Abstract
Titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles (NPs) are widely used in industry and commercial products. Thus, their potential risks to the environment and human health must be evaluated. Doping NPs with certain ions makes it possible to mix properties or generate new ones. Thus, in order to track TiO2 NPs in biological assays, doping with europium (Eu3+) ions was performed, which luminesce in red. Here, we synthesized TiO2 and Eu3+-doped TiO2 nanocrystals (NCs) in anatase phase to verify the toxicity at different concentrations in Drosophila melanogaster and track the distribution of these NCs in vivo. We verified that the incorporation of europium improved the biocompatibility in relation to the pure samples. The presence of Eu3+-doped TiO2 NCs in the gut, brain, and fat body of larvae and intestinal cells of adult animals was detected. Eu3+-doped TiO2 NCs caused significant larval and pupal mortality rates, in addition to leading to the formation of reactive species, especially at high concentrations. Therefore, our data demonstrated it was possible to trace the Eu3+-doped TiO2 NCs, but TiO2 and Eu3+-doped TiO2 NCs in anatase phase were toxic to fruit flies at the tested concentrations, and should be used with caution to minimize health risks.
1. Introduction
Nanotechnology consists of the use of particles with a size range of 1 to 100 nm and has been widely explored, especially in recent years [1]. Nanoparticles in the form of nanocrystals (NCs) of titanium dioxide (TiO2) have three natural forms: rutile, anatase, and brookite, with the anatase phase being the most found and used [2]. TiO2 toxicity is dependent on its size and crystal form, and the anatase phase is considered the most toxic [3].
TiO2 nanocrystals are used in the cosmetic industry in the manufacture of sunscreens due to their UV light absorption properties and high refractive index. They are also found in the manufacture of enamels, to give a whiter color to toothpaste, and in the textile industry to manufacture fabrics [3,4,5], as well as being present in some types of medicines as drug colorants [3]. NCs are also used in the food industry in chewing gum, milk, and to provide a shiny appearance to some types of cheese. The most-used type is anatase in the form of an inactive ingredient (E171) that contains nanocrystals between 17–36% of its composition. It is estimated that the daily consumption of E171 TiO2 by humans is 0.2–2.0 mg kg−1 of body weight [2,6,7].
In contrast to the widespread use of anatase phase TiO2 in industry, there is clear evidence of its toxicity [2,5,6,8,9,10,11,12,13], including the induction of epigenetic mechanisms [14]. The anatase phase of TiO2 leads to few alterations in the development of zebrafish (Danio rerio) larvae [15] and the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster [6,12,16,17], inducing cytotoxicity and genotoxicity in cells [9,18,19], inflammation, metabolic changes and potentially carcinogenesis [7]. It is believed that the mechanism responsible for nanotoxicity of TiO2 NCs is mainly through the induction of cellular oxidative stress, but also through its interaction with cell membranes, intracellular organelles, and macromolecules [2,11].
Due to its plasticity and wide use in industrial and commercial products, it is important not only to understand the toxicological mechanisms of TiO2 but also to investigate technological alternatives to minimize this effect. The incorporation of the chemical element Europium (Eu) to the TiO2 nanoparticle (Eu3+-doped TiO2) confers long-lasting fluorescent properties, photostability, and clear visible emission bandwidth [20,21]. Moreover, it can improve nanocrystal biocompatibility [22], mitigating toxicity problems beyond the influence of optical behavior [23]. These characteristics facilitate in vivo tracking of TiO2 and help in the investigation of its risks to organisms and the relationship between its structure and function. In addition, the fluorescent properties are advantageous as it facilitates detection by image instrumentation and consequently improves the visualization and understanding of biological processes [21,24]. Different Eu-doped nanoparticles, such as Eu-doped SnO2 [25] and fluorapatite [26], showed low cytotoxicity.
The fruit fly D. melanogaster is a well-established model organism widely used in several areas of science, including nanotoxicology. Drosophila has advantageous features for investigating the toxicological effects of a large number of different compounds at various stages of development. Low cost, short life cycle when compared to other model organisms such as mammals and fish [27,28,29], and sophisticated genetic tools made the flies an excellent model system for basic research. Also, the well-documented Drosophila development from embryo to adult stages facilitates the study of bioaccumulation, tracking, and toxicity of NCs in their tissues.
The growing use of nanomaterials has driven researchers to carry out additional studies on the toxicity of these substances both for humans and for the ecosystem. Here, we evaluated the biocompatibility of TiO2 and Eu3+-doped TiO2 NCs during the development of Drosophila to test the hypothesis that the doping process could improve its tracking properties. For this, we performed in vivo tracking of NCs and status redox analysis using fluorescence microscopy, evaluating the mortality of fruit flies after exposure to NCs during their post-embryonic development and verifying the effect of exposure on the longevity of adult individuals.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis and Characterization of TiO2 and Eu3+-Doped TiO2 Nanocrystals
The TiO2 NCs were synthesized by coprecipitation as described by Silva et al. [27]. TiO2 NCs were synthesized at room temperature in aqueous solution containing 300 mL of ultrapure water, 90 mL of nitric acid (HNO3, 70%, Sigma Aldrich, Saint Louis, MO, USA) and 60 mL of titanium isopropoxide (Ti(OCH(CH3)2)4, 97%). The resulting solution was left standing for precipitation of TiO2 NCs. The precipitate was monodispersed in ultrapure water under magnetic stirring and then submitted to centrifugation at 6000 rpm/10 min. The resulting purified precipitate was subjected to annealing treatment in the environmental atmosphere at 500 °C/1 h. Eu3+-doped TiO2 were synthesized using the same procedure adding during the synthesis 1 wt% europium chloride (EuCl2, 99,999%). Subsequently, the thermal treatments were carried out at 500 °C/1 h. All reagents were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich®.
2.2. Characterization
The X-ray diffraction (XRD) was recorded with a DRX-6000 (Shimadzu, Shenzhen, China) using monochromatic radiation Cu-Kα1 (λ = 1.54056 Å) in order to confirm the formation of TiO2 NCs, and crystal structure. FL spectra were performed by Fluorolog 3, Horiba-Jobin Yvon using an excitation line of 325 nm.
The morphology, crystalline structure, and individual diameter were characterized using Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) as described by Qualhato et al. [30]. The TEM images were obtained in a JEOL (JEM-2100, JEOL USA) microscope, using image analysis software Scandium (Version 1.2, Olympus Soft Imaging Solutions GmbH). The individual diameter of a total of 200 particles was measured using the ImageJ software (National Institute of Health, USA). In order to determine the elemental composition of both NCs, the energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) (Thermo scientific NSS Spectral Imaging) was used.
2.3. Tracking of TiO2 and Eu3+-Doped TiO2 Nanocrystals and Fluorescence Intensity Analysis In Vivo
Canton S larvae and adults were dissected to confirm the exposure to NCs during development and to track whether NCs would accumulate in their tissues. Drosophila embryos were stage collected for 1 h in agar plates and left to develop into first instar larvae for 24 h. About 50 larvae were transferred to vials with 4.0 mL of a standard food supplemented with TiO2 or Eu3+-doped TiO2 at a concentration of 4 mg/mL. The gut, fat body, and brain tissues of larvae and adults were dissected in ice-cold Drosophila Ringer’s solution and fixed in paraformaldehyde 4% for 25 min. Tissues were analyzed for the presence of TiO2 and Eu3+-doped TiO2 nanocrystals in a SP8 confocal microscope (Leica Microsystems) under 405 and 552 nm laser exposure, respectively.
2.4. Nanotoxicology Study
2.4.1. Preparation of Stock Solution of the TiO2 and Eu3+-Doped TiO2 and Drosophila Stocks
The samples of TiO2 and Eu3+-doped TiO2 were suspended in ultra-pure water to create 10 mg/mL stock dispersions that were used to prepare the appropriate concentrations for the in vivo analysis. The NCs in dispersion were then dispersed using a 5-W probe sonicator (Elmasonic EASY 60 H, Misonix, USA) for 30 min prior to use.
Animals of the Canton S lineage of D. melanogaster (Diptera, Drosophilidae) were reared on a standard cornmeal media (cornmeal, agar, yeast extract, NaCl, sugar and propionic acid) at 25 ± 1 °C with 60–70% humidity and 12 h light and 12 h dark cycle.
2.4.2. Analysis of Drosophila Development under TiO2 and Eu3+-Doped TiO2 Exposure
The developmental assay is important to evaluate if TiO2 and Eu3+-doped TiO2 nanocrystals could affect the overall development of Drosophila and cause any lethality during each of the developmental stages. In order to perform this experiment, approximately 100 males and females were kept in a 6oz plastic bottle containing a grape juice-based agar cap at the bottom. The embryo collection was carried out in 8-h intervals when the caps were replaced. After 24 h of the egg collection, embryos developed into larvae and these newly hatched larvae were then transferred to experimental vials containing 4 mL of a standard cornmeal media containing one different concentration of TiO2 or Eu3+-doped TiO2 nanocrystal (0.25, 0.50, 1.00, 2.00, 4.00 mg/mL). The standard cornmeal media was used to control. Six replicates containing 35 larvae were set up for each nanocrystal concentration and the animals were monitored during the following stages of development.
The animals that reached the pupal stage were recorded daily followed by the collection of all animals that emerged as adults. The analysis of the daily pupation frequency compared to control was used to determine any delay during larval development. The difference between the initial number of larvae transferred to the media and the total number of pupae represents the larval lethality for each experimental concentration. The difference between the total number of animals that reached the pupal stage and the number of emerging adults represents the pupal lethality for a given TiO2 and Eu3+-doped TiO2 nanocrystal concentration.
2.4.3. Longevity Measurements
All animals that developed in standard cornmeal media containing TiO2 or Eu3+-doped TiO2 nanocrystal concentration that reached adulthood were separated in males and females and kept in vials with standard control media. These animals were transferred to a new vial with fresh standard media every three days. The number of deaths for each experimental group was recorded daily until all individuals were dead. The lifetime of individuals that have developed in media containing TiO2 or Eu3+-doped TiO2 nanocrystals was compared to control animals that developed in a standard media and was expressed as lifespan.
2.4.4. Redox Homeostasis Analysis following Nanocrystals Exposure
UAS-mito-roGFP2-Orp1 flies (mitochondrial H2O2 biosensor probe) were crossed with ppl-GAL4 flies. L1 Larvae genotyped as ppl-GAL4>UAS-mito-roGFP2-Orp1 were exposed for 96 h to concentrations of 0.25 and 4 mg/mL of Eu3+-doped TiO2. Following this exposure period, larvae were dissected and the fat body analyzed under fluorescence microscopy (Microscope EVOS M7000). The roGFP2 probes are sensitive to redox changes, when oxidized the roGFP2 protein is excited at 405 nm while its reduced structure is excited at 488 nm. The animals’ fat body was observed and photographed in the two excitation channels and the images were subsequently analyzed [31]. The analyzes were performed in ImageJ following these steps: 1-We subtracted the background from the images using the “subtract background” option with rolling ball radius = 50 pixels. 2-We convert both images to 32-bit format by selecting type>32-bit. 3-We use the “threshold” option and apply Otsu’s algorithm to create a pixel intensity threshold in the 488 nm channel images. The pixels below the created threshold were defined as “not a number (NaN).” 4-Images with the intensity ratio between oxidation and reduction (ratiometric images) were created from the 405/488 nm division using the “Ratio plus” plugin. 5-The images had their display defined by the “Fire” option. 6-Finally, using the “Measure” option, the average data and standard deviation of the images were obtained.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
All statistical analyses were performed using the Graphpad Prism software (version 8.0, GraphPad Software Inc., San Diego, CA, USA). The pupation rate, larval, and pupal lethality data were submitted to analysis of homogeneity of variance with the Shapiro-Wilk test. Parametric data were subjected to analysis of variance (two-way ANOVA) followed by the Tukey test to mean comparison. The significance level of 5% was adopted and the data are presented as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM). The survival curves (lifespan) were tested for equality between groups using the log-rank test.
3. Results and Discussion
Nanoparticles are widely used in biomedicine, food industry, cosmetics, and textile industry [5,11]. Thus, studies that evaluate the toxicity of these materials are essential to provide safety information. In the present study, we suggest that TiO2 and Eu3+-doped TiO2 NCs are toxic to D. melanogaster from an early stage of development. Furthermore, it was possible to track Eu3+-doped TiO2 NCs by visualizing its red fluorescence in dissected tissues of fruit flies at different stages of development.
3.1. Characterization of TiO2 and Eu+3-Doped TiO2 Nanocrystals
The structural and optical properties of pure and doped NCs with europium ions were investigated using X-ray diffraction and fluorescence spectroscopy, respectively (Figure 1). In the diffractograms, it is observed that both the pure and the doped sample present the characteristic diffraction peaks of TiO2 in the anatase phase (JCPDS card no. 21-1272) (Figure 1a). The doping with europium ions only favored the local disorder, due to the widening of the diffraction peaks, maintaining the same crystalline phase as the pure TiO2 nanocrystals (anatase). Additional peaks were not observed, suggesting that this doping concentration did not favor the formation of other crystals. The inset of the figure shows an illustrative image of the crystalline arrangement of the anatase phase of TiO2, with and without the substitutional incorporation of europium ions in the structure.
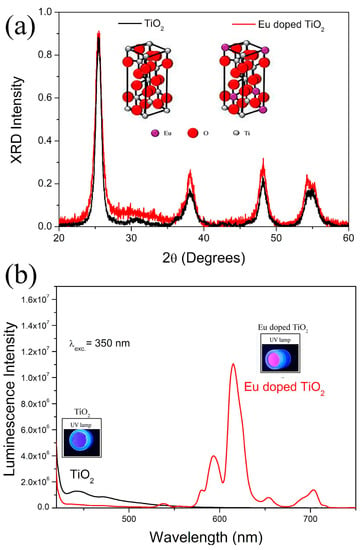
Figure 1.
(a) XRD patterns and (b) luminescence spectra of TiO2 and Eu3+-doped TiO2 (TiO2:Eu) nanocrystals.
In Figure 1b, the fluorescence spectra of pure and Eu3+-doped TiO2 NCs are observed using an excitation line of 325 nm. The samples of pure TiO2 NCs present the luminescence in blue, while in the doped samples the luminescence is seen in blue and more intense in the red spectrum. The red luminescence is characteristic of europium ions (Eu3+) confirming its incorporation into the crystalline structure of TiO2. The inset shows the photo of nanopowders of pure and Eu3+-doped TiO2 NCs under UV light. Therefore, based on these results, we confirm the formation of pure and Eu3+-doped TiO2 NCs.
The TEM showed that the TiO2 and Eu3+-doped TiO2 NCs have crystalline and rounded shapes with individual diameters of 14.52 ± 4 and 15.32 ± 5, respectively (Figure 2). The Energy Dispersive X-Ray Spectroscopy (EDS) results confirmed the chemical composition of both NCs, indicating the presence of Ti and O in both samples. Furthermore, elemental analysis does not detect Eu in Eu3+-doped TiO2 NCs, indicating its low concentration. Thus, these results showed that the NC surface is mainly composed of Ti and O elements.
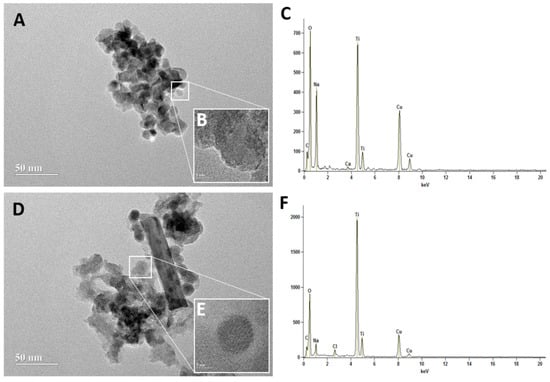
Figure 2.
Transmission Electron Microscopic (TEM) image of TiO2 (A,B) and Eu3+-doped TiO2 (TiO2:Eu) nanocrystals (D,E). Scale bar = 50 nm (A,D) and 5 nm (B,E). The Energy Dispersive X-Ray Spectroscopy (EDS) of TiO2 (C) and Eu3+-doped TiO2 (TiO2: Eu) nanocrystals (F) representing the elemental composition of nanocrystals.
3.2. Tracking of TiO2 and Eu3+-Doped TiO2 Nanocrystals In Vivo
We tracked TiO2 and Eu3+-doped TiO2 NCs in vivo in larvae (Figure 3 and Figure 4) and adults (Figure 5) of D. melanogaster. Canton S flies exposed from the first instar larvae to TiO2 and Eu3+-doped TiO2 at a concentration of 4 mg/mL showed the presence of these NCs in the third instar larval gut, fat body, and brain.
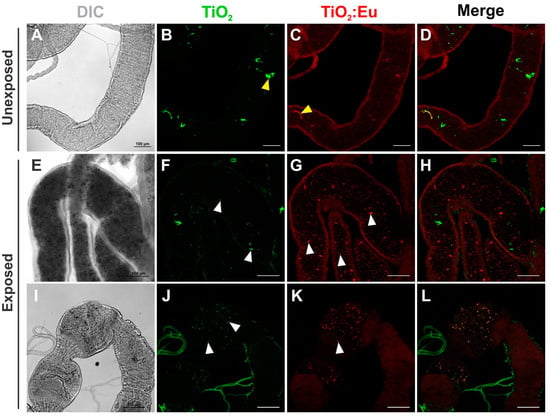
Figure 3.
Confocal images of the distribution of TiO2 and Eu3+-doped TiO2 nanocrystals in the Drosophila third instar larval gut. (A–D) Gut dissected from unexposed third instar larvae fed in standard food medium showing autofluorescence of the food. (E–L) Gut dissected from third instar larvae exposed to 4 mg/mL of TiO2 and Eu3+-doped TiO2 showed nanocrystals dispersed along the lumen of the midgut (E–H) and the foregut (I–L). DIC: differential interference contrast; Green: TiO2 nanocrystals fluorescence under 405 nm excitation; Red: Eu3+-doped TiO2 nanocrystals fluorescence under 552 nm excitation. Yellow arrowheads in (B) and (C) represent autofluorescent cornmeal found in standard Drosophila media and white arrowheads in (F,G,J,K) indicate nanocrystal aggregates. Scale bars = 100 μm.
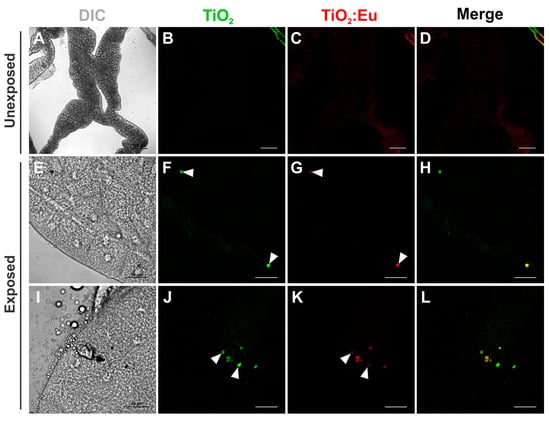
Figure 4.
Confocal images of the distribution of TiO2 and Eu3+-doped TiO2 nanocrystals in the Drosophila third instar larval fat body. (A–D) Fat body dissected from unexposed flies fed in standard food medium show any signal of luminescence. (E–L) Fat body dissected from third instar larvae exposed to 4 mg/mL of TiO2 and Eu3+-doped TiO2 showed aggregates of these nanocrystals in some cells (arrowheads). DIC: differential interference contrast; Green: TiO2 nanocrystals fluorescence under 405 nm excitation; Red: Eu3+-doped TiO2 nanocrystals fluorescence under 552 nm excitation. Scale bars: 100 μm (A–D); 50 μm (E–L).
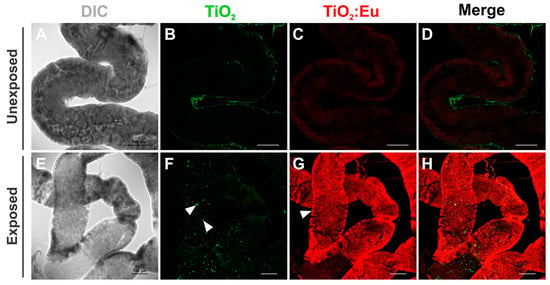
Figure 5.
Confocal images of the distribution of TiO2 and Eu3+-doped TiO2 nanocrystals in the Drosophila adult gut. (A–D) Gut dissected from unexposed flies fed in standard food medium showing a poor signal of autofluorescence of the food. ((E–H) Gut dissected from adult flies developed in 4 mg/mL of TiO2 and Eu3+-doped TiO2 showed these nanocrystals dispersed along the lumen (arrowheads in (F)). Eu3+-doped TiO2 nanocrystals have also been found in the cytoplasm of the cells that form the wall of the gut (arrowhead in (G)). DIC: differential interference contrast; Green: TiO2 nanocrystals fluorescence under 405 nm laser excitation; Red: Eu3+-doped TiO2 nanocrystals fluorescence under 552 nm laser excitation. Scale bars = 100 μm.
It was possible to observe the luminescence of TiO2 and Eu3+-doped TiO2 in the intestinal contents (culture medium) of the larvae (L3) when observed at a wavelength of 405 nm for TiO2 and at 522 nm for Eu3+-doped TiO2. In the gut, NC aggregates appear being dispersed along the lumen (Figure 3E–L, white arrowheads). A poor signal with a different pattern of distribution could also be detected at the lumen in the gut of unexposed flies, which is attributed to the well-known autofluorescence of standard cornmeal media (Figure 3A–D, yellow arrowheads). This result confirms the oral exposure of larvae to NCs during D. melanogaster development.
We also identified NC aggregates in some cells of the fat body and brain of Drosophila L3 larvae (arrowheads in Figure 4 and Figure S1, respectively). Unlike what was detected in the larval gut, NC aggregates in the fat body were located inside the cells (arrowheads in Figure 4F–H,J–L), demonstrating that the NCs crossed the gut cells and that a small amount was accumulated in the fat body cells. A much smaller amount of NC aggregates was also found in larval brains (arrowheads in Figure S1). These findings demonstrate the accumulation of NCs in the larval fat body and brain following exposure during the development of D. melanogaster.
When animals were fed on the medium containing NCs at the beginning of the adult stage, we could also identify the presence of NCs at the lumen of the gut (Figure 5, arrowheads in F). Interestingly, besides the lumen, Eu3+-doped TiO2 NCs were found in the cytoplasm of the cells that form the wall of the gut (arrowhead in Figure 5G), suggesting that these NCs could assume a different pattern of distribution, being able to accumulate longer in the adult gut cells when compared to larvae.
It is noteworthy that the incorporation of Europium (Eu) to TiO2 NCs allowed its in vivo tracking by fluorescence microscopy with greater intensity in the red spectrum, when compared to pure TiO2. Therefore, doping using Eu metal allowed tracking NCs in vivo with greater efficiency and high clarity. This methodology offers advantages not only in the possibility of observing NCs in vivo, but also in the speed of analysis, as it is a simpler and relatively cheaper technique compared to mass spectrometry or electron microscopy. The ability to track the in vivo distribution of these NCs in tissues is important to understand the mechanisms involved in its toxicity, and doping with the metal Eu can improve this tracking. Acquiring luminescent images in vivo is a great advantage as it improves the visualization of biological processes in intact living organisms, and thus provides quantitative information beyond the reach of conventional in vitro and fixed material analysis [20].
However, as seen in previous research, exposure to TiO2 NCs during early fruit fly development causes toxic effects to animals, such as the following: morphological changes in the adult fat body, aberrant phenotypes, and genotoxicity [4,6,8,17]. Therefore, we also investigated the in vivo toxicity of TiO2 and Eu3+-doped TiO2 NCs at different concentrations.
3.3. Nanotoxicology Study
Our goal was to analyze the global development of Drosophila when the TiO2 and Eu3+-doped TiO2 nanocrystals were added to the standard medium. As shown in Figure 6A, developmental delay during larval stages was only observed in larvae that developed in standard media containing TiO2 nanocrystals in the higher concentration (4 mg/mL). However, we did not observe any larval development delay when larvae were exposed to Eu3+-doped TiO2 nanocrystals (Figure 6B). The developmental delay seen in larvae exposed to higher concentrations of TiO2 indicates that the ingestion of these nanocrystals led to toxicity, as expressed by the longer time to reach the pupal stage. Developmental delay following exposure has already been observed by some toxicity studies using titanium dioxide [10,17,32].
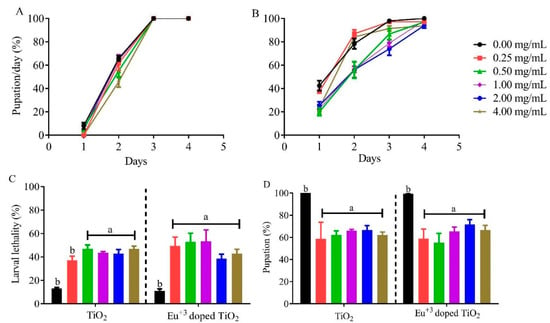
Figure 6.
Larval exposure to TiO2 and Eu3+-doped TiO2 nanocrystals leads to high rates of larval lethality. Daily pupation analysis of Drosophila melanogaster following the exposure to (A) TiO2 or (B) Eu3+-doped TiO2 nanocrystals. Animals that developed in standard cornmeal medium supplemented with TiO2 only showed developmental delay at the higher concentration, while no delay was observed when larvae developed in Eu3+-doped TiO2. Data is represented as a geometric mean. T (C) The lethality rate and (D) pupation rate of Drosophila melanogaster when exposure to TiO2 and Eu3+-doped TiO2 nanocrystals. Data are represented as mean ± SEM.
Next, we analyzed the larval lethality caused by TiO2 and Eu3+-doped TiO2 exposure. As shown in Figure 6C, the exposure to both nanocrystals showed similar larval lethality rates when compared to control, with animals exposed to TiO2 presenting larval lethality higher than 50% for all concentrations above 0.50 mg/mL (Figure 4A). The same effect was observed when animals developed in Eu doped TiO2 nanocrystals. All experimental groups, regardless of concentration tested, showed a larval lethality rate 30–40% higher than the control group (Figure 6C). Consequently, this high larval lethality was reflected in the lower pupation percentage (Figure 6D) caused by TiO2 or Eu3+-doped TiO2 NCs. Altogether, our results indicate that TiO2 and Eu3+-doped TiO2 NCs generate high toxicity during larval development in all tested concentrations.
The TiO2 NC mediates toxicity by inducing the formation of reactive species, mainly superoxide radical anion (O*2−) [11,33]; moreover, it reduces the expression of catalase (CAT) and superoxide dismutase (SOD) [17]. These events can lead to redox imbalance and consequently oxidative stress. Oxidative stress pathways have a dual function, triggering a pro-oxidant effect and also as a target of the hormone ecdysone (the hormone responsible for directing the progression of D. melanogaster development during larval stages and pupal metamorphosis) through a series of oxidation-reduction reactions. The main antioxidant protein that participates in the ecdysone biosynthesis process is glutathione (GSH) [10,34,35]. The decrease in GSH caused by TiO2 [9] can then interfere in larval transitions, reflecting directly in the larval development delay observed when animals were exposed to TiO2 and Eu3+-doped TiO2.
Our next analysis focused on demonstrating the mechanism by which Eu3+-doped TiO2 NCs act as pro-oxidants. For this aim, we used in vivo probes of H2O2 in which reduction and oxidation can be detected as changes in the fluorescence spectrum. The larval fat body of animals that developed in 4 mg/mL Eu3+-doped TiO2 showed higher intensity of fluorescence in 405 nm spectrum when compared to control (Figure 7G–J). These results demonstrate an oxidized tissue, as the higher concentration of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) caused a shift in fluorescence from 488 nm to 405 nm (oxidation), when compared to the control and the lowest concentration tested (0.25 mg/mL). These high levels of H2O2 show that the tissue is in a state of redox imbalance, induced by the nanocrystals, as already reported by other authors [33,36]. Consequently, increased levels of H2O2 can act as a substrate for the formation of other reactive species such as hydroxyl radical (OH*) and hypochlorous acid (HOCl), which leads to oxidative distress and consequently different pathophysiologies [35,36].
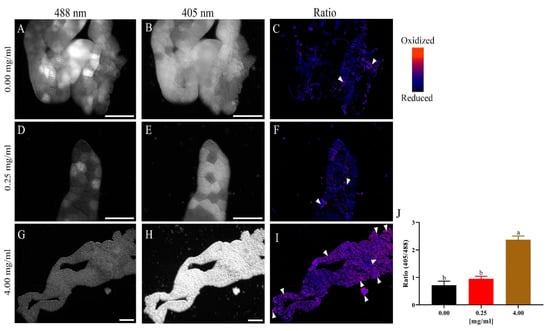
Figure 7.
Larval exposure to Eu3+-doped TiO2 leads to higher levels of tissue oxidation. Representative images of the fat body of L3 larvae expressing the hydrogen peroxide-sensitive mitochondrial probe mito-roGFP2-Orp1, ppl-GAL4>UAS-mito-roGFP2-Orp1 (n = 5 per group). (A–C): representative images of the fat body of animals exposed to the control medium. In (A), the reduction channel (488 nm) for roGFP2 is observed. In (B), the oxidation channel (405 nm) is observed for the same probe. In (C), the ratiometric image (405 nm/488 nm) of the same acquisition is shown. (D–F): Representative images of the fat body of animals exposed to 0.25 mg/mL of Eu3+-doped TiO2, with (D,E) showing the reduction and oxidation channels, respectively. In (F) the ratiometric image (405 nm/488 nm) is formed by images (D,E). (G–I): Representative images of the fat body of animals exposed to 4 mg/mL of Eu3+-doped TiO2, in which we can clearly observe the increase in oxidation (H,J). Scale bars = 150 μm.
The lifespan of adult animals exposed to TiO2 nanocrystals did not differ from the control group (Figure 8A). Fruit flies exposed to TiO2 at similar concentrations to those in this study also showed no changes in adult survival time [9,10]. Interestingly, animals exposed to Eu3+-doped TiO2 survived 15 days longer than the control group, showing greater longevity (Figure 8B). The fact that the exposure to these nanocrystals during larval development did not decrease adult lifespan have been discussed in previous studies [9,13]. It is believed that nanoparticles are stored in the fat body, as seen in this work, and not in the imaginal discs, and then it is not transferred between stage transitions of the fly, such as from larva to pupa [9,13]. In a previous work we observed that the NCs accumulated in the fat body during the pupal stage are excreted soon after adult emergence [20], and thus probably do not interfere with the longevity of adult animals, as observed in this study.
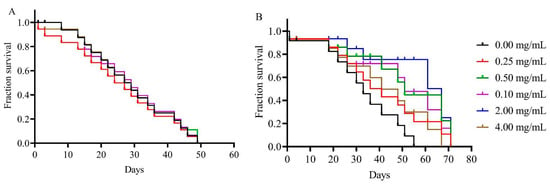
Figure 8.
Larval exposure to TiO2 and Eu3+-doped TiO2 does not interfere with adult lifespan. Drosophila adults that developed in standard medium containing TiO2 (A) or Eu3+-doped TiO2 (B) nanocrystals did not show any significant decrease in adult survival. Data are represented as the log of the percentage of flies that are alive at each age.
Here, we demonstrate for the first time the in vivo tracking of TiO2 and Eu3+-doped TiO2 NCs using the luminescent characteristic of these NCs. The doping of TiO2 with the Eu+3 ions ensured the best visualization of NCs in the tissues and intestinal contents of the animals after exposure. This doping proved to be a good technological approach applicable to biomedical screening work, such as its coupling to biomolecules or drugs. This coupling may allow monitoring at the molecular level, improving tracking techniques in cellular studies. However, this application should be used with caution and in a concentration equal to or less than 0.25 mg/mL, since the Eu3+-doped TiO2 NCs, as well as TiO2, proved to be a pro-oxidant, causing a high rate of larval and pupal mortality. Thus, additional studies are needed to ensure a safer concentration for potential biomedical applications of Eu3+-doped TiO2. A good alternative would be to use the less toxic TiO2 phase doped with Europium, as well as the doping of Eu3+-doped TiO2 nanocrystals with additional coupling partners that could increase its biocompatibility.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/chemosensors11010055/s1, Figure S1: Confocal images of the distribution of TiO2 and Eu3+-doped TiO2 nanocrystals in the Drosophila third instar larval brain.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.A., J.M.d.O. and A.C.A.S.; methodology, F.R.A.d.S., K.T.R.d.S., A.C.A.S., J.P.S.d.C., N.O.D., L.A., J.M.d.O., F.B.V., R.K.O.T. and T.L.R.; validation, A.C.A.S. and J.P.S.d.C., formal analysis, A.C.A.S., L.A. and J.M.d.O.; investigation, A.C.A.S., J.M.d.O., L.A. and K.T.R.d.S.; resources, A.C.A.S., N.O.D. and O.W.d.C.; data curation, A.C.A.S., J.P.S.d.C., J.M.d.O. and L.A.; writing—original draft preparation, J.M.d.O., A.C.A.S., N.O.D. and L.A.; writing—review and editing, A.C.A.S., L.A., O.W.d.C., F.B.V., R.K.O.T. and T.L.R.; visualization, A.C.A.S. and L.A.; supervision, A.C.A.S. and L.A.; project administration, A.C.A.S. and L.A.; funding acquisition, A.C.A.S., N.O.D. and O.W.d.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES), Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de Minas Gerais (FAPEMIG), Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de Alagoas (FAPEAL) and National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq), and Productivity the Nr. 3115 8/2017-3 (N.O.D), Productivity the Nr. 311730/2020-5 (A.C.A.S.) and Productivity the Nr. 306329/2020-4 (Rocha T.L).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
This study did not report any data.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the X-ray diffraction and luminescence measurements performed in the multi-user laboratory of the Physics Institute of the Federal University of Uberlândia. The authors also acknowledge CRTI and LabMic of the Federal University of Goiás for their collaboration in the characterization of nanoparticles (TEM and EDS).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Bayda, S.; Adeel, M.; Tuccinardi, T.; Cordani, M.; Rizzolio, F. The History of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology: From Chemical-Physical Applications to Nanomedicine. Molecules 2020, 25, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranowska-Wójcik, E.; Szwajgier, D.; Oleszczuk, P.; Winiarska-Mieczan, A. Effects of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles Exposure on Human Health—A Review. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2020, 193, 118–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziental, D.; Czarczynska-Goslinska, B.; Mlynarczyk, D.T.; Glowacka-Sobotta, A.; Stanisz, B.; Goslinski, T.; Sobotta, L. Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles: Prospects and Applications in Medicine. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sario, S.; Silva, A.M.; Gaivão, I. Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles: Toxicity and Genotoxicity in Drosophila Melanogaster (SMART Eye-Spot Test and Comet Assay in Neuroblasts). Mutat Res. Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2018, 831, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, M.M.; Tavčer, P.F.; Tomšič, B. Influence of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles on Human Health and the Environment. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovanović, B.; Jovanović, N.; Cvetković, V.J.; Matić, S.; Stanić, S.; Whitley, E.M.; Mitrović, T.L. The Effects of a Human Food Additive, Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles E171, on Drosophila Melanogaster-A 20 Generation Dietary Exposure Experiment. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grande, F.; Tucci, P. Mini-Reviews in Medicinal Chemistry SCIENCE BENTHAM Impact Factor: 2.903 Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles: A Risk for Human Health? Rev. Med. Chem. 2016, 16, 762–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmona, E.R.; Escobar, B.; Vales, G.; Marcos, R. Genotoxic Testing of Titanium Dioxide Anatase Nanoparticles Using the Wing-Spot Test and the Comet Assay in Drosophila. Mutat Res. Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2015, 778, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Sun, J.; Xue, Y. Involvement of JNK and P53 Activation in G2/M Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis Induced by Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles in Neuron Cells. Toxicol. Lett. 2010, 199, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posgai, R.; Cipolla-McCulloch, C.B.; Murphy, K.R.; Hussain, S.M.; Rowe, J.J.; Nielsen, M.G. Differential Toxicity of Silver and Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles on Drosophila Melanogaster Development, Reproductive Effort, and Viability: Size, Coatings and Antioxidants Matter. Chemosphere 2011, 85, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, G.I.; Saeed, M.; Wu, A. 2 Toxicity of TiO2 Nanoparticles; Wiley Online Library: New York, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Cvetković, V.J.; Jovanović, B.; Lazarević, M.; Jovanović, N.; Savić-Zdravković, D.; Mitrović, T.; Žikić, V. Changes in the Wing Shape and Size in Drosophila Melanogaster Treated with Food Grade Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles (E171)—A Multigenerational Study. Chemosphere 2020, 261, 127787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jovanović, B.; Cvetković, V.J.; Mitrović, T.L. Effects of Human Food Grade Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticle Dietary Exposure on Drosophila Melanogaster Survival, Fecundity, Pupation and Expression of Antioxidant Genes. Chemosphere 2016, 144, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pogribna, M.; Koonce, N.A.; Mathew, A.; Word, B.; Patri, A.K.; Lyn-Cook, B.; Hammons, G. Effect of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles on DNA Methylation in Multiple Human Cell Lines. Nanotoxicology 2020, 14, 534–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamboungou, J.; Canedo, A.; Qualhato, G.; Rocha, T.L.; Vieira, L.G. Environmental Risk of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticle and Cadmium Mixture: Developmental Toxicity Assessment in Zebrafish (Danio Rerio). J. Nanopart. Res. 2022, 24, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovanović, B. Critical Review of Public Health Regulations of Titanium Dioxide, a Human Food Additive. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2015, 11, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jovanović, B. Review of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticle Phototoxicity: Developing a Phototoxicity Ratio to Correct the Endpoint Values of Toxicity Tests. Environ. Toxicol Chem. 2015, 34, 1070–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lankoff, A.; Sandberg, W.J.; Wegierek-Ciuk, A.; Lisowska, H.; Refsnes, M.; Sartowska, B.; Schwarze, P.E.; Meczynska-Wielgosz, S.; Wojewodzka, M.; Kruszewski, M. The Effect of Agglomeration State of Silver and Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles on Cellular Response of HepG2, A549 and THP-1 Cells. Toxicol. Lett. 2012, 208, 197–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, M.R.; Shadab, G.G.H.A. Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticle Genotoxicity: A Review of Recent in Vivo and in Vitro Studies. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2020, 36, 514–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.C.A.; Dantas, N.O.; Silva, M.J.B.; Spanó, M.A.; Goulart, L.R. Functional Nanocrystals: Towards Biocompatibility, Nontoxicity and Biospecificity Chapter 2. In Advances in Biochemistry & Applications in Medicine Advances in Biochemistry & Applications in Medicine; Shrestha, R., Ed.; Open Access eBooks: Las Vegas, NV, USA, 2014; Volume 1, pp. 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Sandoval, S.; Yang, J.; Alfaro, J.G.; Liberman, A.; Makale, M.; Chiang, C.E.; Schuller, I.K.; Kummel, A.C.; Trogler, W.C. Europium-Doped TiO2 Hollow Nanoshells: Two-Photon Imaging of Cell Binding. Chem. Mater. 2012, 24, 4222–4230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.C.A.; Alvin, E.A.; dos Santos, F.R.A.; de Matos, S.L.M.; de Oliveira, J.M.; Silva, A.S.; Guimarães, É.v; Vieira, M.S.; Da, E.A.; Filho, S.; et al. Doped Semiconductor Nanocrystals: Development and Applications. In Materials at the Nanoscale, 1st ed.; Mallik, A., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2021; Volume 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norris, D.J.; Efros, A.L.; Erwin, S.C. Doped Nanocrystals. Science 2008, 319, 1776–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padmanabhan, P.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, S.; Chaudhary, R.K.; Gulyás, B. Nanoparticles in Practice for Molecular-Imaging Applications: An Overview. Acta Biomater 2016, 41, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvador, F.F.S.; Francisco, L.H.C.; Brito, H.F.; Felinto, M.C.F.C. Development of Europium-Doped Ultrasmall Luminescent Tin Oxide Nanoparticles for Applications in Nuclear Medicine. In Proceedings of the International Nuclear Atlantic Conference, Virtual Meeting, 29 November–2 December 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, H.; Li, X.; Sun, M.; Wu, S.; Chen, H. Synthesis of Europium-Doped Fluorapatite Nanorods and Their Biomedical Applications in Drug Delivery. Molecules 2017, 22, 753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, M.S. Toxicological Studies on model organism Drosophila melanogaster. EPRA Int. J. Multidiscip. Res. (IJMR)-Peer Rev. J. 2022, 8, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiter, L.T.; Potocki, L.; Chien, S.; Gribskov, M.; Bier, E. A Systematic Analysis of Human Disease-Associated Gene Sequences in Drosophila Melanogaster. Genome Res. 2001, 11, 1114–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, U.B.; Nichols, C.D. Human Disease Models in Drosophila Melanogaster and the Role of the Fly in Therapeutic Drug Discovery. Pharmacol Rev. 2011, 63, 411–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qualhato, G.; Rocha, T.L.; de Oliveira Lima, E.C.; e Silva, D.M.; Cardoso, J.R.; Koppe Grisolia, C.; de Sabóia-Morais, S.M.T. Genotoxic and Mutagenic Assessment of Iron Oxide (Maghemite-Γ-Fe2O3) Nanoparticle in the Guppy Poecilia Reticulata. Chemosphere 2017, 183, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, S.C.; Barata, A.G.; Großhans, J.; Teleman, A.A.; Dick, T.P. In Vivo Mapping of Hydrogen Peroxide and Oxidized Glutathione Reveals Chemical and Regional Specificity of Redox Homeostasis. Cell Metab 2011, 14, 819–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanraj, V.J.; Chen, Y. Nanoparticles-A Review. Trop. J. Pharmaceut. Res. 2006, 5, 561–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaram, D.T.; Payne, C.K. Intracellular Generation of Superoxide by TiO2Nanoparticles Decreases Histone Deacetylase 9 (HDAC9), an Epigenetic Modifier. Bioconjug Chem 2020, 31, 1354–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Connacher, R.P.; O’Connor, M.B. Control of the Insect Metamorphic Transition by Ecdysteroid Production and Secretion. Curr. Opin. Insect. Sci. 2021, 43, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sies, H. Hydrogen Peroxide as a Central Redox Signaling Molecule in Physiological Oxidative Stress: Oxidative Eustress. Redox. Biol. 2017, 11, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrés, C.M.C.; Pérez de la Lastra, J.M.; Juan, C.A.; Plou, F.J.; Pérez-Lebeña, E. Chemistry of Hydrogen Peroxide Formation and Elimination in Mammalian Cells, and Its Role in Various Pathologies. Stresses 2022, 2, 256–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).