3D) macroporous GNP-incorporated rGO-carbon nanotube (CNT) nanocomposites on a glassy carbon electrode (GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE) using a single-step, one-pot electrochemical synthesis without any template, catalyst, or high temperature [28]. A 3D rGO-based nanocomposite has been attracting significant attention in the field of electrochemical sensor due to its large surface area, fast charge transfer, and easy mass transport [29,30]. Therefore, improved electronic characteristics of macroporous rGO nanocomposites will be helpful for separating electrochemical signals of multiple analytes with enhanced currents compared with other electrodes.
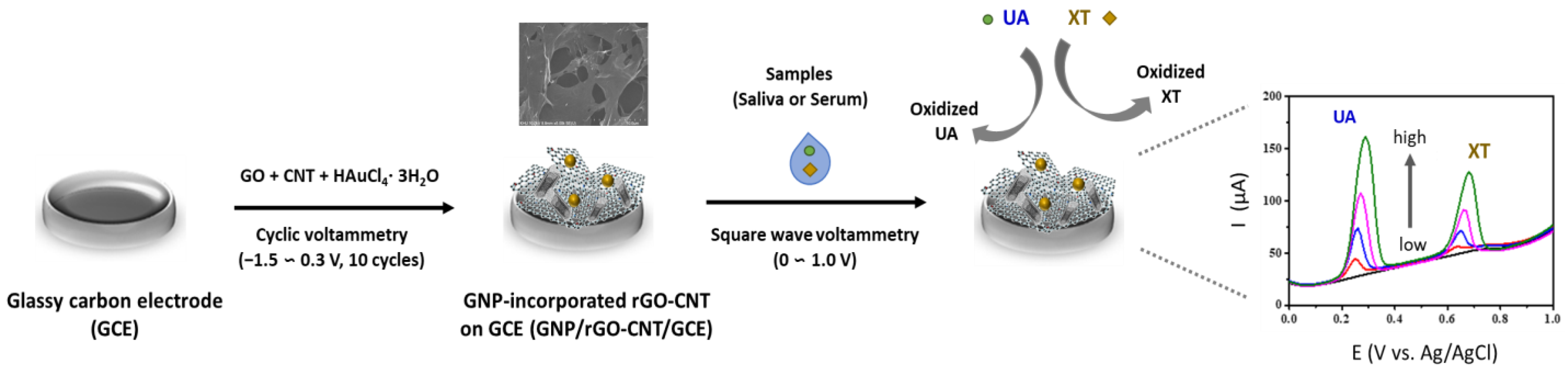
In this study, we introduce a sensitive non-enzymatic electrochemical detection of UA and XT utilizing 3D macroporous GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE fabricated by a one-step electrochemical deposition and co-reduction method. The prepared GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE showed good electrocatalytic activity to the oxidation of UA and XT. We investigated the analytical performance of GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE, including its sensitivity, selectivity, and reproducibility. Finally, it was used for simultaneous detection of UA and XT in human saliva and blood serum samples. A schematic illustration of the fabrication and sensing protocol of the GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE for simultaneous detection of UA and XT is shown in Figure 1.
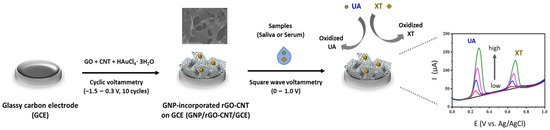
Figure 1.
Schematic illustration of the fabrication and sensing protocol of the gold nanoparticle-incorporated reduced graphene oxide–carbon nanotube nanocomposite on the glassy carbon electrode (GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE) and its current response of uric acid (UA) and xanthine (XT).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
Graphene oxide (GO, 4 mg/mL dispersion in H2O, ≥95.0%), multi-walled CNT (carbon basic, ≥98.0%), gold (lll) chloride trihydrate (HAuCl4·3H2O, ≥99.0% trace metals basic), UA, XT, potassium phosphate monobasic (KH2PO4), potassium phosphate dibasic (K2HPO4), potassium chloride (KCl), potassium hexacyanoferrate (II) (K4Fe(CN)6), potassium hexacyanoferrate (III) (K3Fe(CN)6), dopamine (DA), citric acid (CA), glucose (glu), L-ascorbic acid (AA), sodium chloride (NaCl), calcium chloride (CaCl2), potassium thiocyanate (KSCN), and ammonium chloride (NH4Cl) were purchased from Sigma Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). All chemicals were of analytical grade and were used as received without further purification. All aqueous solutions were prepared using ultrapure deionized water (resistivity = 18.3 MΩ·cm).
2.2. Apparatus
Surface morphology of the prepared electrode was characterized using a field emission scanning electron microscope (FE-SEM; S-4700, Hitachi, Tokyo, Japan). Energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX; S-4700, Hitachi, Tokyo, Japan) was used for analyzing elemental compositions of prepared nanocomposites. All electrochemical methods such as cyclic voltammetry (CV) and square wave voltammetry (SWV) were carried out with a CompactStat (Ivium Technology, Eindhoven, Netherlands) and a three-electrode system with a GCE (diameter of 3 mm) working electrode, platinum wire (diameter of 1 mm) counter electrode, and silver/silver chloride (Ag/AgCl, 1 M KCl) reference.
2.3. Fabrication of GNP-Incorporated 3D rGO-CNT on GCE
Prior to fabrication, bare GCE was sequentially polished with 1.0, 0.3 and 0.05 µm alumina (Al2O3) slurries, sonicated in distilled water, and dried with nitrogen (N2) gas. Before use, GO solution was sonicated for 60 min to disperse it homogeneously. GNP-incorporated rGO-CNT nanocomposite was prepared using a previously described method [28,31] with a minor modification. Briefly, 2.25 mg of CNT powder was dispersed in 9.37 mL of phosphate buffer (PB; 0.067 M, pH 7.4) using an ultrasonic liquid processor (STH-500S; Sonictopia, Cheongju, Korea) at 300 W for 10 min. After filtering the dispersed CNT solution using lens cleaning tissues (105, GE Healthcare Life Sciences, Pittsburgh, PA, USA), 5.63 mL of GO solution (final concentration = 17.83 mg/mL) and 1.4 μL of HAuCl4·3H2O (final concentration = 2.5 μg/mL) were mixed well with 7 mL of CNT solution (final concentration = 1.33 mg/mL). The mixing ratio of GO to CNT was 9:1. The mixed solution was then sonicated for 60 min to disperse it homogeneously. Prior to performing CV, the prepared solution was purged by N2 gas for 10 min. Finally, a one-step electrochemical co-reduction with deposition was performed using CV for 10 cycles in a potential range from 0.3 to −1.5 V (vs. Ag/AgCl reference electrode) at a scan rate 50 mV/s under constant bubbling of N2 gas. The prepared GNP-CNT-rGO on the GCE was washed three times with distilled water and then stored in distilled water to prevent collapse of the 3D structure before use.
2.4. Electrochemical Detection of UA and XT Utilizing GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE
Electrochemical characterization of the GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE was performed with the CV technique in 0.1 M KCl solution containing 2 mM [Fe(CN)6]3−/4− with a scanning range from −0.1 to 0.5 V (vs. Ag/AgCl reference electrode) at a scan rate of 50 mV/s. The sensing capabilities of GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE toward UA and XT were evaluated using SWV technique. SWV measurements were carried out using 25 μM UA and 25 μM XT in 0.1 M phosphate buffered saline (PBS, pH 7.4) with a scanning range from 0 to 1.0 V (vs. Ag/AgCl reference electrode) under the following conditions: 10 mV pulse amplitude, 10 mV E step, and 2 Hz frequency. Simultaneous detection of various concentrations of UA (0, 1.56, 3.125, 6.25, 12.5 and 25 μM) and XT (0, 3.125, 6.25, 12.5 and 25 μM) was performed in 0.1 M PBS (pH 7.4) under the same SWV conditions.
2.5. Real Sample Test
To examine the preliminary feasibility of GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE for detecting UA and XT, a recovery experiment was performed using human saliva and serum samples of healthy subjects (n = 5, respectively). Sample collection was approved by the Ethics Committee of Seoul National University Bundang Hospital (IRB No. B-1911-577-303). Written informed consent was obtained from all participants. Saliva and serum samples were simultaneously collected under fasting conditions. Unstimulated whole saliva samples were collected in a plastic tube using passive drooling and centrifuged at 4500× g for 10 min at 4 °C. Venous blood samples were centrifuged at 1500× g for 15 min at room temperature to obtain serum. Then, all samples were frozen at −80 °C until analysis. For UA and XT analyses, saliva and serum were diluted 100 times and 250 times in 0.1 M PBS (pH 7.4), respectively. SWV current responses were obtained for diluted human saliva and serum spiked with 10 μM of UA and 10 μM XT.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of 3D Macroporous GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE
GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE was easily synthesized by a one-step electrochemical reduction with co-deposition method without any template or complex process. Small amounts of CNTs were used as nanowire spacer to form interconnected rGO networks to improve the effective surface area [28]. In addition, small amounts of GNP could enhance the electrocatalytic activity and conductivity by providing additional pathways for fast electron transfer [28,32]. Figure S1 shows CV curves of one-step electrochemical reduction with co-deposition in GO, CNT, and HAuCl4 2H2O mixtures. At about −1.1 V (peak III), the surface oxygen groups of GO such as epoxy/ether group and hydroxyl group are irreversibly reduced to rGO [33]. In addition, Au3+ is also reduced to gold nanoparticle (GNP) during the same potential range of CV. When the reduction of GO and Au3+ occurs, the reduced forms, such as rGO and GNP, are deposited on the GCE. As shown in Figure S1, anodic peak (I) and cathodic peak (II) currents which represent the redox pair of electrodeposited rGO on the GCE [33] increased varying on the electrodeposition cycle, as well as cathodic current (III). During the electrochemical co-reduction and deposition of GO and Au3+, small amounts of CNTs are intercalated between rGO sheets by π–π interaction.
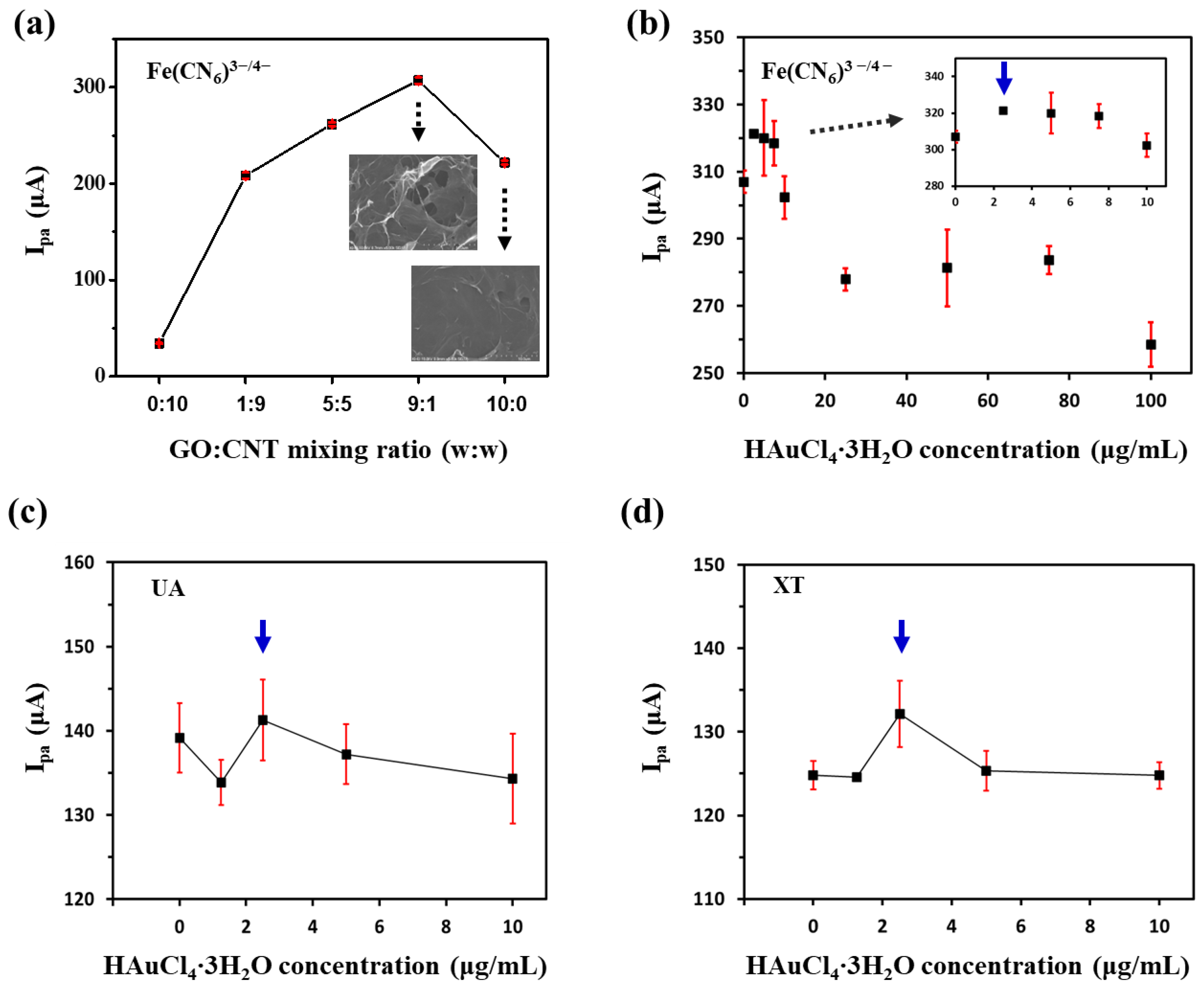
First, we optimized the mixing ratio of GO and CNT and the concentration of HAuCl4·3H2O for GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE. Figure 2a shows the effect of the mixing ratio of GO and CNT on current response of rGO-CNT/GCE to 2 mM [Fe (CN)6]3−/4−, an electrochemically active probe. As shown in Figure 2a, the 9:1 ratio between GO and CNT showed the highest anodic peak current (Ipa) of rGO-CNT/GCE. The SEM image in inset of Figure 2a confirmed successful formation of 3D macroporous structure of rGO-CNT/GCE when it was synthesized at a 9:1 mixing ratio between GO and CNT, different from a film structure of reduced graphene oxide on the GCE (rGO/GCE). However, when more CNT was added, the Ipa response of rGO-CNT/GCE became lower. It might be attributed to the fact that an excess CNT might result in aggregation and subsequently decrease the effective surface area. Figure 2b displays Ipa response of GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE to 2 mM [Fe (CN)6]3−/4− with various concentrations of HAuCl4·3H2O (0, 2.5, 5.0, 7.5, 10, 25, 50, 75 and 100 μg/mL). When a small amount of HAuCl4·3H2O ranging from 2.5 to 7.5 μg/mL was added, Ipa of GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE was higher than that of rGO-CNT/GCE. Then, Ipa decreased with increasing HAuCl4·3H2O concentration from 10 to 100 μg/mL because excess GNP could interfere with the formation of 3D GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE and disturb the electron transfer between the redox probe and electrode [28]. As 2.5 μg/mL of HAuCl4·3H2O showed the maximum Ipa with a low standard deviation, we first selected it as an optimum concentration for GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE.
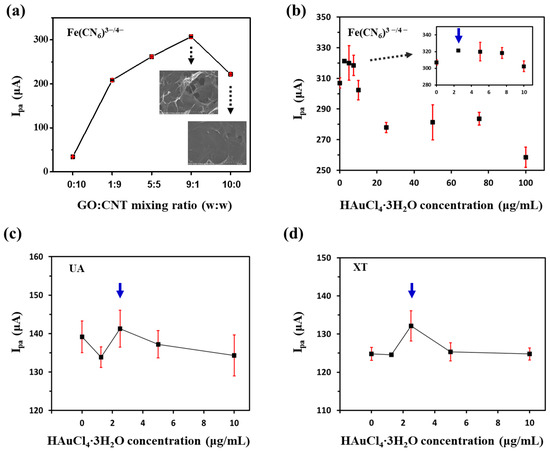
Figure 2.
(a) Changes in anodic peak current (Ipa) of reduced graphene oxide–carbon nanotube nanocomposites on the glassy carbon electrode (rGO-CNT/GCE) to 2 mM [Fe (CN)6]3−/4− by varying the mixing ratio between graphene oxide (GO) and carbon nanotube (CNT). Insets show SEM images of rGO-CNT/GCE and reduced graphene oxide on the GCE (rGO/GCE) with each mixing ratio. Changes in Ipa of the gold nanoparticle-incorporated rGO-CNT/GCE (GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE) to (b) 2 mM [Fe (CN)6]3−/4−, (c) 100 μM uric acid (UA), and (d) 100 μM xanthine (XT) according to HAuCl4·3H2O concentration.
Next, we examined current responses of GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE to UA and XT, respectively, according to concentrations of HAuCl4·3H2O (0, 1.25, 2.5, 5.0, 10 μg/mL). As shown in Figure 2c, Ipa of GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE to UA (100 μM) was similar at all concentrations of HAuCl4·3H2O. However, the maximum Ipa of GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE to XT (100 μM) was observed with 2.5 μg/mL of HAuCl4·3H2O (Figure 2d). Therefore, we finally selected 2.5 μg/mL of HAuCl4·3H2O as the optimum concentration for GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE.
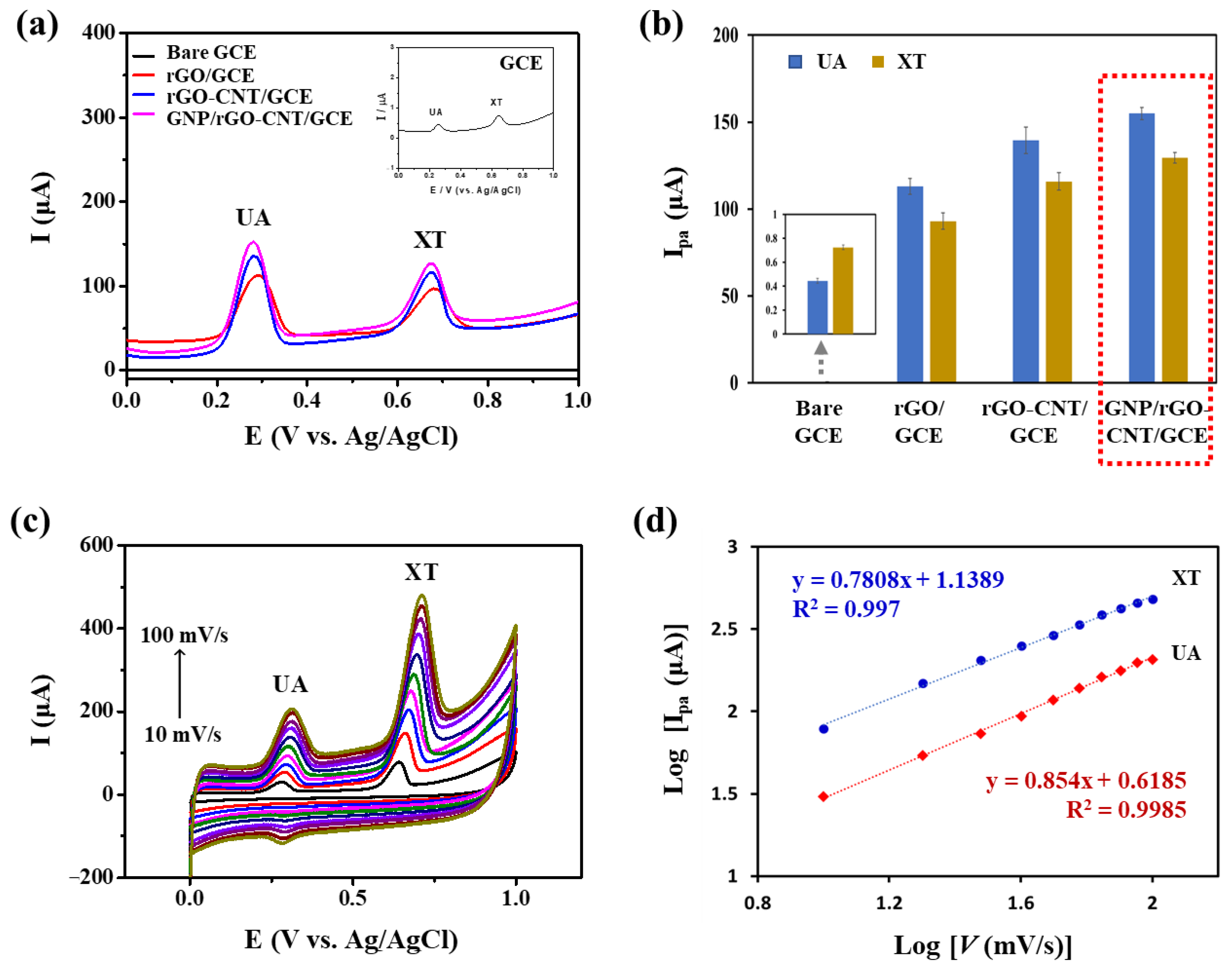
Electrocatalytic activities of modified electrodes were characterized by SWV. Figure 3a,b show CV curves and corresponding Ipa values of bare GCE, rGO/GCE, rGO-CNT/GCE, and GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE in PBS (0.1 M, pH 7.4) containing 25 μM UA and 25 μM XT. As shown in Figure 3a, two well-defined oxidation peaks were observed for all types of electrodes, including bare GCE, rGO/GCE, rGO-CNT/GCE, and GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE. However, anodic current responses of bare GCE toward UA and XT were negligible. On the contrary, the Ipa of rGO/GCE significantly increased to 113.1 ± 5.5 μA for UA and 93.1 ± 5.8 μA for XT. GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE (155.0 ± 4.4 μA for UA and 129.4 ± 3.7 μA for XT) showed higher Ipa values than bare GCE, rGO/GCE, and rGO-CNT/GCE (139.5 ± 9.2 μA for UA and 115.9 ± 6.0 μA for XT). SEM image and EDX spectrum shown in Figure S2 confirmed that GNP/rGO-CNT consisted of carbon, oxygen, and gold. Effective surface area for each modified electrode was calculated using the Randles−Sevcik equation [25,34] from the CV curves obtained using 2 mM [Fe(CN)6]3−/4− at different scan rates (10–100 mV/s) (Figure S3). As a result, the effective surface areas of bare GCE, rGO/GCE, rGO-CNT/GCE, and GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE were 0.068, 1.205, 1.70, and 1.80 cm2, respectively. This result indicated that GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE could improve the effective surface area and enhance the electron transfer because of 3D structures of rGO-CNT nanocomposite with an enhanced conductivity and GNP with a high electrocatalytic activity [28]. Epa values of GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE were 0.28 and 0.68 V for UA and XT, respectively, indicating that simultaneous detection of UA and XT could be effectively achieved without any separation or pretreatment.
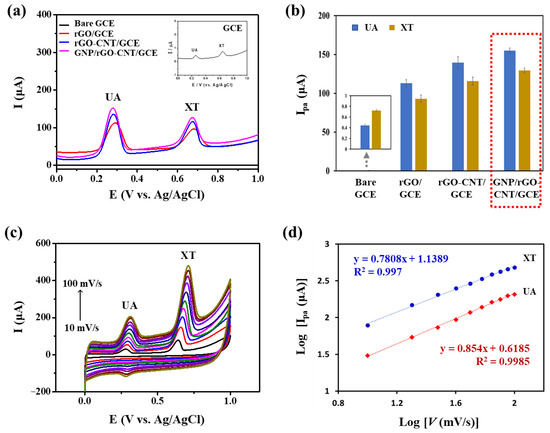
Figure 3.
(a) Square wave voltammetry curves and (b) anodic peak current (Ipa) values of bare glassy carbon electrode (GCE), reduced graphene oxide on the GCE (rGO/GCE), reduced graphene oxide-carbon nanotube nanocomposite on the GCE (rGO-CNT/GCE), and gold nanoparticle-incorporated rGO-CNT/GCE (GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE) in PBS (0.1 M, pH 7.4) containing 25 μM uric acid (UA) and 25 μM xanthine (XT) (n = 3). Inset shows a zoomed graph for bare GCE. (c) Cyclic voltammetry curves of GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE at different scan rates (10–100 mV/s) in PBS (0.1 M, pH 7.4) containing 25 μM UA and 25 μM XT. (d) Corresponding plots of log Ipa vs. log scan rate (v) for UA and XT of GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE.
Effects of scan rates on Ipa of UA and XT in the GNP/rGO–CNT/GCE were also examined by CV at various scan rates ranging from 10 to 100 mV/s. As shown in Figure 3c, current responses of 25 μM UA and 25 μM XT simultaneously increased with an increase in scan rate. Log Ipa value showed a linear relationship with log scan rate (v) in the range of 10~100 mV/s (log Ipa = 0.854 log v + 0.6185, R2 = 0.9985 for UA; log Ipa = 0.7808 log v + 1.1389, R2 = 0.997 for XT) (Figure 3d). These results indicated that an adsorption-controlled process had occurred for simultaneous UA and XT oxidation [24,27,35].
3.2. Optimization for Simultaneous Detection of UA and XT Using GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE
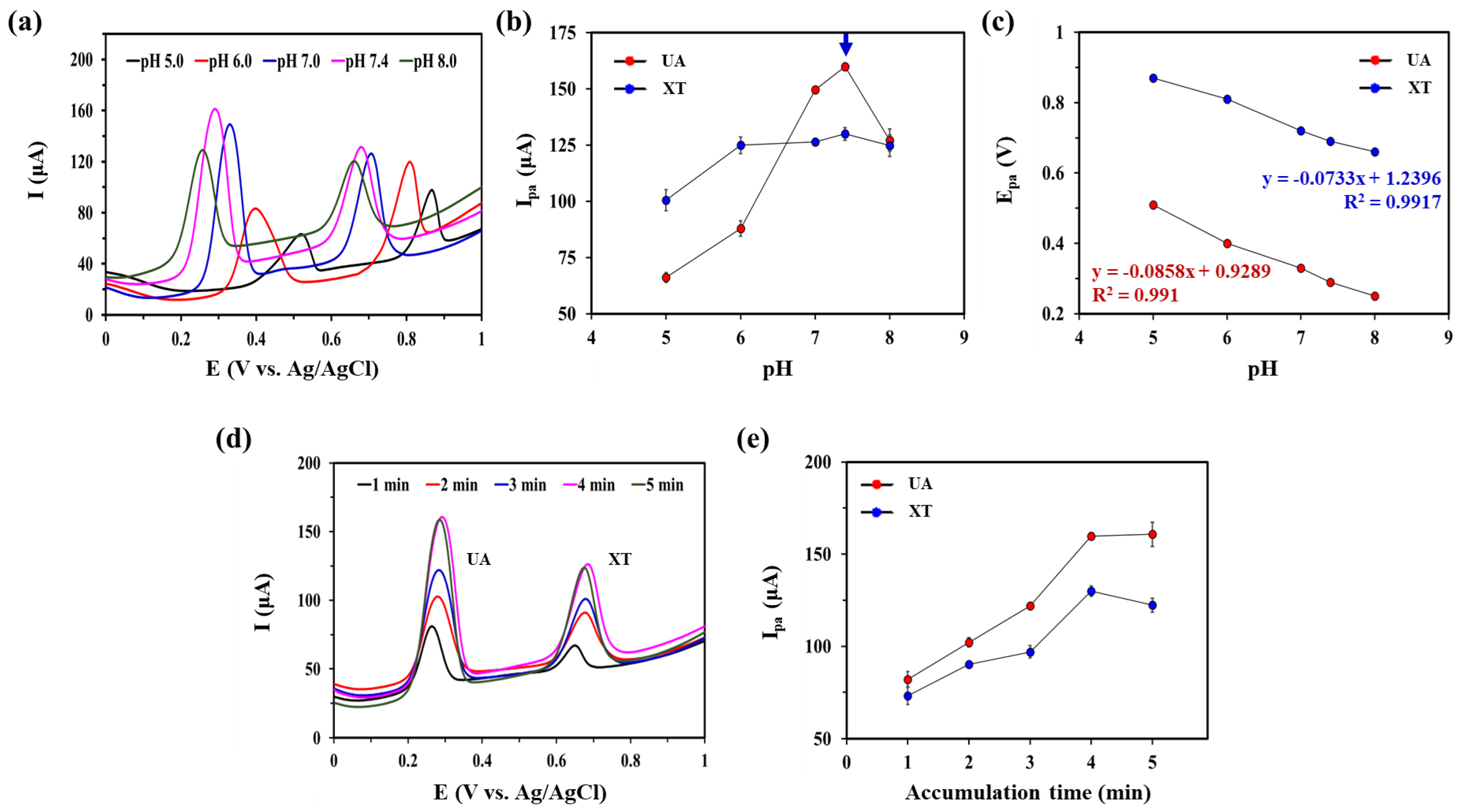
The pH of the supporting electrolyte can have a significant effect on electrochemical oxidation of XA and UA [35,36]. Therefore, we investigated the effect of pH on oxidation current responses of UA and XT at GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE by recording SWV curves from pH 5.0 to 8.0 in 0.1 M PBS containing 25 μM UA and 25 μM XT (Figure 4a). As shown in Figure 4b, the Ipa of UA increased with increasing pH up to 7.4. It then decreased at higher pH (8.0). This effect of pH on Ipa of UA might be attributed to the fact that deprotonated UA at higher pH (8.0) was inefficiently adsorbed on GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE due to electrostatic repulsion [35]. The Ipa of XT did not change in the pH range of 6.0–8.0. Therefore, we selected pH 7.4 as an optimal pH for simultaneous detection of UA and XT. Moreover, as shown in Figure 4c, Epa showed a linear relationship with pH (Epa = −0.0858 pH + 0.9289, R2 = 0.991 for UA; Epa = −0.0733 pH + 1.2396, R2 = 0.9917 for XT). Epa moved to negative potentials with an increase of pH for both UA and XA (Figure 4c), indicating that a proton transfer occurred in the oxidation reaction of UA and XT [19,26,27]. As slopes for UA (85.8 mV/pH) and XT (73.3 mV/pH) were close to the theoretical value of the Nernst equation, we inferred that the oxidation process of UA and XA was related to an equal number of protons and electrons—two protons and two electrons [21,25,36,37]. Thus, the mechanism for UA and XT oxidation can be proposed in Figure S4.
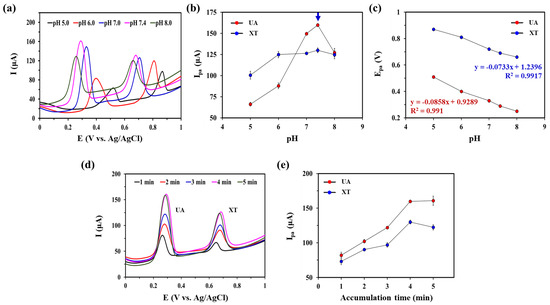
Figure 4.
(a) Square wave voltammetry (SWV) curves of gold nanoparticle-incorporated reduced graphene oxide–carbon nanotube nanocomposite on the glassy carbon electrode (GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE) in presence of 25 μM uric acid (UA) and xanthine (XT) in PBS (0.1 M, pH 7.4) with various pH (5.0, 6.0, 7.0, 7.4, 8.0) at a potential range from 0.0 to 1.0 V (vs. Ag/AgCl). Corresponding plots of (b) Anodic peak current (Ipa) vs. pH and (c) Anodic peak potential (Epa) vs. pH of for UA and XT of GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE. (d) SWV curves of GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE in PBS (0.1 M, pH 7.4) containing 25 μM UA and XT with various accumulation time (1, 2, 3, 4, 5) at a potential range from 0.0 to 1.0 V (vs. Ag/AgCl). (e) Effect of accumulation time on Ipa of UA and XT at GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE.
Next, we optimized the accumulation time to obtain better performance for simultaneous detection of UA and XT. As can be seen in Figure 4d,e, Ipa values of UA and XT sharply increased with an increase of accumulation time until 4 min. Higher Ipa of UA and XA might be due to their greater adsorption on GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE. However, Ipa values of UA and XA became constant at 5 min due to surface saturation. This behavior was consistent with an adsorption-controlled process at the electrode surface. Therefore, the accumulation time for optimal adsorption was selected at 4 min.
3.3. Analytical Performance of GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE for Simultaneous Detection of UA and XT
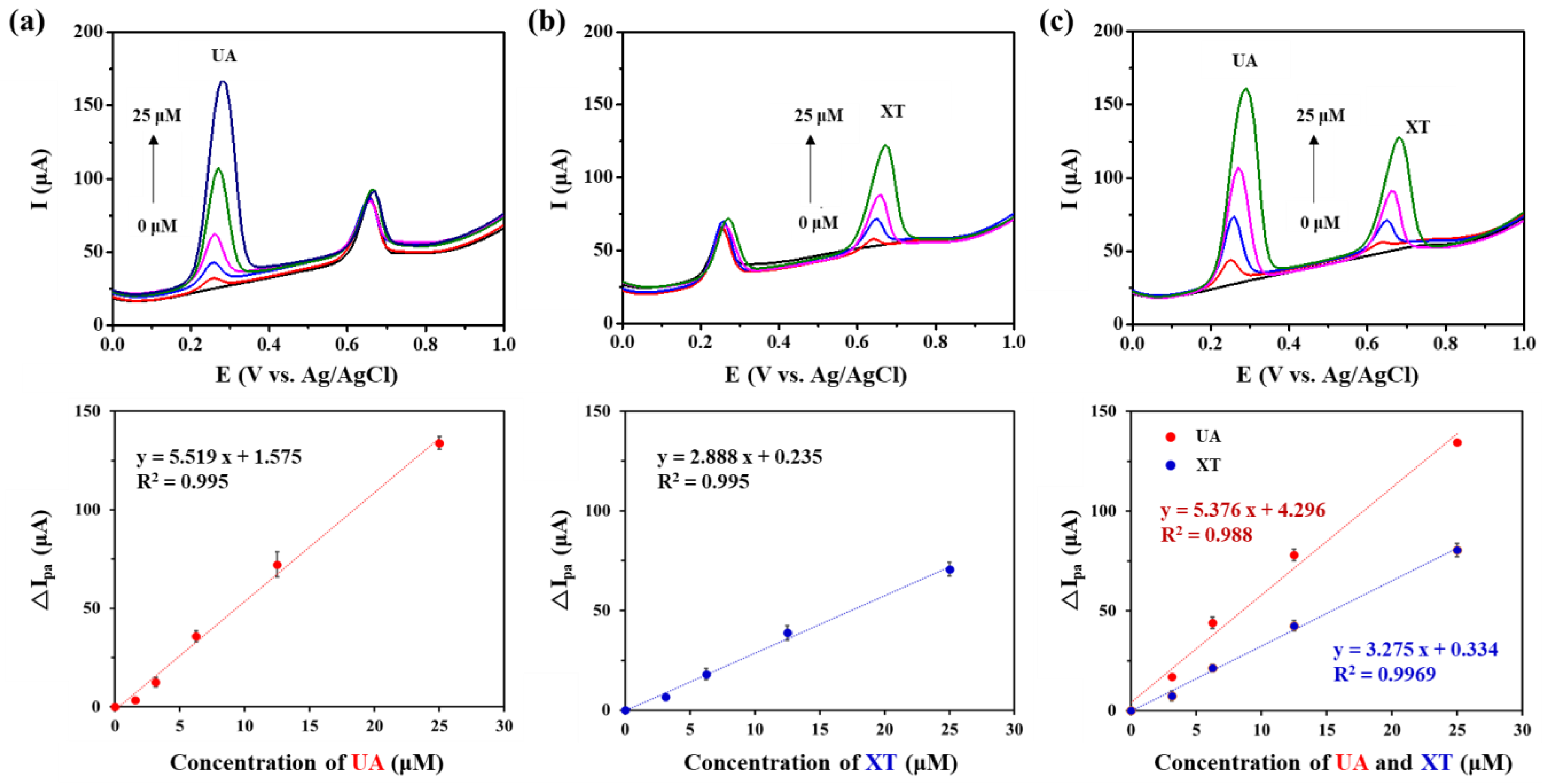
We investigated sensing performance of GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE for simultaneous detection of UA and XT. First, SWV was performed by changing the concentration of UA (0, 1.56, 3.125, 6.25, 12.5, 25.0 μM) in the presence of 12.5 μM XT. As shown in Figure 5a, the Ipa of GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE increased with an increasing UA concentration. The change in Ipa of GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE was linear with UA concentration in the range from 0 to 25.0 μM (R2 = 0.995), showing a sensitivity of 5.518 μA/μM UA. A lower detection limit was 910 nM based on the signal-to-noise ratio of three (S/N = 3). Next, changes in Ipa of GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE were analyzed by changing the concentration of XT (0, 3.125, 6.25, 12.5, 25 μM) in a mixture solution containing 6.25 μM UA. As shown in Figure 5b, the Ipa of GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE also increased with an increasing XT concentration. The change in Ipa of GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE had a linear relationship with XT concentration in the range from 0 to 25.0 μM (R2 = 0.995), with a sensitivity of 2.888 μA/μM XT and a detection limit of 2.57 μM. Finally, SWV was performed by changing concentrations of UA and XT from 0 to 25.0 μM simultaneously. As shown in Figure 5c, Ipa changed linearly depending on the concentration of UA and XT. Sensitivities for UA (5.376 μA/μM UA, R2 = 0.988) and XT (3.275 μA/μM XT, R2 = 0.9969) were similar to those of individual UA or XT. Therefore, the GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE was capable of simultaneous detection and quantitative detection by separating oxidation peaks from each other.
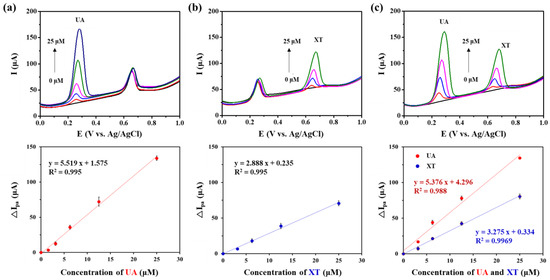
Figure 5.
(a) Square wave voltammetry (SWV) curves and the plot of anodic peak current change (∆Ipa) vs. concentration of uric acid (UA) on gold nanoparticle-incorporated reduced graphene oxide–carbon nanotube nanocomposite on the glassy carbon electrode (GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE) at different concentrations of UA (0, 1.56, 3.125, 6.25, 12.5, 25.0 μM) in presence of 12.5 μM xanthine (XT) in PBS (0.1 M, pH 7.4) at a potential range from 0.0 to 1.0 V (vs. Ag/AgCl) (n = 5). (b) SWV curves and the plot of ∆Ipa vs. concentration of XT (n = 5) on GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE at different concentrations of XT (0, 3.125, 6.25, 12.5, 25 μM) in presence of 6.25 μM UA in PBS (0.1 M, pH 7.4) at the same condition. (c) SWV curves and the plot of ∆Ipa vs. concentration of UA and XT (n = 3) on GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE at different concentrations of both UA and XT (0, 3.125, 6.25, 12.5, 25 μM) at the same condition.
Compared to previous results of other electrochemical methods for simultaneous measurement of UA and XT, sensing performance and condition of our GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE are summarized in Table 1. Although some of other modified electrodes have some advantages, such as low LOD and wide linear range, the prepared GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE showed good performance in terms of high sensitivity at physiological pH, which could be easily applied to analysis of biofluids such as saliva and blood serum. Moreover, it has an additional advantage due to its easy preparation of 3D structure without a complex process.

Table 1.
Comparison of analytical performances between GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE sensor and other GO or rGO-modified GCEs for detection of UA and XT.
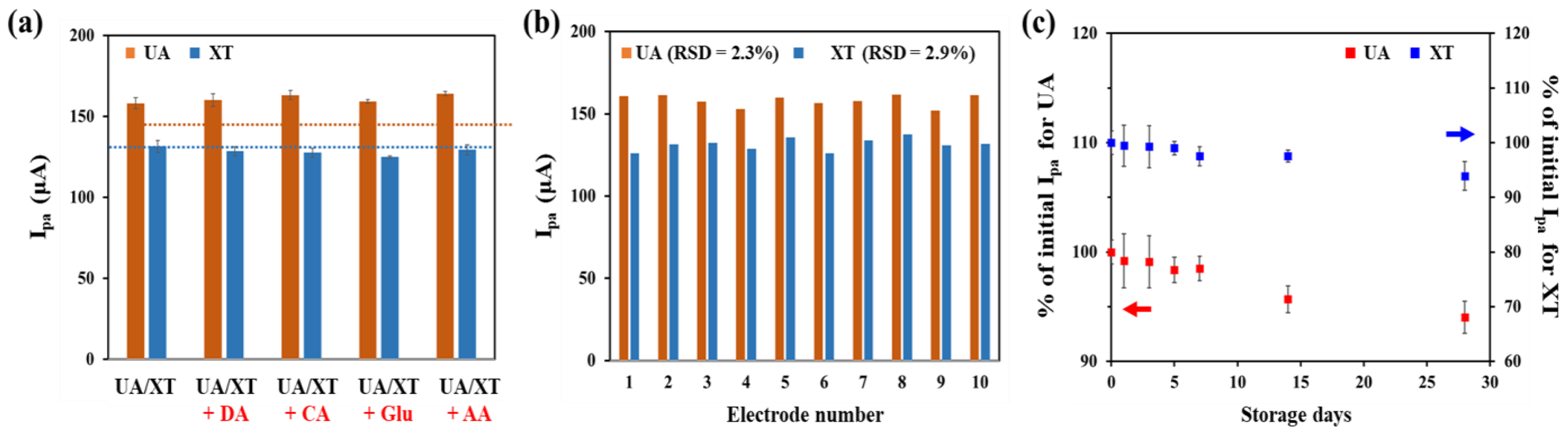
To evaluate selectivity of the GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE, we compared SWV responses of 25 μM UA and 25 μM XT with those of other potential interfering species, including 5 μM DA, 100 μM CA, 100 μM glu and 100 μM AA. As shown in Figure 6a, Ipa values of UA and XT did not change by the addition of each interfering species. This result indicates that the GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE has good selectivity for simultaneous detection of UA and XT without any interfering effect. Moreover, the reproducibility of GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE was investigated by measuring SWV responses to 25 μM UA and 25 μM XT using 10 electrodes on the same fabrication date and 5 electrodes on different fabrication dates, respectively. The relative standard deviation (RSD) of 10 GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE electrodes was 2.3% for UA and 2.9% for XT (Figure 6b). The RSD of five GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE electrodes was 2.3% for UA and 3.4% for XT (Figure S5). Therefore, the GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE was highly reproducible.
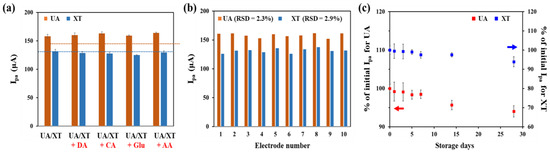
Figure 6.
(a) Selectivity test result of GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE by measuring Ipa values of SWV for 25 μM UA and 25 μM XT in PBS (0.1 M, pH 7.4) under the coexistence of other interfering species including 5 μM DA, 100 μM CA, 100 μM glu, and 100 μM AA (n = 3). (b) Reproducibility test result of GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE with 10 individual electrodes using Ipa of SWV to 25 μM UA and XT in PBS (0.1 M, pH 7.4). (c) Stability test result of GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE by measuring Ipa values of SWV for 25 μM UA and 25 μM XT after 28 days of storage at 4 °C. SWV was performed at a potential range from 0.0 to 1.0 V (vs. Ag/AgCl) (n = 3).
The stability of GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE was examined based on SWV responses to 25 μM UA and XT during storage in distilled water at 4 °C for up to 28 days. As shown in Figure 6c, Ipa values showed 94.0% of initial Ipa for UA and 93.9% of initial Ipa for XT after 28 days of storage. This indicates that the fabricated GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE sensor has a good stability without suffering from surface contamination during storage.
3.4. Real Sample Analysis
To verify the feasibility of using GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE for simultaneous detection of UA and XT, it was applied to real sample analysis with the standard addition method. Table 2 shows recovery test results of UA and XT in human saliva (n = 5) and blood serum (n = 5) samples obtained with GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE for UA and XT spike samples. In human saliva, this sensor produced recoveries in the range of 91.6 to 109.0% for UA and 91.9 to 107.8% for XT. In human blood serum, recoveries were found to be 96.1 to 108.9% for UA and 94.3 to 103.8% for XT. There results indicated that our GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE sensor could be potentially utilized for analyzing UA and XT in real biological fluids.

Table 2.
Simultaneous determination of UA and XT in human saliva (n = 5) and blood serum samples (n = 5).
4. Conclusions
In summary, we demonstrated that utilizing 3D macroporous GNP/rGO-CNT nanocomposites simply prepared by a one-step electrochemical deposition with co-reduction method could simultaneously detect UA and XT. GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE has a high surface area and fast electron transfer due to 3D rGO-CNT nanocomposite and a high electrocatalytic activity due to a small amount of GNP. As a result, this GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE showed high sensitivity and selectivity with excellent stability and good reproducibility in neutral pH. Simultaneous detection of UA and XT in human saliva and blood serum using GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE might also be effectively achieved. To the best of our knowledge, simultaneous detection of UA and XT in human saliva has not been reported. Therefore, the GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE sensor for simultaneous detection of UA and XT could be utilized as an effective tool for clinical diagnosis and management of gout using human body fluids.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/chemosensors11030185/s1, Figure S1: Cyclic voltammetry curves of one-step electrochemical reduction with co-deposition of graphene oxide (GO), carbon nanotube (CNT), and HAuCl4·2H2O mixtures in 0.067 M phosphate buffer (pH 7.4) at a potential range from +0.3 to −1.5 V for 10 cycles at 50 mV/s. Inset shows the photographic image of GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE; Figure S2: (a) SEM image and (b) EDX spectrum of GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE; Figure S3: (a) Cyclic voltammetry curves of GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE at different scan rates (10–100 mV/s) in 0.1 M KCl containing 2 mM Fe(CN)63−/4−. (b) The corresponding plot of anodic peak current (Ipa) versus square root of scan rate for bare GCE, rGO/GCE, rGO-CNT/GCE, and GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE. Effective surface area for each electrode was calculated using the Randles–Sevcik equation [Ip = (2.69 × 105) n3/2 A D1/2 C v1/2], where Ip is the peak current (μA), n is the number of electrons in the reaction (FIn = 1), A is the effective surface area of electrode (cm2), D is the diffusion coefficient of the redox probe in solution (7.6 × 10−6 cm2 s−1), C is the concentration of the redox probe (2 mmol/L), and v is the scan rate (V/s); Figure S4: The proposed mechanism for the electrochemical oxidation of uric acid (UA) and xanthine (XT); Figure S5: Square wave voltammetry responses of five GNP/rGO-CNT/GCE electrodes on different fabrication dates to 25 μM uric acid (UA) and 25 μM xanthine (XT).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.-J.L., K.W.M. and Y.J.L.; Methodology, S.-H.H.; Validation, G.-J.L., K.W.M. and Y.J.L.; Formal analysis, S.-H.H. and G.-J.L.; Investigation, Y.J.L. and K.W.M.; Resources, Y.J.L.; Writing—original draft preparation, G.-J.L. and S.-H.H.; Writing—review and editing, Y.J.L., K.W.M. and G.-J.L.; Visualization, S.-H.H. and G.-J.L.; Supervision, G.-J.L.; Project administration, G.-J.L. and Y.J.L.; Funding acquisition, G.-J.L. and Y.J.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by National Research Foundation grant funded by the Korean Government (No. NRF-2021R1A2C1093825 to GJL) and a grant from Seoul National University Bundang Hospital Research Fund (No. 21-2022-0021 to YJL).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Institutional Review Board of Seoul National University Bundang Hospital (IRB No. B-1911-577-303 in 2019).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Neogi, T.; Jansen, T.L.T.A.; Dalbeth, N.; Fransen, J.; Schumacher, H.R.; Berendsen, D.; Brown, M.; Choi, H.; Edwards, N.L.; Janssens, H.J.E.M.; et al. 2015 Gout Classification Criteria: An American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015, 67, 2557–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safiri, S.; Kolahi, A.A.; Cross, M.; Carson-Chahhoud, K.; Hoy, D.; Almasi-Hashiani, A.; Sepidarkish, M.; Ashrafi-Asgarabad, A.; Moradi-Lakeh, M.; Mansournia, M.A.; et al. Prevalence, Incidence, and Years Lived with Disability Due to Gout and Its Attributable Risk Factors for 195 Countries and Territories 1990–2017: A Systematic Analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020, 72, 1916–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.W.; Ko, D.J.; Yoo, J.J.; Chang, S.H.; Cho, H.J.; Kang, E.H.; Park, J.K.; Song, Y.W.; Lee, Y.J. Clinical factors and treatment outcomes associated with failure in the detection of urate crystal in patients with acute gouty arthritis. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2014, 29, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlesinger, N. Diagnosing and treating gout: A review to aid primary care physicians. Postgrad Med. 2010, 122, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FitzGerald, J.D.; Dalbeth, N.; Mikuls, T.; Brignardello-Petersen, R.; Guyatt, G.; Abeles, A.M.; Gelber, A.C.; Harrold, L.R.; Khanna, D.; King, C.; et al. 2020 American College of Rheumatology Guideline for the Management of Gout. Arthritis Care Res. 2020, 72, 744–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löffler, W.; Fairbanks, L. Refractory gout—Does it exist? Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids 2020, 39, 1410–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vera, M.A.; Marcotte, G.; Rai, S.; Galo, J.S.; Bhole, V. Medication adherence in gout: A systematic review. Arthritis Care Res. 2014, 66, 1551–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamp, L.K.; Merriman, T.; Frampton, C.; Zhang, M.; Wallace, M.; Miner, J.N.; Dalbeth, N. Plasma oxypurinol as a measure of adherence in clinical trials. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 77, 313–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicero, A.F.G.; Fogacci, F.; Cincione, R.I.; Tocci, G.; Borghi, C. Clinical Effects of Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitors in Hyperuricemic Patients. Med. Princ. Pract. 2021, 30, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.Y.; Liang, Q.L.; Luo, G.; Wang, Y.; Zuo, Y.; Jiang, M.; Yu, G.; Zhang, T. Purine metabolites in gout and asymptomatic hyperuricemia: Analysis by HPLC-electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. Clin. Chem. 2005, 51, 1742–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Deng, M.; Deng, B.; Ye, L.; Fei, X.; Huang, Z. Study on the diagnosis of gout with xanthine and hypoxanthine. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2019, 33, e55868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khosravan, R.; Grabowski, B.A.; Wu, J.T.; Joseph-Ridge, N.; Vernillet, L. Pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and safety of febuxostat, a non-purine selective inhibitor of xanthine oxidase, in a dose escalation study in healthy subjects. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2006, 45, 821–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furuhashi, M.; Koyama, M.; Higashiura, Y.; Murase, T.; Nakamura, T.; Matsumoto, M.; Sakai, A.; Ohnishi, H.; Tanaka, M.; Saitoh, S.; et al. Differential regulation of hypoxanthine and xanthine by obesity in a general population. J. Diabetes Investig. 2020, 11, 878–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czauderna, M.; Kowalczyk, J. Quantification of allantoin, uric acid, xanthine and hypoxanthine in ovine urine by high-performance liquid chromatography and photodiode array detection. J. Chromatogr. B 2000, 744, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, N.; Khosravan, R.; Erdmann, C.; Fiene, J.; Lee, J.W. Quantification of uric acid, xanthine and hypoxanthine in human serum by HPLC for pharmacodynamic studies. J. Chromatogr. B 2006, 837, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tong, L.L. Electrochemical sensor for simultaneous determination of uric acid, xanthine and hypoxanthine based on poly (bromocresol purple) modified glassy carbon electrode. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2010, 150, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, F.; Wu, K.; Chen, J.; Zhou, Y. Electrochemical sensor for simultaneous detection of ascorbic acid, uric acid and xanthine based on the surface enhancement effect of mesoporous silica. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2009, 141, 641–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangaraj, R.; Kumar, A.S. Graphitized mesoporous carbon modified glassy carbon electrode for selective sensing of xanthine, hypoxanthine and uric acid. Anal. Methods 2012, 4, 2162–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, C.; Du, Y.; Ye, W. Simultaneous electrochemical determination of uric acid, xanthine and hypoxanthine based on poly (l-arginine)/graphene composite film modified electrode. Talanta 2012, 93, 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, M.A.; John, S.A. Simultaneous determination of uric acid, xanthine, hypoxanthine and caffeine in human blood serum and urine samples using electrochemically reduced graphene oxide modified electrode. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 771, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y. Simultaneous determination of uric acid, xanthine and hypoxanthine at poly(pyrocatechol violet)/functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes composite film modified electrode. Colloid Surf. B Biointerfaces 2011, 88, 614–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, X.F.; Wang, A.J.; Zhang, Q.L.; Huang, H.; Feng, J.J. Ultrafine Fe3C nanoparticles embedded in N-doped graphitic carbon sheets for simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine, uric acid and xanthine. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojani, R.; Alinezhad, A.; Abedi, Z. A highly sensitive electrochemical sensor for simultaneous detection of uric acid, xanthine and hypoxanthine based on poly (l-methionine) modified glassy carbon electrode. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2013, 188, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoan, N.T.V.; Minh, N.N.; Trang, N.T.H.; Thuy, L.T.T.; Van Hoang, C.; Mau, T.X.; Vu, H.X.A.; Thu, P.T.K.; Phong, N.H.; Khieu, D.Q. Simultaneous Voltammetric Determination of Uric Acid, Xanthine, and Hypoxanthine Using CoFe2O4/Reduced Graphene Oxide-Modified Electrode. J. Nanomater. 2020, 2020, 9797509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, S.; Sarkar, P. A simple electrochemical approach to fabricate functionalized MWCNT-nanogold decorated PEDOT nanohybrid for simultaneous quantification of uric acid, xanthine and hypoxanthine. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1114, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanbari, K.; Nejabati, F. Ternary nanocomposite-based reduced graphene oxide/chitosan/Cr2O3 for the simultaneous determination of dopamine, uric acid, xanthine, and hypoxanthine in fish meat. Anal. Methods 2020, 12, 1650–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanbari, M.H.; Mashhadizadeh, M.H.; Norouzi, Z.; Salehzadeh, H. Simultaneous electrochemical detection of uric acid and xanthine based on electrodeposited B, N co-doped reduced graphene oxide, gold nanoparticles and electropolymerized poly (L-cysteine) gradually modified electrode platform. Microchem. J. 2022, 175, 107213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Lee, Y.J.; Eun, Y.G.; Lee, G.J. An ultrasensitive electrochemical detection of tryptase using 3D macroporous reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites by one-pot electrochemical synthesis. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1069, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Q.; Yang, K.; Ge, K.L.; Liua, Z.; Li, F. Direct-laser-writing of three dimensional porous graphene frameworks on indium-tin oxide for sensitive electrochemical biosensing. Analyst 2018, 143, 3327–3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhou, A.; Yang, H.; Wang, F.; Lu, K. 3D graphene-nitrogen doped carbon nanotubes network modified electrode as sensing materials for the determination of urapidil. Materials 2018, 11, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Lee, Y.J.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, G.J. Electrochemical Detection of H2O2 Released from Prostate Cancer Cells Using Pt Nanoparticle-Decorated rGO–CNT Nanocomposite-Modified Screen-Printed Carbon Electrodes. Chemosensors 2020, 8, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindhan, M.; Chen, A. Simultaneous synthesis of gold nanoparticle/graphene nanocomposite for enhanced oxygen reduction reaction. J. Power Sources 2015, 274, 928–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Wang, J.; Engelhard, M.; Wang, C.; Lin, Y. Facile and controllable electrochemical reduction of graphene oxide and its applications. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 743–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, H.; Temerk, Y. Sensitive electrochemical sensor for simultaneous determination of uric acid and xanthine in human biological fluids based on the nano-boron doped ceria modified glassy carbon paste electrode. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2016, 780, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Fei, J.; Wu, K.; Hu, S. Simultaneous electrochemical determination of xanthine and uric acid at a nanoparticle film electrode. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2003, 375, 544–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Ma, W.; Luo, Y.; Sun, D.; Shao, S. Simultaneous Determination of Uric Acid and Xanthine Using a Poly(Methylene Blue) and Electrochemically Reduced Graphene Oxide Composite Film Modified Electrode. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2014, 2014, 984314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.S.; Yu, S.H.; Kim, T.H. One-Step Electrochemical Fabrication of Reduced Graphene Oxide/Gold Nanoparticles Nanocomposite-Modified Electrode for Simultaneous Detection of Dopamine, Ascorbic Acid, and Uric Acid. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).