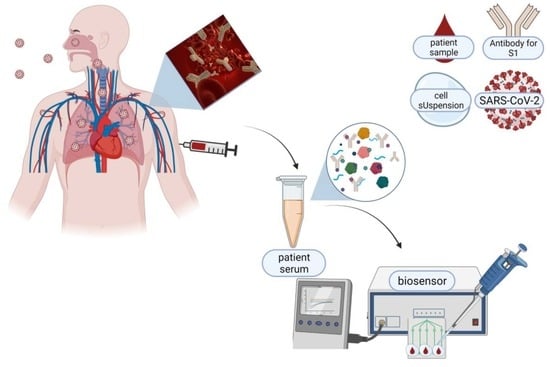
Ultra-Fast and Sensitive Screening for Antibodies against the SARS-CoV-2 S1 Spike Antigen with a Portable Bioelectric Biosensor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Growth Conditions
2.2. Sensor Fabrication from Membrane-Engineered SK-N-SH Cells (SK-N-SH/S1 Spike Protein)
2.3. Measurements
2.4. Serum Specimens Collection
2.5. Data Analysis and Experimental Design
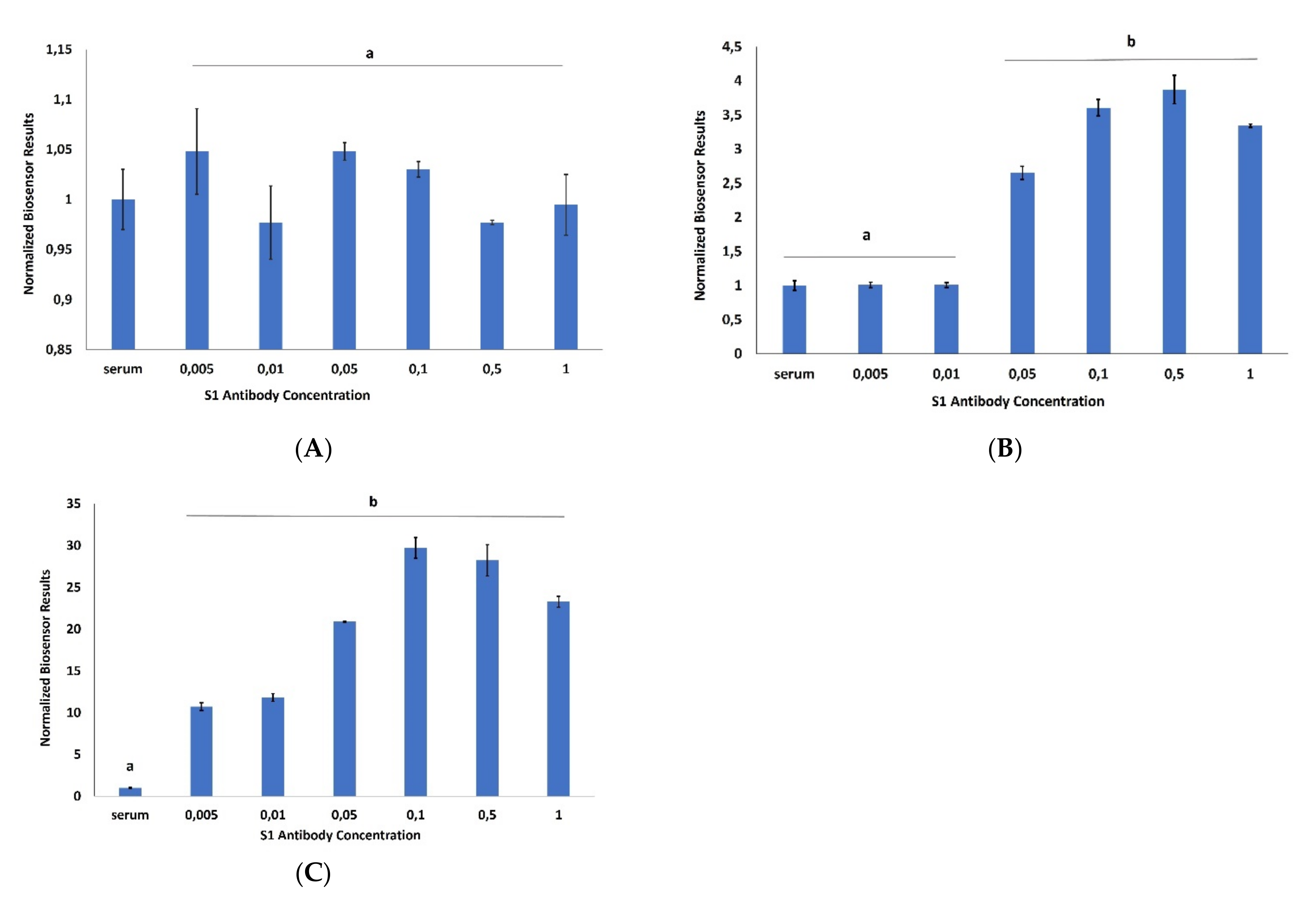
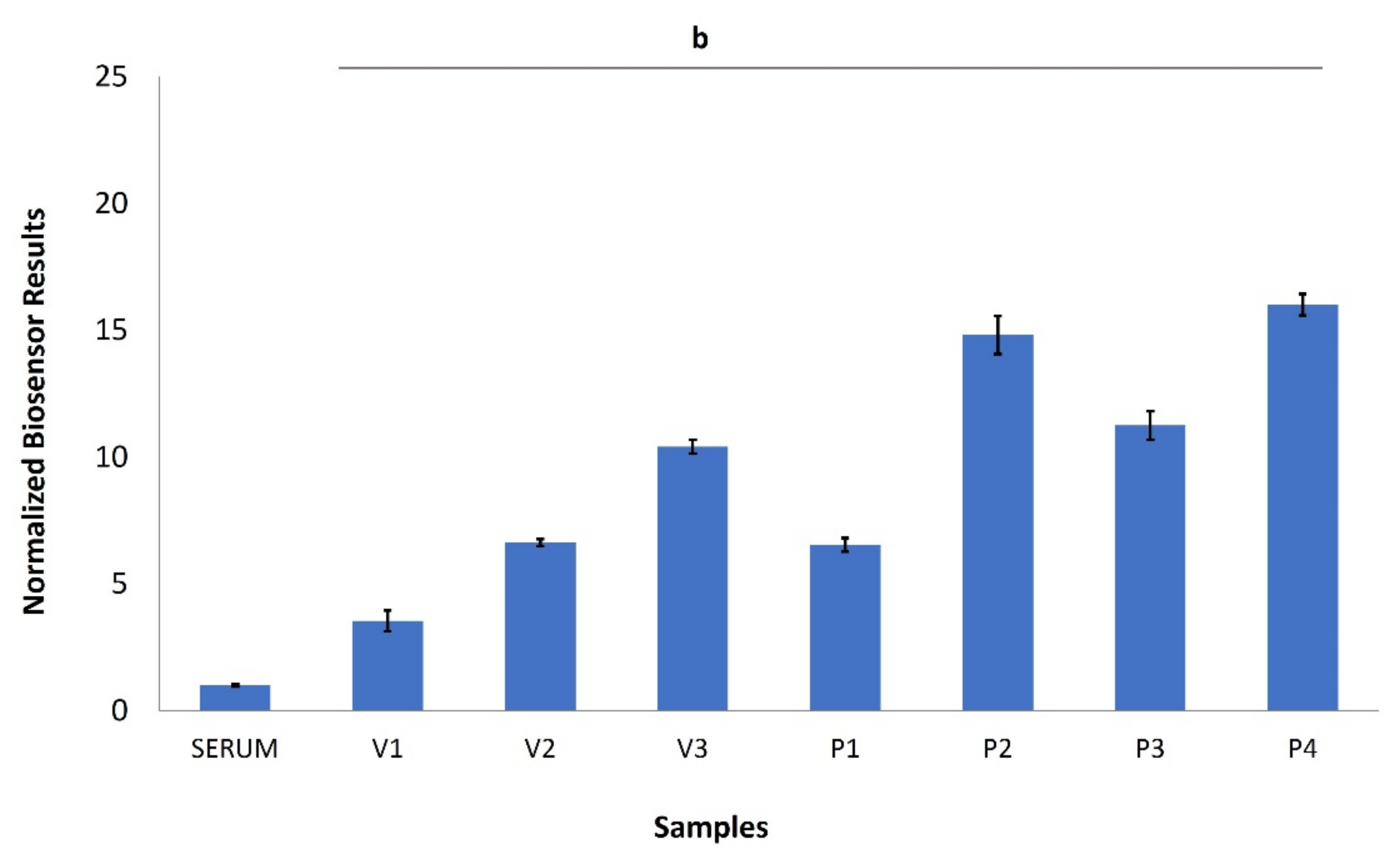
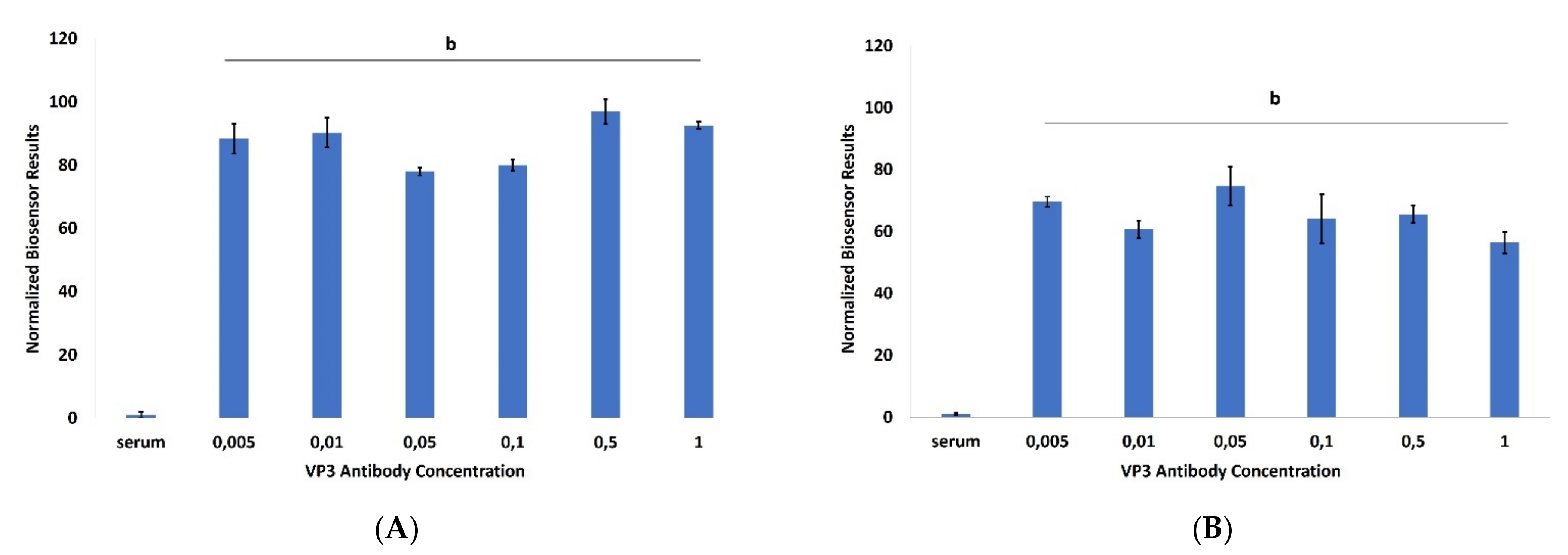
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baden, L.R.; El Sahly, H.M.; Essink, B.; Kotloff, K.; Frey, S.; Novak, R.; Diemert, D.; Spector, S.A.; Rouphael, N.; Creech, C.B.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arkhipova-Jenkins, I.; Helfand, M.; Armstrong, C.; Gean, E.; Anderson, J.; Paynter, R.A.; Mackey, K. Antibody Response After SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Implications for Immunity: A Rapid Living Review. Ann. Intern. Med. 2021, 174, 811–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogata, A.F.; Cheng, C.-A.; Desjardins, M.; Senussi, Y.; Sherman, A.C.; Powell, M.; Novack, L.; Von, S.; Li, X.; Baden, L.R.; et al. Circulating Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Vaccine Antigen Detected in the Plasma of mRNA-1273 Vaccine Recipients. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 74, 715–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradley, B.T.; Bryan, A.; Fink, S.L.; Goecker, E.A.; Roychoudhury, P.; Huang, M.L.; Zhu, H.; Chaudhary, A.; Madarampalli, B.; Lu, J.Y.C.; et al. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Levels Measured by the AdviseDx SARS-CoV-2 Assay Are Concordant with Previously Available Serologic Assays but Are Not Fully Predictive of Sterilizing Immunity. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2021, 59, e0098921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethuraman, N.; Jeremiah, S.S.; Ryo, A. Interpreting Diagnostic Tests for SARS-CoV-2. JAMA 2020, 323, 2249–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padoan, A.; Bonfante, F.; Cosma, C.; Chiara, C.D.; Sciacovelli, L.; Pagliari, M.; Bortolami, A.; Costenaro, P.; Musso, G.; Basso, D.; et al. Analytical and clinical performances of a SARS-CoV-2 S-RBD IgG assay: Comparison with neutralization titers. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2021, 59, 1444–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tré-Hardy, M.; Wilmet, A.; Beukinga, I.; Favresse, J.; Dogné, J.M.; Douxfils, J.; Blairon, L. Analytical and clinical validation of an ELISA for specific SARS-CoV-2 IgG, IgA, and IgM antibodies. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 803–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jääskeläinen, A.J.; Kuivanen, S.; Kekäläinen, E.; Ahava, M.J.; Loginov, R.; Kallio-Kokko, H.; Vapalahti, O.; Jarva, H.; Kurkela, S.; Lappalainen, M. Performance of six SARS-CoV-2 immunoassays in comparison with microneutralisation. J. Clin. Virol. 2020, 129, 104512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Hao, Y.; Miller, E.A.; Tay, D.M.Y.; Yee, E.; Kongsuphol, P.; Jia, H.; McBee, M.; Preiser, P.R.; Sikes, H.D. Vertical Flow Cellulose-Based Assays for SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Detection in Human Serum. ACS Sens. 2021, 6, 1891–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.J.; Zhang, N.; Richardson, S.A.; Wu, J.V. Rapid lateral flow tests for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2021, 21, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokla, A.; Blouchos, P.; Livaniou, E.; Zikos, C.; Kakabakos, S.E.; Petrou, P.S.; Kintzios, S. Visualization of the membrane engineering concept: Evidence for the specific orientation of electroinserted antibodies and selective binding of target analytes. J. Mol. Recognit. 2013, 26, 627–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mavrikou, S.; Moschopoulou, G.; Tsekouras, V.; Kintzios, S. Development of a Portable, Ultra-Rapid and Ultra-Sensitive Cell-Based Biosensor for the Direct Detection of the SARS-CoV-2 S1 Spike Protein Antigen. Sensors 2020, 20, 3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mavrikou, S.; Tsekouras, V.; Hatziagapiou, K.; Tsalidou, A.; Bakakos, P.; Rovina, N.; Koutsoukou, A.; Michos, A.; Nikola, O.; Koniari, E.; et al. Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 (ACE2) As a Novel Biorecognition Element in A Cell-Based Biosensor for the Ultra-Rapid, Ultra-Sensitive Detection of the SARS-CoV-2 S1 Spike Protein Antigen. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostolou, T.; Kyritsi, M.; Vontas, A.; Loizou, K.; Hadjilouka, A.; Speletas, M.; Mouchtouri, V.; Hadjichristodoulou, C. Development and performance characteristics evaluation of a new Bioelectric Recognition Assay (BERA) method for rapid Sars-CoV-2 detection in clinical samples. J. Virol. Methods 2021, 293, 114166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavrikou, S.; Tsekouras, V.; Hatziagapiou, K.; Paradeisi, F.; Bakakos, P.; Michos, A.; Koutsoukou, A.; Konstantellou, E.; Lambrou, G.I.; Koniari, E.; et al. Clinical Application of the Novel Cell-Based Biosensor for the Ultra-Rapid Detection of the SARS-CoV-2 S1 Spike Protein Antigen: A Practical Approach. Biosensors 2021, 11, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moschopoulou, G.; Vitsa, K.; Bem, F.; Vassilakos, N.; Perdikaris, A.; Blouhos, P.; Yialouris, C.; Frosyniotis, D.; Anthopoulos, I.; Mangana, O.; et al. Engineering of the membrane of fibroblast cells with virus-specific antibodies: A novel biosensor tool for virus detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2008, 24, 1033–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kintzios, S.; Pistola, E.; Konstas, J.; Bem, F.; Matakiadis, T.; Alexandropoulos, N.; Biselis, I.; Levin, R. The application of the bioelectric recognition assay for the detection of human and plant viruses: Definition of operational parameters. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2001, 16, 467–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kintzios, S.; Pistola, E.; Panagiotopoulos, P.; Bomsel, M.; Alexandropoulos, N.; Bem, F.; Ekonomou, G.; Biselis, J.; Levin, R. Bioelectric recognition assay (BERA). Biosens. Bioelectron. 2001, 16, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michos, A.; Tatsi, E.-B.; Filippatos, F.; Dellis, C.; Koukou, D.; Efthymiou, V.; Kastrinelli, E.; Mantzou, A.; Syriopoulou, V. Association of total and neutralizing SARS-CoV-2 spike -receptor binding domain antibodies with epidemiological and clinical characteristics after immunization with the 1st and 2nd doses of the BNT162b2 vaccine. Vaccine 2021, 39, 5963–5967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.; Choi, M.; Shim, J.; Park, S. Hook effect detection and detection-range-controllable one-step immunosensor for inflammation monitoring. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 304, 127408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moschopoulou, G.; Kintzios, S. Application of “membrane-engineering” to bioelectric recognition cell sensors for the ultra-sensitive detection of superoxide radical: A novel biosensor principle. Anal. Chim. Acta 2006, 573–574, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdikaris, A.; Alexandropoulos, N.; Kintzios, S. Development of a Novel, Ultra-rapid Biosensor for the Qualitative Detection of Hepatitis B Virus-associated Antigens and Anti-HBV, Based on “Membrane-engineered” Fibroblast Cells with Virus-Specific Antibodies and Antigens. Sensors 2009, 9, 2176–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ross, G.M.S.; Filippini, D.; Nielen, M.W.F.; Salentijn, G.I.J. Unraveling the Hook Effect: A Comprehensive Study of High Antigen Concentration Effects in Sandwich Lateral Flow Immunoassays. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 15587–15595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namburi, R.; Kancherla, V.; Ponnala, A. High-dose hook effect. J. Dr. NTR Univ. Health Sci. 2014, 3, 5–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillström, A.; Hagman, R.; Tvedten, H.; Kjelgaard-Hansen, M. Validation of a commercially available automated canine-specific immunoturbidimetric method for measuring canine C-reactive protein. Vet. Clin. Pathol. 2014, 43, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, Y.K.; Fatima, U.; Dogra, S.; Kaushik, A. Beware of “hook effect” giving false negative pregnancy test on point-of-care kits. J. Postgrad. Med. 2013, 59, 153–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cognetti, J.S.; Steiner, D.J.; Abedin, M.; Bryan, M.R.; Shanahan, C.; Tokranova, N.; Young, E.; Klose, A.M.; Zavriyev, A.; Judy, N.; et al. Disposable photonics for cost-effective clinical bioassays: Application to COVID-19 antibody testing. Lab A Chip 2021, 21, 2913–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basso, C.R.; Malossi, C.D.; Haisi, A.; de Albuquerque Pedrosa, V.; Barbosa, A.N.; Grotto, R.T.; Araujo Junior, J.P. Fast and reliable detection of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies based on surface plasmon resonance. Anal. Methods 2021, 13, 3297–3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Dong, T.; Han, C.; Liu, L.; Zhang, T.; Kang, Q.; Wang, P.; Zhou, F. Regenerable and high-throughput surface plasmon resonance assay for rapid screening of anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibody in serum samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1208, 339830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-González, E.; Garcia-Ramirez, R.; Díaz-Armas, G.G.; Esparza, M.; Aguilar-Avelar, C.; Flores-Contreras, E.A.; Rodríguez-Sánchez, I.P.; Delgado-Balderas, J.R.; Soto-García, B.; Aráiz-Hernández, D.; et al. Automated ELISA On-Chip for the Detection of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies. Sensors 2021, 21, 6785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Wen, T.; Shi, F.-J.; Zeng, X.-Y.; Jiao, Y.-J. Rapid Detection of IgM Antibodies against the SARS-CoV-2 Virus via Colloidal Gold Nanoparticle-Based Lateral-Flow Assay. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 12550–12556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Puig, H.; Timilsina, S.S.; Rainbow, J.; Jolly, P.; Najjar, D.; Durr, N.; Alter, G.; Li, J.Z.; Yu, X.G.; Walt, D.R.; et al. Simultaneous detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA and host antibodies enabled by a multiplexed electrochemical sensor platform. medRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakoh, A.; Pimpitak, U.; Rengpipat, S.; Hirankarn, N.; Chailapakul, O.; Chaiyo, S. Paper-based electrochemical biosensor for diagnosing COVID-19: Detection of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies and antigen. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 176, 112912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenzen, A.L.; Dos Santos, A.M.; Dos Santos, L.P.; da Silva Pinto, L.; Conceição, F.R.; Wolfart, F. PEDOT-AuNPs-based impedimetric immunosensor for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies. Electrochim. Acta 2022, 404, 139757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, S.M.; Alba-Patiño, A.; Vaquer, A.; Clemente, A.; de la Rica, R. Improving the Quantification of Colorimetric Signals in Paper-Based Immunosensors with an Open-Source Reader. Sensors 2022, 22, 1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Duarte, P.A.; Ma, Y.; Savchenko, O.; Shoute, L.; Khaniani, Y.; Babiuk, S.; Zhuo, R.; Abdelrasoul, G.N.; Charlton, C.; et al. An impedimetric biosensor for COVID-19 serology test and modification of sensor performance via dielectrophoresis force. Biosen.s Bioelectron. 2022, 213, 114476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzimianski, J.V.; Lorig-Roach, N.; O’Rourke, S.M.; Alexander, D.L.; Kimmey, J.M.; DuBois, R.M. Rapid and sensitive detection of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies by biolayer interferometry. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, J.L.; Zhang, W.L.; Tu, Z.; Cai, X.F.; Wang, Y.W.; Gan, C.Y.; Deng, H.J.; Cui, J.; Shu, Z.C.; et al. Protein sensors combining both on-and-off model for antibody homogeneous assay. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 209, 114226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo-Lozano, O.; Sierra, M.; Soler, M.; Estévez, M.C.; Chiscano-Camón, L.; Ruiz-Sanmartin, A.; Ruiz-Rodriguez, J.C.; Ferrer, R.; González-López, J.J.; Esperalba, J.; et al. Label-Free Plasmonic Biosensor for Rapid, Quantitative, and Highly Sensitive COVID-19 Serology: Implementation and Clinical Validation. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 975–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochkov, Y.A.; Gern, J.E. Rhinoviruses and Their Receptors: Implications for Allergic Disease. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2016, 16, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdullah, H.; Heaney, L.G.; Cosby, S.L.; McGarvey, L.P.A. Rhinovirus upregulates transient receptor potential channels in a human neuronal cell line: Implications for respiratory virus-induced cough reflex sensitivity. Thorax 2014, 69, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bouillon, M.; Audette, M. Retinoic acid-stimulated intercellular adhesion molecule-1 expression on SK-N-SH cells: Calcium/calmodulin-dependent pathway. Cancer Res. 1994, 54, 4144–4149. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- WHO. Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19): Herd Immunity, Lockdowns and COVID-19. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/questions-and-answers/item/herd-immunity-lockdowns-and-covid-19 (accessed on 12 May 2022).
- De Giorgi, V.; West, K.A.; Henning, A.N.; Chen, L.N.; Holbrook, M.R.; Gross, R.; Liang, J.; Postnikova, E.; Trenbeath, J.; Pogue, S.; et al. Naturally Acquired SARS-CoV-2 Immunity Persists for Up to 11 Months Following Infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 224, 1294–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, R.A.; Rassen, J.A.; Kabelac, C.A.; Turenne, W.; Leonard, S.; Klesh, R.; Meyer, W.A., III; Kaufman, H.W.; Anderson, S.; Cohen, O.; et al. Association of SARS-CoV-2 Seropositive Antibody Test With Risk of Future Infection. JAMA Intern. Med. 2021, 181, 672–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, C.K.; Kim, M.; Lee, S.; Kim, G.; Choe, P.G.; Park, W.B.; Kim, N.J.; Lee, C.-H.; Kim, I.S.; Jung, K.; et al. Longitudinal Analysis of Human Memory T-Cell Response According to the Severity of Illness up to 8 Months After Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 224, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClements, J.; Bar, L.; Singla, P.; Canfarotta, F.; Thomson, A.; Czulak, J.; Johnson, R.E.; Crapnell, R.D.; Banks, C.E.; Payne, B.; et al. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Nanoparticles Enable Rapid, Reliable, and Robust Point-of-Care Thermal Detection of SARS-CoV-2. ACS Sens. 2022, 7, 1122–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Patient | Sex | Age (Years) | Date of PCR Positivity | Date of Venous Blood Sample | Underlying Diseases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Female | 91 | 23 April 2020 | 11 May 2020 | Type 2 diabetes mellitus Hypertension Atrial fibrillation Hemodialysis |
| 2 | Male | 80 | 19 April 2020 | 11 May 2020 | Hypertension Atrial fibrillation Hemodialysis Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) |
| 3 | Female | 50 | 23 April 2020 | 11 May 2020 | Hemodialysis |
| 4 | Male | 86 | 23 April 2020 | 11 May 2020 | Hypertension Hemodialysis |
| Donor | Age (Years) | Sex | Date of Venous Blood Sample |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 69 | Male | 1 October 2020 |
| 2 | 58 | Male | 2 October 2020 |
| 3 | 46 | Female | 1 October 2020 |
| 4 | 45 | Male | 1 October 2020 |
| 5 | 40 | Female | 1 October 2020 |
| 6 | 38 | Female | 2 October 2020 |
| 7 | 36 | Female | 2 October 2020 |
| 8 | 22 | Female | 1 October 2020 |
| 9 | 22 | Male | 1 October 2020 |
| 10 | 20 | Male | 2 October 2020 |
| V1 | 48 | Female | February 2021 |
| V2 | 35 | Female | February 2021 |
| V3 | 24 | Male | February 2021 |
| Sensor | Response Time | Limit of Detection | Clinical Validation | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Multiplexed electrochemical (EC) sensor platform | 60 min | No quantitative assay | Y | [32] |
| Biolayer interferometry immunosorbent assay (BLI-ISA) | 20 min | 0.037 µg/mL | Y | [37] |
| Paper-based electrochemical biosensor | 30 min | 0.14 ng/mL | Y | [33] |
| Surface plasmon resonance | 10 min | No quantitative assay | Y | [28] |
| Automated ELISA On-Chip | 60 min | No quantitative assay | Y | [30] |
| PEDOT-AuNPs-based impedimetric immunosensor | 30 min | No quantitative assay | Y | [34] |
| High-throughput surface plasmon resonance assay | 5–6 min | 0.057 μg/mL | Y | [29] |
| Disposable photonics | 1–5 min | No quantitative assay | Y | [27] |
| Protein sensors-based on allosteric enzymes | 45 min | No quantitative assay | Y | [38] |
| Label-Free plasmonic biosensor | 15 min | 12.75 ng/mL | Y | [39] |
| Paper-Based immunosensors | Several minutes | No quantitative assay | Y | [35] |
| Impedimetric biosensor | 30 min | 200 ng/mL | N | [36] |
| Colloidal gold nanoparticle-based lateral-flow (AuNP-LF) | 15 min | No quantitative assay | Y | [31] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mavrikou, S.; Papaioannou, G.M.; Tsekouras, V.; Hatziagapiou, K.; Tatsi, E.B.; Filippatos, F.; Kanaka-Gantenbein, C.; Michos, A.; Kintzios, S. Ultra-Fast and Sensitive Screening for Antibodies against the SARS-CoV-2 S1 Spike Antigen with a Portable Bioelectric Biosensor. Chemosensors 2022, 10, 254. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10070254
Mavrikou S, Papaioannou GM, Tsekouras V, Hatziagapiou K, Tatsi EB, Filippatos F, Kanaka-Gantenbein C, Michos A, Kintzios S. Ultra-Fast and Sensitive Screening for Antibodies against the SARS-CoV-2 S1 Spike Antigen with a Portable Bioelectric Biosensor. Chemosensors. 2022; 10(7):254. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10070254
Chicago/Turabian StyleMavrikou, Sofia, George Marios Papaioannou, Vasileios Tsekouras, Kyriaki Hatziagapiou, Elizabeth Barbara Tatsi, Filippos Filippatos, Christina Kanaka-Gantenbein, Athanasios Michos, and Spyridon Kintzios. 2022. "Ultra-Fast and Sensitive Screening for Antibodies against the SARS-CoV-2 S1 Spike Antigen with a Portable Bioelectric Biosensor" Chemosensors 10, no. 7: 254. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10070254
APA StyleMavrikou, S., Papaioannou, G. M., Tsekouras, V., Hatziagapiou, K., Tatsi, E. B., Filippatos, F., Kanaka-Gantenbein, C., Michos, A., & Kintzios, S. (2022). Ultra-Fast and Sensitive Screening for Antibodies against the SARS-CoV-2 S1 Spike Antigen with a Portable Bioelectric Biosensor. Chemosensors, 10(7), 254. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10070254