Abstract
Carbon-based quantum dots and their nanocomposites have sparked immense interest for researchers as sensors due to their attractive physico-chemical properties caused by edge effects and quantum confinement. In this review article, we have discussed the synthesis and application of nanocomposites of graphene quantum dots (GQDs) and carbon quantum dots (CQDs). Different synthetic strategies for CQDs, GQDs, and their nanocomposites, are categorized as top-down and bottom-up approaches which include laser ablation, arc-discharge, chemical oxidation, ultrasonication, oxidative cleavage, microwave synthesis, thermal decomposition, solvothermal or hydrothermal method, stepwise organic synthesis, carbonization from small molecules or polymers, and impregnation. A comparison of methodologies is presented. The environmental application of nanocomposites of CQDs/GQDs and pristine quantum dots as sensors are presented in detail. Their applications envisage important domains dealing with the sensing of pollutant molecules. Recent advances and future perspective in the use of CQDs, GQDs, and their nanocomposites as sensors are also explored.
1. Introduction
Carbon-based materials have gained immense attention for environmental decontamination owing to their appealing physicochemical characteristics viz large specific surface area, tunable structure, low toxicity, and outstanding stability. Quantum dots (QDs) are semiconductor nanoparticles (NPs) of a size less than 10 nm, confined inside spatial dimensions with quantized energy states [1,2]. The atoms in the QDs are arranged similarly to those in bulk materials, however because of 3-dimensional truncation, there are more atoms on their surfaces. QDs have exceptional luminescent and electrical features, including a narrow emission, broad and continuous absorption spectrum, and great light stability [3,4].
Semiconductor-based QDs are highly effective inorganic fluorescent probes, having long-term photobleaching resistance. In terms of biocompatibility, chemical inertness, and low cytotoxicity, carbon-based QDs viz. carbon quantum dots (CQDs) and graphene quantum dots (GQDs) outperform the typical semiconductor QDs such as CdSe dots, ZnO dots and others [5,6,7,8]. They utilize easily available natural resources as raw materials, and have a number of advantages, including wavelength-dependent luminescence emission, ease of synthesis, and bioconjugation [9,10]. Their optical characteristics are improved by the non-zero band gap. They also exhibit edge effects caused by the existence of a functional group on their surface. In the case of carbon-based QDs, a broad photoluminescence emission with strong excitation wavelength dependency and broad absorption bands are seen [11]. Most researchers have reported their applications in electrocatalysis [12,13,14,15], light-emitting diodes [16], tumor imaging and therapy [17], cell labelling [18], and cell imaging research [19]. As per data from Science Direct, more than twenty-three hundred articles have been published on CQDs and GQDs to July 2022. However, a review elaborating the sensing properties of nanocomposites made of CQDs, and GQDs, is lacking. In the present review, a complete account on the synthesis of CQDs, GQDs, and their nanocomposites, with various inorganic and organic materials, is given. The current research scenario for their environmental application as sensors, and future thrust areas of research, are explored.
2. CQDs and GQDs
CQDs are small carbon NPs with a size less than 10 nm having excellent conductivity, chemical stability, environmental friendliness, high photostability, broadband optical absorption, low toxicity, photobleaching resistance, high surface area, and ease of modification. The photoluminescent properties of CQDs are their most notable feature [20,21]. CQDs have high fluorescence stability, which indicates that the fluorescence emission intensity can remain constant even after a long time of continuous stimulation. CQDs are an appealing option in sensor applications because of their unique properties [22]. Due to many carboxyl groups on their surface, CQDs have outstanding potential to either contain appropriate chemically reactive groups for functionalization, or to connect with diverse polymeric, organic, biological, inorganics, or natural materials, for surface modification. Surface passivation promotes fluorescence, and surface functionalization improves solubility in both aqueous and non-aqueous media [23]. When there is a lot of oxygen in the air, it creates a new energy state inside the band gap of CQDs, which causes the diameter to shift [24]. Thus, CQDs as sensors have grabbed the interest of researchers [25].
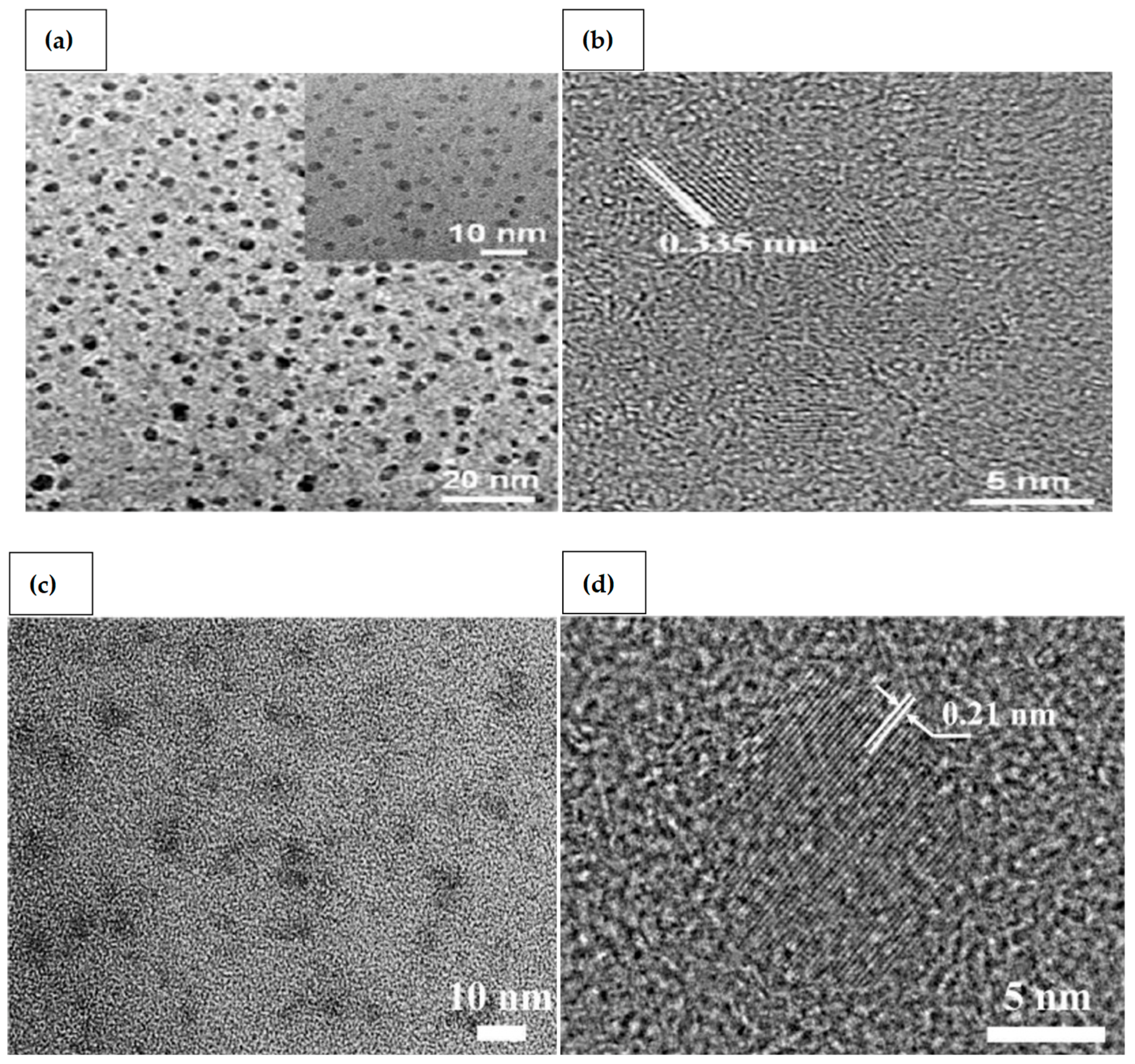
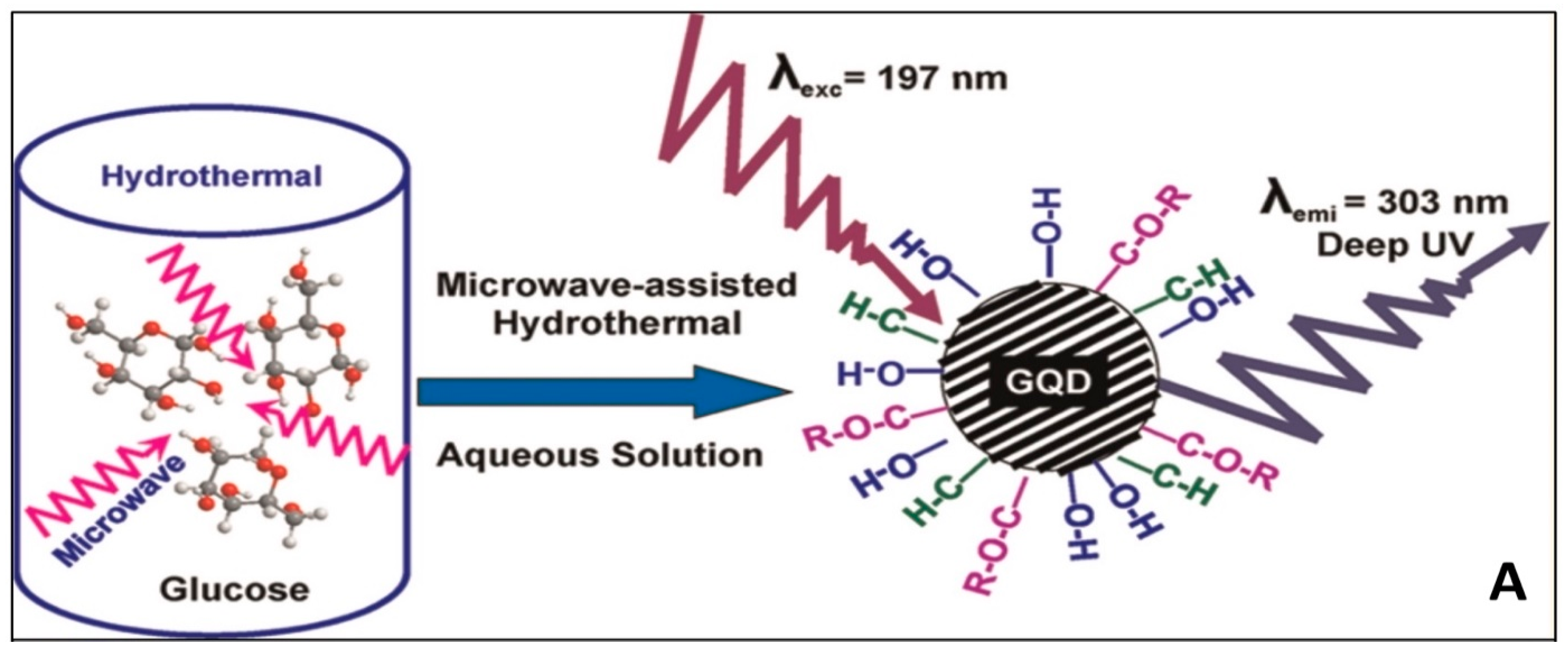
GQDs are two-dimensional nanocrystals composed of small graphene particles with lateral diameters less than 100 nm. Single atomic layered GQDs containing only carbon are ideal. They are also known to include oxygen and hydrogen, as well as many layers having a thickness of less than 10 nm. GQDs have an adjustable band gap energy between 0 and 6 eV. Due to the quantum confinement effect, and conjugated edge effects, the band gap can be tailored by modifying the lateral size or surface chemical characteristics [26]. GQDs have exceptional optoelectronic capabilities, high biocompatibility, and low manufacturing costs, making them a viable alternative to well-known metal chalcogenides-based quantum dots. In addition, compared to typical semiconductor quantum dots, graphene has remarkable thermal and electrical conductivity because of the bonding below and above the atomic plane [27,28]. Tunable photoluminescence (PL), outstanding biocompatibility, remarkable spin property, exceptional UV-blocking capability, and high photo stability, are among the wide range of excellent properties of GQDs, along with other physical characteristics such as high surface area and surface grafting assistance through conjugated network [29]. As the pH of GQDs solution is increased from 1.0 to 11.0, a red shift from 522 to 575 nm is detected [30]. This is caused by deprotonation of oxygen-containing functional groups like carboxyl, hydroxyl, and epoxy. A peak at 626 nm is detected at pH levels of more than 11.0, giving it red florescence. They are quite sensitive to changes in pH and temperature, and even with a small change in temperature or pH, a rapid shift in fluorescence has been reported. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM) images reveal monodispersed GQDs and CQDs [31,32] (Figure 1). Because of their distinctive photoluminescence properties and tendency to conjugate with various biomolecules, CQDs and GQDs have gained much interest in biomedical and bioanalytical applications. The development of sensitive bioanalysis systems for use in point-of-care testing would also benefit from the usage of CQDs and GQDs in conjunction with their unique optical properties. The simple accessibility of several types of carbon dots for therapeutic usage may mark a discernible improvement in their application. Excellent performance and excellent practicality have been demonstrated for the CQDs-based biomacromolecule detection in point-of-care testing for viruses [33]. Very recently, Li et al. [34] successfully used Gd3+ doped CQDs and specific antibody to detect SARS-CoV-2. Yuan et al. [35] utilized GQDs, gold nanoclusters that were conjugated with antibodies to detect pathogens.
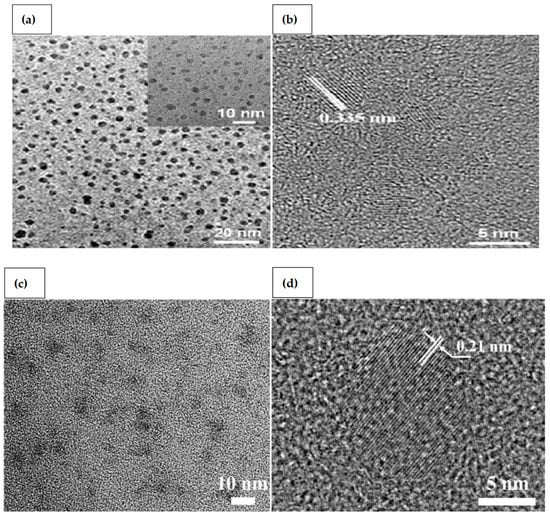
Figure 1.
(a) TEM; (b) HRTEM image of GQDs (Adapted from the Ref. [31] with the permission of catalysts); (c) TEM; and (d) HRTEM image of CQDs (Adapted from the Ref. [32] with the permission of ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces).
3. Difference between CQDs and GQDs
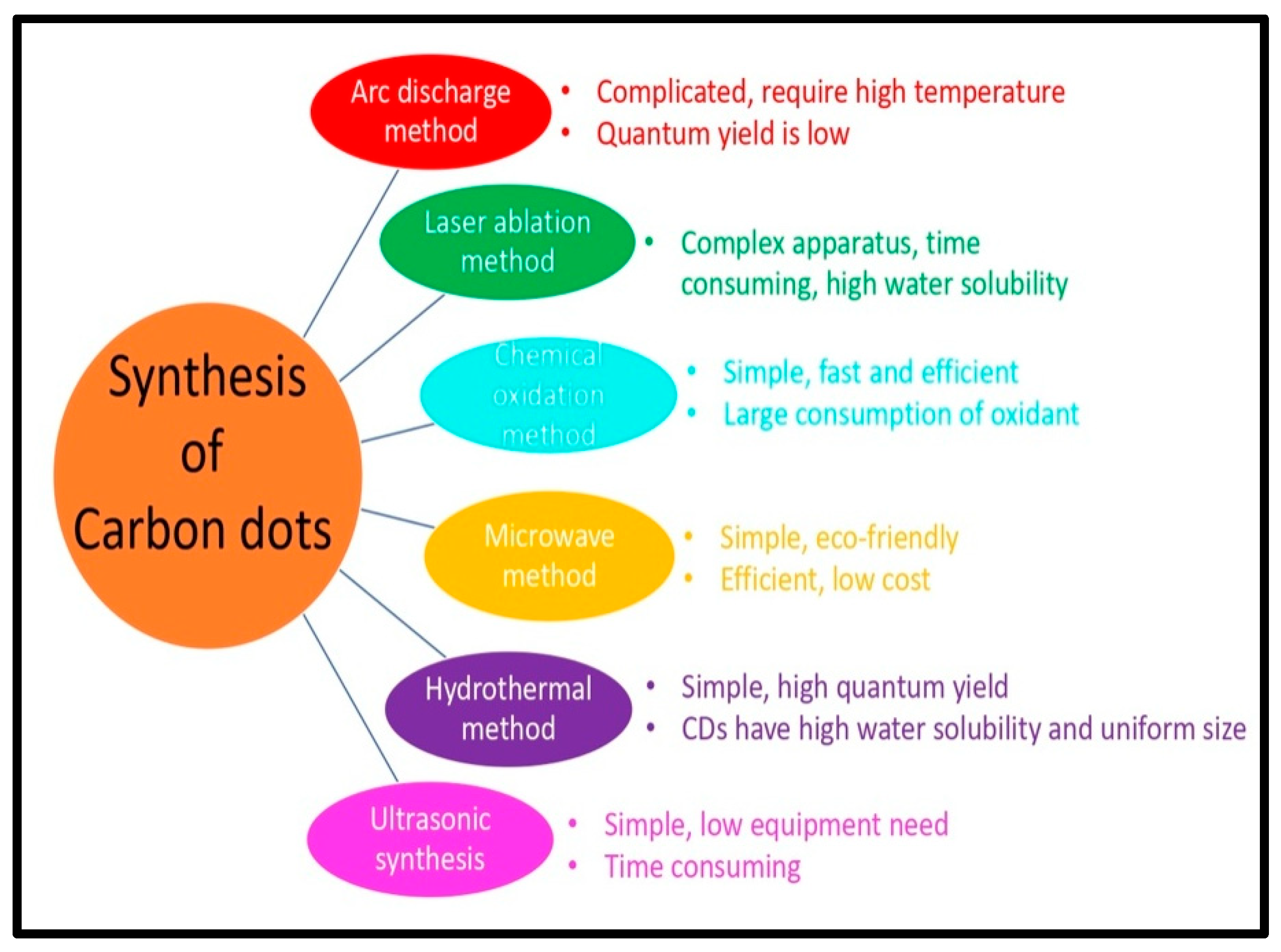
CQDs and GQDs differ in their structural properties. GQDs are crystalline and sp2 hybridized, while CQDs are amorphous and sp3 hybridized. Surface defects produce the fluorescence of CQDs, which have a diameter of less than 10 nm. Quantum confinement causes the fluorescence of GQDs, which range in size from 2 to 20 nm [36]. GQDs are distinguished from carbon dots (CDs) by the graphene sheets within the dots, which is less than 100 nm in size and just 10 layers thick. CDs are usually carbon nanoparticles that are quasi-spherical in shape [37]. GQDs are ideal spherical nanocrystals of sp2 carbon nanosheets, whereas other types of carbon-based dots, such as CQDs, have a more complex structure with a carbogenic core, which in some cases resembles graphene nanolayers coupled with amorphous carbon. Two types of carbogenic spherical structures: one with a crystalline core holding both sp2 and sp3 carbons; and the other with a disordered structural core containing predominantly sp3 carbons, can be present. Bandgap transitions are produced by conjugated domains of QDs, which resemble massive aromatic systems with substantial conjugation of certain electronic energy bandgaps for photoluminescence emissions. Such electronic transitions are caused by the absorption of light by a number of high-density electrons in the sp2 hybridized orbitals, which have a substantial absorption band in the ultraviolet region [38]. The synthesis of CQDs, GQDs, and their nanocomposites, is covered in the next two parts. Figure 2 shows different methods of synthesis of CQDs and GQDs.
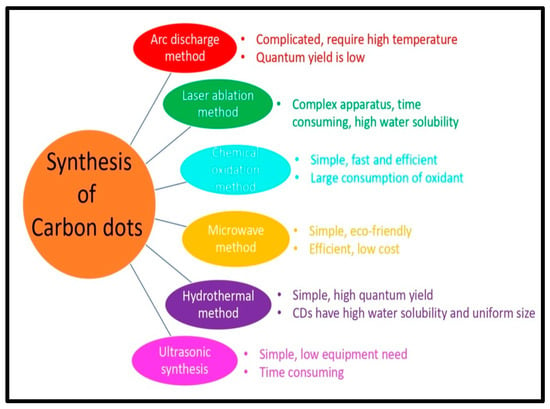
Figure 2.
Different methods for synthesis of CQDs and GQDs and their distinctive features.
4. Synthesis of CQDs, GQDs and Their Nanocomposites
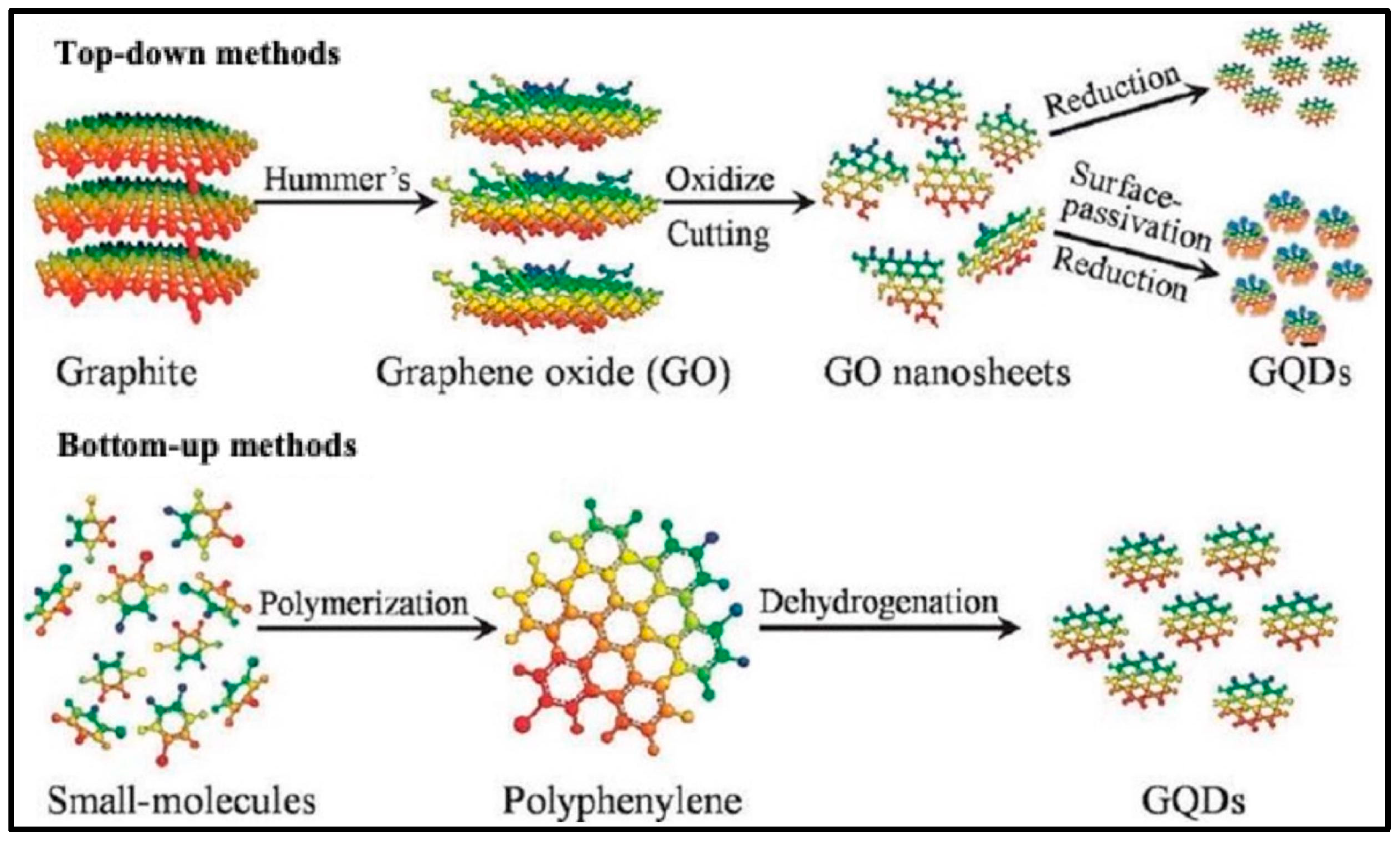
“Top-down” and “bottom-up” methods can be used to synthesize CQDs and GQDs, respectively [31] (Figure 3). Bottom-up methods include carbonization or pyrolysis of tiny organic molecules, as well as step-by-step chemical fusion of smaller aromatic molecules, whereas top-down methods include chemical, electrochemical, or physical decomposition approaches of big sized suitable materials containing carbon, like carbon black, graphene oxide, graphite, or carbon fibers [39,40]. CQDs can operate as electron sinks, transporting electrons from the semiconductor surface to the reactants [41]. The addition of metals (Cu, Ln, Zn, etc.), organic chemicals (L-tryptophan, polyethylenimine, etc.), and inorganic compounds (TiO2, ZnO, Fe3O4, etc.) to CQDs/GQDs improves optical characteristics by causing surface defects and altering the band gap [42,43,44,45,46,47]. The overall qualities required for their application in diverse fields can be enhanced by changes in the electronic structure [48]. The next section elaborates the synthesis of CQDs, GQDs, and their nanocomposites, using both top-down and bottom-up methodologies, as well as some unique synthesis routes.
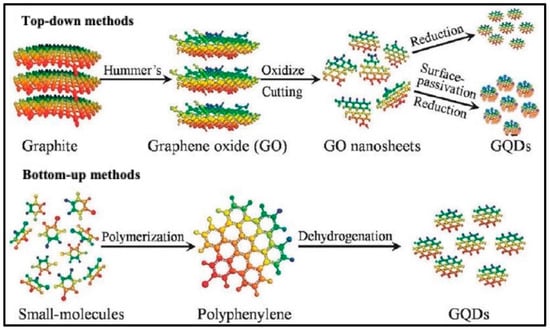
Figure 3.
Schematic representation of GQD synthesis using top-down and bottom-up approach (Adapted from the Ref. [31] with the permission of ACS).
4.1. Top-Down Methods for the Synthesis of CQDs and Their Nanocomposites
Physical or chemical techniques are commonly used to remove and chop massive carbon substrates to make tiny CQDs in the top-down methodology [49,50]. Xu et al. [20] and Bottini et al. [51] synthesized CQDs with varied quantum yields (QY) (0.016) by arc discharge processing of single wall/multi wall carbon nanotubes (SWCNT, MWCNT). This approach can reorder carbon atoms obtained from the breakdown of bulk carbon precursors [52]. Biazar et al. [53] developed a technique for producing CQDs and CQDs/TiO2 by using a direct-current arc discharge among high-purity graphite electrodes with size 27 nm. Though arc discharge was initially engaged in CQDs synthesis, the quantum yield (QY), homogeneity, and size of the generated CQDs are inadequate, and this approach has scale-up limitations as well, as there is the necessity for a small quantity of metal catalysts. As a result, further purification procedures are required. Furthermore, because of the high temperature requirement, this is not an ideal approach for the synthesis of CQDs.
Carbon materials can also be etched with a high-energy laser to produce CQDs with definite fluorescence quantum yield. Sun et al. [54] proposed a CQD synthesis approach that involves laser etching a carbon target in water vapor followed by acid treatment to produce CQDs with intense photoluminescence and a small size, which is beneficial for attaining higher QY. Doate-Buendia et al. [55] and Yu et al. [56] synthesized fluorescent CQDs by illuminating the target carbon glassy particles contained in toluene and polyethylene glycol 200 with laser with QY (15% and 18%) and size (3 and 4.2 nm), respectively. It is feasible to change the surface of CQDs during laser irradiation by using appropriate organic solvents; as a result, the PL properties of the manufactured CQDs can be adjusted [57]. The benefit of using double pulse laser technology over single pulse laser technology is the ability to employ the second pulse’s shock wave ablates the created CQDs even more, resulting in smaller particles [58]. By producing a high number of functional groups on the surface of CQDs, this method can improve their optical and catalytic sensing capabilities. This approach was used by Nguyen et al. [59] to make CQDs as small as 1 nm. Laser etching is among the most efficient way of making CQDs with a narrow size range, a strong fluorescence characteristic, and good water solubility. This approach, however, has a limited practical utility since it requires post-processing activities, sophisticated apparatus, and expensive machinery, and there have only been a small number of examples of GQD produced by laser from environmentally favorable raw materials.
Carbon compounds are treated with powerful oxidants such as hydrogen peroxide, nitric acid, and sulfuric acid, in the chemical oxidation technique. This methodology is simple to use, quick, and highly repeatable, and it allows for large-scale CQD manufacturing. Using nitric acid and concentrated sulfuric acid, Liu et al. [60] and Peng and Travas-Sejdic [61] produced fluorescent and luminous CQDs from candle soot and carbohydrates, respectively. CQDs made from candle soot have an adjustable fluorescence, which opens up a new way to make multicolor luminous CQDs with size smaller than 2 nm and QY of 0.8 to 1.9%. By combining different acids and H2O2, fullerene carbon soot [62] and coal pitch powder [63] can be transformed into CQDs. In addition, by exfoliating carbon fiber fragments with nitric acid reflux and regulating the molecular weight selection and crystallization time, Bao et al. [64] generated CQDs with varied degrees of surface oxidation and sizes (2.5–3.0 nm) with QY of 1.1 to 20.7%. Chen et al. [65] heated and refluxed citric acid and polyethyleneimine (PEI) to produce PEI-CQDs with 1–6 nm size dispersion. The caustic chemical reagents utilized in this approach necessitate tight experimental conditions. As a result, utilization of mild oxidant during chemical oxidation of CQDs is an essential research direction.
In the presence of acid, alkali, or oxidants, ultrasonic waves could be utilized to break down carbon products into nanoparticles, which is a new approach for CQD synthesis that eliminates complex post-treatment operations, allowing for the simple synthesis of CQDs with small sizes. In 2011, Li et al. [66] used ultrasonically processed glucose in the basic or acidic environment to create photoluminescence CQDs with 7% of quantum yield and a radius of less than 2.5 nm. This approach was employed by Qiang et al. [67] to make CQDs from potato starch. Huang et al. [68] and Lu et al. [69] described a thiol-terminated polyethylene glycol functionalized fluorescent CQDs (size: 2–10 nm) and blue fluorescent N-CQDs (QY:3.6 percent and size: 2.5–5.5 nm) synthesis technique using ultrasound. Even when the same solvent is employed in the synthesis procedure as Huang et al., the size of the obtained CQDs is different, highlighting the relevance of the source of carbon used in the procedure. Zhang et al. [70] and Ma et al. [71] created BiOBr/N-CD nanocomposites and nitrogen doped carbon dots (NCDs) utilizing citric acid and ethylenediamine as the starting material in the former case, and aqua ammonia and glucose as the precursor in the latter case. These precursors produced NCDs with high water dispersibility and no surface changes, as well as steady and robust visible emissions and high up-conversion photoluminescence. Dang et al. [72] used a simple and economical process for massive manufacturing of white fluorescent carbon dots (WCDs) using a one-phase ultrasonic technique with polyamide resin with QY of 28.3 % and size (2–4 nm). The ultrasonication process was used to create mesoporous CQDs NC with ZnO films [73]. The presence of CQDs caused the mesopore collapse of the inorganic matrix of ZnO, which resulted in a low surface area of NC. The ultrasound-assisted approach has low equipment needs, is simple to use, and saves time, but the QY of CQDs is typically poor, making the requirements for high fluorescence performance challenging. As a result, the preparation process must be constantly monitored.
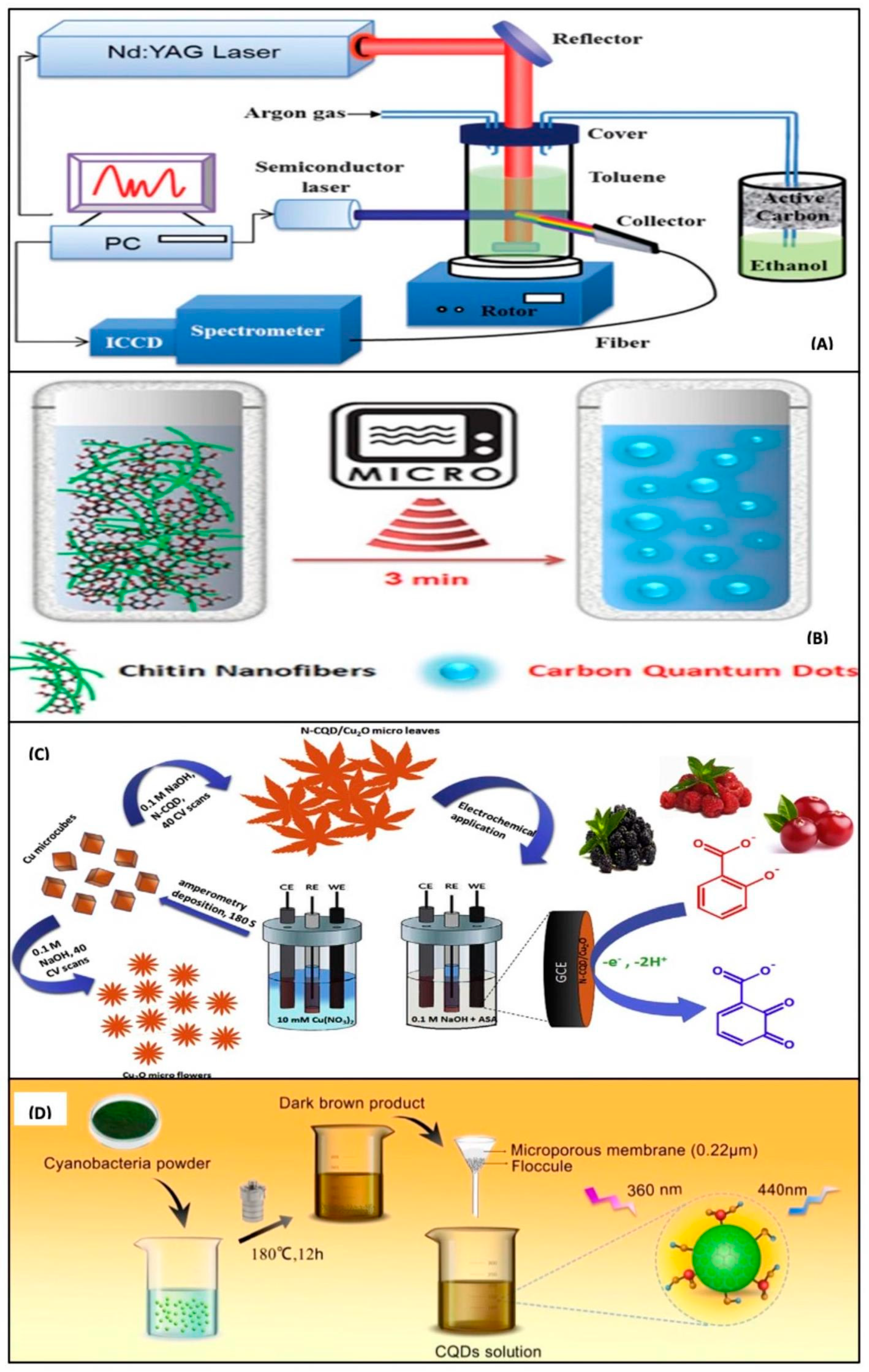
Top-down approaches were generally used in the initial phases of CQD fabrication research since post-processing procedures are challenging [74,75]. The sp2 conjugate structure of CQDs generated with high-energy techniques makes it easier to express inherent luminescence from the carbon nucleus. CQDs with a broad variety of optical characteristics and quantum accuracy can be created by adjusting reaction parameters, delaying the reaction, and fine-tuning the cleansing operations, even if the sizes and quality of CQDs are hard to regulate in these procedures [76]. Figure 4 shows various methods for synthesis of CQDs [77]; they include laser ablation method, microwave, electrochemical, and hydrothermal methods.
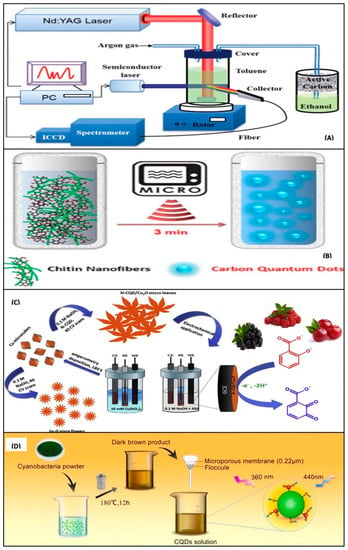
Figure 4.
Synthetic approach for CQDs: (A) laser ablation method; (B) microwave method; (C) electrochemical method; and (D) hydrothermal method (Adapted from the Ref. [77] with the permission of nanomaterials).
4.2. Bottom-Up Methods for Thesynthesis of CQDs and Their Nanocomposites
In the bottom-up synthesis of nanometer-sized CQDs, microwave and hydrothermal radiation are commonly used to assemble tiny organic compounds or oligomer starters [78,79]. The produced CQDs can exhibit greater QY and remarkable optical characteristics when subjected to high frequency, strong radiation, and intense heat [77]. Researchers have been favoring this approach for producing CQDs in recent years since it is simple to prepare and operate, the process parameters are controlled, as well as the raw components being affordable, allowing for one-step high-volume CQD synthesis. CQDs and N-CQDs were made by direct carbonization or pyrolysis of dispersed carbonaceous micro-crystals of asphaltene and ethylene diamine tetra-acetic acid (EDTA), respectively, with QY of 87% and 5.1% by Wang et al. [80] and Ma et al. [81]. Simplified processes, solvent-free techniques, scalable generation, shorter reaction duration, low cost, and a wider precursor tolerance, are advantages of this technology. Furthermore, changes in key parameters such as reaction temperatures, reflux duration, and reaction pH are used to optimize the optical properties of CQDs. Wang et al. [82] synthesized NiS/CQD/ZnIn2S4 nanocomposites by the microwave method.
Different raw materials such as glucose, citric acid [83], and polyacrylamide, have been used to make CQDs via hydrothermal treatment [84]. Nabiyouni et al. [85] synthesized CuFe2O4-CQD nanocomposite by this method. CQDs were synthesized by Zhang et al. [86] and Wang et al. [87] using ascorbic acid and cyanobacteria with an average size of CQDs 2 nm and 2.48 nm, and QY of 6.75 and 9.24%, respectively. Liu et al. [88] synthesized N-CQDs using high temperature (200 °C) with a size of 5 to 6 nm and QY of 46.01%. The size and shape of CQDs, the solvent used, and the reaction duration in the hydrothermal process, have been demonstrated to be substantially linked to their PL efficiency and fluorescence QY. The dust color of CQDs denoted the production of Fe2O3-CQDs composite, via hydrothermal treatment [47]. Due to the presence of CQDs, a faint XRD peak at 26° was noticed. In the XRD pattern of ZnO-CQDs nanocomposites, a similar diffraction peak of CQDs was detected at 26° [46]. By adding glucose to a ternary nanocomposite of CQDs with Fe3O4@mesoporous-TiO2 nano pom-pom balls and processing the resulting solution hydrothermally at 140 °C for 4 h, multiple w:w ratios of ternary nanocomposite of CQDs with Fe3O4@mesoporous-TiO2 koosh balls were synthesized in varying w:w ratios [89]. N-CQDs, TiO2, and Fe3O4, were used to make a similar ternary nanocomposite [90]. Terbium (III)-N-doped carbon dots (N-CDs-Tb-DPA) and copper nanoclusters@nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots (CuNCs–CNQDs) nanohybrids were manufactured in two steps by He et al. [91] and Li et al. [92]. Al-Enizi et al. [93] used a simple hydrothermal approach to make a CQDs/Ce-NiO nanocomposite with a good BET surface area of 731 m2 g−1. One of the most often used methods of CQD synthesis is the hydrothermal method, which has the advantages of ease of use, low-cost, environmental friendliness, and simple equipment. However, this approach needs a high temperature of reaction and a lengthy reaction time.
Microwave synthesis refers to the chemical synthesis of CQDs that takes place in the presence of microwave irradiation. Microwave technology has been recognized as a speedy and cost-effective tool for efficiently slowing down reaction times and providing contemporaneous homogeneous heating, which aids in the production of a smooth size distribution of QDs. Under high frequency microwave, Zhu et al. [94] and Rodrguez-Padrón et al. [95] produced fluorescent CQDs with a narrow size by using polyethylene glycol, and lignocellulosic raw material, respectively. Choi et al. [96] used microwave-induced thermal carbonization to pyrolyze AB2 type lysine and make CQDs that are water soluble and have 23.3% of quantum yield. This synthesis took around 5 min to complete. N-CQDs were produced by microwave heating of xylan as a precursor in the ammonia solution using 2-azidazole and glycerin, respectively, with size (4.4 and 2.8 nm), QY (4% and 27.9%), and LOD (6.49 and 6.3 nm) by Yang et al. [97] and Feng et al. [98]. Mondal et al. [99] used a home microwave oven to make amino functionalized CQDs. Sharma et al. [100] used this technique to study a quaternary composite of CQDs with La, Cu, and Zr elements. The presence of CQDs in La/Cu/Zr trimetallic nanocomposite was confirmed by FT-IR spectra that showed asymmetric and symmetric C-H stretching vibration peak at 2921 and 2849 cm−1, respectively. Microwave heating is an interesting and effective process for preparing carbon materials, particularly CQDs with tiny dimensions. Because of its time and energy savings, predictable operations, and lack of complex equipment, the microwave aided approach has become one of the most widely utilized methods of CQD synthesis.
Nanocomposites of CQDs have also been synthesized using other methods such as simple stirring and calcination. For the synthesis of nanocomposites of ZnO foam with CQDs, Ding et al. [46] employed a simple mixing approach. CQDs were made by treating sucrose hydrothermally at 185 °C for 5 h in a Teflon-lined stainless-steel autoclave. To make ZnS/CQDs NC, Kaur et al. [101] employed ascorbic acid as a precursor. This method was employed by Liu et al. [102] to make CQDs-AgNO3 NC. Briscoe et al. [103] synthesized ZnO nanorods coated with CQDs by simply soaking ZnO prepared over fluorine doped tin oxide substrates in a 0.1 m zinc acetate solution in methanol after spray pyrolysis.
4.3. Top-Down Methods for Synthesis of GQDs and Their Nanocomposites
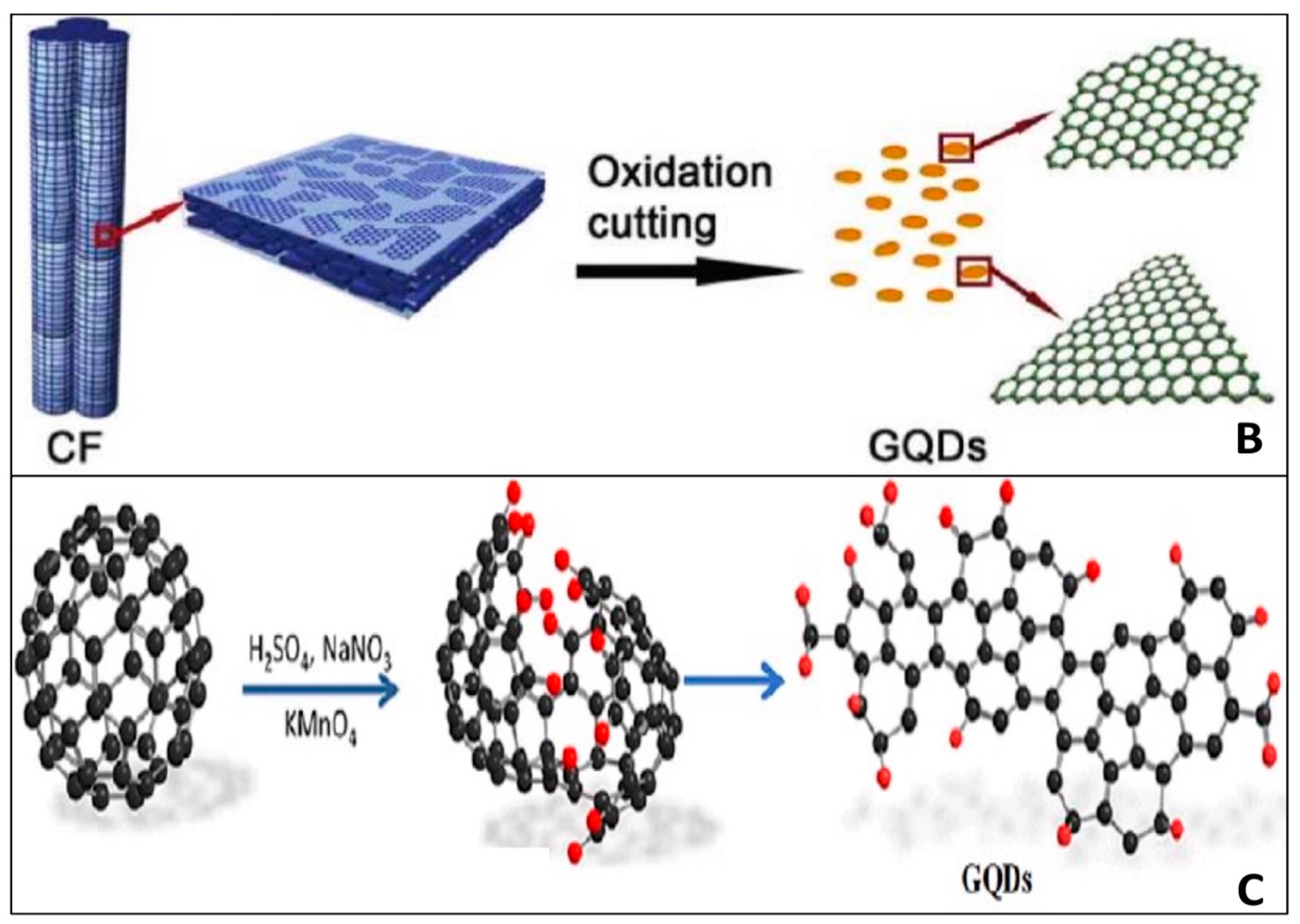
The top-down technique is widely used in the synthesis of GQDs. In a traditional top-down synthesis, resources of carbon, such as carbon nanotube [104], graphite powder [105], carbon black [106], coal [107], and carbon fiber [108], are oxidized, separated, and broken, at the oxidized defect site. Researchers created a weak electrolyte electrochemical approach to expedite the oxidation and cutting process, resulting in a high yield of GQDs, in order to manufacture controllable and highly crystalline GQDs in aquatic conditions. Huang et al. [109] and Chen et al. [110] developed GQDs with ammonia and borax solution, however QY is 28 times higher in the first instance than in the later. Shinde et al. [111] used LiClO4 as the electrolyte in propylene carbonate and cut multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) by a two-step electrochemical oxidation to produce size-tunable GQDs (size = 3, 5, 8.2 nm and QY = 6.3%). A large-scale synthesis of multicolor GQDs, including orange (O)-GQDs, yellow (Y)-GQDs, blue (B)-GQDs, and green (G)-GQDs, was reported using a low-cost energy source, coke, and a simple and straightforward one-step electrochemical technique [112]. The electrochemical oxidation technique provides a stable GQDs solution, but it takes a long time to pre-treat raw materials and purify GQDs products, and the QY is low, making large-scale GQD production difficult.
GQDs were synthesized by Liu et al. [113] and Lu et al. [114] utilizing carbon black as a source of carbon and H2O2 and nitric acid as oxidants, respectively, with size (4.2 and 3–4.5 nm) and QY (5.1 and 4.1%) but the latter technique was reported as faster. To make GQDs, Peng et al. [115] employed GO as a precursor, to obtain a size range of 1–4 nm. The cage-opening, oxidation, and fragmentation processes, were activated after fullerene was treated with a combination of chemical oxidant and strong acid. Acid treatment and chemical exfoliation of multi-walled carbon nanotubes resulted in GQDs with a zigzag edge structure, two-dimensional morphology, and homogenous size distribution (MWCNTs) [116]. However, because strong oxidants such as sulphuric acid and nitric acid are used, the chemical oxidation technique is not particularly eco-friendly, and the waste produced is likely to harm the atmosphere. Chua et al. [117] employed fullerene as carbon precursor to build tiny GQDs (2–3 nm) by the hydrothermal method.
The hydrothermal method is a rapid and easy way to make GQDs. This approach has a number of benefits, including minimal cost, no need of dialysis or purification, high quantum yield, and a straightforward experiment. Higher quantum yield is obtained in this method due to the extreme conditions used in this approach and the lack of material exchange with the environment; the reaction follows both an aromatization and a polymerization process [118]. Without the need of a costly catalyst or any strong acids, this technique simply needs deionized water as a reaction medium [119]. Additionally, this technique does not need dialysis bags to remove extra strong chemicals or acids that were utilized, nor does it require a base solution to balance the pH of the solution [120]. Pan et al. [121] and Zhang et al. [122] employed GO as precursor material for the hydrothermal formation of GQDs and reduced graphene quantum dots (rGQDs) and obtained QY of 6.9% and 24.62%, respectively. Wang et al. [123] described a large-scale manufacturing of GQDs from rice husks with QY of 15%. Experiments revealed that the synthesized GQDs were biocompatible and quickly transferred into the cytoplasm, making them suitable for cell imaging. Starch [116] and neem leaves [124] have also been identified as GQD precursors. They are simple and environmentally benign feedstock for GQD production that does not require the use of acid or oxidation. The GQDs had a strong PL emission, good water solubility, low cytotoxicity, and great biocompatibility, as they were produced. Inserting heteroatoms into GQDs can improve their chemical and physical characteristics. For example, Liu et al. [125] synthesized B, N-GQDs with QY of 5.13% using a one-pot hydrothermal technique. This technique was employed by Pan et al. [126] to make TiO2/GQDs NC. Furthermore, Zhao et al. [127] synthesized NC of GQDs with MoS2. It does, however, constitute a safety concern due to high pressure and temperature, and the long time, generally at least 5 h [128,129]. For the synthesis of water soluble GQDs, Tang et al. [130] used a microwave aided hydrothermal technique.
One of the most prevalent issues when using the oxidative cleavage or hydrothermal/solvothermal methods is the extended reaction time. The microwave technique is extensively used to prepare GQDs because it is a fast-heating process. It can not only reduce reaction time but also increase output yield [131,132]. GQDs and rGQDs were made by cleaving GO and calcining Calotropis gigantea latex to 300 °C under microwave irradiation, by Li et al. [133] and Murugesan et al. [134]. Greenish yellow luminescent GQDs with QY of 11.7% were obtained in the former case. For the synthesis of GQDs, Wen et al. [135] presented a comprehensive O3/H2O2/ultrasound technique and obtained a size of 4–10 nm. In a supercritical CO2/H2O system aided by ultrasound, Gao et al. [136] employed natural graphite, oxide graphite, and expanded graphite, as raw materials to synthesize extended graphene quantum dots (EGQDs), pristine graphene quantum dots (PGQDs), and graphene oxide quantum dots (GOQDs). The results of the studies indicate that this technique is an eco-friendly, fast, less costly, and wide GQD manufacturing technique, that can provide a green option for the manufacturing of a variety of GQDs. Researchers have reported an increasing number of production processes depending on standard methods such as pulsed laser ablation (PLA) and chemical vapor deposition (CVD) due to the unusual shape and good characteristics of GQDs. To open up a novel approach for preparing GQDs, Kang et al. [137] employed pulsed laser ablation to generate GQDs from multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs). The synthesized GQDs had a visible blue photoluminescence with a QY of 12%, as well as adequate brightness and resolution for photoelectric applications.
4.4. Bottom-Up Method for Synthesis of GQDs and Their Nanocomposites
Bottom-up techniques, such as controlled fabrication or carbonization from appropriate organic compounds or polymeric materials, have been reported less frequently than top-down approaches. Bayat et al. [138] and Teymourinia et al. [139] employed glucose and corn flour as precursors for the production of green photoluminescent single-layer graphene quantum dots (SLGQDs) and GQDs, respectively. Corn flour-based GQDs have a diameter of 20–30 nm. Low cost, high yield, and wide scale, are all advantages of the prepared SLGQDs. By combusting trisodium citrate and then ultra-filtering them, Hong et al. [140] developed a novel process for making single layer GQDs with an ultra-small lateral dimension of quantum confinement effect, 1.3 ± 0.5 nm and a QY of 3.6%. The application of the molecular carbonization process is difficult. The GQDs created using this approach are multi-dispersive due to the inability to properly regulate the structure and size of GQDs [141]. Li et al. [142] used controlled synthesis to create GQDs with 168, 132, and 170 carbon atoms. The GQDs have a regular shape and size, as well as a specified number of carbon atoms. The synthesis method, on the other hand, entails a series of multistep, sophisticated chemical reactions that take a lot of time to complete and provide a poor yield. Wang et al. [143] recently developed pyrene-derived GQDs with -OH group with a QY of 63%.
Pyrolysis of carbon-containing sources with chemicals of interest to be added is another method employed by some scientists. Dong et al. [144] stated that Fe3O4@GQDs NC was made by pyrolyzing citric acid. Under stirring for 30 min, an aqueous solution of acetic acid and chitosan was added to the co-precipitated Fe3O4 NPs. Kadian et al. [145] used a bottom-up strategy to produce sulphur doped graphene quantum dots (SGQDs) via direct pyrolysis of citric acid and 3-Mercaptopropionic acid. The synthesis of chitosan (CS)-GQDs NCs with a size of 2.5 nm was carried out by Ou et al. [146] using a simple stirring process. Bu et al. [147] employed this process to make TiO2 from N-GQDs by calcining the mixture at 200 °C for 2 h in a N2 environment. The XRD pattern validated the decorating of N-GQDs on the black TiO2 surface, with all of the products’ diffraction peaks matching the crystal structure of anatase TiO2. GQDs, Bi2O2CO3, and N-Bi2O2CO3/GQDs composites, with a size of 3–5 nm were synthesized by Liu et al. [148] using a refluxing and magnetic stirring approach. Figure 5 shows various method of synthesis of GQDs. Citric acid has been widely used as a precursor in the formation of GQDs. To make blue luminescent N-GQDs by hydrothermal technique, Ju et al. [149] employed citric acid and dicyandiamide as carbon sources and achieved a QY of 32.4%. Deka et al. [150] synthesized hydrophobic graphene quantum dots (h-GQDs) with a size of less than 10 nm, grown through CVD using hydrogen and acetylene as raw materials.
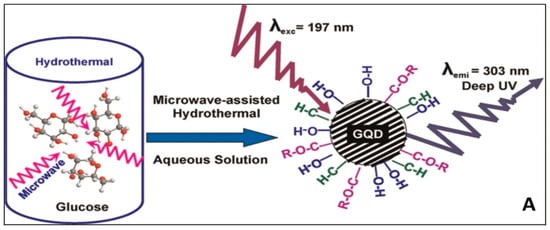
Figure 5.
Synthetic approach for GQDs: (A) microwave assisted hydrothermal method (Adapted from the Ref. [130] with the permission of ACS); (B) oxidation cutting (Adapted from the Ref. [115] with the permission of ACS); (C) hydrothermal method (Adapted from the Ref. [117] with the permission of ACS).
It is worth noting that the yield of GQDs and CQDs was higher when synthesized via bottom-up techniques as compared to top-down. In addition, the physical and chemical features of GQDs, such as shape, morphology and surface condition, can be better controlled via bottom-up techniques. Moreover, the choice of starting material is vast in the bottom-up methods than the top-down methods. The GQDs created using a bottom-up approach had fewer faults than those created using a top-down approach.
4.5. Synthesis of CQDs, GQDs, and Their Nanocomposites from Natural Products
CQDs have been fabricated from various natural sources, such as denatured milk [151], food wastes [152], dried leaf [153], grass [154], and pomelo fruit [155]. Xue et al. [156] and Xue et al. [157] synthesized CQDs and N-CQDs from lychee seeds and peanut shell waste by pyrolysis with a QY of 10.6% and 9.91%, respectively. Bankoti et al. [158] synthesized phosphorous, sulphur, and nitrogen doped CQDs, from onion peel waste by the microwave method. Sugarcane bagasse [159] and corn stalk [160] was used to obtain CQDs with a quantum yield of 17.98% and 16%. Hui et al. [161] synthesized nitrogen, bismuth doped CQDs from rice husk and utilized it for dye degradation and the removal of heavy metal. Bright blue luminescent GQDs were synthesized from sugarcane bagasse with a QY of 12.54% [162]. S-doped GQDs were synthesized from durian by Wang et al. [163] with a QY of 79%. Wang et al. [164] and Ahmed et al. [165] synthesized GQDs from rice husk and corn powder by using the hydrothermal method.
5. Sensing Applications
The outstanding optical and electrical features of inorganic semiconductor QDs are used to construct the sensors. Nonetheless, due to their non-biocompatibility, intrinsic toxicity, and presence of a heavy-metal core, these inorganic QDs have proven to be a failure. Furthermore, their colloidal structure makes it difficult to couple them with appropriate external components. Carbon-based QDs have been investigated for their potential in sensing applications for a wide range of analytes with high selectivity and sensitivity. Carbon-based QDs, unlike other common QDs, are soluble in aqueous solvents and are non-toxic in nature. Surface flaws and excellent optical properties characterize CQD and GQD-based nanocomposites (NCs), making them ideal for use as sensors for the detection and destruction of hazardous pollutants, respectively. The limit of detection (LOD) for CQDs and GQDs is in the nanomolar, picomolar, or even femtomolar levels, making them suitable for use in precision sensor systems [166]. There are many different kinds of sensors, including chemiluminescence, photoluminescence, and electrochemiluminescence.
Due to their inflexibility and expensive pieces of equipment, detection methods like inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS), and atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS) for the identification of metal ions and chemical species, are costlier and cannot be employed rapidly on-site. Photoluminescence-based sensors, on the other hand, are better options for these applications due to their low-cost, straightforward operation, high level of sensitivity, and selectivity. The low value of LODs in CQDs and GQDs fluorescence sensors is one of their key advantages [167]. The sensor is ultrasensitive if LOD has a low value. Additionally, the CQDs and GQDs photoluminescence sensors have the benefit of having strong selectivity, which enables them to identify particular ions or chemical compounds in a mixture of other ions or chemical species. Fe3+ [168], Hg2+ [169], Pb2+ [170], and organophosphorus insecticides [171] have all been detected using CQDs-based sensors.
Chemiluminescence (CL) sensors have become more and more common in sensing due to their benefits of easy equipment, high sensitivity, wide linear range, and no interference from background scattering light [172]. For the detection of Fe2+ [173], Cu2+ [174], H2O2 [175], and 4-nitrophenol [176], CL sensors have been employed.
Because of its straightforward setup, higher sensitivity, and label-free nature, electrochemiluminescence (ECL), also known as electrogenerated chemiluminescence, has been regarded as one of the clever combinations of chemiluminescence and electro-chemistry and has been used increasingly in analytical chemistry. Therefore, in order to demonstrate the ECL emission property that is crucial for the creation of ECL sensors, researchers presented several semi-conductor nano-crystals (also known as semi-conductor QDs, CQDs, and GQDs). When the light-emitting samples have been created in place, close to the electrode surface, the ECL exhibits practically little background, giving the opportunity to regulate the reaction’s location and timing [177].
There are currently just a few research articles on the direct usage of carbon-based QDs as sensors. The majority of research, however, have described the utilization of carbon-based QDs in combination with other materials. The next subsections address the key sensing applications of CQDs and GQD-based NCs.
5.1. CQDs and Their Nanocomposites as Sensing Platforms
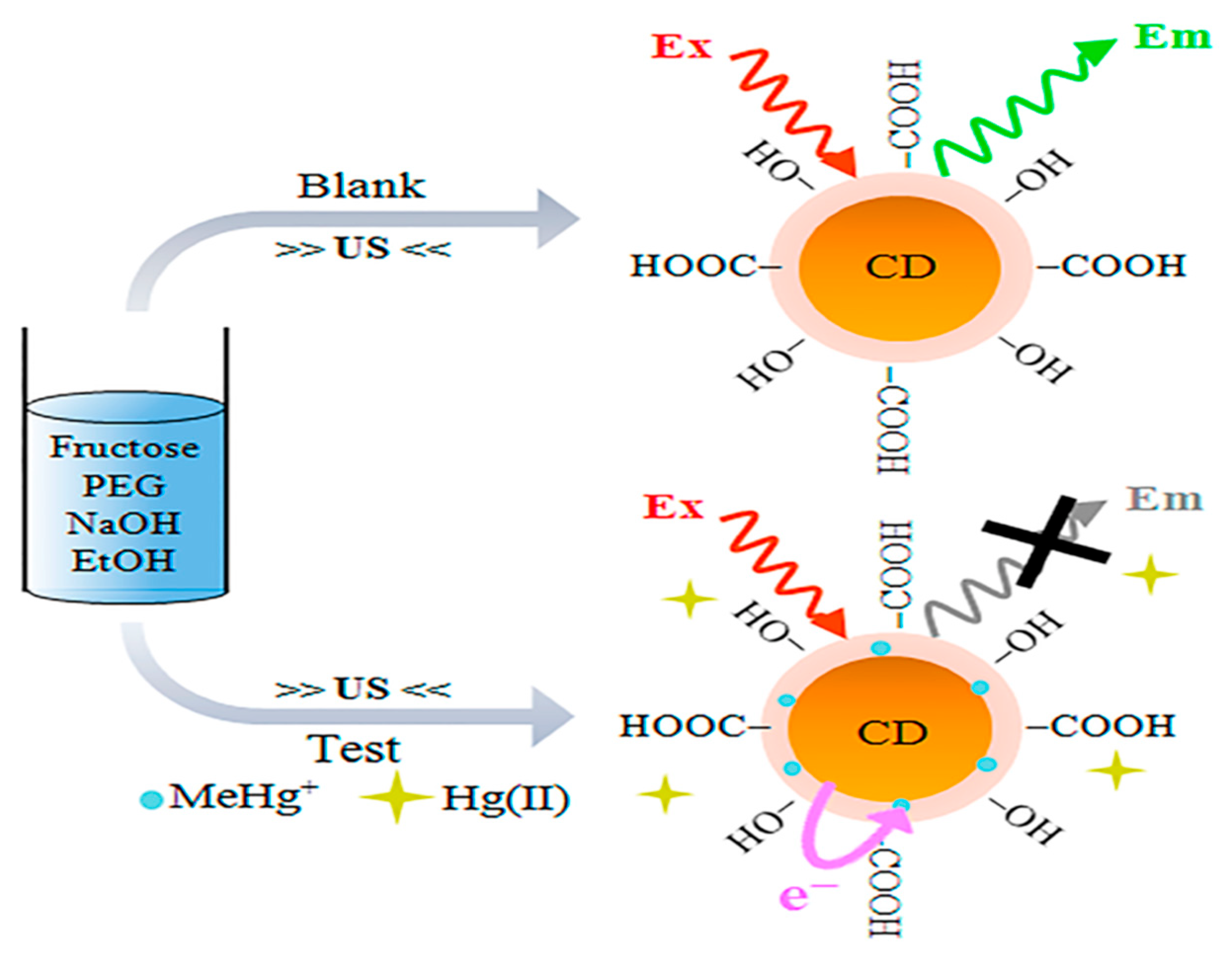
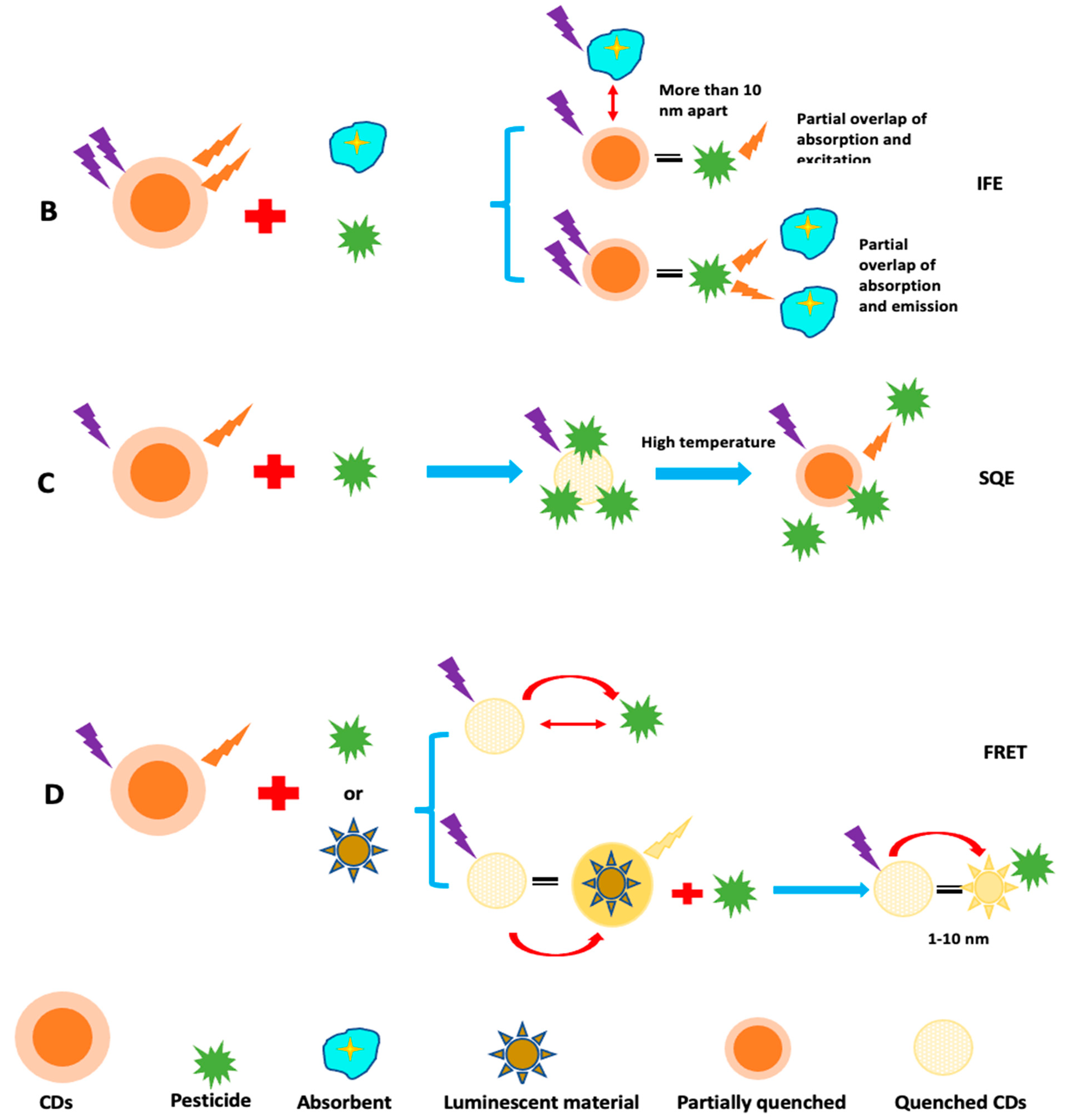
CQDs have attracted interest in sensor fabrication because of their unique chemical and physical features. CQDs offer distinct qualities such as nontoxicity, outstanding biodegradability, remarkable chemical inertness, large surface area, fantastic water consistency, and porosity, all while keeping health, environmental, and eco-friendliness in mind. As a result of these remarkable characteristics, they are becoming brilliant and attractive basic components for efficient fluorescence sensing platforms [178,179]. The optical characteristics of CQDs are considerably altered by doping with heteroatoms. For example, it was discovered that the excitation bands of Tb-CQDs [180], Eu-CQDs [181], and Co-CQDs [182], overlapped with the absorption bands of 2,4,6-trinitrophenol, tetracycline, and Cr (VI) ions, respectively, although the lifespan of each CQDs-based NC remained unaltered. As a consequence, the extremely effective inner filter effect (IFE) was primarily responsible for the fluorescence quenching of doped-CQDs in the sensing of 2,4,6-trinitrophenol, tetracycline, and Cr (VI) ions. They displayed good specificity and accuracy with a detection limit of 200 nm for TNP, 0.3 mM for tetracycline, and 1.17 mM for Cr6+ ions. Because of the interaction between Fe3+ and the phenolic hydroxyl group on the surface of Cu-CQDs, Xu et al. [183] employed Cu doped CQDs for Fe3+ detection. As a consequence, Fe3+ and Cu-CQDs created an electron transport mechanism. Tb doped CQDs, on the other hand, were employed to detect harmful Hg2+ and were extremely sensitive even when other metal ions were present. Under a UV lamp (=365 nm), an instant color change from blue to green was seen in the presence of a very small quantity of Hg2+ [99]. Costas-Mora et al. [184] used carbon dots for the detection of methyl mercury (Figure 6).
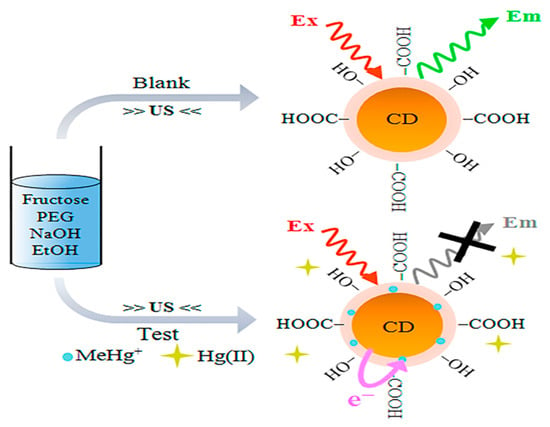
Figure 6.
Scheme for illustrating the process of sensing methylmercury with the use of CQDs as probe (Adapted from the Ref. [184] with the permission of ACS).
CQDs with surface coatings, such as Ag/CQDs, can alter their characteristics. In the presence of Ag NPs, Hg2+ ions convert to Hg and disintegrate into minute fragments, which subsequently join with Ag NPs to produce an AgHg amalgam coating on the surface, lowering absorbance. In Ag/CQDs, the CQD has aided in the quick electron transference from Ag NPs to Hg2+ ions [102]. Wan et al. [185] employed L-Tryptophan capped CQDs (L-CQDs) in aqueous solution to detect Hg2+ ions (LOD of 11 nm) with a fast response time (within 1 min). This is because of strong interaction between Hg2+, amino, and carbonyl moiety in L-CQDs, which resulted in an electronic structural modification. This fluctuation drives the charge transfer mechanism, causing excitons to recombine, suppressing the fluorescence emission.
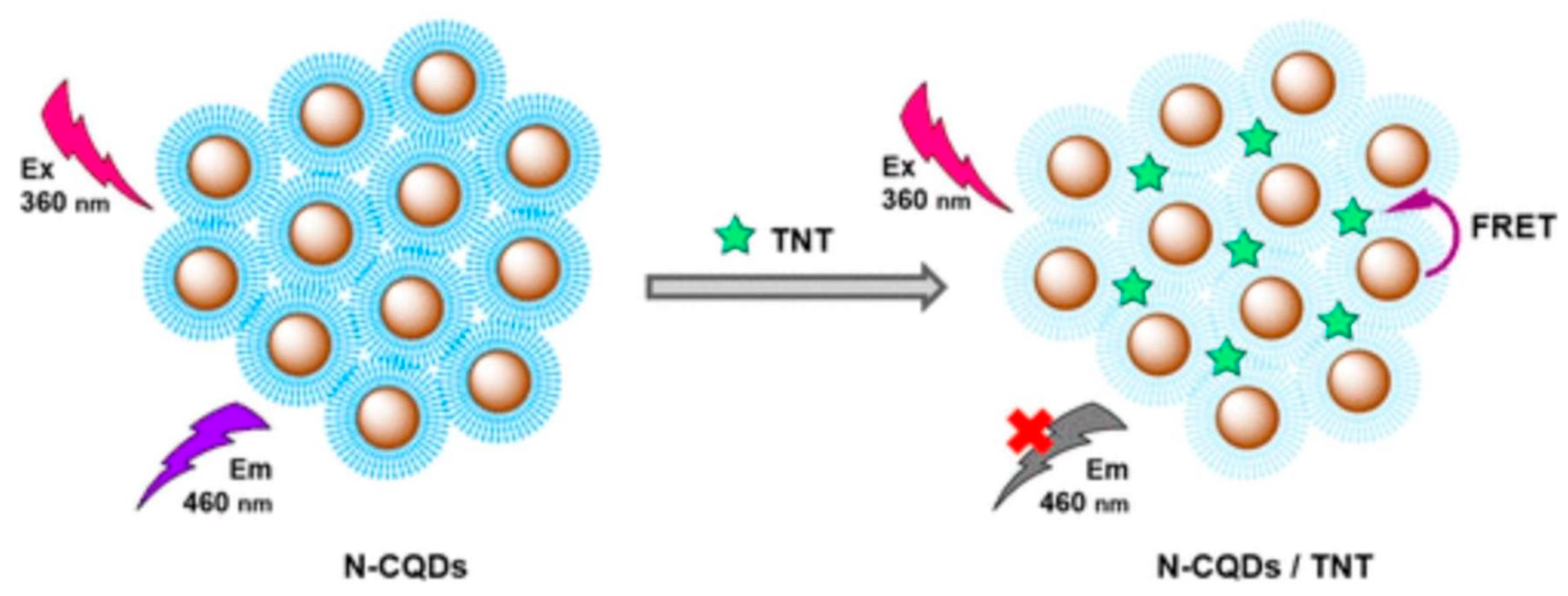
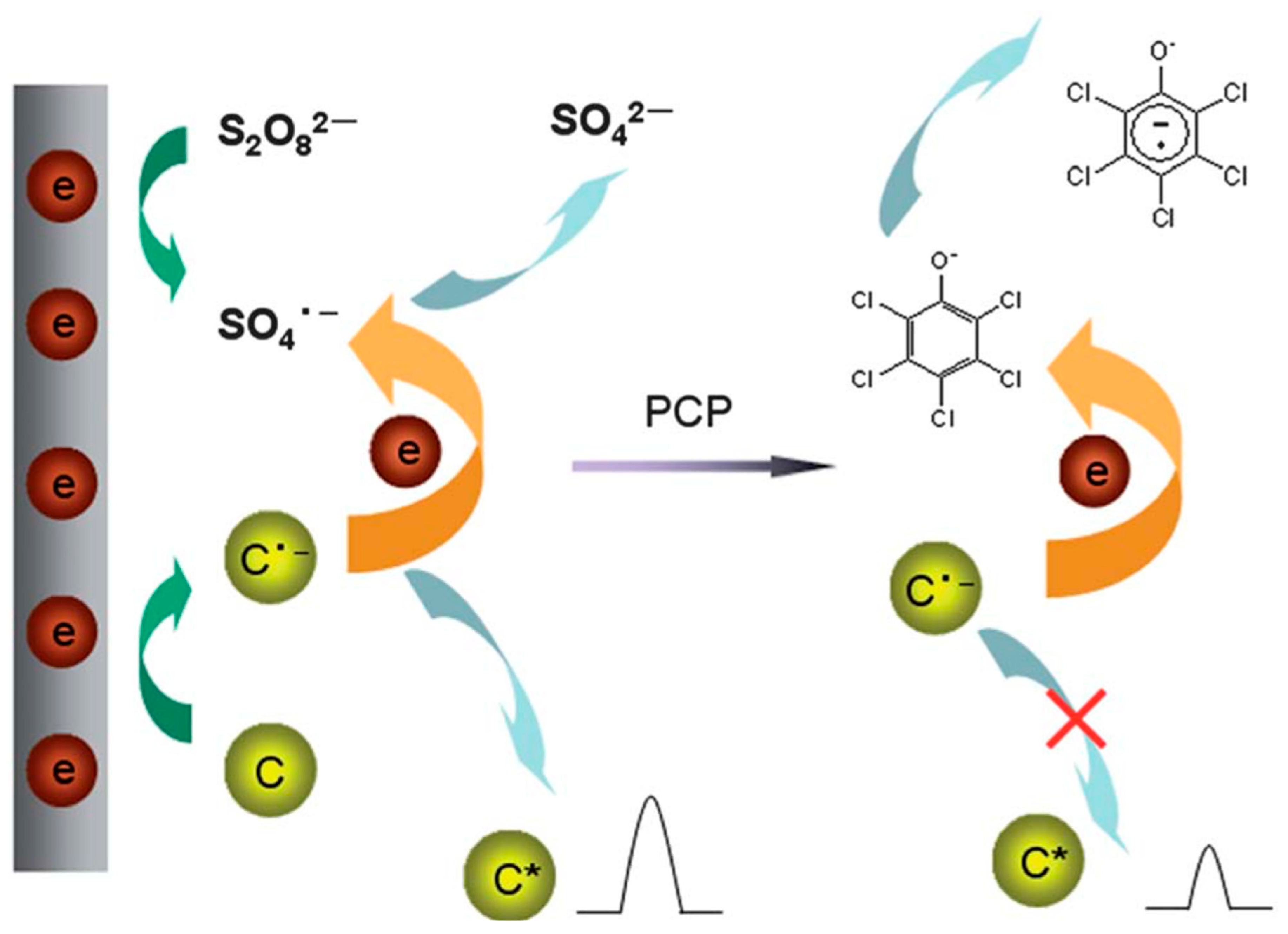
For the detection of Pb2+ ions in porphyria, surface coated and heteroatom doped CQDs, i.e., copper nanoclusters@nitrogen-doped carbon dots (CuNCs-CNQDs), were utilized. The self-calibration signal was provided by CNQDs, whose fluorescence kept almost unaltered in the presence of Pb2+. CuNCs-CNQDs nanohybrids were employed as ratio metric probes to detect Pb2+ at concentrations ranging from 0.010 to 2.5 mgL−1, with LOD of 0.0031 mgL−1 depending on the fluorescence intensity ratio difference between the fluorophores [92]. Finally, the probe was found to be effective in detecting Pb2+ in porphyria with relative standard deviations (RSDs) smaller than 5%. He et al. [91] accomplished a similar detection of Hg2+ in sea food using Terbium (III)-referenced N-doped carbon dots (N-CQDs-Tb). At Hg2+ concentrations of 1–161.51 M, the fluorescence ratio (F436/F543) revealed a clear straight proportionality with a low LOD of 37 nm. With recoveries of 86.45–114.47 percent and RSDs of 0.20–1.92 percent, the sensor demonstrated great precision, high reliability, and selectivity in the identification of Hg2+ in seafood. Glucose [186], DNA [187], heavy metals [188], nitro-explosives [189] (Figure 7), and pesticides [190,191,192,193,194,195], are only a few examples of CQD-based sensors that have been used to identify particular targets. Li et al. [196] removed pentachlorophenol by using CQDs in presence of S2O82− (Figure 8). Zhang et al. [197] modified carbon dots by combination with aptamers (Apt), nano-particles (NPs), molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs), antibodies (Abs), and enzymes for the detection of pesticides. An electrochemical carbonization process utilizing urea and sodium citrate, for example, with limits of detection of 3.3 nm and 0.5 nm, respectively, displayed exceptional specificity and accuracy regarding Hg2+ and photoluminescence emission, in the manufacture of CQDs [198,199]. Sn2+, Cr6+, Fe3+, Mn2+, Pb2+, and Cu2+, were among the heavy metals that were successfully detected [200]. H2O2 in an aqueous solution was monitored using CQD-based fluorescence turn-on sensors. The photo-induced electron transfer method gives the sensor great specificity and accuracy, with a LOD of 84 nm [201]. Due to unique properties of carbon-based quantum dots, they are used in multianalyte sensing. Qin et al. [202] synthesized AC-CQDs from activated carbon and conjugated five amino acids with it and detected eleven metal ions (Cr3+, Ni2+, Co2+, Mn2+, Er3+, Mo5+, Cu2+, Fe3+, Yb3+, Mn2+, and La3+). Song et al. [203] synthesized CQDs for sensing of glucose, H2O2 and Fe3+ with LOD of 1.71, 0.82 and 0.25 µM, respectively.
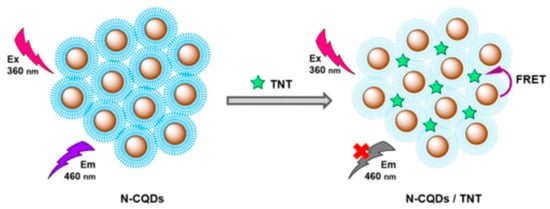
Figure 7.
Schematic illustration of 2,4,6-Trinitrotoluene (TNT) detection based on fluorescence quenching of N-CQDs (Adapted from the Ref. [189] with the permission of ACS).
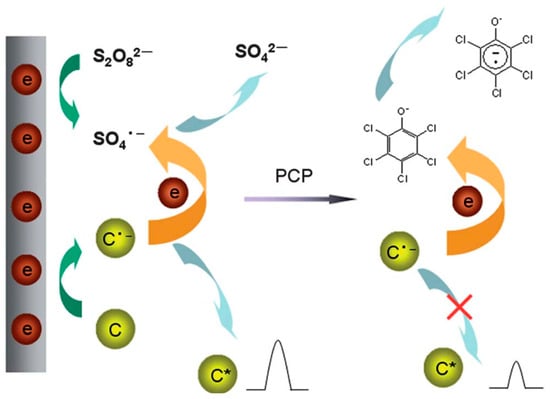
Figure 8.
Schematic showing the ECL detection of pentachlorophenol by using CQDs in S2O82− solution (Adapted from the Ref. [196] with the permission of ACS).
5.2. GQDs and Their Nanocomposites as Sensing Platforms
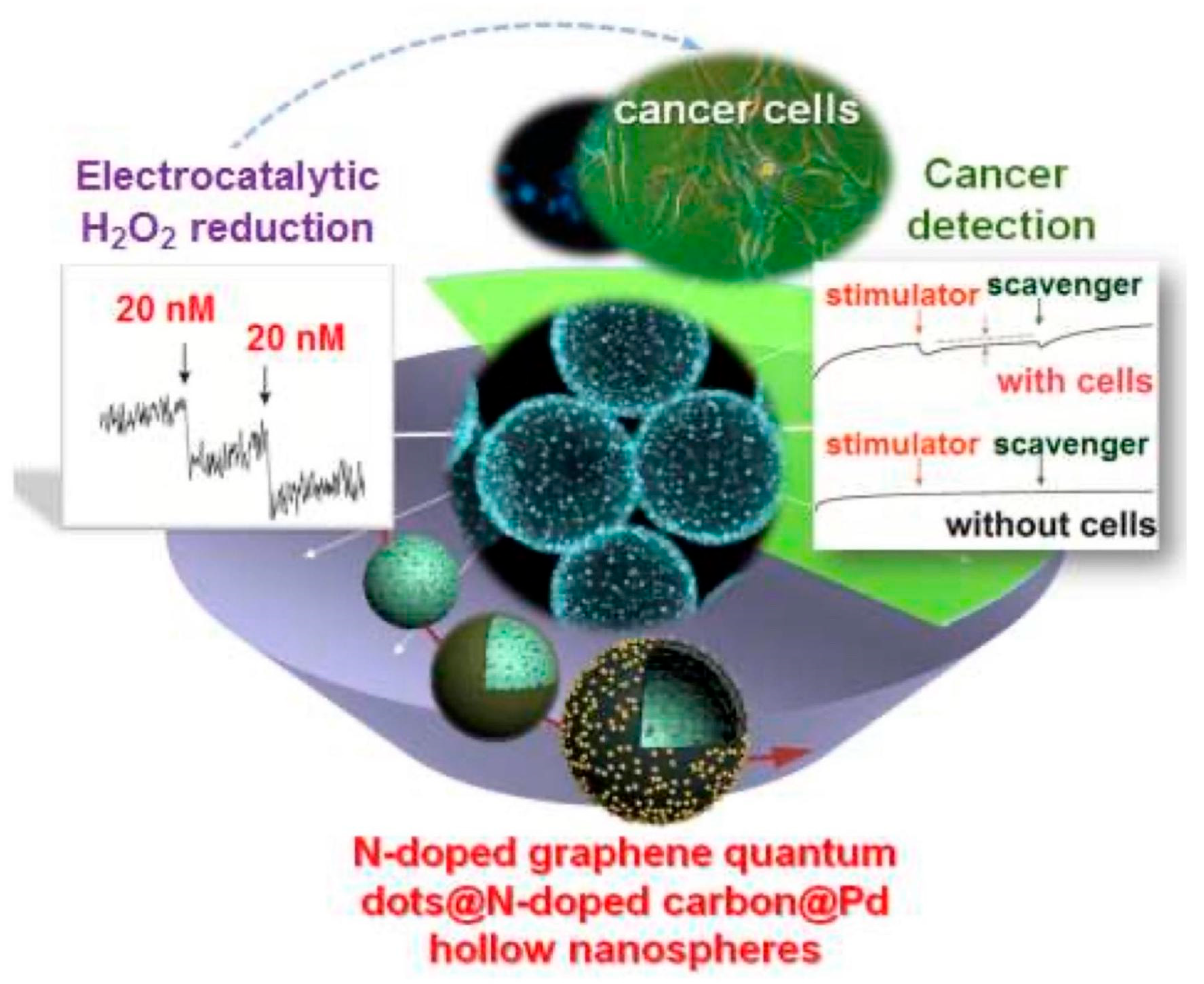
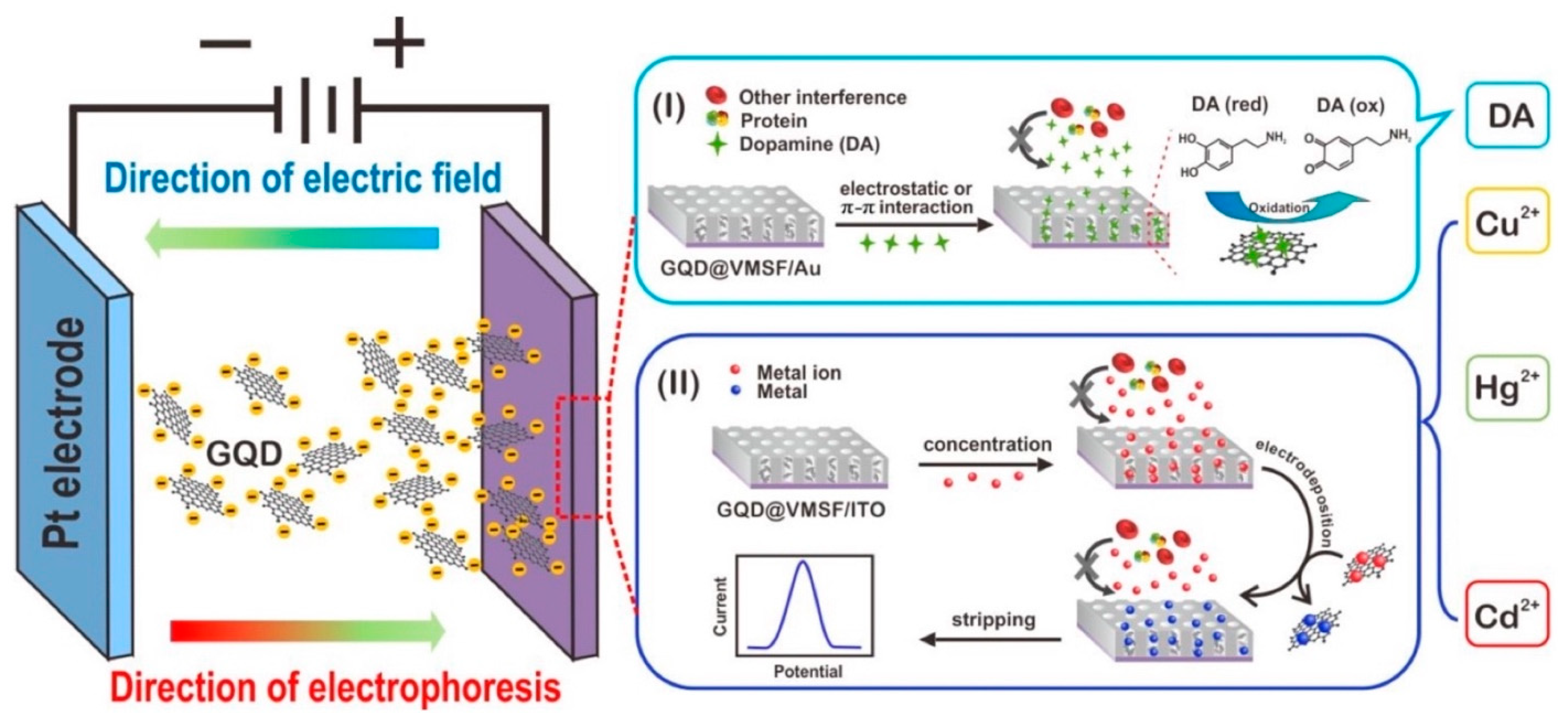
GQDs have a larger edge dimension than their vertex, resulting in single or many panels of graphene with chemical moieties on their lateral surface, providing a large number of chemical functionalization sites [204]. Using the π-π interaction, they can readily be conjugated with a range of nanomaterials, resulting in hybrid nanomaterials [205]. Due to their dimensional similarities to antibodies, proteins, aptamers, and small-nucleic acids, GQDs can also be grafted with these molecules. They may effectively improve the surface of biosensors so that a large number of receptors can be absorbed. A form of low molecular weight single-stranded ribonucleic acid or deoxyribonucleic acid sequence, known as an aptamer, is selected from a random oligonucleotide library using the method of ligand systematic evolution by exponential enrichment [206,207,208]. GQDs can be used as nanozymes or electrocatalysts to catalyze hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) in order to identify target analytes in a label-free manner. They have catalytic properties similar to peroxidase (POD), resulting in a redox reaction between H2O2 and an electron-donating substrate. Palladium nanoparticles loaded N-GQDs and N doped carbon hollow nanospheres was used for the sensing of H2O2 by Xi et al. [209] (Figure 9). The photocurrent response of an NGQDs/MoS2 based photoelectrochemical (PEC) sensor decreased when the quantity of acetamiprid in the testing solution rose, according to Jiang et al. [210]. The best time for the construction of the PEC apta sensor was found to be 40 min. This is due to the fact that the presence of acetamiprid around indium tin oxide (ITO)-NGQDs/MoS2 caused the creation of an acetamiprid-aptamer complex, which increased the electrode’s resistance from 87.4 to 160.1, lowering the photocurrent. N-GQDs produced by Liu et al. [211] and Yang et al. [212] were utilized to detect Hg2+ with LODs of 2.5 M and 0.45 nM, respectively. Pb2+ detection is especially critical since this metal ion can harm the respiratory tract severely. For the detection of Pb2+, Zn2+, and Cd2+, Ou et al. [146] created chitosan-GQDs (CSGQDs) nanocomposite and modified glassy carbon electrode (GCE), which they then paired with in situ plated bismuth film. Lu et al. [213] created ultrasensitive biosensors based on GQDs for the sensing of Cd2+, Cu2+, and Hg2+ ions, with LODs of 4.3 pm, 8.3 nm, and 9.8 pm, respectively (Figure 10).
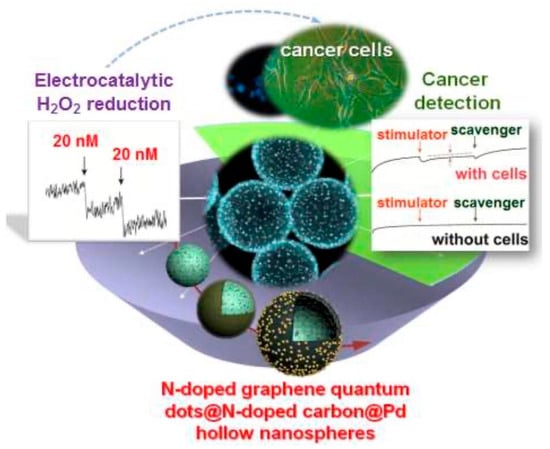
Figure 9.
H2O2 detection in cancer cells using GQD-based sensors depending on palladium (Pd) nanoparticle-loaded N-GQDs and N-doped carbon hollow nanospheres (HNS) (Adapted from the Ref. [209] with the permission of ACS).
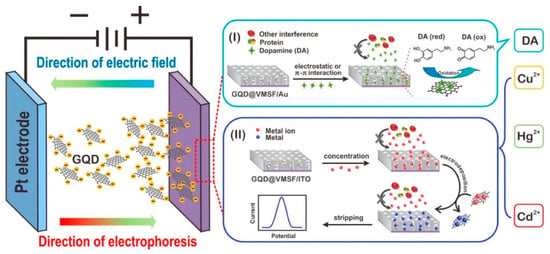
Figure 10.
For the identification of Cd2+, Cu2+, and Hg2+ ions, a GQD@mesoporous silica-nanochannel film (VMSF) was electrophoretically deposited on the electrode surface (Adapted from the Ref. [213] with the permission of ACS nano).
Carbon-based QDs and related NCs have detection limits in the femtomolar and picomolar ranges with good selectivity, however, there are significant challenges to overcome. In comparison to typical QDs, they have a lower quantum yield and intensity. The impact of oxygenase functional groups on the optical characteristics and selectivity of sensors should also be explored. Nair et al. [214] used PVA/S-GQD films to detect carbamate pesticides (carbofuran and thiram) in an ultrasensitive and selective fluorescent manner, with detection limits of 60 ppb and 210 ppb for carbofuran and thiram, respectively. The composite film luminescence properties revealed that the polymer matrix prevented S-GQDs from clumping together, preserving their emission qualities. The application of coffee grounds-derived poly(ethylene imine) (PEI) functionalized GQDs as a PL sensor for detecting Fe3+ and Cu2+ ions in the environment was described by Wang et al. [120]. The significant chelating impact and binding capacity of Fe3+ and Cu2+ ions with the N functional groups of PEI functionalized GQDs was attributed to the PL quenching process. Wang et al. [163] presented a report on synthesis of GQDs from Durian that were then changed with sulfhydryl to generate a PL sensor that could detect a range of metal ions (Hg+, Zn+, Ag+, and Cd+). Suryawanshi et al. [215] described the formation of amine ending GQDs from biomass as an efficient and accurate ON-OFF-ON sensing platform of Ag+ ion in water, due to their intense luminescence and precise functionalization. The light absorption of Am-GQDs (II) was lowered when additional metal ions were added, such as Cu (II), Co (II), Hg (II), Fe (II), Fe (III), Ni (II), and Pb (II). Although different metal ions quenched the fluorescence of Am-GQDs, this system was adjusted to allow for the identification of Ag+ ions alone. The amino acid “L-cysteine,” that has a strong affinity for Ag+ ions, was used to accomplish this. Because Ag+ ion was removed from Am-GQDs and attached to a -SH group of L-cysteine, the quenched fluorescence was restored by adding L-cysteine to the Am-GQDs-Ag+ combination. Fan et al. [216] employed GQDs to identify trinitrotoluene (TNT) in solution depends on the fluorescence quenching of GQDs caused by TNT. This demonstrates that TNT is deposited on the surface of GQDs by a π-π contact. Using the electrochemical fluorescence emission features of GQDs, Xu et al. [217] developed a novel type of electrochemical fluorescent sensor to detect Fe3+ ions. The Table 1 and Table 2 below shows the detection of various heavy metal ions and pesticides using CQDs, GQDs, and their nanocomposites. CQDs and GQDs conjugate with specific recognition elements or biomolecules such as aptamers, antibodies, and peptides, for sensing of pollutants. N-CQDs were conjugated with anti-aflatoxin M1 antibody for production of the fluorescent nanosensor. This nanosensor possess a high sensitivity of 0.2–0.8 ng/mL and LOD of 0.07 ng/mL towards anti-aflatoxin M1 [218]. Wang et al. [219] synthesized fluorescent apta sensor for the detection of acetamiprid pesticide with a LOD of 1.08 µg/L. With excellent stability, low-cost, and high specificity to targets, aptamers are often used as the preferred recognition elements to replace antibodies in the construction of various sensors. Wu et al. [220] fabricated the magnetic microspheres-vinyl phosphate-modified CDs (MMIPs-CDs@VPA) fluorescent sensor exhibiting excellent sensitivity for organophosphorous detection within 2 min with LOD of 0.0015 mmol/L.

Table 1.
Sensing behavior of CQDs and GQDs for detection of heavy metal ions.

Table 2.
Sensing behavior of CQDs and GQDs for detection of pesticides.
5.3. Mechanism of Sensing
For the detection of different metal ions or other chemical species, photoluminescence sensors can be utilized. Band gap transitions resulting from conjugated π domains are necessary to understand the process of fluorescence emission. Electrons shift to legally permitted excited states as a result of photoexcitation. When these photoexcited electrons return to their equilibrium states they release the extra energy, which can be used for both radiative and non-radiative processes, and light may or may not be released. This energy emission is caused by a difference in the energy levels of two electron states that are engaged in switching between the excited and equilibrium states. Any fluorescence change associated with the concentration of various analytes, including changes in intensity, wavelength, anisotropy, or lifetime, theoretically has the ability to be employed as a sensor. The fluorescence variations of CQDs and GQDs, which have been used in sensing applications, are caused by a number of causes [221]. The CQD and GQD sensors work by quenching or preventing the fluorescence emission from quenching in the existence of the analyte, which could be a metal ion or another species [222]. The charge transfer mechanism may be the cause of the quenching of fluorescence emission. For example, pesticides may alter the optical signal strength of CQDs and GQDs in a certain environment. A PL sensor can be created for precise target pesticide detection based on the established relationship between the added pesticide content and the signal change of CDs.
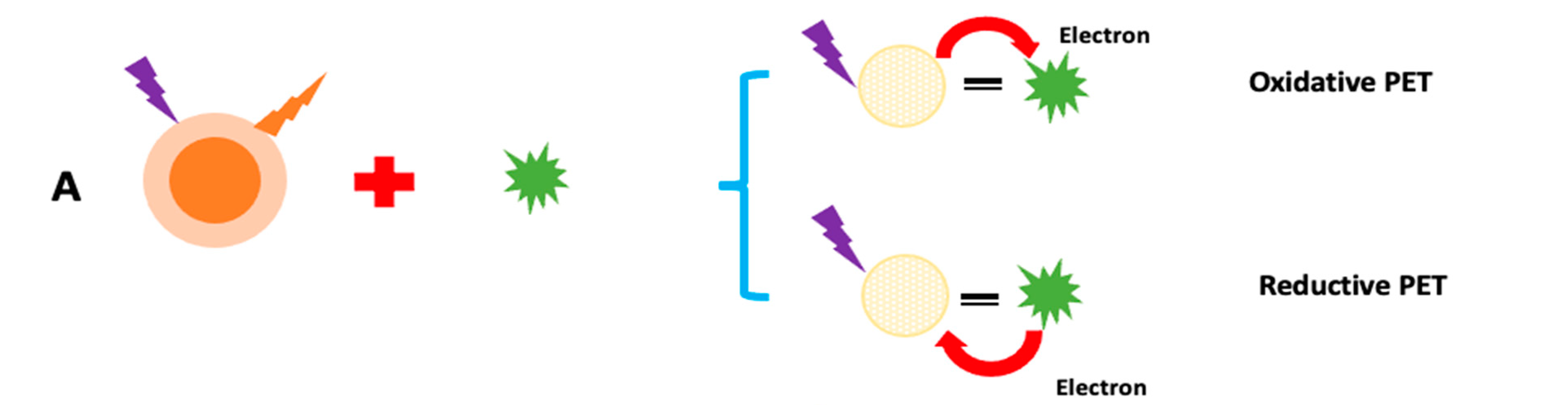
Fluorescence quenching has been thoroughly investigated for exploring photogenerated redox processes in carbon nanoparticles. A number of processes regulate fluorescence detection using C-dots. These hypotheses are built on the presumption that any interactions between C-dots and analyte reduces the quenching effect, resulting in a drop in fluorescence intensity or a rise in fluorescence intensity. Dynamic quenching, static quenching, Forster resonance energy transfer (FRET), photoinduced electron transfer (PET), and inner filter effect (IFE), are all examples of quenching mechanisms in CQDs and GQDs (Figure 11). When C-dots and analyte interact, a non-fluorescent complex (ground state) forms, which subsequently returns to the ground state without emitting any photons, this is known as static quenching [223]. Because of charge or energy transfer between the analyte and C-dots, dynamic quenching occurs when an excited state comes back to the ground state. FRET occurs when the quencher’s (ground state) absorption spectra intersect with the C-dots’ emission spectrum (excited state). In the PET quenching mechanism, the transfer of energy between C-dots and the quencher results in the production of cationic and anionic radicals, respectively. IFE quenching occurs when the quencher’s absorption spectra intersect with the C-dots’ excitation or emission spectra. Chemiluminescence is a chemical reaction that involves at least two reagents and produces light when an excited intermediate or product relaxes to its ground state. The source of light emission in CL sensors is a chemical process. A photodetector, a readout device, and a reaction cell, are the instruments found in CL sensors. This approach is extremely sensitive because just a little amount of CL’s emitting light is observed when there is no background noise. Additionally, the reagent purity rather than detector sensitivity is what causes low levels of LOD in CL. A solution system can generate active intermediates by complicated physical or chemical changes, such as electron transfer, under the induction effects of applied current or voltage. To produce electrochemiluminescence signals through the creation of excited state species, these reactive intermediates can engage in redox chemical reactions with either luminophore (anodic or cathodic core actant mechanism) or self (free radical annihilation process). This approach, known as electrochemiluminescence (ECL) sensing, exhibits significantly lower background noise because it does not require an external light source and is free from stray light interference. A wide detection range may be obtained by repeating and accurately measuring ECL signals due to sensitive regulation of micro-current. Additionally, ECL sensors can be used in conjunction with a portable, inexpensive ECL analyzer to identify various pesticide residues in real time on the spot.
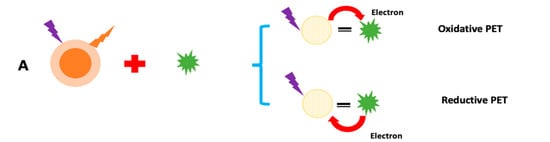
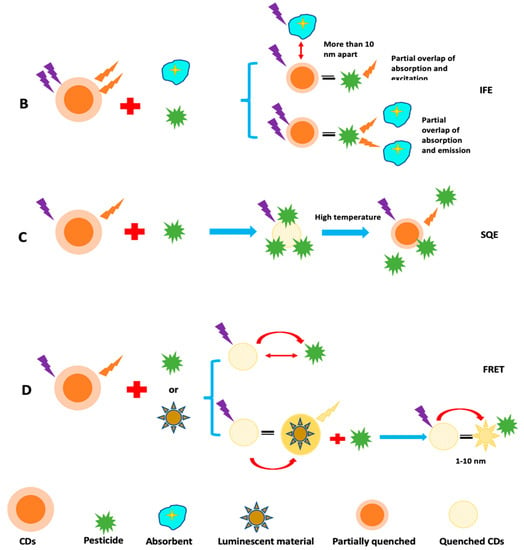
Figure 11.
Sensing mechanism of fluorescent CDs: (A) PET; (B) IFE; (C) SQE; and (D) FRET.
6. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
In this article, the emerging carbon-based quantum dots viz carbon quantum dots (CQDs), graphene quantum dots (GQDs), and their nanocomposites, are explored in detail and their synthesis and applications as sensors have been discussed. They have carbon core with oxygenase functional moieties on their surfaces with several exciting advantages over conventional metals based QDs, along with chemical stability and low toxicity. However, study of carbon-based QDs is in its initial stages. Even though considerable research on synthesis techniques has been reported in the last decade, finding a scalable, productive, but simple manufacturing pathway for the synthesis of carbon-based QDs with good quality remains a difficulty. Sensing activity of carbon-based QDs is mainly due to an abundance of functional groups, large surface area up-conversion photoluminescence, and the electron reservoir properties of CQDs. The π-π interaction of carbon-based QDs are mainly responsible for detection of pollutants.
These carbon-based QDs have opened up a plethora of interesting possibilities in environmental and biochemical sensing applications, allowing for unparalleled levels of flexibility and integration for multi-analyte detection. Despite excellent breakthroughs in the domain of carbon-based QDs-based sensors, commercialization initiatives for such sensors lag behind. One possible solution is to guarantee that academic research is properly integrated with stringent scale-up protocols and rigorous validation procedures, which would surely make a significant difference in the eventual deployment of such devices in clinical diagnostics and other industries.
Author Contributions
Writing—original draft preparation, A.K., K.P. and M.K.; Writing—review and editing, A.K., M.K., R.K. and N.V.; Supervision, M.K. and R.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sharma, G.; Kumar, A.; Naushad, M.; Kumar, A.; Al-Muhtaseb, A.H.; Dhiman, P.; Ghfar, A.A.; Stadler, F.J.; Khan, M.R. Photoremediation of toxic dye from aqueous environment using monometallic and bimetallic quantum dots-based nanocomposites. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 2919–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Shandilya, P.; Raizada, P.; Sudhaik, A.; Rahmani-Sani, A.; Hosseini- Bandegharaei, A. Review on various strategies for enhancing photocatalytic activity of graphene-based nanocomposites for water purification. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 3498–3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reshma, V.G.; Mohanan, P.V. Quantum dots: Applications and safety consequences. J. Lumin. 2019, 205, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.M.; Fei, G.T.; Zhang, L.D. Synthesis and tunable emission of Ga2S3 quantumdots. Mater. Lett. 2019, 239, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagiwara, K.; Horikoshi, S.; Serpone, N. Luminescent monodispersed carbon quantum dots by a microwave solvothermal method toward bioimaging applications. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2021, 415, 113310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Gao, Y.; Ni, B.; Yang, X. Green synthesis of biomass-derived carbon quantum dots as fluorescent probe for Fe3+ detection. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2021, 130, 108636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaghmandfard, A.; Sedighi, O.; Tabatabaei Rezaei, N.; Abbas Abedini, A.; Malek Khachatourian, A.; Toprak, M.S.; Seifalian, A. Recent advances in the modification of carbon-based quantum dots for biomedical applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 120, 111756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, X.-Y.; Zhou, Z.-J.; Wu, Y.-M.; Li, Y.; Li, J.-C.; Bai, Y.-H.; Wang, J.-L. Application Progress of Fluorescent Carbon Quantum Dots in Food Analysis. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2020, 48, 1288–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd Rani, U.; Yong Ng, L.; Yin Ng, C.; Mahmoudi, E. A review of carbon quantum dots and their applications in wastewater treatment. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 278, 102124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahal, M.; Atassi, Y.; Alghoraibi, I. Quenching photoluminescence of Carbon Quantum Dots for detecting and tracking the release of Minocycline. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2021, 412, 113257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei Heng, Z.; Chan Chong, W.; Ling Pang, Y.; Hoon Koo, C. An overview of the recent advances of carbon quantum dots/metal oxides in the application of heterogeneous photocatalysis in photodegradation of pollutants towards visible-light and solar energy exploitation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju-Meng, W.; Bi-Tao, L.; Xin, Z.; Chang-Chun, S. One-pot synthesis of N, S co-doped photoluminescent carbon quantum dots for Hg2+ ion detection. New Carbon Mater. 2018, 33, 333–340. [Google Scholar]
- Cirone, J.; Rahin Ahmed, S.; Wood, P.C.; Chen, A. Green synthesis and electrochemical study of cobalt/graphene quantum dots for efficient water splitting. J. Phys. Chem. C 2019, 123, 9183–9191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.; Guo, J.; Zhao, T.; Guo, Z. Functionalized carbon dots on graphene as outstanding non-metal bifunctional oxygen electrocatalyst. Small 2019, 15, 1900296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Bin, D.; Wei, J.-S.; Niu, X.-Q.; Chen, X.-B.; Xia, Y.-Y.; Xiong, H.-M. Efficient oxygen electrocatalyst for Zn-air batteries: Carbon dots and Co9S8nanoparticles in a N, S-codoped carbon matrix. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 14085–14094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Zhou, X.-X.; Zhang, Z.-H.; Zhao, Y.-P.; Wei, J.-S.; Xiong, H.-M. Large scale synthesis of full-color emissive carbon dots from a single carbon source by a solvent-free method. Nano Res. 2021, 15, 3548–3555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Miao, Q.; Liang, G. Quantum dots as multifunctional materials for tumor imaging and therapy. Materials 2013, 6, 483–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Li, D.; Tian, L.; Xiang, W.; Wang, T.; Hu, W.; Hu, Y.; Chen, S.; Chen, J.; Dai, Z. Synthesis of graphene quantum dots from natural polymer starch for cell imaging. Green Chem. 2018, 20, 4438–4442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Hou, F.; Hu, S.; Wu, B.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, B.; Fu, H. Graphene quantum-dot-modified hexagonal tubular carbon nitride for visible-light photocatalytic hydrogen evolution. ChemCatChem 2018, 10, 1330–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Ray, R.; Gu, Y.; Ploehn, H.J.; Gearheart, L.; Raker, K.; Scrivens, W.A. Electrophoretic Analysis and Purification of Fluorescent Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube Fragments. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 12736–12737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad Nazri, N.A.; HidayahAzeman, N.; Luo, Y.; Ashrif, A.; Bakar, A. Carbon quantum dots for optical sensor applications: A review. Opt. Laser Technol. 2021, 139, 106928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar Barman, M.; Patra, A. Current status and prospects on chemical structure driven photoluminescence behaviour of carbon dots. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C 2018, 37, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying Lim, S.; Shen, W.; Gao, Z. Carbon quantum dots and their applications. Chem. Soc. 2015, 44, 362–381. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.; Liu, J.; Yu, Y.; Zuo, S.; Li, B. Preparation and visible light photocatalytic activity of carbon quantum dots/TiO2 nanosheet composites. Carbon 2014, 68, 718–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JafarMolaei, M. Principles, mechanisms, and application of carbon quantum dots in sensors: A review. Anal. Methods 2020, 12, 1266–1287. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.; Tang, Y.; Wang, G.; Mao, J.; Liu, Z.; Sun, T.; Wang, M.; Chen, D.; Yang, Y.; Li, J.; et al. Green, rapid, and universal preparation approach of graphene quantum dots under ultraviolet irradiation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 14470–14477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Zhang, L.; Ruan, Y.-F.; Zhao, W.-W.; Xu, J.-J.; Chen, H.-Y. Quantum-dots-based photoelectrochemical bioanalysis highlighted with recent examples. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 94, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Gao, X.; Song, F.; Wang, C.; Chu, F.; Wu, S. A sensing approach for dopamine determination by boronic acid- functionalized molecularly imprinted graphene quantum dots composite. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 423, 810–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Wang, J.; Hou, K.; Yang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Han, X.; Yang, S. Small but strong: The influence of fluorine atoms on formation and performance of graphene quantum dots using a gradient F-sacrifice strategy. Carbon 2017, 112, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Ding, L.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Fan, L.; Zhou, S.; Fang, D.; Yang, S. Multicolor fluorescent graphene quantum dots colorimetrically responsive to all-pH and a wide temperature range. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 11727–11733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra Biswas, M.; Islam, T.; Kumar Nandy, P.; Hossain, M. Graphene Quantum Dots (GQDs) for bioimaging and drug delivery applications: A review. ACS Mater. Lett. 2021, 3, 889–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.; Li, J.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Shen, T.; Guo, Y.; Wang, L.; Mei, T.; Wang, J.; Wang, X. Functional Carbon Quantum Dots towards Highly Sensitive Graphene Transistors for Cu2+ Ion Detection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 4797–4803. [Google Scholar]
- Madurani, K.A.; Suprapto, S.; Syahputra, M.Y.; Puspita, I.; Masudi, A.; Rizqi, H.D.; Hatta, A.M.; Juniastuti, J.; Lusida, M.I.; Kurniawan, F. Recent development of detection methods for controlling COVID-19 outbreak. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2021, 168, 37511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ma, P.; Tao, Q.; Krause, H.J.; Yang, S.; Ding, G.; Dong, H.; Xie, X. Magnetic graphene quantum dots facilitate closed-tube one-step detection of SARS-CoV-2 with ultra-low field NMR relaxometry. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 337, 129786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Lin, J.-H.; Dong, Z.-S.; Chen, W.-T.; Chan, Y.K.; Yeh, Y.-C.; Chang, H.-T.; Chen, C.-F. Detection of pathogens using graphene quantum dots and gold nanoclusters on paper-based analytical devices. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 363, 131824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, W.-S.; Chen, H.-H.; Chen, S.-Y.; Chang, C.-Y.; Chen, P.-C.; Hou, Y.-I.; Shao, Y.-T.; Kao, H.-F.; Lilian Hsu, C.-L.; Chen, Y.-C.; et al. Graphene quantum dots with nitrogen-doped content dependence for highly efficient dual-modality photodynamic antimicrobial therapy and bioimaging. Biomaterials 2017, 120, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Qian, Z. Functional carbon quantum dots: A versatile platform for chemosensing and biosensing. Chem. Rec. 2018, 18, 491–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Meng, Q.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Song, Y.; Jin, H.; Zhang, K.; Sun, H.; Wang, H.; Yang, B. Highly photoluminescent carbon dots for multicolor patterning, sensors, and bioimaging. Angew. Chem. 2013, 125, 4045–4049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Qi, G.; Chen, K.; Zou, M.; Yuwen, L.; Zhang, X.; Huang, W.; Wang, L. Microwave-Assisted Preparation of White Fluorescent Graphene Quantum Dots as a Novel Phosphor for Enhanced White-Light-Emitting Diodes. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 2739–2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martindale, B.C.M.; Hutton, G.A.; Caputo, C.A.; Reisner, E. Solar hydrogen production using carbon quantum dots and a molecular nickel catalyst. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 6018–6025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, X.; MacFarlane, D.R. Carbon Quantum Dots/Cu2O Heterostructures for Solar-Light-Driven Conversion of CO2 to Methanol. Adv. Energy Mater. 2015, 5, 1401077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuerhong, M.; Xu, Y.; Yin, X.-B. Review on Carbon Dots and Their Applications. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2017, 45, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Li, D.; Wang, X. Effect of modified graphene quantum dots on photocatalytic degradation property. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2016, 69, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liu, R.; Kong, W.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, X.; Lee, S.-T.; Kang, Z. Carbon quantum dots with photo-generated proton property as efficient visible light controlled acid catalyst. Nanoscale 2013, 6, 867–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wang, M.; Zhu, L.; Li, Y.; Yan, Z.; Shen, Z.; Cao, X. Facile microwave assisted synthesis of N-rich carbon quantum dots/dual-phase TiO2 heterostructured nanocomposites with high activity in CO2photoreduction. Appl. Catal. B 2018, 231, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, D.; Lan, W.; Yang, Z.; Zhao, X.; Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Su, Q.; Xie, E. A simple method for preparing ZnO foam/carbon quantum dots nanocomposite and their photocatalytic applications. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2016, 47, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ming, H.; Lian, S.; Huang, H.; Li, H.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.; Kang, Z.; Lee, S.-T. Fe2O3/carbon quantum dots complex photocatalysts and their enhanced photocatalytic activity under visible light. Dalton Trans. 2011, 40, 10822–10825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Han, Y.; Huang, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Liu, R.; Liu, Y.; Kang, Z. Synthesis of carbon quantum dots/SiO2porous nanocomposites and their catalytic ability for photo- enhanced hydrocarbon selective oxidation. Dalton Trans. 2013, 42, 10380–10383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosconi, D.; Mazzier, D.; Silvestrini, S.; Privitera, A.; Marega, C.; Franco, L.; Moretto, A. Synthesis and photochemical applications of processable polymers enclosing photoluminescent carbon quantum dots. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 4156–4164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-C.; Hung, Y.-S.; Weng, Y.-M.; Chen, W.; Lai, Y.-S. Sustainable development of carbon nanodots technology: Natural products as a carbon source and applications to food safety. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 86, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottini, M.; Tautz, L.; Huynh, H.; Monosov, E.; Bottini, N.; Dawson, M.I.; Bellucci, S.; Mustelin, T. Covalent decoration of multi-walled carbon nanotubes with silica nanoparticles. Chem. Commun. 2005, 6, 758–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, N.; Sharma, N.N. Arc discharge synthesis of carbon nanotubes: Comprehensive review. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2014, 50, 135–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biazar, N.; Poursalehi, R.; Delavari, H. Optical and Structural Properties of Carbon dots/TiO2 Nanostructures Prepared via DC arc Discharge in Liquid. In Proceedings of the 6th International Biennial Conference on Ultrafine Grained and Nanostructured Materials (UFGNSM), Kish Island, Iran, 12–13 November 2017; Sohi, M.H., Zamani, C., Eds.; AIP Publishing LLC: Melville, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.-P.; Zhou, B.; Lin, Y.; Wang, W.; ShiralFernando, K.A.; Pathak, P.; JaouadMeziani, M.; Harruff, B.A.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.F.; et al. Quantum-sized carbon dots for bright and colorful photoluminescence. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 7756–7757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doñate-Buendia, C.; Torres-Mendieta, R.; Pyatenko, A.; Falomir, E.; Fernández-Alonso, M.; Mínguez-Vega, G. Fabrication by laser irradiation in a continuous flow jet of carbon quantum dots for fluorescence imaging. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 27352742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Li, X.; Zeng, X.; Lu, Y. Preparation of carbon dots by non-focusing pulsed laser irradiation in toluene. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 819–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.-L.; Niu, K.-Y.; Sun, J.; Yang, J.; Zhao, N.-Q.; Du, X.-W. One-step synthesis of fluorescent carbon nanoparticles by laser irradiation. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 484–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemizadeh, F.; Malekfar, R.; Parvin, P. Pulsed laser ablation synthesis of carbon nanoparticles in vacuum. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2017, 104, 252–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.; Zhao, N.; Yan, L.; Zhong, P.; CanhNguyen, V.; HuuLe, P. Double-pulse femtosecond laser ablation for synthesis of ultrasmall carbon nanodots. Mater. Res. Express 2020, 7, 015606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Ye, T.; Mao, C. Fluorescent carbon nanoparticles derived from candle soot. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 6473–6475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Travas-Sejdic, J. Simple aqueous solution route to luminescent carbogenic dots from carbohydrates. Chem. Mater. 2009, 21, 5563–5565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Sun, X.; Ruan, H.; Yin, K.; Li, H. Production of yellow-emitting carbon quantum dots from fullerene carbon soot. Sci. China Mater. 2017, 60, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Chang, Q.; Xue, C.; Yang, J.; Hu, S. Full-colour carbon dots: From energy-efficient synthesis to concentration-dependent photoluminescence properties. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 3074–3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, L.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Z.-L.; Pang, D.-W. Photoluminescence-tunable carbon nanodots: Surface-state energy-gap tuning. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 1663–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.-H.; Han, X.-Y.; Lin, Z.-Y.; Fan, Y.-L.; Shi, G.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, M. Facile reflux synthesis of polyethyleneimine-capped fluorescent carbon dots for sequential bioassays toward Cu2+/H2S and its application for a logic system. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2019, 66, 426–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; He, X.; Liu, Y.; Huang, H.; Lian, S.; Lee, S.-T.; Kang, Z. One-step ultrasonic synthesis of water-soluble carbon nanoparticles with excellent photoluminescent properties. Carbon 2011, 49, 605–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiang, R.; Yang, S.; Hou, K.; Wang, J. Synthesis of carbon quantum dots with green luminescence from potato starch. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 10826–10833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Cui, Y.; Liu, M.; Chen, J.; Wan, Q.; Wen, Y.; Deng, F.; Zhou, N.; Zhang, X.; Wei, Y. A one-step ultrasonic irradiation assisted strategy for the preparation of polymer-functionalized carbon quantum dots and their biological imaging. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 532, 767–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, M.; Zhou, L. One-step sonochemical synthesis of versatile nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots for sensitive detection of Fe2+ions and temperature in vitro. Mater. Sci. Eng. C-Mater. 2019, 101, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Park, M.; Yong Kim, H.; Ding, B.; Park, S.-J. A facile ultrasonic-assisted fabrication of nitrogen-doped carbon dots/BiOBr up-conversion nanocomposites for visible light photocatalytic enhancements. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Ming, H.; Huang, H.; Liu, Y.; Kang, Z. One-step ultrasonic synthesis of fluorescent N-doped carbon dots from glucose and their visible-light sensitive photocatalytic ability. New J. Chem. 2012, 36, 861–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, H.; Huang, L.K.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.-F.; Chen, S. Large-scale ultrasonic fabrication of white fluorescent carbon dots. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 5335–5341. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, K.; Malfatti, L.; Carboni, D.; Loche, D.; Casula, M.; Moretto, A.; Maggini, M.; Takahashi, M.; Innocenzi, P. Energy Transfer Induced by Carbon Quantum Dots in Porous Zinc Oxide Nanocomposite Films. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 2837–2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Sahu, S.; Cao, L.; Anilkumar, P.; Tackett, K.N.; Qian, H.; Bunker, C.E.; Guliants, E.A.; Parenzan, A.; Sun, Y.-P. Carbon nanoparticles as chromophores for photon harvesting and photoconversion. ChemPhysChem 2011, 12, 3604–3608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Posudievsky, O.Y.; Khazieieva, O.A.; Koshechko, V.G.; Pokhodenko, V.D. Preparation of graphene oxide by solvent-free mechanochemical oxidation of graphite. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 12465–12467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.; Yan, L.; Si, J.; Hou, X. Femtosecond laser-assisted synthesis of highly photoluminescent carbon nanodots for Fe3+detection with high sensitivity and selectivity. Opt. Mater. Express 2016, 6, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, M.; Xie, X.; Liu, K.; Yang, J.; Hong, L.; Wang, S. Fluorescent Carbon Quantum Dots—Synthesis, Functionalization and Sensing Application in Food Analysis. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Mi, Z.; Hu, Q.; Li, C.; Li, X.; Feng, F. Green synthesis of fluorescent carbon dots as an effective fluorescence probe for morin detection. Anal. Methods 2019, 11, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Verma, N.C.; Khan, S.; Tiwari, S.; Chaudhary, A.; Nandi, C.K. Paper strip based and live cell ultrasensitive lead sensor using carbon dots synthesized from biological media. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 232, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Ning, G.; He, X.; Ma, X.; Yang, F.; Xu, Z.; Li, Y. Carbon quantum dots derived by direct carbonization of carbonaceous microcrystals in mesophase pitch. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 21492–21498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.-B.; Zhu, Z.-T.; Wang, H.-X.; Huang, X.; Zhang, X.; Qi, X.; Zhang, H.-L.; Zhu, Y.; Deng, X.; Peng, Y.; et al. General solid-state synthesis of chemically-doped fluorescent graphene quantum dots for bioimaging and optoelectronic applications. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 10162–10169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Ding, Y.; Deng, Z.; Li, Z. Rational design of ternary NiS/CQDs/ZnIn2S4 nanocomposites as efficient noble-metal-free photocatalyst for hydrogen evolution under visible light. Chin. J. Catal. 2019, 40, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, T.; Wang, Q.; Guo, Z.; Kuang, J.; Cao, W. Hydrothermal synthesis of carbon quantum dots using different precursors and their combination with TiO2 for enhanced photocatalytic activity. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 11828–11834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Jiao, Y.; Hua, J.; Yang, J.; Yang, Y. Hydrothermal synthesis of nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots as fluorescent probes for the detection of dopamine. J. Fluoresc. 2018, 28, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabiyouni, G.; Ghanbari, D. Hydrothermal Synthesis of Magnetic and Photoluminescence CuFe2O4-carbon dots nanocomposite as a sensor for detecting of Hg(II) ions. J. Nanostruct. 2020, 10, 760–768. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Liu, C.-Y.; Liu, Y. A novel one-step approach to synthesize fluorescent carbon nanoparticles. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 28, 4411–4414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yang, P.; Feng, Q.; Meng, T.; Wei, J.; Xu, C.; Han, J. Green preparation of fluorescent carbon quantum dots from cyanobacteria for biological imaging. Polymers 2019, 11, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, W.; Cui, Y.H.; Li, T.T.; Diao, H.P.; Wei, S.Y.; Li, L.H.; Chang, H.H.; Zhang, B.; Wei, W.L. Green and facile synthesis of highly photoluminescent nitrogen-doped carbon dots for sensors and cell imaging. Chem. Lett. 2018, 47, 421–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, R.K.; Kar, J.P.; Mohapatra, S. Enhanced photodegradation of organic pollutants by carbon quantum dot (CQD) deposited Fe3O4@ mTiO2 nano-pom-pom balls. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2016, 55, 5902–5910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghamali, A.; Khosravi, M.; Hamishehkar, H.; Modirshahla, N.; Behnajady, M.A. Preparation of novel high performance recoverable and natural sunlight-driven nanocomposite photocatalyst of Fe3O4/C/TiO2/N-CQDs. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2018, 87, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Han, Y.; Luo, X.; Yang, W.; Li, C.; Tang, W.; Yue, T.; Li, Z. Terbium (III)-referenced N-doped carbon dots for ratiometric fluorescent sensing of mercury (II) in seafood. Food Chem. 2020, 320, 126624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Hu, X.; Li, Q.; Shi, Y.; Zhai, X.; Xu, Y.; Li, Z.; Huang, X.; Wang, X.; Shi, J.; et al. Copper nanoclusters@nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots-based ratiometric fluorescence probe for lead (II) ions detection in porphyra. Food Chem. 2020, 320, 126623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Enizi, A.M.; Ubaidullah, M.; Kumar, D. Carbon quantum dots (CQDs)/Ce doped NiO nanocomposite for high performance supercapacitor. Mater. Today Commun. 2021, 27, 102340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yang, F.; Yang, X. Microwave synthesis of fluorescent carbon nanoparticles with electrochemiluminescence properties. Chem. Commun. 2009, 1, 5118–5120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Padrón, D.; Algarra, M.; Tarelho, L.A.C.; Frade, J.; Franco, A.; De Miguel, G.; Luque, R. Catalyzed microwave-assisted preparation of carbon quantum dots from lignocellulosic residues. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 7200–7205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Thongsai, N.; Chae, A.; Jo, S.; Bi Kang, E.; Paoprasert, P.; Young Park, S.; In, I. Microwave-assisted synthesis of luminescent and biocompatible lysine-based carbon quantum dots. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2017, 47, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Zhu, Z.; Chen, M.; Chen, W.; Zhou, X. Microwave-assisted synthesis of xylan-derived carbon quantum dots for tetracycline sensing. Opt. Mater. 2018, 85, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Zhao, X.; Bian, W.; Tang, X. Microwave-assisted synthesis of nitrogen-rich carbon dots as effective fluorescent probe for sensitive detection of Ag+. Mater. Chem. Front. 2019, 3, 2751–2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar Mondal, T.; Kumar Ghorai, U.; Saha, S.K. Dual-emissive carbon quantum dot-Tb nanocomposite as a fluorescent indicator for a highly selective visual detection of Hg (II) in water. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 11439–11446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.; Bhogal, S.; Naushad, M.; Kumar, A.; Stadler, F.J. Microwave assisted fabrication of La/Cu/Zr/carbon dots trimetallic nanocomposites with their adsorptional vs photocatalytic efficiency for remediation of persistent organic pollutants. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2017, 347, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, S.; Sharma, S.; Kansal, S. Synthesis of ZnS/CQDs nanocomposite and its application as a photocatalyst for the degradation of an anionic dye. Superlattices Microstruct. 2016, 98, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Xue Dong, J.; Gang Liu, S.; Li, N.; Min Lin, S.; Zhu Fan, Y.; Lie Lei, J.; Qun Luo, H.; Bing Li, N. Carbon quantum dots prepared with polyethyleneimine as both reducing agent and stabilizer for synthesis of Ag/CQDs composite for Hg2+ ions detection. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 322, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briscoe, J.; Marinovic, A.; Sevilla, M.; Dunn, S.; Titirici, M. Biomass-derived carbon quantum dot sensitizers for solid-state nanostructured solar cells. Angew. Chem. 2015, 54, 4463–4468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvand, M.; Hemmati, S. Magnetic nanoparticles embedded with graphene quantum dots and multiwalled carbon nanotubes as a sensing platform for electrochemical detection of progesterone. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 238, 346–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.K.; Kumar, R.; Singh, D.P.; Savu, R.; Moshkalev, S.A. Progress in microwave-assisted synthesis of quantum dots (graphene/carbon/semiconducting) for bioapplications: A review. Mater. Today Chem. 2019, 12, 282–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.-D.; Lai, G.-W.; Mahmudul Huq, M. Hydrothermal route to graphene quantum dots: Effects of precursor and temperature. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2017, 79, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhu, J.; Qing, Y.; Fan, C.; Wang, L.; Huang, Y.; Sheng, R.; Guo, Y.; Wang, T.; Pan, Y.; et al. Construction of hierarchical porous carbon nanosheets from template-assisted assembly of coal-based graphene quantum dots for high performance supercapacitor electrodes. Mater. Today Energy 2017, 6, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Zhao, C.; Yu, Y.; Yang, J. Graphene quantum dots derived from carbon fibers for oxidation of dopamine. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. Mater. Sci. Ed. 2016, 31, 1294–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Yang, S.; Li, Q.; Yang, Y.; Wang, G.; You, X.; Mao, B.; Wang, H.; Ma, Y.; He, P.; et al. Electrochemical cutting in weak aqueous electrolytes: The strategy for efficient and controllable preparation of graphene quantum dots. Langmuir 2018, 34, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Wu, C.; Du, P.; Feng, X.; Wu, P.; Cai, C. Electrolyzing synthesis of boron-doped graphene quantum dots for fluorescence determination of Fe3+ions in water samples. Talanta 2017, 164, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinde, D.B.; Pillai, V.K. Electrochemical preparation of luminescent graphene quantum dots from multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Chem. Eur. J. 2012, 18, 12522–12528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Guo, X.; Huang, J.; Shen, H.; Zeng, Q.; Wang, L. Mass production of tunable multicolor graphene quantum dots from an energy resource of coke by a one-step electrochemical exfoliation. Carbon 2018, 140, 508–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Sun, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Tang, N.; Li, M.; Zhong, W.; Du, Y. Gram-scale synthesis of high-purity graphene quantum dots with multicolor photoluminescence. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 103428–103432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Wu, C.; Liu, D.; Wang, H.; Su, W.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, S. A facile and simple method for synthesis of graphene oxide quantum dots from black carbon. Green Chem. 2017, 19, 900–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Gao, W.; Kumar Gupta, B.; Liu, Z.; Romero-Aburto, R.; Ge, L.; Song, L.; Alemany, L.B.; Zhan, X.; Gao, G.; et al. Graphene Quantum Dots Derived from Carbon Fibers. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 844–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Li, F.; Wu, C.; Guo, T. Optical properties of fluorescent zigzag graphene quantum dots derived from multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 104, 063109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiang Chua, C.; Sofer, Z.; Šimek, P.; Jankovský, O.; Klímová, K.; Bakardjieva, S.; HrdlickovaKuckova, S.; Pumera, M. Synthesis of strongly fluorescent graphene quantum dots by cage-opening buckminsterfullerene. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 2548–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castaneda-Serna, H.U.; Calderon-Dominguez, G.; Garcia-Borquez, A.; Salgado-Cruz, M.; Rebollo, R.R.F. Structural and luminescent properties of CQDs produced by microwave andconventional hydrothermal methods using pelagic Sargassum ascarbon source. Opt. Mater. 2022, 126, 112156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q.; Ma, W.; Shi, Y.; Li, Z.; Yang, X. Easy synthesis of highly fluorescent carbon quantum dots from gelatin and their luminescent properties and applications. Carbon 2013, 60, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, W.; Wu, B.; Li, Z.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Pan, D.; Wu, M. Facile synthesis of fluorescent graphene quantum dots from coffee grounds for bioimaging and sensing. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 300, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, D.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z. Hydrothermal route for cutting graphene sheets into blue-luminescent graphene quantum dots. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 734–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-H.; Sun, T.; Niu, A.; Tang, Y.-M.; Deng, S.; Luo, W.; Xu, Q.; Wei, D.; Pei, D.-S. Perturbation effect of reduced graphene oxide quantum dots (rGOQDs) on aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) pathway in zebrafish. Biomaterials 2017, 133, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Yu, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, N.; Liu, B.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; et al. Large-scale and controllable synthesis of graphene quantum dots from rice husk biomass: A comprehensive utilization strategy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 1434–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, P.; Prakash Periasamy, A.; Chuang, C.; Liou, Y.-R.; Chen, Y.-F.; Joly, J.; Liang, C.-T.; Chang, H.-T. Plant leaf-derived graphene quantum dots and applications for white LEDs. New J. Chem. 2014, 38, 4946–4951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Mo, Z.; Niu, X.; Yang, X.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, P.; Liu, N.; Guo, R. Highly sensitive fluorescence sensor for mercury (II) based on boron-and nitrogen-co-doped graphene quantum dots. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 566, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, D.; Jiao, J.; Li, Z.; Guo, Y.; Feng, C.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Wu, M. Efficient Separation of Electron–Hole Pairs in Graphene Quantum Dots by TiO2 Heterojunctions for Dye Degradation. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 2405–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Wang, Z.; Gao, Y.; Chen, L.; Lu, M.; Jiao, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Ding, Y.; Cheng, L. Hydrothermal synthesis of layer-controlled MoS2/graphene composite aerogels for lithium-ion battery anode materials. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 390, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Li, M.; Sun, L.; Xu, Y.; Hu, G.; Tang, T.; Wen, J.; Li, X. Tuning the photoluminescence of graphene quantum dots by co-doping of nitrogen and sulfur. J. Nanopart. Res. 2017, 19, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Ding, J.; Yuan, N.; Sun, P.; Lv, M.; Ding, G.; Zhu, C. Graphene quantum dot incorporated perovskite films: Passivating grain boundaries and facilitating electron extraction. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 6057–6063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Ji, R.; Cao, X.; Lin, J.; Jiang, H.; Li, X.; Seng Teng, K.; Man Luk, C.; Zeng, S.; Hao, J.; et al. Deep ultraviolet photoluminescence of water-soluble self-passivated graphene quantum dots. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 5102–5110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kop Alves, A.; Shuh Frantz, A.C.; Amorim Berutti, F. Microwave-assisted oleothermal synthesis of graphene-TiO2quantum dots for photoelectrochemical oxygen evolution reaction. FlatChem 2018, 12, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fresco-Cala, B.; Soriano, M.L.; Sciortino, A.; Cannas, M.; Messina, F.; Cardenas, S. One-pot synthesis of graphene quantum dots and simultaneous nanostructured self-assembly via a novel microwave-assisted method: Impact on triazine removal and efficiency monitoring. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 29939–29946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.-L.; Ji, J.; Fei, R.; Wang, C.-Z.; Lu, Q.; Zhang, J.-R.; Jiang, L.-P.; Zhu, J.-J. A facile microwave avenue to electrochemiluminescent two-color graphene quantum dots. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 2971–2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugesan, B.; Sonamuthu, J.; Pandiyan, N.; Pandi, B.; Samayanan, S.; Mahalingam, S. Photoluminescent reduced graphene oxide quantum dots from latex of Calotropis gigantea for metal sensing, radical scavenging, cytotoxicity, and bioimaging in Artemia salina: A greener route. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2018, 178, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, J.; Li, M.; Xiao, J.; Liu, C.; Li, Z.; Xie, Y.; Ning, P.; Cao, H.; Zhang, Y. Novel oxidative cutting graphene oxide to graphene quantum dots for electrochemical sensing application. Mater. Today Commun. 2016, 8, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Xue, C.; Hu, G.; Zhu, K. Production of graphene quantum dots by ultrasound-assisted exfoliation in supercritical CO2/H2O medium. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 37, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun Kang, S.; Mhin, S.; Han, H.; Min Kim, K.; Jones, J.L.; Ryu, J.H.; Seop Kang, J.; Hee Kim, S.; Bo Shim, K. Ultrafast method for selective design of graphene quantum dots with highly efficient blue emission. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bayat, A.; Saievar-Iranizad, E. Synthesis of green-photoluminescent single layer graphene quantum dots: Determination of HOMO and LUMO energy states. J. Lumin. 2017, 192, 180–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teymourinia, H.; Salavati-Niasari, M.; Amiri, O.; Safardoust-Hojaghan, H. Synthesis of graphene quantum dots from corn powder and their application in reduce charge recombination and increase free charge carriers. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 242, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, G.-L.; Zhao, H.-L.; Deng, H.-H.; Yang, H.-J.; Peng, H.-P.; Liu, Y.-H.; Chen, W. Fabrication of ultra-small monolayer graphene quantum dots by pyrolysis of trisodium citrate for fluorescent cell imaging. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 4807–4815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, M.T.; Gonzalez-Rodriguez, R.; Ryan, C.; Faerber, N.; Coffer, J.L.; Naumov, A.V. Photo-and electroluminescence from nitrogen-doped and nitrogen-sulfurcodoped graphene quantum dots. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1804337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hu, Y.; Zhao, Y. An electrochemical avenue to green-luminescent graphene quantum dots as potential electron- acceptors for photovoltaics. J. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 776–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Xu, T.; Liao, H.; Yao, C.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z.; Chen, Z.; Pan, D.; Sun, L.; et al. Gram-scale synthesis of single-crystalline graphene quantum dots with superior optical properties. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Chen, C.; Zheng, X.; Gao, L.; Cui, Z.; Yang, H.; Guo, C.; Chi, Y.; Ming Li, C. One-step and high yield simultaneous preparation of single-and multi-layer graphene quantum dots from CX-72 carbon black. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 8764–8766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadian, S.; Manik, G. Sulfur doped graphene quantum dots as a potential sensitive fluorescent probe for the detection of quercetin. Food Chem. 2020, 317, 126457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, J.; Tao, Y.; Ma, J.; Kong, Y. Well-dispersed chitosan-graphene quantum dots nanocomposites for electrochemical sensing platform. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2015, 162, H884–H889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, X.; Yang, S.; Bu, Y.; He, P.; Yang, Y.; Wang, G.; Li, H.; Wang, P.; Wang, X.; Ding, G.; et al. Highly Active Black TiO2/N-doped Graphene Quantum Dots Nanocomposites for Sunlight Driven Photocatalytic Sewage Treatment. ChemistrySelect 2018, 3, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, S.; Xie, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, K.; Mossin, S.; Lin, W.; Meng, J.; Pullerits, T.; et al. Defect State Assisted Z-scheme Charge Recombination in Bi2O2CO3/Graphene Quantum Dot Composites for Photocatalytic Oxidation of NO. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2020, 3, 772–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, J.; Zhang, R.; He, S.; Chen, W. Nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots-based fluorescent probe for the sensitive turn- on detection of glutathione and its cellular imaging. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 52583–52589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyti Deka, M.; Chowdhury, D. CVD assisted hydrophobic graphene quantum dots: Fluorescence sensor for aromatic amino acids. ChemistrySelect 2017, 2, 1999–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athika, M.; Prasath, A.; Duraisamy, E.; Devi, V.S.; Sharma, A.S.; Elumalai, P. Carbon-quantum dots derived from denatured milk for efficient chromium-ion sensing and supercapacitor applications. Mater. Lett. 2019, 241, 156–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Zhang, M.; Bhandari, B.; Yang, C.H. Food waste as a carbon source in carbon quantum dots technology and their applications in food safety detection. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 95, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, P.N.; Mathias, A.; Mishra, A.; Mathias, A. Synthesis of ecofriendly fluorescent car- bon dots and their biomedical and environmental applications. Mater. Technol. 2018, 33, 672–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabet, M.; Mahdavi, K. Green synthesis of high photoluminescence nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots from grass via a simple hydrothermal method for removing organic and inorganic water pollutions. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 463, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramar, V.; Moothattu, S.; Balasubramanian, K. Metal free, sunlight and white light based photocatalysis using carbon quantum dots from Citrus grandis: A green way to remove pollution. Sol. Energy 2018, 169, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, M.Y.; Zou, M.B.; Zhao, J.J.; Zhan, Z.H.; Zhao, S.L. Green preparation of fluorescent carbon dots from lychee seeds and their application for the selective detection of methylene blue and imaging in living cells. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 6783–6789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, M.Y.; Zhan, Z.H.; Zou, M.B.; Zhang, L.L.; Zhao, S.L. Green synthesis of stable and biocompatible fluorescent carbon dots from peanut shells for multicolor living cell imaging. New J. Chem. 2016, 40, 1698–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankoti, K.; Rameshbabu, A.P.; Datta, S.; Das, B.; Mitra, A.; Dhara, S. Onion derived carbon nanodots for live cell imaging and accelerated skin wound healing. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 6579–6592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandiyan, S.; Arumugam, L.; Srirengan, S.P.; Pitchan, R.; Sevugan, P.; Kannan, K.; Pitchan, G.; Hegde, T.A.; Gandhirajan, V. Biocompatible Carbon Quantum Dots Derived from Sugarcane Industrial Wastes for Effective Nonlinear Optical Behavior and Antimicrobial Activity Applications. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 30363–30372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Zhao, S.; Zhong, S.; Xu, L.; Gao, Y.; Cui, X. Green synthesis of carbon quantum dots from corn stalk shell by hydrothermal approach in near-critical water and applications in detecting and bioimaging. Microchem. J. 2021, 166, 106250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, K.C.; Ang, W.L.; Sambudi, N.S. Nitrogen and bismuth-doped rice husk-derived carbon quantum dots for dye degradation and heavy metal removal. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2021, 418, 113411. [Google Scholar]
- Baweja, H.; Jeet, K. Economical and green synthesis of graphene and carbon quantum dots from agriculture waste. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 0850g8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Guo, Q.; Chen, D.; Liu, Z.; Zheng, X.; Xu, A.; Yang, S.; Ding, G. Facile and Highly Effective Synthesis of Controllable Lattice Sulfur-Doped Graphene Quantum Dots via Hydrothermal Treatment of Durian. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 5750–5759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Wang, Z.; Liu, J.; Peng, Y.; Yu, X.; Wang, W. One-Pot Facile Synthesis of Graphene Quantum Dots from Rice Husks for Fe3+ Sensing. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 9144–9150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, D.S.; Mohammed, M.; Majeed, S.M. Green Synthesis of Eco-Friendly Graphene Quantum Dots for Highly Efficient Perovskite Solar Cells. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2020, 3, 10863–10871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Gong, F.; Cao, Z.; Zou, W.; Gu, T. Highly cysteine-selective fluorescent nanoprobes based on ultrabright and directly synthesized carbon quantum dots. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 2961–2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xu, C.; Lu, Y.; Chen, X.; Yuan, H.; Wei, G.; Ye, G.; Chen, J. Fluorescence Sensor Array based on Amino Acid Derived Carbon Dots for Pattern-based Detection of Toxic Metal Ions. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 241, 1324–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Jiang, Y.-W.; Jia, H.-R.; Yang, J.; Wu, F.-G. On-off-on fluorescent nanosensor for Fe3+ detection and cancer/normal cell differentiation via silicon-doped carbon quantum dots. Carbon 2018, 134, 232–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Liu, W.; Ren, Y.; Sun, X.; Pan, W.; Wang, J. The selectivity of the carboxylate groups terminated carbon dots switched by buffer solutions for the detection of multi-metal ions. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 240, 941–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinod Kumar, V.; Raman, T.; Philip Anthony, S. Fluorescent carbon quantum dots chemosensor for selective turn-on sensing of Zn2+ and turn-off sensing of Pb2+ in aqueous medium and Zebra fish egg. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 15157–15164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Song, Y.; Zhu, C.; Li, H.; Du, D.; Su, X.; Lin, Y. MnO2nanosheet-carbon dots sensing platform for sensitive detection of organophosphorus pesticides. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 2618–2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Chen, H.; Lin, J.-M. Peroxide induced ultra-weak chemiluminescence and its application in analytical chemistry. Analyst 2013, 138, 5182–5193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali Shah, S.N.; Dou, X.; Khan, M.; Uchiyama, K.; Lin, J.-M. N-doped carbon dots/H2O2 chemiluminescence system for selective detection of Fe2+ ion in environmental samples. Talanta 2019, 196, 370–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amjadi, M.; Manzoori, J.L.; Hallaj, T.; Azizi, N. Sulfur and nitrogen co-doped carbon quantum dots as the chemiluminescence probe for detection of Cu2+ ions. J. Lumin. 2017, 182, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, K.; Honda, T.; Yamasaki, K.; Tanaka, Y.; Taniguchi, K.; Ishimatsu, R.; Imato, T. Carbon quantum dots as fluorescent component in peroxyoxalate chemiluminescence for hydrogen peroxide determination. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2018, 91, 1128–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amjadi, M.; Hallaj, T. Dramatic enhancement effect of carbon quantum dots on the chemiluminescence of Ru (bpy)32+–Ce (IV) reaction and application to the determination of 4-nitrophenol. J. Lumin. 2016, 171, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Wu, L.; Wei, W.; Qu, X. Recent advances in graphene quantum dots for sensing. Mater. Today 2013, 16, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Zhou, B.; Gu, S.; Lv, S.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, B. Facile synthesis of fluorescent carbon nanodots from cornstalk and their application as a sensing platform for detection of Cu2+ ions. Sci. Adv. Mater. 2017, 9, 901–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, G.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Ma, X.; Mei, T.; Li, J.; Ma, P.; Wang, X. Dual-mode high sensitive detection of Fe(III) ions via fluorescent photonic crystal films based on co-assembly of silica colloids and carbon dots. Sci. Adv. Mater. 2017, 9, 873–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin Chen, B.; Xi Liu, Z.; Yan Zou, H.; Zhi Huang, C. Highly selective detection of 2,4,6-trinitrophenol by using newly developed terbium-doped blue carbon dots. Analyst 2016, 141, 2676–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li Liu, M.; Bin Chen, B.; Yang, T.; Wang, J.; Dong Liu, X.; Zhi Huang, C. One-pot carbonization synthesis of europium-doped carbon quantum dots for highly selective detection of tetracycline. Methods Appl. Fluoresc. 2017, 5, 015003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.-Y.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, S.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.-H.; Feng, L. Rapid detection of Cr(VI) ions based on cobalt(II)-doped carbon dots. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 87, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.; Wei, J.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, N.; Chen, Y.; Gao, C.; Zhang, W.; Sreenivasan Sreeprased, T. Facile synthesis of copper doped carbon dots and their application as a “turn-off” fluorescent probe in the detection of Fe3þ ions. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 28745–28750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costas-Mora, I.; Romero, V.; Lavilla, I.; Bendicho, C. In Situ Building of a Nanoprobe Based on Fluorescent Carbon Dots for Methylmercury Detection. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 4536–4543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, X.; Li, S.; Zhuang, L.; Tang, J. L-Tryptophan-capped carbon quantum dots for the sensitive and selective fluorescence detection of mercury ion in aqueous solution. J. Nanopart. Res. 2016, 18, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Wang, Q.; Long, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Chen, S.; Zheng, H.; Huang, Y. Carbon nanodots as peroxidase mimetics and their applications to glucose detection. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 6695–6697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Ge, S.; Wang, S.; Yan, M.; Zang, D.; Yu, J. Facile and sensitive paper-based chemiluminescence DNA biosensor using carbon dots dotted nanoporous gold signal amplification label. Anal. Methods 2013, 5, 1328–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Chowdhuri, A.R.; Laha, D.; Mahto, T.K.; Karmakar, P.; Sahu, S.K. Green synthesis of carbon dots from Ocimumsanctum for effective fluorescent sensing of Pb2+ ions and live cell imaging. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 242, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KaanKoc, O.; Uzer, A.; Apak, R. High Quantum Yield Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Quantum Dot-Based Fluorescent Probes for Selective Sensing of 2,4,6-Trinitrotoluene. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2022, 5, 5868–5881. [Google Scholar]
- Ashrafi Tafreshi, F.; Fatahi, Z.; Fatemeh Ghasemi, S.; Taherian, A.; Esfandiari, N. Ultrasensitive fluorescent detection of pesticides in real sample by using green carbon dots. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0230646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaledian, S.; Noroozi-Aghideh, A.; Kahrizi, D.; Moradi, S.; Abdoli, M.; Haji Ghasemalian, A.; FoadHeidari, M. Rapid detection of diazinon as an organophosphorus poison in real samples using fluorescence carbon dots. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2021, 130, 108676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali Kamyabi, M.; Moharramnezhad, M. A novel cathodic electrochemiluminescent sensor based on CuS/carbon quantum dots/g-C3N4 nanosheets and boron nitride quantum dots for the sensitive detection of organophosphate pesticide. Microchem. J. 2022, 179, 107421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.; Du, X.; Zhao, H.; Sun, Y.; Liu, W. Sensitive and selective sensing system of metallothioneins based on Carbon Quantum Dots and gold nanoparticles. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1125, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Fang, G.; Wang, X.; Zhang, F.; Liu, J.; Zheng, W.; Wang, S. Electrochemiluminescent graphene quantum dots enhanced by MoS2 as sensing platform: A novel molecularly imprinted electrochemiluminescence sensor for 2-methyl-4-chlorophenoxyacetic acid assay. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 228, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sammi, H.; Kukkar, D.; Singh, J.; Kukkar, P.; Kaur, R.; Kaur, H.; Rawat, M.; Singh, G.; Kim, K.-H. Serendipity in solution–GQDs zeolitic imidazole frameworks nanocomposites for highly sensitive detection of sulfide ions. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 255, 3047–3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, N.; Tran, T.T.; Huang, C.; Chen, L.; Yuan, L.; Zhou, L.; Shen, R.; Cai, Q. Electrogenerated chemiluminescence detection of trace level pentachlorophenol using carbon quantum dots. Analyst 2013, 138, 2038–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liao, X.; Hou, Y.; Jia, B.; Fu, L.; Jia, M.; Zhou, L.; Lu, J.; Kong, W. Recent advances in synthesis and modification of carbon dots for optical sensing of pesticides. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 422, 126881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Lu, W.; Asiri, A.M.; Al-Youbi, A.O.; Sun, X. Microwave-assisted rapid green synthesis of photoluminescent carbon nanodots from flour and their applications for sensitive and selective detection of mercury(II) ions. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 184, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Lu, Q.; Deng, J.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y. One-pot electrochemical synthesis of functionalized fluorescent carbon dots and their selective sensing for mercury ion. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 866, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogoi, N.; Barooah, M.; Majumdar, G.; Chowdhury, D. Carbon dots rooted agarose hydrogel hybrid platform for optical detection and separation of heavy metal ions. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 3058–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, M.; Di, Y.; Zhu, X.; Ng, T.-W.; Xia, J.; Liu, W.; Meng, X.; Wang, P.; Lee, C.-S.; Zhang, W. A carbon dot-based fluorescence turn-on sensor for hydrogen peroxide with a photo-induced electron transfer mechanism. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 15574–15577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, T.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Guo, S. Carbon Quantum Dots Based Chemosensor Array for Monitoring Multiple Metal Ions. Molecules 2022, 27, 3843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, P.; Zhang, L.; Long, H.; Meng, M.; Liu, T.; Yin, Y.; Xi, R. A multianalyte fluorescent carbon dots sensing system constructed based on specific recognition of Fe(III) ions. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 28637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faridbod, F.; Sanati, A.L. Graphene Quantum Dots in Electrochemical Sensors/Biosensors. Curr. Anal. Chem. 2018, 15, 103–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tachi, S.; Morita, H.; Takahashi, M.; Okabayashi, Y.; Hosokai, T.; Sugai, T.; Kuwahara, S. Quantum Yield Enhancement in Graphene Quantum Dots via Esterification with Benzyl Alcohol. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrero, M.; Campuzano, S.; Pingarrón, J.M. Quantum dots as components of electrochemical sensing platforms for the detection of environmental and food pollutants: A review. J. AOAC Int. 2017, 100, 950–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roushani, M.; Valipour, A. The potentiality of graphene quantum dots functionalized by nitrogen and thiol-doped (GQDs-N-S) to stabilize the antibodies in designing of human chorionic gonadotropin immunosensor. Nanochem. Res. 2019, 4, 20–26. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, F.; Li, C.-C.; Zhang, C.-Y. Development of quantum dot-based biosensors: Principles and applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 6173–6190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, J.; Xie, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Xiao, J.; Duan, X.; Ren, J.; Xiao, F.; Wang, S. Pd nanoparticles decorated N-Doped graphene quantumdots@N-Dopedcarbon hollow nanospheres with high electrochemical sensing performance in cancer detection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 22563–22573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Du, X.; Qian, L.; Hao, N.; Wang, K. MoS2/nitrogen doped graphene hydrogels p-n heterojunction: Efficient charge transfer property for highly sensitive and selective photoelectrochemical analysis of chloramphenicol. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 126, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Tang, X.; Deng, M.; Cao, Y.; Li, Y.; Zheng, H.; Li, F.; Yan, F.; Lan, T.; Shi, L.; et al. Nitrogen doped graphene quantum dots as a fluorescent probe for mercury(II) ions. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xiao, X.; Xing, X.; Wang, Z.; Zou, T.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, R.; Wang, Y. One-pot synthesis of N-doped graphene quantum dots as highly sensitive fluorescent sensor for detection of mercury ions water solutions. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 095615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Zhou, L.; Chen, J.; Yan, F.; Liu, J.; Dong, X.; Xi, F.; Chen, P. Nanochannel-Confined Graphene Quantum Dots for Ultrasensitive Electrochemical Analysis of Complex Samples. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 12673–12681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, R.V.; Thankam Thomas, R.; Mohamed, A.P.; Pillai, S. Fluorescent turn-off sensor based on sulphur-doped graphene quantum dots in colloidal and film forms for the ultrasensitive detection of carbamate pesticides. Microchem. J. 2020, 157, 104971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryawanshi, A.; Biswal, M.; Mhamane, D.; Gokhale, R.; Patil, S.; Guin, D.; Ogale, S. Large scale synthesis of graphene quantum dots (GQDs) from waste biomass and their use as an efficient and selective photoluminescence on–off–on probe for Ag+ ions. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 11664–11670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Hu, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Li, F.; Han, D.; Niu, L. Fluorescence resonance energy transfer quenching at the surface of graphene quantum dots for ultrasensitive detection of TNT. Talanta 2012, 101, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, F.; Shi, H.; He, X.; Wang, K.; He, D.; Yan, L.; Ye, X.; Tang, J.; Shangguan, J.; Luo, L. Masking agent-free and channel-switch-mode simultaneous sensing of Fe3+and Hg2+using dual-excitation graphene quantum dots. Analyst 2015, 140, 3925–3928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, H.; Singh, S.; Bharwaj, S.K.; Kaur, G.; Khatri, M.; Deep, A.; Bhardwaj, N. Development of carbon quantum dot-based lateral flow immunoassay for sensitive detection of aflatoxin M1 in milk. Food Chem. 2022, 393, 13374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, P.; Yang, W.; Tao, H.; Qiu, S.; Feng, C. A novel fluorescent aptasensor for ultrasensitive and selective detection of acetamiprid pesticide based on inner filter effect between gold nanoparticles and carbon dots. Analyst 2018, 143, 5151–5160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Fan, Y.; Li, J.; Lu, D.; Guo, Y.; Xie, L.; Wu, Y. Vinyl Phosphate-Functionalized, Magnetic, Molecularly-Imprinted Polymeric Microspheres’ Enrichment and Carbon Dots’ Fluorescence-Detection of Organophosphorus Pesticide Residues. Polymers 2019, 11, 1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Hu, A. Carbon Quantum Dots. Synthesis, Properties and Applications. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 6921–6939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molaei, M.J. A review on nanostructured carbon quantum dots and their applications in biotechnology, sensors, and chemiluminescence. Talanta 2019, 196, 456–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Umar, A.; Sood, S.; Kumar Mehta, S.; Kumar Kansal, S. Photoluminescent C-dots: An overview on the recent development in the synthesis, physiochemical properties and potential applications. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 748, 818–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).