3-Thienylboronic Acid as a Receptor for Diol-Containing Compounds: A Study by Isothermal Titration Calorimetry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
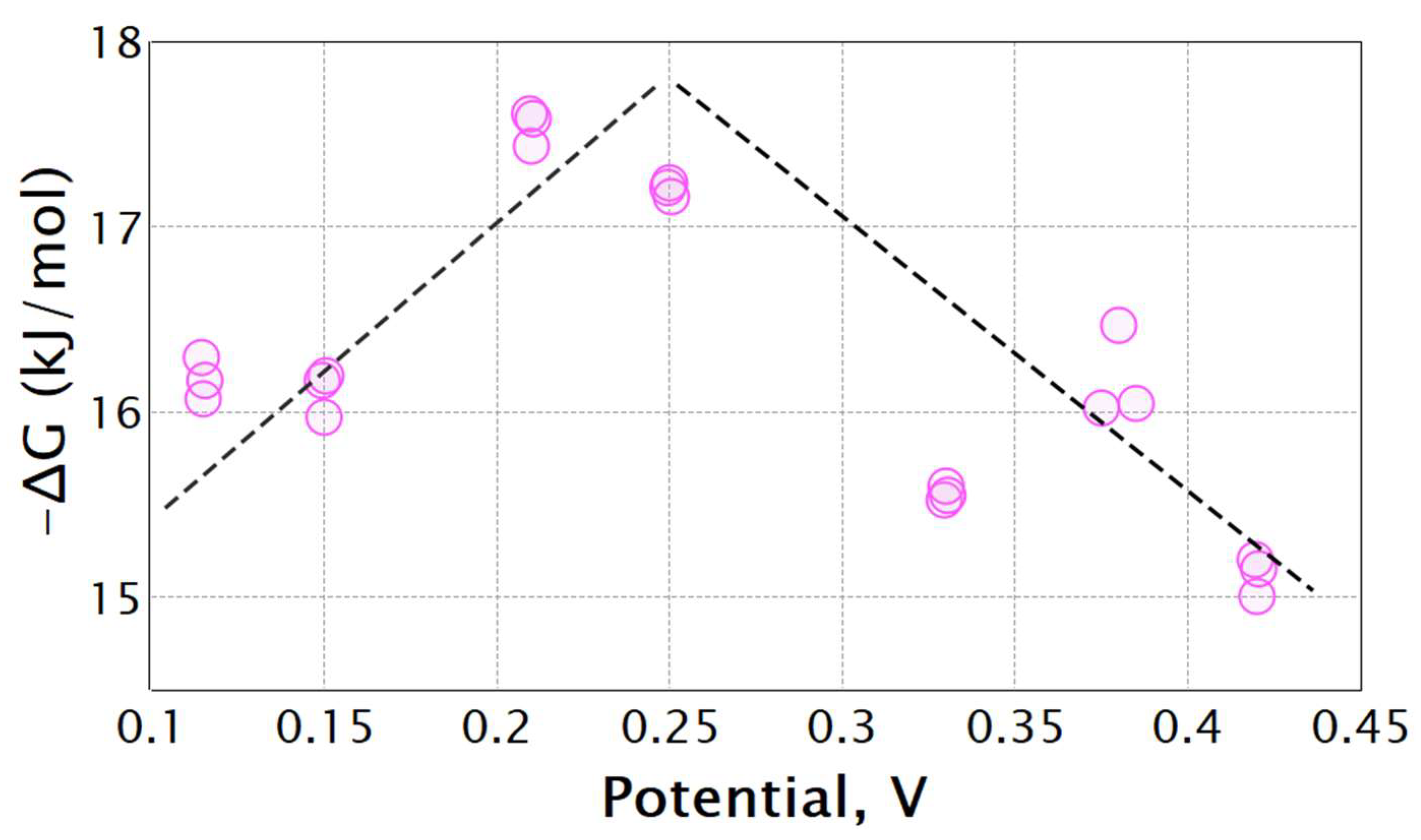
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guryanov, I.; Fiorucci, S.; Tennikova, T. Receptor-ligand interactions: Advanced biomedical applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 68, 890–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilson, M.K.; Given, J.A.; Head, M.S. A new class of models for computing receptor-ligand binding affinities. Chem. Biol. 1997, 4, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirsky, V.M. Quantitative characterization of affinity properties of immobilized receptors. In Artificial Receptors for Chemical Sensors; Mirsky, V.M., Yatsmimirsky, K.A., Eds.; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co., KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2011; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Mirsky, V.M. Quantitative affinity data on selected artificial receptors. In Artificial Receptors for Chemical Sensors; Mirsky, V.M., Yatsmimirsky, K.A., Eds.; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co., KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2011; pp. 439–459. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, H.; Yatsmimirsky, K.A. Selectivity of chemical receptors. In Artificial Receptors for Chemical Sensors; Mirsky, V.M., Yatsmimirsky, K.A., Eds.; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co., KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2011; pp. 17–65. [Google Scholar]
- Mirsky, V.M. Combinatorial development of chemosensitive conducting polymers. In Combinatorial Methods for Chemical and Biological Sensors; Potyrailo, R.A., Mirsky, V.M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 315–330. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Guo, Q.X. The driving forces in the inclusion complexation of cyclodextrins. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2002, 42, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majerski, K.M.; Kragol, G. Design, synthesis and cation-binding properties of novel adamantine and 2-oxaadamantane-containing crown ethers. Tetrahedron 2001, 57, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korochkina, M.; Fontanella, M.; Casnati, A.; Arduini, A.; Sansone, F.; Ungaro, R.; Latypov, S.; Kataev, V.; Alfonsov, V. Synthesis and spectroscopic studies of isosteviol calix[4]arene and calix[6]arene conjugates. Tetrahedron 2005, 61, 5457–5463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, T.; Kettenberger, H.; Wolfbeis, O.S.; Mirsky, V.M. A simple strategy for preparation of sensor arrays: Nanostructured monolayers as recognition elements. Chem. Commun. 2003, 432–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossi, A.; Bonini, F.; Turner, A.; Piletsky, S. Molecularly imprinted polymers for the recognition of proteins the state of art. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 22, 1131–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, T.D. Boronic acid-based receptors and sensors for saccharides. In Boronic Acids: Preparation and Applications in Organic Synthesis and Medicine; Dennis, G.H., Ed.; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co., KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2005; pp. 441–479. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, D.G. Structure, properties, and preparation of boronic acids derivatives. In Boronic Acids: Preparation and Applications in Organic Synthesis and Medicine; Dennis, G.H., Ed.; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co., KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2005; pp. 1–99. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Cheng, Z.; Jin, S.; Wang, B. Boronic acid-based receptors and chemosensors. In Artificial Receptors for Chemical Sensors; Mirsky, V.M., Yatsmimirsky, K.A., Eds.; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co., KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2011; pp. 169–189. [Google Scholar]
- Sienkiewicz, P.A.; Roberts, D.C. pH dependence of boronic acid-diol affinity in aqueous solution. J. Inorg. Nucl. Chem. 1980, 42, 1559–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babcock, L.; Pizer, R. Dynamics of boron acid complexation reactions. Formation of 1:1 boron acid-ligand complexes. Inorg. Chem. 1980, 19, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mader, H.S.; Wolfbeis, O.S. Boronic acid based probes for microdeternination of saccharides and glycosylated biomolecules: A review. Microchim. Acta 2008, 162, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappin, B.; Kiefel, M.J.; Houston, T.A. Boron-Carbohydrate interactions. In Carbohydrates—Comprehensive Studies on Glycobiology and Glycotechnology; Chang, C.-F., Ed.; InTech: Tokyo, Japan, 2012; pp. 37–54. [Google Scholar]
- Nagasaki, T.; Shinmori, H.; Shinkai, S. Attempts to change the color of dye molecules by saccharides. Tetrahedron Lett. 1994, 35, 2201–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Kaur, G.; Wang, B. Progress in boronic acid-based fluorescent glucose sensors. J. Fluoresc. 2004, 14, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Şenel, M.; Dervisevic, M.; Çevik, E. A novel amperometric glucose biosensor based on recognition of glucose oxidase on thiophene-3-boronic acid polymer layer. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2013, 13, 1199–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoji, E.; Freund, M.S. Potentiometric saccharide detection based on the pKa changes of poly(aniline boronic acid). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 12486–12493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dervisevic, M.; Senel, M.; Cevik, E. Novel impedimetric dopamine biosensor based on boronic acid functional polythiophene modified electrodes. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 72, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torun, Ö.; Dudak, F.C.; Bas, D. Tamer, U.; Boyaci, I.H. Thermodynamic analysis of the interaction between 3-aminophenylboronic acid and monosaccharides for development of biosensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2009, 140, 597–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.; Czarnik, A.W. Fluorescent chemosensors of carbohydrates. A means of chemically communicating the binding of polyols in water based on chelation-enhanced quenching. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992, 114, 5874–5875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, W.; Fan, H.; Gao, X.; Karnati, V.V.R.; Ni, W.; Hooks, W.B.; Carson, J.; Weston, B. Wang, B. The first diboronic acid sensor specific for heptacellular carcinoma cells expressing sialyl Lewis X. Chem. Biol. 2004, 11, 439–448. [Google Scholar]
- James, T.D.; Sandanayake, K.R.A.S.; Iguchi, R.; Shinkai, S. Novel saccharide-photoinduced electron transfer sensors based on the interaction of boronic acid and amine. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 8982–8987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, Y.J.; Shibata, H.; Okitsu, T.; Kawanishi, T.; Takeuchi, S. Long-term in vivo glucose monitoring using fluorescent hydrogel fibers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 13399–133403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vancoillie, G.; Hoogenboom, R. Synthesis and polymerization of boronic acid containing monomers. Polym. Chem. 2016, 7, 5484–5495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cambre, J.N.; Sumerlin, B.S. Biomedical applications of boronic acid polymers. Polymer 2011, 52, 4631–4643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, W.; Sumerlin, B.S. Synthesis and applications of boronic acid-containing polymers: From materials to medicine. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 1375–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pringsheim, E.; Terpetsehnig, E.; Piletsky, S.A.; Wolfbeis, O.S. A polyaniline with near-infrared optical response to saccharides. Adv. Mater. 1999, 11, 865–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; He, X.; Wang, L.; Gu, A.; Huang, Z.; Fang, B.; Geng, B.; Zhang, X. Non-enyzmatic electrochemical sensing of glucose. Microchim. Acta 2013, 18, 161–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çiftci, H.; Tamer, U.; Teker, M.Ş.; Pekmey, N.Ö. An enzyme free potentiometric detection of glucose based on conducting polymer poly (3-aminophenylboronic acid-co-3-cotylthiophene). Electr. Acta 2013, 90, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aytaç, S.; Kuralay, F.; Boyaci, H.; Unaleroglu, C. A novel polypyrrole-phenylboronic acid based electrochemical saccharide sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 160, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishkanova, T.; Fitl, R.; Kral, V.; Barek, J. Nanoparticles functionalized with phenylboronic acid for the potentiometric detection of saccharides. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2013, 761, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deore, B.A.; Hachey, S.; Freund, M.S. Electroactivity of electrochemically synthesized poly(aniline boronic acid) as a function of pH: Role of self-doping. Chem. Mater. 2004, 16, 1427–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efremenko, Y.; Mirsky, V.M. Poly-3-thienylboronic acid: A chemosensitive derivative of polythiophene. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2020, 24, 3105–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falconer, R.J.; Penkova, A.; Jelesarov, I.; Collins, B.M. Survey of the year 2008: Applications of isothermal titration calorimetry. J. Mo. Recognit. 2010, 33, 395–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freyer, M.W.; Lewis, E.A. Isothermal titration calorimetry: Experimental design, data analysis, and probing macromolecule/ligand binding and kinetic interactions. Methods Cell Biol. 2008, 84, 79–113. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, N.; Laughlin, S.; Wang, Z.; Yheng, Z.F.; Wang, B. Probing the general time scale question of boronic acid binding with sugars in aqueous solution at physiological pH. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2012, 20, 2957–2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turnbull, W.B.; Daranas, A.H. On the value of c: Can low affinity systems be studied by isothermal titration calorimetry? J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 14859–14866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kantonen, S.A.; Henriksen, N.M.; Gilson, M.K. Evaluation and minimization of uncertainty in ITC binding measurements: Heat error, concentration error, saturation, and stoichiometry. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2017, 1861, 485–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lodge, T.P.; Muthukumar, M. Physical chemistry of polymers: Entropy, interactions, and dynamics. J. Phys. Chem. 1996, 100, 13275–13292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch, L.I.; Fyles, T.M.; James, T.D. Binary and ternary phenylboronic acid complexes with saccharides and Lewis bases. Tetrahedron 2004, 60, 11175–11190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Springstenn, G.; Wang, B. A detailed examination of boronic acid-diol complexation. Tetrahedron 2002, 58, 5291–5300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Springstenn, G.; Deeter, S.; Wang, B. The relationship among pKa, pH, and binding constants in the interactions between boronic acids and diols—It is not as simple as it appears. Tetrahedron 2004, 60, 11205–11209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Bagia, C.; Mpourmpakis, G. Determination of proton affinities and acidity constants of sugars. J. Phys. Chem. A 2013, 117, 5211–5219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efremenko, Y.; Mirsky, V.M. Virtual sensor array consisting of a single sensor element with variable affinity: An application for analysis of fish freshness. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 241, 652–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, U.; Mirsky, V.M. Integrated electrochemical transistor as a fast recoverable gas sensor. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 687, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lange, U.; Mirsky, V.M. Polythiophene films on gold electrodes: A comparison of bulk contact resistances in aqueous and organic media. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2011, 15, 2377–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efremenko, Y.; Mirsky, V.M. Electrically controlled variation of receptor affinity. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 7283–7287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Lange, U.; Mirsky, V.M. Chemoresistors based on conducting polymers: A review on measurement techniques. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 687, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Li, Z.; Chen, X.; Fossey, J.S.; James, T.D.; Jiang, Y. Selective sensing of saccharides using simple boronic acids and their aggregates. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 8032–8048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
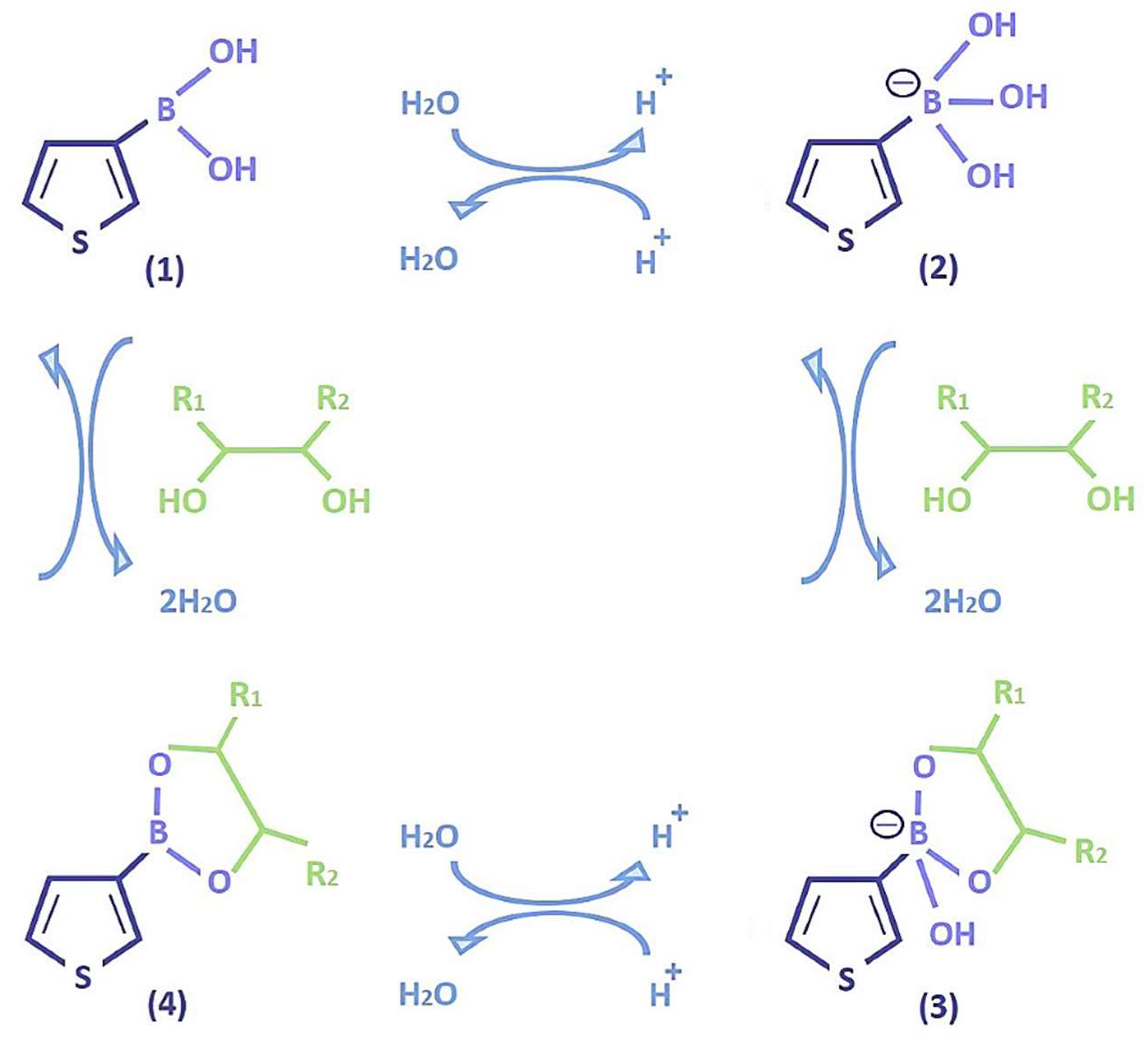
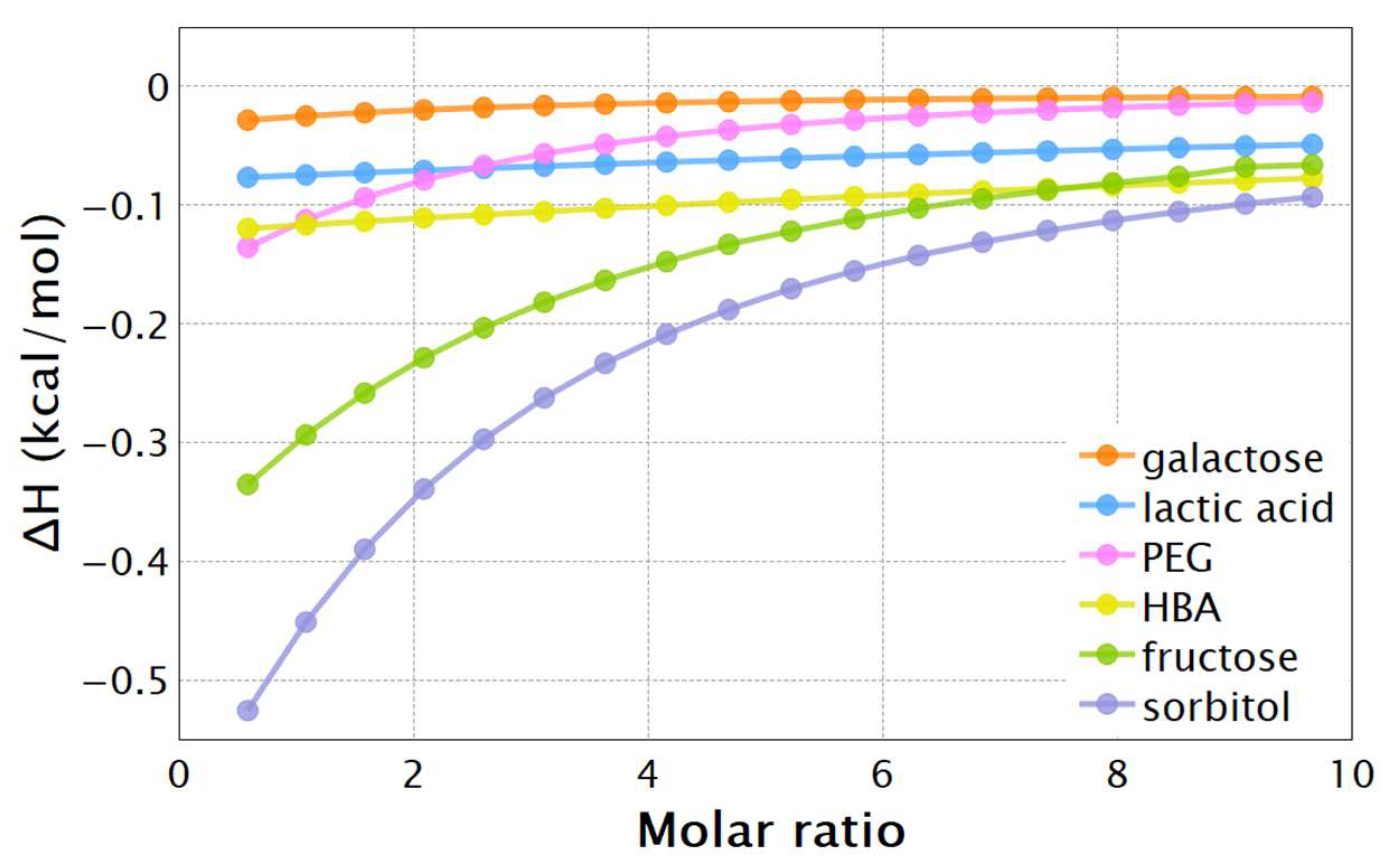
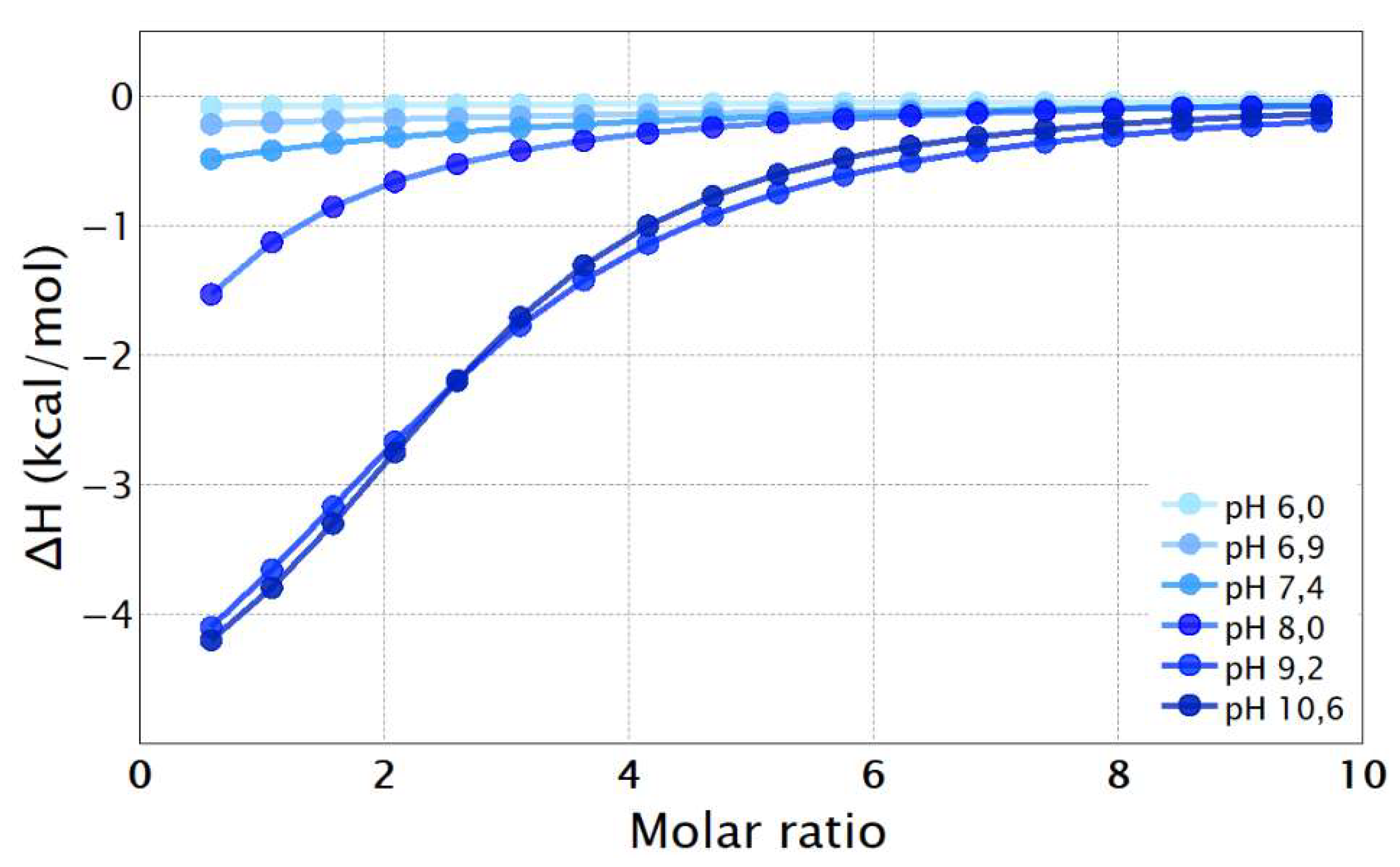
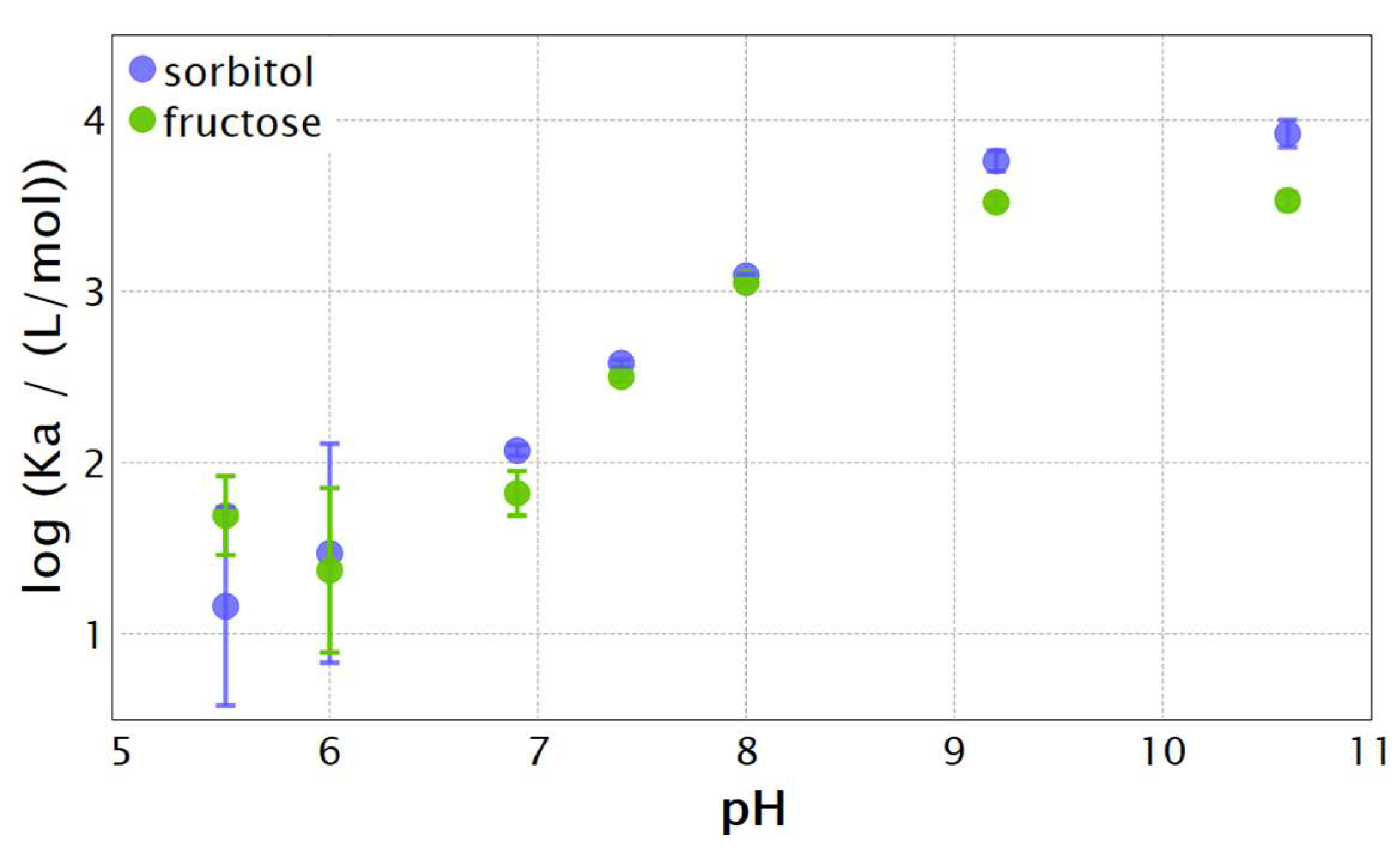
| pH | PBA | TBA | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ka (L/mol) | −ΔG (kJ/mol) | Ka (L/mol) | −ΔG (kJ/mol) | |
| 7.4 | 209 ± 4 | 13.3 ± 0.42 | 212 ± 10 | 13.4 ± 0.13 |
| 8.0 | 522 ± 17 | 15.6 ± 0.08 | 533 ± 15 | 15.7 ± 0.08 |
| 9.2 | 3090 ± 222 | 20.0 ± 0.17 | 2700 ± 400 | 19.1 ± 0.84 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Efremenko, Y.; Mirsky, V.M. 3-Thienylboronic Acid as a Receptor for Diol-Containing Compounds: A Study by Isothermal Titration Calorimetry. Chemosensors 2022, 10, 251. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10070251
Efremenko Y, Mirsky VM. 3-Thienylboronic Acid as a Receptor for Diol-Containing Compounds: A Study by Isothermal Titration Calorimetry. Chemosensors. 2022; 10(7):251. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10070251
Chicago/Turabian StyleEfremenko, Yulia, and Vladimir M. Mirsky. 2022. "3-Thienylboronic Acid as a Receptor for Diol-Containing Compounds: A Study by Isothermal Titration Calorimetry" Chemosensors 10, no. 7: 251. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10070251
APA StyleEfremenko, Y., & Mirsky, V. M. (2022). 3-Thienylboronic Acid as a Receptor for Diol-Containing Compounds: A Study by Isothermal Titration Calorimetry. Chemosensors, 10(7), 251. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10070251







